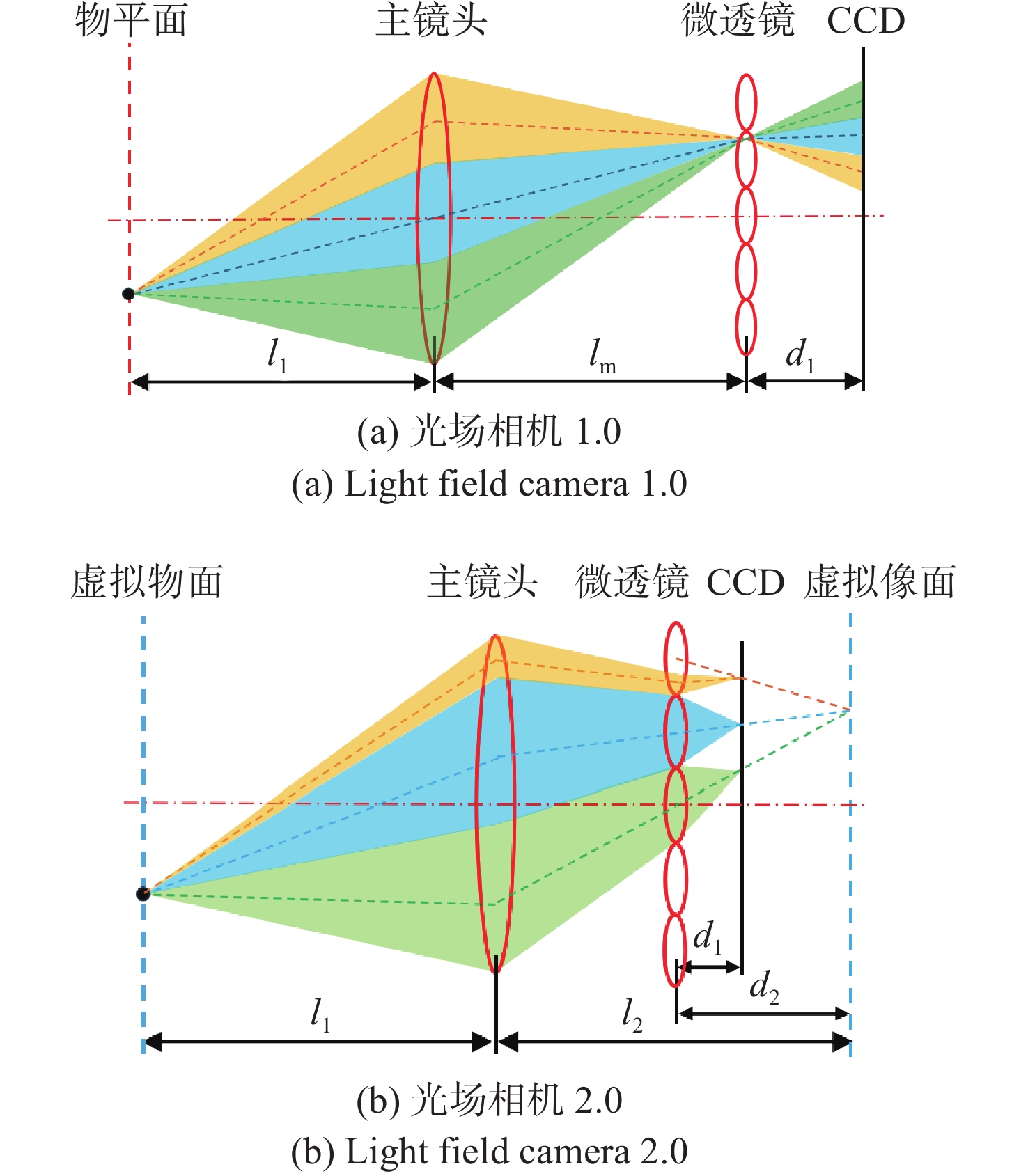
Research on spatial resolution of a single light field camera based on forward ray tracing technique
-
摘要:
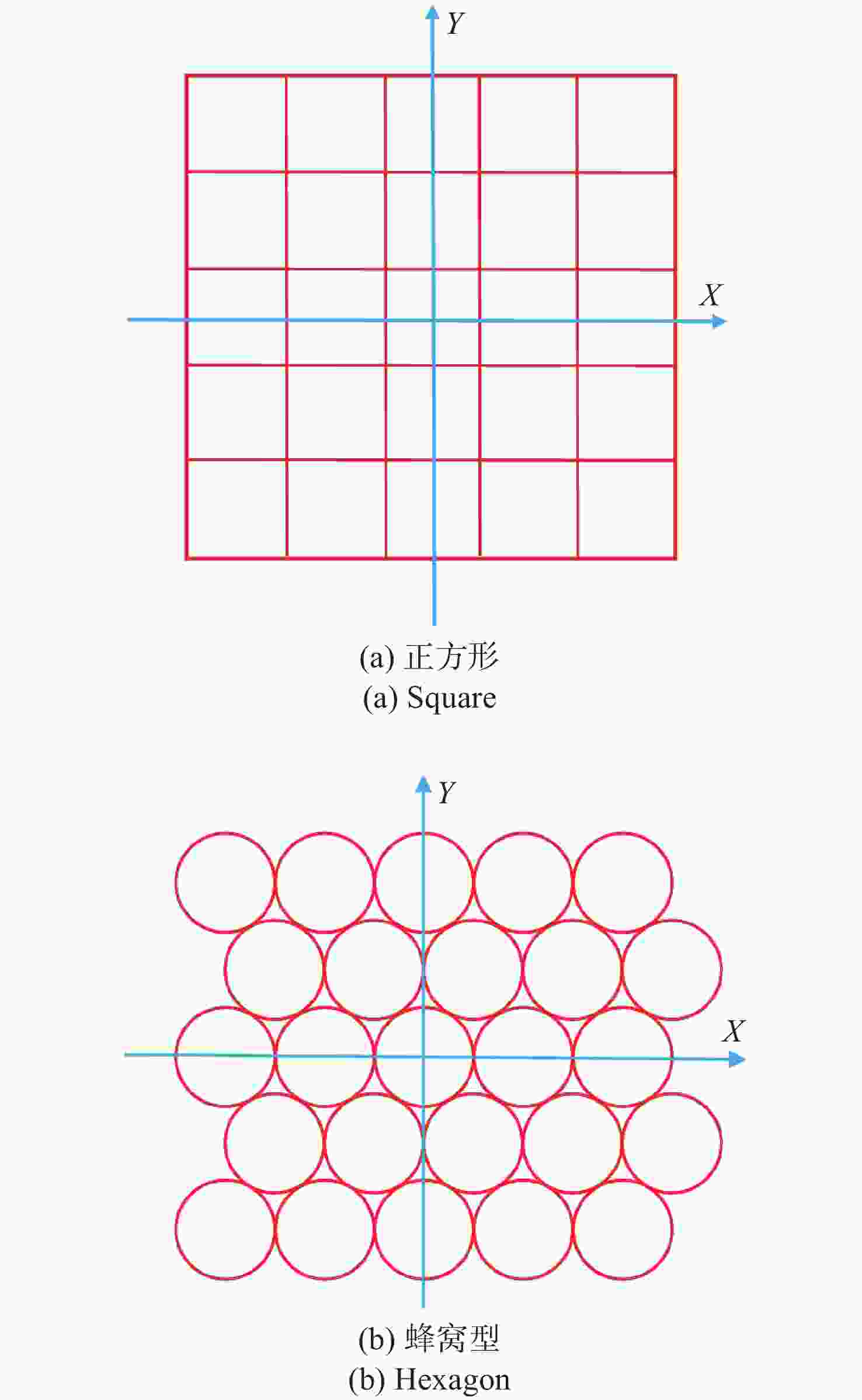
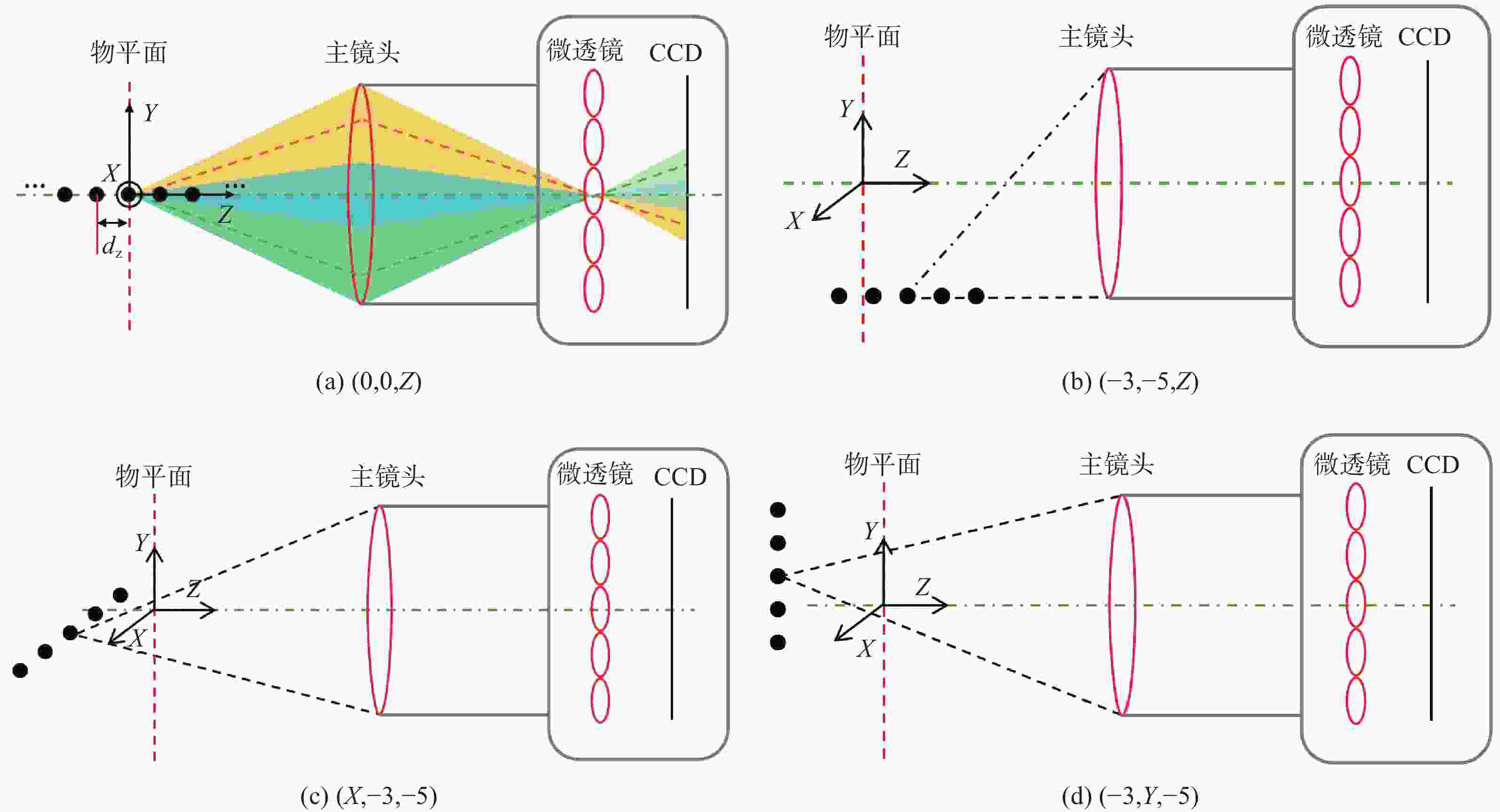
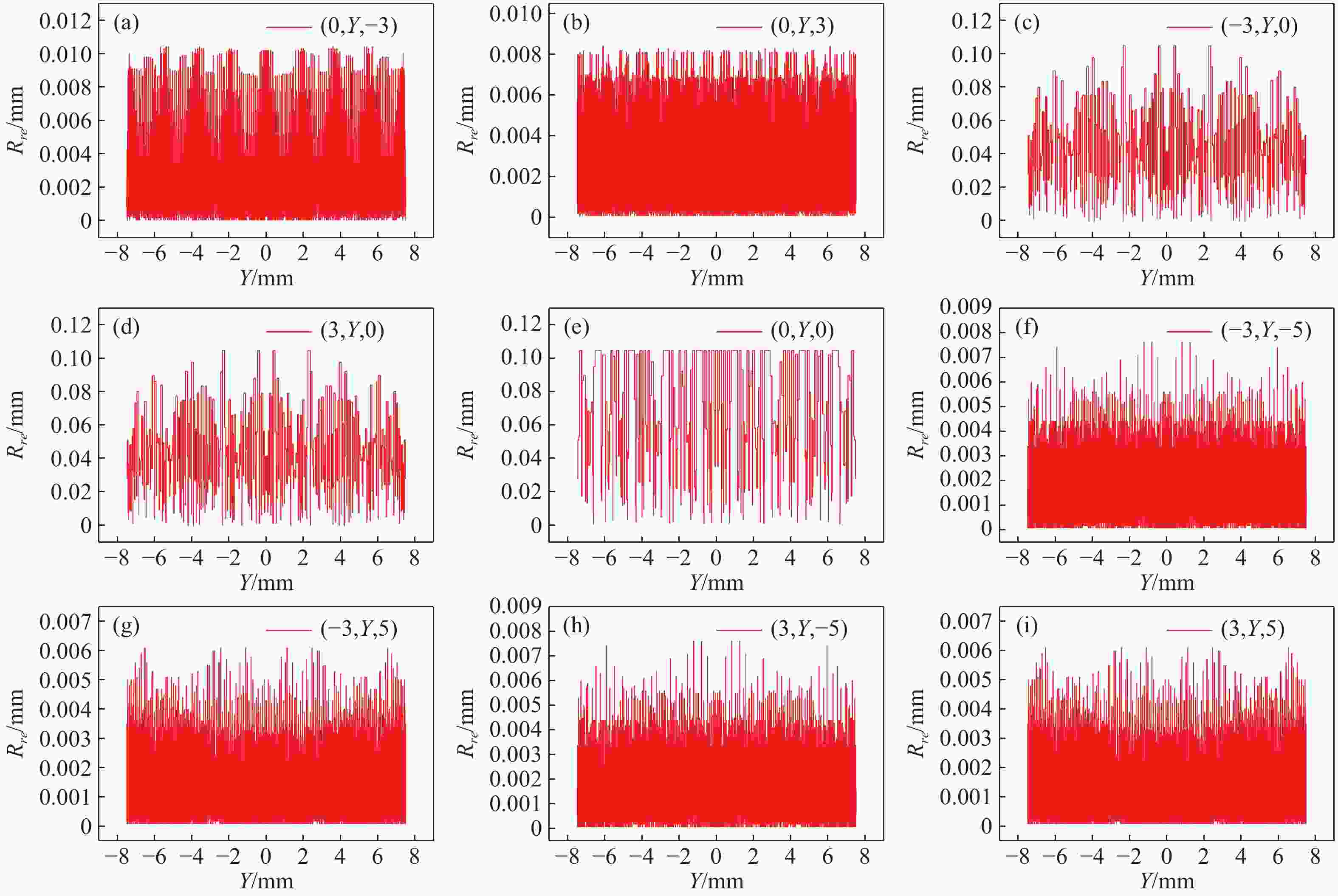
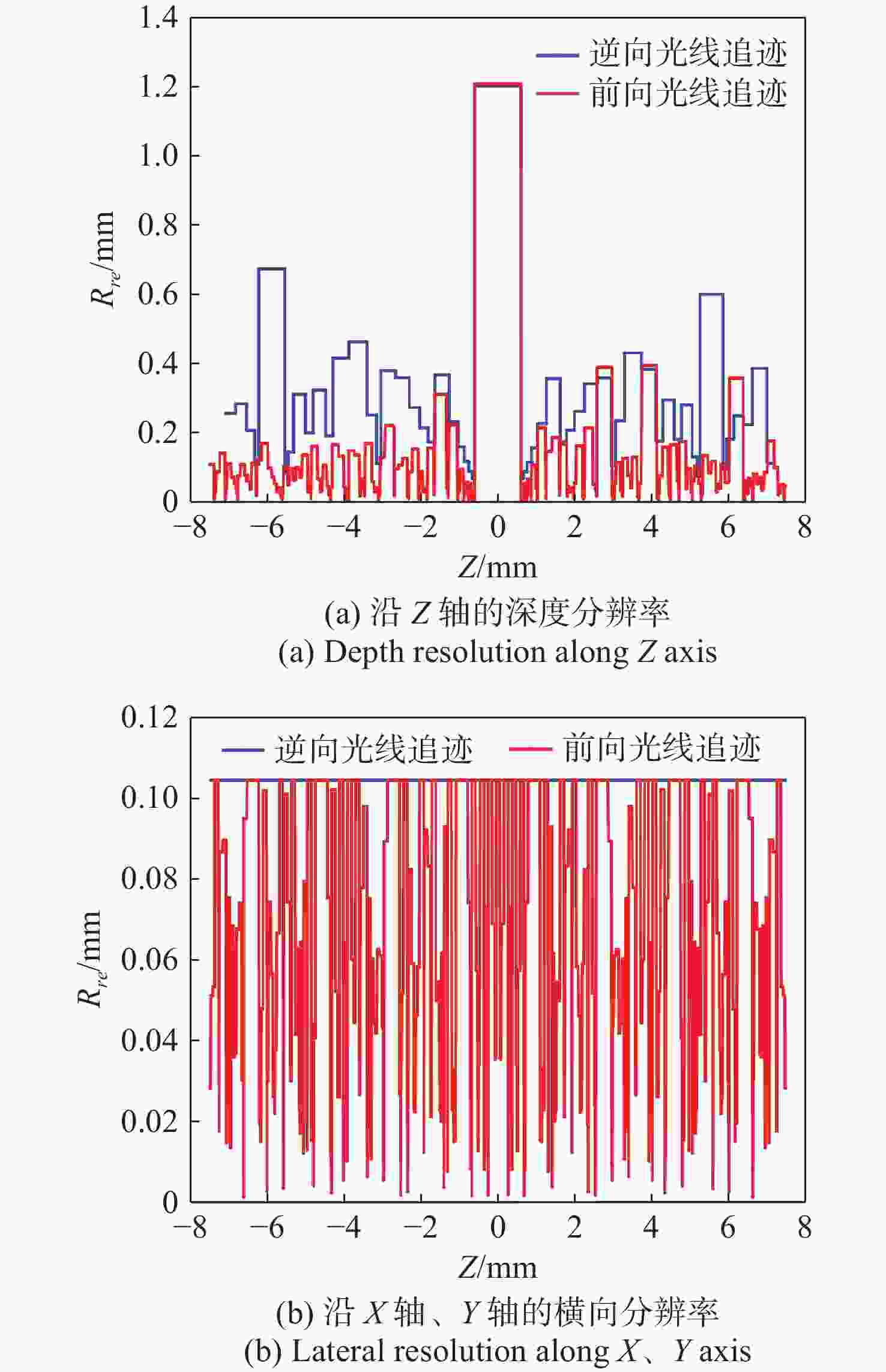
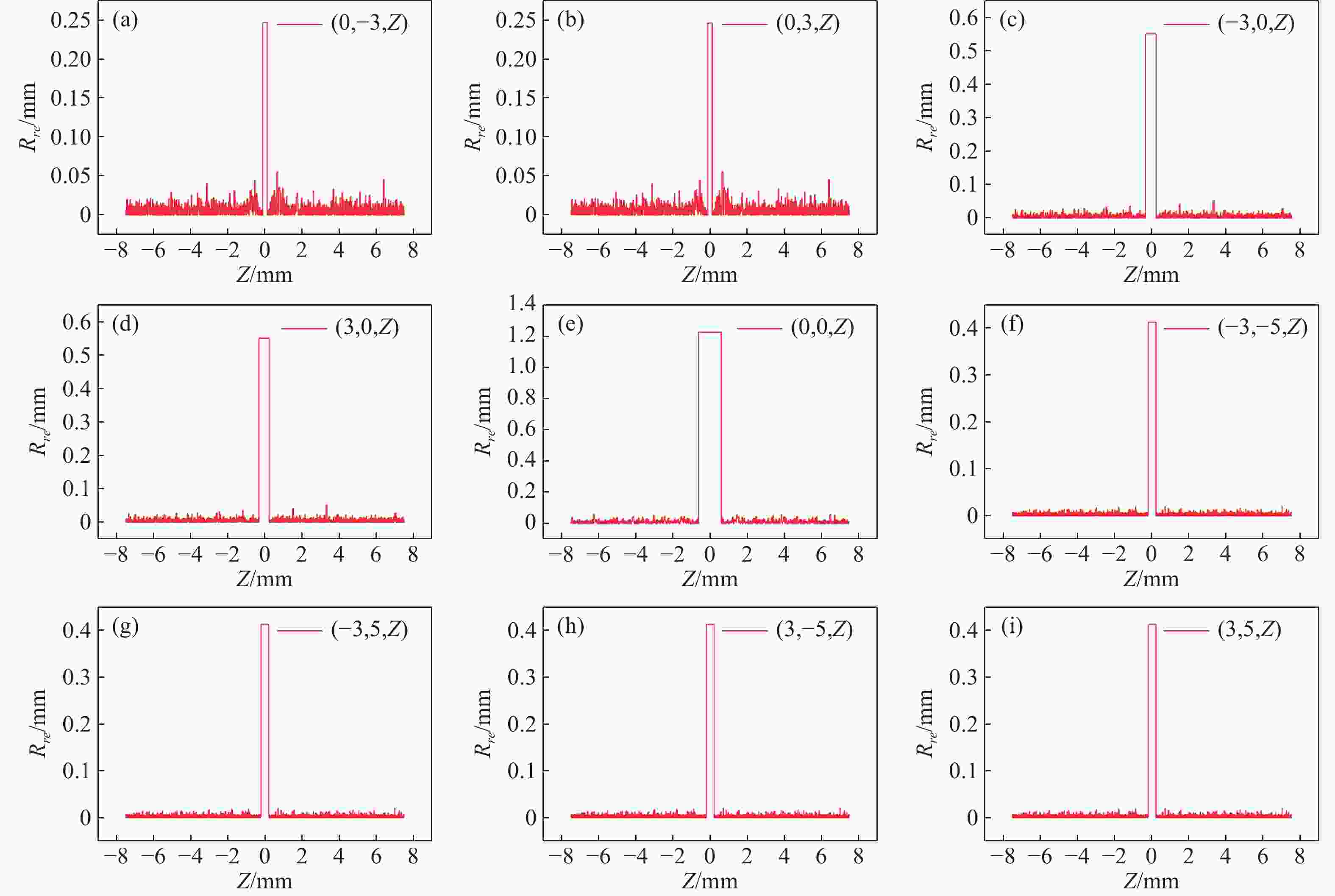
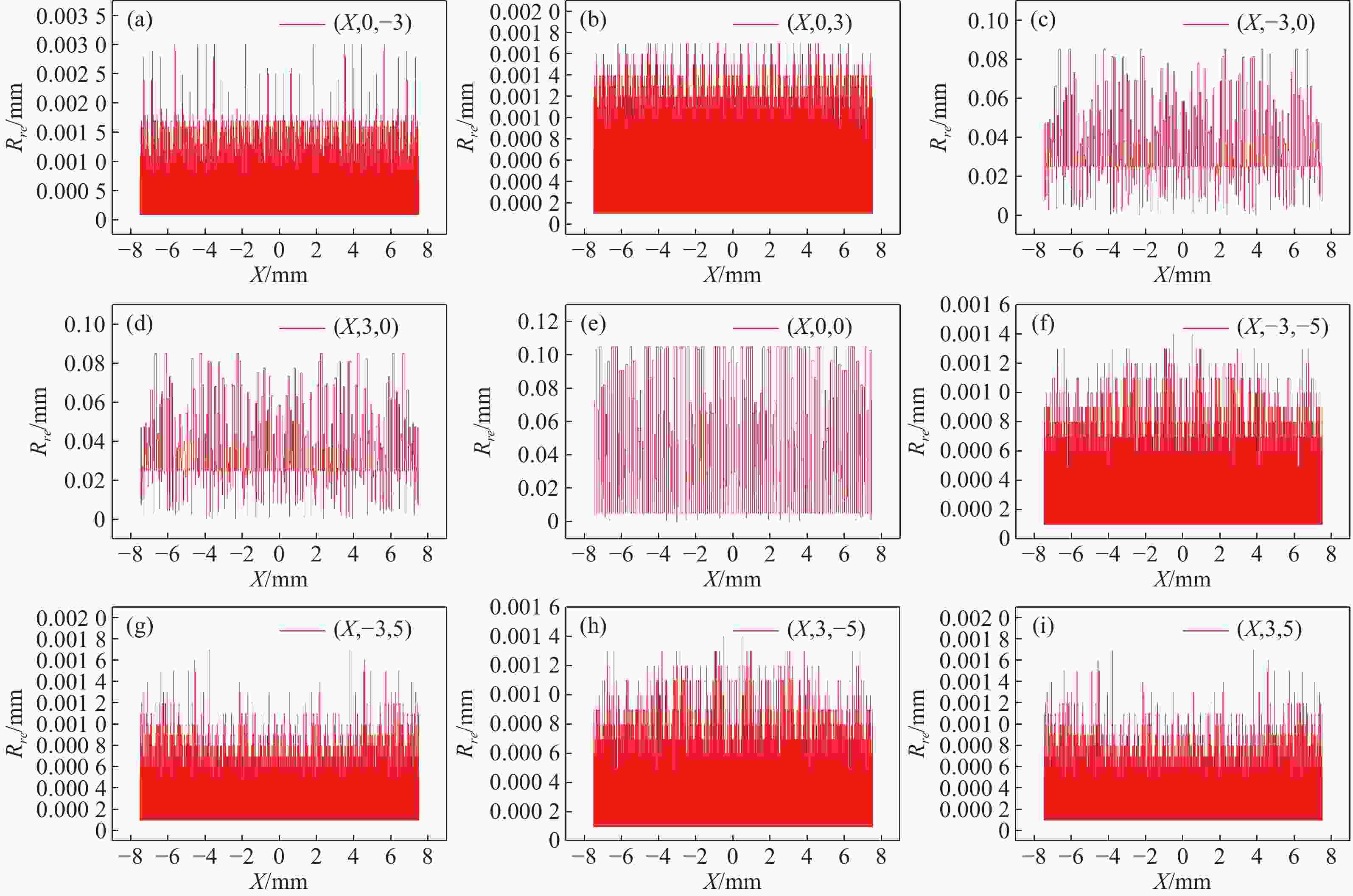
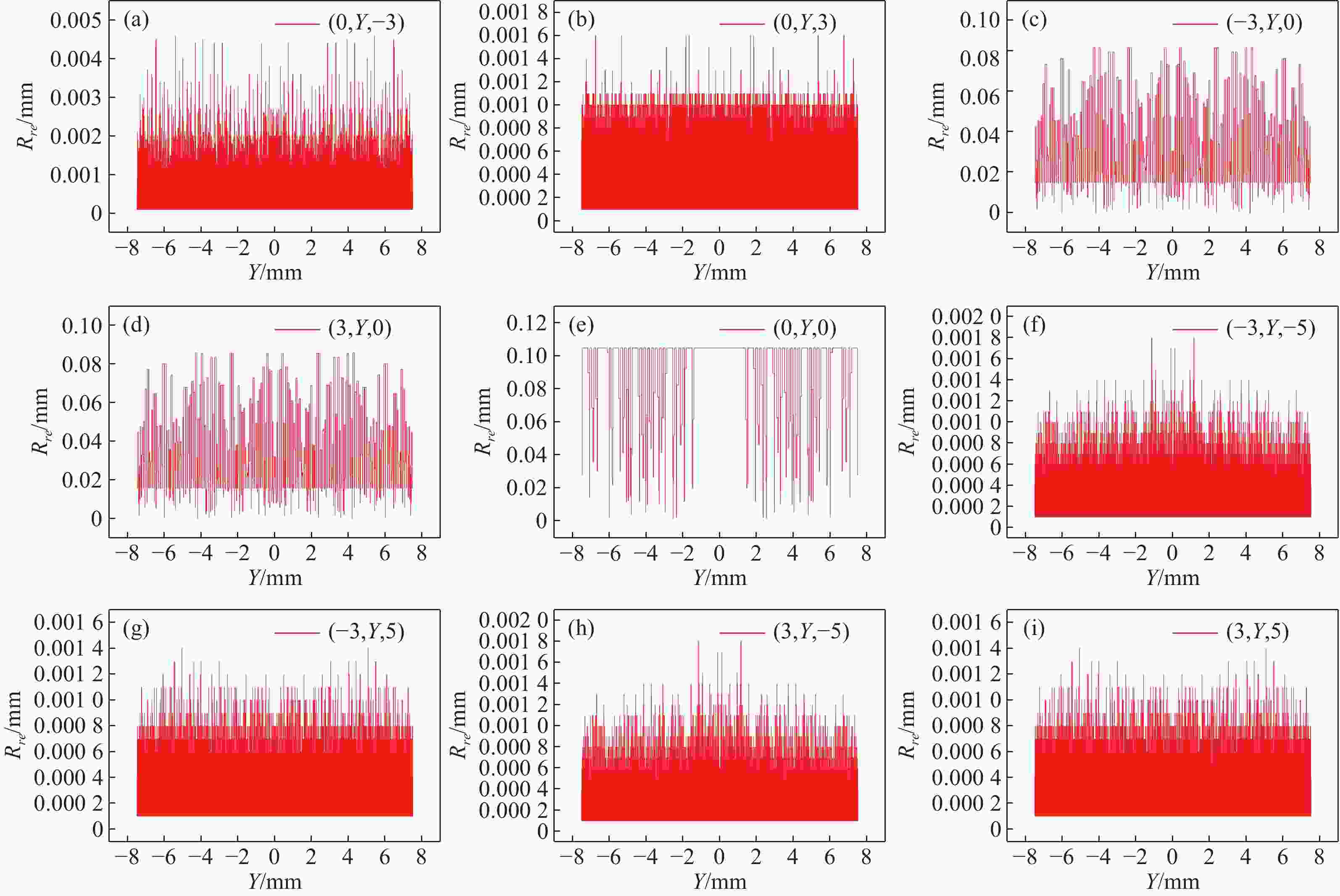
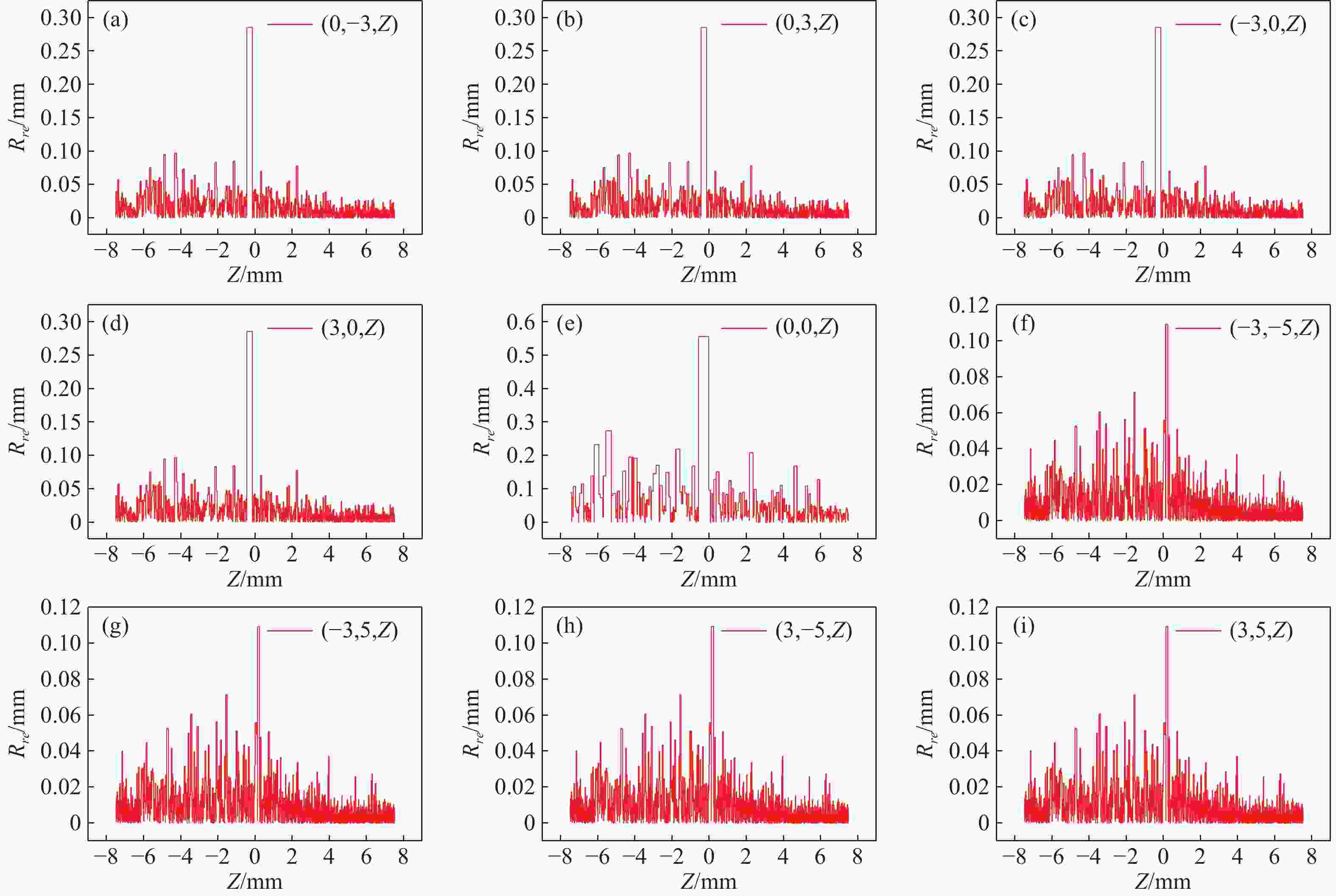
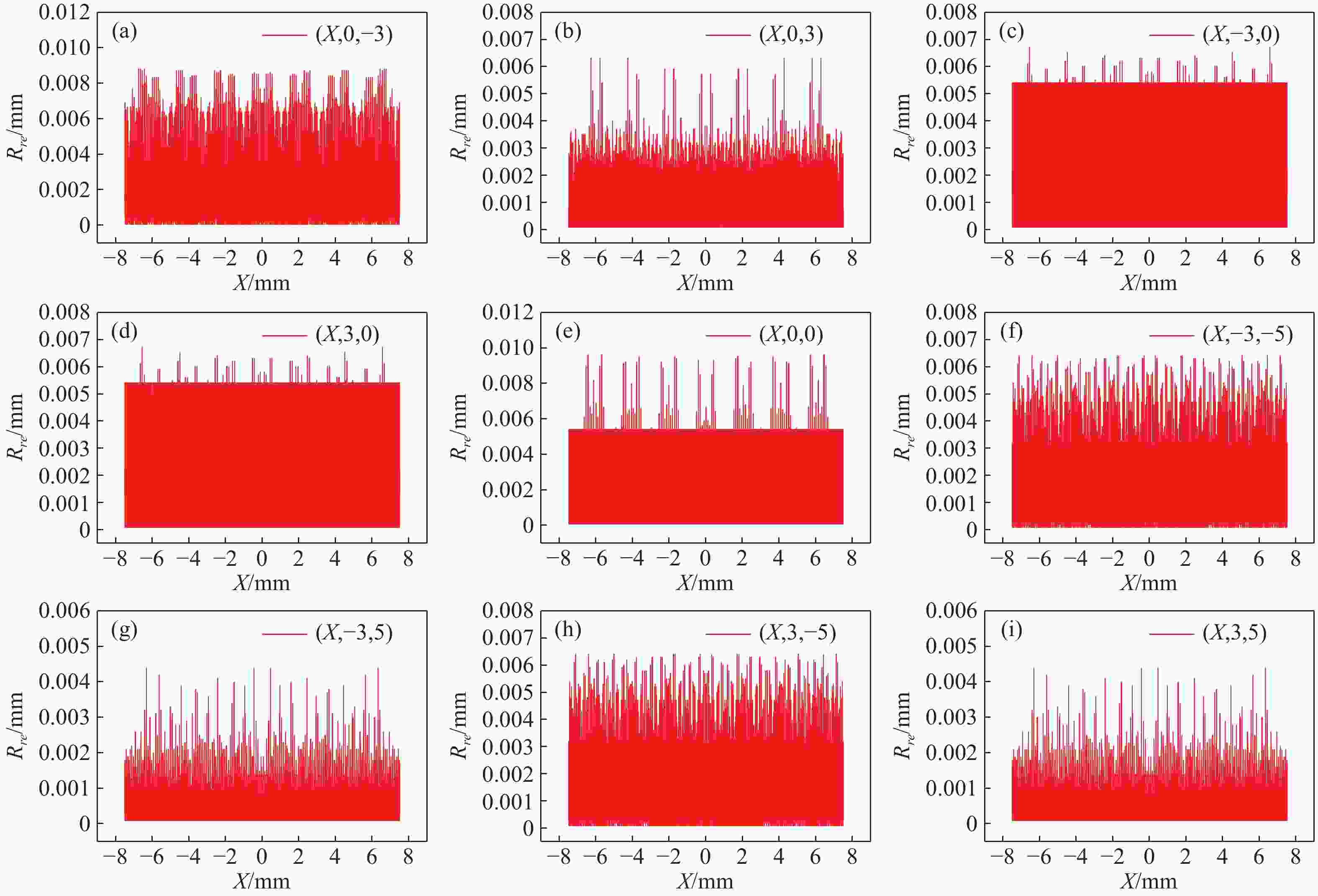
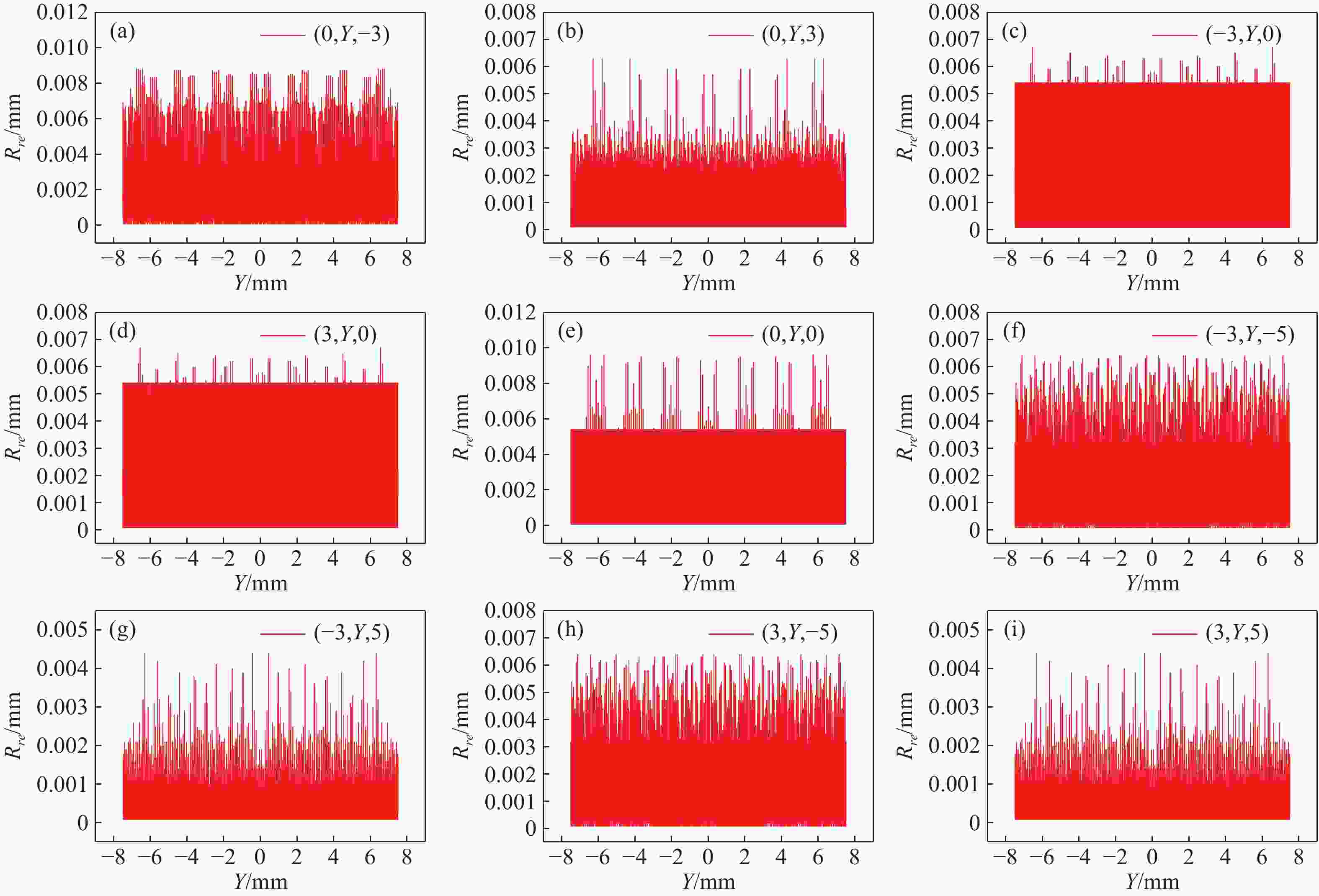
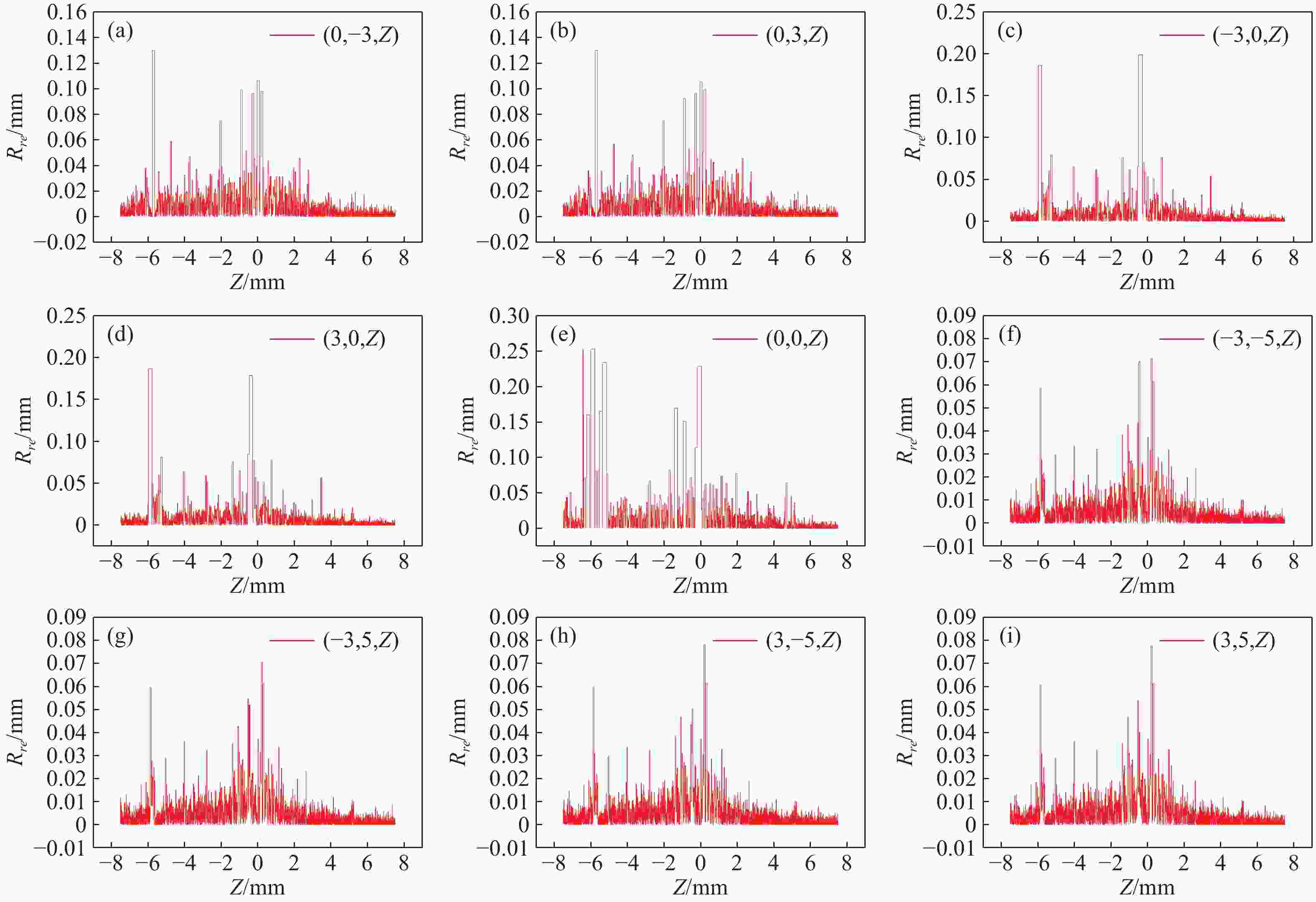
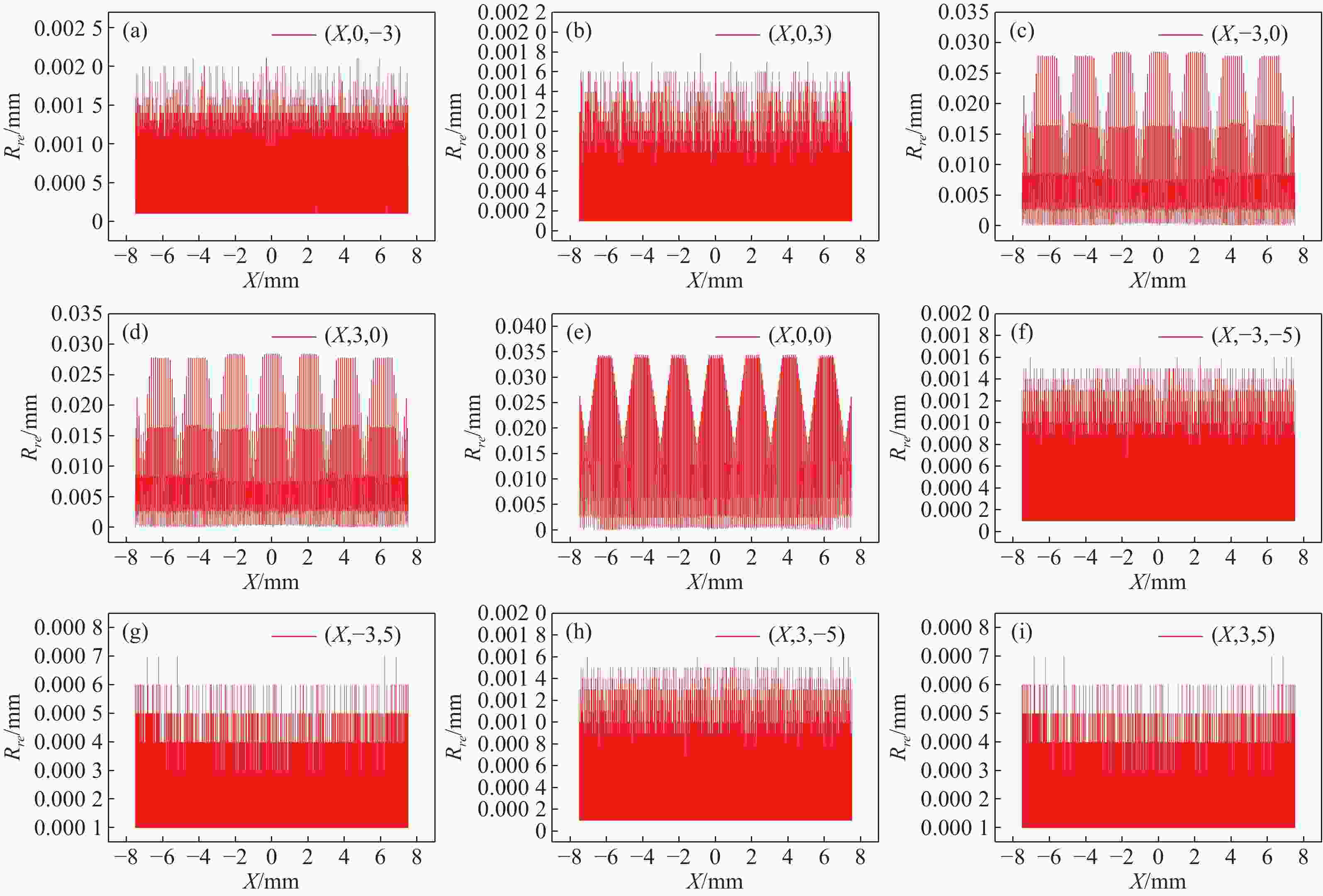
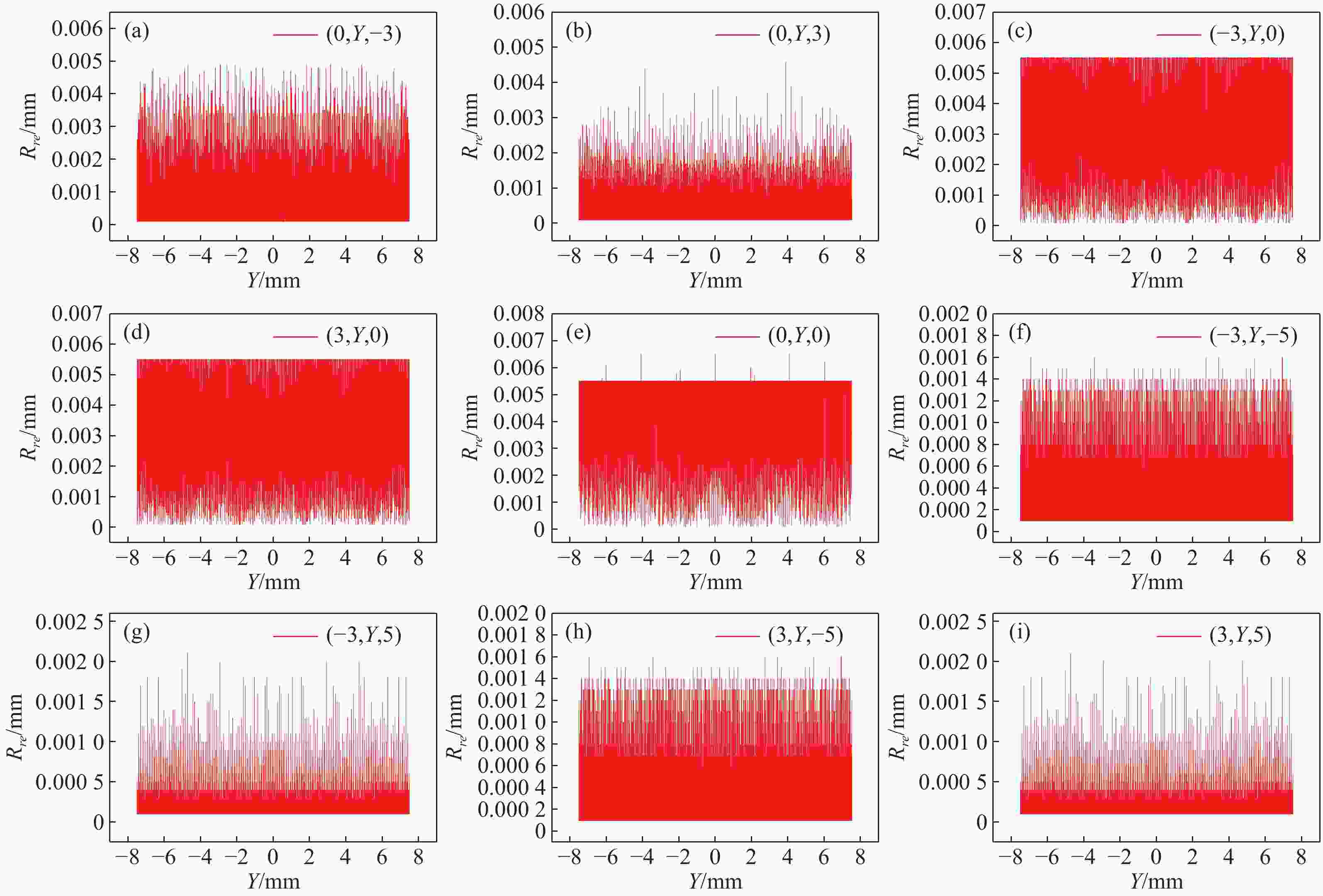
在三维场景重建过程中,光场相机的空间分辨率会影响可恢复的空间细节和深度分辨率,从而影响三维重建的准确性。因此,对光场相机的空间分辨率进行计算与分析,对于高分辨率和低分辨率区域的识别十分重要。本文利用前向光线追迹技术的高精度优点,研究了一种基于前向光线追迹技术的光场相机空间分辨率计算方法。对不同微透镜阵列排列方式下的光场相机1.0和2.0的空间分辨率进行了定量计算和比较。进一步研究了不同的主镜头逆放大率(
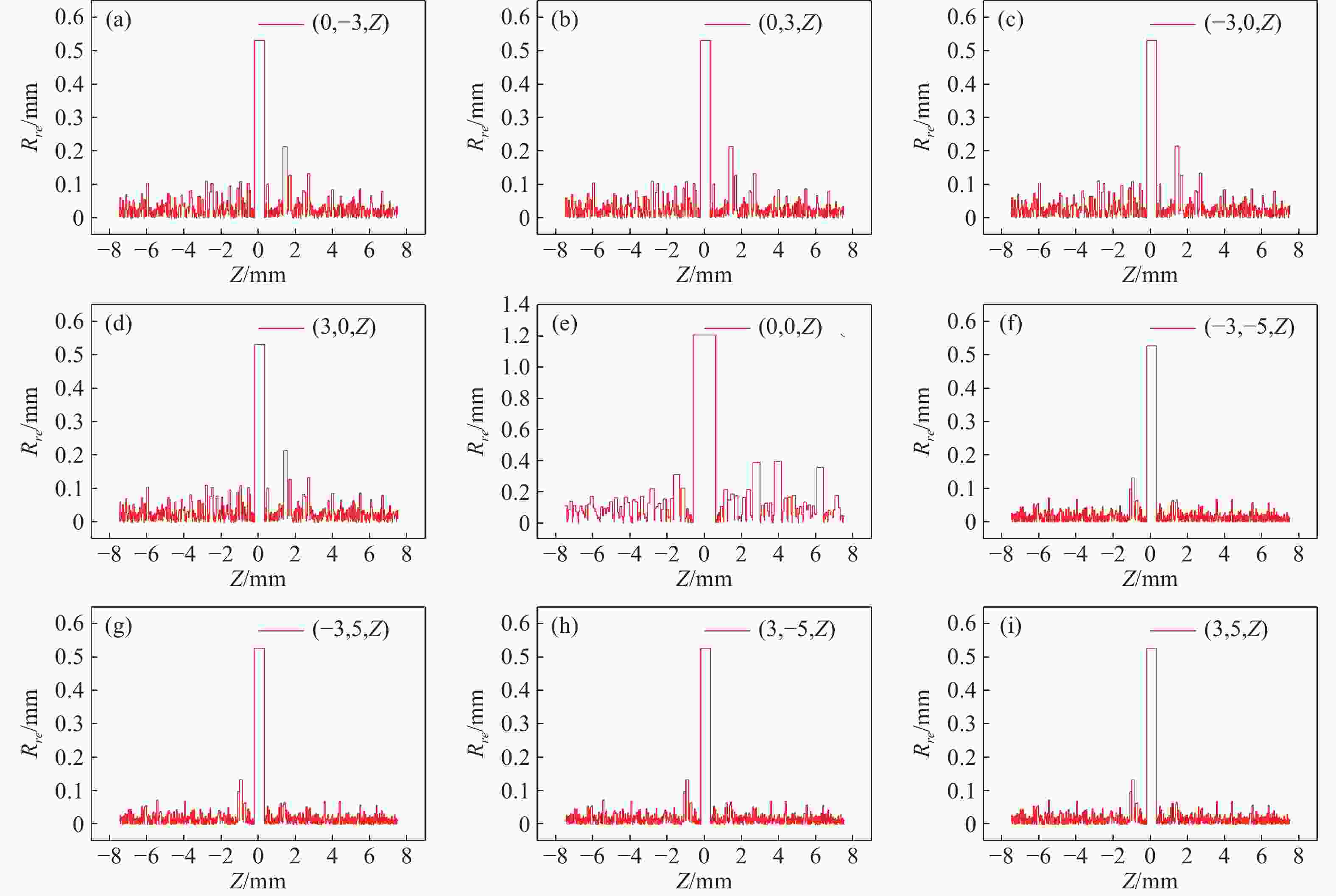
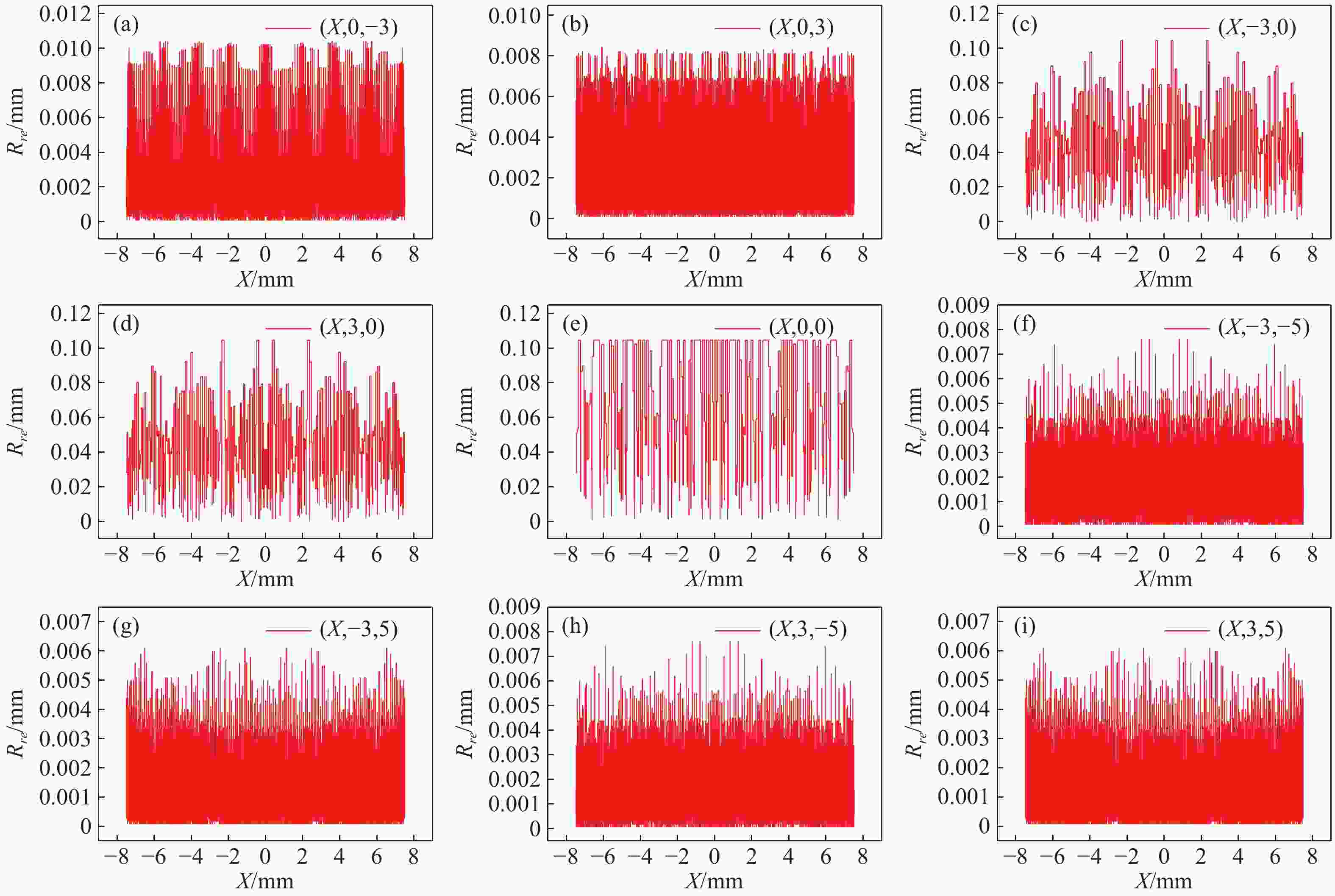
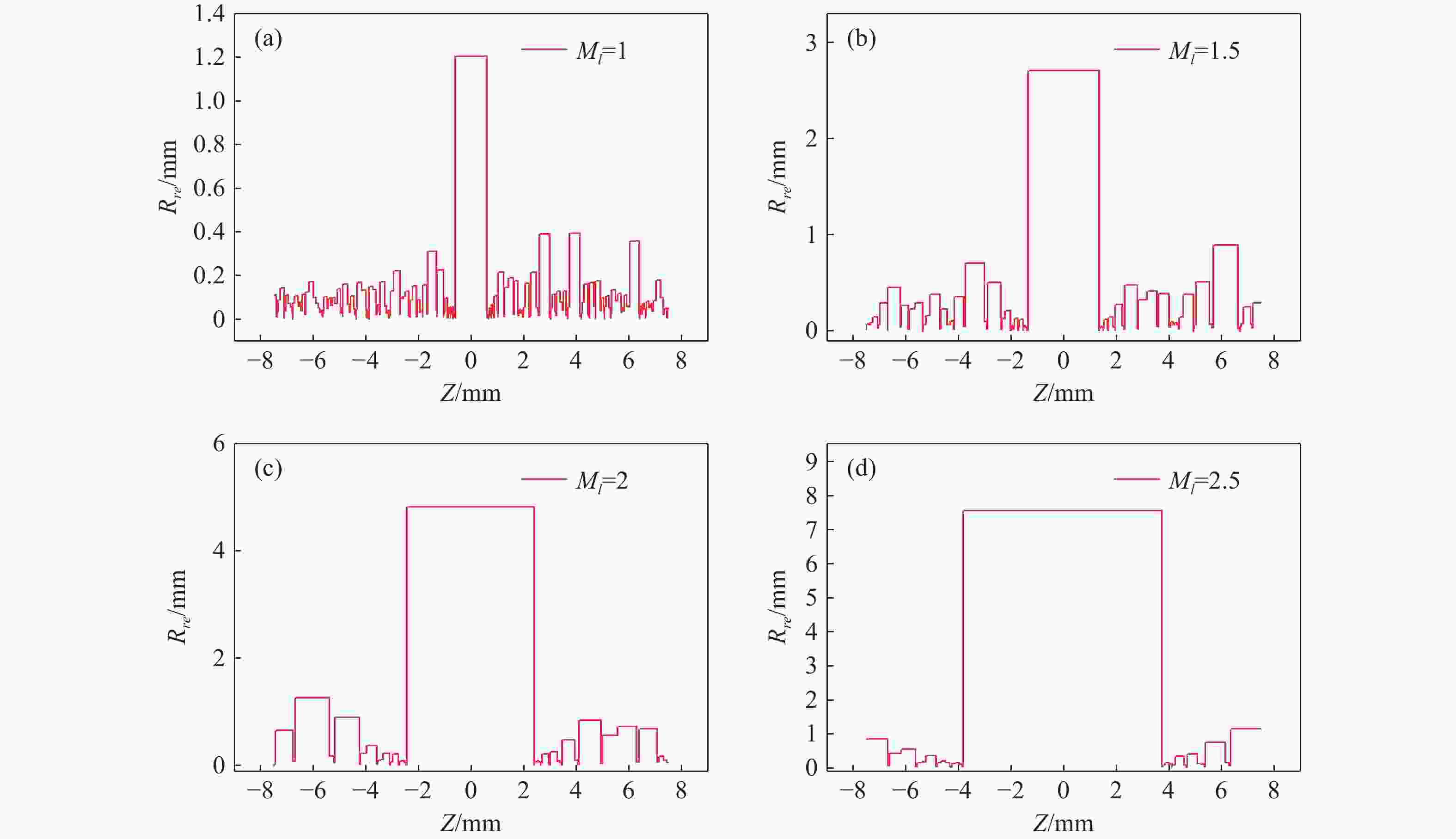
M l )对光场相机深度分辨率的影响。结果表明,光场相机在物平面与光轴交点附近以外的区域具有较高的深度分辨率。光场相机2.0在(0,0,0)附近区域的深度分辨率优于光场相机1.0。对于正方形排列的微透镜阵列,光场相机2.0的横向分辨率较光场相机1.0略有提升。光场相机1.0的深度分辨率随着M l 的增大而逐渐降低。Abstract:In the process of 3D scene reconstruction, the spatial resolution of the light field camera (LFC) affects the recoverable spatial details as well as the depth resolution, thereby influencing the accuracy of the 3D reconstruction. Therefore, calculating and analyzing the spatial resolution of the LFC is crucial for identifying the high and low resolution regions. In this paper, a calculation method for the spatial resolution of an LFC is explored based on the forward ray-tracing technique, which has the advantage of high accuracy. The spatial resolutions of LFC 1.0 and LFC 2.0 under different microlens array configurations are quantitatively calculated and compared. In addition, the effects of the inverse magnification (
M l ) of the main lens on the depth resolution of the LFC are investigated. The results show that the LFC exhibits higher depth resolution in regions away from the intersection of the object plane and the optical axis. The depth resolution of LFC 2.0 near the region of (0,0,0) is better than that of LFC 1.0. For a microlens array arranged in a square pattern, the lateral resolution of LFC 2.0 shows a slight improvement over that of LFC 1.0. The depth resolution of the LFC 1.0 gradually decreases asM l increases.-
Key words:
- light field camera /
- spatial resolution /
- reconstruction /
- ray tracing /
- depth resolution
-
表 1 光场相机1.0的光学参数
Table 1. Parameters of the light field camera 1.0
d1
(mm)d2
(mm)fm
(mm)f
(mm)l1
(mm)lm
(mm)Pm
(mm)Px
(μm)0.6 - 0.6 100 200 200 0.1045 5.5 表 2 光场相机2.0的光学参数
Table 2. Parameters of the light field camera 2.0
d1
(mm)d2
(mm)fm
(mm)f
(mm)l1
(mm)l2
(mm)Pm
(mm)Px
(μm)0.54 5.4 0.6 100 200 200 0.1045 5.5 表 3 不同Ml下光场相机1.0的光学参数
Table 3. Parameters of the light field camera 1.0 with different Ml
d1 (mm) fm (mm) f (mm) Ml l1 (mm) lm (mm) Pm (mm) Px (μm) 0.6 0.6 100 1 200 200 0.1045 5.5 0.6 0.6 100 1.5 250 166.667 0.1045 5.5 0.6 0.6 100 2 300 150 0.1045 5.5 0.6 0.6 100 2.5 350 140 0.1045 5.5 -
[1] 朱效宇. 单相机光场成像三维流场测量方法与系统研究[D]. 南京: 东南大学, 2022.ZHU X Y. Study of three-dimensional flow field measurement with a single light field camera[D]. Nanjing: Southeast University, 2022. (in Chinese). [2] LYNCH K, FAHRINGER T, THUROW B. Three-dimensional particle image velocimetry using a plenoptic camera[C]//50th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting Including the New Horizons Forum and Aerospace Exposition, AIAA, 2012: AIAA 2012-1056. [3] 吴治安. 光场成像三维流场测量系统体标定方法研究[D]. 南京: 东南大学, 2021.WU ZH A. Study on volumetric calibration method of light field particle image velocimetry for 3D flow measurement[D]. Nanjing: Southeast University, 2021. (in Chinese). [4] SHI SH X, DING J F, NEW T H, et al. Volumetric calibration enhancements for single-camera light-field PIV[J]. Experiments in Fluids, 2019, 60(1): 21. doi: 10.1007/s00348-018-2670-5 [5] 顾高霏, 赵军, 孔明, 等. 基于光场相机层析法的颗粒三维位置测量[J]. 光子学报, 2020, 49(8): 0812002.GU G F, ZHAO J, KONG M, et al. Tomographic three-dimensional particle position measurement based on light field camera[J]. Acta Photonica Sinica, 2020, 49(8): 0812002. (in Chinese). [6] SHI SH X, DING J F, NEW T H, et al. Light-field camera-based 3D volumetric particle image velocimetry with dense ray tracing reconstruction technique[J]. Experiments in Fluids, 2017, 58(7): 78. doi: 10.1007/s00348-017-2365-3 [7] 吴旗, 朱效宇, 许传龙. 基于物理方程的高分辨率光场层析粒子图像测速技术[J]. 光学学报, 2025, 45(1): 0112007.WU Q, ZHU X Y, XU CH L. High-resolution light field chromatography particle image velocimetry based on physical equation[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2025, 45(1): 0112007. (in Chinese). [8] SHI SH X, DING J F, ATKINSON C, et al. A detailed comparison of single-camera light-field PIV and tomographic PIV[J]. Experiments in Fluids, 2018, 59(3): 46. doi: 10.1007/s00348-018-2500-9 [9] MEI D, DING J F, SHI SH X, et al. High resolution volumetric dual-camera light-field PIV[J]. Experiments in Fluids, 2019, 60(8): 132. doi: 10.1007/s00348-019-2781-7 [10] ZHU X Y, HOSSAIN M M, LI J, et al. Weight coefficient calculation through equivalent ray tracing method for light field particle image velocimetry[J]. Measurement, 2022, 193: 110982. doi: 10.1016/j.measurement.2022.110982 [11] CAO L X, ZHANG B, LI J, et al. Characteristics of tomographic reconstruction of light-field Tomo-PIV[J]. Optics Communications, 2019, 442: 132-147. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2019.03.026 [12] ZHU X Y, ZHANG B, LI J, et al. Volumetric resolution of light field imaging and its effect on the reconstruction of light field PIV[J]. Optics Communications, 2020, 462: 125263. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2020.125263 [13] ZHU X Y, WU ZH A, LI J, et al. A pre-recognition SART algorithm for the volumetric reconstruction of the light field PIV[J]. Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 2021, 143: 106625. [14] ZHU X Y, XU CH L, HOSSAIN M M, et al. Approach to select optimal cross-correlation parameters for light field particle image velocimetry[J]. Physics of Fluids, 2022, 34(7): 073601. doi: 10.1063/5.0098933 [15] CAO L X, ZHANG B, HOSSAIN M M, et al. Tomographic reconstruction of light field PIV based on a backward ray-tracing technique[J]. Measurement Science and Technology, 2021, 32(4): 044007. doi: 10.1088/1361-6501/abd281 [16] ZHU X Y, XU CH L, HOSSAIN M M, et al. Fast and accurate flow measurement through dual-camera light field particle image velocimetry and ordered-subset algorithm[J]. Physics of Fluids, 2023, 35(6): 063603. doi: 10.1063/5.0153135 [17] FAHRINGER T W, THUROW B S. Filtered refocusing: a volumetric reconstruction algorithm for plenoptic-PIV[J]. Measurement Science and Technology, 2016, 27(9): 094005. doi: 10.1088/0957-0233/27/9/094005 [18] 张志远. 三维流场层析粒子图像变分光流速度测量算法研究[D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2024.ZHANG ZH Y. Research on variational optical flow velocity measurement algorithm for three-dimensional flow field tomographic particle image[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 2024. (in Chinese). [19] ZHAO ZH, YAO CH H, SHI SH X, et al. Resolution analysis on light-field particle image velocimetry[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America A, 2023, 40(4): 729-740. doi: 10.1364/JOSAA.474866 [20] DEEM E A, ZHANG Y, CATTAFESTA L N, et al. On the resolution of plenoptic PIV[J]. Measurement Science and Technology, 2016, 27(8): 084003. doi: 10.1088/0957-0233/27/8/084003 [21] RUAN L Y, CHEN B, LI J ZH, et al. Learning to deblur using light field generated and real defocus images[C]//Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), IEEE, 2022: 16283-16292. [22] ZHAO ZH, JI Y, HE Y L, et al. Binocular Scheimpflug light-field PIV[J]. Optics Communications, 2025, 574: 131176. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2024.131176 [23] LIU Y D, ZHU M J, WANG T X, et al. Spatial resolution of light field sectioning pyrometry for flame temperature measurement[J]. Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 2021, 140: 106545. doi: 10.1016/j.optlaseng.2021.106545 [24] LYU W Q, SHENG H, KE W, et al. Advances in light field spatial super-resolution: a comprehensive literature survey[J]. IEEE Access, 2025, 13: 18470-18497. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2025.3532610 -





 下载:
下载: