Thermal radiation suppression and cooling optimization in infrared and laser composite detection systems
-
摘要:
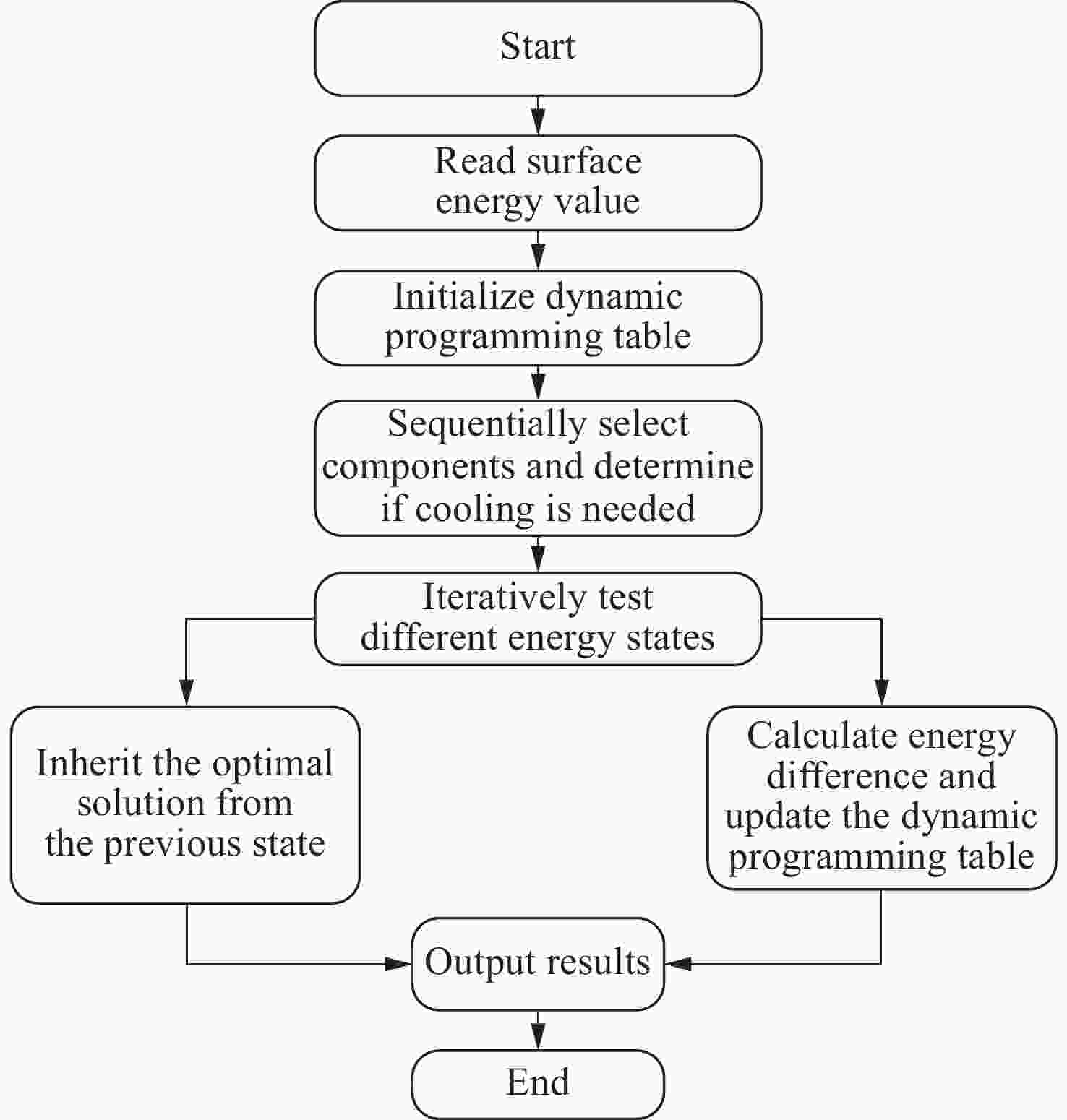
针对远距离暗弱目标探测中红外系统热辐射噪声抑制的关键技术难题,本文设计了一种复合探测系统并提出热辐射制冷抑制优化方案。通过R-C光学结构与分色镜-次镜中空设计,实现长波红外与激光双波段共口径探测。为解决热辐射噪声问题,结合普朗克公式与非序列光线追迹,分析230 K~320 K温度区间的热辐射特性,并建立结合噪声项的改进式探测距离模型。通过动态规划算法优化制冷策略,确定主镜/折转镜遮光罩制冷至220 K的最优方案。结果表明300 K环境下的探测距离从300 km提升至430 km,230 K~320 K环境下探测距离始终大于400 km。本研究提出的双波段复合探测方案与分区制冷方法,为远距离暗弱目标探测及冷光学设计提供了参考。
Abstract:Addressing the critical challenge of thermal radiation noise suppression in infrared systems for long-range dim target detection, this paper presents a composite detection system with an optimized cooling-based thermal radiation suppression scheme. A common-aperture optical configuration capable of simultaneous long-wave infrared and laser dual-band detection is achieved through a Ritchey-Chrétien (R-C) optical structure and a dichroic-secondary mirror with a hollow design. To mitigate thermal radiation noise, the thermal emission characteristics within the temperature range of 230 K to 320 K were analyzed using Planck’s law and non-sequential ray tracing. An improved detection range model incorporating noise terms was developed. The cooling strategy was optimized via dynamic programming, leading to an optimal solution where the main mirror and folding mirror baffles are cooled to 220 K. Experimental results demonstrate that the detection range at 300 K ambient temperature increases from 300 km to 430 km, and remains above 400 km across the entire 230−320 K range. The proposed dual-band composite detection scheme and zoned cooling methodology provide a valuable reference for the design of cold optical systems and long-range weak target detection.
-
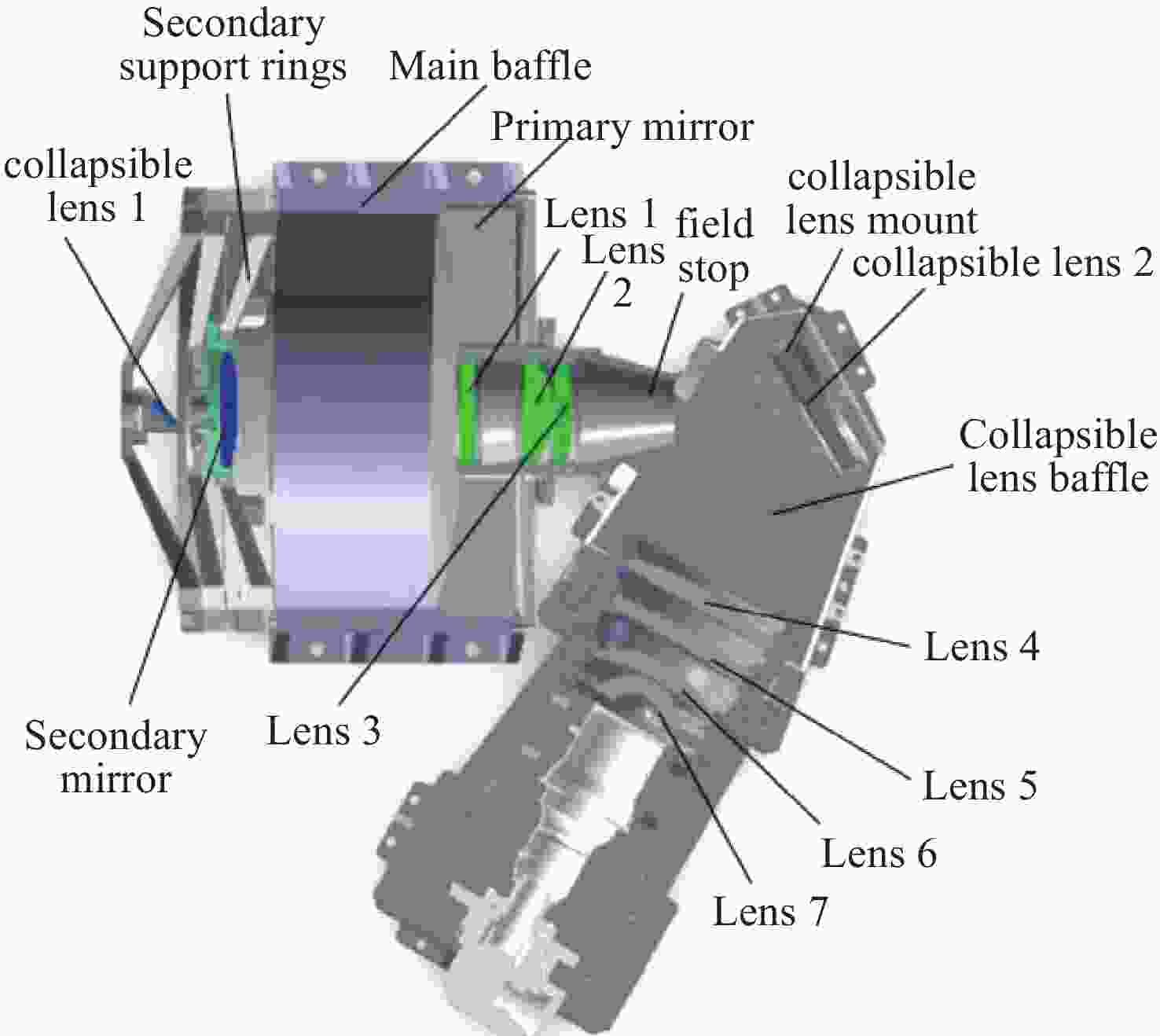
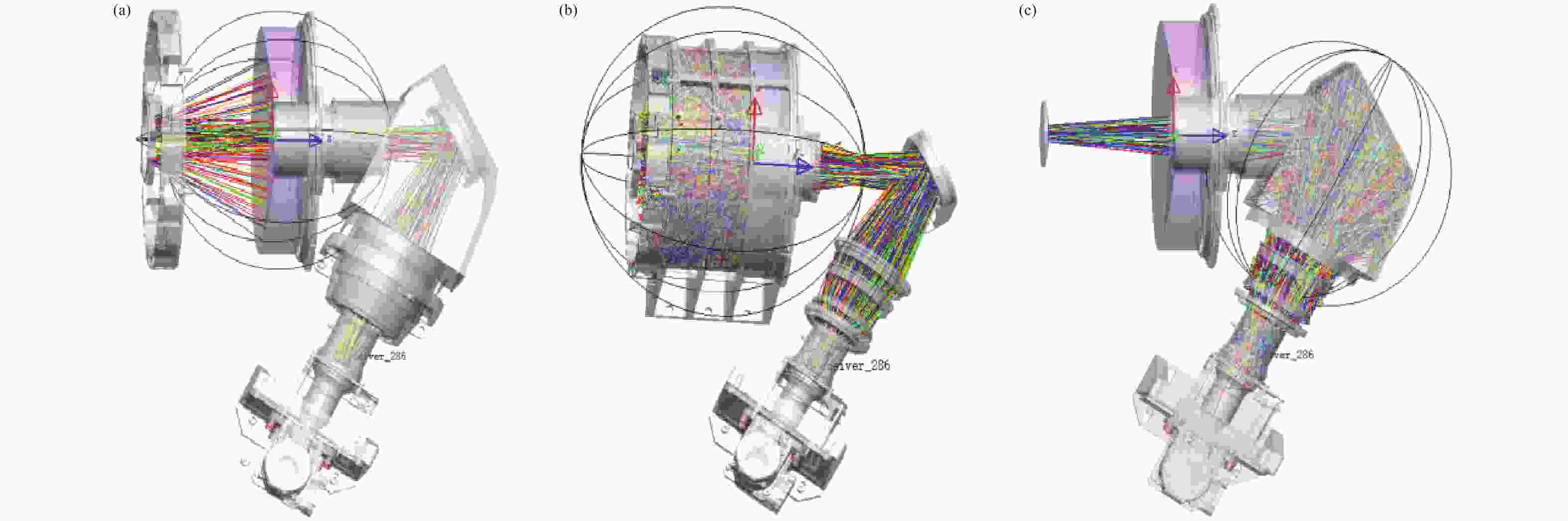
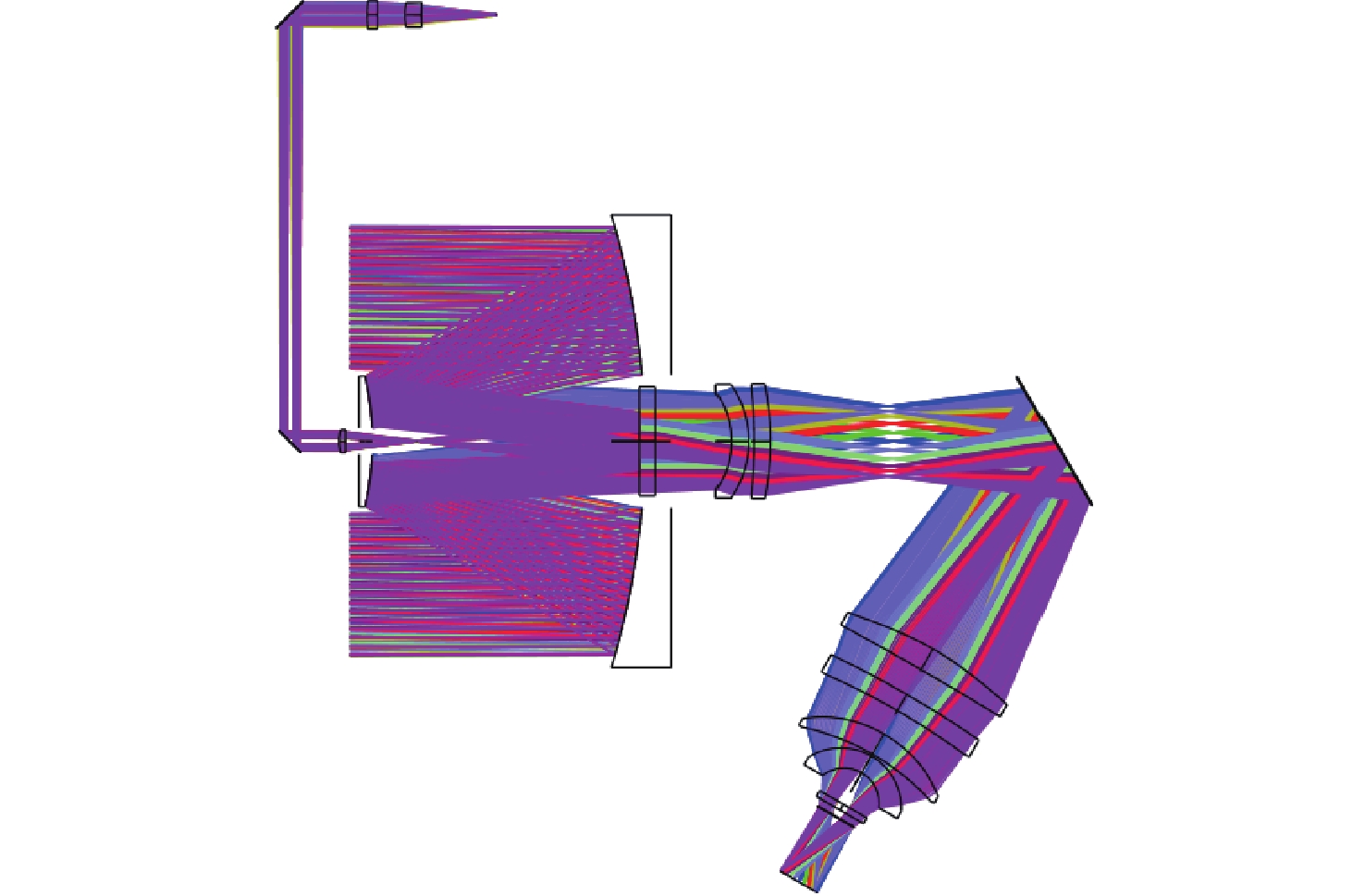
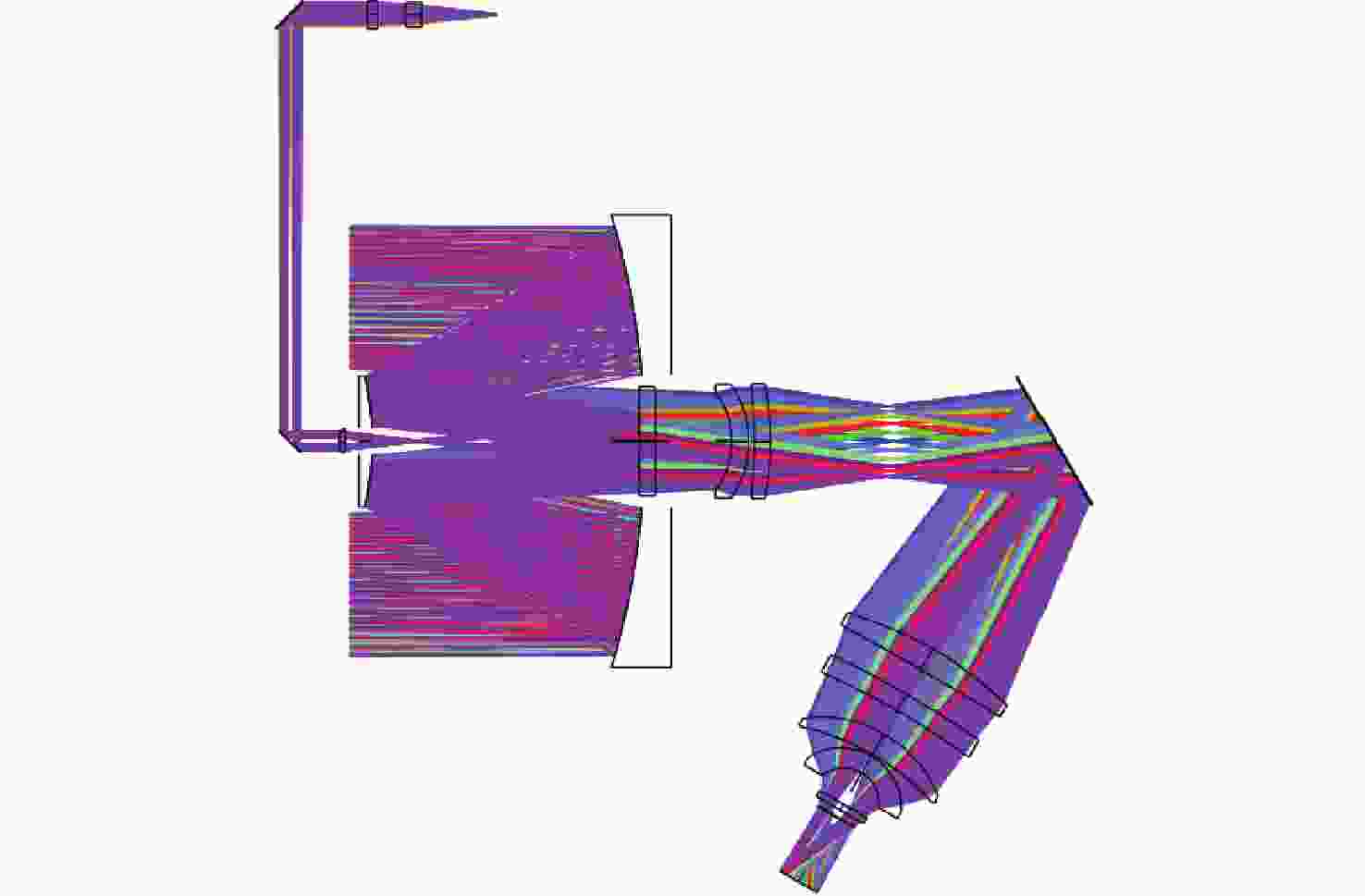
图 6 光机系统的杂散辐射分析示意图(a)主镜杂散辐射分析(b)主镜遮光罩杂散辐射分析(c)折转镜遮光罩杂散辐射分析
Figure 6. Schematic diagram of stray radiation analysis for the optomechanical system: (a) Stray radiation analysis of the primary mirror, (b) Stray radiation analysis of the primary mirror baffle, (c) Stray radiation analysis of the folding mirror baffle.
表 1 复合探测系统参数指标
Table 1. Composite Detection System Parameter Indicators
Parameters LWIR Laser receiving Wavelength 8 µm−10 µm 1064 nm±10 nm Focal length 320 mm 900 mm Detector specification 640×512@25 μm 100 μm×100 μm,
像元数:4×4Field of view 2.86°×2.29° >600 μrad F/# 2 5.6 表 2 长波红外材料的性能
Table 2. Properties of LWIR materials
LWIR
materialRefractive index
at 10 μmTransmission
range (µm)Absorption coefficient at
289 K and 10.6µm (cm−1)GE 4.0032 1.8−17 0.035 Znse 2.4006 0.5−16 0.0005 Zns 2.2002 1−12 0.08 IRG206 2.777 1.0−17 0.03 表 3 常用的红外结构涂层的 ABg 参数
Table 3. ABg Parameters of Common Infrared Structural Coatings
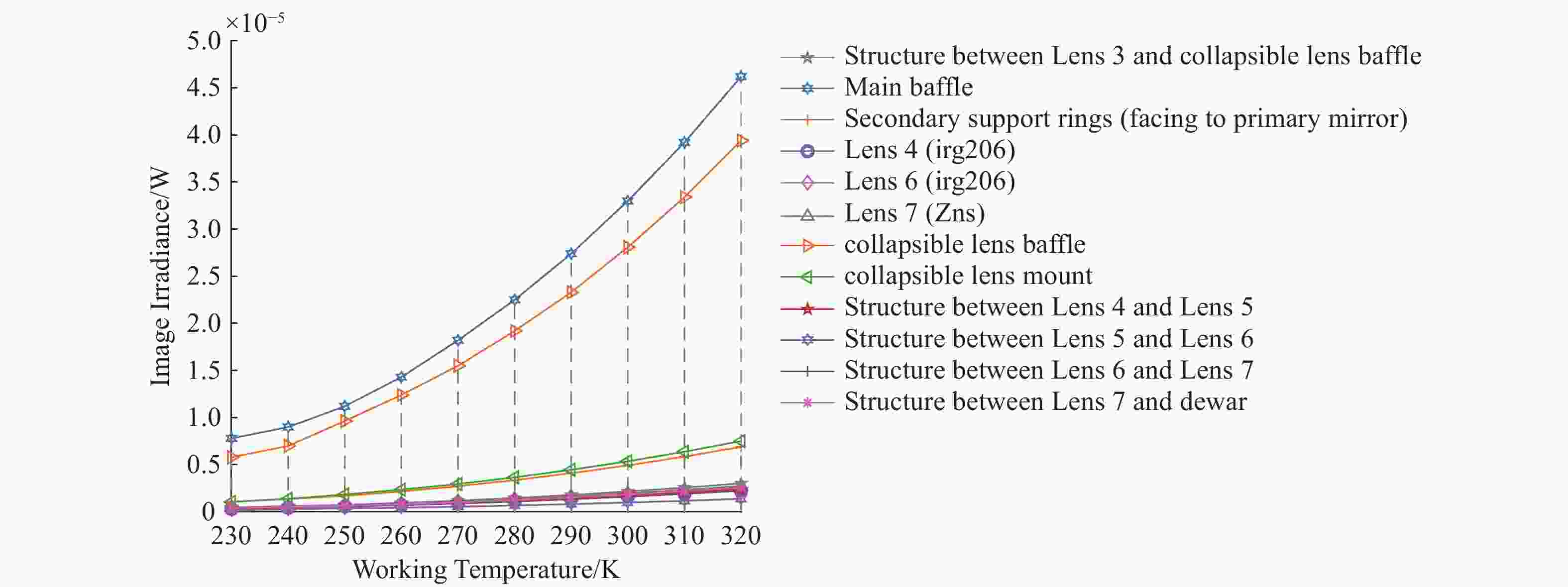
Materials TIS A B g High-Absorption Coating 0.1 0.006366 1 0 Black Nickel 0.14 0.08912 1 0 Z306 0.095 0.06047 1 0 表 4 不同温度下红外系统各表面到达像面的自身杂散辐射分布
Table 4. Distribution of self-scattered radiation at the image plane for infrared system surfaces at different temperatures
Componen Emissivity Radiation Energy Received on the Image Plane from Each Surface at Different Temperatures (W) 230 K 250 K 270 K 290 K 310 K 320 K Primary mirror 0.01 4.79E-08 7.64E-08 1.23E-07 1.85E-07 2.65E-07 3.11E-07 Secondary mirror 0.01 9.95E-09 1.59E-08 2.55E-08 3.84E-08 5.50E-08 6.47E-08 Lens 1 (Ge) 0.012 2.27E-08 3.59E-08 5.76E-08 8.69E-08 1.24E-07 1.46E-07 Lens 2 (ZnS) 0.0728 3.41E-08 5.16E-08 8.29E-08 1.21E-07 1.79E-07 2.10E-07 Lens 3 (ZnSe) 0.0003 7.23E-11 1.82E-10 2.92E-10 4.40E-10 6.29E-10 7.41E-10 Structure between Lens 1 and Lens 2 0.8 9.88E-10 2.37E-09 3.82E-09 5.86E-09 8.45E-08 9.98E-08 Structure between Lens 2 and Lens3 0.8 9.79E-10 2.48E-09 3.98E-09 6.00E-09 8.58E-09 1.01E-08 Structure between Lens 3 and
collapsible lens baffle0.8 4.65E-07 7.41E-07 1.19E-06 1.79E-06 2.57E-06 3.02E-06 Main baffle 0.8 8.47E-06 1.12E-05 1.82E-05 2.74E-05 3.92E-05 4.62E-05 Secondary support rings 0.1 1.06E-06 1.69E-06 2.72E-06 4.10E-06 5.86E-06 6.90E-06 field stop 0.9 4.39E-08 6.92E-08 1.11E-07 1.68E-07 2.40E-07 2.82E-07 collapsible lens 1 0.01 5.10E-08 8.35E-08 1.34E-07 2.02E-07 2.89E-07 3.41E-07 Lens 4 (irg206) 0.023 3.04E-07 5.63E-07 9.04E-07 1.36E-06 1.95E-06 2.23E-06 Lens 5 (ZnSe) 0.00035 5.72E-09 8.27E-09 1.33E-08 2.00E-08 2.86E-08 3.37E-08 Lens 6 (irg206) 0.022 3.60E-07 5.87E-07 9.44E-07 1.42E-06 2.04E-06 2.40E-06 Lens 7 (Zns) 0.0768 4.67E-07 6.73E-07 1.081E-06 1.63E-06 2.33E-06 2.74E-06 collapsible lens 2 0.01 7.65E-09 1.88E-08 3.02E-08 3.73E-08 6.51E-08 7.66E-08 collapsible lens baffle 0.8 5.54E-06 9.64E-06 1.55E-05 2.33E-05 3.34E-05 3.94E-05 collapsible lens mount 0.8 2.92E-07 1.84E-06 2.96E-06 4.46E-06 6.38E-06 7.51E-06 Structure between Lens 4 and Lens 5 0.8 3.34E-07 6.25E-07 1.00E-06 1.51E-06 2.07E-06 2.36E-06 Structure between Lens 5 and Lens 6 0.8 1.58E-07 3.69E-07 5.43E-07 8.15E-07 1.17E-06 1.38E-06 Structure between Lens 6 and Lens 7 0.8 3.47E-07 5.53E-07 8.88E-07 1.34E-06 1.91E-06 2.25E-06 Structure between Lens 7 and dewar 0.1 3.96E-07 6.30E-07 1.01E-06 1.53E-06 2.19E-06 2.57E-06 Total - 1.84E-05 2.95E-05 4.75E-05 7.16E-05 1.02E-04 1.21E-04 表 5 系统参数对比
Table 5. Comparison of system parameters
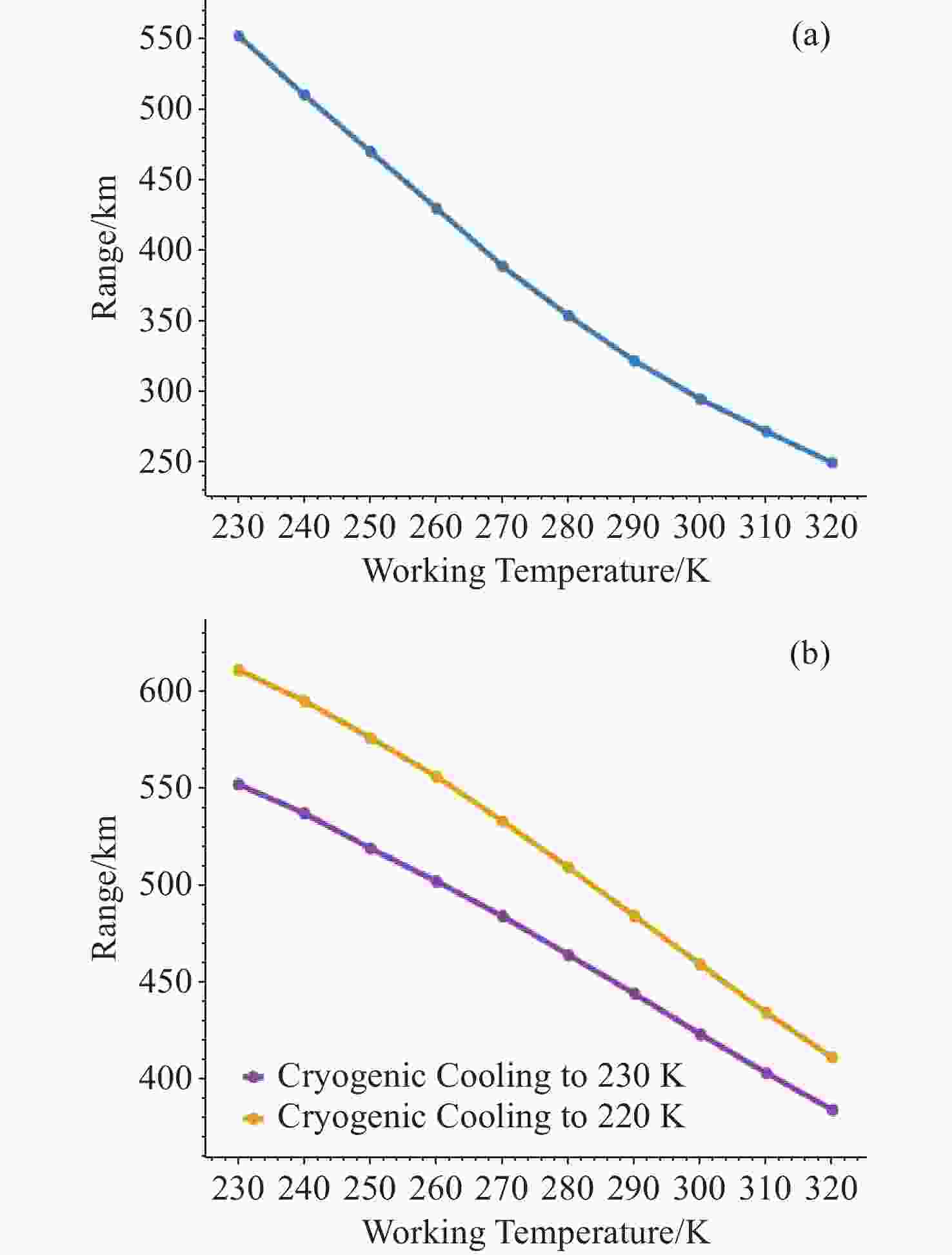
Parameters This Study System Other Study System Aperture 160 mm 300 mm Focal 320 mm 600 mm Wavelength 8µm—10 μm 3µm—5µm Detection Range(work
temperature:20 °C)Without Cooling:300 km
With Cooling:430 km400 km -
[1] ZHANG CH R, PIAO M X, XIE Y F, et al. Optical design of a monolithic compressed folding imaging lens for infrared/laser dual-band[J]. Optics Express, 2023, 31(16): 25691-25706. doi: 10.1364/OE.496908 [2] 陈洁, 夏团结, 杨童, 等. 长波红外与激光共孔径双模导引光学系统研究[J]. 光学学报, 2023, 43(12): 1222001. doi: 10.3788/AOS221609CHEN J, XIA T J, YANG T, et al. Research on long-wave infrared and laser common-aperture dual-mode guided optical system[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2023, 43(12): 1222001. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/AOS221609 [3] 颜洪雷. 红外与激光复合探测关键技术研究[D]. 上海: 中国科学院研究生院(上海技术物理研究所), 2014.YAN H L. Research on key technologies of infrared and laser composite detection[D]. Shanghai: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Shanghai Institute of Technical Physics), 2014. (in Chinese). [4] 吴洪波, 张新, 王灵杰, 等. 单光子激光与中波红外共口径探测光学系统[J]. 光学 精密工程, 2021, 29(6): 1260-1269. doi: 10.37188/OPE.20212906.1260WU H B, ZHANG X, WANG L J, et al. Common aperture optical system of single photon laser and medium wave infrared[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2021, 29(6): 1260-1269. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/OPE.20212906.1260 [5] ZHU Y, ZHANG X, LIU T, et al. Internal and external stray radiation suppression for LWIR catadioptric telescope using non-sequential ray tracing[J]. Infrared Physics & Technology, 2015, 71: 163-170. [6] 牛金星, 周仁魁, 刘朝晖, 等. 红外探测系统自身热辐射杂散光的分析[J]. 光学学报, 2010, 30(8): 2267-2271. doi: 10.3788/AOS20103008.2267NIU J X, ZHOU R K, LIU ZH H, et al. Analysis of stray light caused by thermal radiation of infrared detection system[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2010, 30(8): 2267-2271. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/AOS20103008.2267 [7] 朱海勇, 陈俊林, 曾智江, 等. 用于冷光学长波红外杜瓦组件杂散光分析与抑制[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2023, 52(7): 20220823. doi: 10.3788/IRLA20220823ZHU H Y, CHEN J L, ZENG ZH J, et al. Stray light analysis and suppression of long-wave infrared Dewar component for cold optics[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2023, 52(7): 20220823. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/IRLA20220823 [8] SUN CH M, ZHAO F, ZHANG Z. Stray light analysis of large aperture optical telescope using TracePro[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2014, 9298: 92981F. [9] SHEN L M, LI ZH G, LIU K. Analysis of the internal stray radiation in infrared imaging system based on ambient temperature[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2021, 12061: 120611D. [10] 余菲, 任栖锋, 李华, 等. 同轴全反红外光学系统自身热辐射测量方法[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2018, 47(1): 0104003. doi: 10.3788/IRLA201847.0104003YU F, REN Q F, LI H, et al. Measurement method of self-thermal radiation for coaxial total reflection infrared optical system[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2018, 47(1): 0104003. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/IRLA201847.0104003 [11] 李宝库, 柳乐, 徐伟, 等. 红外系统自身热辐射导致的分布式探测距离变化分析[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2023, 52(3): 20220417. doi: 10.3788/IRLA20220417LI B K, LIU L, XU W, et al. Analysis of distributed detection range changes caused by infrared system self-thermal radiation[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2023, 52(3): 20220417. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/IRLA20220417 [12] 牟达, 韩红霞. 红外系统作用距离方程的比较与分析[J]. 长春理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2012, 35(4): 5-9.MU D, HAN H X. Comparison and analysis for operating range equations of infrared system[J]. Journal of Changchun University of Science and Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2012, 35(4): 5-9. (in Chinese). [13] 陈闽, 吴学铭, 王海晏, 等. 飞行目标红外辐射特性研究及仿真实现[J]. 电光与控制, 2017, 24(6): 57-60.CHEN M, WU X M, WANG H Y, et al. Research and simulation of aircraft infrared radiation characteristics[J]. Electronics Optics & Control, 2017, 24(6): 57-60. (in Chinese). [14] 黄强, 钮新华, 沈学民. 红外光学系统内部热辐射引起的杂散辐射分析[J]. 红外技术, 2006, 28(6): 348-352.HUANG Q, NIU X H, SHEN X M. Stray radiation analysis caused by interior heat radiation in infrared optical systems[J]. Infrared Technology, 2006, 28(6): 348-352. (in Chinese). [15] 曲锐. 机载多波段共孔径动态成像光学系统研究[D]. 西安: 中国科学院大学(中国科学院西安光学精密机械研究所), 2023.QU R. Research on airborne multi-band common aperture dynamic imaging optical system[D]. Xi'an: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Xi'an Institute of Optics & Precision Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences), 2023. (in Chinese). [16] 张发强, 张维光, 万文博. 基于光线追迹的红外探测光学系统杂散辐射研究[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2019, 48(9): 0904006. doi: 10.3788/IRLA201948.0904006ZHANG F Q, ZHANG W G, WAN W B. Research on stray radiation of infrared detection optical system based on ray-tracing[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2019, 48(9): 0904006. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/IRLA201948.0904006 [17] TIAN J G, LI X L, HOU L B, et al. Analysis and suppression of stray radiation in an infrared telescope system in geosynchronous orbit[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2020, 11548: 115480I. [18] 谢鑫龙, 朱晓晓, 朱嘉诚, 等. 非制冷热红外成像光谱仪内部杂散辐射的分析与抑制[J]. 光学学报, 2022, 42(15): 1512006. doi: 10.3788/AOS202242.1512006XIE X L, ZHU X X, ZHU J CH, et al. Analysis and suppression of stray radiation in uncooled thermal infrared imaging spectrometer[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2022, 42(15): 1512006. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/AOS202242.1512006 [19] LACROIX L, KURZIUS S. Peeling the onion: an heuristic overview of hit-to-kill missile defense in the 21st century[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2005, 5732: 225-249. doi: 10.1117/12.583369 [20] 崇元, 艾葳, 王玉坤. 红外点目标探测距离估算模型[J]. 指挥控制与仿真, 2020, 42(6): 59-62.CHONG Y, AI W, WANG Y K. Operating distance estimation model of infrared point target[J]. Command Control & Simulation, 2020, 42(6): 59-62. (in Chinese). [21] ZOU Y G, YANG Y L, ZHANG Y X, et al. Computationally efficient assessment of fuel economy of multi-modes and multi-gears hybrid electric vehicles: a hyper rapid dynamic programming approach[J]. Energy, 2024, 313: 133811. doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2024.133811 [22] 曾妮, 陈俊豪, 傅清爽. 基于贪心算法的动态规划策略[J]. 电脑知识与技术, 2021, 17(20): 141-143,152.ZENG N, CHEN J H, FU Q SH. Dynamic programming strategy based on greedy algorithm[J]. Computer Knowledge and Technology, 2021, 17(20): 141-143,152. (in Chinese). [23] 吴洪波. 远距离暗弱目标探测光学系统关键技术研究[D]. 长春: 中国科学院大学(中国科学院长春光学精密机械与物理研究所), 2022.WU H B. Research on key technologies of optical systems for remote weak target detection[D]. Changchun: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences), 2022. (in Chinese). -





 下载:
下载: