-
摘要:
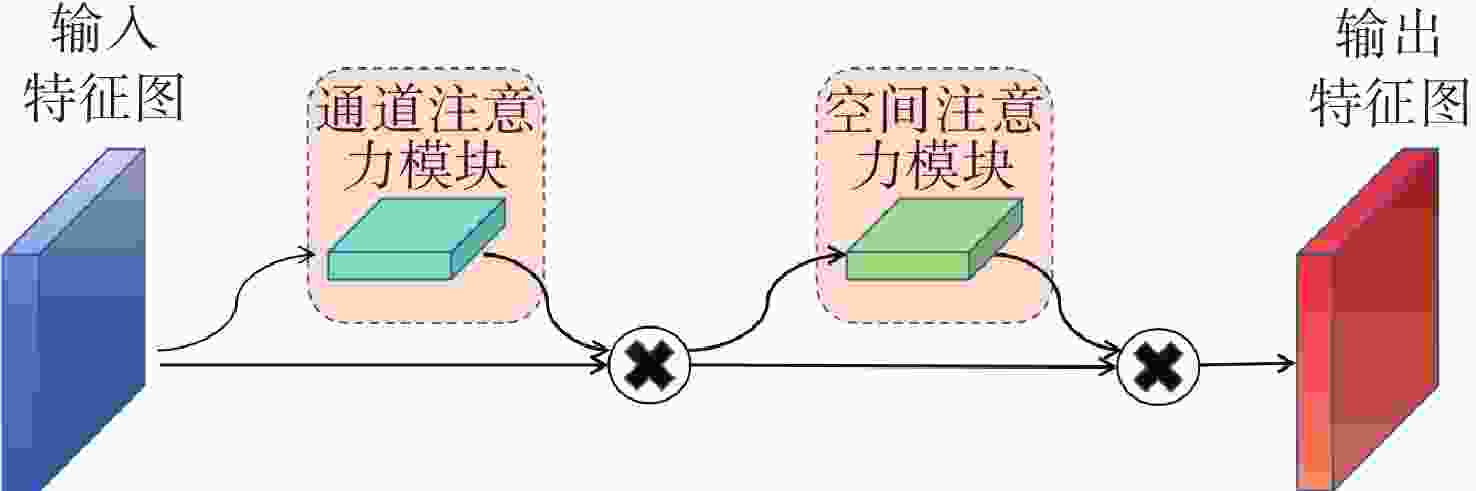
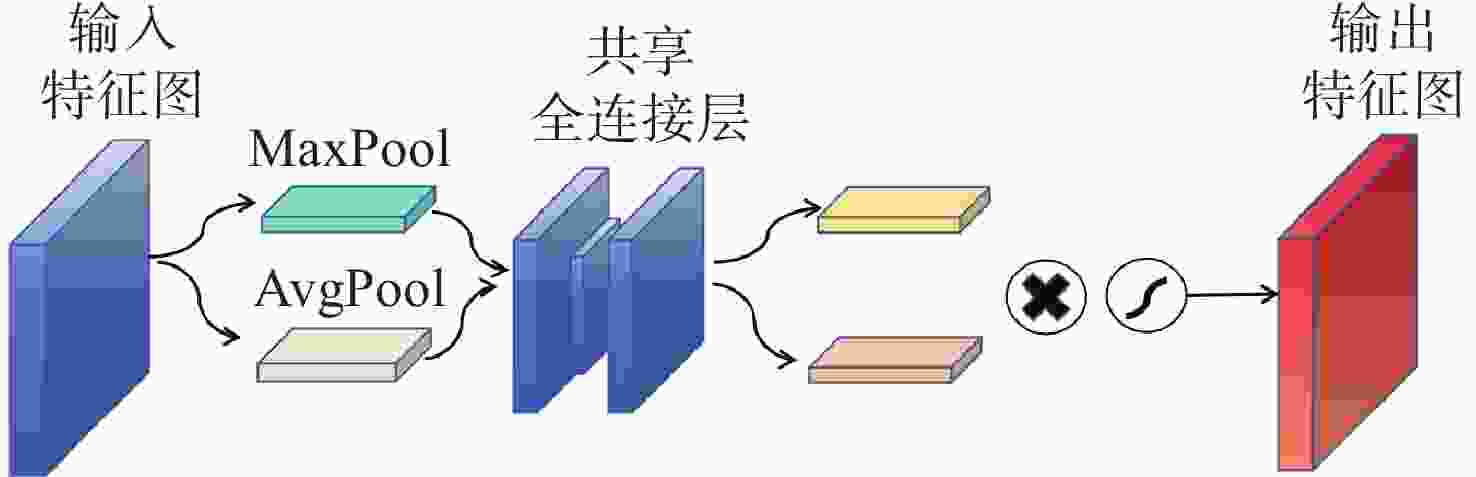
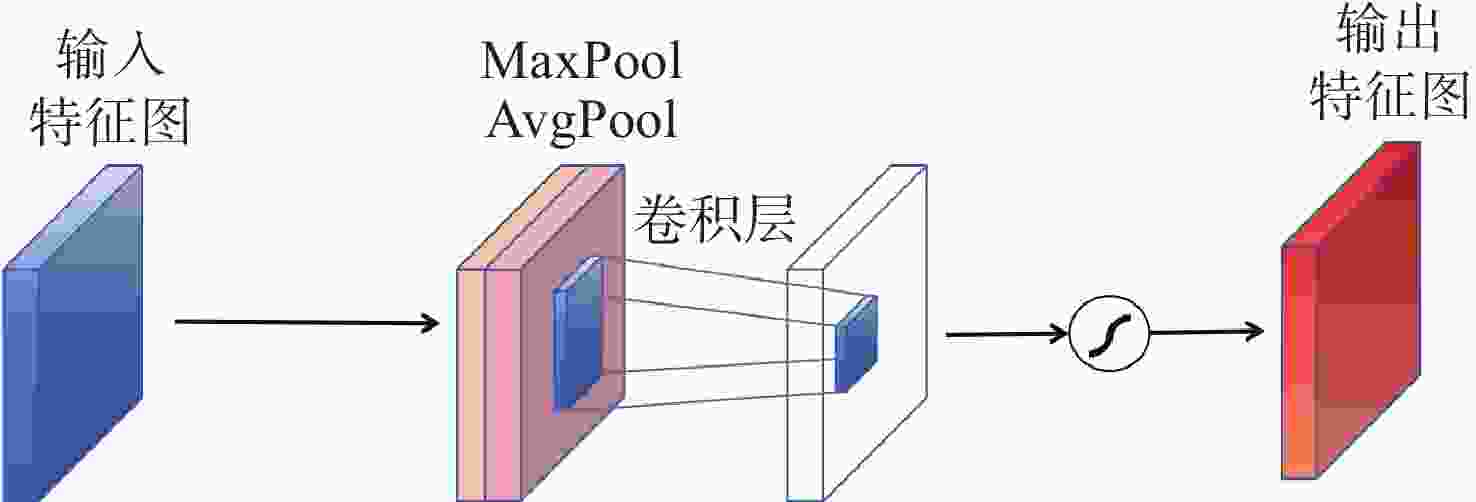
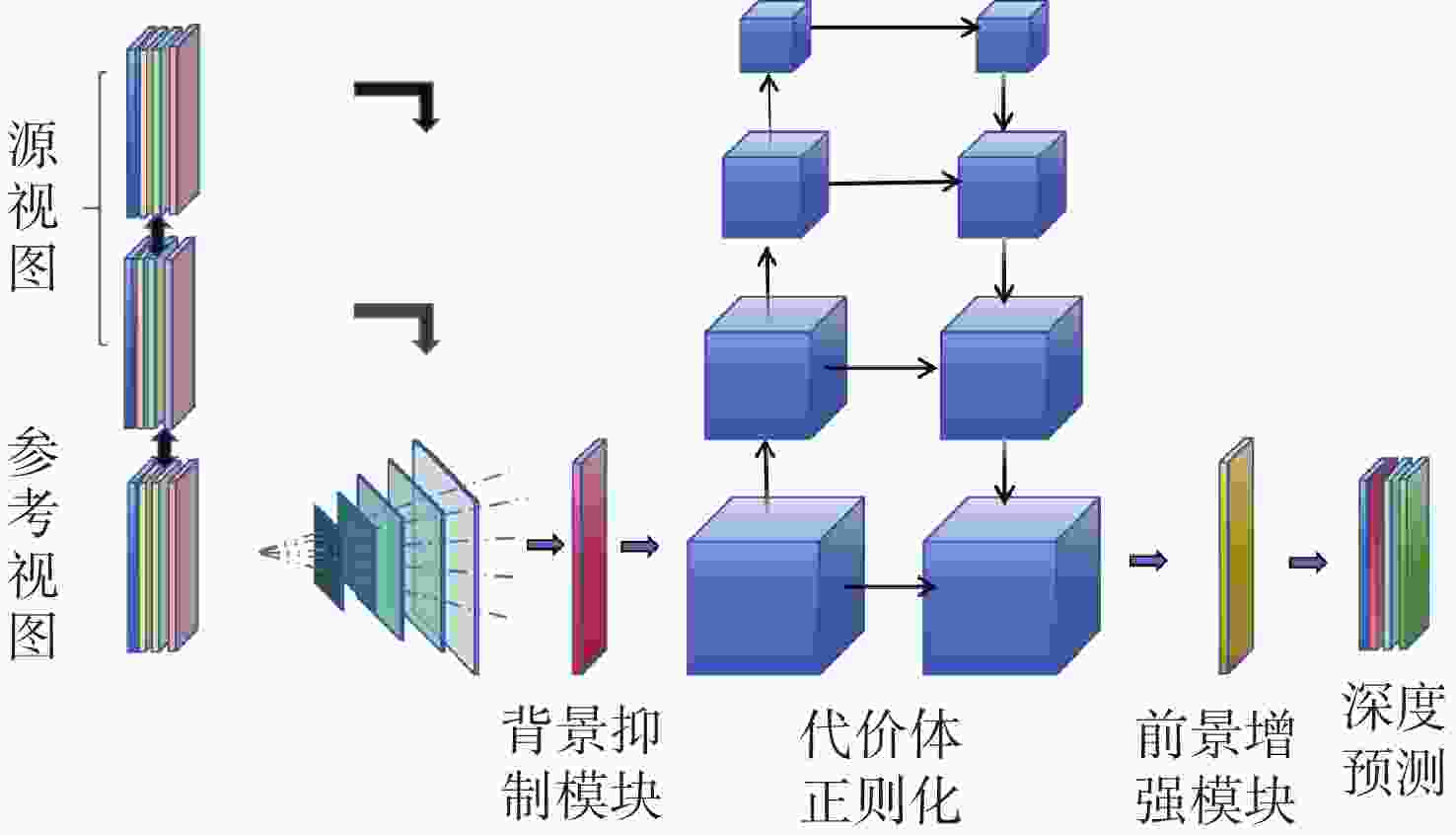
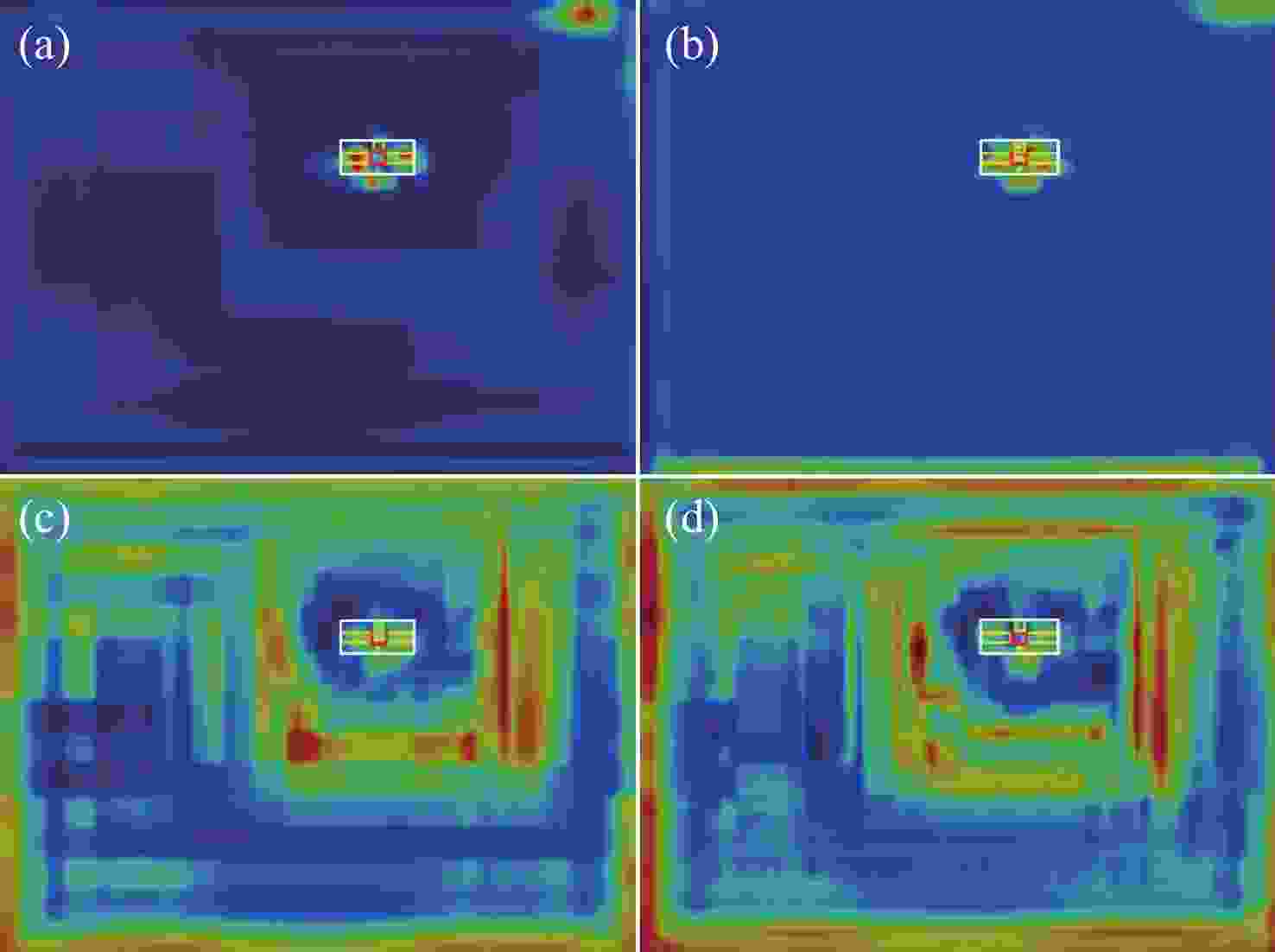
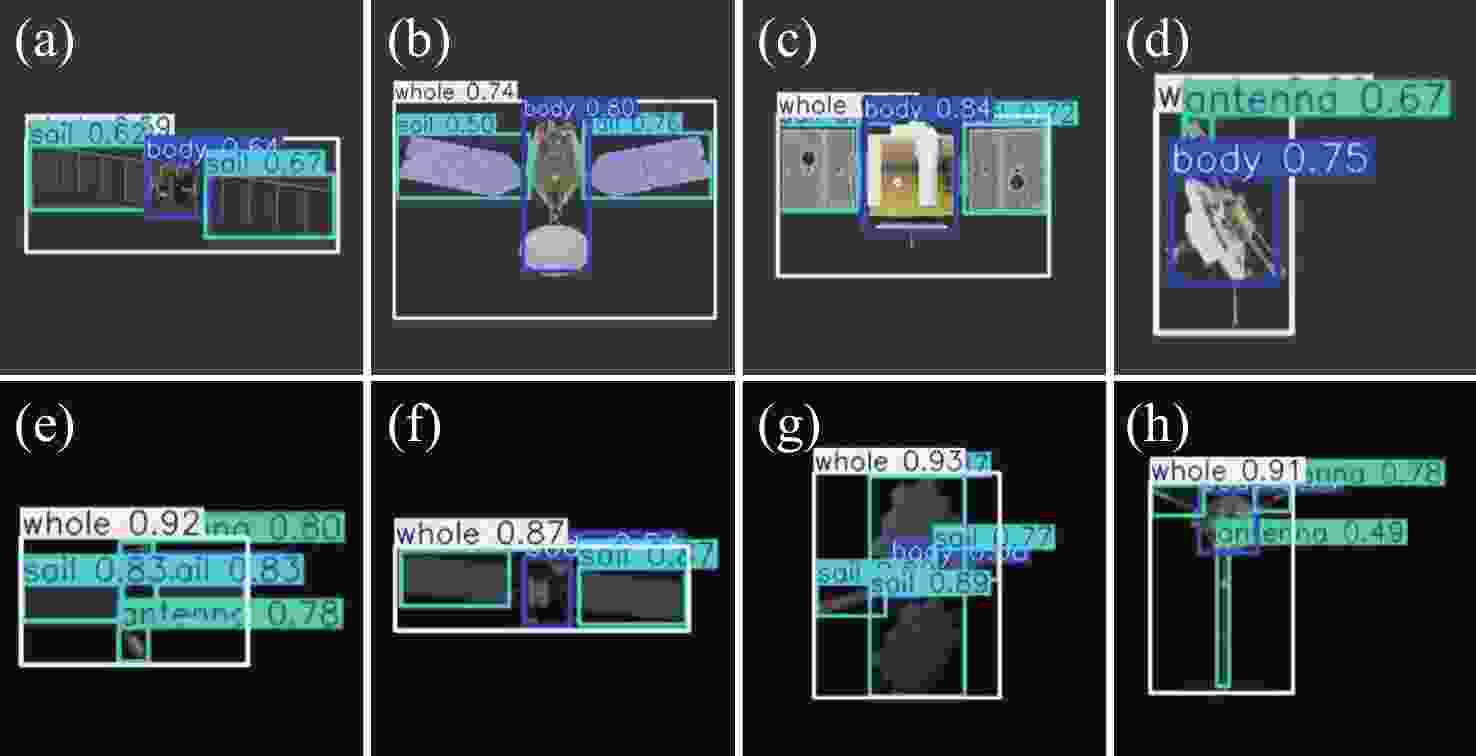
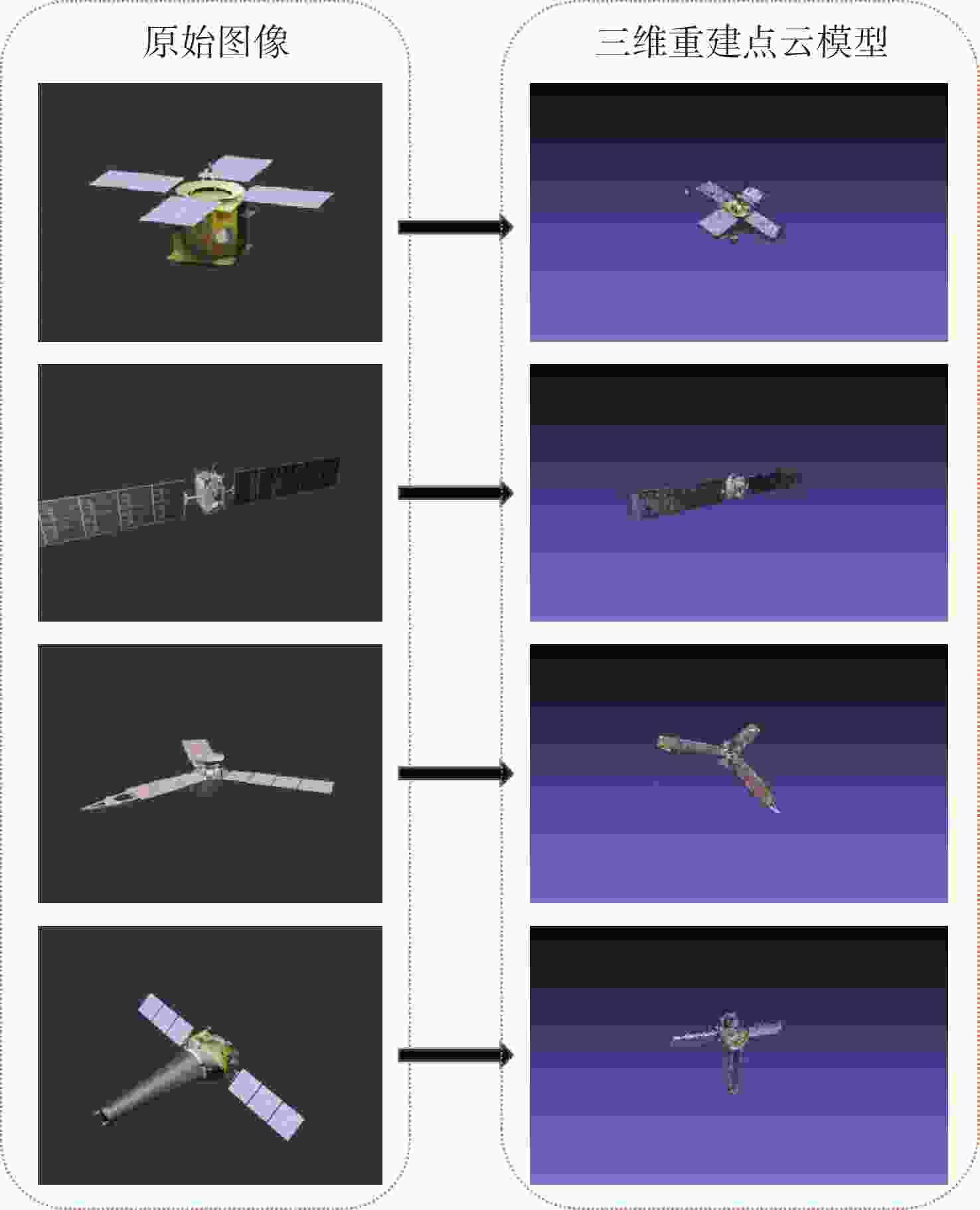
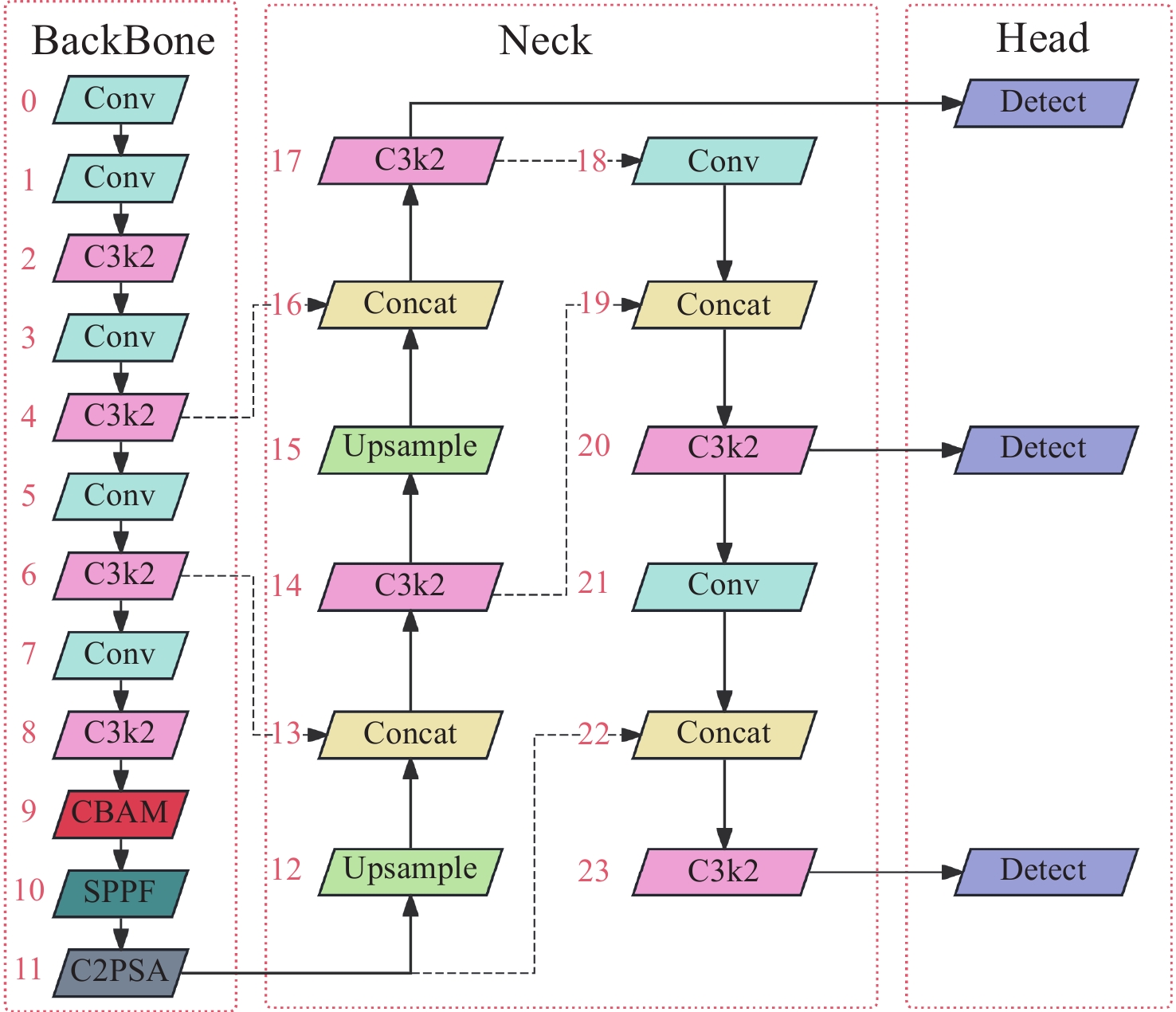
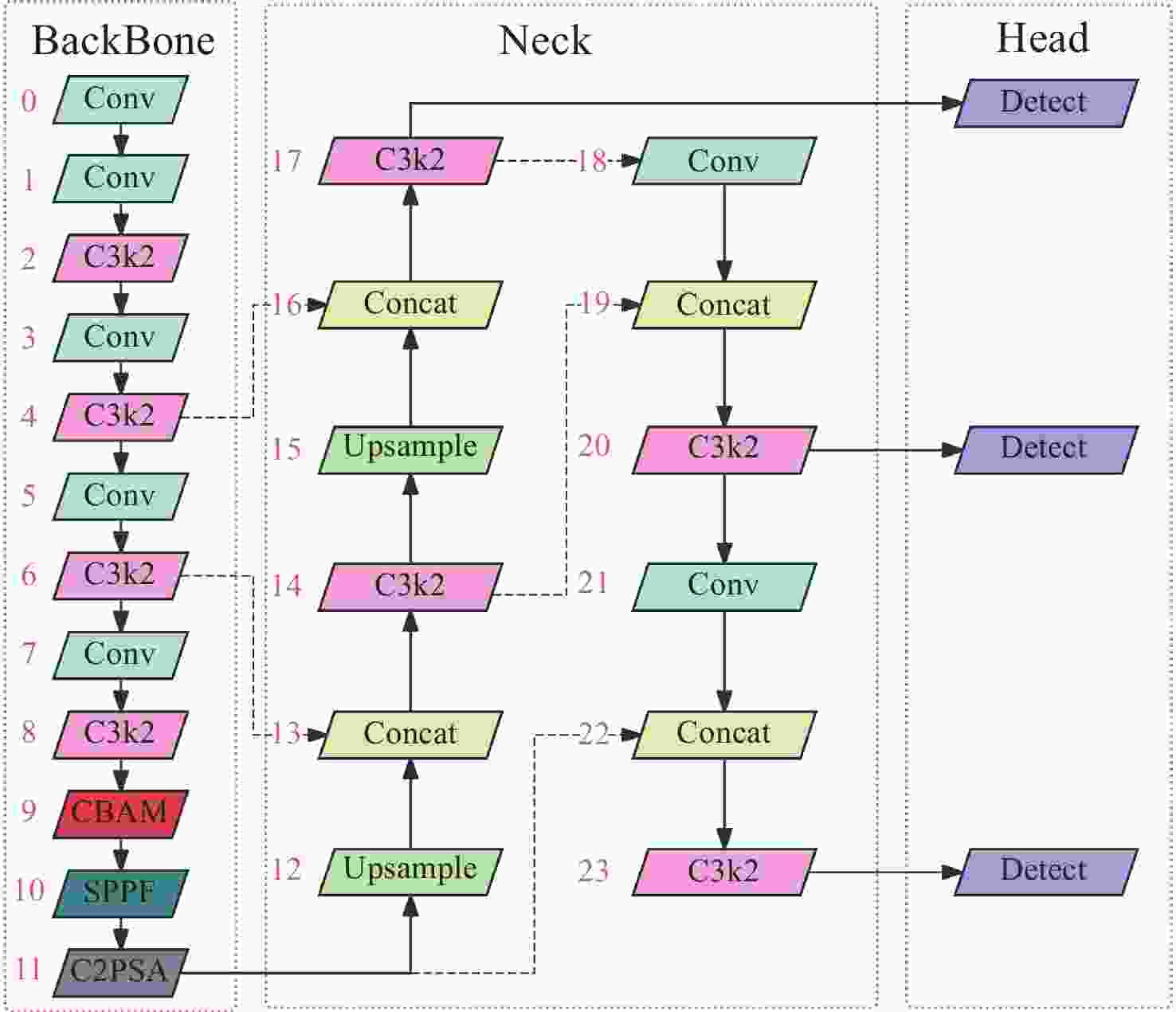
在空间态势感知任务中,为了实现复杂低纹理环境下空间目标部组件的识别和三维重建,本文提出了一种基于深度学习的端到端空间目标智能感知框架,实现空间目标关键部件的智能识别和高精度三维重建。本文首先基于YOLOv11s轻量化网络,引入注意力机制聚焦特征,在保证实时性前提下实现空间目标及其关键部件的精确定位与识别,有助于提取目标区域从而进行精准三维重建。然后,提出了一种适用于空间低纹理目标的三维重建算法Sat-TransMVSNet,该算法采用多尺度特征增强网络提取特征,采用全新的代价体正则化方法强化空间目标边缘几何约束,提出背景抑制-前景增强模块并结合动态深度采样策略精确重建空间目标。最后,通过自建不同类型的多角度空间目标数据集对整体框架进行测试。实验结果表明:卫星部组件识别算法mAP50为0.95,三维重建综合误差为
0.2886 mm。基本满足高精度空间目标三维重建和关键部位的高精度智能识别。Abstract:To achieve the recognition and 3D reconstruction of space target components in complex, low-texture environments for space situational awareness tasks, we propose an end-to-end intelligent perception framework for space targets based on deep learning. This framework enables intelligent recognition and high-precision 3D reconstruction of key space target components. First, based on the lightweight YOLOv11s network, an attention mechanism is introduced to focus features, achieving precise localization and recognition of space targets and their key components while ensuring real-time performance. This facilitates the extraction of target regions for accurate 3D reconstruction. Subsequently, a novel 3D reconstruction algorithm named Sat-TransMVSNet, specifically designed for low-texture space targets, is proposed. This algorithm employs a multi-scale feature enhancement network for feature extraction and utilizes a novel cost volume regularization method to strengthen geometric constraints at space target edges. It incorporates a background-suppression and foreground-enhancement module, combined with a dynamic depth sampling strategy, to accurately reconstruct space targets. Finally, the overall framework is tested using a self-built multi-angle space target dataset comprising various types. Experimental results indicate that the component recognition algorithm achieves an mAP50 of 0.95, and the comprehensive 3D reconstruction error is
0.2886 mm. This demonstrates the framework’s capability to meet the requirements for high-precision 3D reconstruction of space targets and intelligent recognition of key components.-
Key words:
- 3D reconstruction /
- component recognition /
- deep learning /
- space targets
-
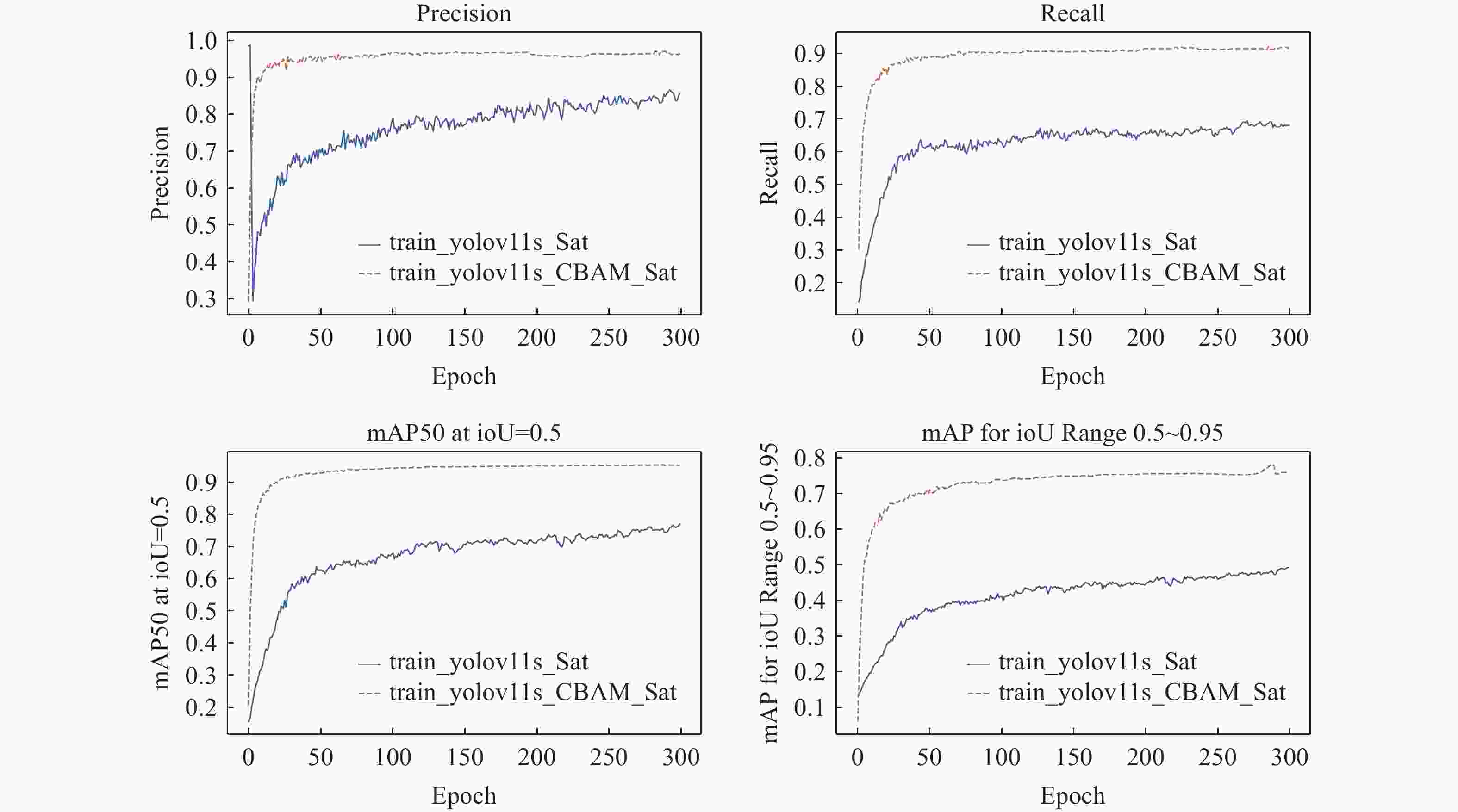
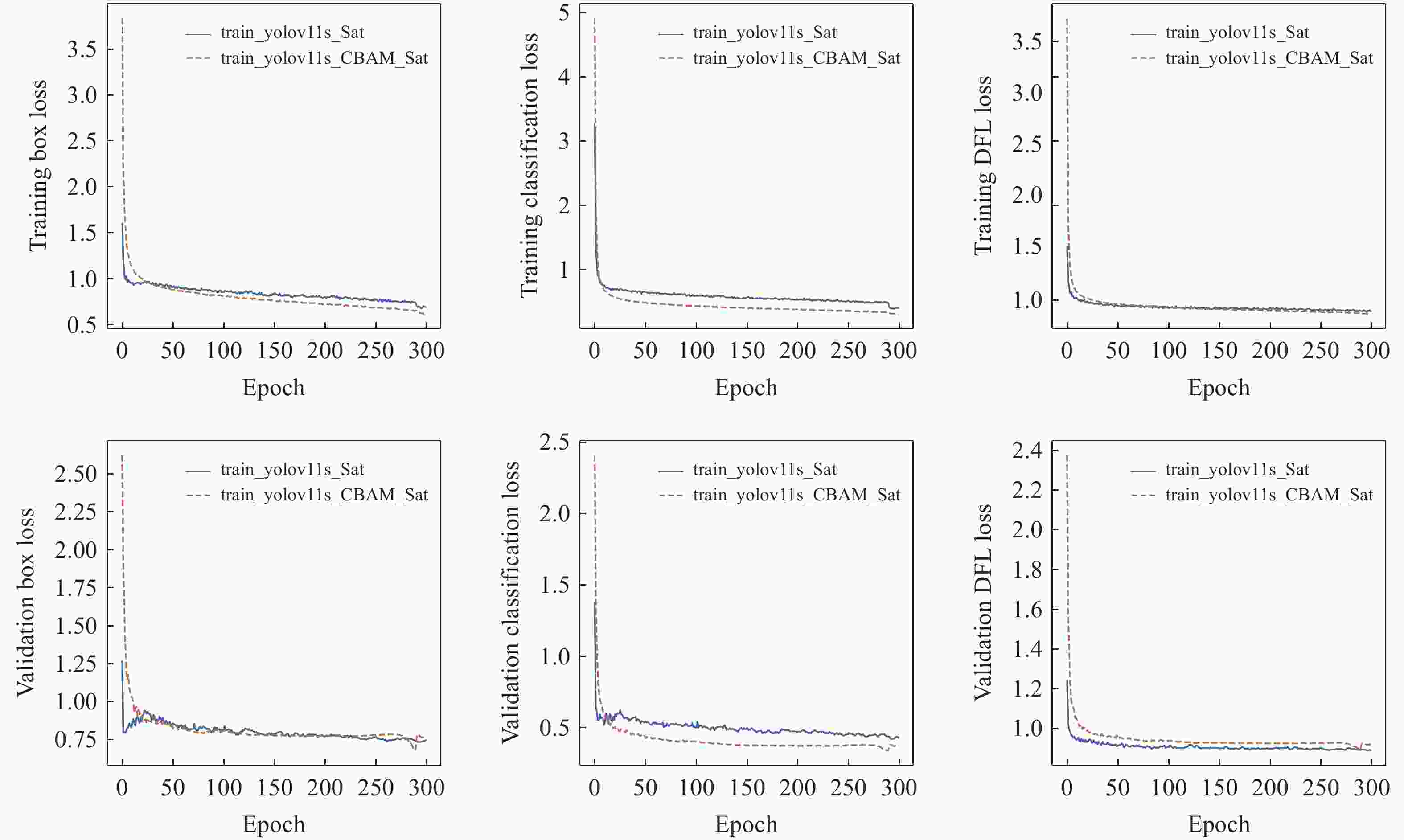
表 1 几种算法空间目标部组件目标识别性能对比
Table 1. Comparison of target recognition performance of spatial target components by different algorithms
算法名称 mAP50 Precision Recall YOLOV8s 0.909 0.918 0.903 YOLOV5s 0.899 0.953 0.809 Faster R-CNN 0.782 0.893 0.792 SSD 0.693 0.784 0.681 YOLOV11s-CBAM 0.961 0.965 0.927 表 2 三维重建算法训练结果对比
Table 2. Comparison of the training results of 3D reconstruction algorithms (Unit: mm)
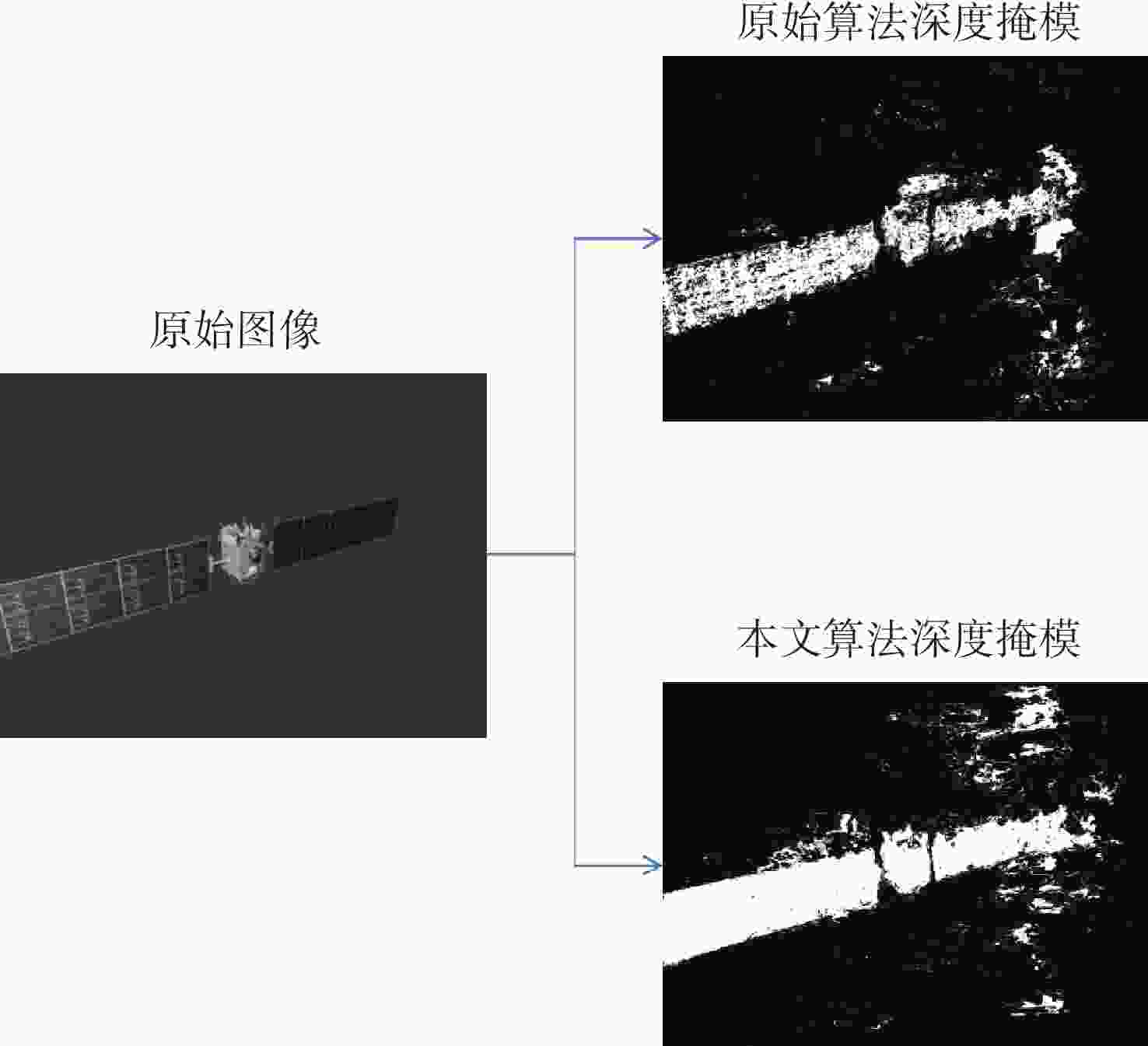
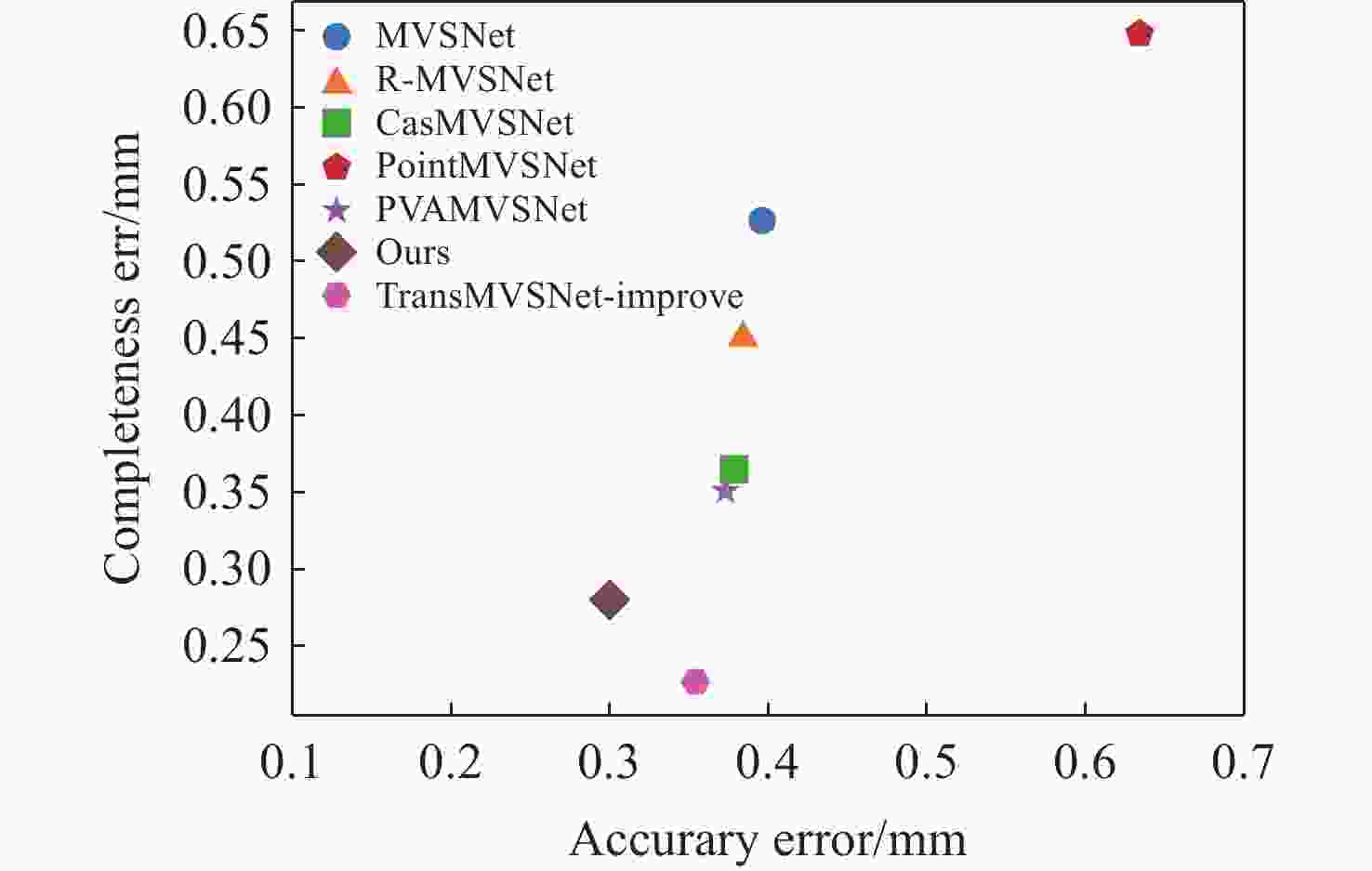
算法名称 总损失 深度损失 绝对误差损失 阈值误差 原始算法 5.139 5.263 5.737 0.197 本文算法 4.539 5.1683 5.383 0.155 -
[1] 王锋, 张哲, 叶昊, 等. 国外空间态势感知能力分析与发展趋势(特邀)[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2024, 61(20): 2011006.WANG F, ZHANG ZH, YE H, et al. Development status and trends of foreign space situation awareness ability(invited)[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2024, 61(20): 2011006. (in Chinese). [2] 陶江. 基于视觉的空间碎片智能感知方法研究[D]. 南京: 南京航空航天大学, 2023.TAO J. Research on visual based space debris intel-ligent perception method[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2023. (in Chinese). [3] ALIZADEH M, ZHU ZH H. A comprehensive survey of space robotic manipulators for on-orbit servicing[J]. Frontiers in Robotics and AI, 2024, 11: 1470950. doi: 10.3389/frobt.2024.1470950 [4] 李学仕, 马益, 陈英, 等. 基于天基平台的空中高机动目标检测方法研究[J]. 现代雷达, 2024, 46(3): 47-53.LI X SH, MA Y, CHEN Y, et al. A study on air high maneuvering target detection method based on the space-based platform[J]. Modern Radar, 2024, 46(3): 47-53. (in Chinese). [5] 田旭东. 复杂观测条件下的空间微动目标识别方法研究[D]. 西安: 西安电子科技大学, 2024.TIAN X D. Study on space micro-motion target recognition method under complex observation conditions[D]. Xi’an: Xidian University, 2024. (in Chinese). [6] 王思启, 张家强, 李丽圆, 等. MVSNet在空间目标三维重建中的应用[J]. 中国激光, 2022, 49(23): 2310003. doi: 10.3788/CJL202249.2310003WANG S Q, ZHANG J Q, LI L Y, et al. Application of MVSNet in 3D reconstruction of space objects[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2022, 49(23): 2310003. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/CJL202249.2310003 [7] 陈心如. 基于SIFT算法的图像匹配优化分析[J]. 电子技术, 2025, 54(2): 407-409.CHEN X R. Analysis of image matching optimization based on sift algorithm[J]. Electronic Technology, 2025, 54(2): 407-409. (in Chinese). [8] 李蓉, 胡可馨. 基于DTW算法的翻译机器人错误自动化校正控制系统设计[J]. 电子设计工程, 2025, 33(11): 81-85.LI R, HU K X. Design of automatic error correction control system for translation robot based on DTW algorithm[J]. Electronic Design Engineering, 2025, 33(11): 81-85. (in Chinese). [9] 崔劲杰, 韩晶, 李洁, 等. 基于CNN与HOG特征融合的视觉手势识别[J]. 兵器装备工程学报, 2024, 45(12): 289-297.CUI J J, HAN J, LI J, et al. Visual gesture recognition based on fusion of VGG16 and HOG features[J]. Journal of Ordnance Equipment Engineering, 2024, 45(12): 289-297. (in Chinese). [10] 刘福才, 张晓. 空间非合作目标航天器太阳帆板识别方法研究[J]. 高技术通讯, 2021, 31(6): 628-638.LIU F C, ZHANG X. Research on solar panel recognition method of space non-cooperative target spacecraft[J]. Chinese High Technology Letters, 2021, 31(6): 628-638. (in Chinese). [11] JIANG Z, TAIRA H, MIYASHITA N, et al. Vio-aided structure from motion under challenging environments[C]. Proceedings of the 2021 22nd IEEE International Conference on Industrial Technology (ICIT), IEEE, 2021: 950-957. [12] LI SH H, XIAO X W, GUO B X, et al. A novel OpenMVS-based texture reconstruction method based on the fully automatic plane segmentation for 3D mesh models[J]. Remote Sensing, 2020, 12(23): 3908. doi: 10.3390/rs12233908 [13] 韩鑫豪, 何月顺, 陈杰, 等. 基于Swin Transformer的岩石岩性智能识别研究[J]. 现代电子技术, 2024, 47(7): 37-44.HAN X H, HE Y SH, CHEN J, et al. Research on rock lithology intelligent identification based on Swin Transformer[J]. Modern Electronics Technique, 2024, 47(7): 37-44. (in Chinese). [14] 邢航. 基于深度学习的多视图立体匹配三维重建[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2024.XING H. Multi-view 3D reconstruction based on deep learning[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2024. (in Chinese). [15] QU Z H, LIU H Y, KONG W G, et al. LP-YOLO: an improved lightweight pedestrian detection algorithm based on YOLOv11[J]. Digital Signal Processing, 2025, 165: 105343. [16] 瞿伟, 宫明利, 徐荣堂, 等. 一种基于CBAM注意力机制优化YOLOv8n的滑坡检测方法[J/OL]. 应用基础与工程科学学报, (2025-05-23). https://link.cnki.net/urlid/11.3242.TB.20250523.1402.006.QU W, GONG M L, XU R T, et al. A landslide detection method based on CBAM attention mechanism optimized for YOLOv8n[J/OL]. Journal of Basic Science and Engineering, (2025-05-23). https://link.cnki.net/urlid/11.3242.TB.20250523.1402.006. (in Chinese). [17] TENG J W, SUN H J, LIU P X, et al. An improved TransMVSNet algorithm for three-dimensional reconstruction in the unmanned aerial vehicle remote sensing domain[J]. Sensors, 2024, 24(7): 2064. [18] DING Y K, YUAN W T, ZHU Q T, et al. Transmvsnet: global context-aware multi-view stereo network with transformers[C]. Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE, 2022: 8585-8594. [19] 苏佳, 罗都, 梁奔, 等. 基于YOLO-Z的果实识别检测算法[J]. 计算机工程与设计, 2025, 46(5): 1503-1511.SU J, LUO D, LIANG B, et al. Fruit recognition and detection algorithm based on YOLO-Z[J]. Computer Engineering and Design, 2025, 46(5): 1503-1511. (in Chinese). [20] 胡鹏宇, 钟倩文, 郑树彬. 基于PatchmatchNet的钢轨表面三维重构[J/OL]. 电子科技, (2025-05-30). https://link.cnki.net/urlid/61.1291.tn.20250530.1140.002.HU P Y, ZHONG Q W, ZHENG SH B. Three-dimensional reconstruction of rail surface based on PatchmatchNet[J/OL]. Electronic Science and Technology, (2025-05-30). https://link.cnki.net/urlid/61.1291.tn.20250530.1140.002. (in Chinese). [21] WANG B H, TENG Y L, LAU V, et al. CCA-Net: a lightweight network using criss-cross attention for CSI feedback[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2023, 27(7): 1879-1883. [22] ZHAO Y P, ZHONG R, CUI L Y. Intelligent recognition of spacecraft components from photorealistic images based on Unreal Engine 4[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2023, 71(9): 3761-3774. doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2022.09.045 [23] 孙建起, 王向哲, 杨凯, 等. 基于Blender医疗康复机器人设计与仿真[J]. 物联网技术, 2025, 15(8): 85-88.SUN J Q, WANG X ZH, YANG K, et al. Design and simulation of medical rehabilitation robots based on blender[J]. Internet of Things Technologies, 2025, 15(8): 85-88. (in Chinese). [24] 张浩鹏, 刘正一, 姜志国, 等. BUAA-SID1.0空间目标图像数据库[J]. 航天返回与遥感, 2010, 31(4): 65-71.ZHANG H P, LIU ZH Y, JIANG ZH G, et al. BUAA-SID1.0 space object image dataset[J]. Spacecraft Recovery & Remote Sensing, 2010, 31(4): 65-71. (in Chinese). [25] 王景鑫, 潘欣. 一种基于Labelimg的辅助标注方法[J]. 科技创新与应用, 2023, 13(29): 145-148.WANG J X, PAN X. An auxiliary annotation method based on Labelimg[J]. Technology Innovation and Application, 2023, 13(29): 145-148. (in Chinese). [26] AANÆS H, JENSEN R R, VOGIATZIS G, et al. Large-scale data for multiple-view stereopsis[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2016, 120(2): 153-168. doi: 10.1007/s11263-016-0902-9 [27] YAO Y, LUO Z X, LI S W, et al. MVSNet: depth inference for unstructured multi-view stereo[C]. Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Science, Springer, 2018: 785-801. [28] YAO Y, LUO Z X, LI SH W, et al. Recurrent MVSNet for high-resolution multi-view stereo depth inference[C]. Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), IEEE, 2019: 5520-5529. [29] GU X D, FAN ZH W, ZHU S Y, et al. Cascade cost volume for high-resolution multi-view stereo and stereo matching[C]. Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE, 2020: 2492-2501. [30] CHEN R, HAN S F, XU J, et al. Point-based multi-view stereo network[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, IEEE, 2019: 1538-1547. [31] YI H W, WEI Z ZH, DING M Y, et al. Pyramid multi-view stereo net with self-adaptive view aggregation[C]. Proceedings of the 16th European Conference on Computer Vision, Springer, 2020: 766-782. -





 下载:
下载: