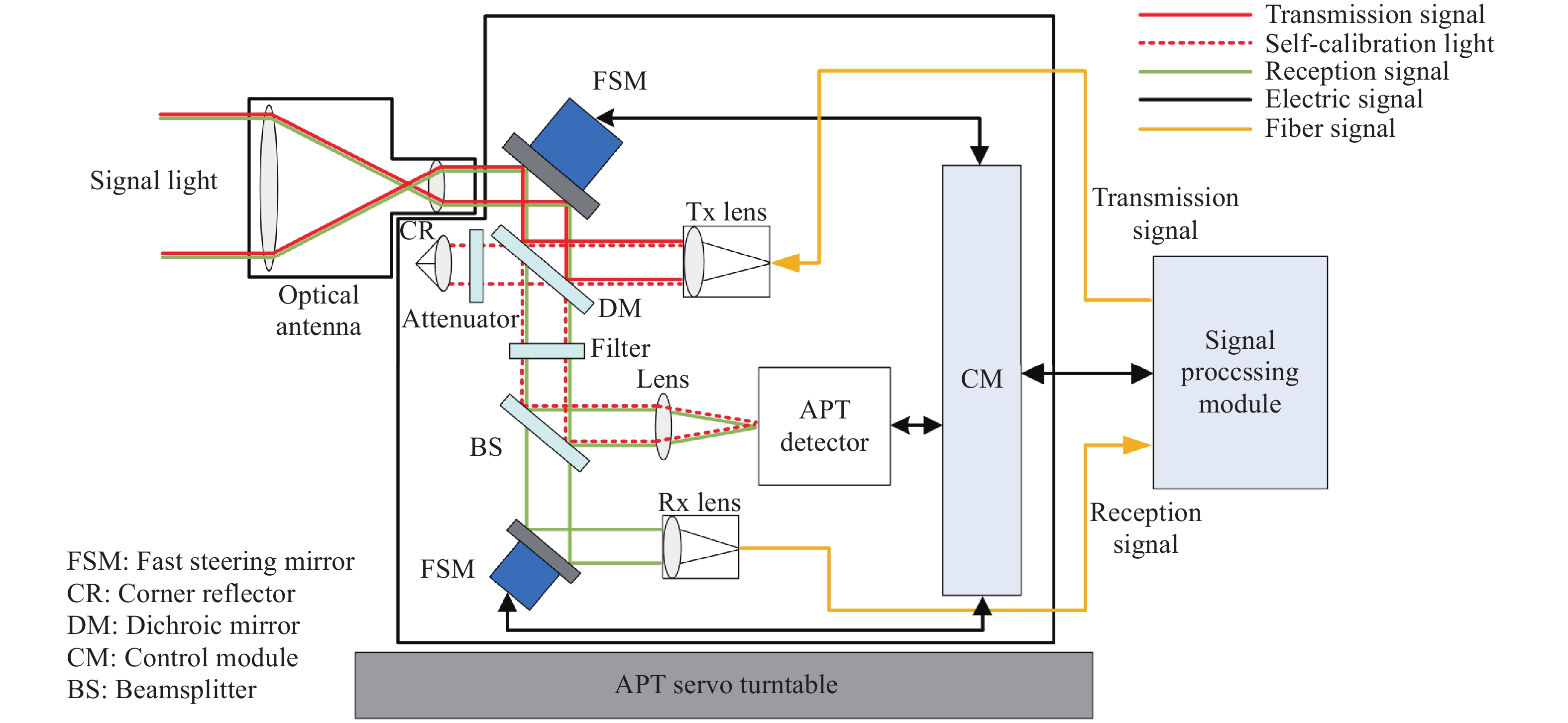
A mass-production-oriented alignment method for optical antennas of inter-satellite laser communication payloads
-
摘要:
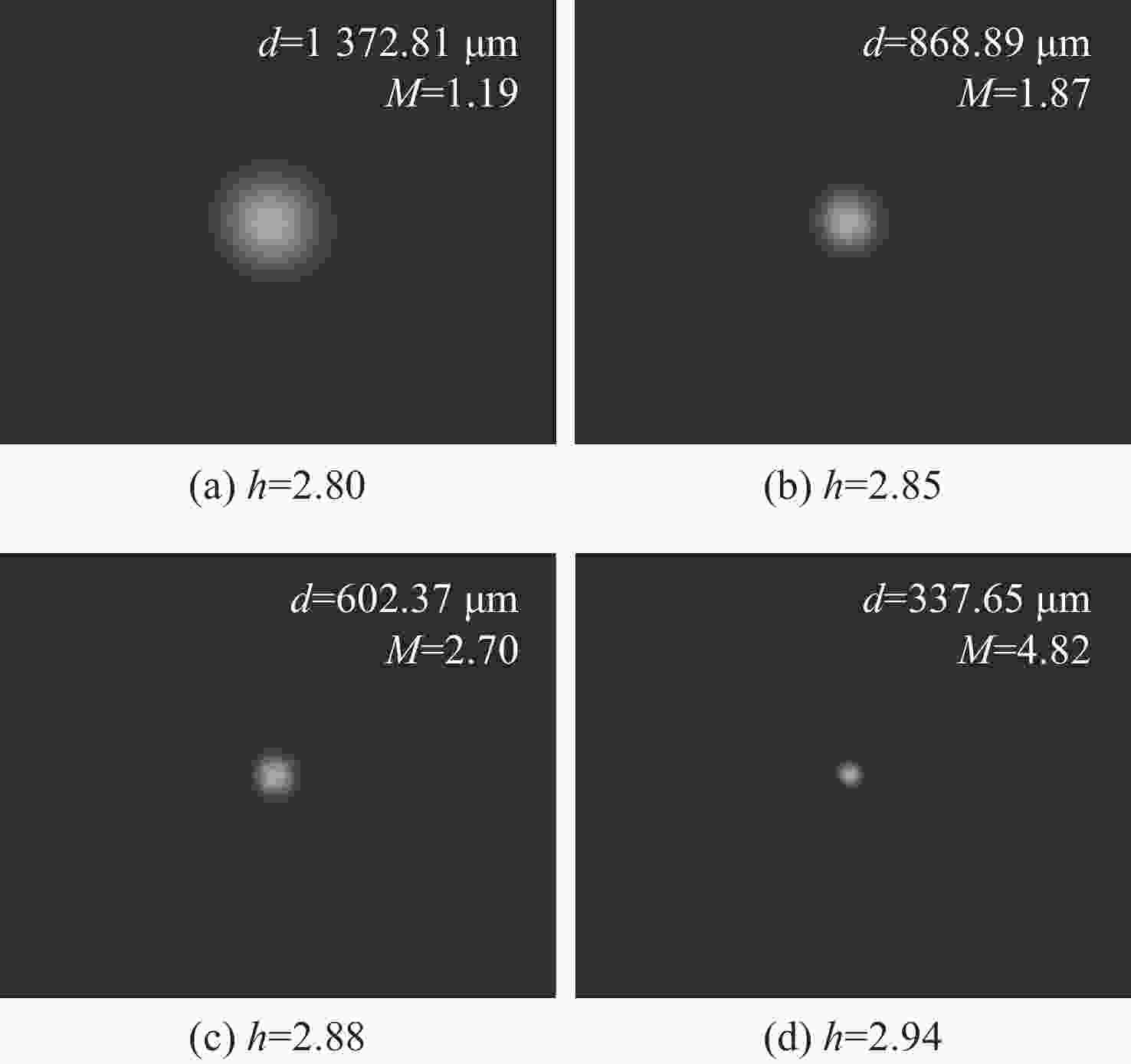
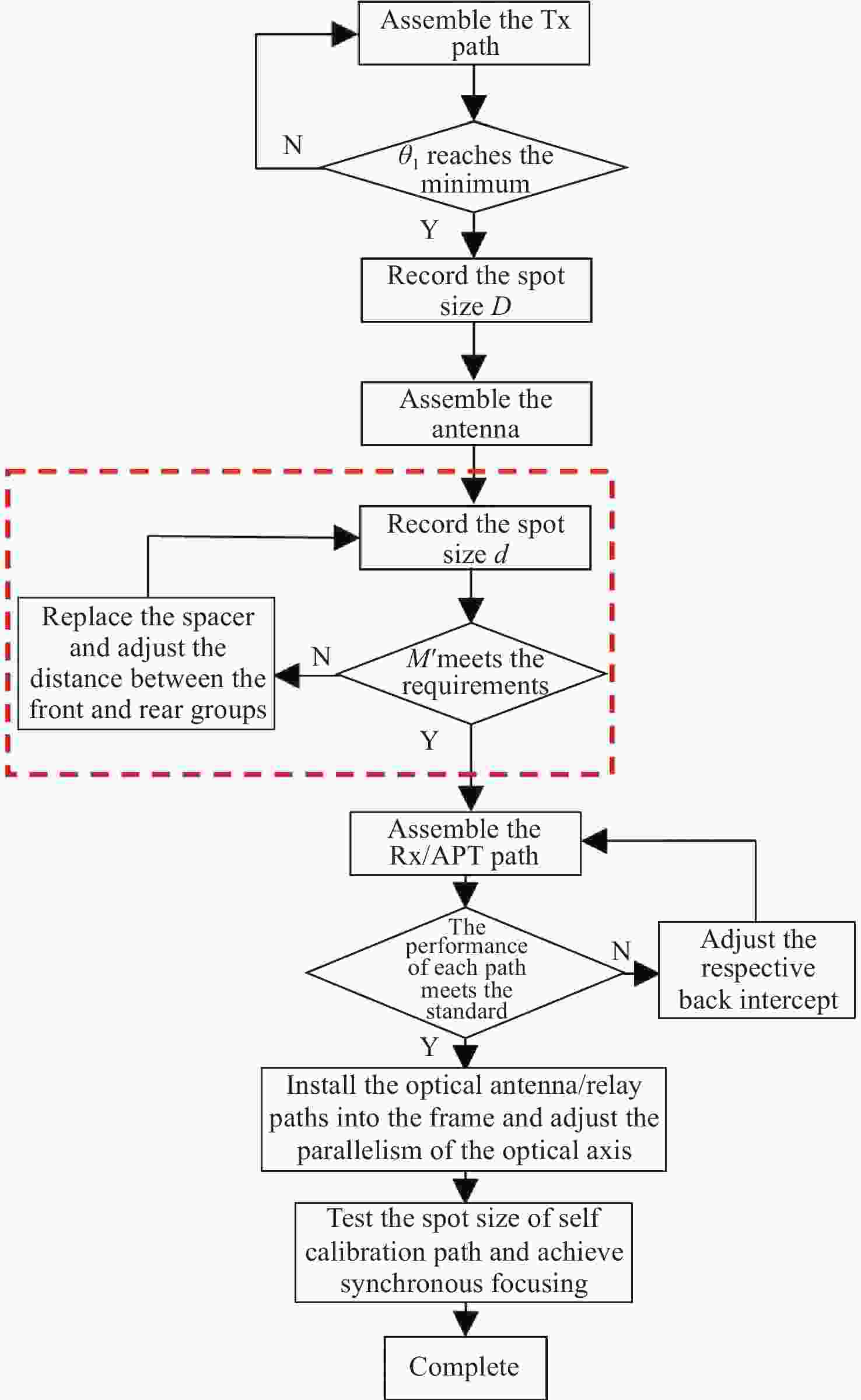
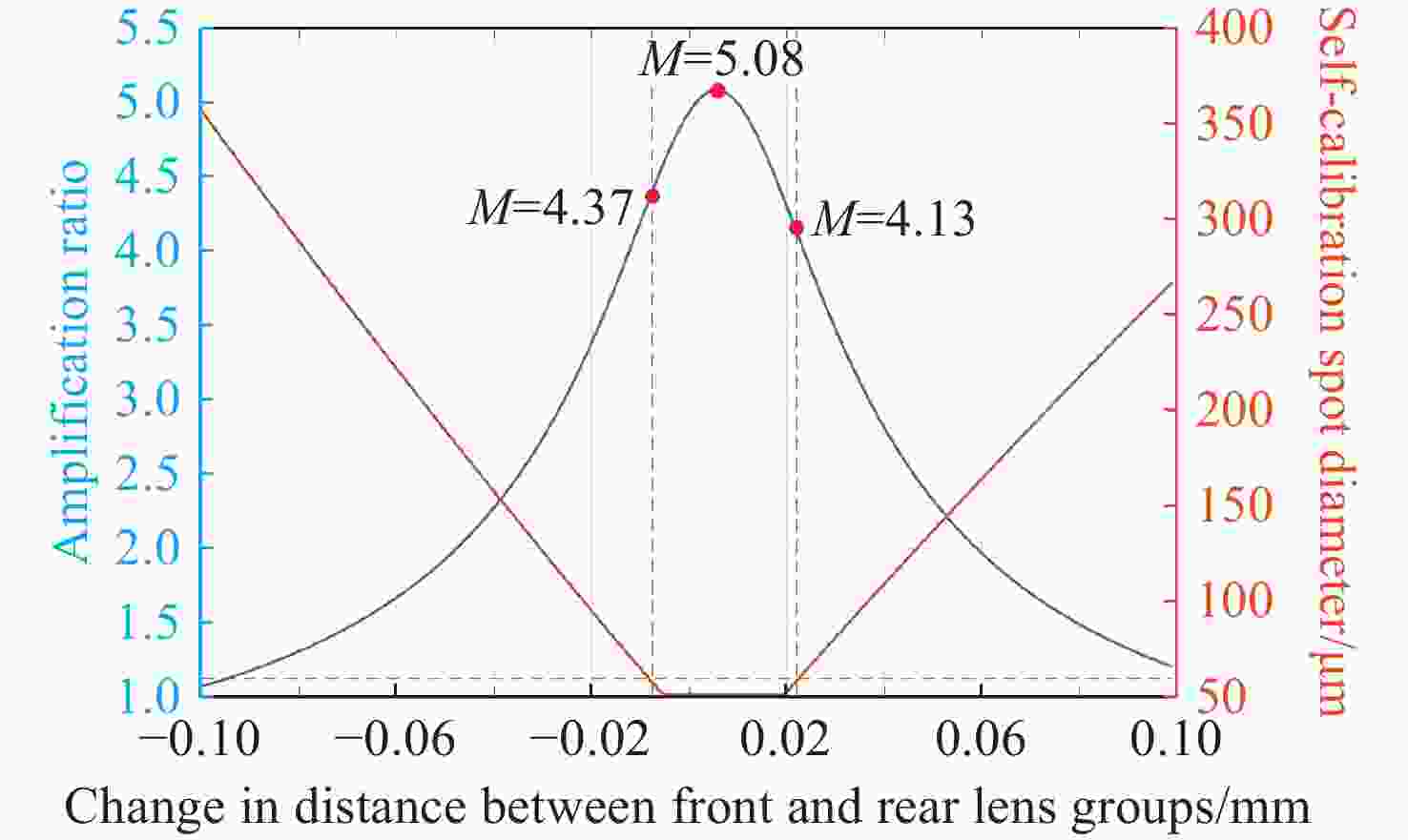
随着空间激光通信技术的快速发展,高速星间链路组网需求日益强烈。然而,国内现阶段对星间激光通信载荷的研究仍以试验验证性质为主,光学系统设计复杂,加工、装调、检测时间长且成本高,不利于激光终端的低成本快速批产。为解决这一问题,本文提出了一种单波段消色差的透射式光学天线,以及基于平行光管检测光学天线放大倍率的快速装调方法。通过减小色差校正范围,使得光学天线的长度缩短了15.83%,透镜数量从6片减少到4片,降低了加工成本。仿真模拟给出放大倍率的装调范围为4.37~5.08。实际装调后,放大倍率实测值为4.82,信号发射光路的发散角为67.53 μrad,信号接收光路的耦合效率为51.42%,自标校光斑尺寸在12 pixel×12pixel以内。同时还进行了对照试验,结果显示所提方法的装调时间还未到干涉仪法的10%。装调测试结果表明,本方法既可在设计上实现光学天线的轻小型化设计,也可大幅度降低装调检测时间,并实现信号收发、捕跟探测与自标校光路的同步合焦。
Abstract:With the rapid development of space laser communication technology, the demand for high-speed inter-satellite networking has been growing significantly. However, existing research on inter-satellite laser communication payload is still primarily experimental, featuring complex optical system designs that require lengthy and costly processes for manufacturing, alignment, and testing-posing challenges for low-cost and rapid mass production. To address this issue, a transmissive optical antenna with single-band achromatic design is proposed in this paper, along with a rapid alignment method for measuring the magnification of the optical antenna based on a collimator. By narrowing the chromatic aberration correction range, the length of the optical antenna is reduced by 15.83%, the number of lenses is decreased from six to four, and the manufacturing cost of a single optical antenna is reduced. Simulation results indicate that the alignment tolerance range for magnification is 4.37 to 5.08. After actual alignment, the measured magnification is 4.82, with a beam divergence of 67.53 μrad on the transmission path and a coupling efficiency of 51.42% on the receiving path. The self-calibration spot size is within 12×12 pixels. A comparative experiment is also conducted, and the proposed method demonstrates a noticeably shorter alignment time than the interferometer method. The alignment and testing results demonstrate that the proposed method not only enables a lightweight and compact design of the optical antenna, but also significantly reduces the alignment time. Simultaneous focal alignment of signal transmission, acquisition-pointing-tracking, and self-calibration optical paths is also achieved.
-
Key words:
- laser communication /
- optical antenna /
- optical design /
- alignment method
-
表 1 激光通信载荷的主要指标参数
Table 1. Index of the laser communication payload
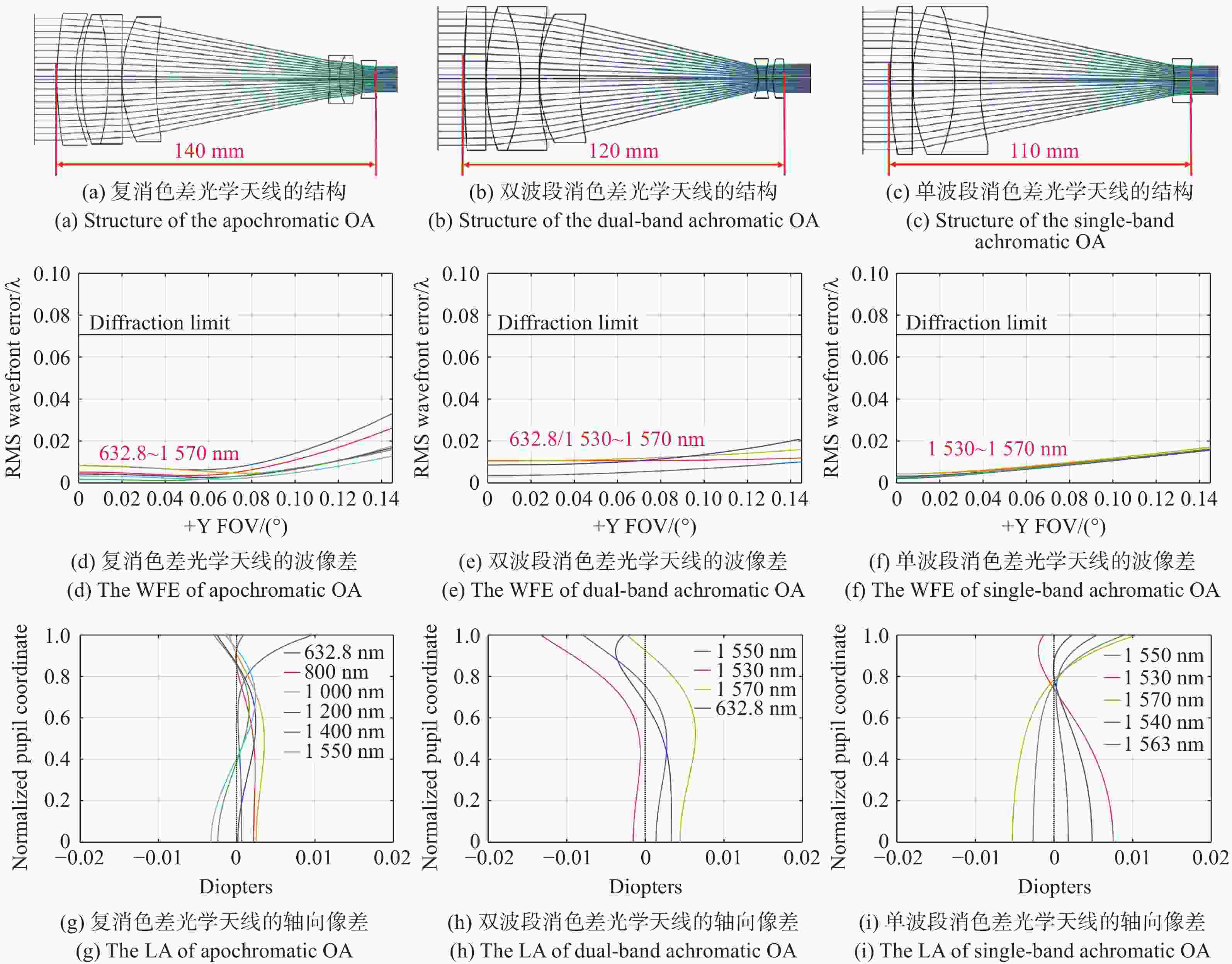
Item Index Communication distance ≥ 1000 kmWavelength 1540 nm(t)/1563 nm(r)1563 nm(t)/1540 nm(r)Optical antenna diameter 50 mm OA magnification 5 Field of view (FOV) ≥±2.5 mard Transmit beam divergence (65±3) μrad(1/e2) Receiving coupling efficiency ≥50% Temperature (20±5) °C 表 2 三种类型光学天线的性能比较
Table 2. Performance comparison of three types of OAs
Item Apochromatic OA Dual-band achromatic OA Single-band achromatic OA Number of lenses 7 6 4 Length/mm 140 120 101 Weight/g 451 436 353 Optical transmittance 90.27% 91.37% 94.16% Full field wavefront error
(λ = 1550 nm)< 0.0036 λ@0° FOV
<0.0115 λ@edge FOV< 0.0034 λ@0° FOV
<0.0099 λ@edge FOV< 0.0020 λ@0° FOV
<0.0200 λ@edge FOVWavefront error@0° FOV
(λ = 632.8 nm)< 0.0051 λ< 0.0103 λ~ 40.0000 λ表 3 公差分配
Table 3. Tolerance allocation
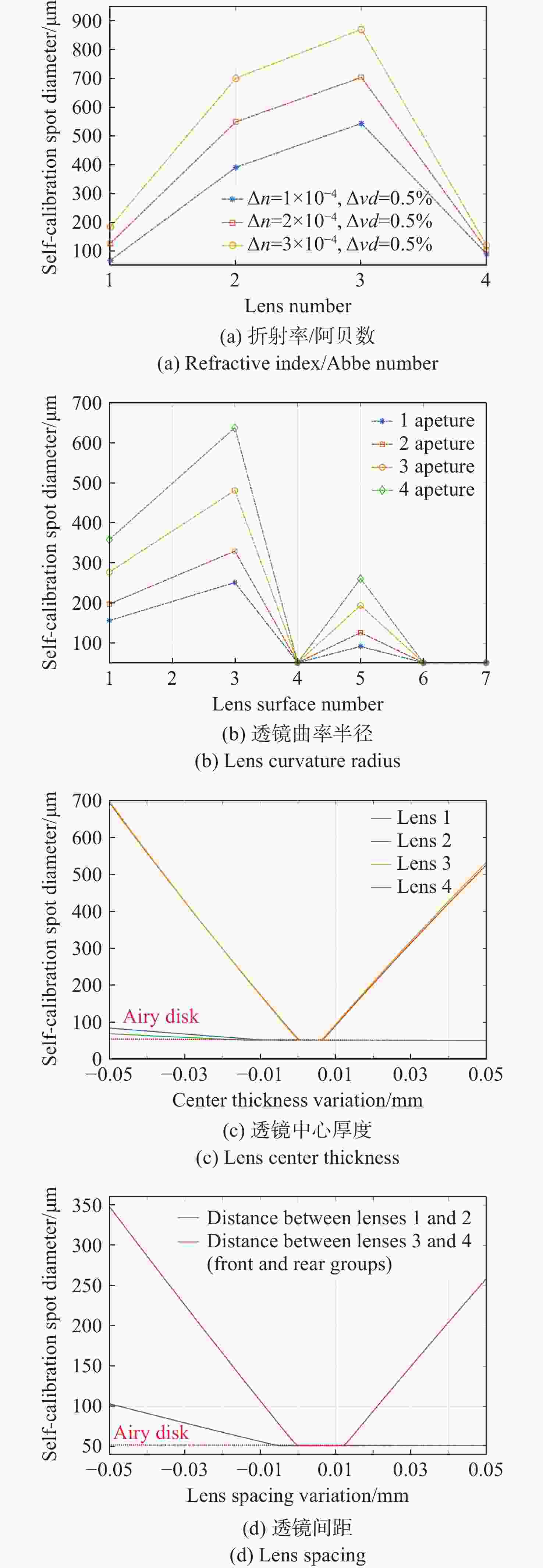
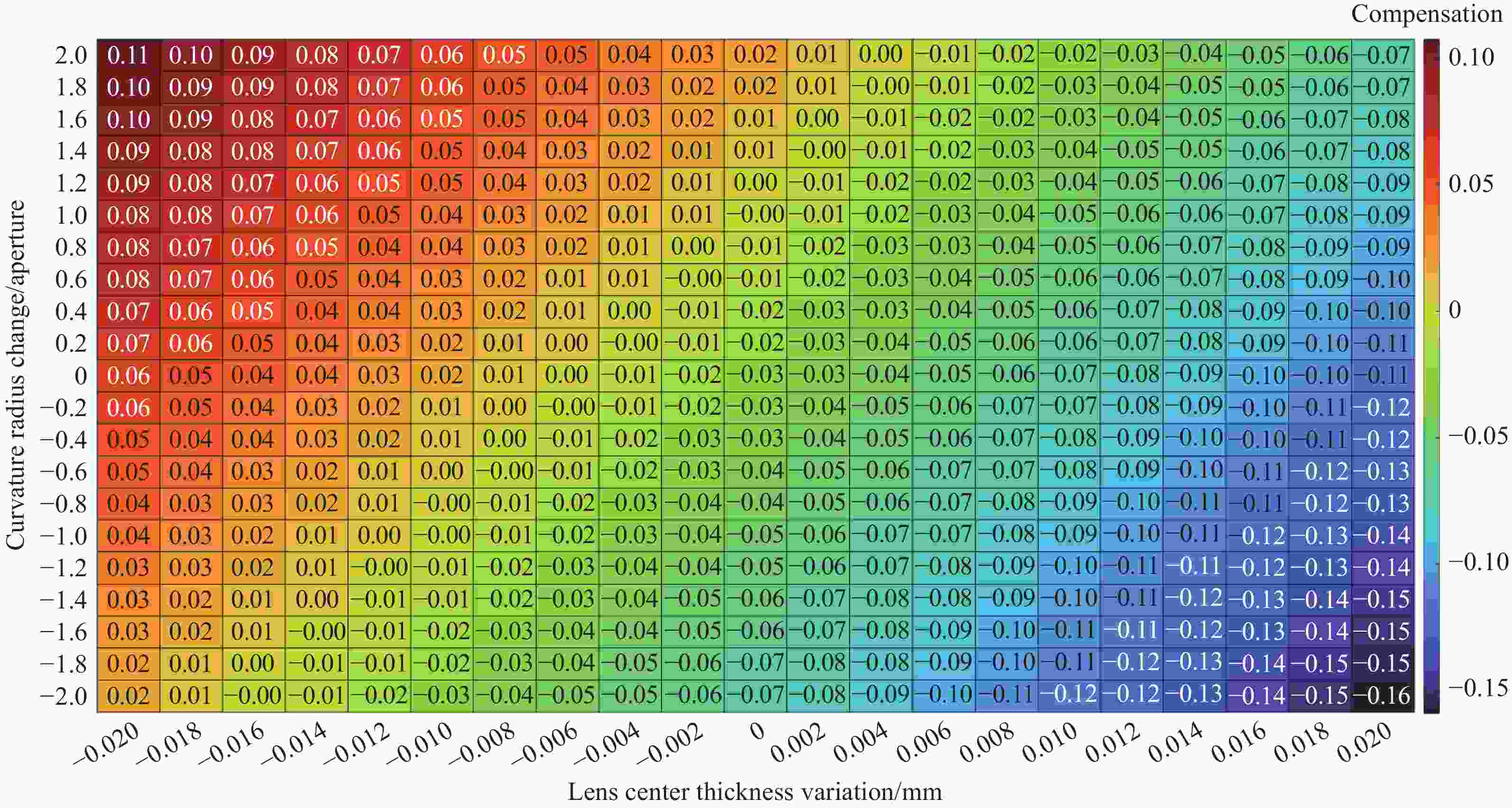
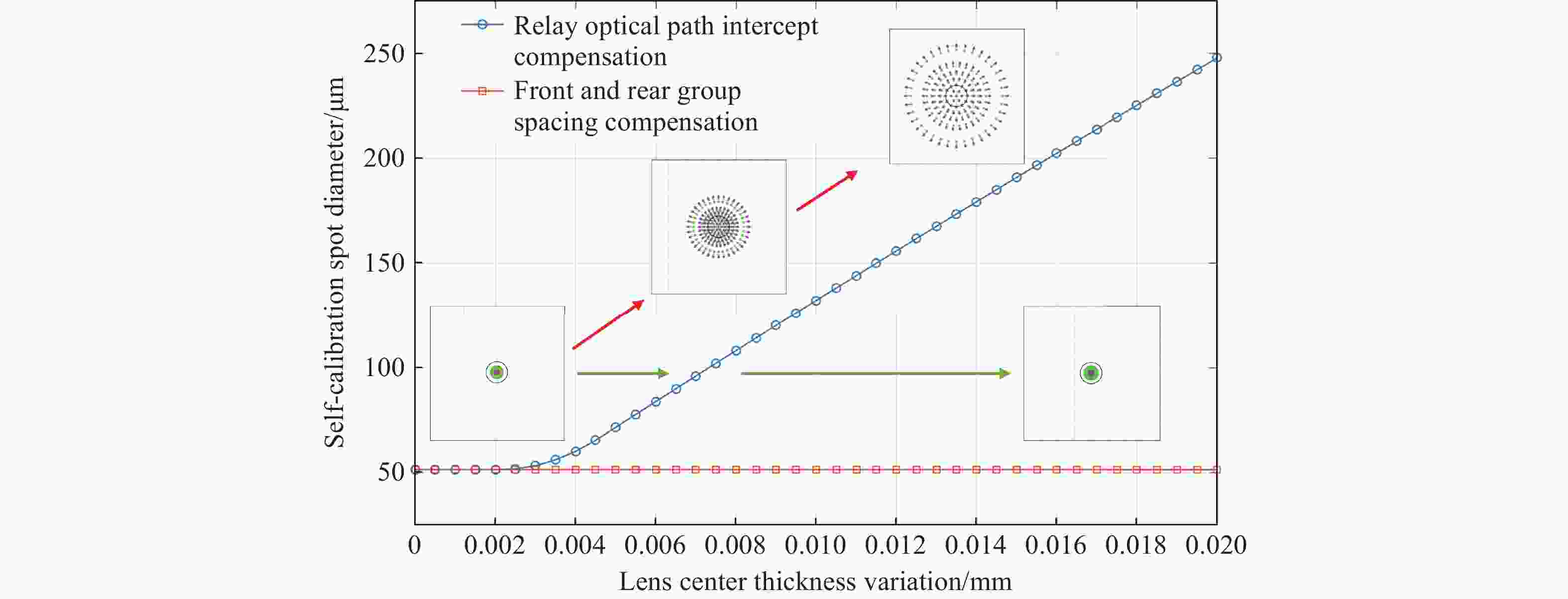
Item Index Radius of curvature 3 fringes Lens center thickness 0.02 mm Surface irregularity 0.3 fringes Surface decenter 0.03 mm Surface tilt 0.03° Element decenter 0.03 mm Element tilt 0.03° Index 0.001 Abbe number 0.5% Test wavelength 1550 nm表 4 公差分析结果
Table 4. Tolerance analysis results
Item RMS Wavefront
error (Rate = 90%)RMS Wavefront
error (Rate = 50%)Apochromatic OA 0.3424 λ0.1987 λDual-band achromatic OA 0.0534 λ0.0223 λSingle-band achromatic OA 0.0300 λ0.0205 λ表 5 中继光路指标参数
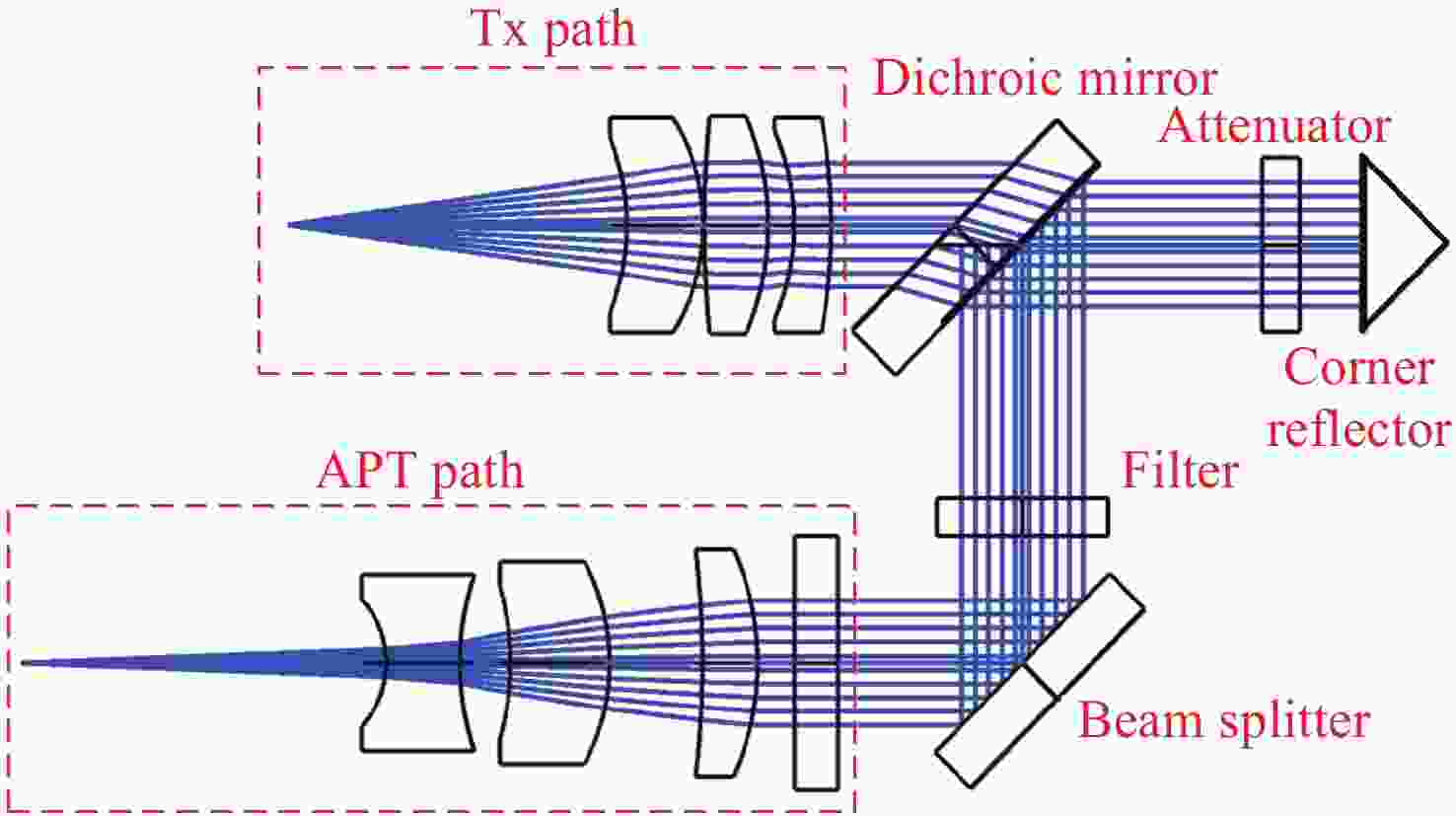
Table 5. The parameters of relay optical paths
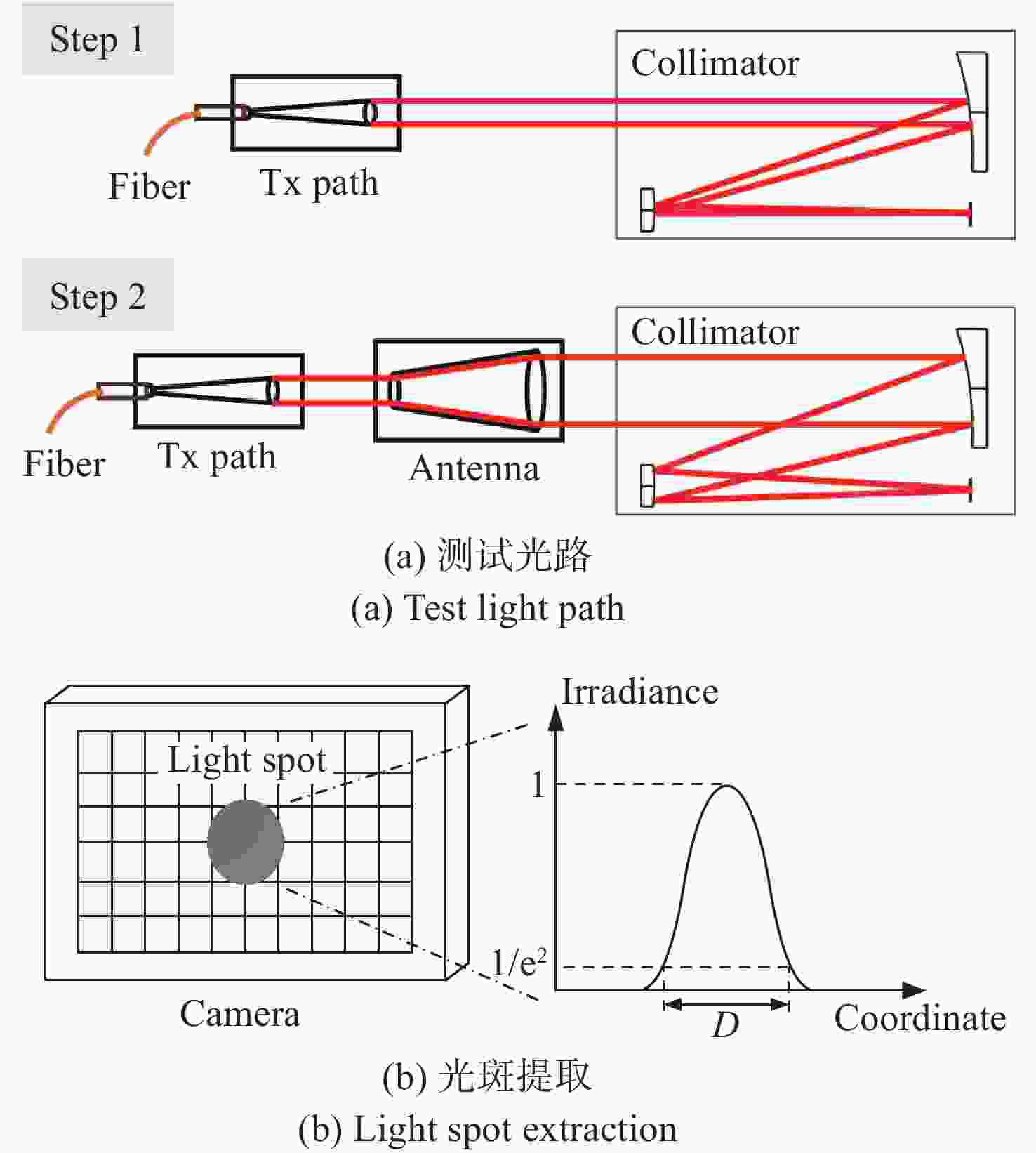
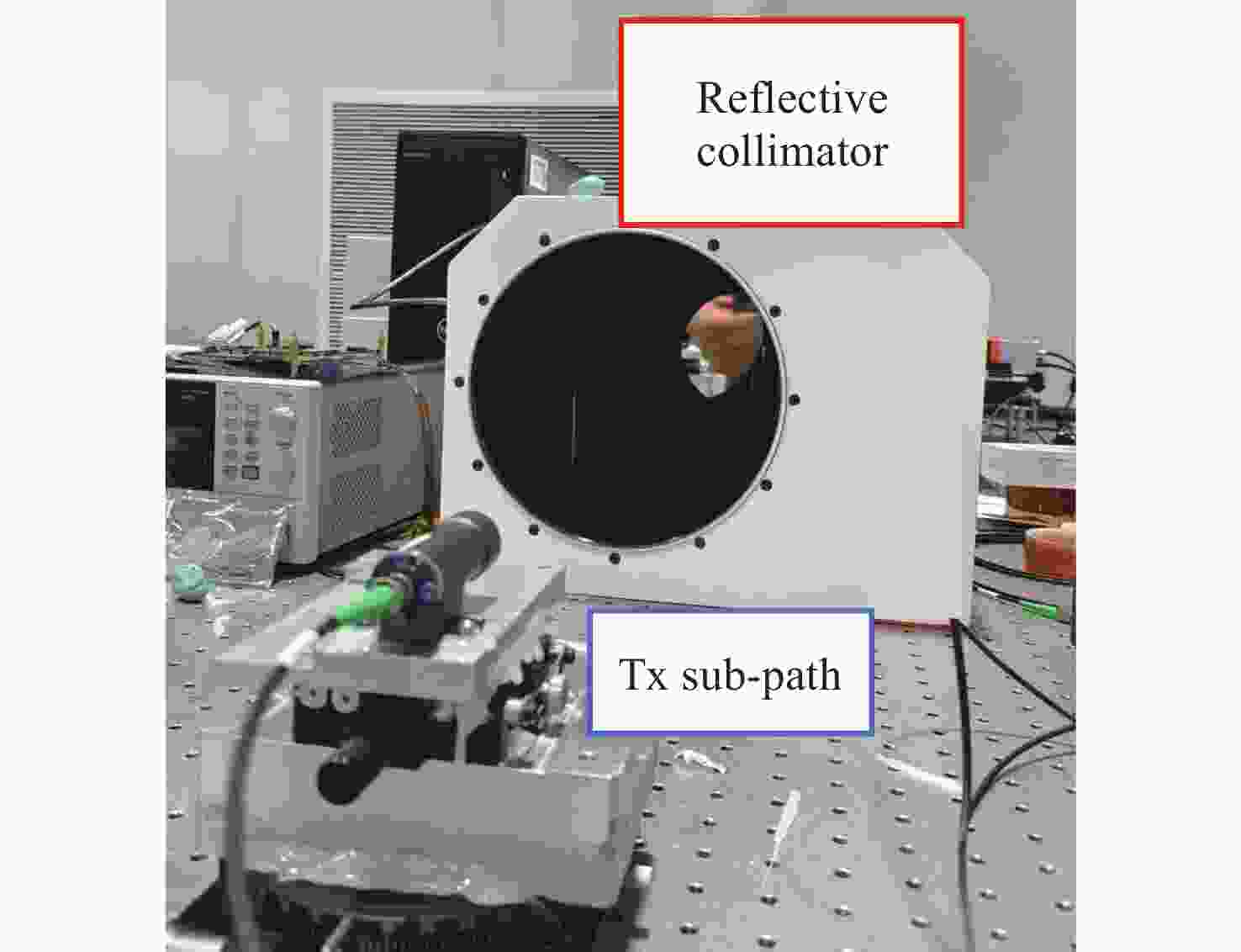
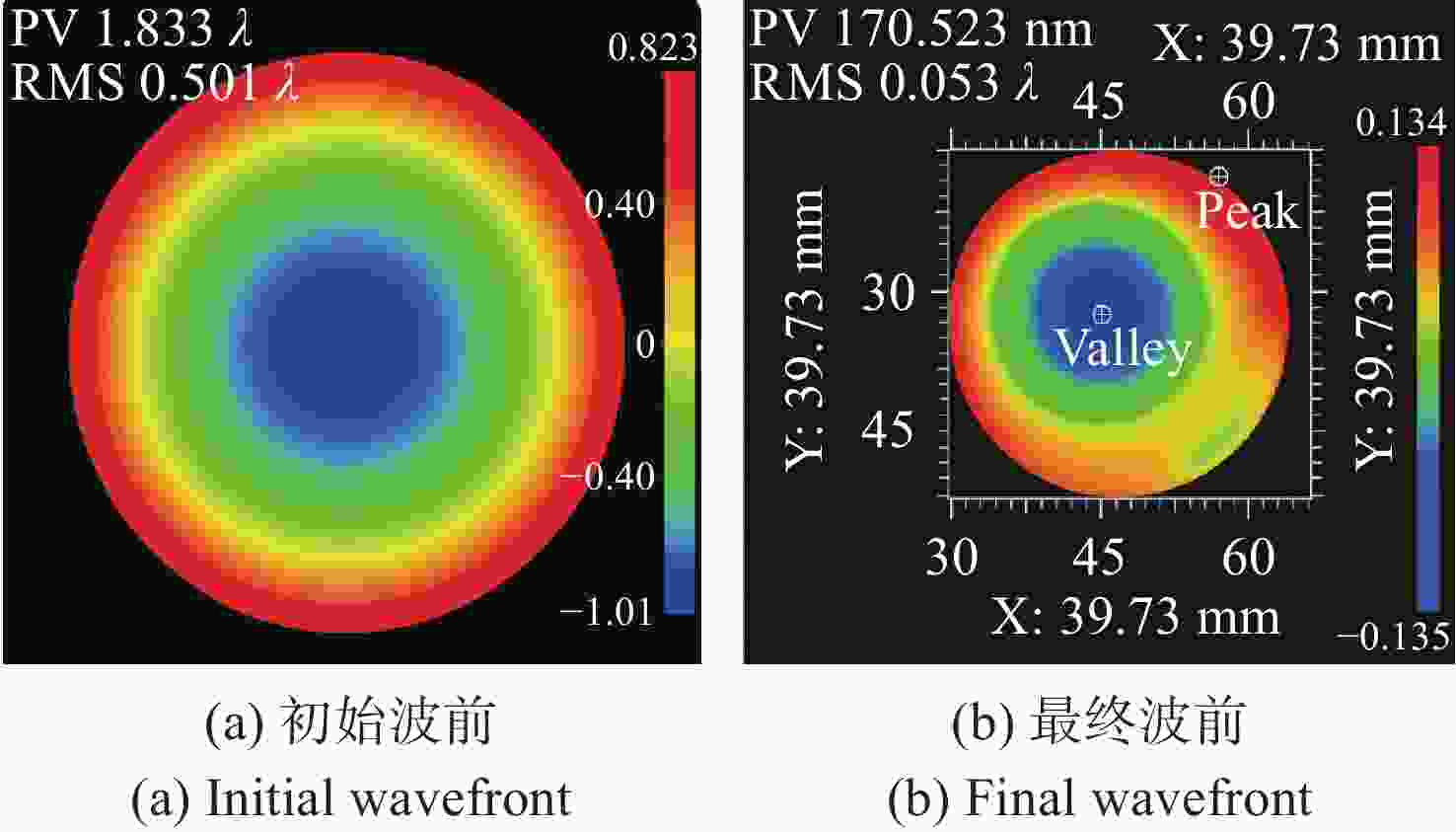
Item Index Tx path focal length 175 mm Fiber NA 0.14 Fiber mode field diameter (10.4±0.5) μm@1550 nm Divergence angle (2θ) 65.02 μrad Tx path RMS WFE ≤0.021 Rx path focal length 235 mm Rx path F# 4.7 Coupling efficiency 81.23% Rx path RMS WFE ≤0.010λ APT path focal length 676 mm APT path RMS WFE ≤0.032λ 表 6 装调结果对比
Table 6. Comparison of alignment results
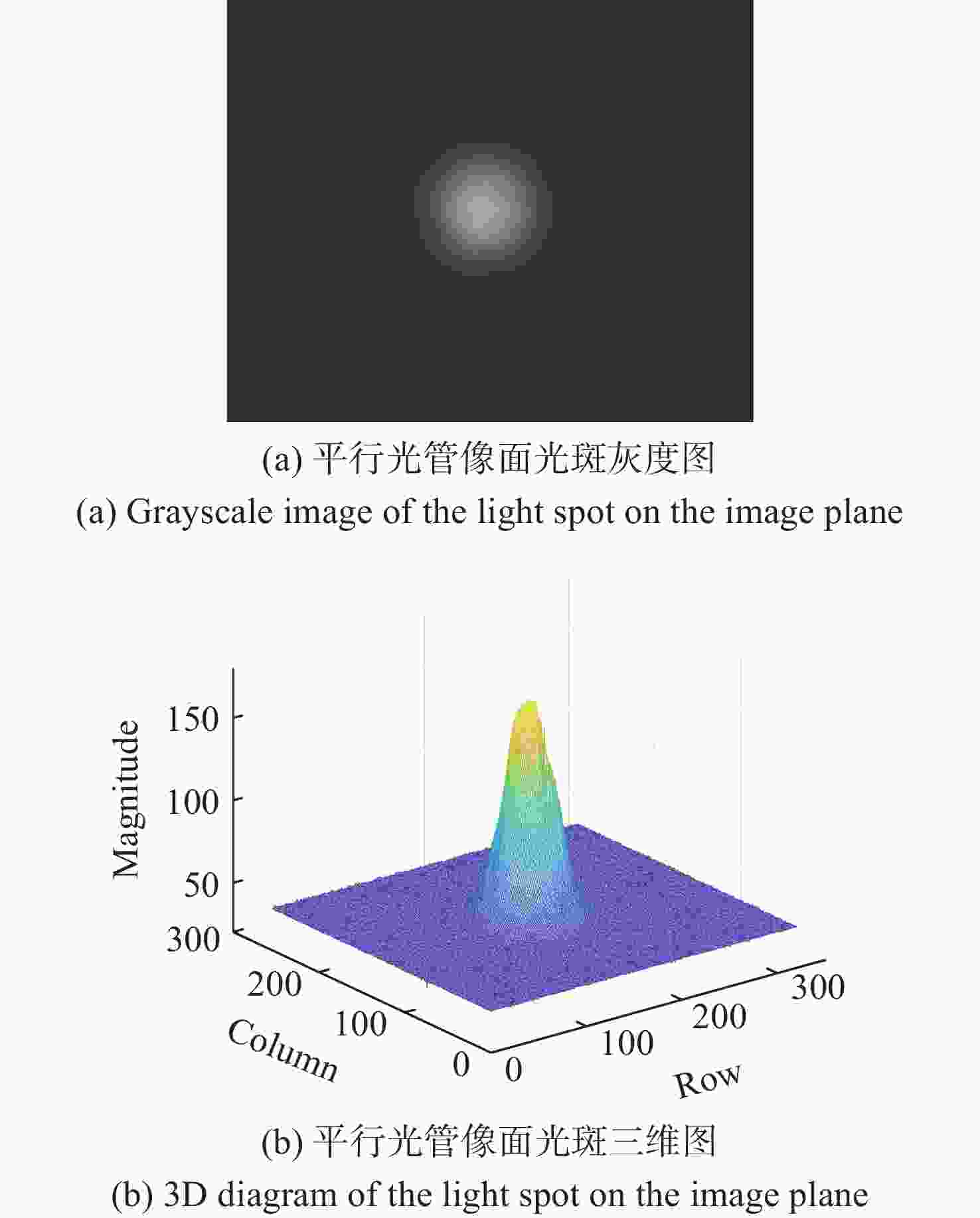
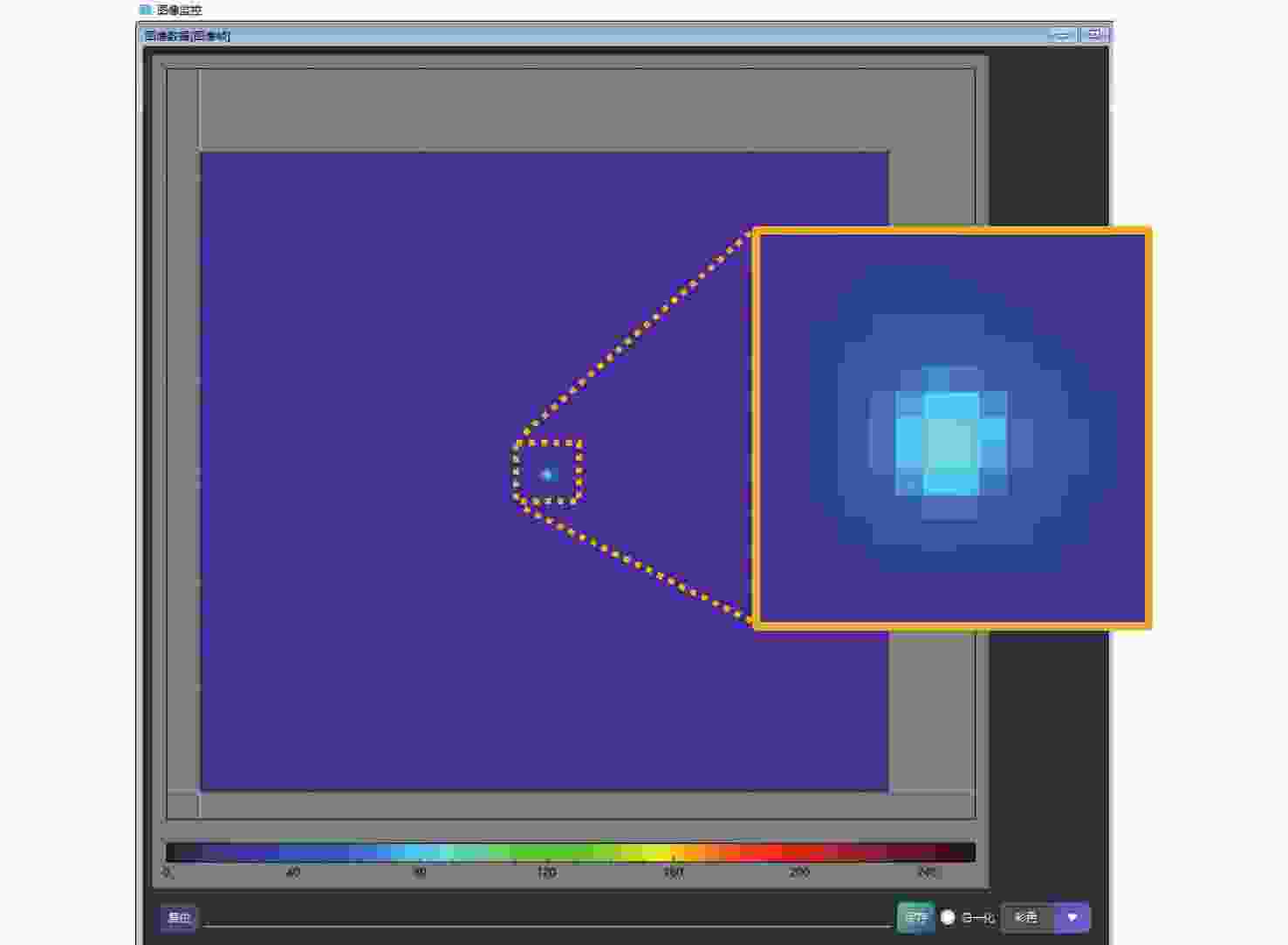
Item Magnification method Interferometer method Tx divergence angle 67.53 μrad 65.41 μrad Rx coupling efficiency 51.42% 53.68% APT spot 12×12 pixels 10×10 pixels Self-calibration spot 12×12 pixels 10×10 pixels Alignment time 3 hours 2 days -
[1] ZHANG J J, LI J. Laser Inter-Satellite Links Technology[M]. Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons, 2023: 14-19. [2] WANG G H, YANG F, SONG J, et al. Free space optical communication for inter-satellite link: architecture, potentials and trends[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2024, 62(3): 110-116. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.002.2300024 [3] TOYOSHIMA M. Recent trends in space laser communications for small satellites and constellations[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2021, 39(3): 693-699. doi: 10.1109/JLT.2020.3009505 [4] 于帅北, 曹艳波, 费强, 等. 轻量化量子跟踪系统复合轴精密控制[J]. 光学 精密工程, 2024, 32(23): 3469-3478. doi: 10.37188/OPE.20243223.3469YU SH B, CAO Y B, FEI Q, et al. Precision control on composite axis of lightweight quantum tracking system[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2024, 32(23): 3469-3478. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/OPE.20243223.3469 [5] 李滨宇, 冯悦姝, 滕云杰, 等. 12.7 km水平信道空间激光通信闪烁抑制[J]. 光学 精密工程, 2022, 30(5): 545-554. doi: 10.37188/OPE.20223005.0545LI B Y, FENG Y SH, TENG Y J, et al. Scintillation suppression along 12.7 km space laser communication horizontal path[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2022, 30(5): 545-554. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/OPE.20223005.0545 [6] 刘智, 蒋青芳, 刘树通, 等. 空间激光通信组网技术与应用研究进展[J]. 中国光学(中英文), 2025, 18(3): 429-451. doi: 10.37188/CO.2023-0140LIU ZH, JIANG Q F, LIU SH T, et al. Research progress of space laser communication networking technology[J]. Chinese Optics, 2025, 18(3): 429-451. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/CO.2023-0140 [7] CHAUDHRY A U, YANIKOMEROGLU H. Laser intersatellite links in a Starlink constellation: a classification and analysis[J]. IEEE Vehicular Technology Magazine, 2021, 16(2): 48-56. doi: 10.1109/MVT.2021.3063706 [8] HAUSCHILDT H, ELIA C, MOELLER H L, et al. HydRON: high thRoughput optical network[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2020, 11272: 112720B. [9] MUNEMASA Y, SAITO Y, CARRASCO-CASADO A, et al. Feasibility study of a scalable laser communication terminal in NICT for next-generation space networks[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2019, 11180: 111805W. [10] 李锐, 林宝军, 刘迎春, 等. 激光星间链路发展综述: 现状、趋势、展望[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2023, 52(3): 20220393. doi: 10.3788/IRLA20220393LI R, LIN B J, LIU Y CH, et al. Review on laser intersatellite link: current status, trends, and prospects[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2023, 52(3): 20220393. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/IRLA20220393 [11] 云行. 世界首颗量子科学实验卫星“墨子号”[J]. 卫星应用, 2016(9): 86.YUN X. The world’s first quantum science experimental satellite “Mozi”[J]. Satellite Application, 2016(9): 86. (in Chinese). [12] 赵云, 王汉, 董滨滨, 等. 星地激光通信研究现状与前沿技术[J]. 空间科学学报, 2025, 45(2): 612-628.ZHAO Y, WANG H, DONG B B, et al. Research progress and fronts in satellite-to-ground laser communication[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2025, 45(2): 612-628. (in Chinese). [13] 王行行, 霍占伟, 牟洪元, 等. 吉林一号卫星激光通信数据传输试验及应用[J]. 国际太空, 2024(2): 42-49.WANG H H, HUO ZH W, MOU H Y, et al. Laser communication data transmission experiment and application of Jilin-1 satellite[J]. Space International, 2024(2): 42-49. (in Chinese). [14] 侯霞, 刘哲绮, 常亦迪, 等. 卫星激光通信技术发展现状与趋势分析[J]. 中国激光, 2024, 51(11): 1101013.HOU X, LIU ZH Q, CHANG Y D, et al. Analysis on development status and trend of space laser communication technology[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2024, 51(11): 1101013. (in Chinese). [15] YOUNUS O I, RIAZ A, BINNS R, et al. Overview of space-based laser communication missions and payloads: insights from the autonomous laser inter-satellite gigabit network (ALIGN)[J]. Aerospace, 2024, 11(11): 907. doi: 10.3390/aerospace11110907 [16] 孙远琪. 基于自由曲面的大视场光学天线系统研究[D]. 沈阳: 东北大学, 2022: 35-58.SUN Y Q. Research on large field of view optical antenna system based on free-form surface[D]. Shenyang: Northeastern University, 2022: 35-38. (in Chinese). [17] 徐新瑞, 孟祥翔, 吴世臣, 等. 大容差中波红外激光通信终端光学天线研制[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2021, 50(6): 20200331. doi: 10.3788/IRLA20200331XU X R, MENG X X, WU SH CH, et al. Development of optical antenna for middle infrared laser communication terminal[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2021, 50(6): 20200331. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/IRLA20200331 [18] 田棋杰, 张建华, 张缓缓, 等. 长出瞳距离轴四反光学天线的设计研究[J]. 光学学报, 2020, 40(18): 1822001. doi: 10.3788/AOS202040.1822001TIAN Q J, ZHANG J H, ZHANG H H, et al. Design of off-axis four-mirror optical antenna with long exit pupil distance[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2020, 40(18): 1822001. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/AOS202040.1822001 [19] 高伟饶, 董科研, 江伦. 单波长激光通信终端的隔离度[J]. 中国光学(中英文), 2023, 16(5): 1137-1148. doi: 10.37188/CO.2022-0253GAO W R, DONG K Y, JIANG L. Isolation of single wavelength laser communication terminals[J]. Chinese Optics, 2023, 16(5): 1137-1148. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/CO.2022-0253 [20] 李洪利, 刘欣悦, 杜博军, 等. 面向自由空间光通信波前校正的改进模拟退火算法[J]. 中国光学(中英文), 2025, 18(4): 784-793. doi: 10.37188/CO.2025-0028LI H L, LIU X Y, DU B J, et al. Improved simulated annealing algorithm for wavefront correction in free-space optical communication[J]. Chinese Optics, 2025, 18(4): 784-793. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/CO.2025-0028 [21] 刘维, 徐珺楠, 金玳冉, 等. 基于CNN-SPGD算法的相干光通信像差校正方法研究[J]. 光学 精密工程, 2022, 30(6): 743-754. doi: 10.37188/OPE.20223006.0743LIU W, XU J N, JIN D R, et al. Research on aberration correction method of coherent optical communication based on CNN-SPGD algorithm[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2022, 30(6): 743-754. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/OPE.20223006.0743 -





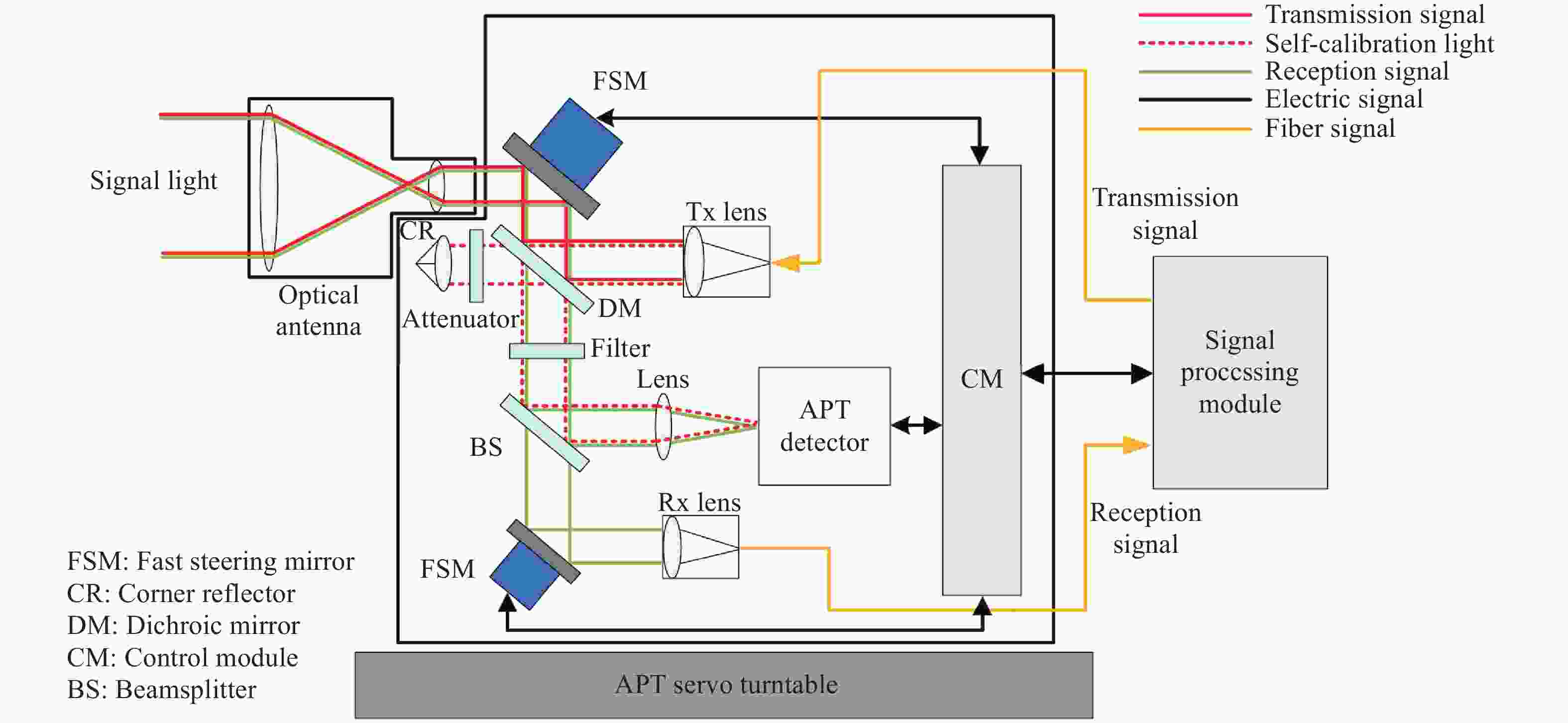
 下载:
下载: