Sensitivity-enhanced fiber-optic temperature sensor using cascaded Lyot-Sagnac and Fabry-Pérot interferometers
-
摘要:
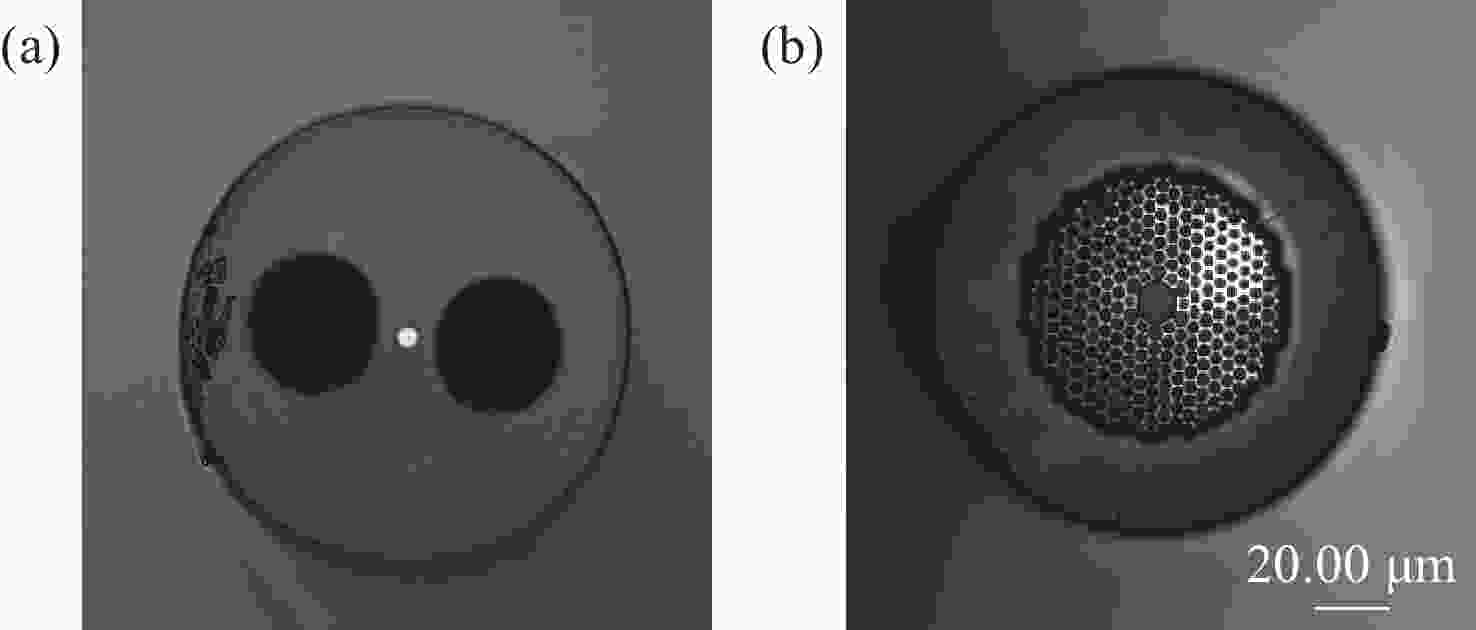
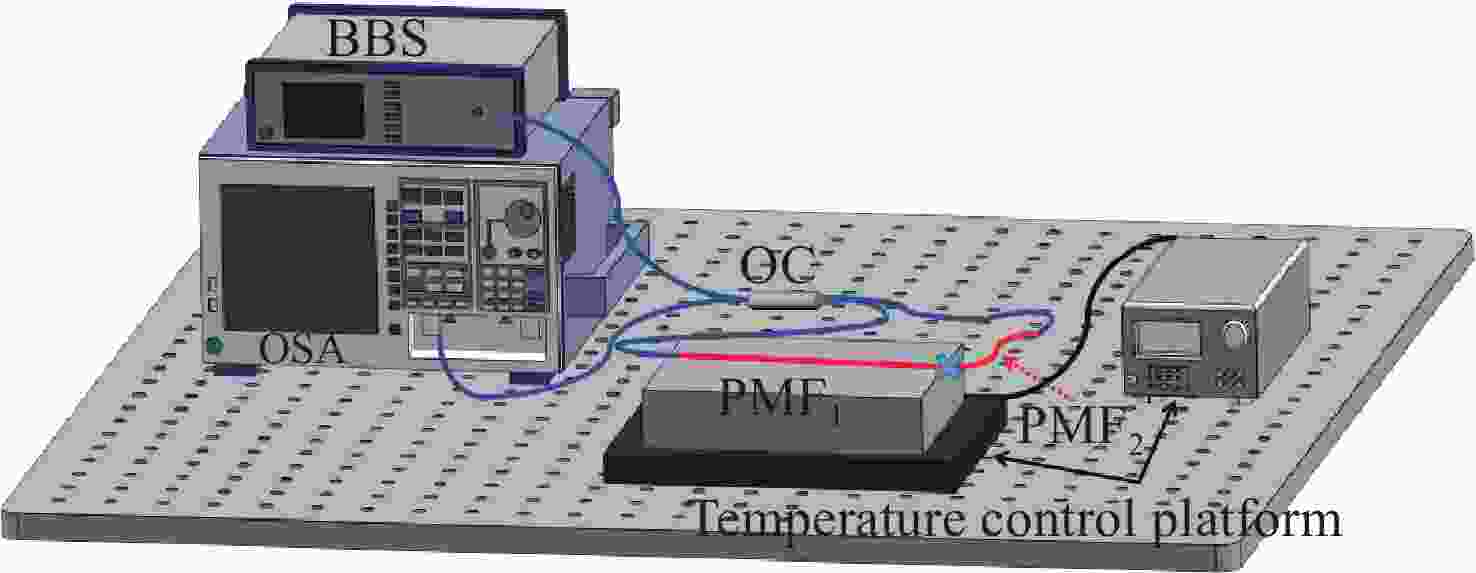
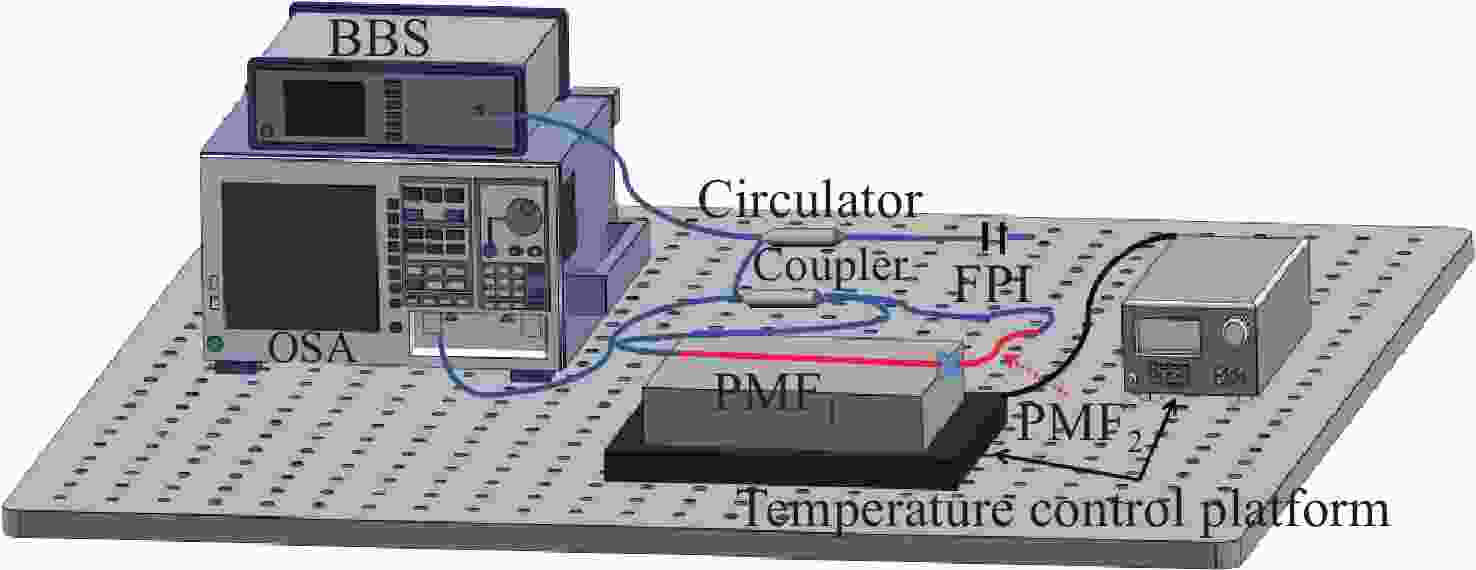
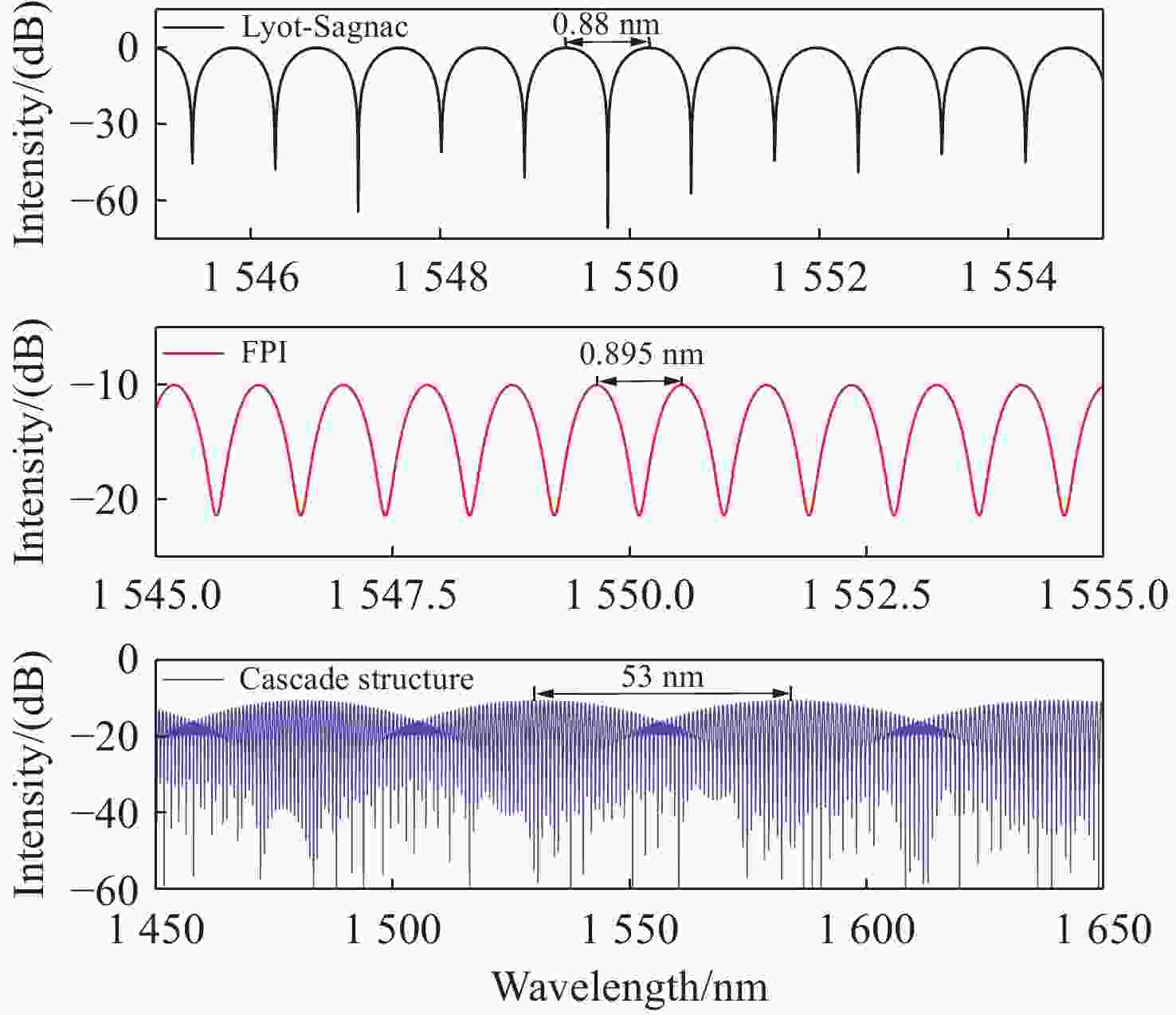
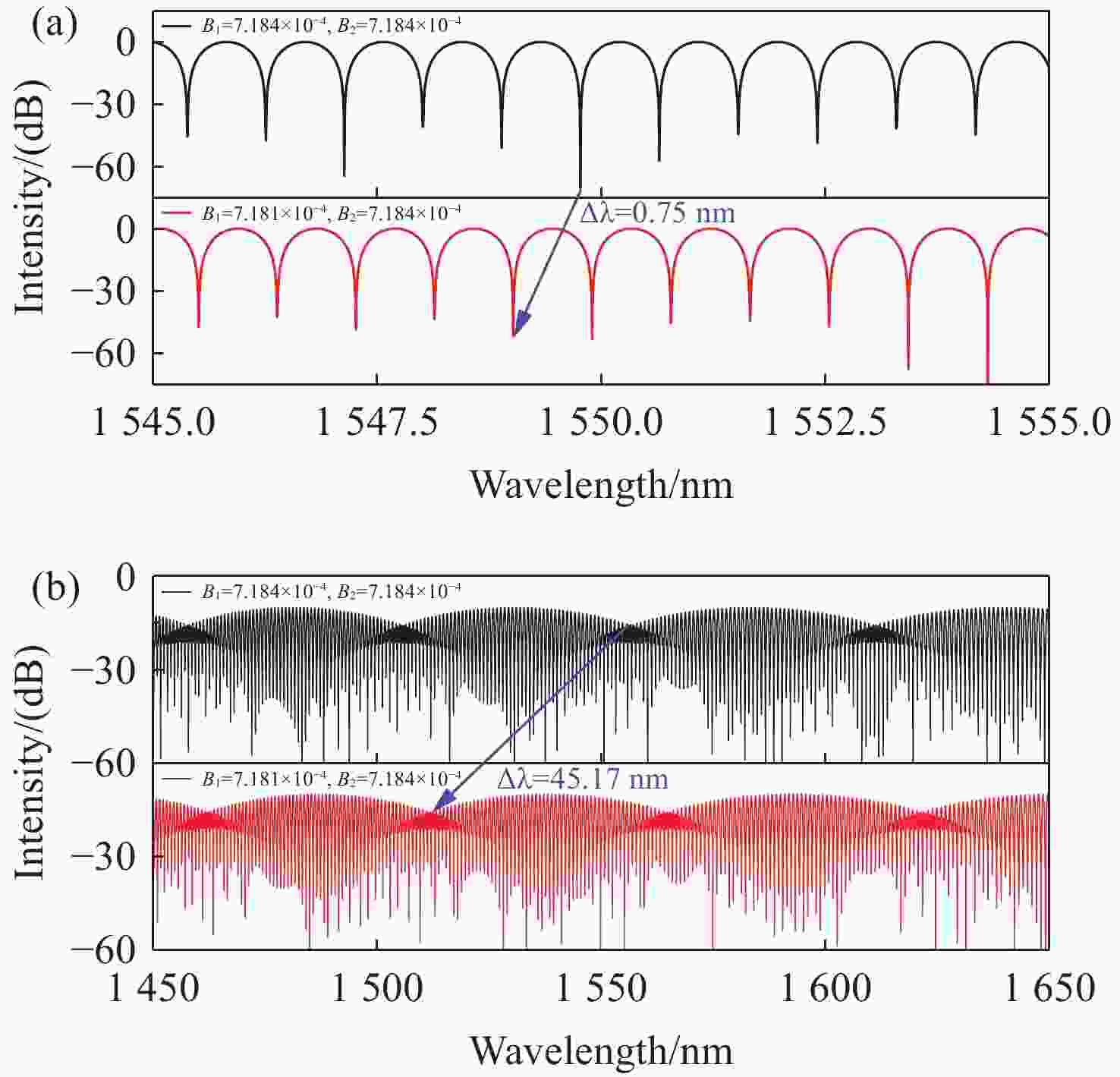
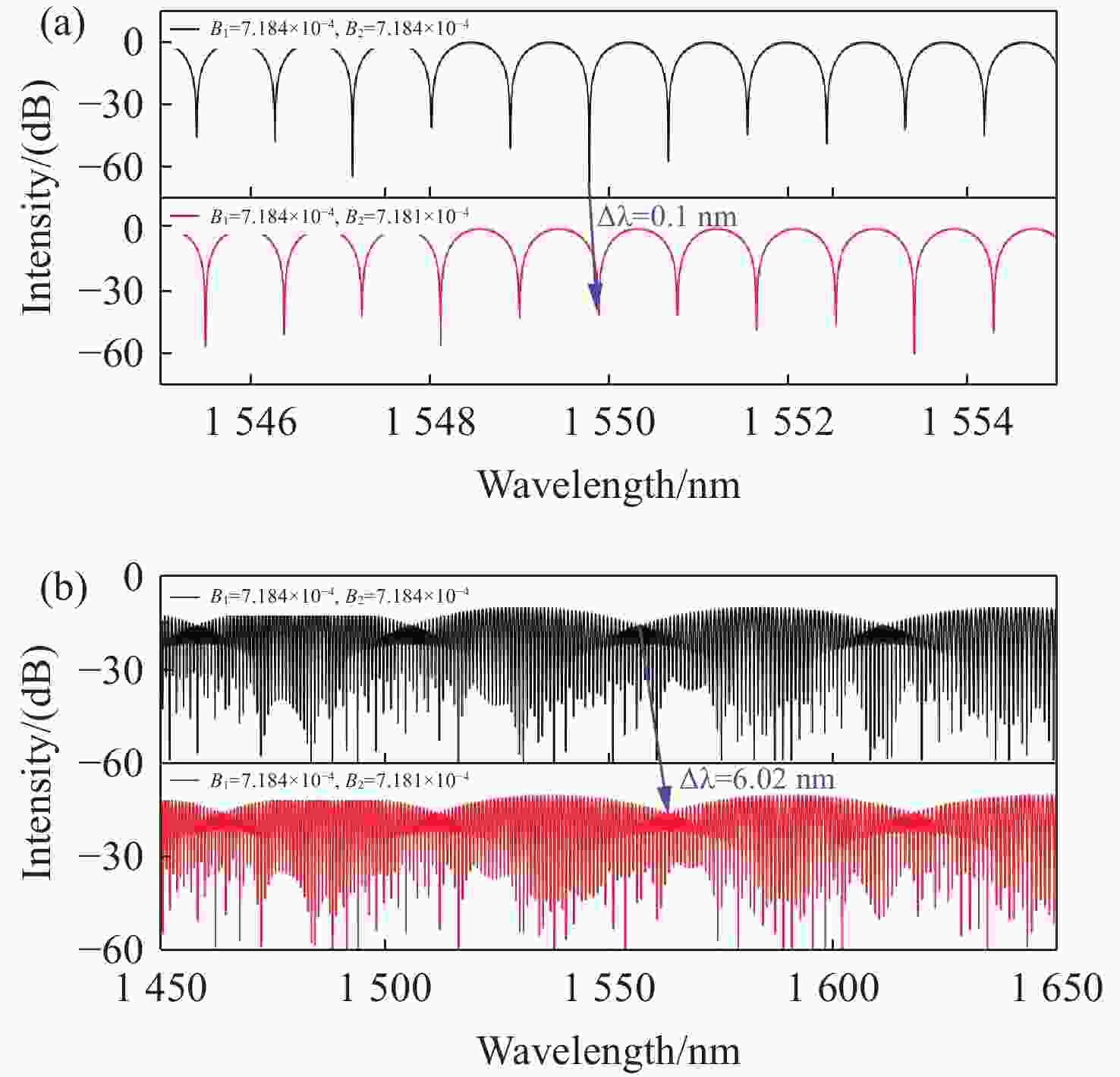
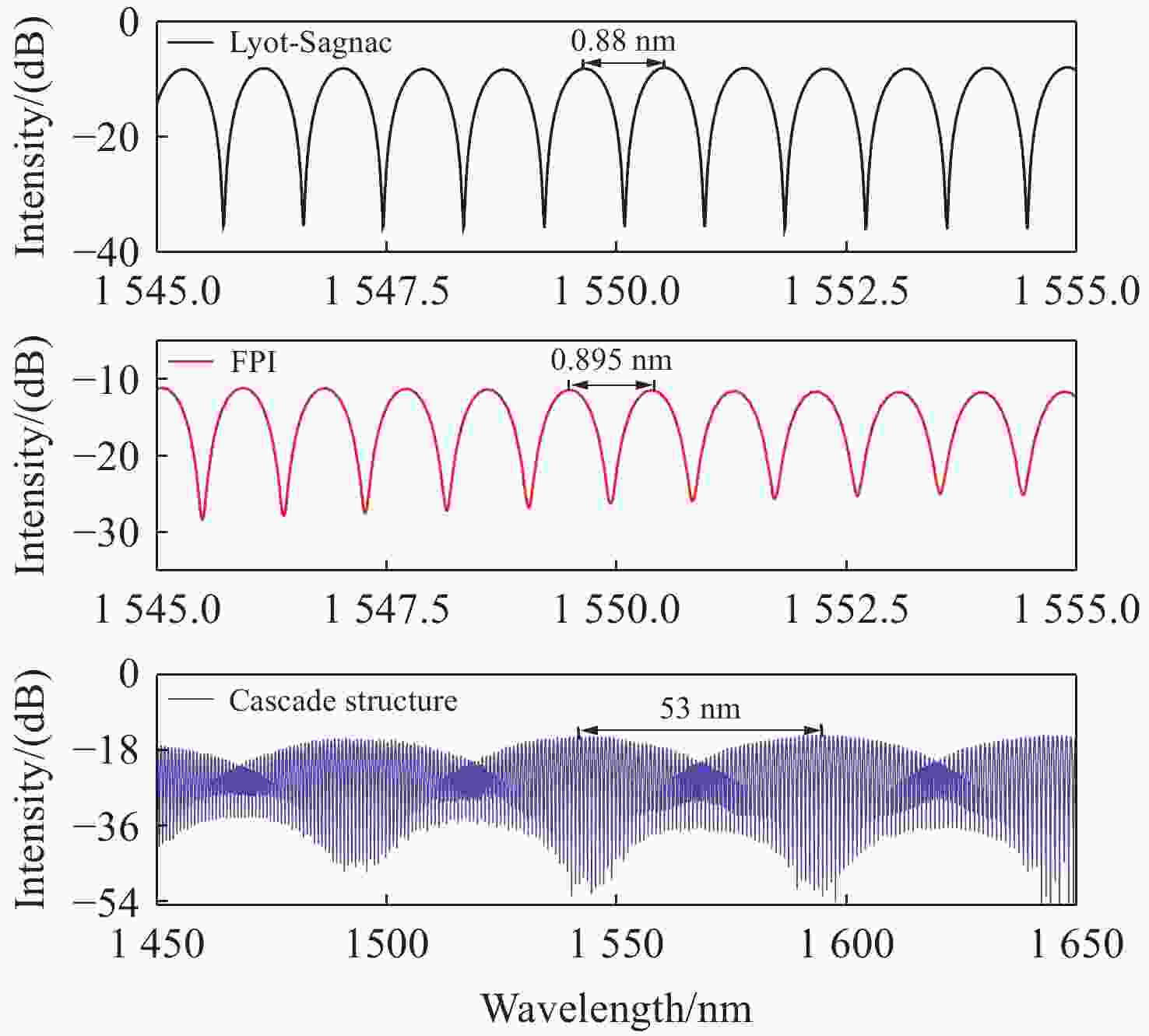
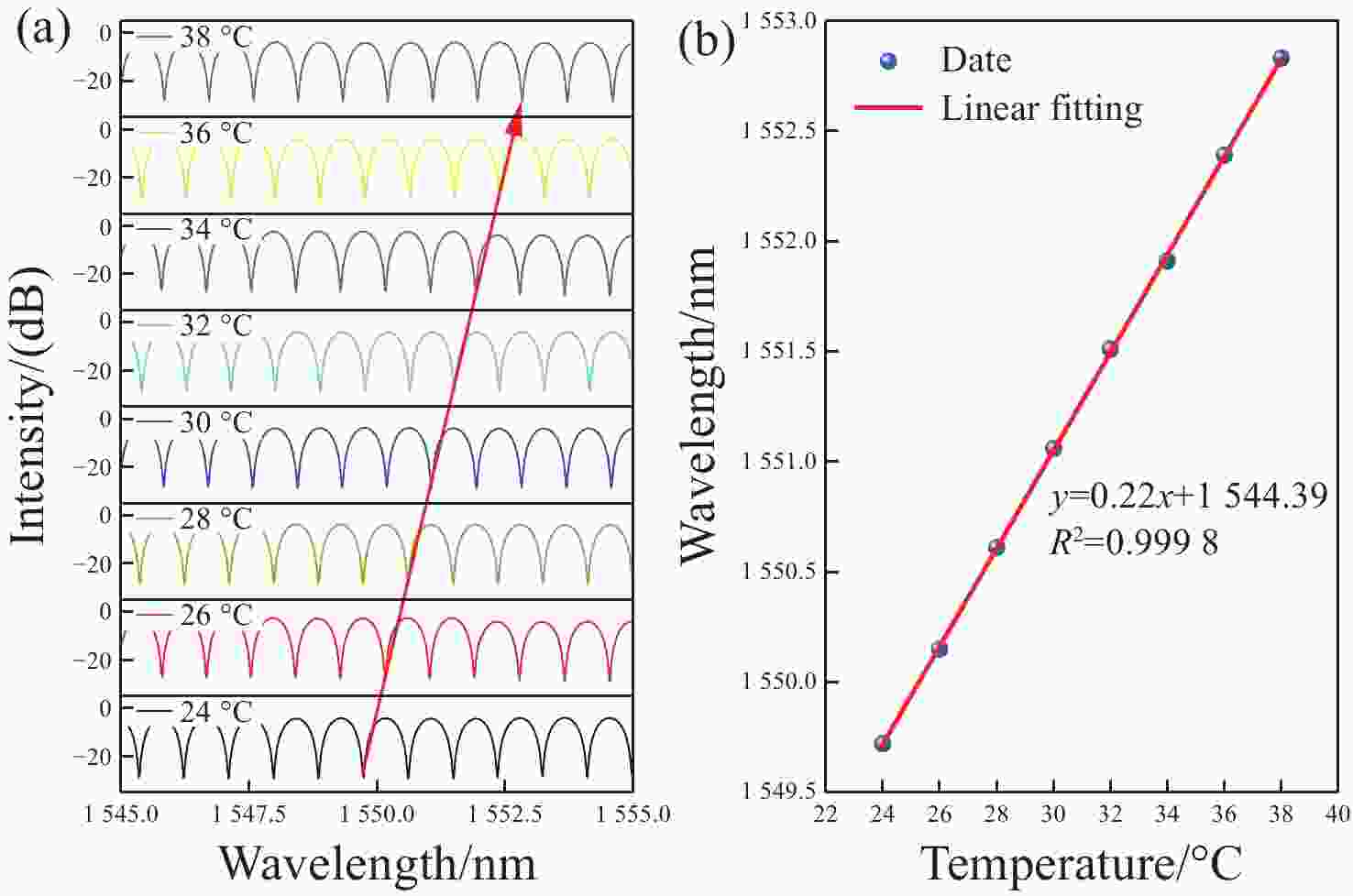
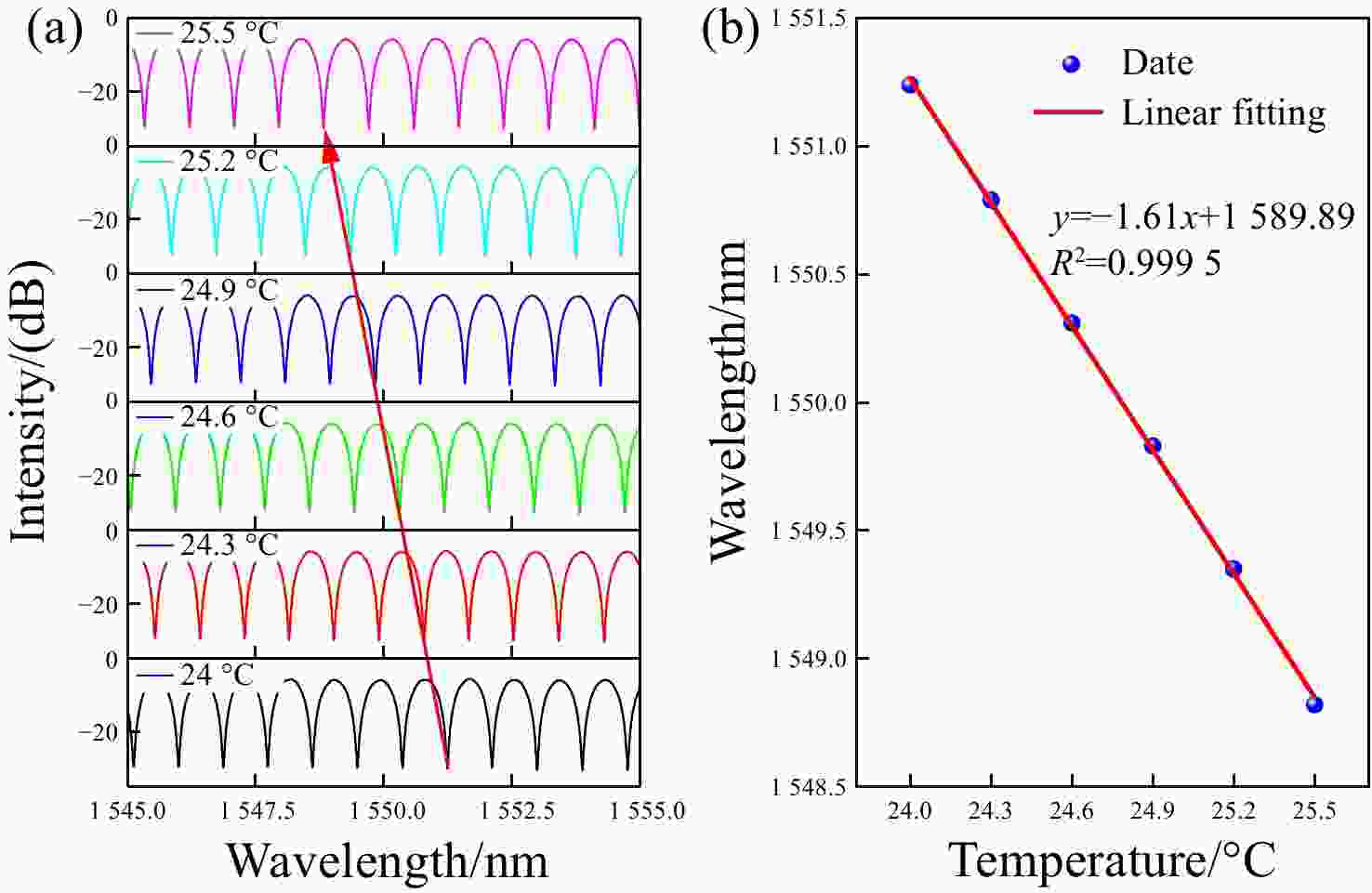
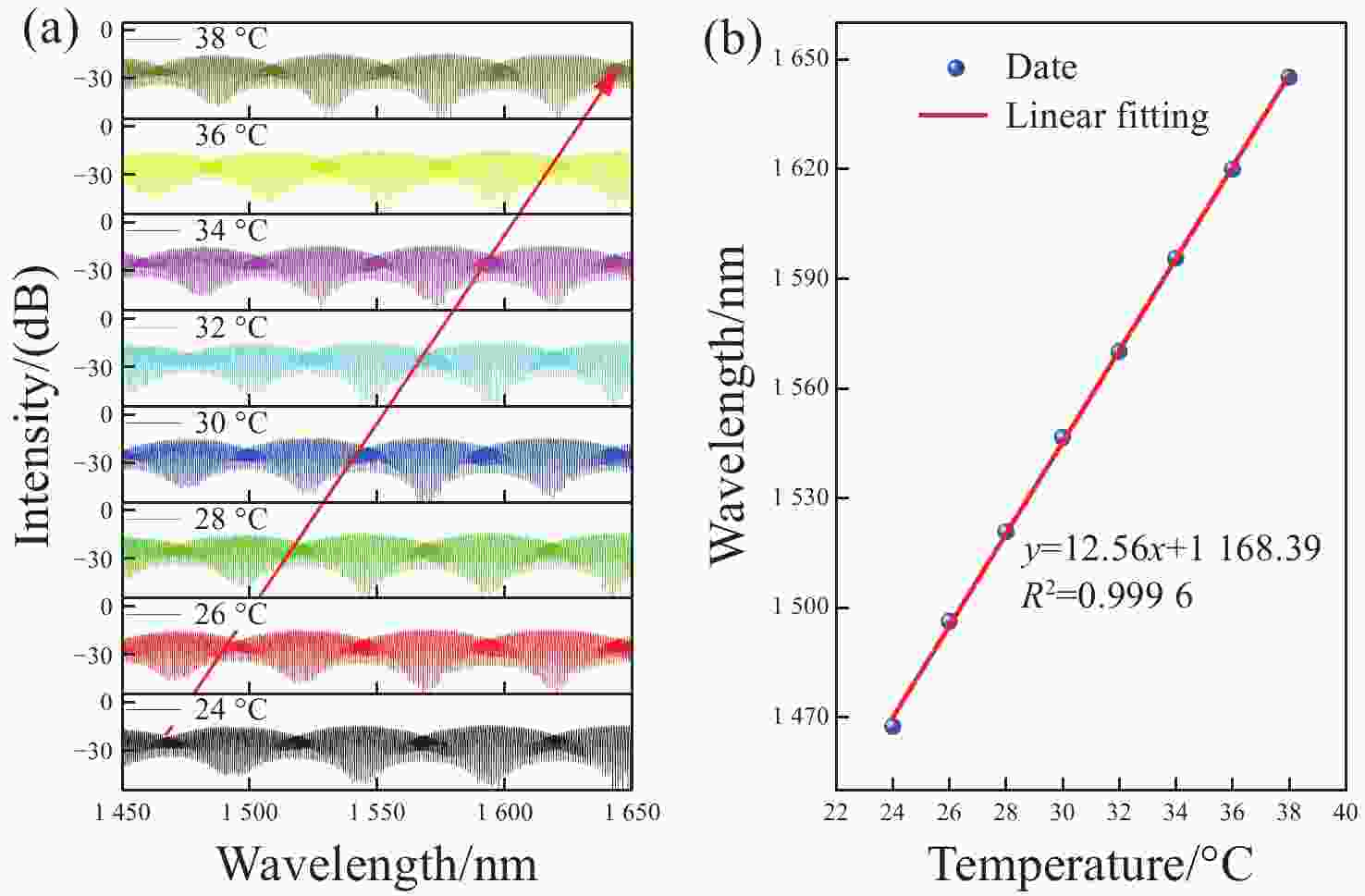
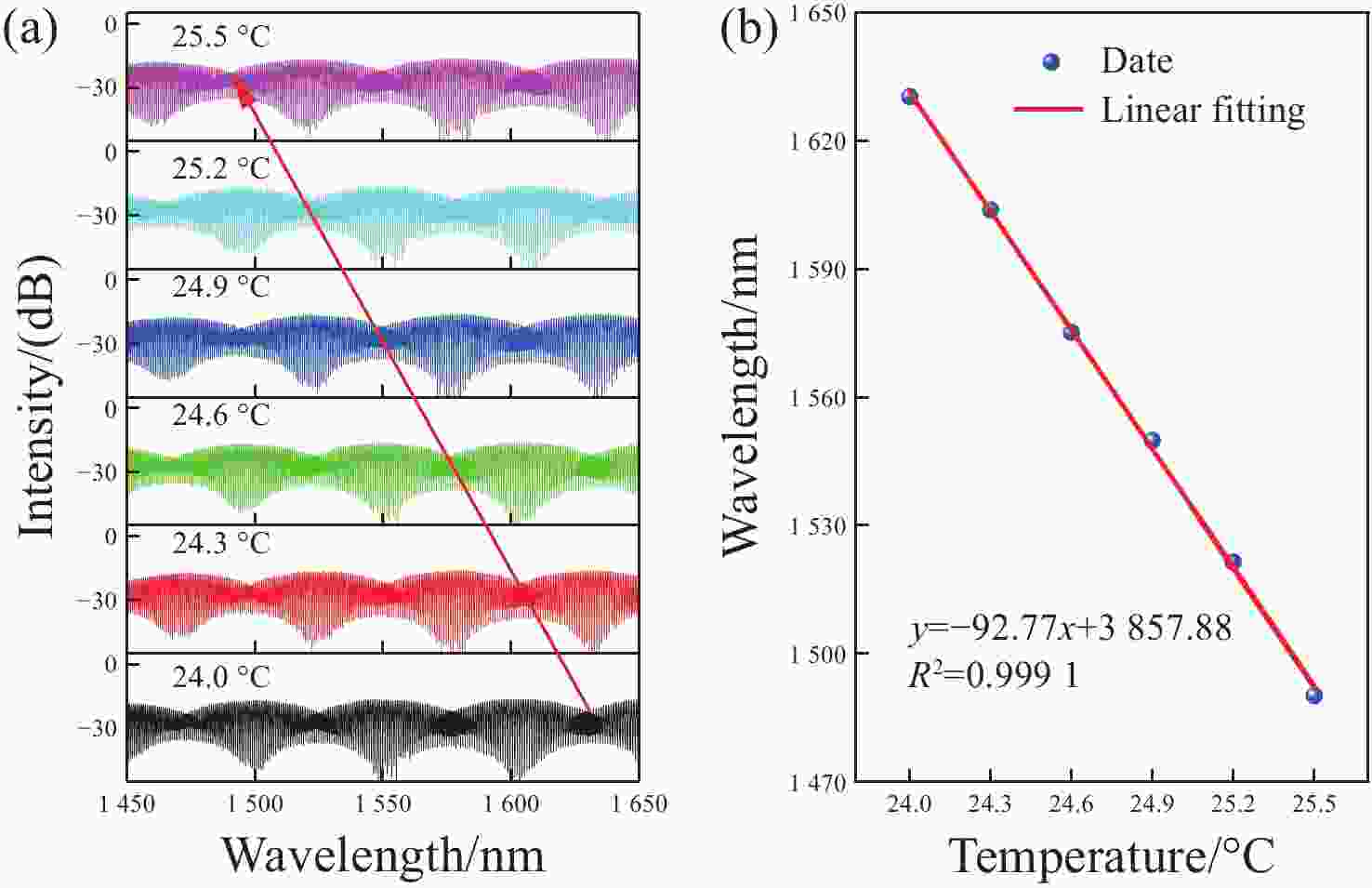
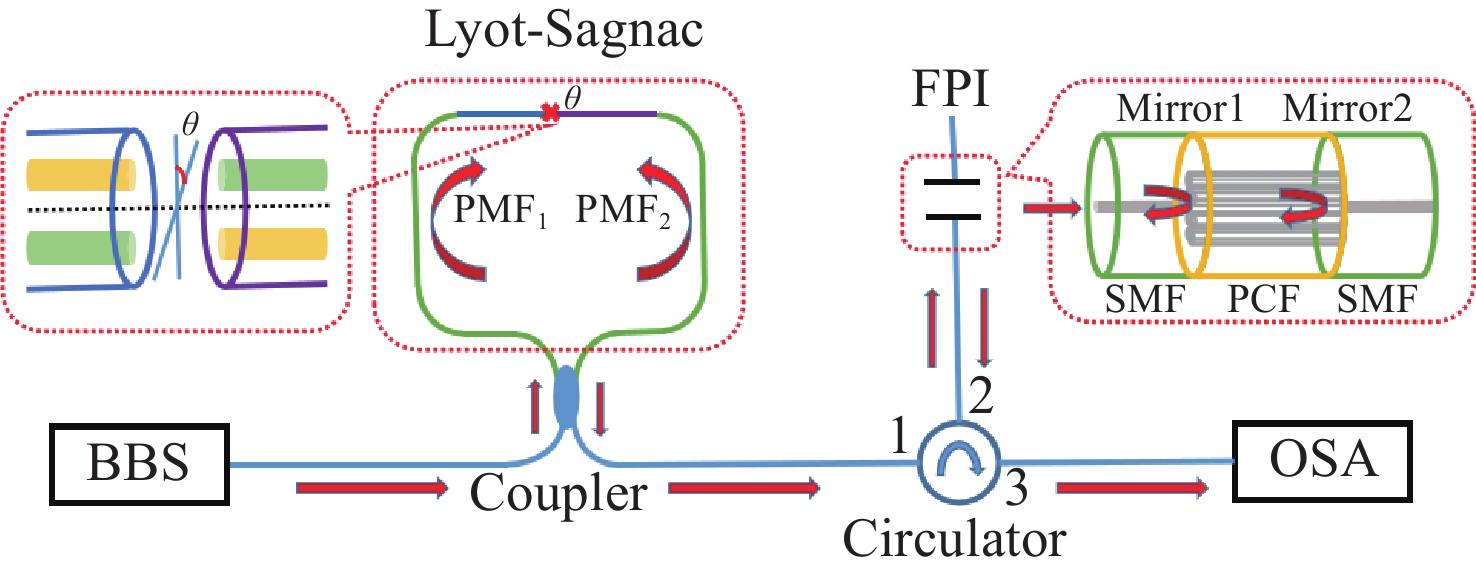
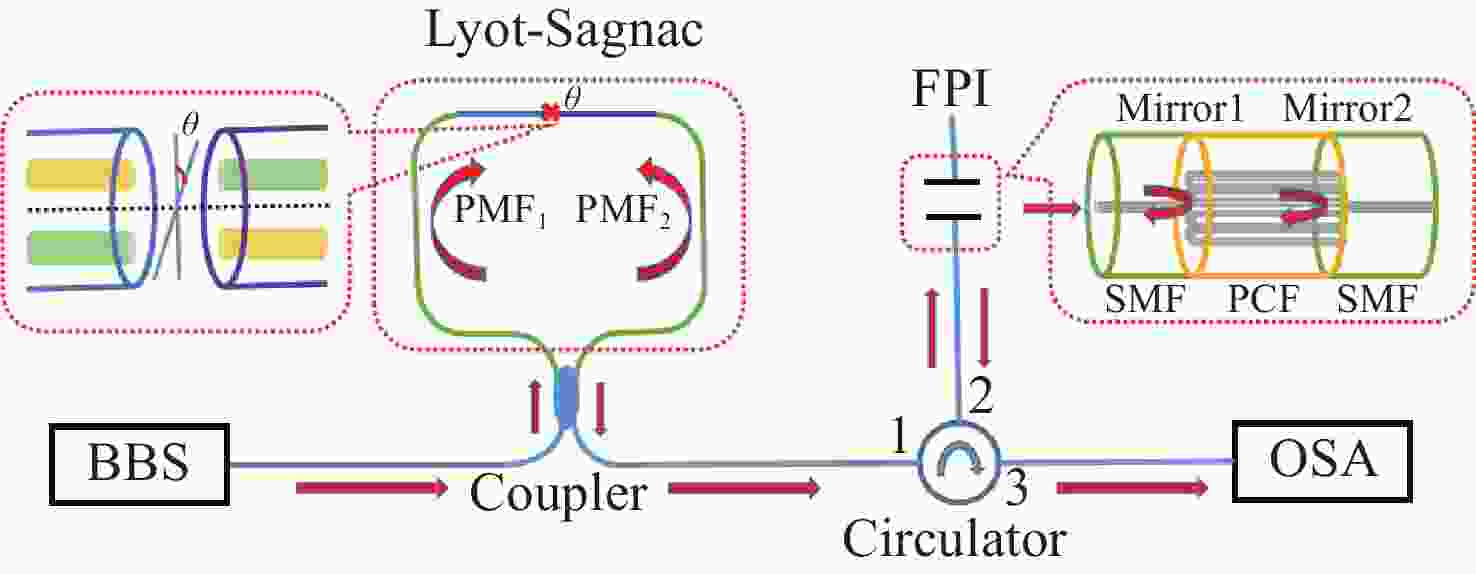
为了有效提高检测灵敏度和实用性,本文提出了一种基于游标效应增敏的Lyot-Sagnac传感结构与Fabry-Pérot干涉仪(FPI)级联的光纤温度传感器。其中,Lyot-Sagnac传感结构是通过90°旋转熔接不同长度保偏光纤(PMF)制作而成的,FPI是利用空芯光子晶体光纤作为F-P腔制作的。理论分析结果表明,通过90°旋转熔接方法制作的Lyot-Sagnac传感结构输出光谱包络良好,与FPI级联利用游标效应能够显著提高传感器温度检测灵敏度。实验结果表明,级联传感器分别以Lyot-Sagnac传感结构中不同长度的PMF作为传感部位时,温度检测灵敏度为12.56 nm/°C和 92.77 nm/°C。相比于单独的Lyot-Sagnac干涉结构,本文提出的传感器灵敏度提升了约57倍。此外,在同一测量带宽下,PMF1模式的测量范围是PMF2模式的9.3倍。因此,相较于传统游标效应光纤温度传感器,本文提出的双响应模式温度传感器不仅具有良好的检测灵敏度,而且利用同一光谱检测设备可有效适配不同检测范围与灵敏度需求的应用场景,为性能可调式光纤温度传感器的研发提供了一种新思路。
-
关键词:
- 光纤温度传感器 /
- Lyot-Sagnac结构 /
- 游标效应 /
- Fabry-Pérot干涉仪
Abstract:To effectively enhance detection sensitivity and practicality, this paper proposes a fiber-optic temperature sensor based on a cascaded Lyot-Sagnac sensing structure sensitized by the Vernier effect and a Fabry-Pérot interferometer (FPI). The Lyot-Sagnac structure is fabricated by splicing polarization-maintaining fibers (PMFs) of different lengths with a 90° rotation, while the FPI is constructed using a hollow-core photonic crystal fiber (HCPCF) as the Fabry-Pérot cavity. The results of theoretical analysis demonstrates that the Lyot-Sagnac structure fabricated via the 90° rotated splicing method exhibits a well-defined output spectral envelope. When cascaded with an FPI, it can significantly improve temperature detection sensitivity through the Vernier effect. The experimental results show that the temperature sensitivity of the cascaded sensor is 12.56 nm/°C and 92.77 nm/°C when utilizing PMFs of different lengths in the Lyot-Sagnac sensor structure as the sensing regions. Compared to the standalone Lyot-Sagnac interferometeric structure, the sensitivity of the proposed sensor is improved by approximately 57 times. In addition, under the same measurement bandwidth, the measurement range of PMF1 mode is 9.3 times that of PMF2 mode. Therefore, compared to the traditional vernier-effect-based fiber-optic temperature sensors, the dual-response-mode temperature sensor proposed in this paper not only exhibits superior detection sensitivity, but also enables effective adaptation to application scenarios requiring different detection ranges and sensitivity levels using the same spectral detection equipment, providing a new idea for developing tunable-performance fiber-optic temperature sensors.
-
表 1 与其它基于游标效应的光纤温度传感器对比分析
Table 1. Comparative analysis with other Vernier-effect-based fiber-optic temperature sensors
-
[1] 李爱武, 单天奇, 国旗, 等. 光纤法布里-珀罗干涉仪高温传感器研究进展[J]. 中国光学(中英文), 2022, 15(4): 609-624. doi: 10.37188/CO.2021-0219LI A W, SHAN T Q, GUO Q, et al. Research progress of optical fiber Fabry-Perot interferometer high temperature sensors[J]. Chinese Optics, 2022, 15(4): 609-624. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/CO.2021-0219 [2] 席婷苇, 温嘉琳, 董玉明, 等. 光纤法布里珀罗超声传感器解调方法进展[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2025, 62(5): 0500001.XI T W, WEN J L, DONG Y M, et al. Research progress of demodulation method for fiber optic Fabry-Perot ultrasonic interferometer[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2025, 62(5): 0500001. (in Chinese). [3] CHENG T L, LIU W, SONG D CH, et al. A reliable anti-interference temperature sensor based on a four-hole microstructure optical fiber Mach-Zehnder interferometer[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2023, 72: 9508609. [4] LIU Y H, LIN W H, ZHAO F, et al. Dual-parameter fiber sensors for salinity and temperature measurement based on a tapered PMF incorporated with an FBG in Sagnac loop[J]. IEEE Photonics Journal, 2024, 16(1): 6300107. [5] HUANG B, WANG Y, MAO CH. Lyot filter with femtosecond laser-induced high birefringence single-mode fiber for torsion, transverse load and temperature sensing[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 25764-25769. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2968729 [6] 李建新, 朱伟, 任建乔, 等. 基于FBG传感技术的混凝土开裂损伤研究[J]. 传感器与微系统, 2025, 44(4): 17-20.LI J, ZHU W, REN J Q, et al. Research on concrete cracks damage based on FBG sensing technology[J]. Transducer and Microsystem Technologies, 2025, 44(4): 17-20. (in Chinese). [7] LI L Y, LIU Y, HE Y Y, et al. In situ and continuous decoding hydrogen generation in solar water-splitting cells[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2024, 96(29): 12155-12164. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.4c02323 [8] SHAO L Y, ZHANG X P, HE H J, et al. Optical fiber temperature and torsion sensor based on Lyot-Sagnac interferometer[J]. Sensors, 2016, 16(10): 1774. doi: 10.3390/s16101774 [9] WANG Y, CAO ZH G, LUO W D, et al. Method for controlling temperature sensitivity of the fiber intermodal sensor and its application in the torsion sensor[J]. Optics Express, 2021, 29(5): 6756-6767. doi: 10.1364/OE.415206 [10] ZHANG W J, LU Y G. Simultaneous measurement of temperature, liquid level and axial strain based on torsional taper Mach-Zehnder interferometer with Vernier effect[J]. Measurement, 2024, 230: 114504. doi: 10.1016/j.measurement.2024.114504 [11] YANG H N, DONG B, ZHAO W, et al. Er/Yb codoped double clad fiber modal interferometer and its application as fiber sensor[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2019, 37(11): 2681-2685. doi: 10.1109/JLT.2018.2875539 [12] PAN X P, DONG Y H, ZHENG J J, et al. Enhanced FBG temperature sensitivity in PbS-doped silica optical fiber[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2019, 37(18): 4902-4907. doi: 10.1109/JLT.2019.2937138 [13] ZHU X J, LIU W, SUN A, et al. Highly sensitive temperature and curvature sensor based on seven-core fiber[J]. Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 2023, 169: 107725. doi: 10.1016/j.optlaseng.2023.107725 [14] XU SH SH, CHEN H L, FENG W L. Fiber-optic curvature and temperature sensor based on the lateral-offset spliced SMF-FCF-SMF interference structure[J]. Optics & Laser Technology, 2021, 141: 107174. [15] SHAO M, CAO ZH W, GAO H, et al. Optical fiber ultrasonic sensor based on partial filling PDMS in hollow-core fiber[J]. Optics & Laser Technology, 2023, 167: 109648. [16] 王彦雄, 陈仟龙, 周小满, 等. 基于聚二甲基硅氧烷微流控芯片的微波生物传感器研究进展[J]. 分析化学, 2024, 52(12): 1797-1806.WANG Y X, CHEN Q L, ZHOU X M, et al. Research progress of microwave biosensors based on polydimethylsiloxane microfluidic chips[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2024, 52(12): 1797-1806. (in Chinese). [17] 马宽明, 刘梓轩, 刘培元, 等. 液晶填充光纤U型腔的偏振光谱及温度特性[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2019, 56(17): 170621.MA K M, LIU Z X, LIU P Y, et al. Polarization spectra of U-shaped optical fiber cavities filled with liquid crystal and their temperature characteristics[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2019, 56(17): 170621. (in Chinese). [18] YANG H K, WANG CH, JIN G Y, et al. Liquid crystal-embedded fiber optic Fabry Perot temperature sensor based on Vernier effect[J]. Measurement, 2024, 225: 113910. doi: 10.1016/j.measurement.2023.113910 [19] LEAL-JUNIOR A G, DÍAZ C R, MARQUES C, et al. Analysis of viscoelastic properties influence on strain and temperature responses of Fabry-Perot cavities based on UV-curable resins[J]. Optics & Laser Technology, 2019, 120: 105743. [20] ZHENG Y W, CHEN Y ZH, ZHANG Q F, et al. High-sensitivity temperature sensor based on fiber Fabry-Pérot interferometer with UV glue-filled hollow capillary fiber[J]. Sensors, 2023, 23(18): 7687. doi: 10.3390/s23187687 [21] WANG J, WU SH L, REN W Y. Epoxy resin cap-based low-finesse fiber Fabry-Pérot interferometer for temperature sensing[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2015, 15(11): 6385-6389. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2015.2458895 [22] SAMPATH U, KIM D G, KIM H, et al. Cryogenic temperature sensor based on Fresnel reflection from a polymer-coated facet of optical fiber[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2018, 18(9): 3640-3644. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2018.2813303 [23] 柯欣怡, 常建华, 闵洋, 等. 基于游标效应的并联光纤法布里-珀罗温湿度传感器[J]. 光学学报, 2025, 45(2): 0206001. doi: 10.3788/AOS241425KE X Y, CHANG J H, MIN Y, et al. Parallel fiber Fabry-Perot temperature and humidity sensor based on vernier effect[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2025, 45(2): 0206001. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/AOS241425 [24] CHEN Y H, ZHAO L, HAO SH, et al. Advanced fiber sensors based on the vernier effect[J]. Sensors, 2022, 22(7): 2694. doi: 10.3390/s22072694 [25] YANG Y Q, WANG Y G, ZHAO Y X, et al. Sensitivity-enhanced temperature sensor by hybrid cascaded configuration of a Sagnac loop and a F-P cavity[J]. Optics Express, 2017, 25(26): 33290-33296. doi: 10.1364/OE.25.033290 [26] LIU Y D, CHEN H L, CHEN Q, et al. Experimental study on dual-parameter sensing based on cascaded Sagnac interferometers with two PANDA fibers[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2022, 40(9): 3090-3097. doi: 10.1109/JLT.2022.3145004 [27] ZUO CH, WU K Y, SHI J H, et al. Sensitivity-enhanced temperature and strain sensor based on a UFPMF Sagnac loop cascaded with a SCMOF probe[J]. Sensors and Actuators A: Physical, 2023, 361: 114610. doi: 10.1016/j.sna.2023.114610 [28] ZHAO Y F, DAI M L, CHEN ZH M, et al. Ultrasensitive temperature sensor with Vernier-effect improved fiber Michelson interferometer[J]. Optics Express, 2021, 29(2): 1090-1101. doi: 10.1364/OE.415857 [29] SONG J, SUN S M, JIANG CH, et al. Ultra-sensitive temperature and pressure sensor based on PDMS-based FPI and Vernier effect[J]. Optics Letters, 2023, 48(7): 1674-1677. doi: 10.1364/OL.480506 [30] TONG R J, XING B, CHEN Z H, et al. High-sensitivity fiber optic temperature sensor based on enhanced vernier effect[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2024, 73: 7003408. [31] FAN X Y, CHEN H L, ZHENG Y, et al. Ultrasensitive fiber-optic temperature sensor based on cascaded Sagnac interferometers with a nematic liquid crystal film[J]. Optics & Laser Technology, 2022, 152: 108169. -





 下载:
下载: