-
摘要:
激光清洗技术作为一种高效、环保的表面处理手段,在芯片封装模具清洗领域具有重要的应用潜力。本文系统探究了激光参数(脉冲宽度、重复频率、平均功率)对基材为 P20 合金和 ASP23 合金镀铬的模具表面环氧塑封料 (EMC) 污染物的清洗效果影响。实验采用
1064 nm掺钕脉冲激光器,将高斯光束整形为平顶光束,结合振镜"弓"字扫描路径,以单一变量法优化工艺参数。实验结果表明,激光能量密度为 0.55−0.77 J/cm2 时,需协同调节脉冲宽度与重复频率,以平衡热输入,可实现污染物完全去除且基材零损伤。参数敏感性分析显示,最佳占空比范围为 0.8%~1.0%。此外,功率超过阈值(150 ns,50%或200 ns,50%)会导致基材损伤,表明参数匹配对清洗效果与材料保护至关重要。本研究为芯片封装模具提供了一种高精度、非接触的绿色清洗方案,验证了激光清洗技术在集成电路领域的可行性。Abstract:Laser cleaning technology, as an efficient and environmentally friendly surface treatment method, plays significant application potential in the field of chip packaging molds cleaning. This research systematically investigated the effects of laser parameters (pulse duration, repetition rate, average power) on the cleaning effect of Epoxy Molding Compound (EMC) contaminates from mold surface coated with chromium on P20 alloy and ASP23 alloy substrates. The experiment employed a
1064 nm Nd-doped pulsed laser, reshaping the Gaussian beam into a flat-top beam, and combining with a "bow" shape scanning path of the galvanometer mirror. The process parameters were optimized using a single-variable method. The experimental results indicate that when the laser energy density is in 0.55−0.77 J/cm2, the pulse duration and repetition rate need to be adjusted in coordination to balance the thermal input, enabling complete removal of contaminants without any damage to the substrate. Parameter sensitivity analysis reveals that the optimal duty cycle range is from 0.8% to 1.0%. Furthermore, when the power exceeds the threshold (150 ns@50% average power or 200 ns@50% average power), it may cause damage to the substrate, which indicates that laser parameter matching is crucial for the cleaning effect and material protection. This research provides a high-precision, non-contact and environmentally friendly cleaning solution for chip packaging molds, and verifies the feasibility of laser cleaning technology in the field of integrated circuits.-
Key words:
- laser cleaning technology /
- chip packaging mold /
- duty cycle /
- surface treatment
-
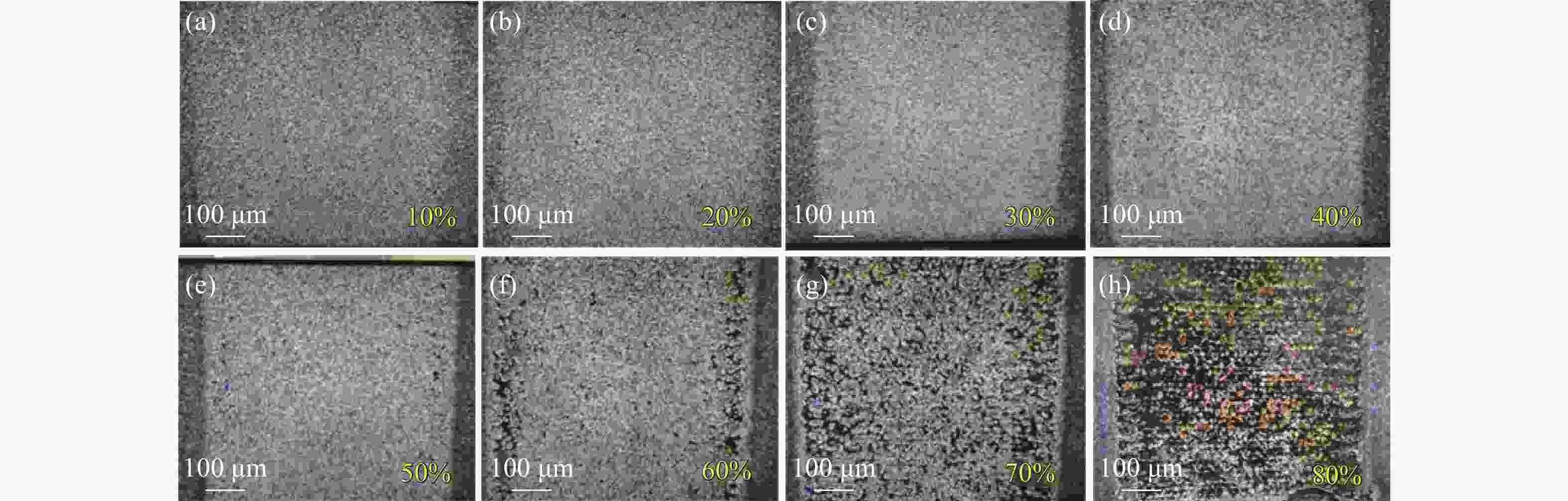
图 5 脉宽为150 ns和重频为54 kHz,功率分别为最大功率的(a) 10%、(b) 20%、(c) 30%、(d) 40%、(e) 50%、(f) 60%、(g) 70%、(h) 80%时,激光清洗显微镜样貌图
Figure 5. Microscopic images of the surfaces cleaned by lasers with a pulse width of 150 ns and repetition rate of 54 kHz, and (a) 10%, (b) 20%, (c) 30%, (d) 40%, (e) 50%, (f) 60%, (g) 70%, (h) 80% of the maximum power
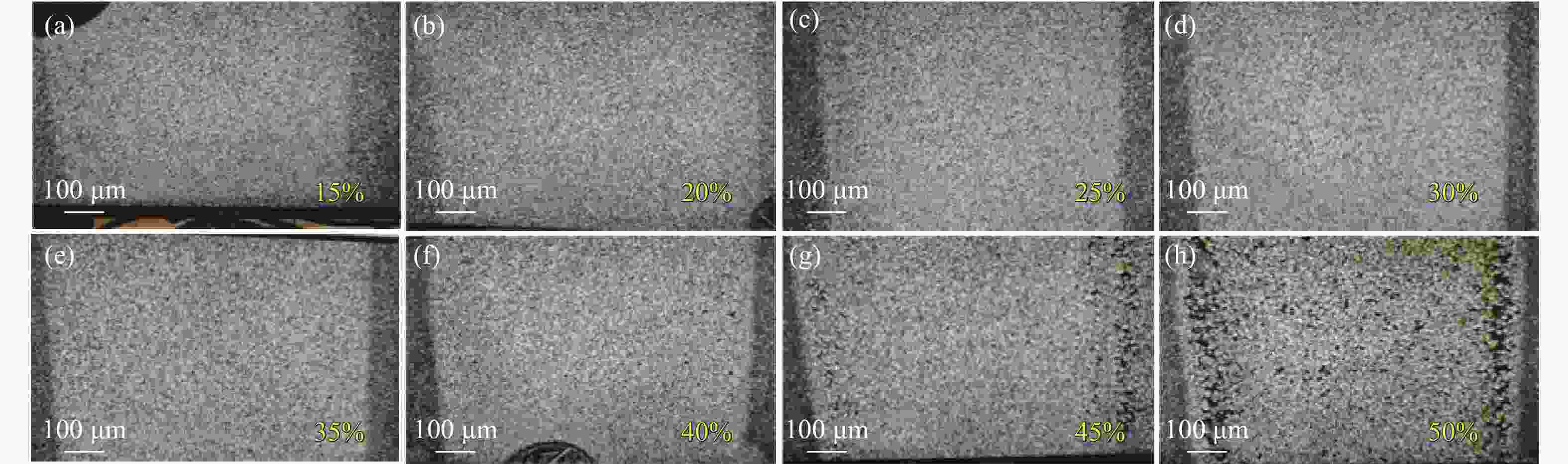
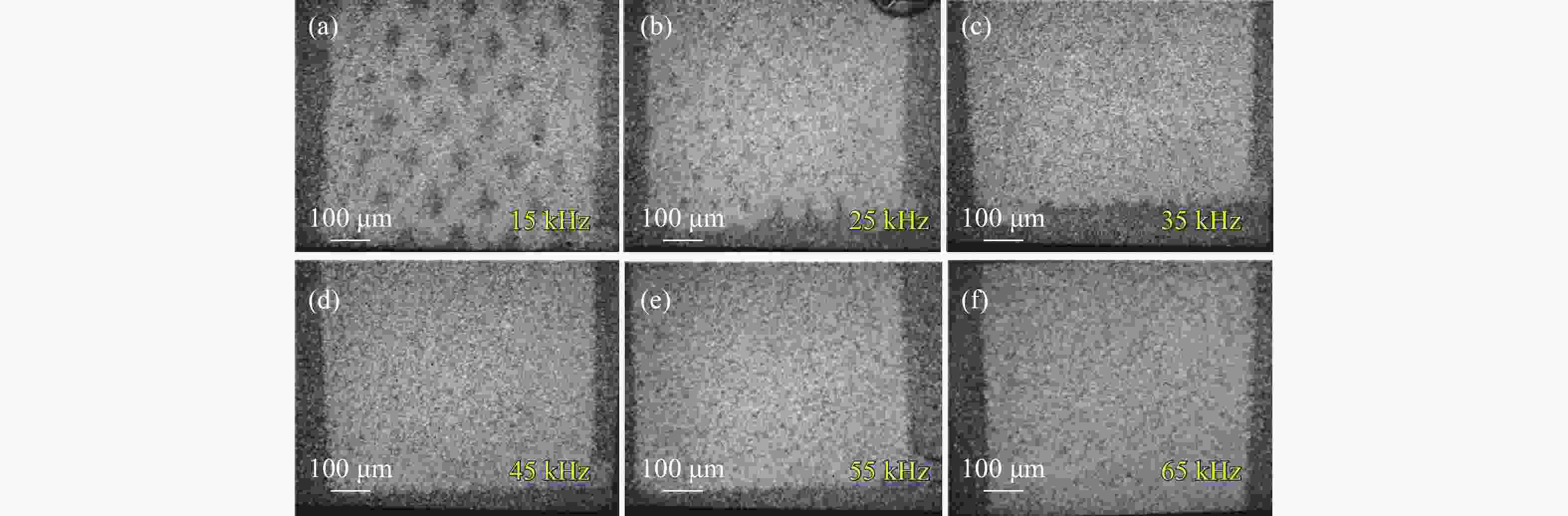
图 7 脉宽200 ns 和重频45 kHz时,功率分别为最大功率的(a) 15%、(b) 20%、(c) 25%、(d) 30%、(e) 35%、(f) 40%、(g) 45%、(h) 50%激光清洗显微镜样貌图
Figure 7. Microscopic morphology images of the surfaces cleaned by lasers with a pulse width of 200 ns, repetition frequency of 45 kHz, and (a) 15%, (b) 20%, (c) 25%, (d) 30%, (e) 35%, (f) 40%, (g) 45%, (h) 50% of the maximum power
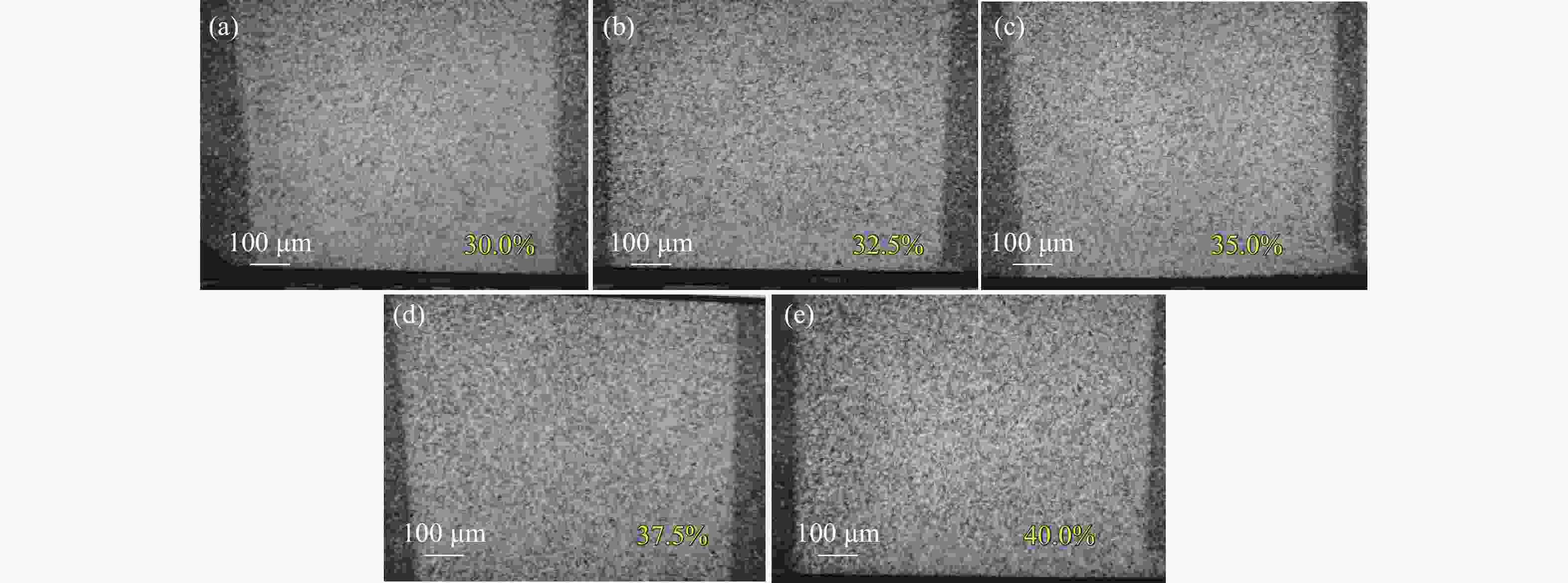
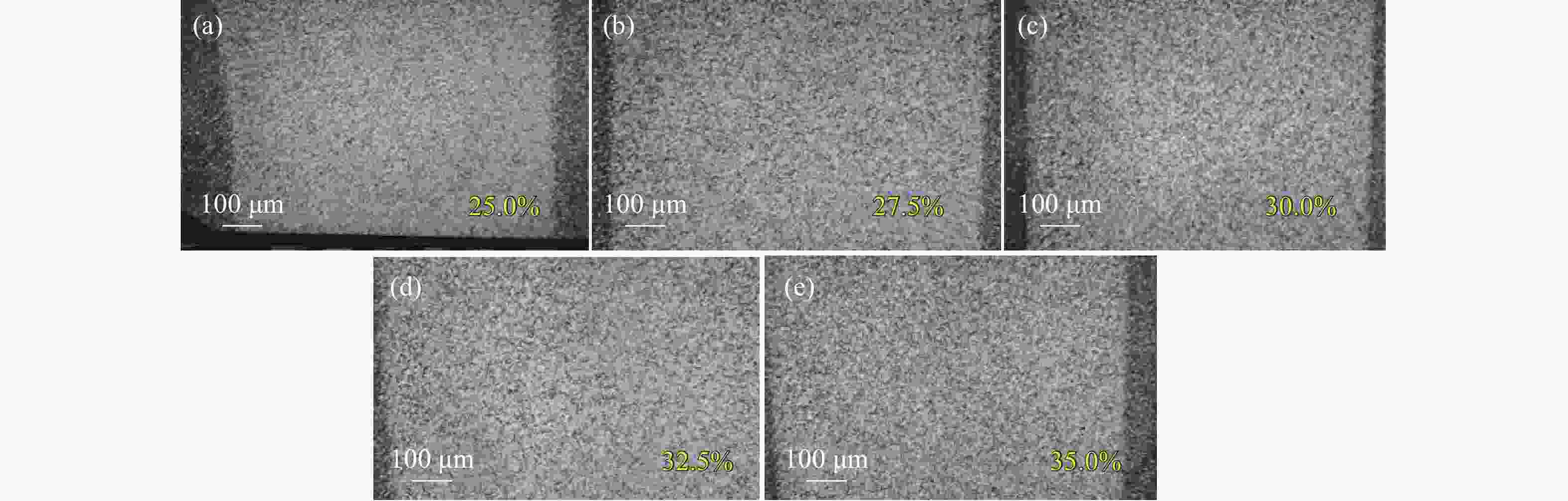
图 8 脉宽200 ns、重频45 kHz时,功率分别为最大功率的(a) 25%、(b) 27.5%、(c) 30%、(d) 32.5%、(e) 35%对应的激光清洗显微镜样貌
Figure 8. Microscopic morphology of the surfaces cleaned by lasers with a pulse width of 200 ns, a repetition frequency of 45 kHz, and powers of (a) 25%, (b) 27.5%, (c) 30%, (d) 32.5%, (e) 35% of the maximum power
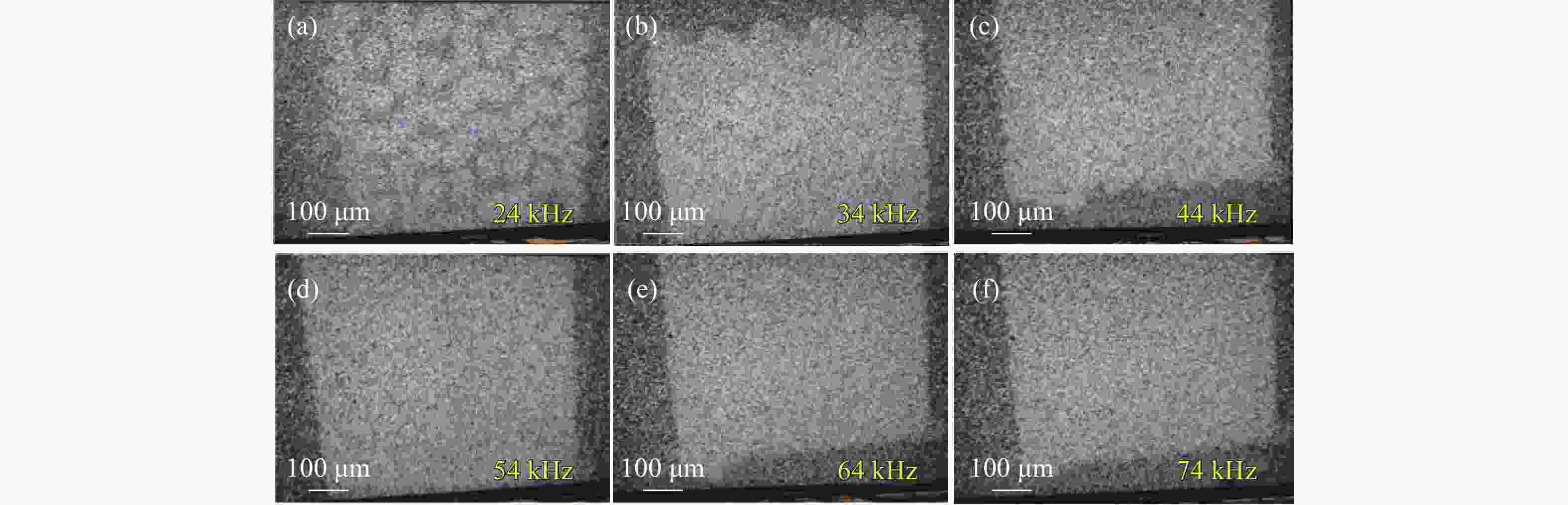
图 11 脉宽 200 ns和功率 175 W (35%),重复频率分别为 15 kHz、 25 kHz、 35 kHz、 45 kHz、 55 kHz、 65 kHz激光清洗显微镜样貌图
Figure 11. Microscopic morphology images of the surfaces cleaned by lasers with a pulse width of 200 ns, a power of 175 W (35%), and repetition frequencies of 15 kHz, 25 kHz, 35 kHz, 45 kHz, 55 kHz, 65 kHz
表 1 激光器单模和多模清洗效果对比
Table 1. Comparison of single-mode and multimode laser cleaning effect
激光模式 能量分布 工作能力 工作效率 基材损伤 适用场景 单模 中间强,两翼弱 强 较差 有/轻微 除锈 多模 分布均匀 较差 强 轻微/无 模具 表 2 激光器和清洗系统参数
Table 2. Parameters of the laser and cleaning system
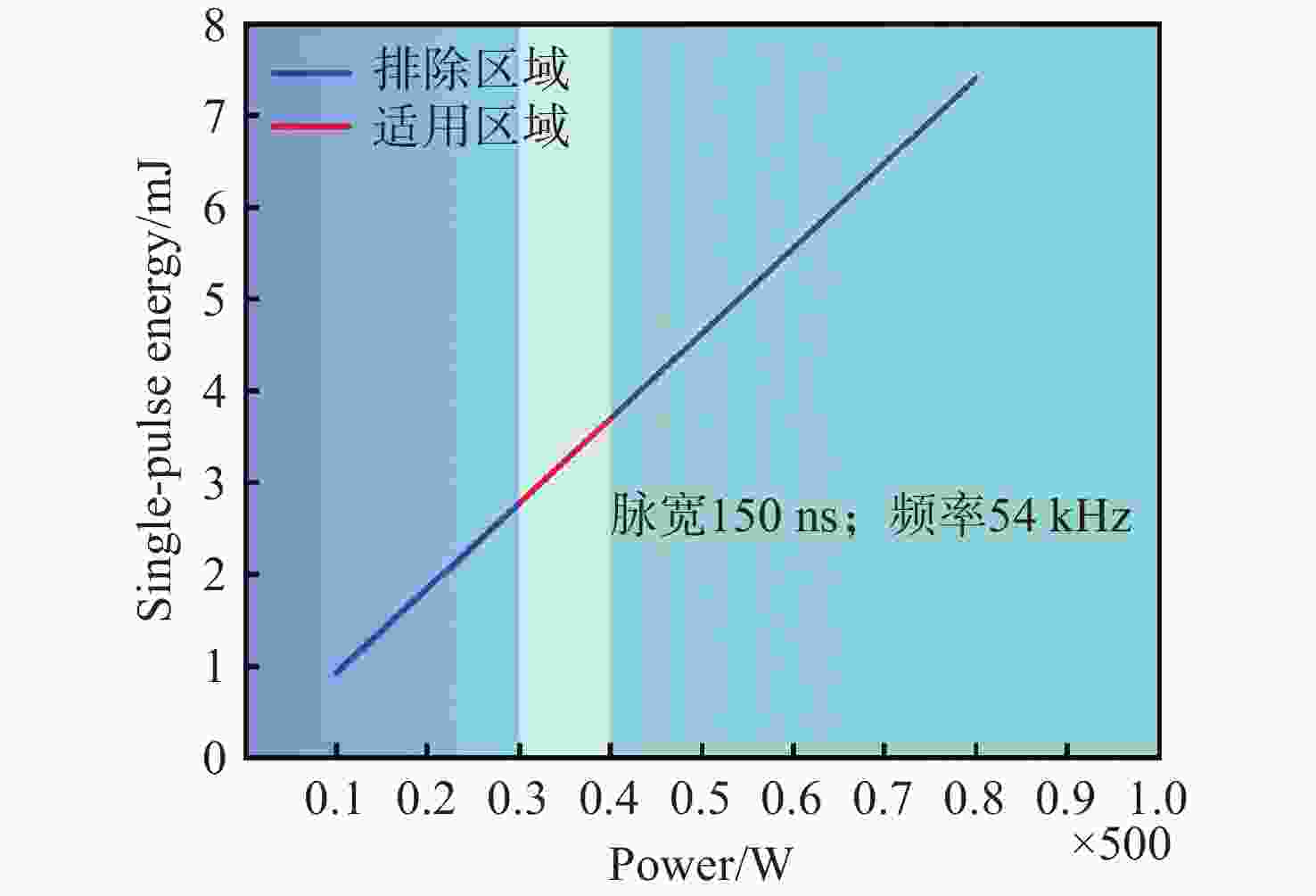
名称 数值 波长(λ)/nm 1064 平均功率(P)/W 0~500 脉冲宽度(w)/ns 30~500 重复频率(f)/kHz 1~ 4000 振镜规格/mm 110×110 表 3 脉宽 150 ns 和重频 54 kHz下,不同功率对应单脉冲能量的值
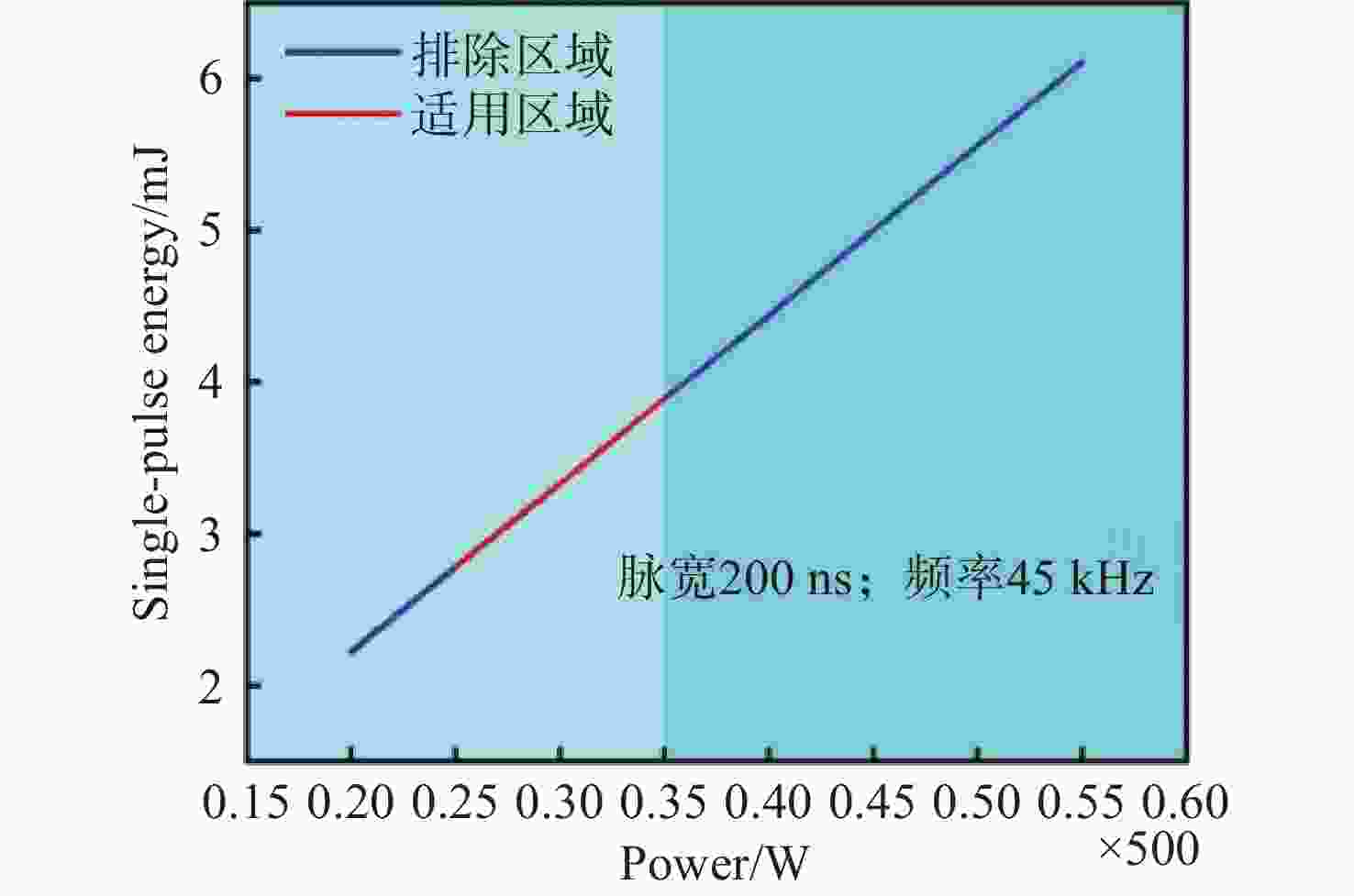
Table 3. Single-pulse energy at different power levels under a pulse width of 150 ns and a repetition rate of 54 kHz
功率(500 W) 单脉冲能量(mJ) 功率(500 W) 单脉冲能量(mJ) 10% 0.93 30.0% 2.78 20% 1.85 32.5% 3.01 30% 2.78 35.0% 3.24 40% 3.70 37.5% 3.47 50% 4.63 40.0% 3.70 60% 5.56 \ \ 70% 6.48 \ \ 80% 7.41 \ \ 表 4 脉宽200 ns、重频 45 kHz时不同功率对应单脉冲能量
Table 4. Single-pulse energy at different power levels under a pulse width of 200 ns and a repetition rate of 45 kHz
功率(500 W) 单脉冲能量(mJ) 功率(500 W) 单脉冲能量(mJ) 20% 2.22 25% 2.78 25% 2.78 27.5% 3.06 30% 3.33 30% 3.33 35% 3.89 32.5% 3.61 40% 4.44 35.0% 3.89 45% 5.00 \ \ 50% 5.56 \ \ 55% 6.11 \ \ -
[1] 张自豪, 余晓畅, 王英, 等. 脉冲YAG激光清洗轮胎模具的实验研究[J]. 激光技术, 2018, 42(1): 127-130. doi: 10.7510/jgjs.issn.1001-3806.2018.01.025ZHANG Z H, YU X C, WANG Y, et al. Experimental study about cleaning of tire molds with pulse YAG laser[J]. Laser Technology, 2018, 42(1): 127-130. (in Chinese). doi: 10.7510/jgjs.issn.1001-3806.2018.01.025 [2] YANG H, LIU H X, GAO R X, et al. Numerical simulation of paint stripping on CFRP by pulsed laser[J]. Optics & Laser Technology, 2022, 145: 107450. [3] ASMUS J F, MURPHY C G, MUNK W H. Studies on the interaction of laser radiation with art artifacts[C]. Proceedings of SPIE 0041, Developments in laser Technology II, SPIE, 1974: 19-30. [4] ZHOU ZH H, SUN W P, WU J J, et al. The fundamental mechanisms of laser cleaning technology and its typical applications in industry[J]. Processes, 2023, 11(5): 1445. doi: 10.3390/pr11051445 [5] LEI Z L, TIAN Z, CHEN Y B. Laser cleaning technology in industrial fields[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2018, 55(3): 030005. [6] 王宏睿. 激光清洗原理与应用研究[J]. 清洗世界, 2006, 22(9): 20-23. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-8909.2006.09.005WANG H R. Principle and applied research on laser cleaning[J]. Cleaning World, 2006, 22(9): 20-23. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-8909.2006.09.005 [7] STEEN W M, MAZUMDER J. Laser cleaning[M]//STEEN W M, MAZUMDER J. Laser Material Processing. London: Springer, 2010: 417-440. [8] 林乔, 石敏球, 张欣, 等. 激光清洗及其应用进展[J]. 广州化工, 2010, 38(6): 23-25.LIN Q, SHI M Q, ZHANG X, et al. Laser cleaning and its applications[J]. Guangzhou Chemical Industry, 2010, 38(6): 23-25. (in Chinese). [9] SCHAWLOW A L. Lasers: the intense, monochromatic, coherent light from these new sources shows many unfamiliar properties[J]. Science, 1965, 149(3679): 13-22. doi: 10.1126/science.149.3679.13 [10] ZHOU K, SANG S G, WANG C Y, et al. Principle, application and development trend of laser cleaning[J]. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2022, 2383(1): 012075. doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/2383/1/012075 [11] 李浩宇, 杨峰, 郭嘉伟, 等. 激光清洗的发展现状与前景[J]. 激光技术, 2021, 45(5): 654-661.LI H Y, YANG F, GUO J W, et al. Development status and prospect of laser cleaning[J]. Laser Technology, 2021, 45(5): 654-661. (in Chinese). [12] ZHAO H CH, QIAO Y L, DU X, et al. Laser cleaning performance and mechanism in stripping of Polyacrylate resin paint[J]. Applied Physics A, 2020, 126(5): 360. doi: 10.1007/s00339-020-03551-0 [13] 刘锴, 范卫星, 王平秋, 等. 激光等离子体法清洗微纳颗粒的物态变化研究[J]. 激光技术, 2021, 45(4): 405-410.LIU K, FAN W X, WANG P Q, et al. Study on the state change characteristics of cleaning micro-nano particles by laser plasma method[J]. Laser Technology, 2021, 45(4): 405-410. (in Chinese). [14] BEDAIR S M, SMITH H P. Atomically clean surfaces by pulsed laser bombardment[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 1969, 40(12): 4776-4781. doi: 10.1063/1.1657288 [15] ZHU G D, WANG SH R, CHENG W, et al. Corrosion and wear performance of aircraft skin after laser cleaning[J]. Optics & Laser Technology, 2020, 132: 106475. [16] WANG S R, ZHANG M Y, et al. Application of laser cleaning in postwelding treatment of aluminum alloy[J]. Applied Optics, 2020, 59(34): 10967-10972. [17] ZHU G D, WANG S R, CHENG W, et al. Investigation on the surface properties of 5A12 aluminum alloy after Nd: YAG laser cleaning[J]. Coatings, 2019, 9(9): 578-593. [18] 朱国栋, 王守仁, 成巍, 等. 激光清洗在金属表面处理中的应用研究进展[J]. 山东科学, 2019, 32(4): 38-45,73.ZHU G D, WANG SH R, CHENG W, et al. Advances in the application of laser cleaning to metal surface treatment[J]. Shandong Science, 2019, 32(4): 38-45,73. (in Chinese). [19] 谭东晖, 陆冬生, 宋文栋, 等. 准分子激光直接清洗硅片上油脂的实验研究[J]. 激光技术, 1995, 19(5): 319-320.TAN D H, LU D SH, SONG W D, et al. Experiment studies of excimer laser cleaning of grease-contaminated Si substrate[J]. Laser Technology, 1995, 19(5): 319-320. (in Chinese). [20] 谭东晖, 陆冬生, 宋文栋, 等. 激光清洗基片表面温度的有限元分析及讨论[J]. 华中理工大学学报, 1996, 24(6): 50-53.TAN D H, LU D S, SONG W D, et al. A finite element analysis of the temperature distribution on a substrate surface during laser cleaning[J]. Journal of Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 1996, 24(6): 50-53. (in Chinese). [21] 王泽敏, 曾晓雁, 黄维玲. 脉冲激光除漆机理及工艺参数的研究[J]. 材料保护, 2000, 33(4): 21-22,59.WANG Z M, ZENG X Y, HUANG W L. Parameters and mechanisms of paintcoat laser cleaning[J]. Materiais Protection, 2000, 33(4): 21-22,59. (in Chinese). [22] 史兴宽, 徐传义, 任敬心, 等. 光学基片表面镀金薄膜的激光清洗阈值和损伤阈值[J]. 航空制造技术, 2000(5): 34-36.SHI X K, XU CH Y, REN J X, et al. Laser cleaning threshold and damage threshold of gold-plating thin film on optical substrate surface[J]. Aeronautical Manufacturing Technology, 2000(5): 34-36. (in Chinese). [23] 邹涛, 杨和逸, 仇连波. 活络模激光清洗技术的开发应用及发展方向[J]. 橡塑技术与装备, 2023, 49(3): 5-13.ZOU T, YANG H Y, QIU L B. Development application and direction of laser cleaning technology for active mode[J]. China Rubber/Plastics Technology and Equipment, 2023, 49(3): 5-13. (in Chinese). [24] CUCCI C, DE PASCALE O, SENESI G S. Assessing laser cleaning of a limestone monument by fiber optics reflectance spectroscopy (FORS) and visible and near-infrared (VNIR) hyperspectral imaging (HSI)[J]. Minerals, 2020, 10(12): 1052. doi: 10.3390/min10121052 [25] GU J Y, SU X, JIN Y, et al. Research progress and prospects of laser cleaning for CFRP: a review[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing, 2024, 185: 108349. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2024.108349 [26] WANG Y X, YU ZH H, YU L SH, et al. Study on removal mechanism of TC4 oxide film by nanosecond pulsed laser cleaning in air environment[J]. Optics & Laser Technology, 2025, 181: 111856. [27] RAZAB M K A A, NOOR A M, JAAFAR M S, et al. A review of incorporating Nd: YAG laser cleaning principal in automotive industry[J]. Journal of Radiation Research and Applied Sciences, 2018, 11(4): 393-402. doi: 10.1016/j.jrras.2018.08.002 [28] 张雨阳, 杨伟, 牛富增, 等. 纳秒激光对硅基底上的微纳颗粒的清洗研究[J]. 激光与红外, 2025, 55(9): 1406-1413. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5078.2025.09.011ZHANG Y Y, YANG W, NIU F Z, et al. Nanosecond laser cleaning of micro particles on silicon substrates[J]. Laser & Infrared, 2025, 55(9): 1406-1413. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5078.2025.09.011 [29] WAN ZH, YANG X F, XIA G F, et al. Effect of laser power on cleaning mechanism and surface properties[J]. Applied Optics, 2020, 59(30): 9482-9490. doi: 10.1364/AO.399691 [30] 陈玲, 王非森, 文申柳, 等. 激光清洗对超低碳贝氏体钢腐蚀性能的影响[J/OL]. 应用激光, 1-10 [2025-12-19].CHEN L, WANG F S, WEN SH L, et al. Effect of Laser Cleaning on Mechanical Properties of Ultra-Low Carbon Bainitic Steel[J/OL]. Applied Laser, 1-10 [2025-12-19]. [31] ANTONOPOULOU-ATHERA N, KALATHAKIS C, CHATZITHEODORIDIS E, et al. Theoretical and experimental approach on laser cleaning of coins[J]. SN Applied Sciences, 2019, 1(3): 238. doi: 10.1007/s42452-019-0255-4 [32] PELOSI C, FODARO D, SFORZINI L, et al. Study of the laser cleaning on plaster sculptures. The effect of laser irradiation on the surfaces[J]. Optics and Spectroscopy, 2013, 114(6): 917-928. doi: 10.1134/S0030400X13060118 [33] 王伟, 王蔚, 姚天昊, 等. 激光去除碳纤维复合材料表面树脂工艺试验及胶接性能研究[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2025, 54(6): 182-194. doi: 10.3788/IRLA20240556WANG W, WANG W, YAO T H, et al. Experimental study on laser removal of surface resin in carbon fiber composites and adhesive bonding performance[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2025, 54(6): 182-194. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/IRLA20240556 [34] RAUH B, KRELING S, KOLB M, et al. UV-laser cleaning and surface characterization of an aerospace carbon fibre reinforced polymer[J]. International Journal of Adhesion and Adhesives, 2018, 82: 50-59. doi: 10.1016/j.ijadhadh.2017.12.016 [35] 李晨毓, 胡文哲, 张雪雁, 等. 双波长纳秒激光清洗技术在大理石文物上的应用[J]. 中国光学(中英文), 2024, 17(5): 1050-1059. doi: 10.37188/CO.2024-0002LI C L, HU W ZH, ZHANG X Y. Application of dual-wavelength nanosecond laser cleaning technology on stone artifacts[J]. Chinese Optics, 2024, 17(5): 1050-1059. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/CO.2024-0002 [36] 葛春晖, 刘妍君, 年福东, 等. 基于半监督度量学习的激光诱导击穿光谱检测白芍中的重金属含量[J]. 分析化学, 2024, 53(4): 1254-1265. .GE C H, LIU Y J, CHEN M S, et al. Prediction of Wind Turbine Lubricating Oil’s Acid Value by Ordinary Least Square Method Based on Attenuated Total Reflectance-Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy Through Higher-Order Derivative Combined with Angular Metric[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2024, 53(4): 1254-1265. (in Chinese). -





 下载:
下载: