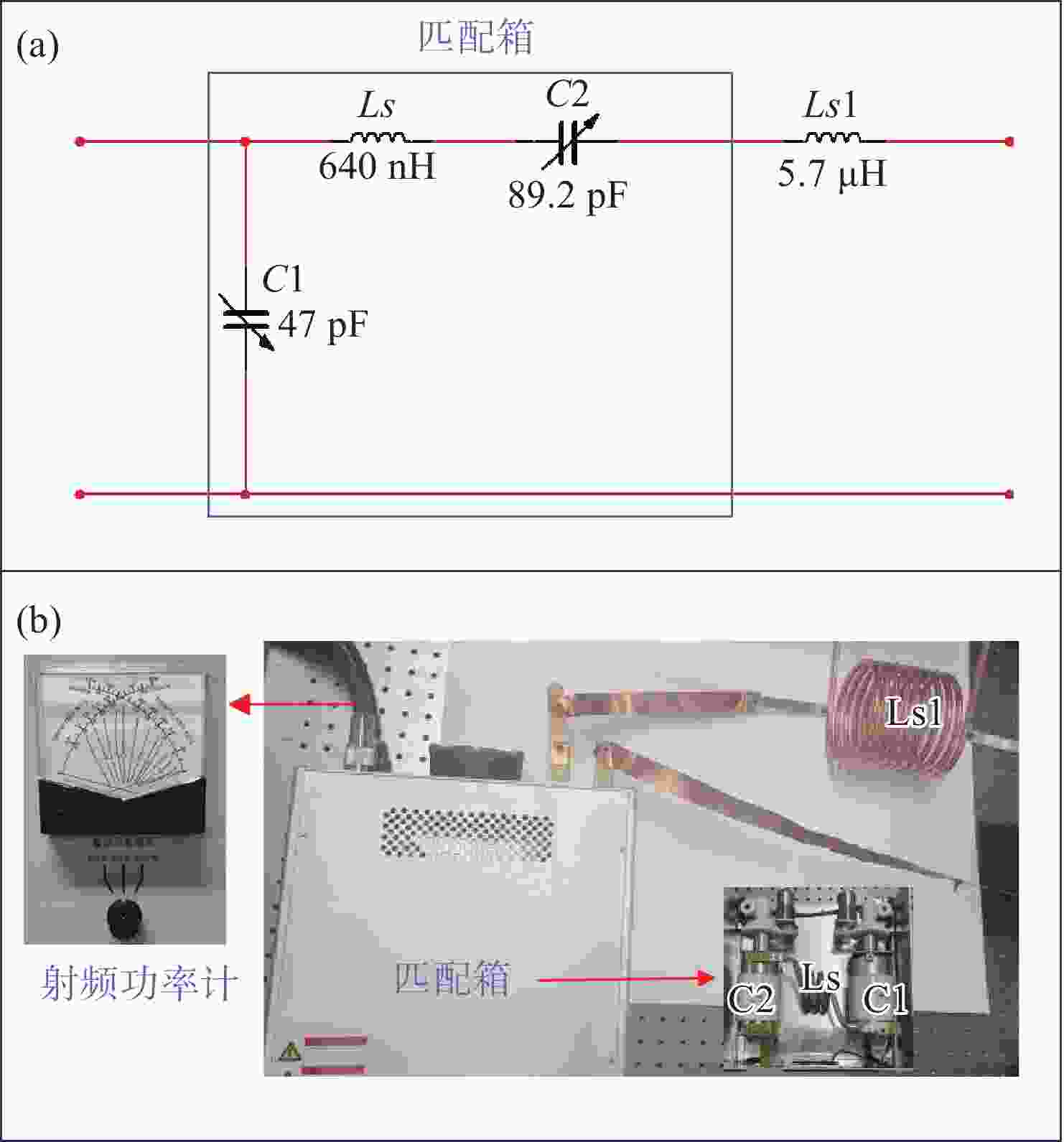
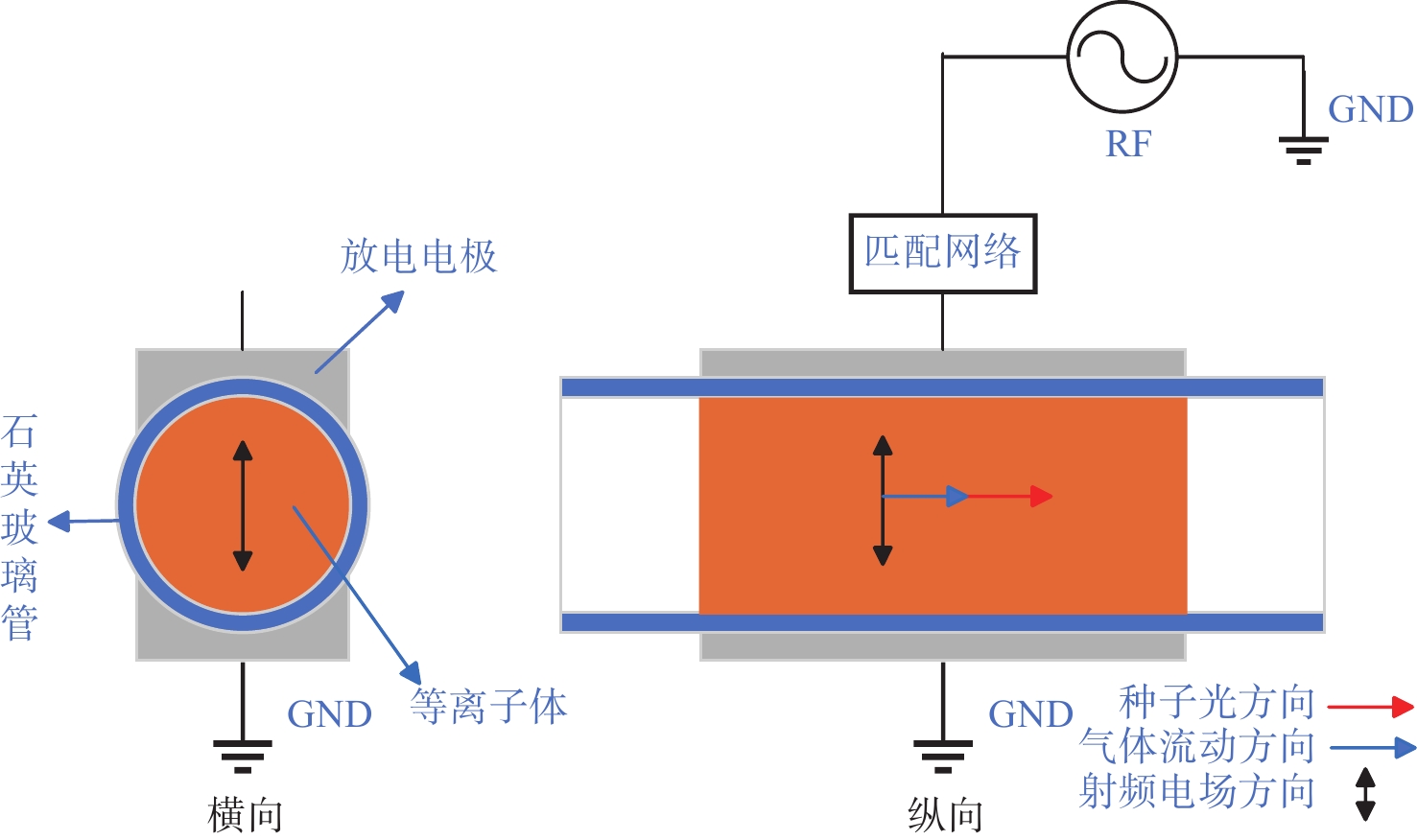
Design of dynamic L-type impedance matching network in RF excited fast axial flow CO2 lasers
-
摘要:
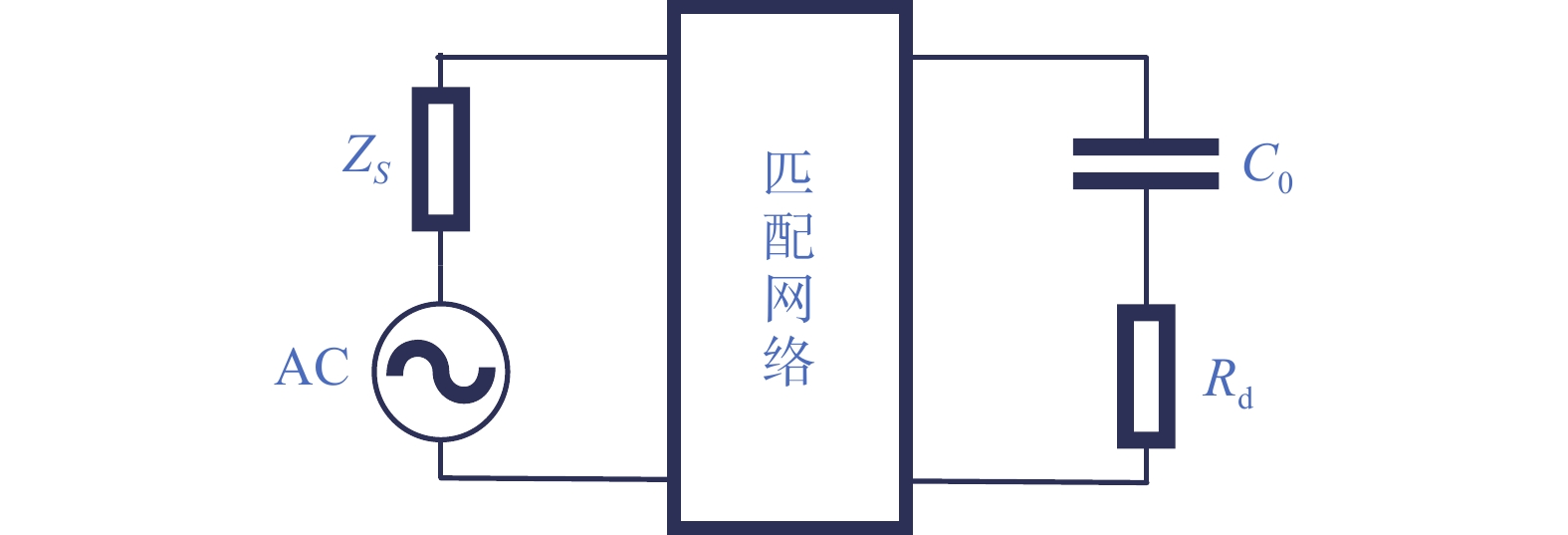
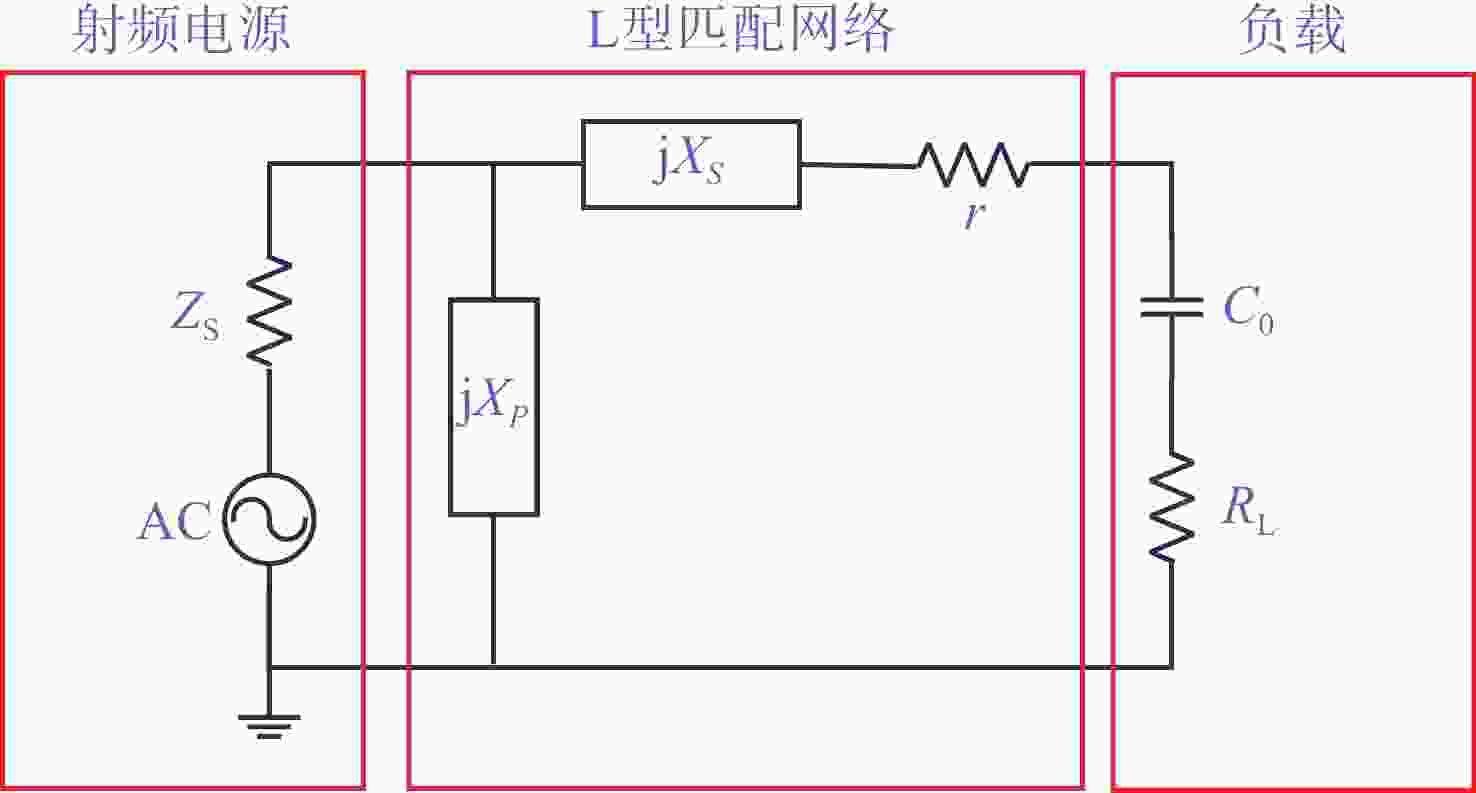
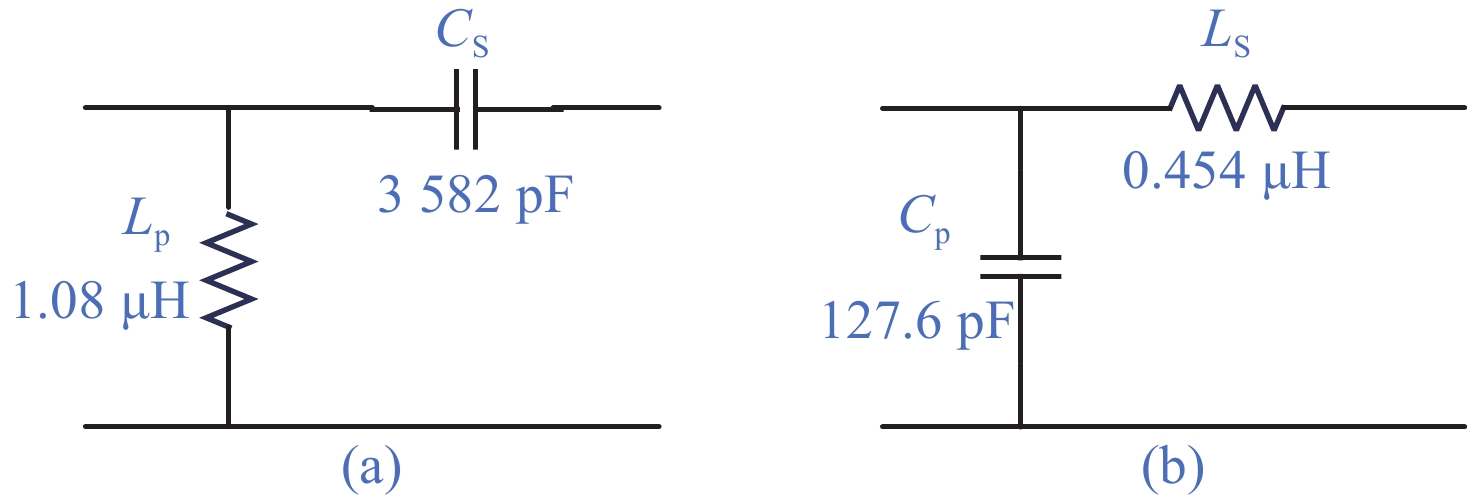
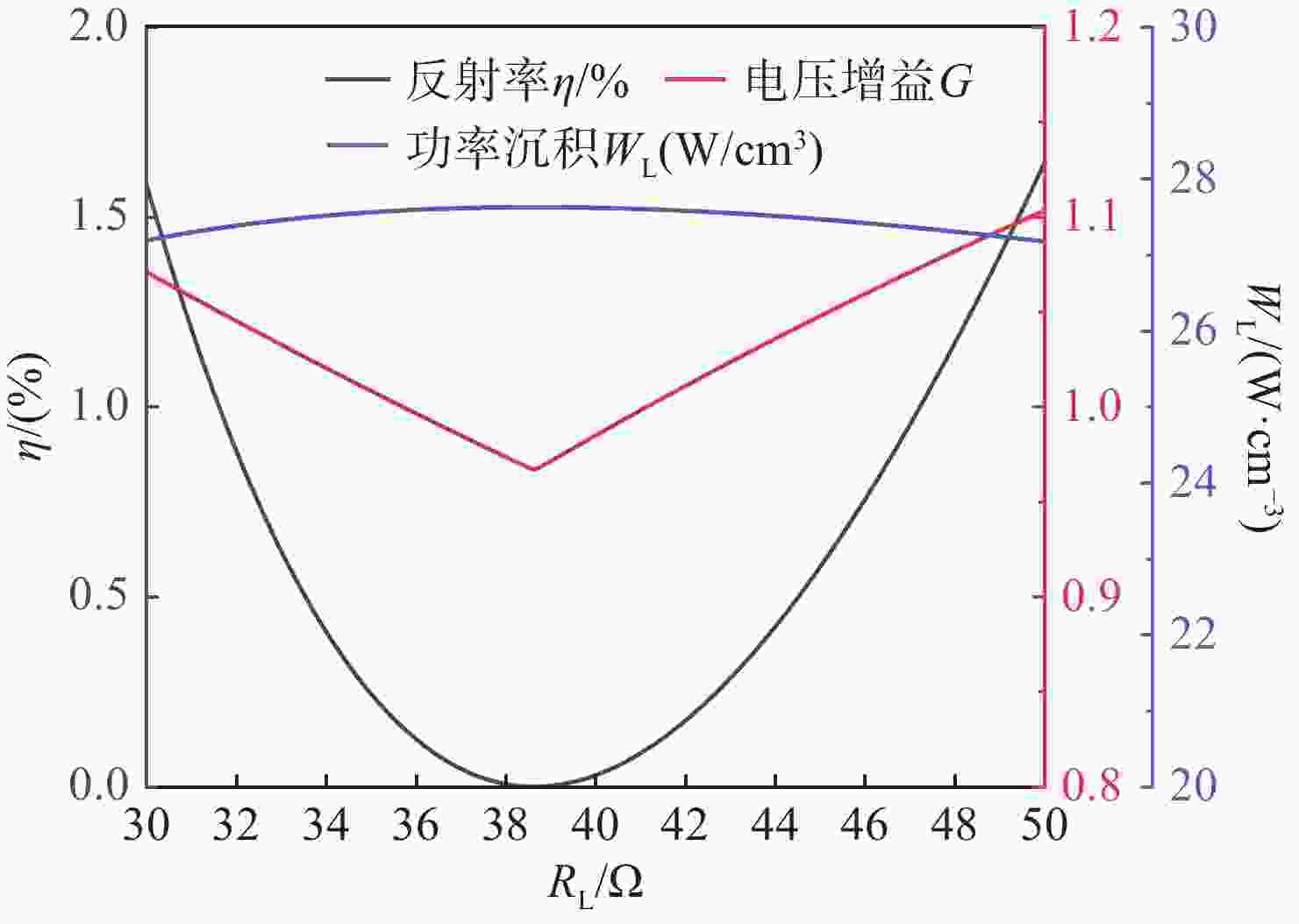
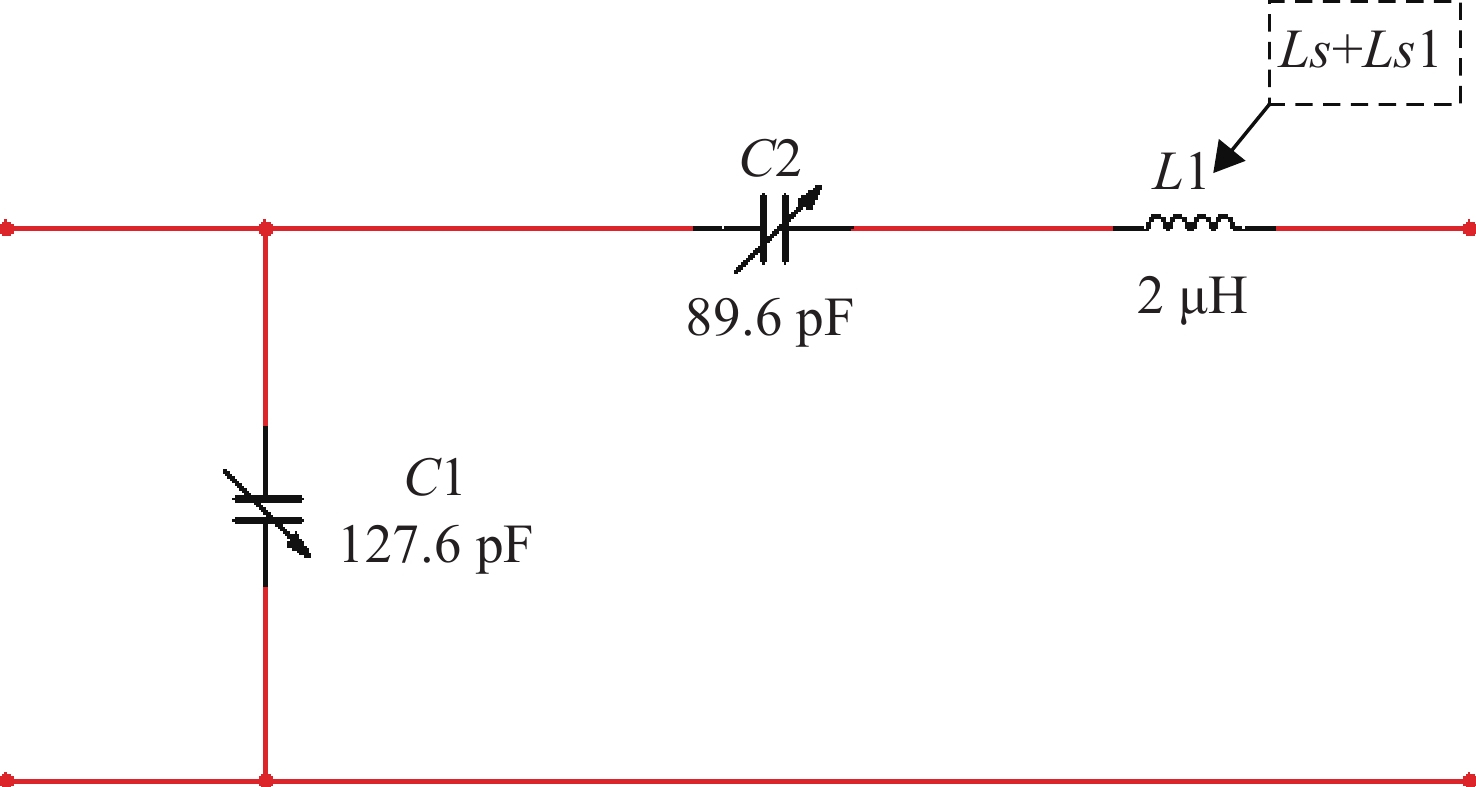
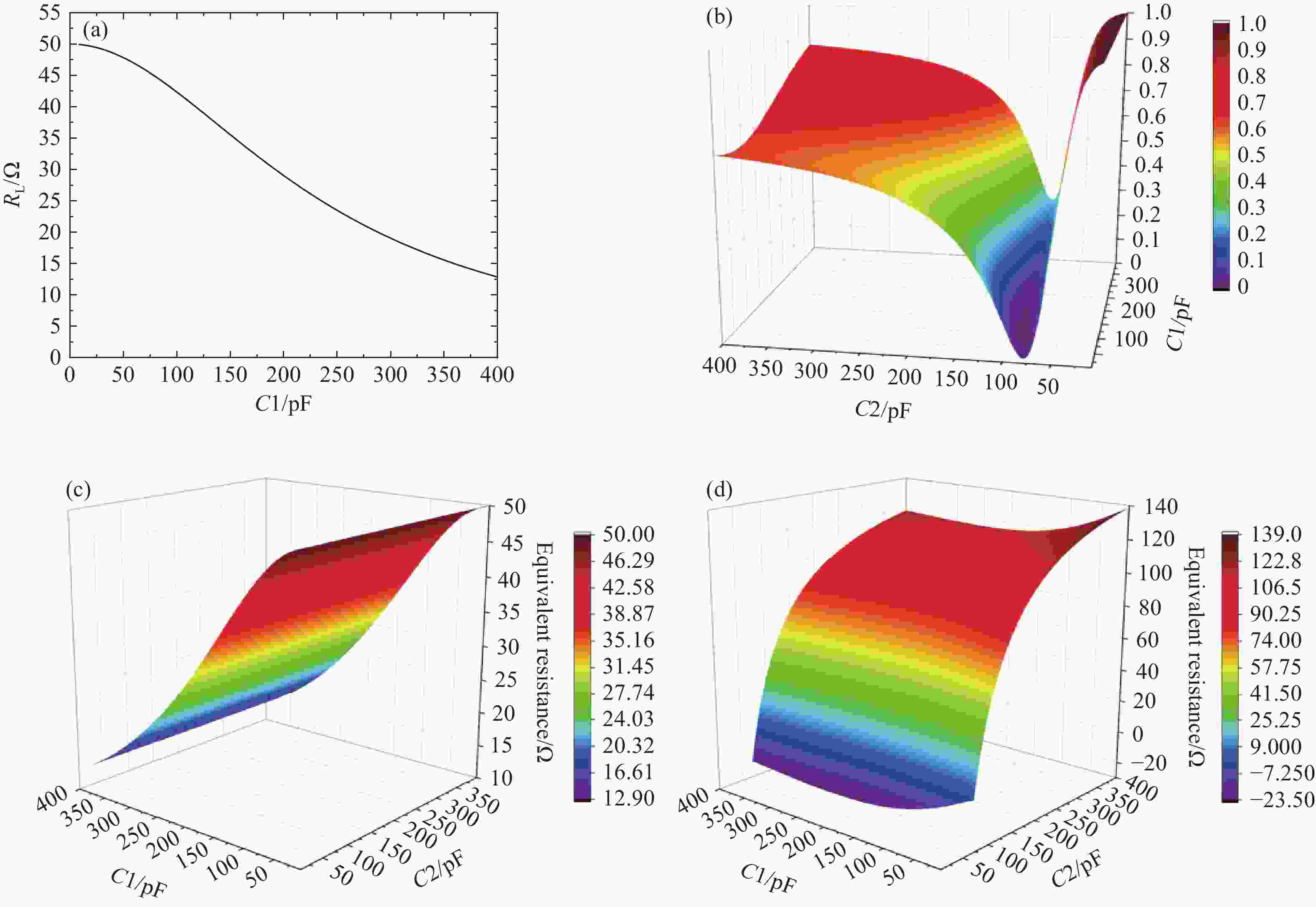
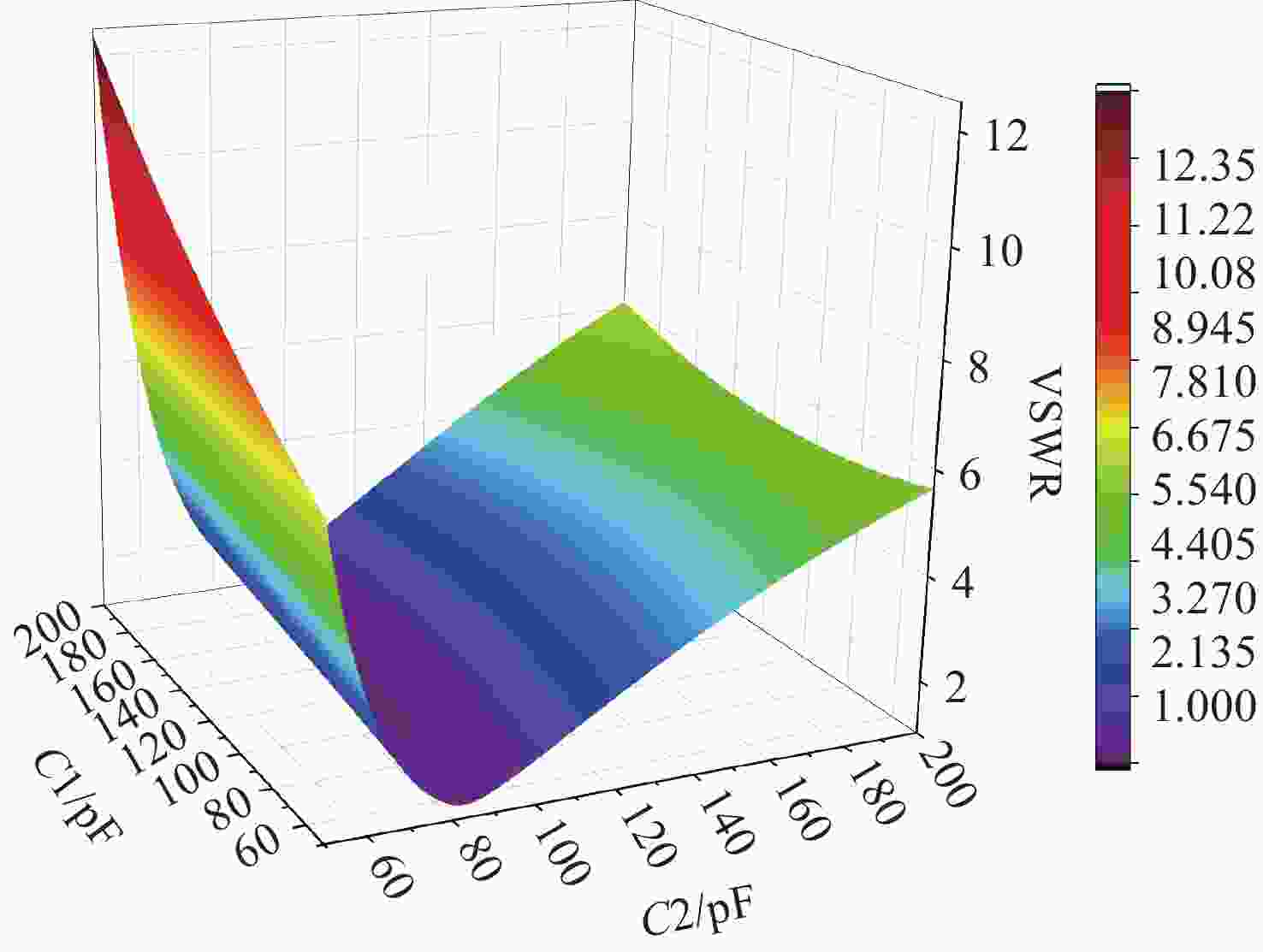
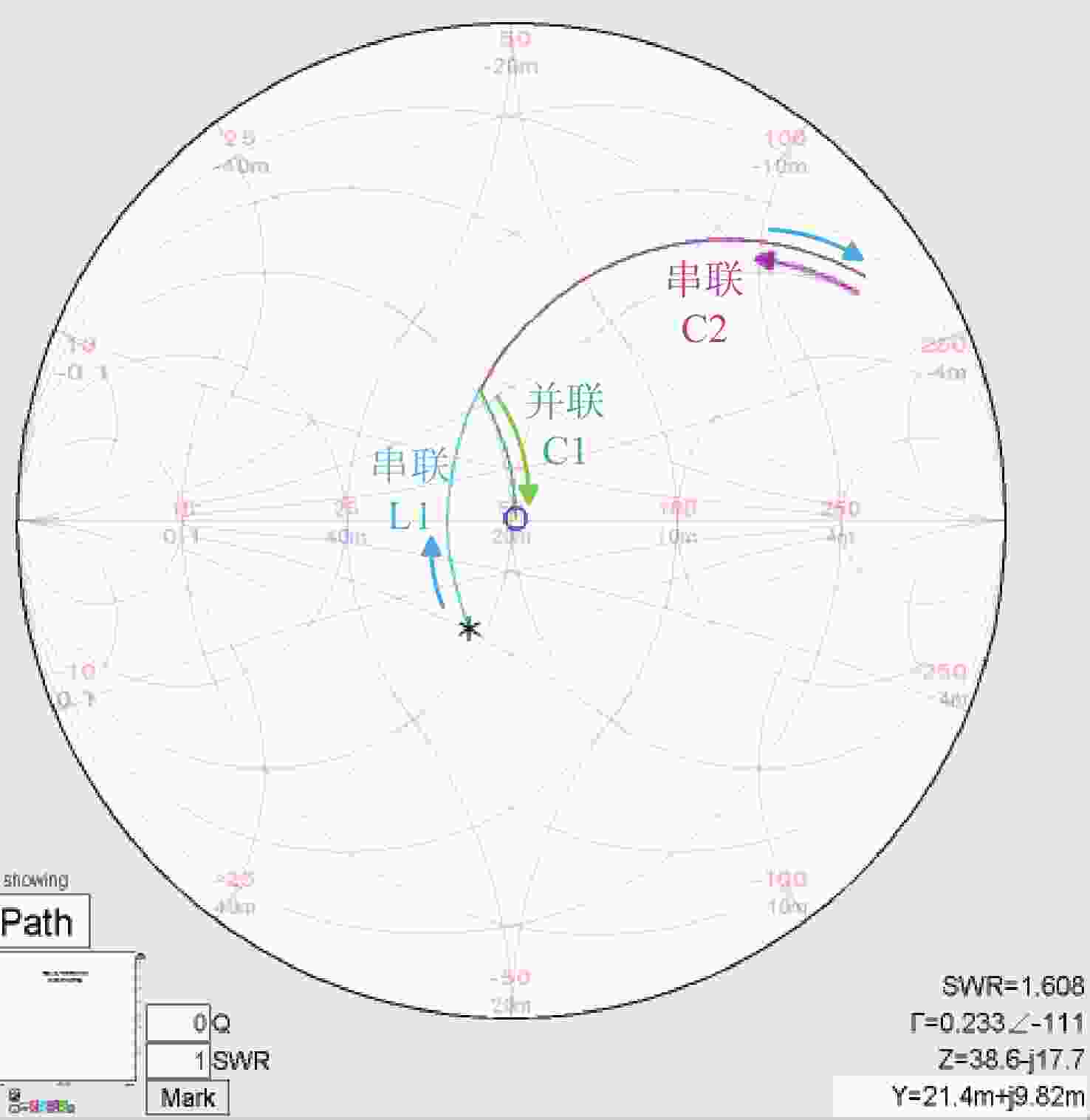
针对高功率轴快流CO2激光器射频放电阻抗的匹配问题,本文设计了低反射率、高动态匹配范围的阻抗匹配网络,以实现射频激励轴快流CO2激光器在不同放电结构下射频功率的高效利用。基于射频电路阻抗匹配理论,构建了多电极等效电路模型,提出向匹配网络中引入可调高压陶瓷电容的方法,设计了适用于高功率射频激励轴快流CO2激光器的动态L型匹配网络。模拟的动态L型匹配网络可向16根放电管注入60 kW射频功率,在12.81 Ω~49.94 Ω总负载阻抗范围内反射率小于1%。搭建了单管射频放电实验装置,实验测得动态L型匹配网络在4 kW注入功率下反射率小于1%,与仿真结果相符。上述结果表明引入可调高压陶瓷电容的动态L型匹配网络能够实现高动态范围内的阻抗匹配,基本满足高功率射频激励轴快流CO2激光器匹配电路的设计要求。
Abstract:In order to solve the problem of RF discharge impedance matching of high-power fast axial flow CO2 lasers, an impedance matching network with low reflectivity and high dynamic matching range was designed to realize the efficient utilization of RF excited fast axial flow CO2 lasers under different discharge structures. Based on the impedance matching theory of RF circuits, a multi-electrode equivalent circuit model was constructed, a method of introducing tunable high-voltage ceramic capacitors into the matching network was proposed, and a dynamic L-type matching network suitable for high-power RF excited fast axial flow CO2 lasers was designed. The simulated dynamic L-type matching network can inject 60 kW RF power into 16 discharge tubes and achieve a reflectivity of less than 1% in the range of total load impedance of 12.81 Ω~49.94 Ω. A single-tube RF discharge experimental device was built, and the reflectivity of the dynamic L-type matching network was measured as less than 1% at 4 kW injection power, which was consistent with the simulation results. It is proved that the dynamic L-type matching network with adjustable high-voltage ceramic capacitors can achieve impedance matching in the high dynamic range, which meets the design requirements of high-power RF excited fast axial flow CO2 laser matching circuits.
-
Key words:
- fast axial flow CO2 laser /
- RF excitation /
- impedance matching /
- L-type dynamic matching
-
表 1 激光器工作参数
Table 1. Laser operating parameters
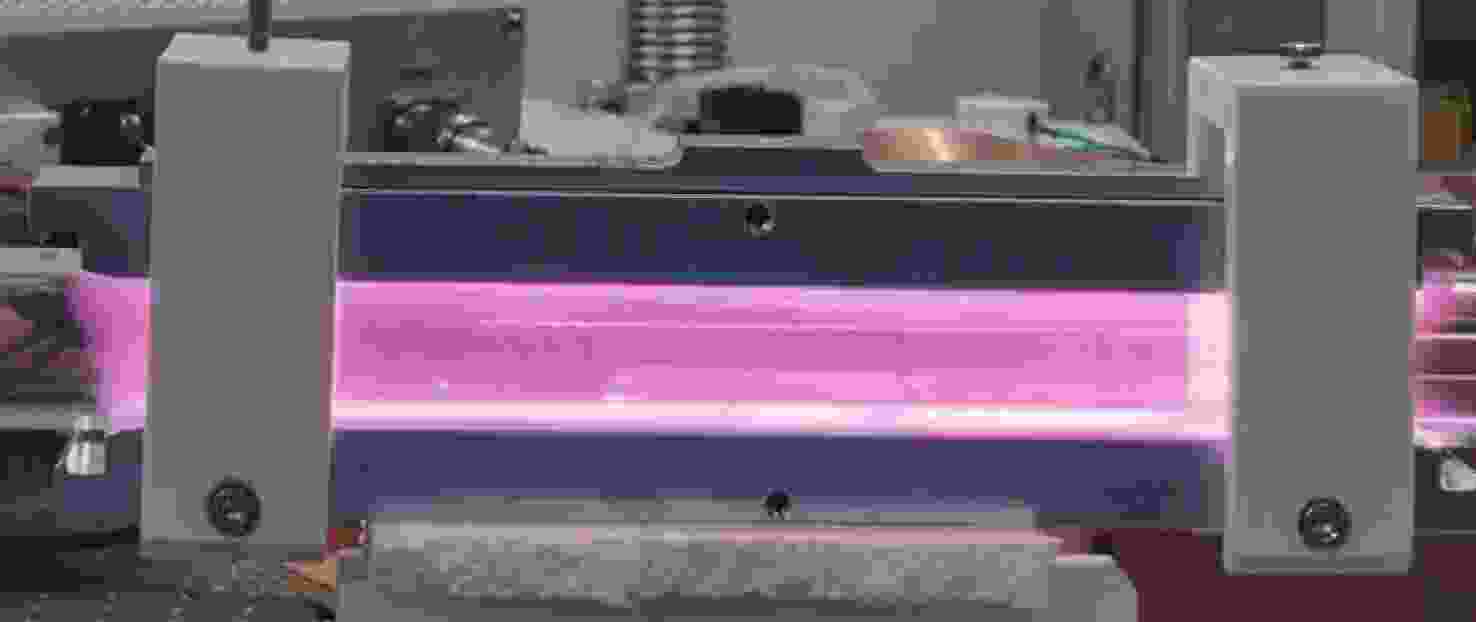
电源功率 射频频率 内径 外径 电极长度 电极面积 工作气压 工作温度 60 kW 13.56 MHz 24 mm 28 mm 300 mm 5.37×10−3 m2 10 kPa 400 K -
[1] 游聪, 黄维, 林高洁, 等. 基于遗传算法的快轴流CO2激光放大器的参数优化[J]. 中国激光, 2024, 51(7): 0701016. doi: 10.3788/CJL231509YOU C, HUANG W, LIN G J, et al. Optimization of fast axial flow CO2 laser amplifier parameters based on genetic algorithm[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2024, 51(7): 0701016. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/CJL231509 [2] 黄维, 游聪, 林高洁, 等. 射频激励轴快流CO2激光放大器增益性能的研究[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2024, 61(23): 02.HUANG W, YOU C, LIN G J, et al. Research on gain performance of radio frequency excited axial fast flow CO2 laser amplifier[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2024, 61(23): 02. (in Chinese). [3] 李艳丽, 刘显和, 伍强. 先进光刻技术的发展历程与最新进展[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2022, 59(9): 0922006.LI Y L, LIU X H, WU Q. Evolution and updates of advanced photolithography technology[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2022, 59(9): 0922006. (in Chinese). [4] 林楠, 杨文河, 陈韫懿, 等. 极紫外光刻光源的研究进展及发展趋势[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2022, 59(9): 0922002.LIN N, YANG W H, CHEN Y Y, et al. Research progress and development trend of extreme ultraviolet lithography source[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2022, 59(9): 0922002. (in Chinese). [5] YU S M, CHEN Z L, WU H, et al. Best impedance matching seeking of single-frequency capacitively coupled plasmas by numerical simulations[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2022, 132(8): 083302. doi: 10.1063/5.0096910 [6] HAGEN J B. 射频电子学: 电路与应用[M]. 鲍景富, 麦文, 牟飞燕, 等译. 2版. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2013.HAGEN J B. Radio-Frequency Electronics: Circuits and Applications[M]. BAO J F, MAI W, MU F Y, et al. trans. 2nd ed. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2013. (in Chinese). [7] 王懿. 容性耦合式射频等离子体放电装置的设计及应用研究[D]. 柳州: 广西科技大学, 2023.WANG Y. Design and application research of capacitive coupled RF plasma discharge device[D]. Liuzhou: Guangxi University of Science and Technology, 2023. (in Chinese). [8] 张浩. ICP源中负载匹配网络的设计[D]. 烟台: 烟台大学, 2023.ZHANG H. Design of load matching network in ICP source[D]. Yantai: Yantai University, 2023. (in Chinese). [9] RODRIGUEZ C, VIOLA J, CHEN Y Q, et al. Modeling and control of L-type network impedance matching for semiconductor plasma etch[J]. Journal of Vacuum Science & Technology B, 2024, 42(2): 022212. [10] HERTZLER C, WOLLERMANN-WINDGASSE R, HABICH U, et al. 30-kW fast-axial-flow CO2 laser with rf excitation[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 1996, 2788: 14-23. doi: 10.1117/12.248621 [11] 李波. 高功率轴快流CO2激光器高效稳定放电方法研究[D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2010.LI B. Study on stable high-effective discharge of high power fast axial flow CO2 laser[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 2010. (in Chinese). [12] BHAGAT M S, BISWAS A K, RANA L B, et al. Impedance matching in RF excited fast axial flow CO2 laser: the role of the capacitance due to laser head[J]. Optics & Laser Technology, 2012, 44(7): 2217-2222. [13] SHIN D, HONG S J. Improved impedance matching speed with gradient descent for advanced RF plasma system[J]. Journal of Vacuum Science & Technology B, 2023, 41(6): 064002. [14] SILAKHORI K, NESHATI R, GHOOCHANI D E, et al. A parametric study on the effects of the electrode size on the performance of a small-size RF-excited fast-axial-flow CO2 laser[J]. Journal of Russian Laser Research, 2023, 44(4): 399-406. doi: 10.1007/s10946-023-10147-5 [15] MOGHBELI F, HE D, ALLCOCK G, et al. Impedance matching in radio-frequency discharge excited waveguide lasers[J]. Journal of Physics E: Scientific Instruments, 1984, 17(12): 1159-1164. doi: 10.1088/0022-3735/17/12/019 [16] 杨金法, 彭虎. 非线性电子线路[M]. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2003.YANG J F, PENG H. Nonlinear Electronic Circuits[M]. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2003. (in Chinese). -





 下载:
下载: