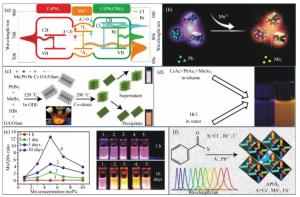
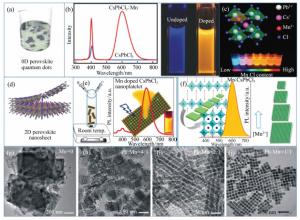
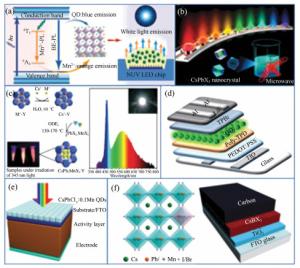
Mn2+-doped CsPbX3 (X=Cl, Br and I) perovskite nanocrystals and their applications
doi: 10.3788/CO.20191205.0933
-
摘要: 胶体锰离子掺杂的纯无机钙钛矿纳米晶由于其优异的光电性质,使其作为一种新兴的荧光发射材料,被研究者们广泛研究。不仅如此,纯无机钙钛矿纳米晶的锰离子掺杂行为也揭示了由于掺杂过程和掺杂剂本身引起的新的光学性质。通过不同的合成方法和选择不同的锰前驱体可以实现不同的掺杂行为,以及由此引发不同的荧光性质。在高带隙钙钛矿主体中进行锰离子掺杂时,其中激发能量由钙钛矿主体转移到掺杂锰离子位点的d态,进而产生橙黄色d-d发射荧光。研究者们一直致力于理解锰离子掺杂过程并由此设计高效掺杂的纳米晶。这些锰离子掺杂的钙钛矿纳米晶由于具有独特的电子和光学特性使其在发光二极管和太阳能电池等应用中发挥了巨大的作用。结合之前的相关工作和进展,本综述重点总结了锰离子掺杂的纯无机钙钛矿纳米晶的合成方法、发光来源、发光机理和潜在应用的最新进展,并提出了未来潜在合理的研究方向。Abstract: Colloidal Mn2+ doped CsPbX3(X=Cl, Br, I) nanocrystals(NCs) are being explored extensively as alternative emitting materials, wherein highly efficient optical and optoelectronic processes can be achieved. Mn2+ doping in perovskite NCs also reveals several new fundamental aspects of doping and new dopant-induced optical properties through different methods of synthesis. Mn2+ doping exists in wide-band-gap perovskite hosts where the excitation energy is transferred to an Mn d-state, resulting in short-range tunable yellow-orange d-d emissions. Enormous efforts have been expended on understanding the doping process and designing highly efficient doped NCs. The unique electronic and fluorescent properties endow these Mn2+ doped perovskite NCs with various optoelectronic applications in light-emitting diodes(LEDs) and solar cells. Combining all these facts, this review focuses on the recent progress in synthesis methods, emission mechanism, and potential applications of Mn2+ doped CsPbX3 perovskite NCs and provides an outline for plausible future studies.
-
Key words:
- perovskite /
- fluorescence /
- Mn2+ doped /
- CsPbX3 perovskite nanocrystals
-
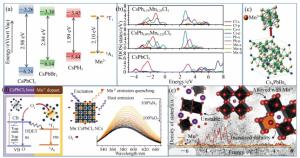
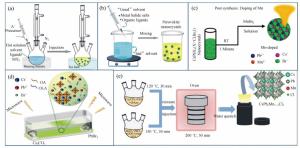
Figure 2. Summary of the selection of Mn sources for various synthesis methods of the Mn2+-doped CsPbX3 NCs. The most used MnCl2(a) and (b)MnBr2 with the aid of HBr(c) MnAc2 with the aid of HCl(d) Mn-stearate(e) manganese acetate, manganese acetylacetonate, and manganese halides with the aid of benzoyl halide(f) as the Mn sources participated in the reaction
Figure 4. (a) The host CsPbX3 band gap and relative positions of Mn2+4T1 and 6A1 states, (b)PDOS of CsPbCl3, CsPb0.875Mn0.125Cl3 and CsPb0.75Mn0.25Cl3, respectively, (c)the synthesis scheme of CsPbxM1-xBr3 NCs by triggering Cs4PbBr6 NCs transformation with MnBr2 salts, (d-e)overview of enhanced stability in optical and structural properties of CsPbxMn1-xI3 NCs(color version please see in the journal website)
Table 1. Comparison of the performance parameters of PLEDs based on different Mn-substitution ratio
Von
(V)Max
EQE(%)Max.CE
(cd·A-1)Max.PE
(lm·W-1)Device structure PLED-pure 3.6 0.81 3.71 0.70 ITO/poly-TPD orPVK/QDs/TPBI/LiF/Al PLED-Mn2.6 3.5 0.95 4.33 0.72 ITO/poly-TPD orPVK/QDs/TPBI/LiF/Al PLED-Mn3.8 4.2 1.49 6.41 1.14 ITO/poly-TPD orPVK/QDs/TPBI/LiF/Al Table 2. Comparison of the performance parameters of PSCs based on different CsPbBrI2 films
Jsc(mA/cm2) Voc/V FF/% PCE/% Jsc(EQE)(mA/cm2) MnCl2-0.5% 14.21 1.133 76.8 12.36 13.86 MnCl2-1% 14.29 1.144 79.9 13.07 13.93 MnCl2-2% 14.37 1.172 80.0 13.47 14.09 Table 3. Key J-V parameters of PSCs with different coated layer thicknesses of CsPbCl3:0.1Mn QDs
QDs(mg/mL) Jsc(mA/cm2) Voc/V FF/% PCE/% CsPbCl3-xMn 1 21.42 1.105 76.4 18.08 CsPbCl3-xMn 5 22.03 1.105 76.3 18.57 CsPbCl3-xMn 20 20.73 1.105 76.6 17.55 -
[1] PAN J, QUAN L N, ZHAO Y B, et al.. Highly efficient perovskite-quantum-dot light-emitting diodes by surface engineering[J]. Advanced Materials, 2016, 28(39):8718-8725. doi: 10.1002/adma.201600784 [2] LI X M, YU D J, CAO F, et al.. Healing all-inorganic perovskitefilms via recyclable dissolution recyrstallization for compact and smooth carrier channels of optoelectronic devices with high stability[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2016, 26(32):5903-5912. doi: 10.1002/adfm.201601571 [3] ZHANG X L, XU B, ZHANG J B, et al.. All-inorganic perovskite nanocrystals for high-efficiency light emitting diodes:dual-phase CsPbBr3-CsPb2Br5 composites[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2016, 26(25):4595-4600. doi: 10.1002/adfm.201600958 [4] NOZIK A J. Nanophotonics:making the most of photons[J]. Nature Nanotechnology, 2009, 4(9):548-549. doi: 10.1038/nnano.2009.253 [5] YOON H C, KANG H, LEE S, et al.. Study of perovskite QD down-converted LEDs and six-color white LEDs for future displays with excellent color performance[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2016, 8(28):18189-18200. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=d62ee5f31802f1f554bd0ab4c556332c [6] ZHANG X J, WANG H C, TANG A C, et al.. Robust and stable narrow-band green emitter:an option for advanced wide-color-gamut backlight display[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2016, 28(23):8493-8497. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.6b04107 [7] ZHANG X Y, LIN H, HUANG H, et al.. Enhancing the brightness of cesium lead halide perovskite nanocrystal based green light-emitting devices through the interface engineering with perfluorinate dionomer[J]. Nano Letters, 2016, 16(2):1415-1420. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.5b04959 [8] DE ROO J, IBÁÑEZ M, GEIREGAT P, et al.. Highly dynamic ligand binding and light absorption coefficient of cesium lead bromide perovskite nanocrystals[J]. ACS Nano, 2016, 10(2):2071-2081. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.5b06295 [9] PARK Y S, GUO SH J, Makarov N S, et al.. Room temperature single-photon emission from individual perovskite quantum dots[J]. ACS Nano, 2015, 9(10):10386-10393. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.5b04584 [10] LI X M, WU Y, ZHANG SH L, et al.. CsPbX3 quantum dots for lighting and displays:room-temperature synthesis, photoluminescence superiorities, underlying origins and white light-emitting diodes[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2016, 26(15):2435-2445. doi: 10.1002/adfm.201600109 [11] MEYNS M, PERÁLVAREZ M, HEUER-JUNGEMANN A, et al.. Polymer-enhanced stability of inorganic perovskite nanocrystals and their application in color conversion LEDs[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2016, 8(30):19579-19586. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=8b7bf7a0c31ea260ea0dc34f56b8052f [12] WEI ZH H, PERUMAL A, SU R, et al..Solution-processed highly bright and durable cesium lead halide perovskite light-emitting diodes[J]. Nanoscale, 2016, 8(42):18021-18026. doi: 10.1039/C6NR05330K [13] DAS ADHIKARIS, GURIA A K, PRADHAN N. Insights of doping and the photoluminescence properties of Mn-doped perovskite nanocrystals[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 2019, 10(9):2250-2257. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.9b00182 [14] VLASKIN V A, JANSSEN N, VAN RIJSSEL J, et al.. Tunable dual emission in doped semiconductor nanocrystals[J]. Nano Letters, 2010, 10(9):3670-3674. doi: 10.1021/nl102135k [15] XIE R G, PENG X G. Synthesis of Cu-doped InP nanocrystals(d-dots) with ZnSe diffusion barrier as efficient and color-tunable NIR emitters[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2009, 131(30):10645-10651. doi: 10.1021/ja903558r [16] VLASKIN V A, BARROWS C J, ERICKSON C S, et al.. Nanocrystaldiffusion doping[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2013, 135(38):14380-14389. doi: 10.1021/ja4072207 [17] MAGANA D, PERERA S C, HARTER A G, et al.. Switching-on superparamagnetism in Mn/CdS equantum dots[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2006, 128(9):2931-2939. doi: 10.1021/ja055785t [18] STOWELL C A, WIACEK R J, SAUNDERS A E, et al.. Synthesis and characterization of dilutemagnetic semiconductor manganese-doped indium arsenide nanocrystals[J]. Nano Letters, 2003, 3(10):1441-1447. doi: 10.1021/nl034419+ [19] NORRISD J, YAO N, CHARNOCK F T, et al.. High-quality manganese-doped ZnS nanocrystals[J]. Nano Letters, 2001, 1(1):3-7. doi: 10.1021/nl005503h [20] PRADHAN N, GOORSKEY D, THESSING J, et al.. An alternative of CdSe nanocrystale mitters:pure and tunable impurity emissions in ZnSe nanocrystals[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2005, 127(50):17586-17587. doi: 10.1021/ja055557z [21] PRADHAN N, BATTAGLIA D M, LIU Y CH, et al.. Efficient, stable, small, and water-soluble doped ZnSe nanocrystalemitters as non-cadmium biomedical labels[J]. Nano Letters, 2007, 7(2):312-317. doi: 10.1021/nl062336y [22] SRIVASTAVA B B, JANA S, PRADHAN N. Doping Cu in semiconductor nanocrystals:some old and some new physicalinsights[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2011, 133(4):1007-1015. doi: 10.1021/ja1089809 [23] MANNA G, JANA S, BOSE R, et al.. Mn-doped multinary CIZS and AIZS nanocrystals[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 2012, 3(18):2528-2534. doi: 10.1021/jz300978r [24] ACHARYA S, SARKAR S, PRADHAN N. Material diffusion anddoping of Mn in wurtzite ZnSe nanorods[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2013, 117(11):6006-6012. doi: 10.1021/jp400456t [25] KAMAT P V. Semiconductor nanocrystals:to dope or not todope[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 2011, 2(21):2832-2833. doi: 10.1021/jz201345y [26] SANTRA P K, KAMAT P V. Mn-doped quantum dot sensitized solar cells:a strategy to boost efficiency over 5%[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2012, 134(5):2508-2511. doi: 10.1021/ja211224s [27] SARKAR S, GURIA A K, PRADHAN N. Influence of doping on semiconductor nanocrystals mediated charge transfer and photocatalytic organic reaction[J]. Chemical Communications, 2013, 49(54):6018-6020. doi: 10.1039/c3cc41599f [28] PRADHAN N, SARMA D D. Advances in light-emitting doped semiconductor nanocrystals[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 2011, 2(21):2818-2826. doi: 10.1021/jz201132s [29] LIU W Y, LIN Q L, LI H B, et al.. Mn2+-doped lead halide perovskite nanocrystals with dual-color emission controlled by halide content[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2016, 138(45):14954-14961. doi: 10.1021/jacs.6b08085 [30] PAROBEK D, ROMAN B J, DONG Y T, et al.. Exciton-to-dopant energy transfer in Mn-doped cesium lead halide perovskite nanocrystals[J]. Nano Letters, 2016, 16(12):7376-7380. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.6b02772 [31] LIU H W, WU ZH N, SHAO J R, et al.. CsPbxMn1-xCl3 perovskite quantum dots with high Mn substitution ratio[J]. ACS Nano, 2017, 11(2):2239-2247. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.6b08747 [32] GURIA A K, DUTTA S K, DAS ADHIKARI S, et al.. Doping Mn2+ in lead halide perovskite nanocrystals:successes and challenges[J]. ACS Energy Letters, 2017, 2(5):1014-1021. doi: 10.1021/acsenergylett.7b00177 [33] SWARNKAR A, RAVI V K, NAG A. Beyond colloidal cesium lead halide perovskite nanocrystals:analogous metal halides and doping[J]. ACS Energy Letters, 2017, 2(5):1089-1098. doi: 10.1021/acsenergylett.7b00191 [34] ZHOU Y, CHEN J, BAKR O M, et al.. Metal-doped lead halide perovskites:synthesis, properties, and optoelectronic applications[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2018, 30(19):6589-6613. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.8b02989 [35] CAI D, ZHU D H, YUAN X, et al.. Thermally stable luminescence of Mn2+ in Mn doped CsPbCl3 nanocrystals embedded in polydimethylsiloxane films[J]. Journal of Luminescence, 2018, 202:157-162. doi: 10.1016/j.jlumin.2018.05.061 [36] HE M L, CHENG Y Z, YUAN R R, et al.. Mn-doped cesium lead halide perovskite nanocrystals with dual-color emission for WLED[J]. Dyesand Pigments, 2018, 152:146-154. doi: 10.1016/j.dyepig.2018.01.045 [37] HE M L, CHENG Y Z, SHEN L L, et al.. Mn-doped CsPbCl3 perovskite quantum dots(PQDs) incorporated into silica/alumina particles used for WLEDs[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2018, 448:400-406. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.04.098 [38] HE T CH, LI J Z, REN C, et al.. Strong two-photon absorption of Mn-doped CsPbCl3 perovskite nanocrystals[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2017, 111(21):211105. doi: 10.1063/1.5008437 [39] LIN CH CH, XU K Y, WANG D, et al.. Luminescent manganese-doped CsPbCl3 perovskite quantum dots[J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7:45906. doi: 10.1038/srep45906 [40] XU W, LI F M, LIN F Y, et al.. Synthesis of CsPbCl3-Mn nanocrystals via cation exchange[J]. Advanced Optical Materials, 2017, 5(21):1700520. doi: 10.1002/adom.201700520 [41] XU K Y, MEIJERINK A. Tuning exciton-Mn2+ energy transfer in mixed halide perovskite nanocrystals[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2018, 30(15):5346-5352. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.8b02157 [42] YE SH, ZHAO M J, SONG J, et al.. Controllable emission bands and morphologies of high-quality CsPbX3 perovskite nanocrystals prepared in octane[J]. Nano Research, 2018, 11(9):4654-4663. doi: 10.1007/s12274-018-2046-4 [43] HU Q S, LI ZH, TAN ZH F, et al.. Rare earth ion-doped CsPbBr3 nanocrystals[J]. Advanced Optical Materials, 2018, 6(2):1700864. doi: 10.1002/adom.201700864 [44] HUANG G G, WANG CH L, XU SH H, et al.Postsynthetic doping of MnCl2 molecules into preformed CsPbBr3 perovskite nanocrystals via a halide exchange-driven cation exchange[J]. Advanced Materials, 2017, 29(29):1700095. doi: 10.1002/adma.201700095 [45] HE M L, CHENG Y Z, SHEN L L, et al.. Doping manganese into CsPb(Cl/Br)3 quantum dots glasses:dual-color emission and super thermal stability[J]. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2019, 102(3):1090-1100. doi: 10.1111/jace.15945 [46] WANG P CH, DONG B H, CUI ZH J, et al.. Synthesis and characterization of Mn-doped CsPb(Cl/Br)3 perovskite nanocrystals with controllable dual-color emission[J]. RSC Advances, 2018, 8(4):1940-1947. doi: 10.1039/C7RA13306E [47] LI F, XIA ZH G, GONG Y, et al.. Optical properties of Mn2+ doped cesium lead halide perovskite nanocrystals via a cation-anion co-substitution exchange reaction[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2017, 5(36):9281-9287. doi: 10.1039/C7TC03575F [48] WU H, XU SH H, SHAO H B, et al.. Single component Mn-doped perovskite-related CsPb2ClxBr5-x nanoplatelets with a record white light quantum yield of 49%:a new single layer color conversion material for light-emitting diodes[J]. Nanoscale, 2017, 9(43):16858-16863. doi: 10.1039/C7NR06538H [49] ERWIN S C, ZU L J, HAFTEL M I, et al.. Doping semiconductor nanocrystals[J]. Nature, 2005, 436(7047):91-94. doi: 10.1038/nature03832 [50] ACHARYA S, SARMA D D, JANA N R, et al.. An alternate route to high-quality ZnSe and Mn-Doped ZnSe nanocrystals[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 2010, 1(2):485-488. doi: 10.1021/jz900291a [51] AMIT Y, LI Y Y, FRENKEL A I, et al.. From impurity doping to metallic growth in diffusion doping:properties and structure of silver-doped InAs nanocrystals[J]. ACS Nano, 2015, 9(11):10790-10800. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.5b03044 [52] NELSON H D, BRADSHAW L R, BARROWS C J, et al.. Picosecond dynamics of excitonic magnetic polarons in colloidal diffusion-doped Cd1-xMnxSe quantum dots[J]. ACS Nano, 2015, 9(11):11177-11191. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.5b04719 [53] PROTESESCU L, YAKUNIN S, BODNARCHUK M I, et al.. Nanocrystals of cesium lead halide perovskites(CsPbX3, X=Cl, Br, and I):novel optoelectronic materials showing bright emission with wide color gamut[J]. Nano Letters, 2015, 15(6):3692-3696. doi: 10.1021/nl5048779 [54] ZHU J R, YANG X L, ZHU Y H, et al.. Room-temperature synthesis of Mn-doped cesium lead halide quantum dots with high Mn substitution ratio[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 2017, 8(17):4167-4171. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.7b01820 [55] MIR W J, MAHOR Y, LOHAR A, et al.. Postsynthesis doping of Mn and Yb into CsPbX3(X=Cl, Br, or I) perovskite nanocrystals for down-conversion emission[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2018, 30(22):8170-8178. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.8b03066 [56] BAGHBANZADEH M, CARBONE L, COZZOLI P D, et al.. Microwave-assisted synthesis of colloidal inorganic nanocrystals[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2011, 50(48):11312-11359. doi: 10.1002/anie.201101274 [57] LI L L, JI J, FEI R, et al.. A facile microwave avenue to electrochemiluminescent two-color graphene quantum dots[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2012, 22(14):2971-2979. doi: 10.1002/adfm.201200166 [58] HE Y, ZHONG Y L, PENG F, et al.. One-pot microwave synthesis of water-dispersible, ultra photo-and pH-stable, and highly fluorescent silicon quantum dots[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2011, 133(36):14192-14195. doi: 10.1021/ja2048804 [59] HE Y, LU H T, SAI L M, et al.. Microwave synthesis of water-dispersed CdTe/CdS/Zn Score-shell-shell quantum dots with excellent photostability and biocompatibility[J]. Advanced Materials, 2008, 20(18):3416-3421. doi: 10.1002/adma.200701166 [60] DING K L, LU H, ZHANG Y CH, et al.. Microwave synthesis of microstructured and nanostructured metal chalcogenides from elemental precursors in phosphonium ionic liquids[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2014, 136(44):15465-15468. doi: 10.1021/ja508628q [61] LIU H W, WU ZH N, GAO H, et al.. One-step preparation of cesium lead halide CsPbX3(X=Cl, Br, and I) perovskite nanocrystals by microwave irradiation[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2017, 9(49):42919-42927. doi: 10.1021/acsami.7b14677 [62] LONG Z, REN H, SUN J H, et al.. High-throughput and tunable synthesis of colloidal CsPbX3 perovskite nanocrystals in a heterogeneous system by microwave irradiation[J]. Chemical Communications, 2017, 53(71):9914-9917. doi: 10.1039/C7CC04862A [63] PAN Q, HU H CH, ZOU Y T, et al.. Microwave-assisted synthesis of high-quality "all-inorganic" CsPbX3(X=Cl, Br, I) perovskite nanocrystals and their application in light emitting diodes[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2017, 5(42):10947-10954. doi: 10.1039/C7TC03774K [64] LI Y X, HUANG H, XIONG Y, et al.. Revealing the formation mechanism of CsPbBr3 perovskite nanocrystals produced via a slowed-down microwave-assisted synthesis[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2018, 57(20):5833-5837. doi: 10.1002/anie.201713332 [65] DENG D H, PAN X L, YU L, et al.. Toward N-doped graphene via solvothermal synthesis[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2011, 23(5):1188-1193. doi: 10.1021/cm102666r [66] LI X M, LIU Y L, SONG X F, et al.. Intercrossed carbon nanorings with pure surface states as low-cost and environment-friendly phosphors for white-light-emitting diodes[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2015, 54(6):1759-1764. doi: 10.1002/anie.201406836 [67] YANG H G, LIU G, QIAO SH ZH, et al.. Solvothermal synthesis and photoreactivity of anatase TiO2 nanosheets with dominant {001} facets[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2009, 131(11):4078-4083. doi: 10.1021/ja808790p [68] ZHONG D, CAI B, WANG X L, et al.. Synthesis of oriented TiO2 nanocones with fast charge transfer for perovskite solar cells[J]. Nano Energy, 2015, 11:409-418. doi: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2014.11.014 [69] CHEN D Q, FANG G L, CHEN X, et al.. Mn-doped CsPbCl3 perovskite nanocrystals:solvothermal synthesis, dual-color luminescence and improved stability[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2018, 6(33):8990-8998. doi: 10.1039/C8TC03139H [70] QIAO T, PAROBEK D, DONG Y T, et al.. Photoinduced Mn doping in cesium lead halide perovskite nanocrystals[J]. Nanoscale, 2019, 11(12):5247-5253. doi: 10.1039/C8NR10439E [71] PAROBEK D, DONG Y T, QIAO T, et al.. Direct hot-injection synthesis of Mn-doped CsPbBr3 nanocrystals[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2018, 30(9):2939-2944. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.8b00310 [72] XU K Y, LIN CH CH, XIE X B, et al.. Efficient and stable luminescence from Mn2+ in core and core-isocrystalline shell CsPbCl3 perovskite nanocrystals[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2017, 29(10):4265-4272. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.7b00345 [73] IMRAN M, CALIGIURI V, WANG M J, et al.. Benzoyl halides as alternative precursors for the colloidal synthesis of lead-based halide perovskite nanocrystals[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2018, 140(7):2656-2664. doi: 10.1021/jacs.7b13477 [74] LI X M, CAO F, YU D J, et al.. All inorganic halide perovskites nano system:synthesis, structural features, optical properties and optoelectronic applications[J]. Small, 2017, 13(9):1603996. doi: 10.1002/smll.201603996 [75] ZHANG Y P, LIU J Y, WANG Z Y, et al.. Synthesis, properties, and optical applications of low-dimensional perovskites[J]. Chemical Communications, 2016, 52(94):13637-13655. doi: 10.1039/C6CC06425F [76] MIR W J, JAGADEESWARARAO M, DAS S, et al.. Colloidal Mn-doped cesium lead halide perovskite nanoplatelets[J]. ACS Energy Letters, 2017, 2(3):537-543. doi: 10.1021/acsenergylett.6b00741 [77] BISWAS A, BAKTHAVATSALAM R, KUNDU J. Efficient exciton to dopant energy transfer in Mn2+-doped(C4H9NH3)2-PbBr4 two-dimensional(2D) layered perovskites[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2017, 29(18):7816-7825. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.7b02429 [78] DAS ADHIKARI S, DUTTA A, DUTTA S K, et al.. Layered perovskites L2(Pb1-xMnx)Cl4 to Mn-doped CsPbCl3 perovskite platelets[J]. ACS Energy Letters, 2018, 3(6):1247-1253. doi: 10.1021/acsenergylett.8b00653 [79] DE A, MONDAL N, SAMANTA A. Luminescence tuning and exciton dynamics of Mn-doped CsPbCl3 nanocrystals[J]. Nanoscale, 2017, 9(43):16722-16727. doi: 10.1039/C7NR06745C [80] SHEN ZH H, QIAO B, XU ZH, et al.. The luminescence properties of CsPbxM1-xBr3 perovskite nanocrystals transformed from Cs4PbBr6 mediated by various divalent bromide MBr2 salts[J]. Nanoscale, 2019, 11(9):4008-4014. doi: 10.1039/C8NR09845J [81] SHAO H, BAI X, CUI H N, et al.. White light emission in Bi3+/Mn2+ ion co-doped CsPbCl3 perovskite nanocrystals[J]. Nanoscale, 2018, 10(3):1023-1029. doi: 10.1039/C7NR08136G [82] AKKERMAN Q A, MEGGIOLARO D, DANG ZH Y, et al.. Fluorescent alloy CsPbxMn1-xI3 perovskite nanocrystals with high structural and optical stability[J]. ACS Energy Letters, 2017, 2(9):2183-2186. doi: 10.1021/acsenergylett.7b00707 [83] LIN F Y, LI F M, LAI ZH W, et al.. MnⅡ-doped cesium lead chloride perovskite nanocrystals:demonstration of oxygen sensing capability based on luminescent dopants and host-dopant energy transfer[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2018, 10(27):23335-23343. doi: 10.1021/acsami.8b06329 [84] YE SH, SUN J Y, HAN Y H, et al.. Confining Mn2+-doped lead halide perovskite in Zeolite-Y as ultrastable orange-red phosphor composites for white light-emitting diodes[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2018, 10(29):24656-24664. doi: 10.1021/acsami.8b08342 [85] ZOU SH H, LIU Y SH, LI J H, et al.. Stabilizing cesium lead halide perovskite lattice through Mn(Ⅱ) substitution for air-stable light-emitting diodes[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2017, 139(33):11443-11450. doi: 10.1021/jacs.7b04000 [86] BAI D L, ZHANG J R, JIN ZH W, et al.. Interstitial Mn2+-driven high-aspect-ratio grain growth for low-trap-density microcrystalline films for record efficiency CsPbI2Br solar cells[J]. ACS Energy Letters, 2018, 3(4):970-978. doi: 10.1021/acsenergylett.8b00270 [87] WANG Q, ZHANG X SH, JIN ZH W, et al.. Energy-down-shift CsPbCl3:Mn quantum dots for boosting the efficiency and stability of perovskite solar cells[J]. ACS Energy Letters, 2017, 2(7):1479-1486. doi: 10.1021/acsenergylett.7b00375 [88] LIANG J, LIU Z H, QIU L B, et al.. Enhancing optical, electronic, crystalline, and morphological properties of cesium lead halide by Mn substitution for high-stability all-inorganic perovskite solar cells with carbon electrodes[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2018, 8(20):1800504. doi: 10.1002/aenm.201800504 [89] LOCARDI F, CIRIGNANO M, BARANOV D, et al.. Colloidal synthesis of double perovskite Cs2AgInCl6 and Mn-doped Cs2AgInCl6 nanocrystals[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2018, 140(40):12989-12995. doi: 10.1021/jacs.8b07983 [90] NANDHA K N, NAG A. Synthesis and luminescence of Mn-doped Cs2AgInCl6 double perovskites[J]. Chemical Communications, 2018, 54(41):5205-5208. doi: 10.1039/C8CC01982G [91] TANG CH, CHEN CH Y, XU W W, et al.. Design of doped cesium lead halide perovskite as a photo-catalytic CO2 reduction catalyst[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2019, 7(12):6911-6919. doi: 10.1039/C9TA00550A -





 下载:
下载: