Characterization of multiple scattering effects in dust particles via Mie-T-Matrix coupling and Monte Carlo verification
-
摘要:
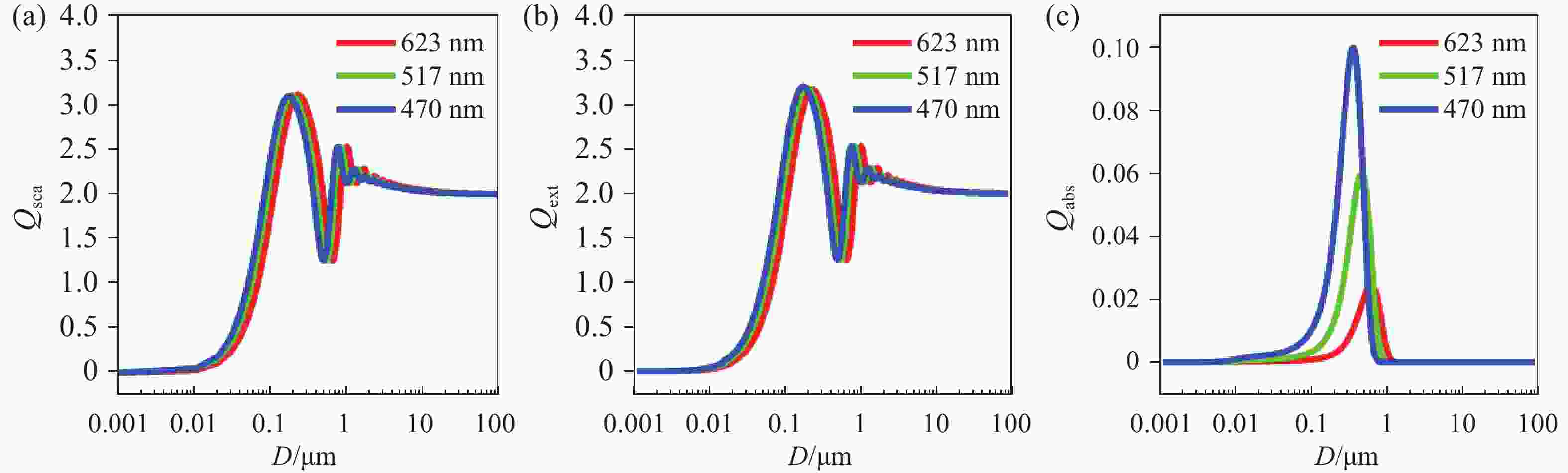
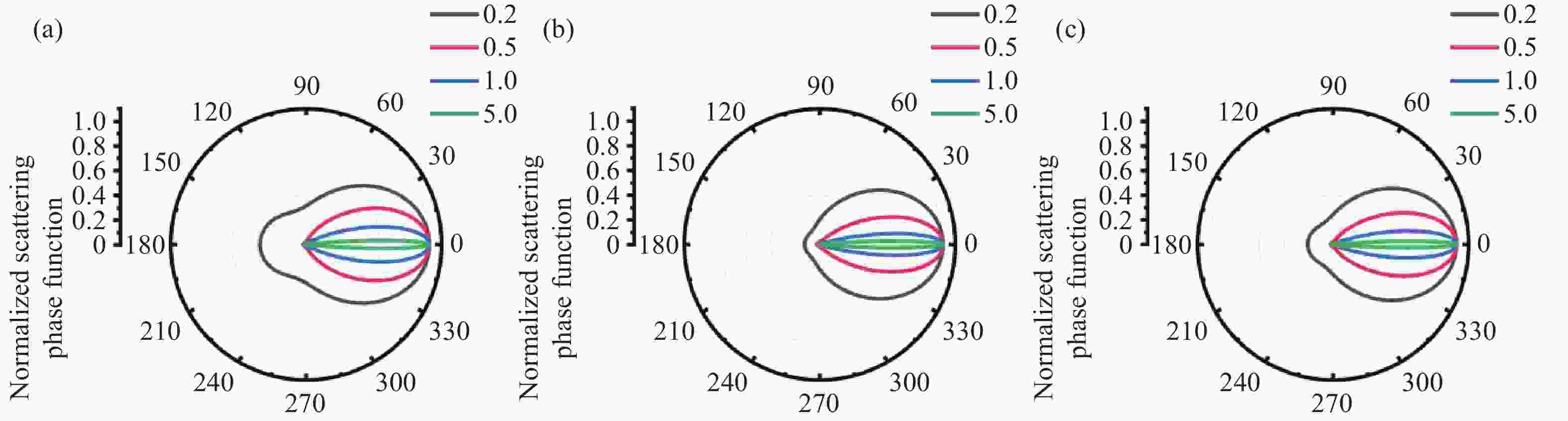
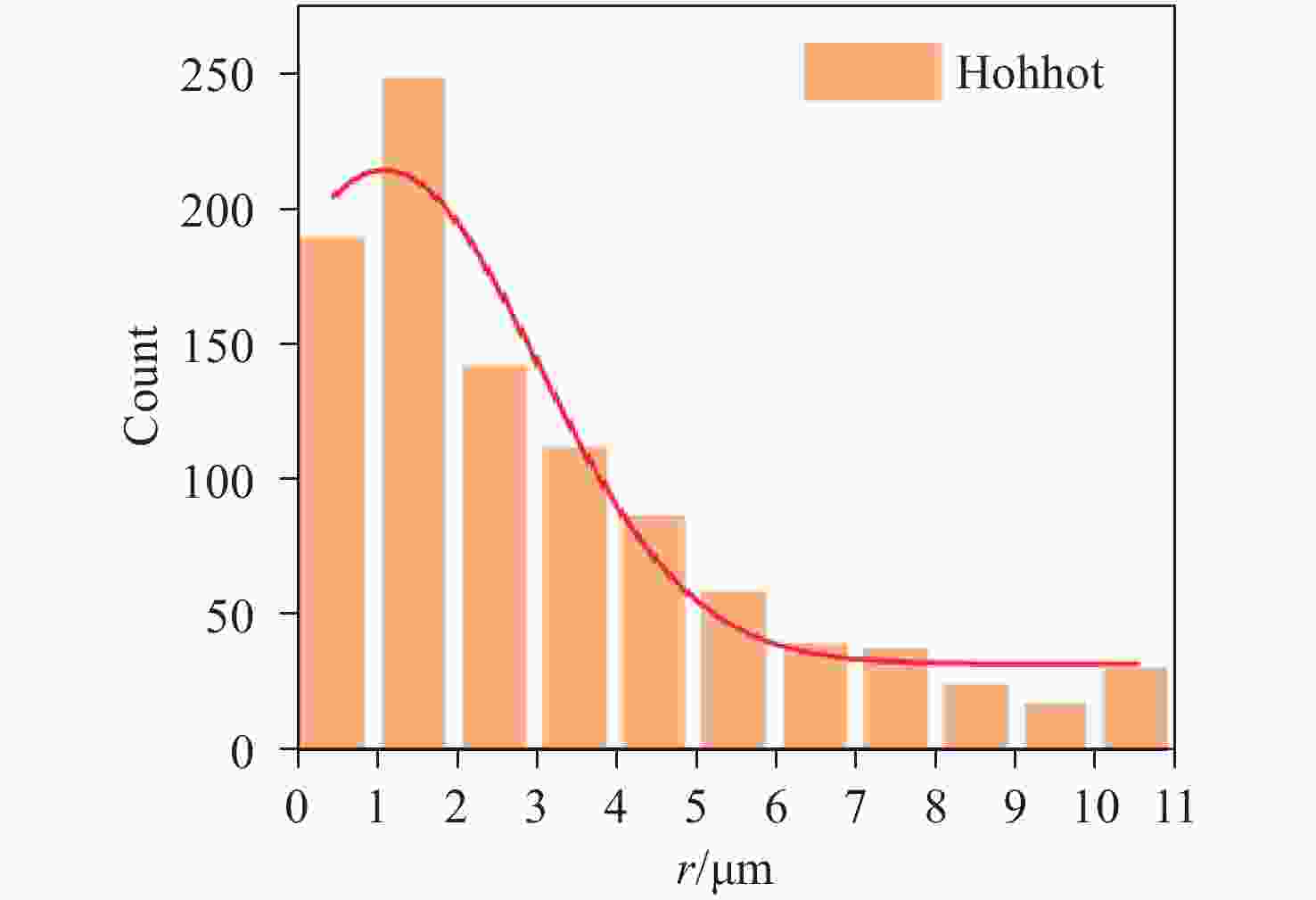
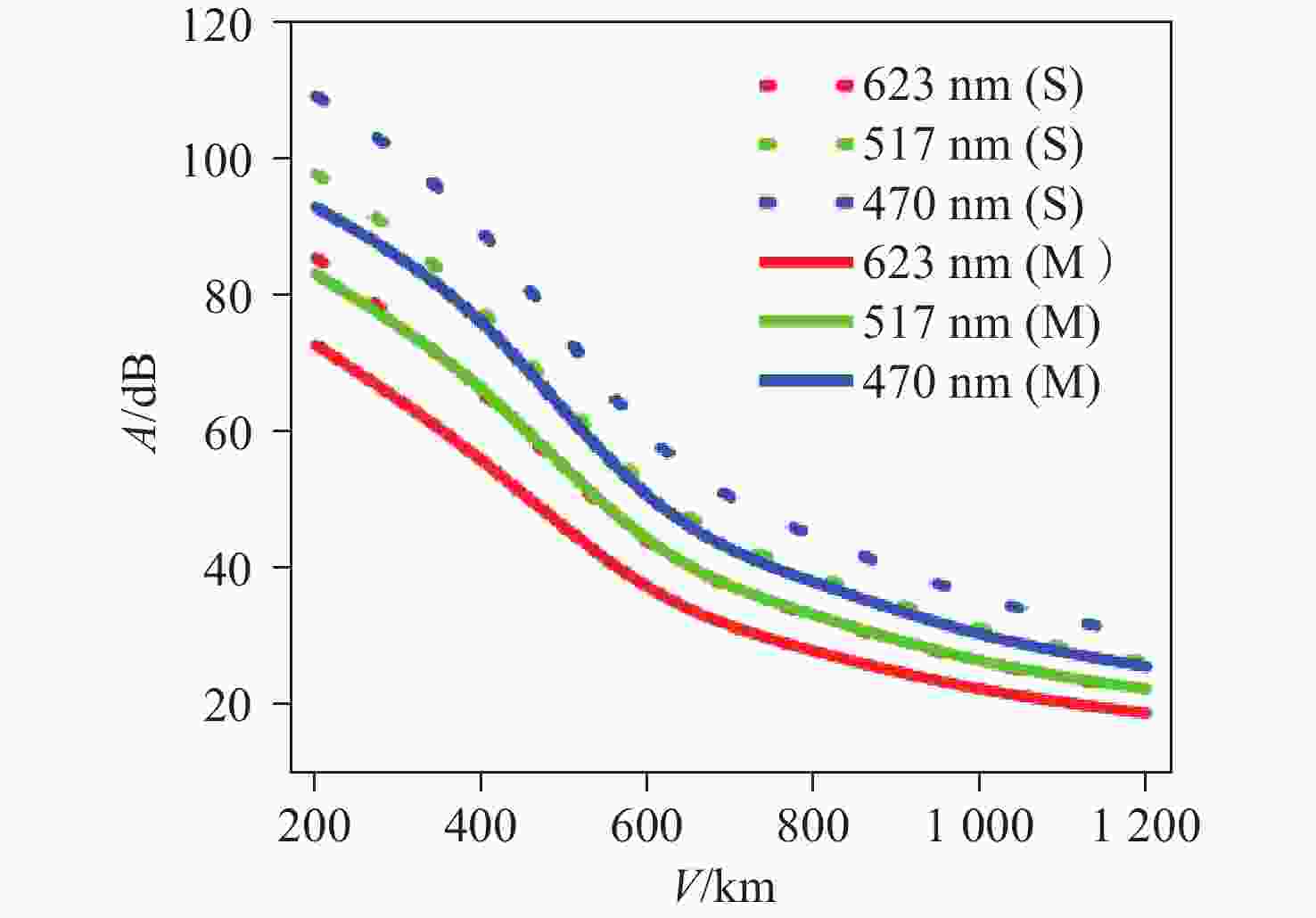
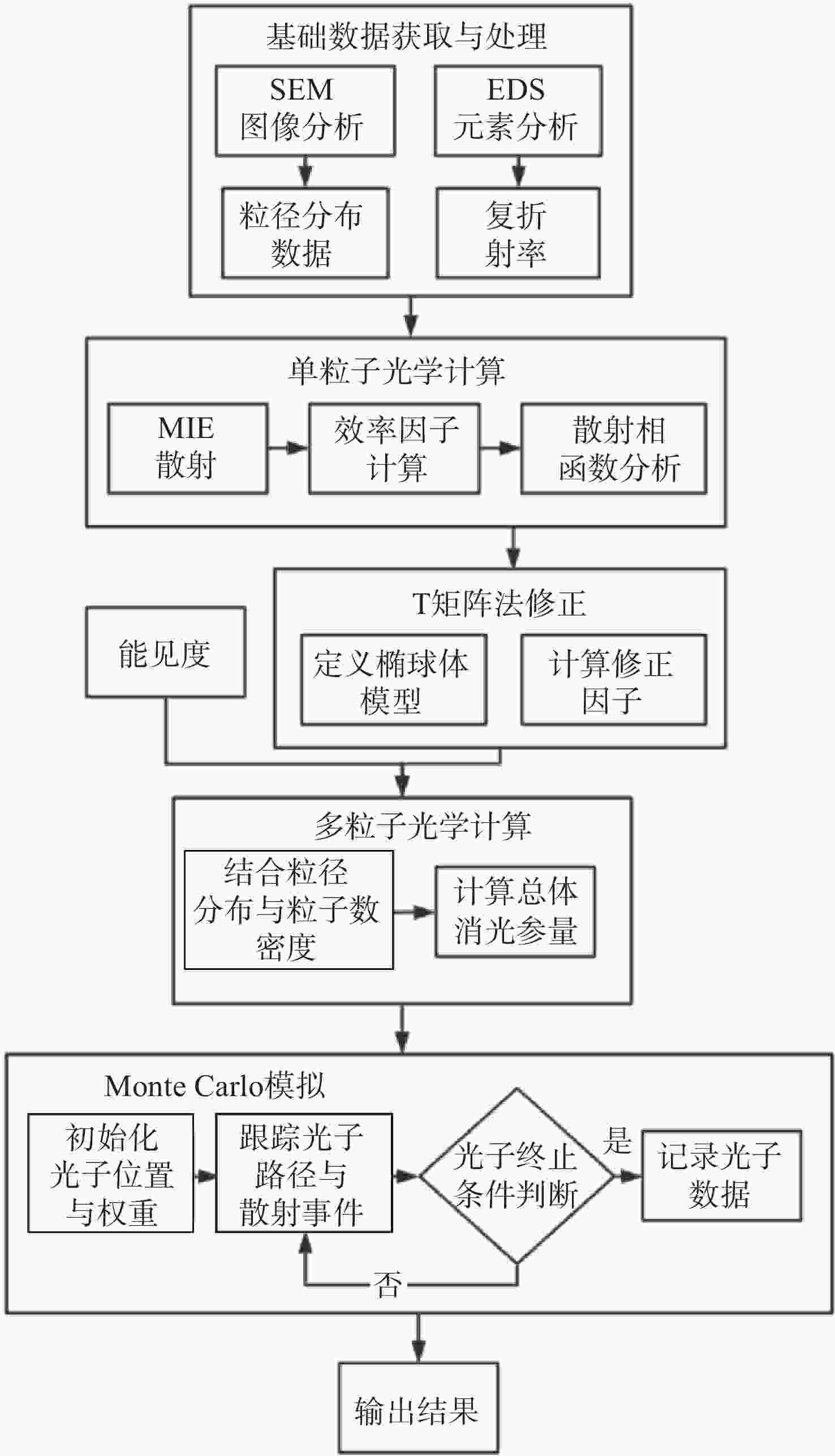
为精确量化沙尘天气对城市光电系统可见光传输的衰减影响,本研究以呼和浩特地区为例,构建了融合非球形粒子修正的光传输预测模型。基于Mie散射理论,结合本地沙尘样品的扫描电镜与能谱分析数据,计算三基色红绿蓝波段的沙尘粒子消光特性;进而采用T矩阵法对非球形粒子的散射参数进行修正,并利用Monte Carlo方法模拟光子的多次散射过程,系统比较单次与多次散射模型下的衰减率差异。结果表明,单次散射模型会系统性高估衰减率,蓝光波段最大误差达18.3%;经多次散射修正后,衰减率平均降低12.4%。在本例中,能见度为400 m,蓝光衰减率约为95 dB/km,显著高于红光的衰减率(约70 dB/km)。本研究构建的混合模型显著提升了沙尘环境下可见光衰减的预测精度,明确多次散射效应的关键影响,为城市光电系统在沙尘天气下的可见光传输提供了可靠的理论依据与数据支持。
Abstract:To accurately quantify the attenuation of visible light in urban optoelectronic systems during dust weather, we establish a predictive model that integrates corrections for non-spherical particles, using the Hohhot region as a case study. Utilizing Mie scattering theory alongside scanning electron microscopy and energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy data from local dust samples, the extinction characteristics of dust particles in typical red green and blue wavebands were calculated. Scattering parameters for non-spherical particles were corrected via the T-matrix method. Photon multiple scattering was then simulated with the Monte Carlo method to systematically compare attenuation rates between single and multiple scattering models. The results demonstrate that the single-scattering model systematically overestimates the attenuation rate, with a maximum error of 18.3% in the blue band. After multiple scattering correction, the attenuation rate decreased by an average of 12.4%. In this case, when the visibility is 400 meters, the attenuation rate for blue light was approximately 95 dB/km, significantly exceeding the value of 70 dB/km for red light. The hybrid model developed significantly enhances the prediction accuracy for visible light attenuation in dusty environments, elucidating the critical roles of multiple scattering effects. This work provides a reliable theoretical and data-driven foundation for optimizing urban optoelectronic systems in dust-prone conditions.
-
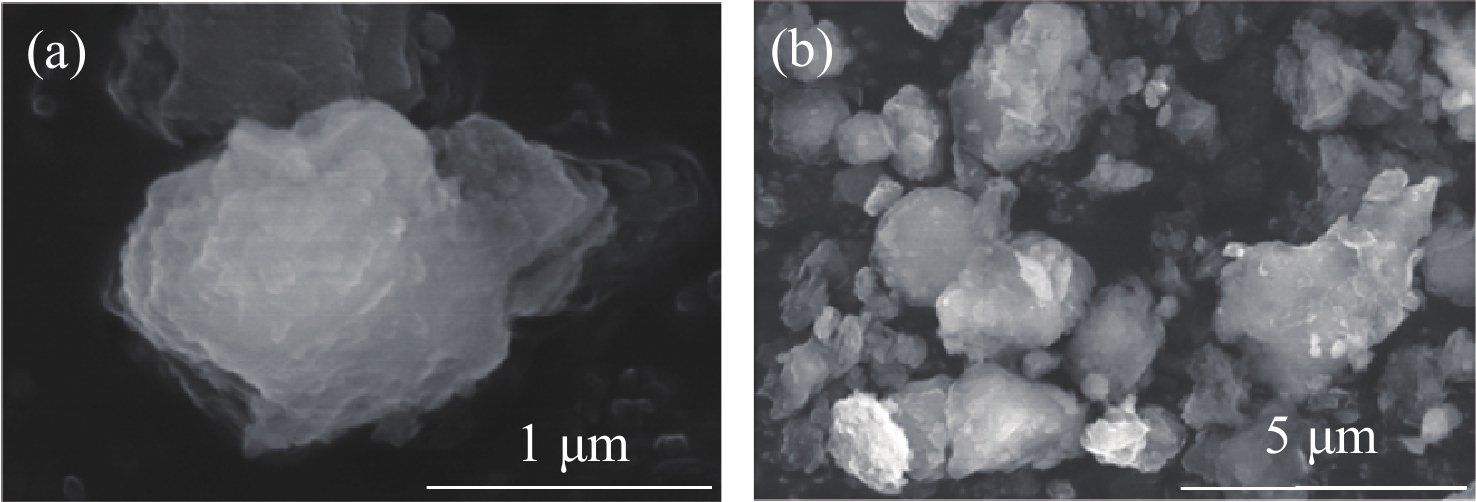
表 1 EDS分析沙尘样本元素组成
Table 1. EDS analysis of the elemental composition of the dust sample
元素 wt% $ {\sigma }_{\text{1}} $ O 58.91 0.08 Si 29.82 0.07 Al 6.10 0.03 Fe 2.56 0.04 Ca 1.73 0.02 K 0.89 0.02 表 2 不同光学能见度下的消光参量
Table 2. Extinction parameter as a function of optical visibility
光学
能见度红光(623 nm) $ \mu $ $ { \omega } $ $ {g} $ 1000 0.055 0.872 0.743 800 0.069 0.867 0.739 600 0.092 0.861 0.734 400 0.138 0.852 0.728 光学
能见度绿光(517nm) $ \mu $ $ { \omega } $ $ {g} $ 1000 0.065 0.858 0.772 800 0.082 0.853 0.768 600 0.109 0.846 0.763 400 0.163 0.837 0.756 光学
能见度蓝光(470 nm) $ \mu $ $ { \omega } $ $ {g} $ 1000 0.075 0.840 0.802 800 0.094 0.834 0.798 600 0.125 0.827 0.793 400 0.187 0.817 0.786 -
[1] MEZAAL M T, ARIPIN N B M, OTHMAN N S, et al. Empirical modelling of dust storm path attenuation for 5G mmWave[J]. Results in Engineering, 2024, 22: 102092. doi: 10.1016/j.rineng.2024.102092 [2] 饶瑞中. 现代大气光学及其应用[J]. 大气与环境光学学报, 2006, 1(1): 2-13.RAO R ZH. Modern atmospheric optics and its applications[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Environmental Optics, 2006, 1(1): 2-13. (in Chinese). [3] 汪杰君, 刘小燕, 张玉婷, 等. 偏振光在气溶胶中的传输特性研究[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2018, 55(8): 080103. doi: 10.3788/LOP55.080103WANG J J, LIU X Y, ZHANG Y T, et al. Transmission characteristics of polarized light in aerosol[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2018, 55(8): 080103. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/LOP55.080103 [4] 高晶, 陈金琪, 石茹琳, 等. 近23 a中国北方强沙尘暴时空分布特征及环流分析[J]. 山地气象学报, 2025, 49(3): 93-98. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6598.2025.03.012GAO J, CHEN J Q, SHI R L, et al. Spatio-temporal distribution characteristics and circulation analysis of strong sandstorms in northern China in the nearly 23 years[J]. Journal of Mountain Meteorology, 2025, 49(3): 93-98. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6598.2025.03.012 [5] 王志楠, 王萌萌, 朱嘉毅. 呼和浩特市沙尘天气预报指标分析[J]. 内蒙古科技与经济, 2025(1): 117-120,129.WANG ZH N, WANG M M, ZHU J Y. Analysis of forecast indicators for sand-dust weather in Hohhot City[J]. Inner Mongolia Science Technology & Economy, 2025(1): 117-120,129. (in Chinese) [6] MÜLLER T, SCHLADITZ A, MASSLING A, et al. Spectral absorption coefficients and imaginary parts of refractive indices of Saharan dust during SAMUM-1[J]. Tellus B: Chemical and Physical Meteorology, 2009, 61(1): 79-95. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0889.2008.00399.x [7] WAGNER R, AJTAI T, KANDLER K, et al. Complex refractive indices of Saharan dust samples at visible and near UV wavelengths: a laboratory study[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 2012, 12(5): 2491-2512. doi: 10.5194/acp-12-2491-2012 [8] 李学彬, 徐青山, 魏合理, 等. 1次沙尘暴天气的消光特性研究[J]. 激光技术, 2008, 32(6): 566-567,575.LI X B, XU Q SH, WEI H L, et al. Extinction character of one sand and dust blowing[J]. Laser Technology, 2008, 32(6): 566-567,575. (in Chinese). [9] 冯倩, 邹斌, 赵崴. 可见光波段非球形沙尘气溶胶散射和辐射特性的理论模拟[J]. 大气与环境光学学报, 2015, 10(1): 1-10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-6141.2015.01.001FENG Q, ZOU B, ZHAO W. Theoretical simulation of scattering and radiative properties of nonspherical dust aerosols at visible wavelength[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Environmental Optics, 2015, 10(1): 1-10. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-6141.2015.01.001 [10] 李曙光, 刘晓东, 侯蓝田, 等. 沙尘暴对大气能见度影响的数值模拟与分析[J]. 应用激光, 2003, 23(2): 87-90. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-372X.2003.02.008LI SH G, LIU X D, HOU L T, et al. Theoretical calculation about influence of sand storm on atmospheric visibility[J]. Applied Laser, 2003, 23(2): 87-90. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-372X.2003.02.008 [11] 孙琦云, 徐军, 高旸, 等. 可见光在不同类型气溶胶中的传输特性[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2018, 55(11): 110103. doi: 10.3788/LOP55.110103SUN Q Y, XU J, GAO Y, et al. Transmission characteristics of visible light in different types of aerosols[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2018, 55(11): 110103. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/LOP55.110103 [12] 王惠琴, 王彦刚, 曹明华, 等. 沙尘天气下大气能见度对激光光强的影响[J]. 光子学报, 2015, 44(2): 0229001. doi: 10.3788/gzxb20154402.0229001WANG H Q, WANG Y G, CAO M H, et al. Impact of atmospheric visibility on laser intensity in sand and dust weather[J]. Acta Photonica Sinica, 2015, 44(2): 0229001. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/gzxb20154402.0229001 [13] 徐强, 王东琴, 吴振森. 大气灰霾高浓度气溶胶光学散射传输特性研究进展[J]. 大气与环境光学学报, 2015, 10(6): 437-444. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-6141.2015.06.001XU Q, WANG D Q, WU ZH S. Research progress of optical scattering transmission properties of haze and other high concentration of atmospheric aerosol[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Environmental Optics, 2015, 10(6): 437-444. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-6141.2015.06.001 [14] MA O J, TIAN Y L, REN Y ZH, et al. Long-term (2017-2020) aerosol optical depth observations in Hohhot city in Mongolian plateau and the impacts from different types of aerosol[J]. Atmosphere, 2022, 13(5): 737. doi: 10.3390/atmos13050737 [15] AHMED A S. Role of particle-size distributions on millimetre-wave propagation in sand/dust storms[J]. IEE Proceedings H (Microwaves, Antennas and Propagation), 1987, 134(1): 55-59. doi: 10.1049/ip-h-2.1987.0011 [16] 王鹏程, 张肃, 申成彪, 等. 偏振光在椭球细粒子中多次散射传输特性[J]. 中国光学(中英文), 2023, 16(2): 348-357. doi: 10.37188/CO.2022-0144WANG P CH, ZHANG S, SHEN CH B, et al. Multiple scattering transmission characteristic of polarized light in ellipsoidal fine particles[J]. Chinese Optics, 2023, 16(2): 348-357. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/CO.2022-0144 [17] 宗思光, 张鑫, 杨劭鹏, 等. 舰船尾流气泡目标激光后向散射特性研究[J]. 中国光学(中英文), 2023, 16(6): 1333-1342.ZONG S G, ZHANG X, YANG S P, et al. Laser backscattering characteristics of ship wake bubble targets[J]. Chinese Journal of Optics, 2023, 16(6): 1333-1342. (in Chinese). [18] 陈洁, 童奕澄, 肖达, 等. 大气气溶胶消光后向散射比反演方法研究[J]. 中国光学(中英文), 2021, 14(6): 1305-1316.CHEN J, TONG Y C, XIAO D, et al. Retrieval method of extinction-to-backscatter ratio for atmospheric aerosols[J]. Chinese Journal of Optics, 2021, 14(6): 1305-1316. (in Chinese). [19] BI L, YANG P, KATTAWAR G W, et al. Efficient implementation of the invariant imbedding T-matrix method and the separation of variables method applied to large nonspherical inhomogeneous particles[J]. Journal of Quantitative Spectroscopy and Radiative Transfer, 2013, 116: 169-183. doi: 10.1016/j.jqsrt.2012.11.014 [20] PAN H L, HUANG J, KUMAR K R, et al. The CALIPSO retrieved spatiotemporal and vertical distributions of AOD and extinction coefficient for different aerosol types during 2007-2019: a recent perspective over global and regional scales[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2022, 274: 118986. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2022.118986 [21] BI L, YANG P. Accurate simulation of the optical properties of atmospheric ice crystals with the invariant imbedding T-matrix method[J]. Journal of Quantitative Spectroscopy and Radiative Transfer, 2014, 138: 17-35. doi: 10.1016/j.jqsrt.2014.01.013 [22] LODGE M G, WAKEFORD H R, LEINHARDT Z M. Aerosols are not spherical cows: using discrete dipole approximation to model the properties of fractal particles[J]. Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 2024, 527(4): 11113-11137. [23] 何欣波, 魏兵. 基于悬挂变量的显式无条件稳定时域有限差分亚网格算法[J]. 物理学报, 2024, 73(8): 080202. doi: 10.7498/aps.73.20231813HE X B, WEI B. Explicit and unconditionally stable finite-difference time-domain subgridding algorithm based on hanging variables[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2024, 73(8): 080202. (in Chinese). doi: 10.7498/aps.73.20231813 [24] 郭旭, 胡春晖, 颜昌翔, 等. 基于蒙特卡罗法的星载太阳辐照度光谱仪对日指向误差分析[J]. 光学精密工程, 2021, 29(3): 474-483.GUO X, HU C H, YAN C X, et al. Analysis of sun-pointing error for spaceborne solar irradiance spectrometer based on Monte Carlo method[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2021, 29(3): 474-483. (in Chinese). [25] 张合勇, 王挺峰, 邵俊峰, 等. 基于Mie散射的CO2激光大气传输特性测量[J]. 中国光学与应用光学, 2010, 3(4): 353-362. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1531.2010.04.008ZHANG H Y, WANG T F, SHAO J F, et al. Measurement of CO2 laser atmospheric transmission property based on Mie scattering[J]. Chinese Journal of Optics and Applied Optics, 2010, 3(4): 353-362. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1531.2010.04.008 [26] 王鹏程, 张肃, 申成彪, 等. 偏振光在椭球细粒子中多次散射传输特性[J]. 中国光学(中英文), 2023, 16(02): 348-357.WANG P C, ZHANG S, SHEN C B, et al. Multiple scattering transmission characteristics of polarized light in ellipsoidal fine particles[J]. Chinese Journal of Optics, 2023, 16(02): 348-357. (in Chinese). [27] 陈鹏, 赵继广, 杜小平, 等. 基于粒子群优化的近似散射相函数拟合方法[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2019, 48(12): 120300.CHEN P, ZHAO J G, DU X P, et al. Approximate scattering phase function fitting method based on particle swarm optimization[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2019, 48(12): 120300. (in Chinese). -





 下载:
下载: