-
摘要:
为深入研究在几何相位原理下的超构表面成像功能,本文利用超透镜的几何相位成像原理推导出任意曲线的成像公式,并利用标量衍射理论验证其可行性与正确性,同时将此理论应用于入射光偏振状态的检测中。结果表明,基于几何相位原理的超构表面相位调控能实现任意曲线的成像以及对入射光偏振状态检测的功能,这对于全息成像、光通信、量子科学等领域的研究都有一定的启发意义。
Abstract:In order to investigate the imaging function of metasurface based on geometric phase theory, this article deduces the imaging formulation of arbitrary curve with the theory of geometric phase imaging on metalens, and its feasibility and correctness is verified by scalar diffraction theory. The imaging formulation is further applied in polarization detection of the incident beam. The results show that phase manipulation of metasurface based on geometric phase can achieve the functions of arbitrary curve imaging and polarization detection of the incident beam, which is of great significance in the field of holographic imaging, optical communication and quantum science.
-
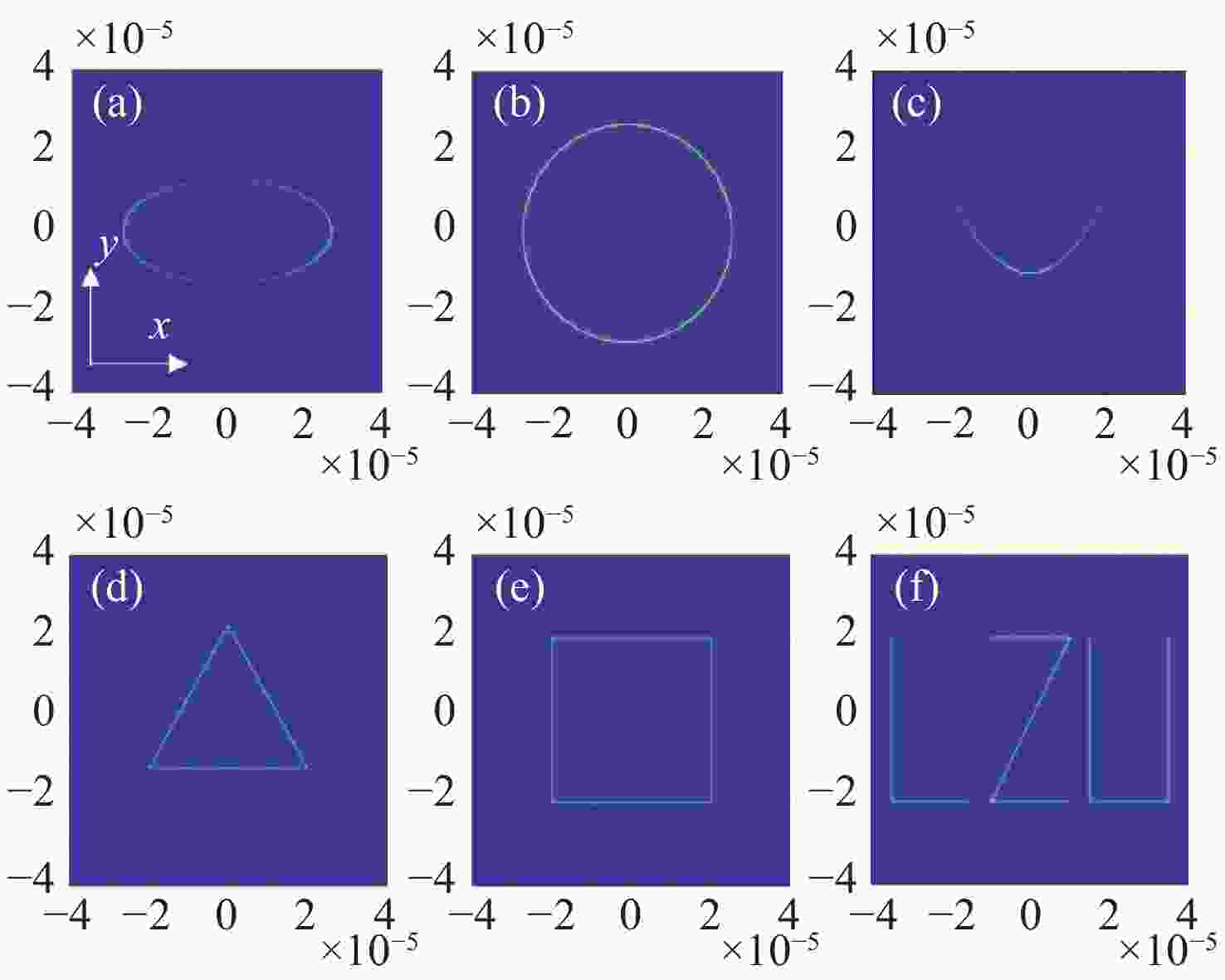
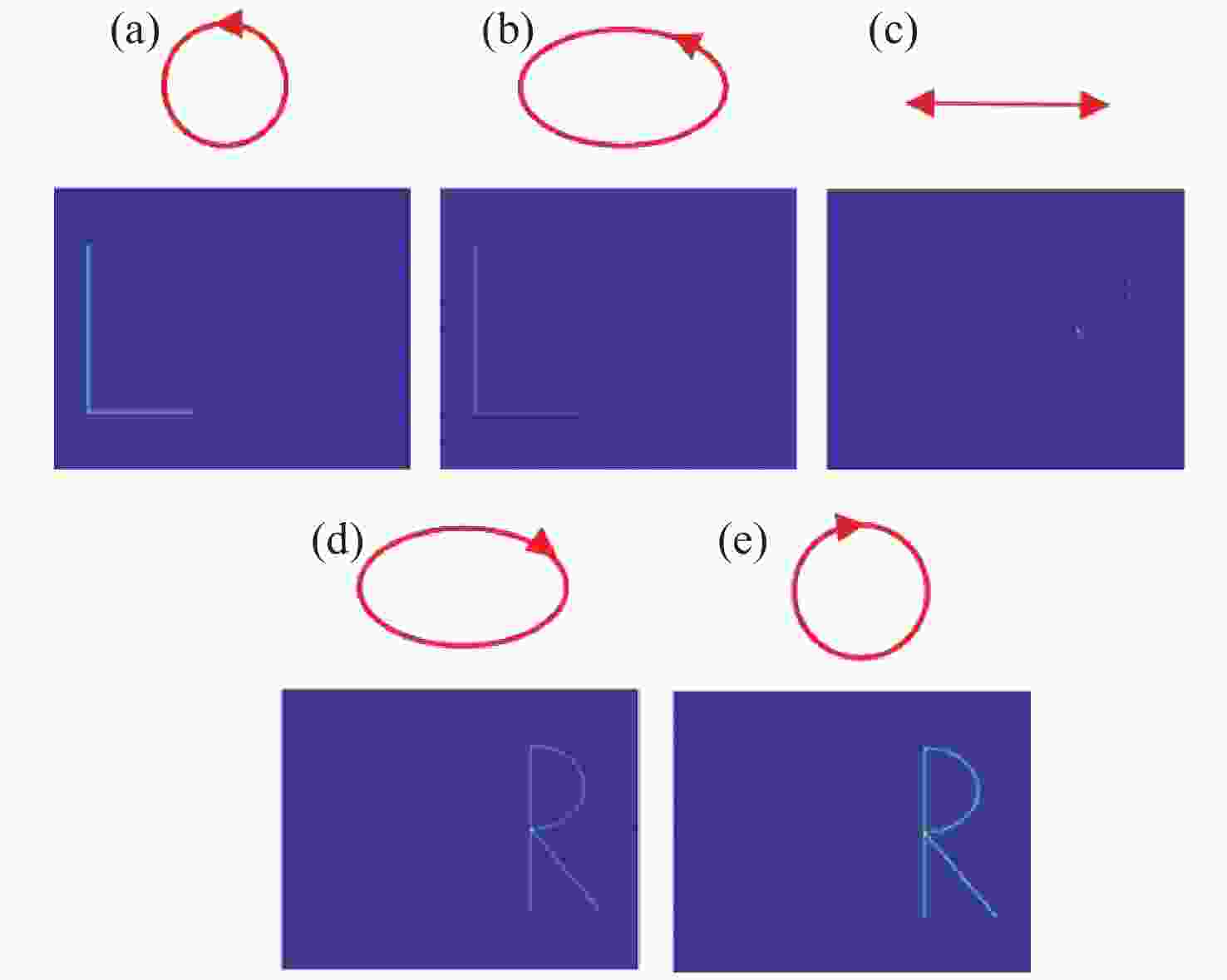
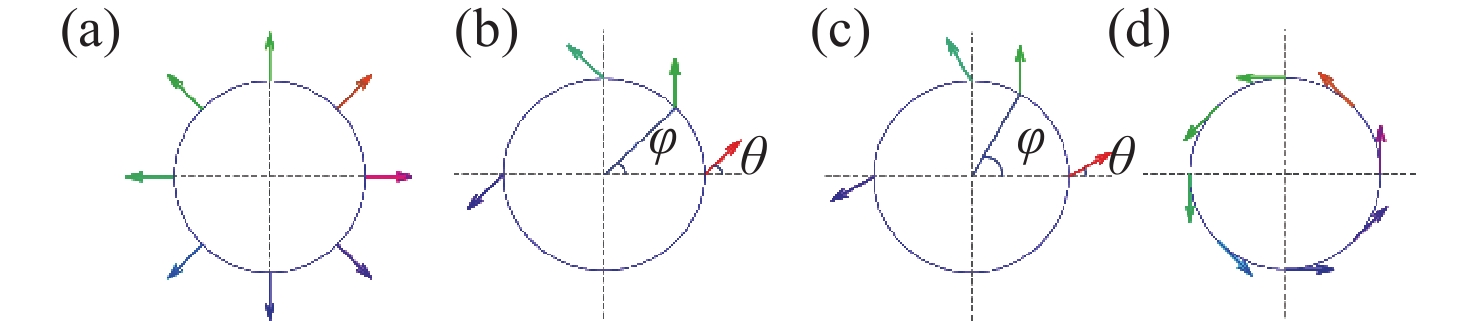
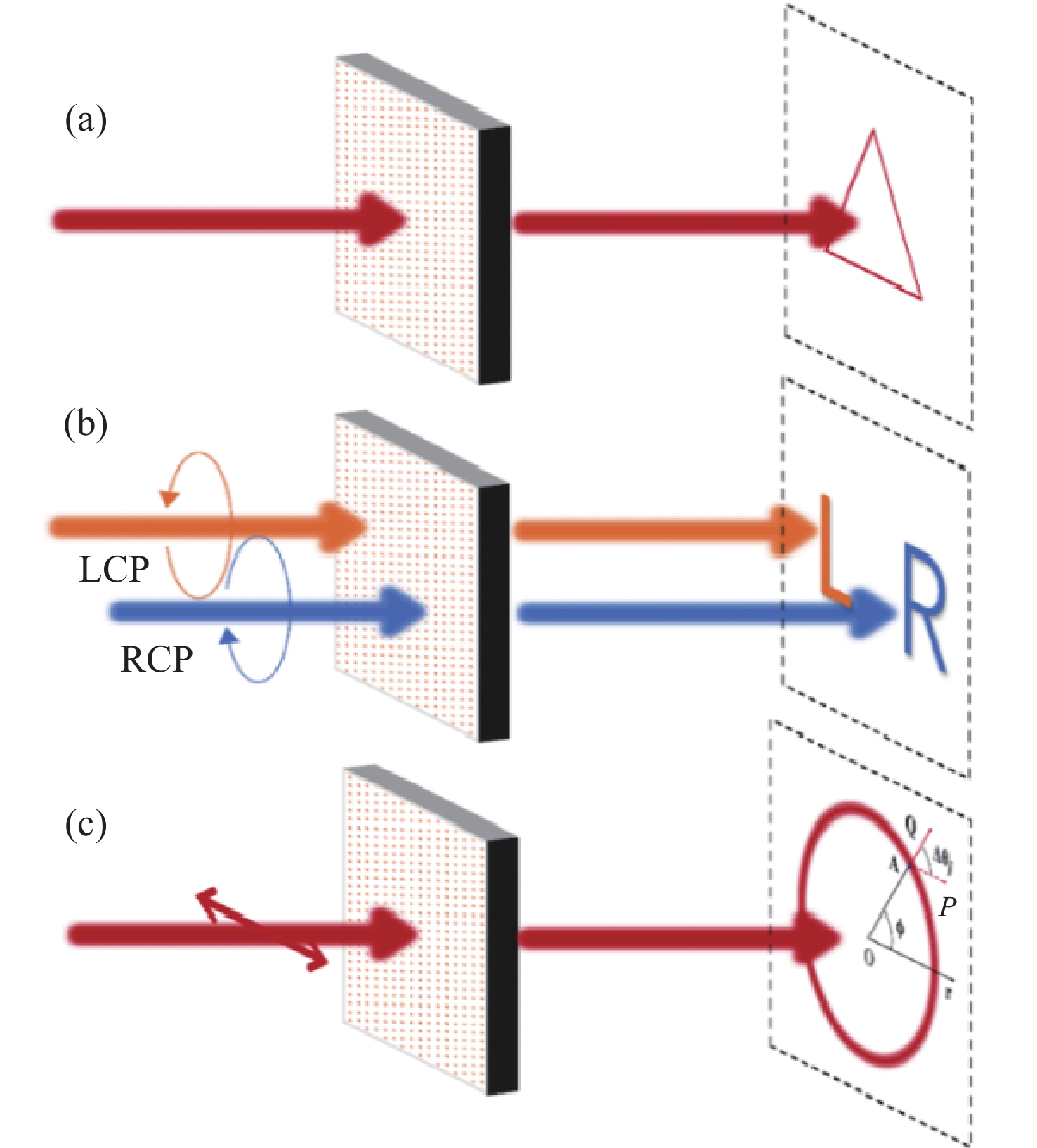
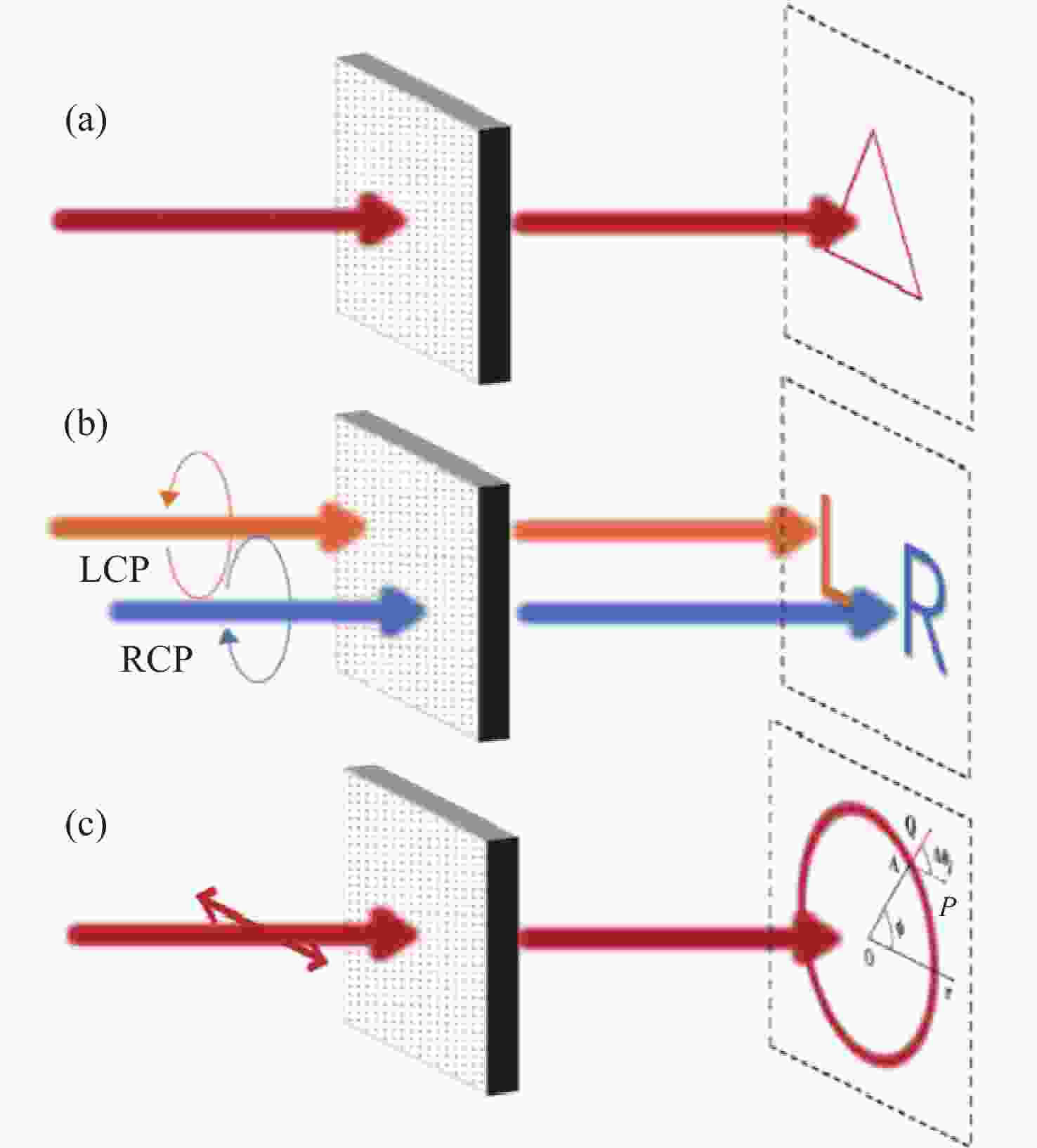
图 1 不同几何相位设计实现不同成像功能示意图。(a)在焦平面实现任意曲线成像;(b) 定性检测入射光偏振类型;(c) 定量检测线偏振光偏振方向,A为圆上的第j个点,AP为入射线偏振光的方向,AQ为点A处线偏振光的方向,AQ经过圆心
Figure 1. Schematic diagram illustrating the realization of different imaging fuctions through various geometric phase designs. (a) Achieving of arbitrary curve imaging on focal plane; (b) qualitative detection of the polarization type of incident light; (c) quantitative detection of the polarization direction of linearly polarized light, where A is the j-th point on the circle, AP is the direction of the incident linearly polarized light, AQ is the direction of the linearly polarized light at point A, and AQ passes through the center of the circle
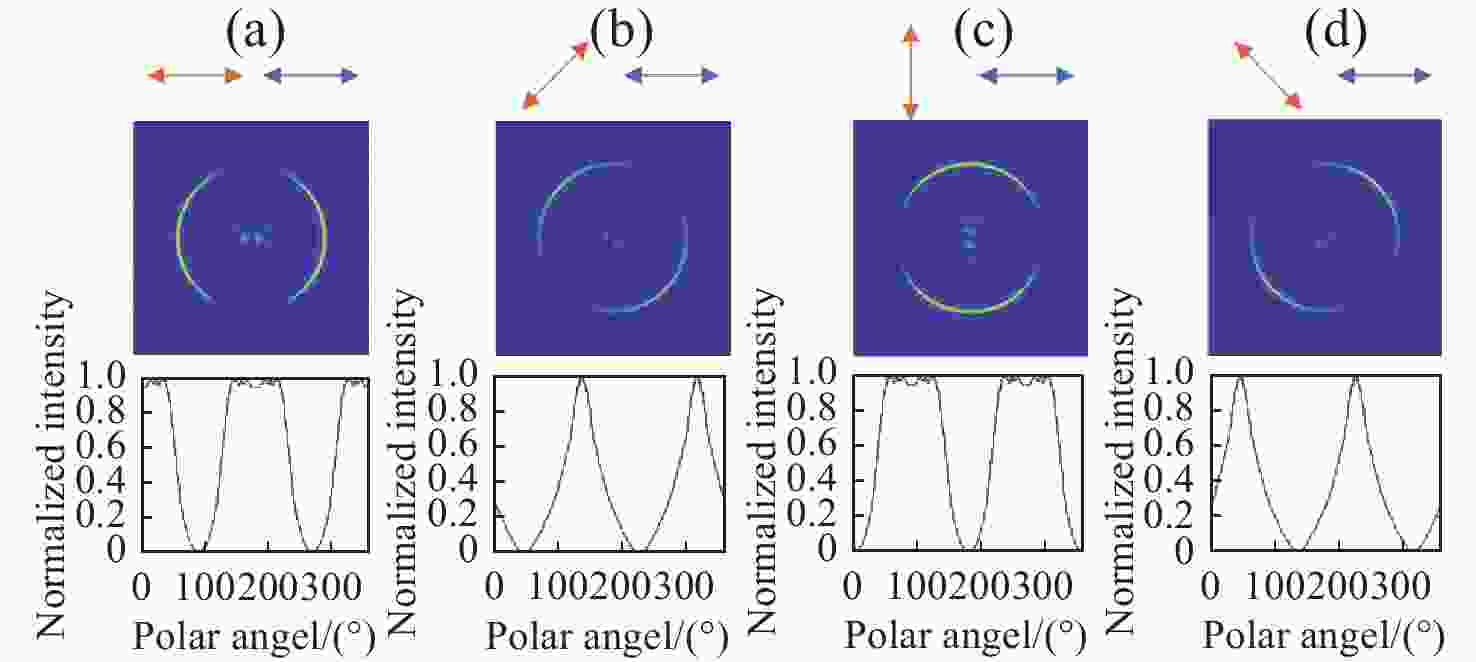
图 5 不同偏振入射光对应的图像。(a)左旋圆偏振光入射;(b) 左旋椭圆偏振光入射;(c) 线偏振光入射;(d) 右旋椭圆偏振光入射;(b) 右旋圆偏振光入射。上面表示入射的偏振状态,下面表示相应偏振态入射时焦平面处的图像
Figure 5. Incident light with different polarizations and their corresponding images. (a) Incident of LCP light; (b) incident of left-handed elliptically polarized light; (c) incident of linear polarized light; (d) incident of right-handed elliptically polarized light; (e) incident of RCP light. The up denotes the incident polarized state and the down denotes corresponding images at the focal plane
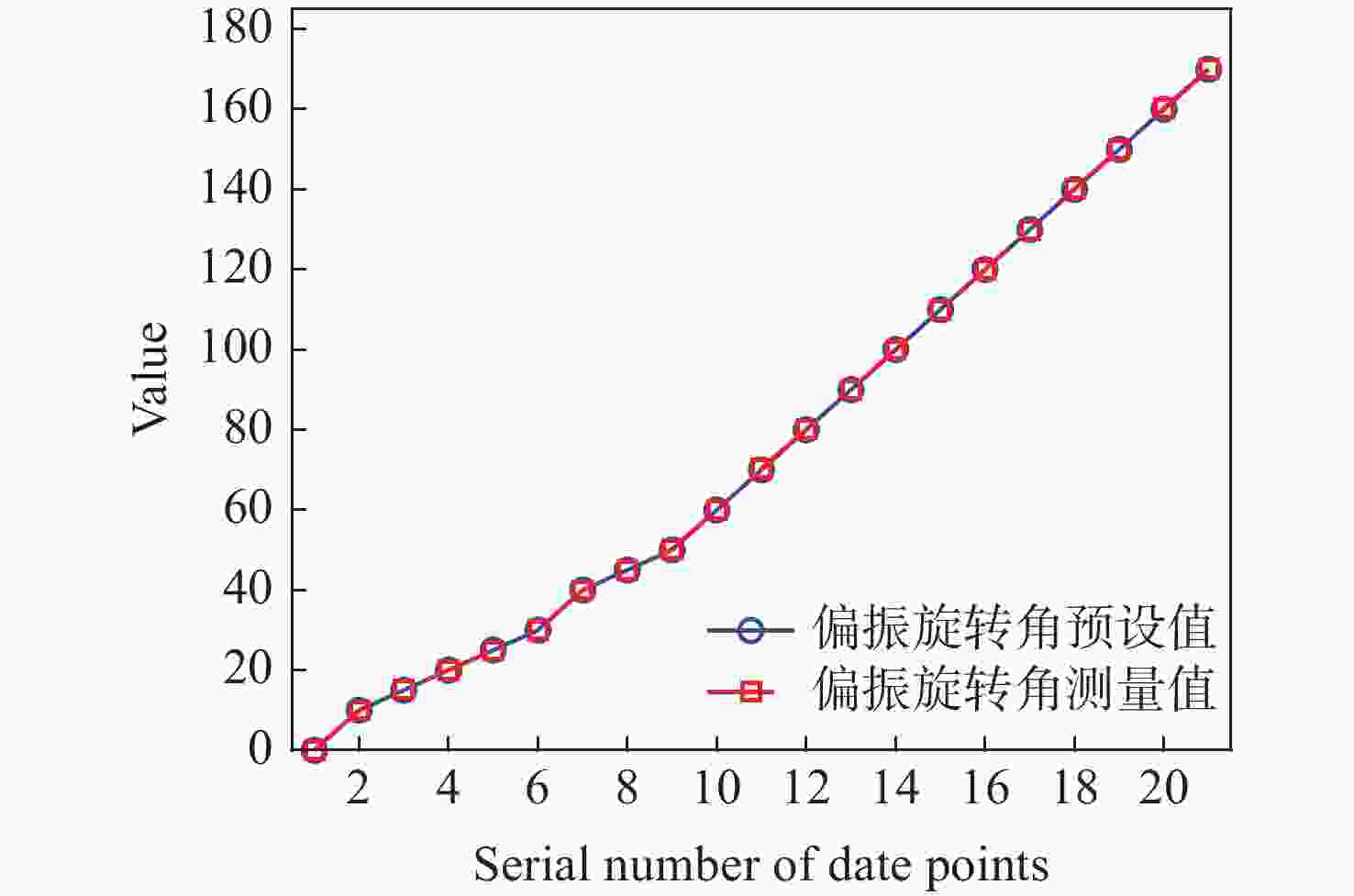
图 6 测量偏振方向角原理图。入射偏振方向角为θ,极坐标方位角为
$\varphi $ 。(a) θ=$ 0 $ ,(b) θ=$ \dfrac{\mathrm{{\text{π}} }}{4} $ ,(c) θ=$ \dfrac{\mathrm{{\text{π}} }}{6} $ ,(d) θ=$ \dfrac{3\mathrm{{\text{π}} }}{2} $ Figure 6. Illustrates the schematic diagram for measuring the polarization rotation angle. The incident polarization angle is θ and the polar coordinate azimuth angle is
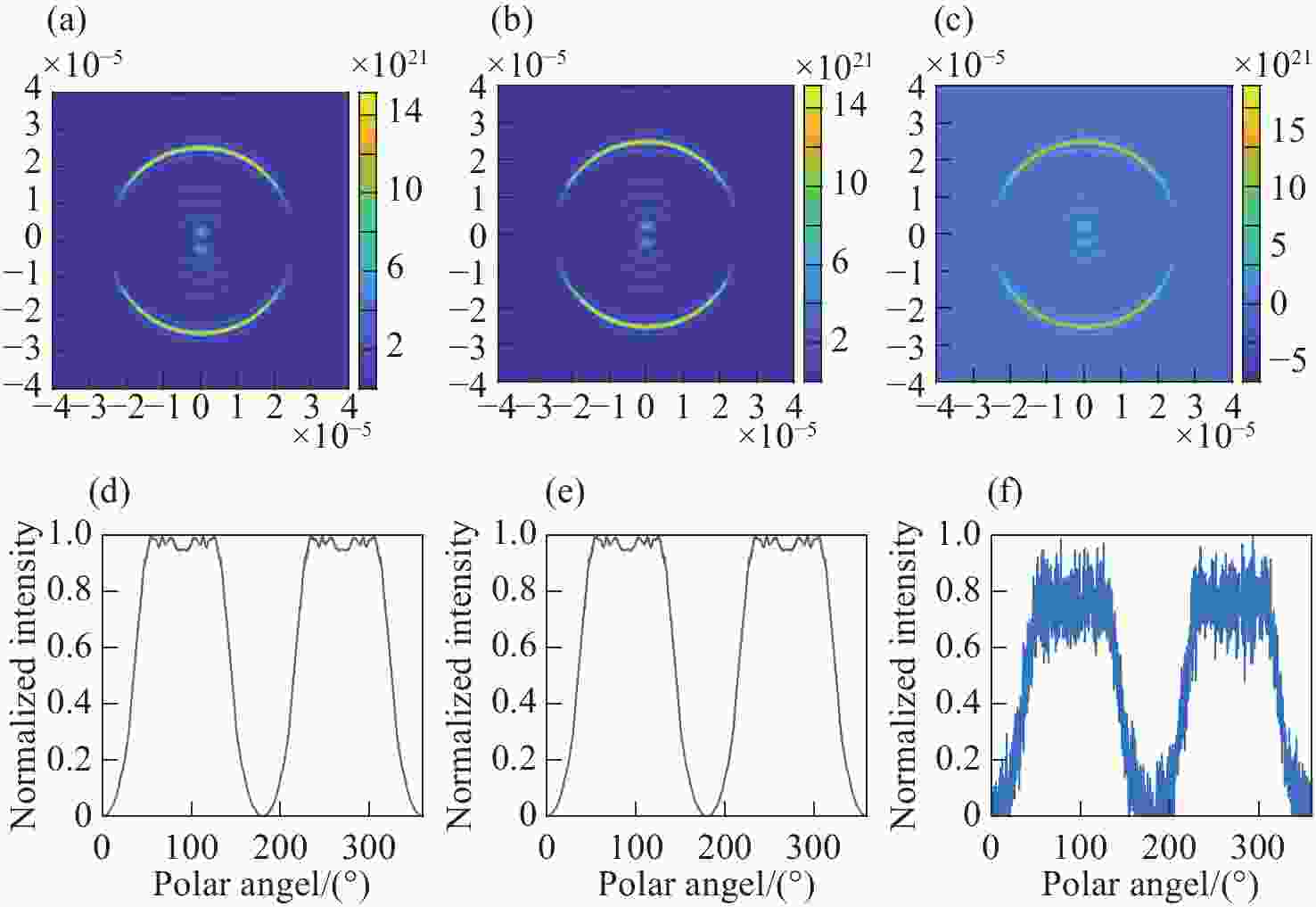
$\varphi $ . (a) θ=$ 0 $ , (b) θ=$ \dfrac{\mathrm{{\text{π}} }}{4} $ , (c) θ=$ \dfrac{\mathrm{{\text{π}} }}{6} $ , (d) θ=$ \dfrac{3\mathrm{{\text{π}} }}{2} $ 图 7 光强随入射偏振方向角变化的图像及其归一化强度分布曲线。入射偏振光的旋转角度分别是(a)
$ 0 $ ,(b)$ \dfrac{\mathrm{{\text{π}} }}{4} $ ,(c)$ \dfrac{\mathrm{{\text{π}} }}{2} $ ,(d)$ \dfrac{3\mathrm{{\text{π}} }}{4} $ 。图中第一行左侧箭头表示入射线偏振光的方向,右侧箭头表示焦平面前偏振片传输轴的方向Figure 7. Lignt intensity varies with the polar angle and their normalized intensity distribution curves. The rotation angles of incident polarized light are (a)
$ 0 $ , (b)$ \dfrac{\mathrm{{\text{π}} }}{4} $ , (c)$ \dfrac{\mathrm{{\text{π}} }}{2} $ , (d)$ \dfrac{3\mathrm{{\text{π}} }}{4} $ , respectively. The left arrow in the first row shows the direction of incident polarized light, while the right arrow shows the direction of the transmission axis of the analyzer before the focal plane -
[1] 颜昌翔, 张源, 泊建, 等. 高光谱偏振技术的研究进展及展望[J]. 光学精密工程, 2024, 32(14): 2141-2165.YAN CH X, ZHANG Y, BO J, et al. Development and prospect of hyperspectral polarization[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2024, 32(14): 2141-2165. (in Chinese). [2] DUBEY K, SRIVASTAVA V, DALAL K. In vivo automated quantification of thermally damaged human tissue using polarization sensitive optical coherence tomography[J]. Computerized Medical Imaging and Graphics, 2018, 64: 22-28. doi: 10.1016/j.compmedimag.2018.01.002 [3] SHIN A, PARK J, DEMER J L. Opto-mechanical characterization of sclera by polarization sensitive optical coherence tomography[J]. Journal of Biomechanics, 2018, 72: 173-179. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiomech.2018.03.017 [4] UGRYUMOVA N, JACOBS J, BONESI M, et al. Novel optical imaging technique to determine the 3-D orientation of collagen fibers in cartilage: variable-incidence angle polarization-sensitive optical coherence tomography[J]. Osteoarthritis and Cartilage, 2009, 17(1): 33-42. doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2008.05.005 [5] WANG R X, HAN J, LIU J L, et al. Multi-foci metalens for terahertz polarization detection[J]. Optics Letters, 2020, 45(13): 3506-3509. doi: 10.1364/OL.395580 [6] YUE ZH, LI J T, ZHENG C L, et al. Manipulation of polarization conversion and multiplexing via all-silicon phase-modulated metasurfaces[J]. Chinese Optics Letters, 2022, 20(4): 043601. doi: 10.3788/COL202220.043601 [7] HE G L, ZHENG Y Q, ZHOU CH D, et al. Multiplexed manipulation of orbital angular momentum and wavelength in metasurfaces based on arbitrary complex-amplitude control[J]. Light: Science & Applications, 2024, 13(1): 98. [8] WAHEED M, MAHMOOD N, SHAFQAT M D, et al. Advancing broadband light structuring through single-size nanostructured all-dielectric meta-devices[J]. Materials Today Communications, 2023, 36: 106584. doi: 10.1016/j.mtcomm.2023.106584 [9] XIONG B, LIU Y, XU Y H, et al. Breaking the limitation of polarization multiplexing in optical metasurfaces with engineered noise[J]. Science, 2023, 379(6629): 294-299. doi: 10.1126/science.ade5140 [10] RIND Y M, MAHMOOD N, MEHMOOD M Q, et al. Multidimensional and multifunctional metasurface design using hybrid spin decoupling[J]. Optical Materials Express, 2023, 13(4): 1150-1162. doi: 10.1364/OME.481912 [11] MA ZH Y, TIAN T T, LIAO Y X, et al. Electrically switchable 2N-channel wave-front control for certain functionalities with N cascaded polarization-dependent metasurfaces[J]. Nature Communications, 2024, 15(1): 8370. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-52676-w [12] JI J T, LI J, WANG ZH ZH, et al. On-chip multifunctional metasurfaces with full-parametric multiplexed Jones matrix[J]. Nature Communications, 2024, 15(1): 8271. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-52476-2 [13] YUE Z, SIPAHI T, AHMED H, et al. Multispectral polarization states generation with a single metasurface[J]. Laser & Photonics Reviews, 2024, 18(10): 2400176. [14] CHEN M J, WEN L, PAN D H, et al. Full-color nanorouter for high-resolution imaging[J]. Nanoscale, 2021, 13(30): 13024-13029. doi: 10.1039/D1NR02166D [15] 陈沁, 文龙, 杨先光, 等. 面向高像素密度图像传感器的结构色技术[J]. 光学学报, 2021, 41(8): 0823010. doi: 10.3788/AOS202141.0823010CHEN Q, WEN L, YANG X G, et al. Structural color technology for high pixel density image sensors[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2021, 41(8): 0823010. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/AOS202141.0823010 [16] ASAD A, KIM J, KHALIQ H S, et al. Spin-isolated ultraviolet-visible dynamic meta-holographic displays with liquid crystal modulators[J]. Nanoscale Horizons, 2023, 8(6): 759-766. doi: 10.1039/D2NH00555G [17] 陈磊, 严金华, 郭焕祥, 等. 基于硅基超表面的高效率大角度光束偏转[J]. 光学学报, 2021, 41(3): 0305001. doi: 10.3788/AOS202141.0305001CHEN L, YAN J H, GUO H X, et al. Highly efficient large-angle beam deflection based on silicon-based metasurface[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2021, 41(3): 0305001. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/AOS202141.0305001 [18] 牛昊, 王永丽, 姜增璇, 等. 基于集成氮化硅超表面VCSEL的涡旋光输出[J]. 发光学报, 2025, 46(2): 326-333.NIU H, WANG Y L, JIANG Z X, et al. Vortex light output based on integrated silicon nitride metasurface VCSEL[J]. Chinese Journal of Luminescence, 2025, 46(2): 326-333. (in Chinese). [19] LI J X, YU P, ZHANG SH, et al. Electrically-controlled digital metasurface device for light projection displays[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11(1): 3574. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-17390-3 [20] BAO L, WU B, WU R Y, et al. On-chip multidimensional manipulations of spatial laser fields by jointly controlling amplitude and phase of metasurface[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2025, 35(9): 2415983. doi: 10.1002/adfm.202415983 [21] LI S, CHEN CH, WANG G X, et al. Metasurface polarization optics: phase manipulation for arbitrary polarization conversion condition[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2025, 134(2): 023803. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.134.023803 [22] XU M ZH, CAO Y, SUN X J, et al. Circular polarization detection metasurface inspired by the polarized vision of mantis shrimp[J]. Optics Communications, 2022, 507: 127599. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2021.127599 [23] ZANG H P, YANG Z Y, ZHOU X Y, et al. Full-stokes polarization detection enabled by a terahertz all-dielectric metasurface[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2024, 135(18): 183103. doi: 10.1063/5.0208045 [24] ZENG J W, LI L, YANG X D, et al. Generating and separating twisted light by gradient–rotation split-ring antenna metasurfaces[J]. Nano Letters, 2016, 16(5): 3101-3108. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.6b00360 [25] 刘梦蛟, 李添悦, 戈钦, 等. 多功能超构表面的相位调控机制及研究进展[J]. 光学学报, 2022, 42(21): 2126004. doi: 10.3788/AOS202242.2126004LIU M J, LI T Y, GE Q, et al. Phase modulation mechanism and research progress of multifunctional metasurfaces[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2022, 42(21): 2126004. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/AOS202242.2126004 [26] KAMALI S M, ARBABI A, ARBABI E, et al. Decoupling optical function and geometrical form using conformal flexible dielectric metasurfaces[J]. Nature Communications, 2016, 7(1): 11618. doi: 10.1038/ncomms11618 [27] LIU X, CAO Q, ZHANG N J, et al. Spatiotemporal optical vortices with controllable radial and azimuthal quantum numbers[J]. Nature Communications, 2024, 15(1): 5435. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-49819-4 [28] DENG Z L, HU M X, QIU SH F, et al. Poincaré sphere trajectory encoding metasurfaces based on generalized Malus’ law[J]. Nature Communications, 2024, 15(1): 2380. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-46758-y -





 下载:
下载: