-
摘要:
传统微波天线的空间分辨率受限于衍射极限,难以突破波长量级的约束,限制了其在高分辨率微波传感与检测中的应用。为克服这一问题,本文设计了一种全介质超衍射极限聚焦天线。首先,基于广义斯涅尔定律,利用非对称散射超构光栅阵列对天线表面功能化,通过调控电磁波前实现亚波长尺度高效光束聚焦。然后,对超构光栅的几何结构设计进行优化,实现高调控效率。最后,分析超构天线所生成焦斑的电场强度分布以及尺寸。仿真结果表明:超构天线调控效率达到98.50%,衍射效率为72.56%,且焦斑最小尺寸小于0.73
λ ,焦深约为15.11λ 。本文设计的超构天线兼具长焦深与高效率特性,其亚波长聚焦特性显著提升了空间分辨率,为微波成像及无损检测等领域的高精度传感检测提供了新的解决方案,具有潜在的应用价值。Abstract:Limited by the diffraction limit, the spatial resolution of traditional microwave antennas is difficult to break through the constraint of the wavelength scale, which hinders their application in high-resolution microwave sensing and detection. In this paper, we design an all-dielectric integrated meta-antenna beyond the physical diffraction limit. Firstly, the meta-antenna is functionalized using asymmetric scattering metagrating array based on the generalized Snell's law. High-efficiency focusing beam in the sub-wavelength scale is obtained by manipulating the electromagnetic wavefront. Then, by optimizing the geometric structure of the metagrating to achieve high manipulation efficiency. Finally, the electric field intensity distribution of the generated focal spot is analyzed. The simulation results demonstrate that the manipulation and diffraction efficiencies of the metalens reach 98.50% and 72.56%. The metalens shows a focal spot with the diameter of 0.73λ and depth of focus (DOF) of 15.11λ. The designed meta-antennas possess the characteristics of long focal depth and high efficiency. Its sub-wavelength focusing property significantly enhances the spatial resolution, which provides a new method for high-precision sensing and detection in the fields such as microwave imaging and non-destructive testing, possessing potential application value.
-
Key words:
- metasurface /
- antenna /
- diffraction limit /
- long depth of focus
-
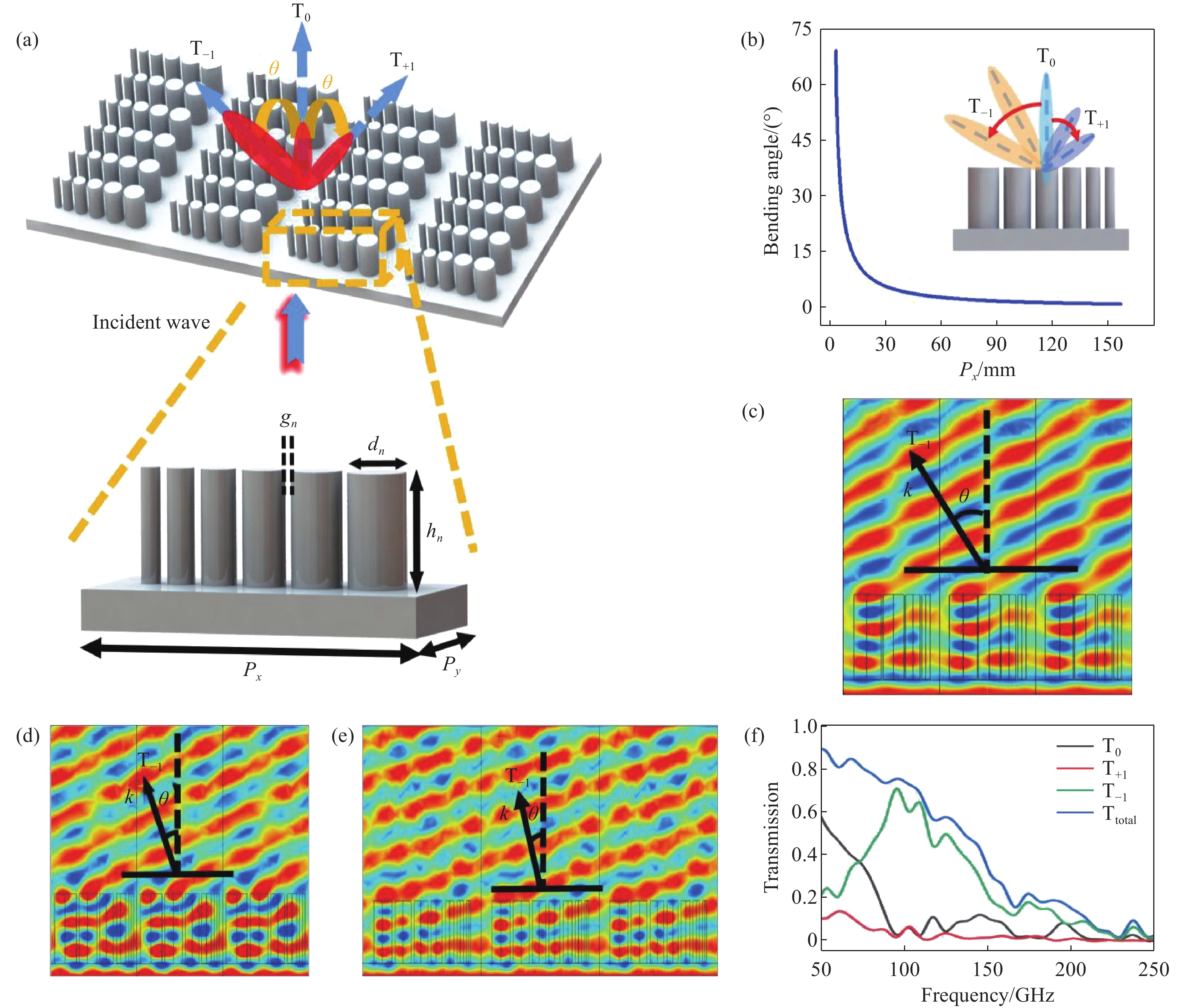
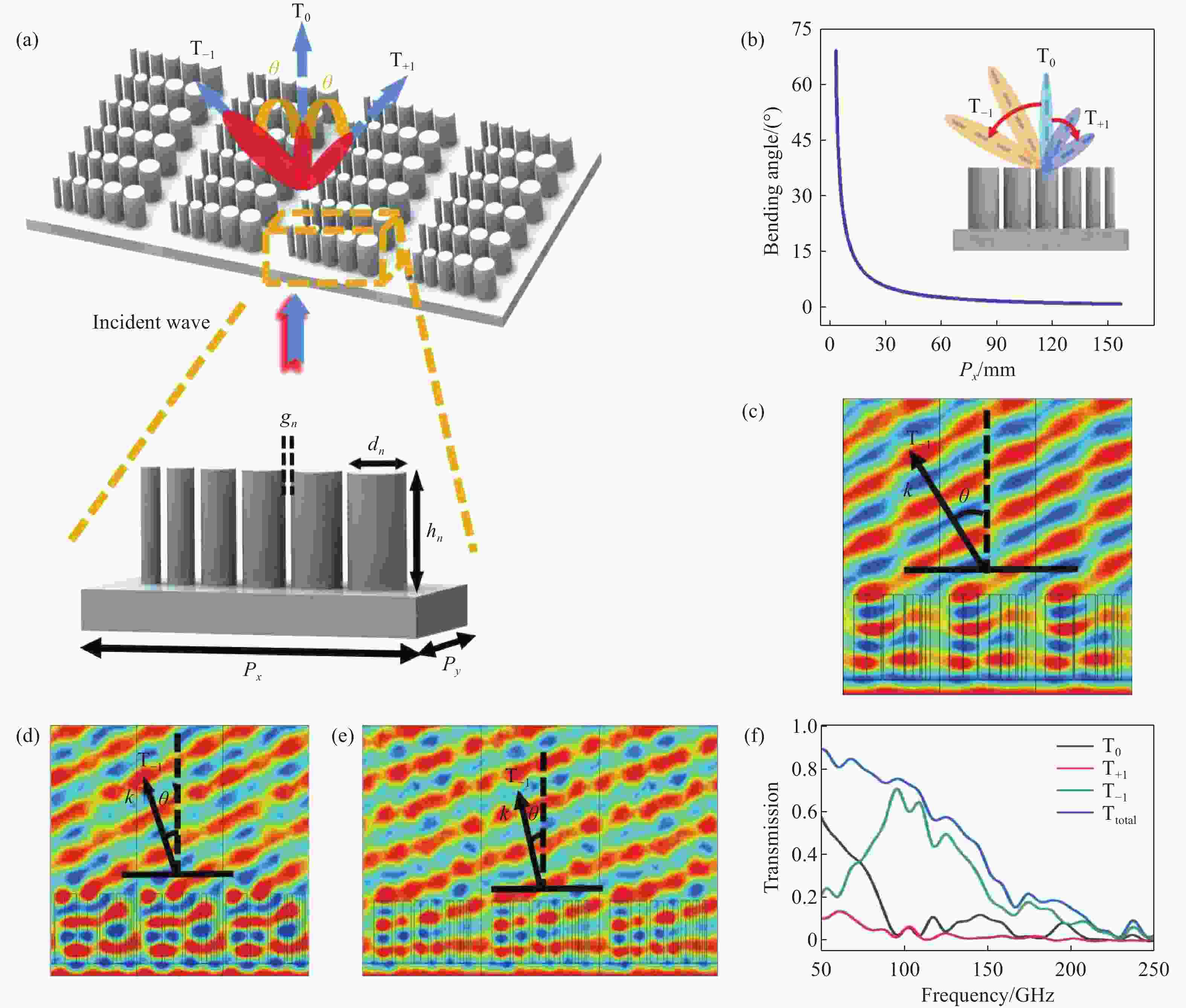
图 1 超构光栅的原理和特性。(a) 基于非对称单元结构的超构光栅阵列结构示意图;(b) 不同衍射周期T−1阶的偏折角度;(c-e) 微波入射超构光栅阵列时,偏折角度分别为32.01°、22.05°和12.13°的模拟电场分布;(f) 不同衍射阶的透射光谱(T0、T−1、T+1、Ttotal分别表示衍射阶0、−1、+1和total的透射率)
Figure 1. Principle and characteristics of the metagrating. (a) Schematic diagram of the metagrating array structure based on asymmetric unit cells; (b) the deflection angles of T−1 order with different diffraction periods; (c−e) simulated electric field distributions for microwave incidence on a metagrating array at deflection angles of 32.01°, 22.05°, and 12.13°; (f) transmission spectra for different diffraction orders. T0, T−1, T+1, and Ttotal represent the transmittance for diffraction orders 0, −1, +1 and total, respectively
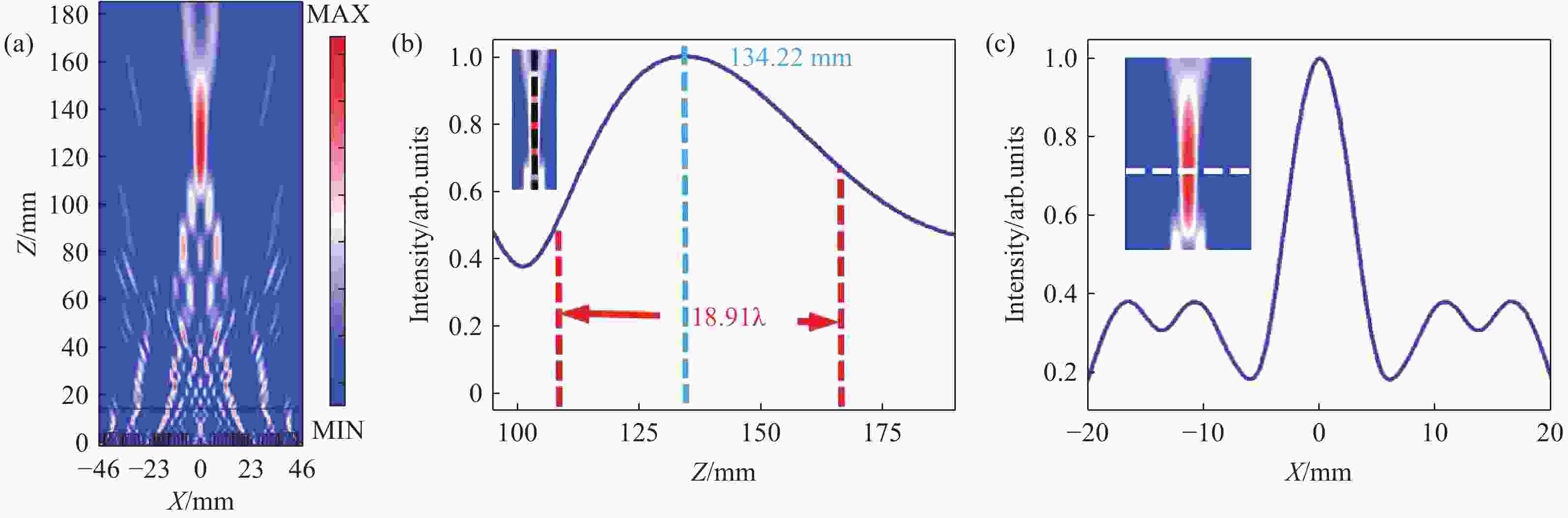
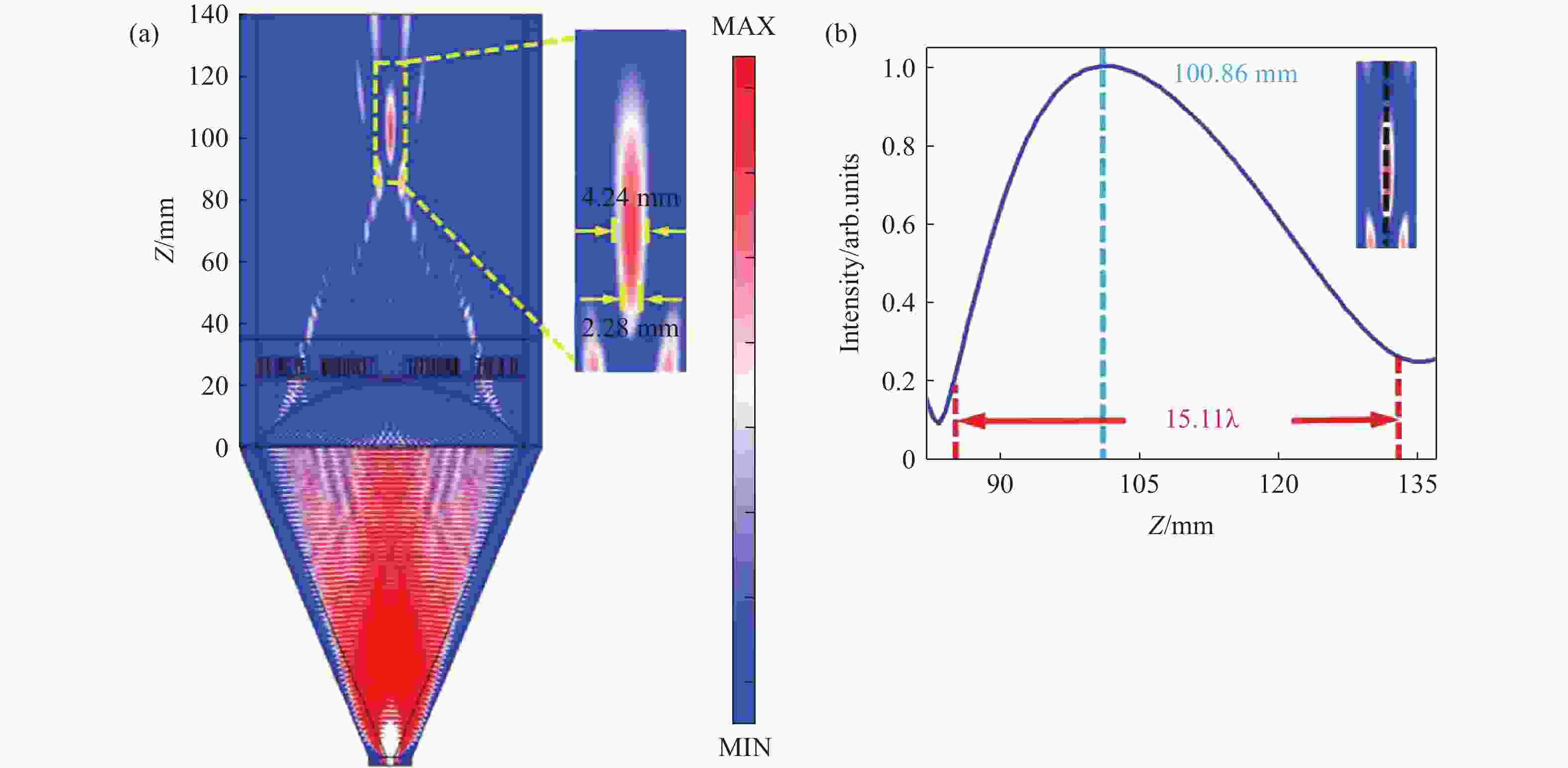
图 4 (a) 超构透镜的电场强度分布;(b) 沿z轴方向的归一化强度分布图;(c) 在焦平面上沿x轴方向的归一化强度分布图
Figure 4. (a) Electric field distributions of the metalens; (b) normalized intensity distribution along the z-axis direction, the inset marks the measurement position; (c) normalized intensity distribution in the focal plane along the x-axis direction, the inset marks the measurement position in focal plane
表 1 本文设计的全介质超构天线与最近报道的超构透镜性能的比较
Table 1. Comparison of the performance between the all-dielectric metasurface antennas in this paper and recently reported metalens
-
[1] LI S M, CUI ZH Z, YE X W, et al. Chip-based microwave-photonic radar for high-resolution imaging[J]. Laser & Photonics Reviews, 2020, 14(10): 1900239. [2] HAN-OH S, DING K, SONG D, et al. Feasibility study of fiducial marker localization using microwave radar[J]. Medical Physics, 2021, 48(11): 7271-7282. doi: 10.1002/mp.15197 [3] MOHINDRU P. Development of liquid level measurement technology: a review[J]. Flow Measurement and Instrumentation, 2023, 89: 102295. doi: 10.1016/j.flowmeasinst.2022.102295 [4] XIAO G L, CHEN J Y, YANG H Y, et al. Doublet metalens for polarization conversion as well as focusing[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2024, 42(6): 2076-2082. doi: 10.1109/JLT.2023.3331543 [5] CHEN M K, WU Y F, FENG L, et al. Principles, functions, and applications of optical meta-lens[J]. Advanced Optical Materials, 2021, 9(4): 2001414. doi: 10.1002/adom.202001414 [6] ZHANG P, FANG B, ZHAO T Q, et al. Terahertz wave tunable metalens based on phase change material coded metasurface[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2023, 41(23): 7162-7168. doi: 10.1109/JLT.2023.3262509 [7] LIU Y Q, SUN J H, CHE Y X, et al. High numerical aperture microwave metalens[J]. Optics Letters, 2020, 45(22): 6262-6265. doi: 10.1364/OL.412040 [8] WEN SH, XUE X Y, WANG SH, et al. Metasurface array for single-shot spectroscopic ellipsometry[J]. Light: Science & Applications, 2024, 13(1): 88. [9] 吴广坤, 丁华峰, 陈建军. 金属微纳结构操控单光子发射体辐射[J]. 量子电子学报, 2024, 41(2): 185-193.WU G K, DING H F, CHEN J J. Tailoring single-photon emission with metallic nano-structures[J]. Chinese Journal of Quantum Electronics, 2024, 41(2): 185-193. (in Chinese). [10] ZHENG CH L, NI P N, XIE Y Y, et al. On-chip light control of semiconductor optoelectronic devices using integrated metasurfaces[J]. Opto-Electronic Advances, 2025, 8(1): 240159. doi: 10.29026/oea.2025.240159 [11] 周俊焯, 郝佳, 余晓畅, 等. 面向偏振成像的超构表面研究进展[J]. 中国光学(中英文), 2023, 16(5): 973-995. doi: 10.37188/CO.2022-0234ZHOU J ZH, HAO J, YU X CH, et al. Recent advances in metasurfaces for polarization imaging[J]. Chinese Optics, 2023, 16(5): 973-995. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/CO.2022-0234 [12] HE X Y, ZHONG X, LIN F T, et al. Investigation of graphene assisted tunable terahertz metamaterials absorber[J]. Optical Materials Express, 2016, 6(2): 331-342. doi: 10.1364/OME.6.000331 [13] FANG B, LI B Y, PENG Y D, et al. Polarization-independent multiband metamaterials absorber by fundamental cavity mode of multilayer microstructure[J]. Microwave and Optical Technology Letters, 2019, 61(10): 2385-2391. doi: 10.1002/mop.31890 [14] 倪赛健, 王晗, 王勇, 等. 金属-介质-金属三棱柱结构超表面中的磁电耦合[J]. 量子电子学报, 2019, 36(5): 532-538.NI S J, WANG H, WANG Y, et al. Magnetoelectric coupling in metal-dielectric-metal triangular prism structure metasurface[J]. Chinese Journal of Quantum Electronics, 2019, 36(5): 532-538. (in Chinese). [15] 刘逸天, 陈琦凯, 唐志远, 等. 超表面透镜的像差分析和成像技术研究[J]. 中国光学, 2021, 14(4): 831-850. doi: 10.37188/CO.2021-0014LIU Y T, CHEN Q K, TANG ZH Y, et al. Research progress of aberration analysis and imaging technology based on metalens[J]. Chinese Optics, 2021, 14(4): 831-850. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/CO.2021-0014 [16] ZHANG J H, ELKABBASH M, WEI R, et al. Plasmonic metasurfaces with 42.3% transmission efficiency in the visible[J]. Light: Science & Applications, 2019, 8: 53. [17] YANG J, YANG W X, QU K, et al. Active polarization-converting metasurface with electrically controlled magnitude amplification[J]. Optics Express, 2023, 31(18): 28979-28986. doi: 10.1364/OE.499458 [18] HUANG P SH, CHU C H, HUANG S H, et al. Varifocal metalenses: harnessing polarization-dependent superposition for continuous focal length control[J]. Nano Letters, 2023, 23(22): 10432-10440. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.3c03056 [19] LIU Y Q, ZHU Y, YIN H CH, et al. Broadband high-efficiency plasmonic metalens with negative dispersion characteristic[J]. Photonics Research, 2024, 12(4): 813-820. doi: 10.1364/PRJ.513990 [20] 徐平, 李雄超, 肖钰斐, 等. 长红外双波长共聚焦超透镜设计研究[J]. 物理学报, 2023, 72(1): 014208. doi: 10.7498/aps.72.20221752XU P, LI X CH, XIAO Y F, et al. Design and research of long-infrared dual-wavelength confocal metalens[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2023, 72(1): 014208. (in Chinese). doi: 10.7498/aps.72.20221752 [21] 张振宇, 张伟, 刘睿, 等. 利用级联超构表面同时测量径向角位移和纵向线位移[J]. 中国光学(中英文), 2025, 18(5): 1016-1026.ZHANG Z Y, ZHANG W, LIU R, et al. Simultaneous measurement of radial angular displacement and longitudinal linear displacement with cascade metasurfaces[J]. Chinese Optics, 2025, 18(5): 1016-1026. (in Chinese). [22] 黄昊华, 李玮, 刘睿, 等. 可见连续波段大视场消色差单片超构表面透镜[J]. 中国光学(中英文), 2025, 18(6): 1267-1276.HUANG H H, LI W, LIU R, et al. Achromatic monolayer metalens with elongated field of view in a continuous waveband[J]. Chinese Optics, 2025, 18(6): 1267-1276. (in Chinese). [23] CHEN ZH N, LI T, QING X M, et al. Microwave metalens antennas[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2023, 111(8): 978-1010. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2023.3287599 [24] WU G B, DAI J Y, SHUM K M, et al. A universal metasurface antenna to manipulate all fundamental characteristics of electromagnetic waves[J]. Nature Communications, 2023, 14(1): 5155. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-40717-9 [25] LIU X CH, WANG X Y, WANG Y, et al. High-gain multiband metasurface antenna with frequency and polarization reconfigurability for millimeter-wave applications[J]. Optics Express, 2025, 33(6): 14221-14235. doi: 10.1364/OE.558906 [26] YU N F, GENEVET P, KATS M A, et al. Light propagation with phase discontinuities: generalized laws of reflection and refraction[J]. Science, 2011, 334(6054): 333-337. doi: 10.1126/science.1210713 [27] LIU J M, FANG X, HE F, et al. Directional conversion of a THz propagating wave into surface waves in deformable metagratings[J]. Optics Express, 2021, 29(14): 21749-21762. doi: 10.1364/OE.431817 [28] LIU Z H, LI X J, YIN J, et al. Asymmetric all silicon micro-antenna array for high angle beam bending in terahertz band[J]. IEEE Photonics Journal, 2019, 11(2): 5900509. [29] SHI J, GAO H, JIA X, et al. All-dielectric tunable terahertz metagrating for diffraction control[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2022, 14(49): 55174-55182. [30] PANIAGUA-DOMÍNGUEZ R, YU Y F, KHAIDAROV E, et al. A metalens with a near-unity numerical aperture[J]. Nano Letters, 2018, 18(3): 2124-2132. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.8b00368 [31] LEGARIA S, TENIENTE J, KUZNETSOV S, et al. Highly efficient focusing of terahertz waves with an ultrathin superoscillatory metalens: experimental demonstration[J]. Advanced Photonics Research, 2021, 2(9): 2000165. doi: 10.1002/adpr.202000165 [32] YANG M Y, SHEN X, LI Z P, et al. High focusing efficiency metalens with large numerical aperture at terahertz frequency[J]. Optics Letters, 2023, 48(17): 4677-4680. doi: 10.1364/OL.498397 [33] JANG D, RYU H, MAENG I, et al. All-dielectric terahertz metalens using 3D-printing[J]. Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 2023, 171: 107834. doi: 10.1016/j.optlaseng.2023.107834 [34] LI X J, LIU Z H, YAN D X, et al. Experimental demonstration of 3D printed terahertz polarization-insensitive flat devices based on low-index meta-gratings[J]. Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 2020, 53(50): 505301. doi: 10.1088/1361-6463/abb272 -





 下载:
下载: