Study on the transmission characteristics of Silicon-Based grating-type fabry-perot-microring coupled resonators
-
摘要:
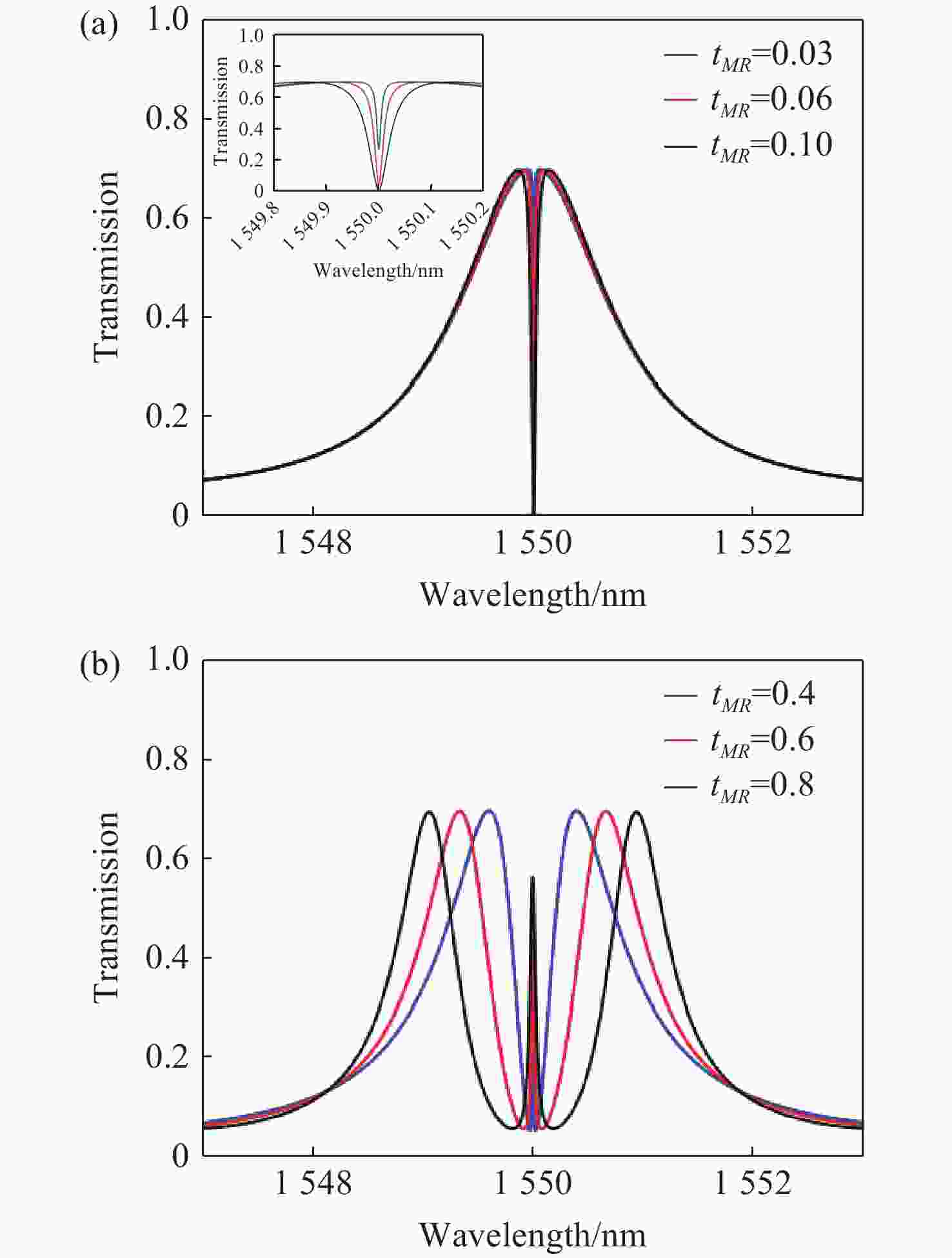
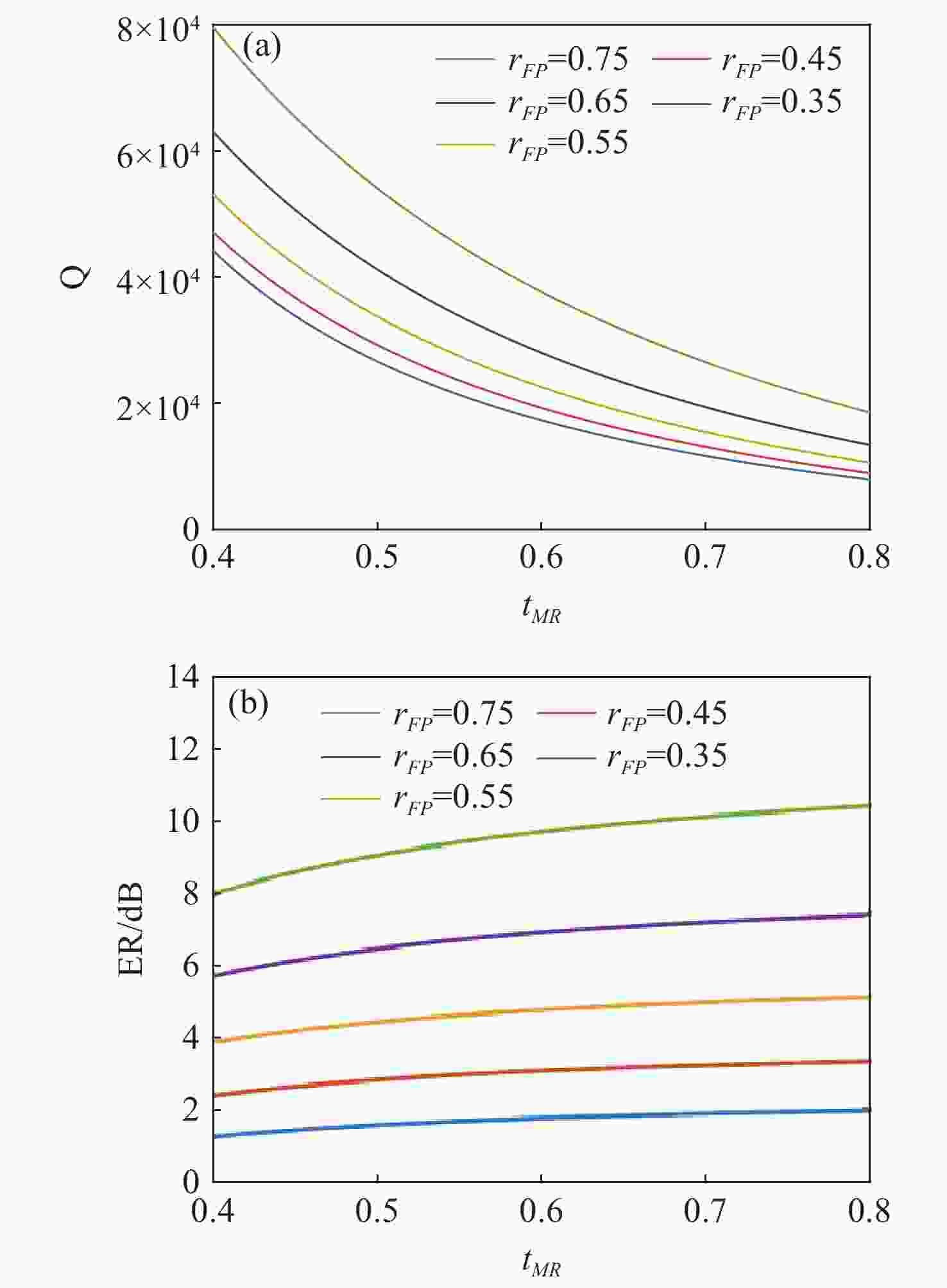
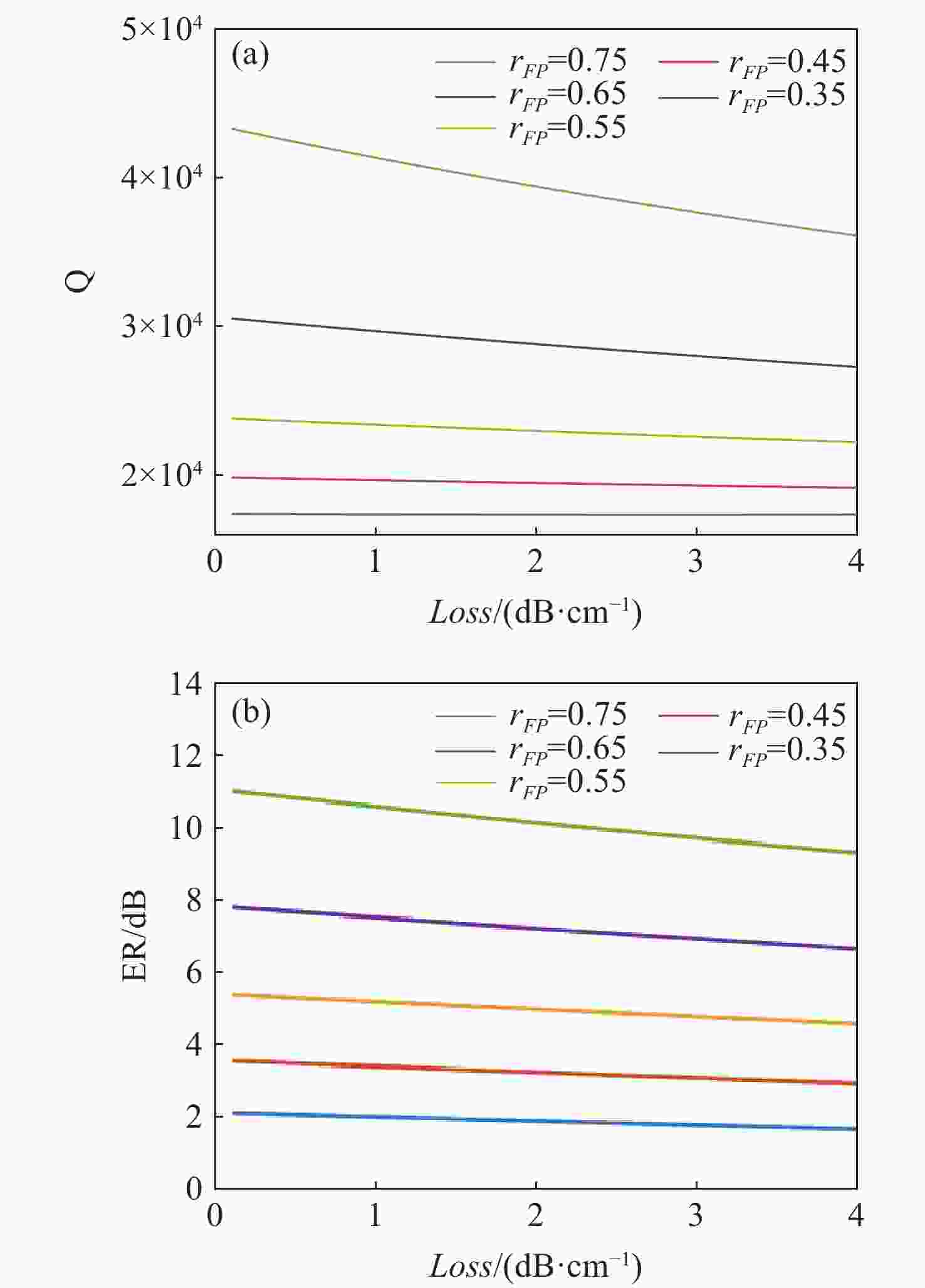
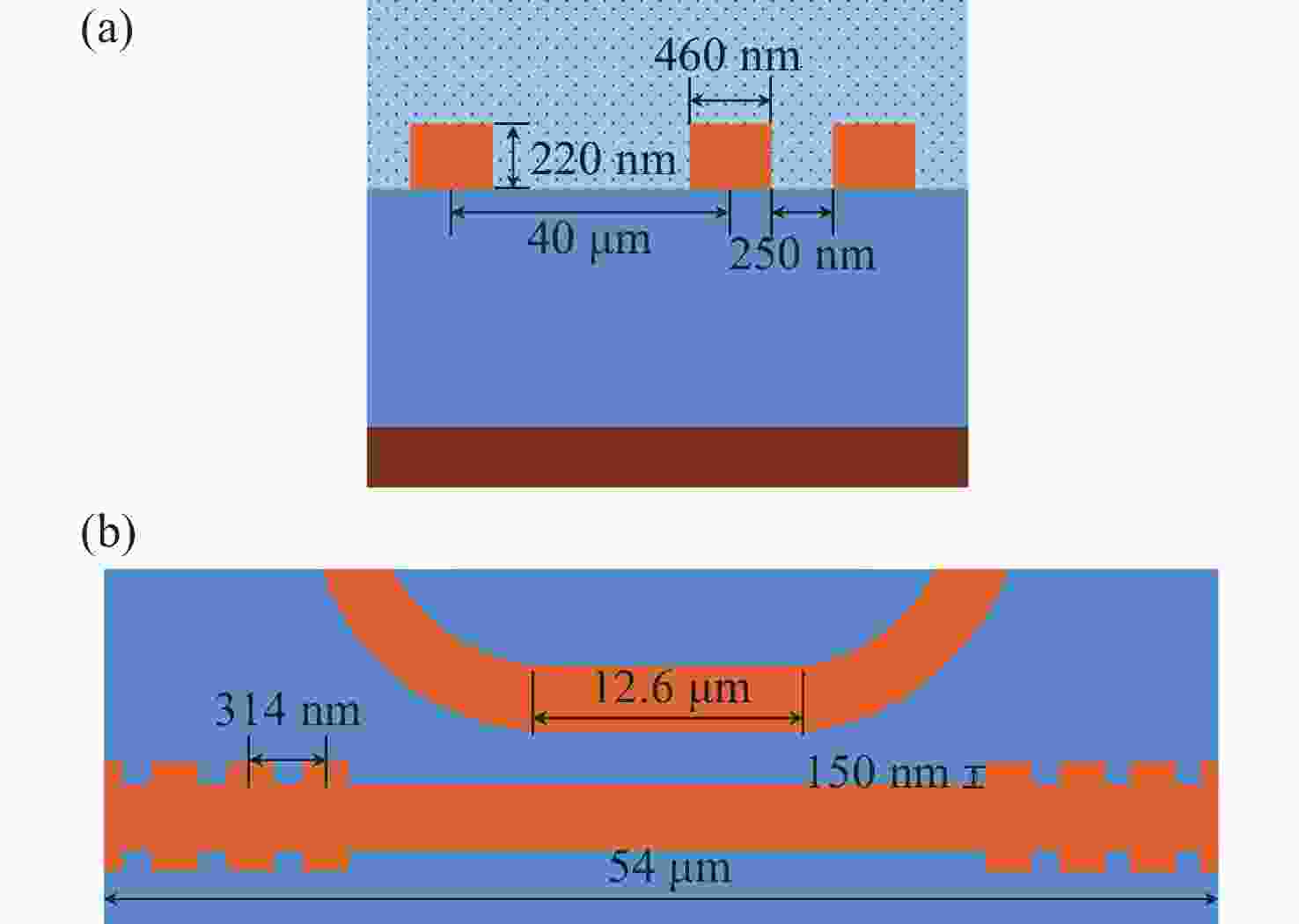
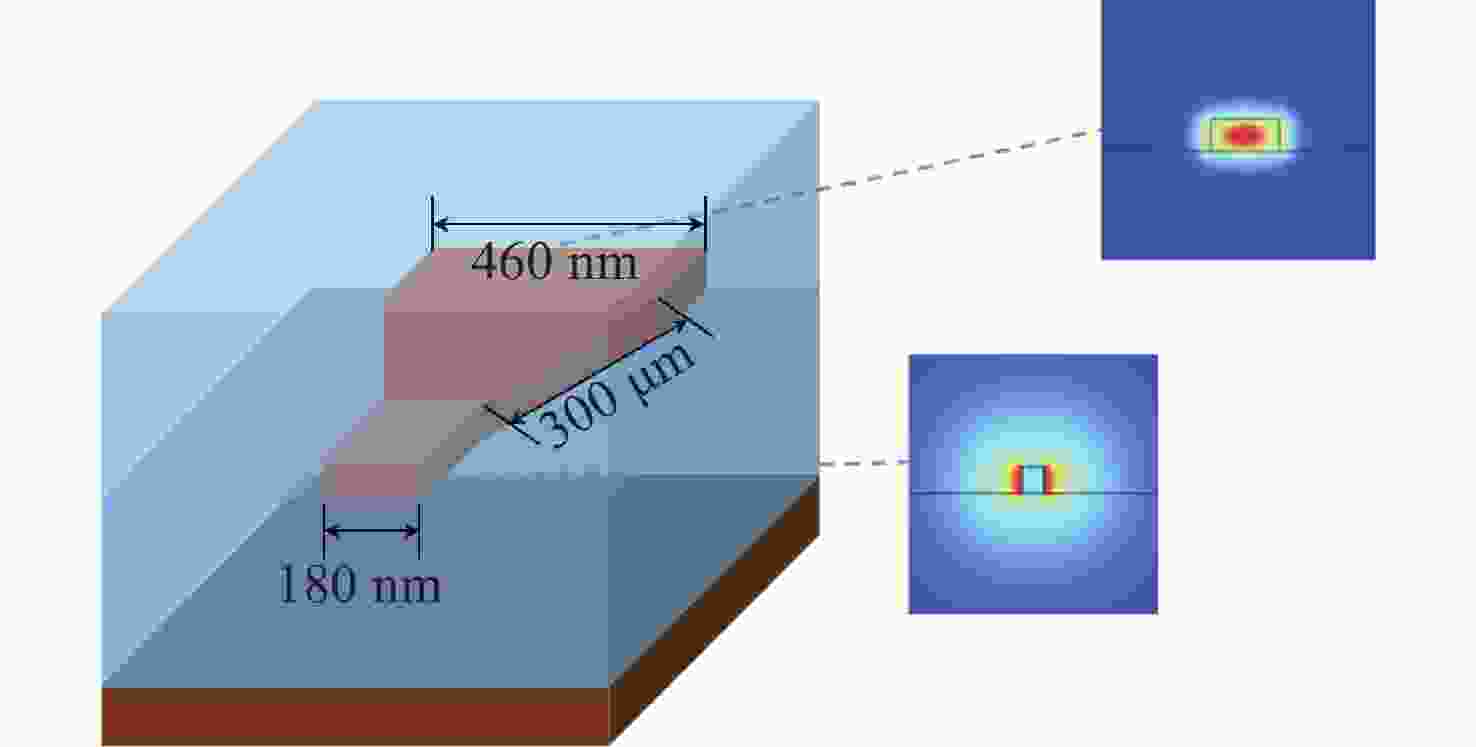
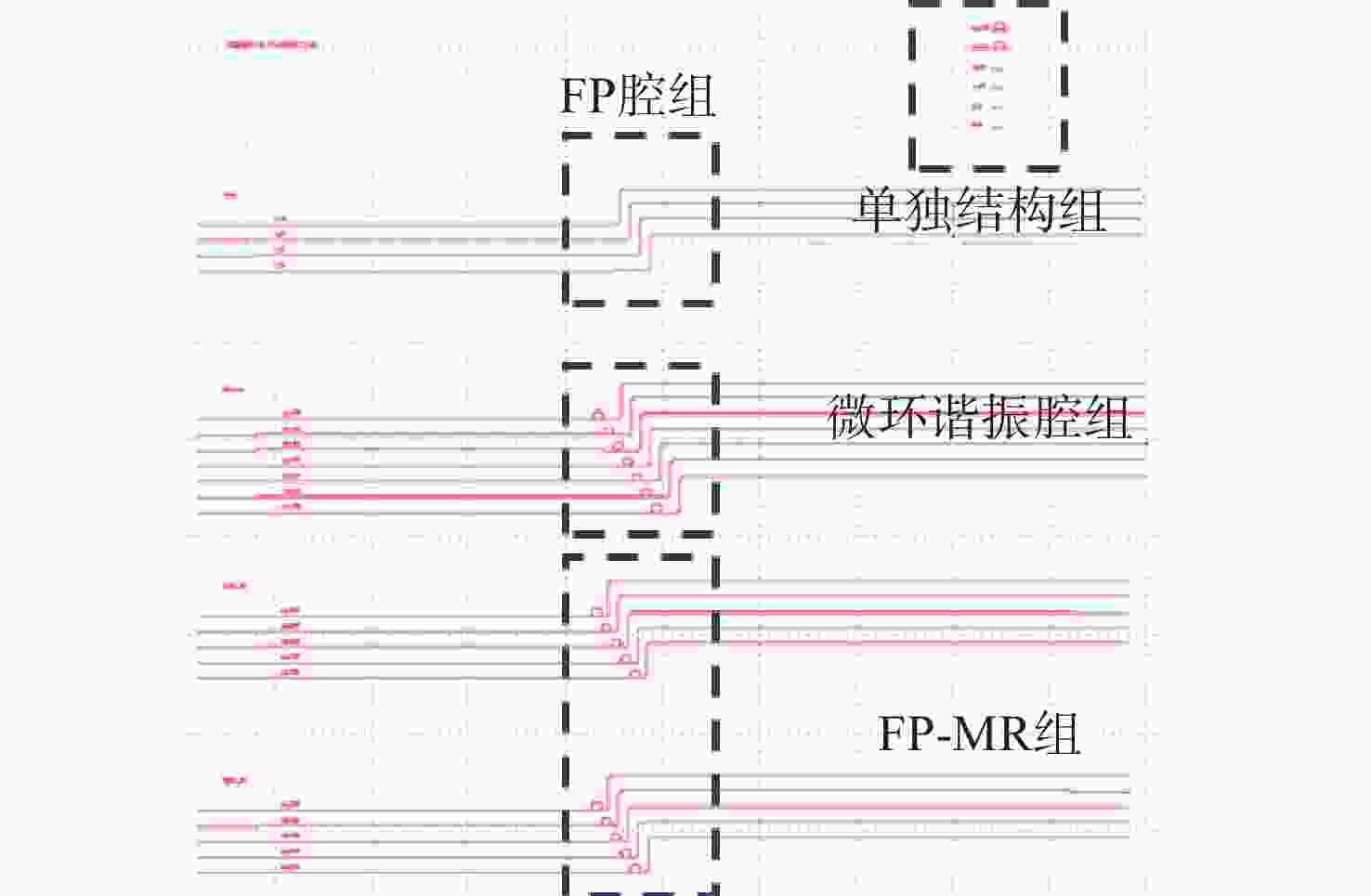
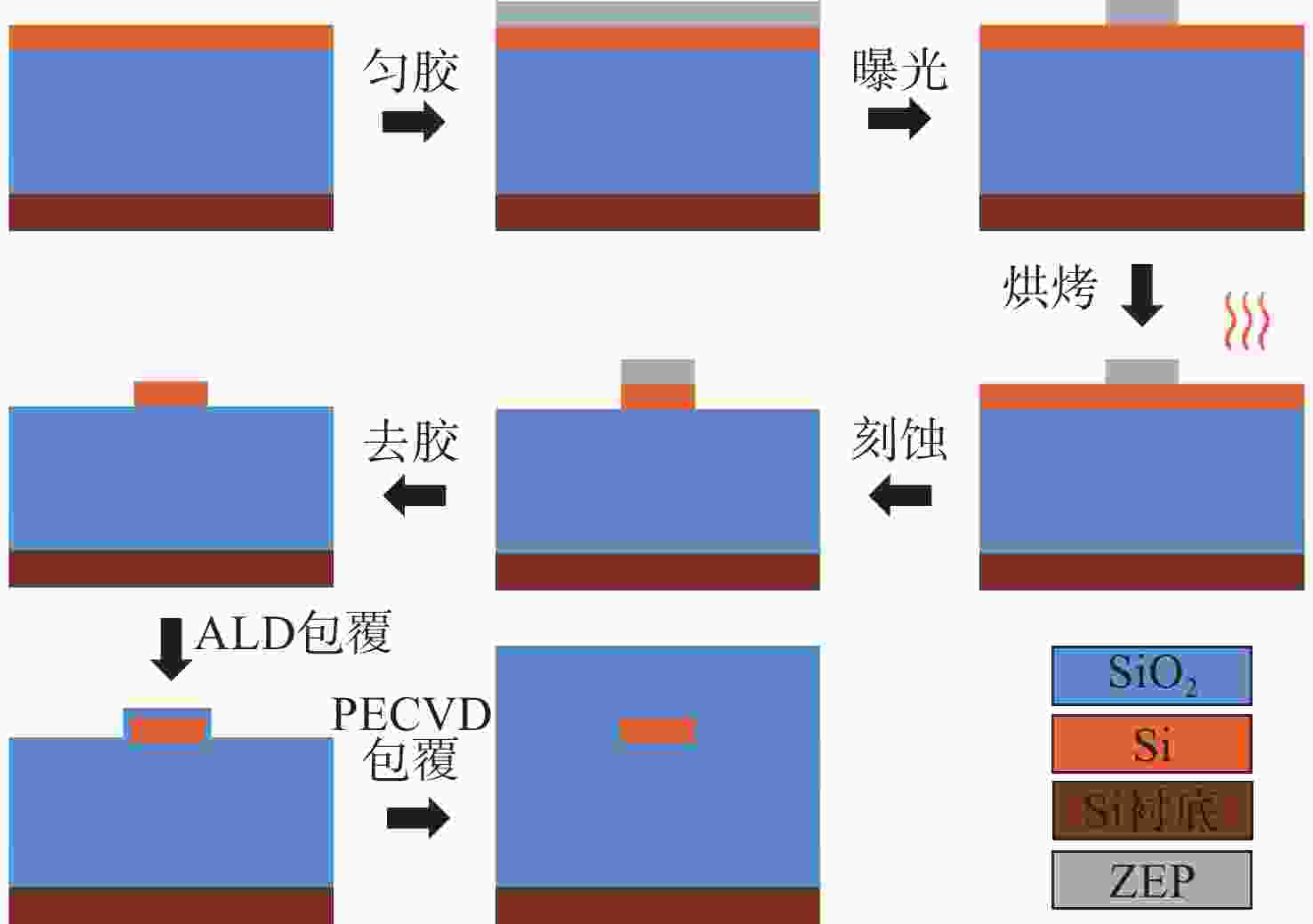
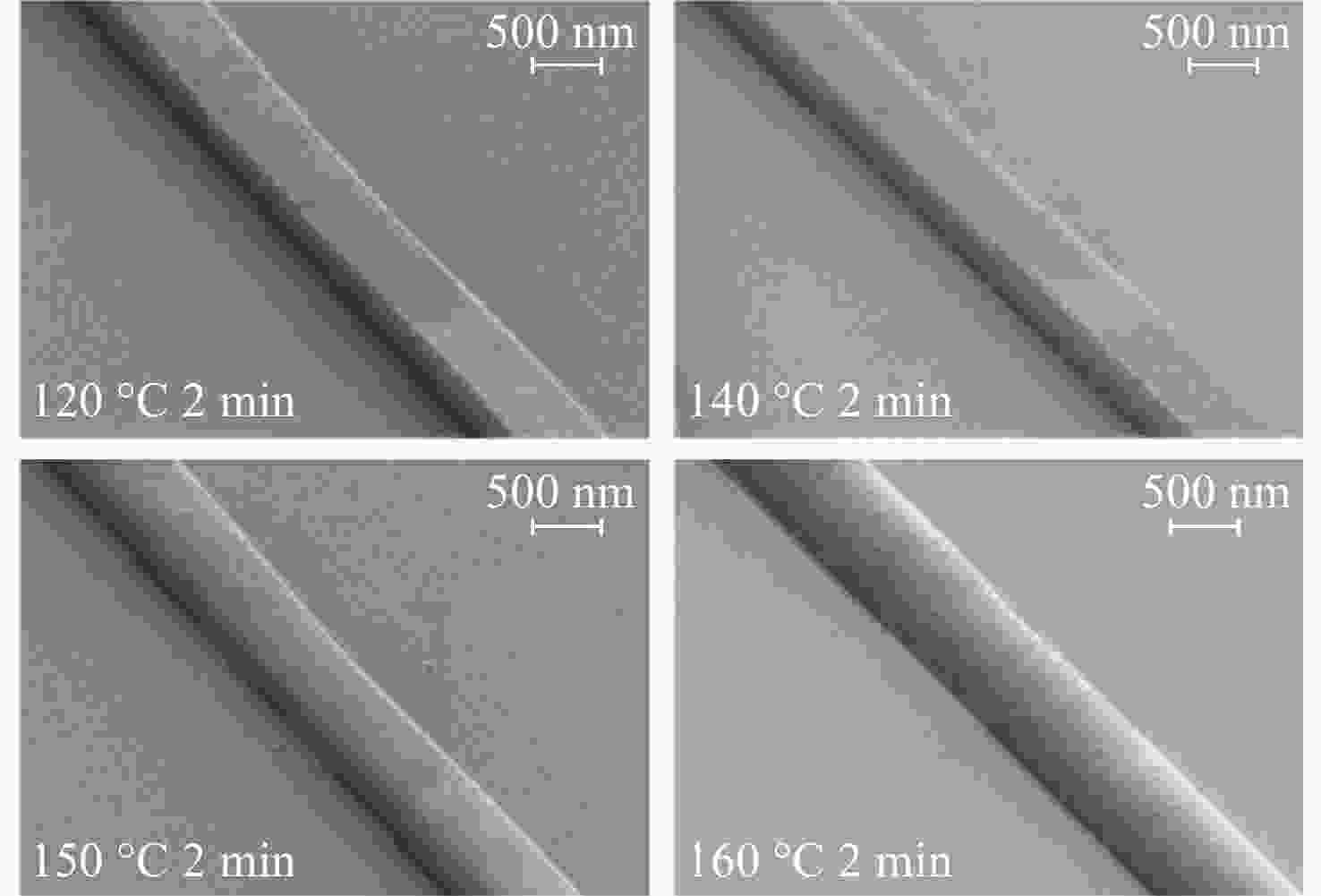
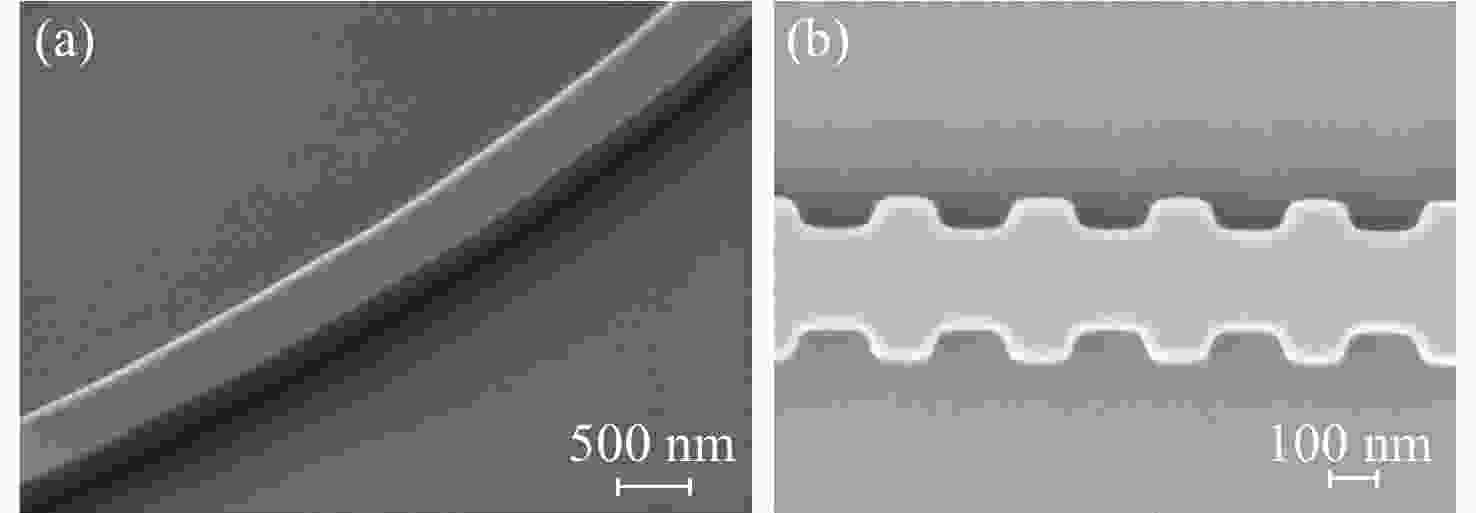
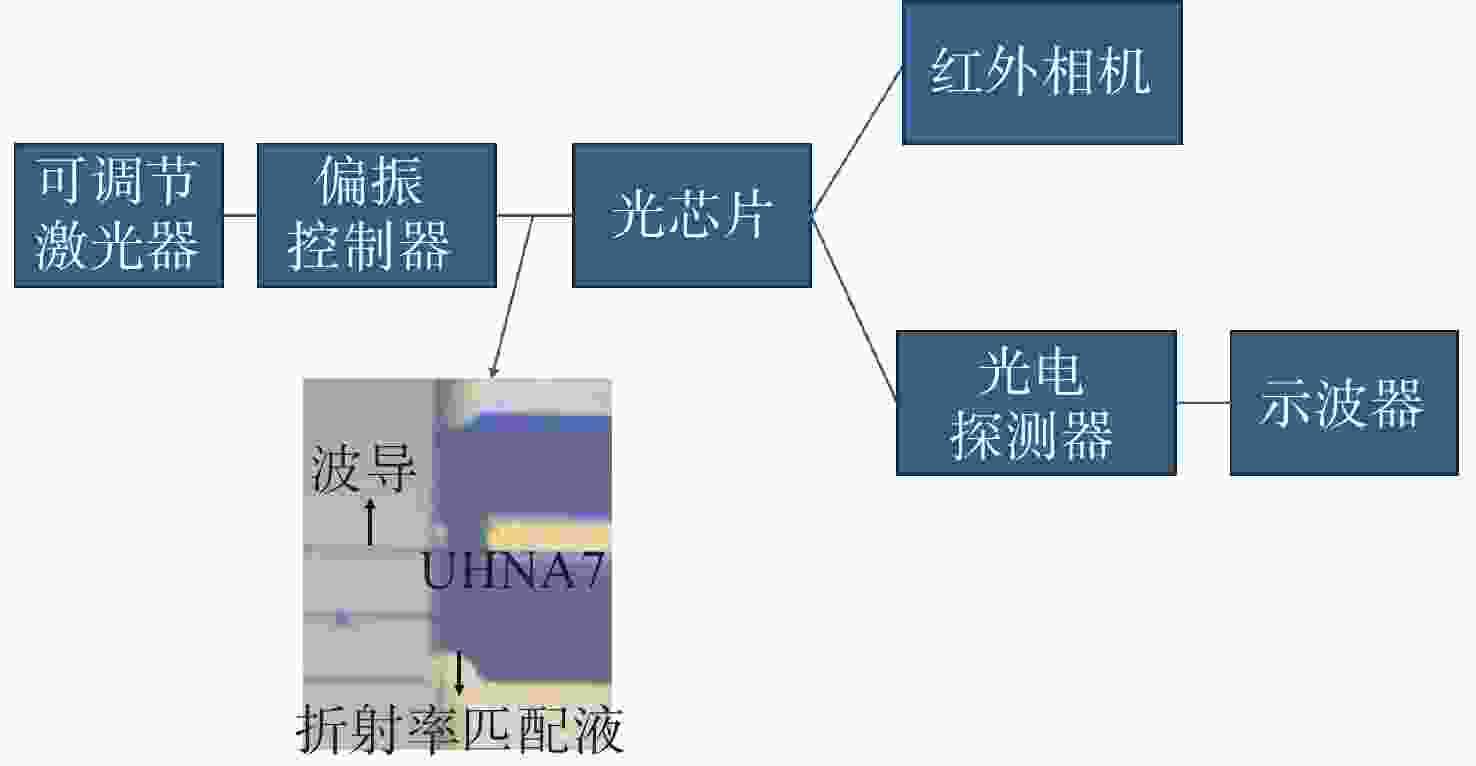
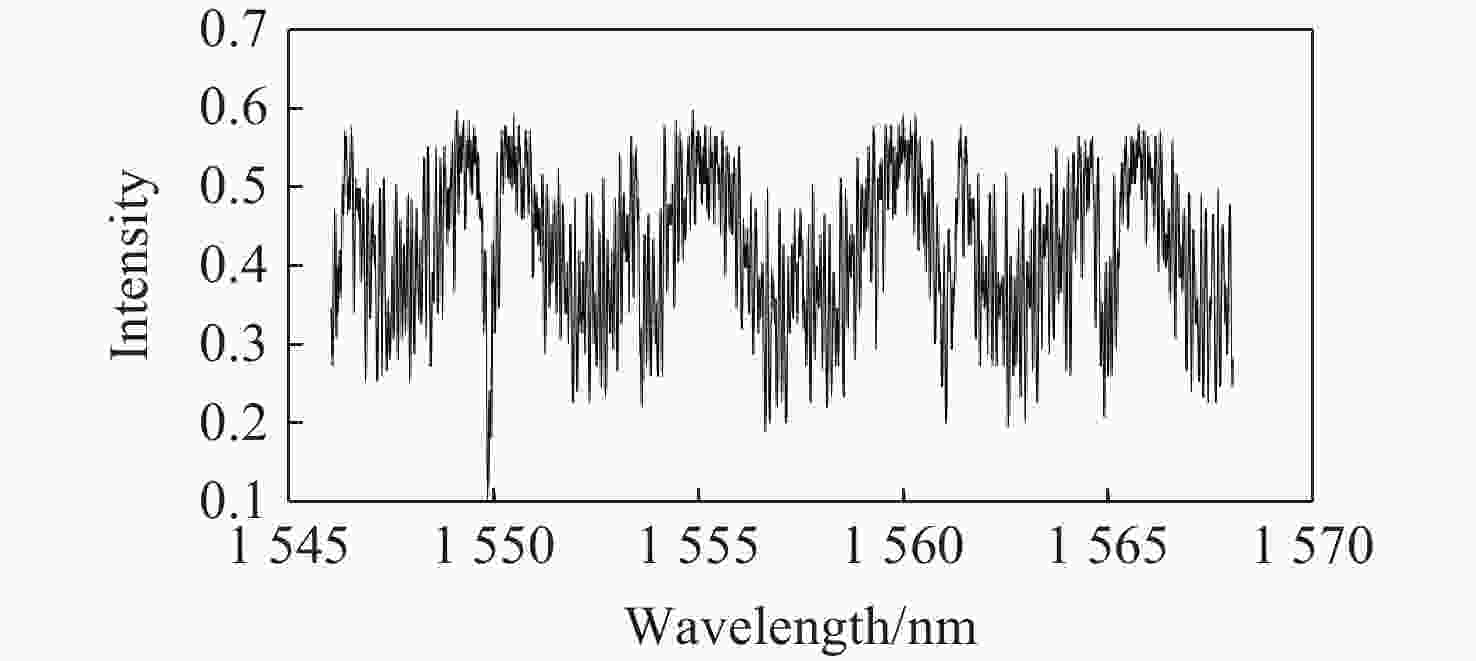
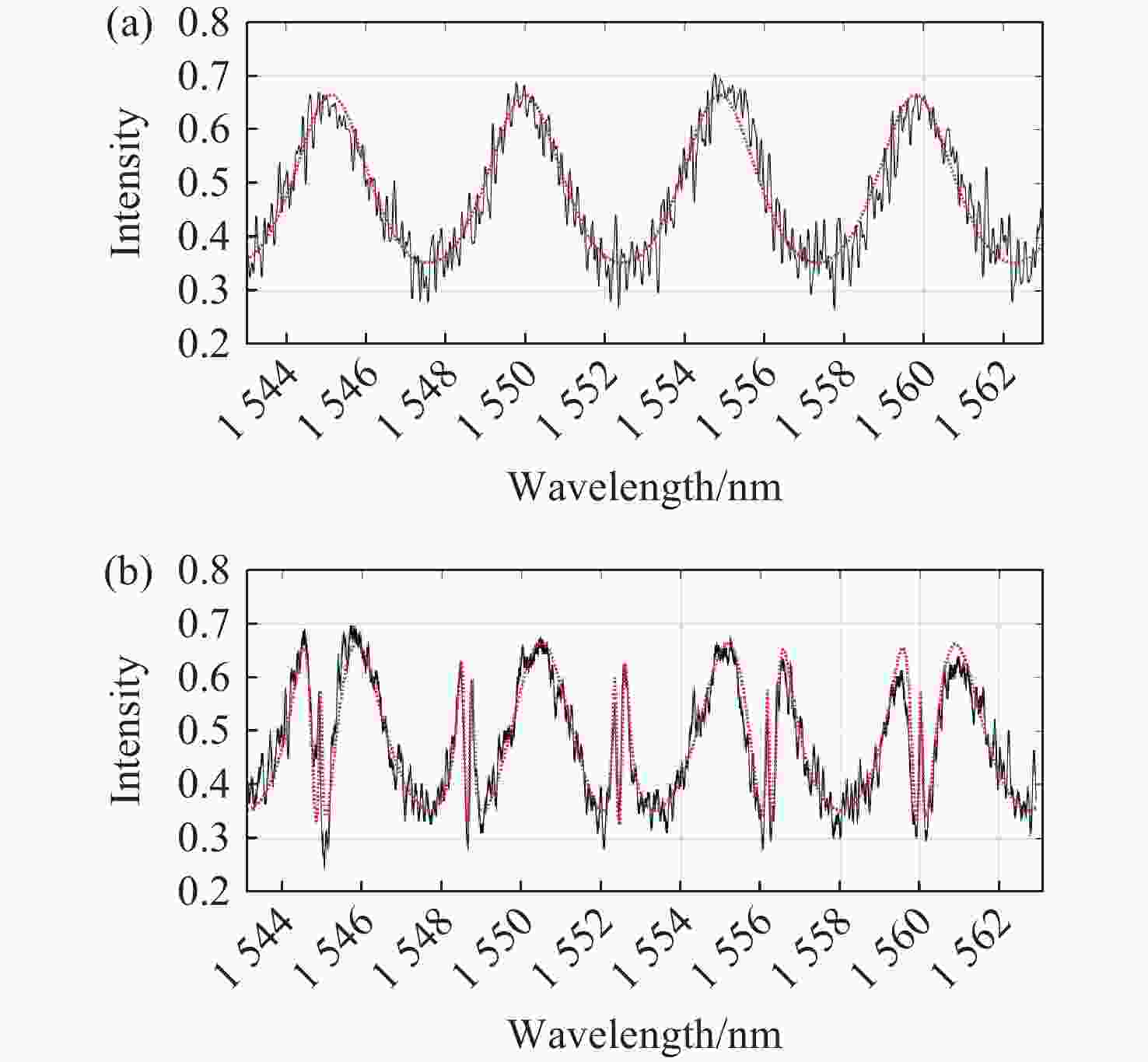
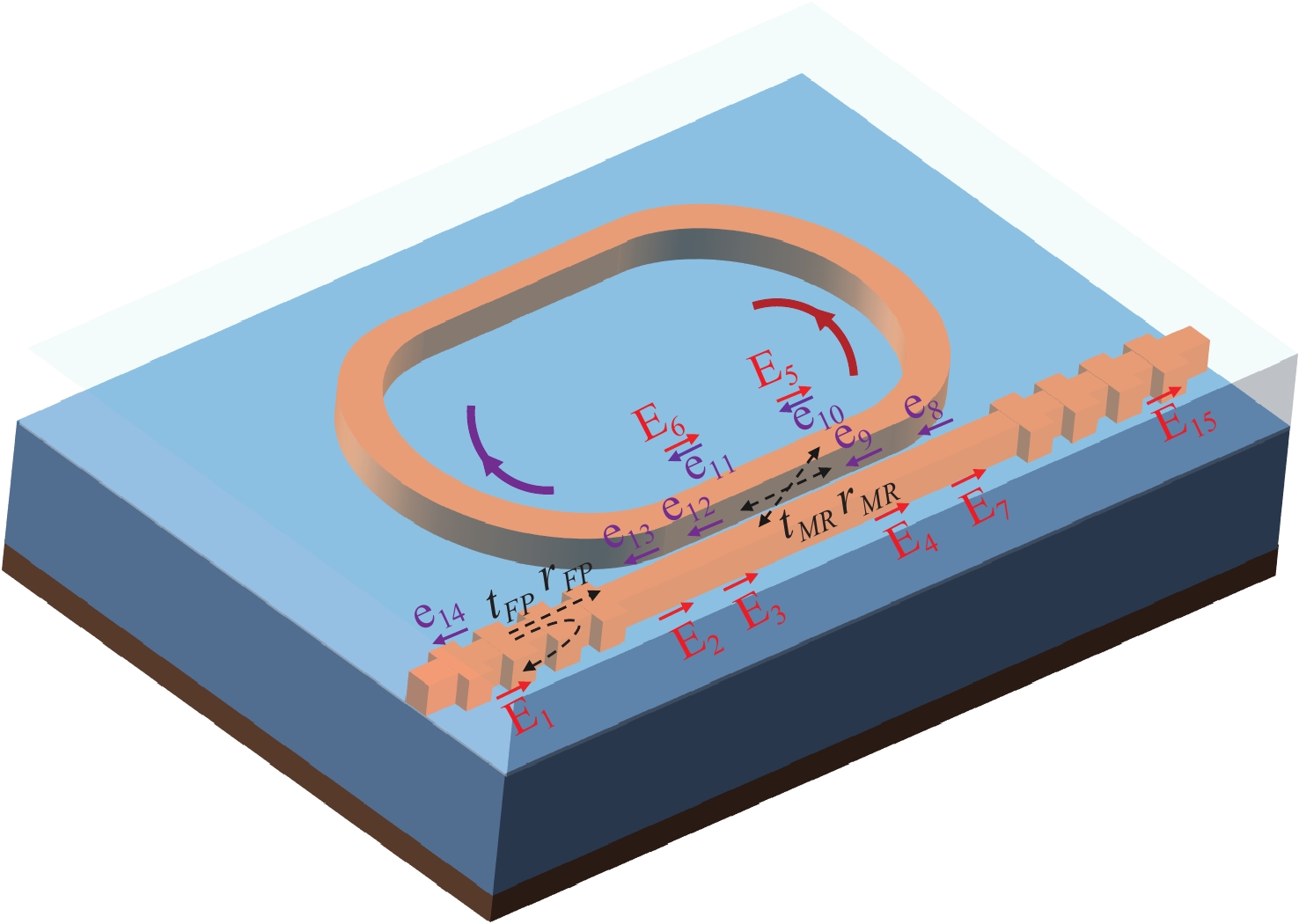
本文针对一种由微环谐振腔与法布里-珀罗腔耦合构成的集成结构,开展了传输光谱特性的理论与实验研究。该结构通过在单边耦合型微环的直波导中引入光栅反射镜形成法布里-珀罗腔,在双谐振结构中实现了新颖的多腔耦合传输谱形。成功建立系统理论模型后,分析了多腔耦合传输谱形出现的条件并进行了器件参数优化。在硅基芯片上成功制备了光栅型法布里珀罗-微环耦合谐振腔器件,首次观测到与理论预测一致的多腔耦合传输谱形,包括嵌套类电磁感应透明和双法诺共振线形。实验结果表明,在3.43 dB/cm的波导损耗条件下,电磁感应透明的中心峰可实现1.40×104的品质因子,双法诺共振的斜率最高可达到37.70 dB/nm。研究结果为集成光子耦合谐振系统的机理理解提供了新视角,并为实现高集成度、高性能的光子器件平台提供了可行技术路径,在高灵敏光学传感、窄带滤波及高速调制等领域具有重要的应用潜力。
Abstract:This paper presents comprehensive theoretical and experimental investigations on the transmission spectral characteristics of an integrated photonic structure consisting of a microring resonator coupled with a Fabry–Perot (FP) cavity. The FP cavity is realized by introducing a grating reflector into the straight waveguide of a single-side-coupled microring. Within this dual-resonator configuration, novel multi-cavity coupled transmission spectra are achieved. A systematic theoretical model is established to analyze the conditions under which these multi-cavity coupled spectral profiles appear, and the structural parameters are subsequently optimized. A grating-type Fabry–Perot–microring coupled resonator device was successfully fabricated on a silicon-on-insulator (SOI) platform. For the first time, multi-cavity coupled transmission spectra consistent with theoretical predictions were experimentally observed, including nested electromagnetically induced transparency (EIT)-like and double Fano resonance line shapes. Experimental measurements indicate that, under a waveguide loss of 3.43 dB/cm, the EIT central peak exhibits a quality factor of 1.40×104, while the slope of the double Fano resonance reaches 37.70 dB/nm. These results provide new insight into the underlying mechanisms of integrated photonic coupled resonator systems and demonstrate a viable approach toward highly integrated, high-performance photonic device platforms. The proposed structure shows strong potential for applications in high-sensitivity optical sensing, narrowband filtering, and high-speed modulation.
-
-
[1] JALALI B, FATHPOUR S. Silicon photonics[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2006, 24(12): 4600-4615. doi: 10.1109/JLT.2006.885782 [2] SHEKHAR S, BOGAERTS W, CHROSTOWSKI L, et al. Roadmapping the next generation of silicon photonics[J]. Nature Communications, 2024, 15(1): 751. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-44750-0 [3] SIEW S Y, LI B, GAO F, et al. Review of silicon photonics technology and platform development[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2021, 39(13): 4374-4389. doi: 10.1109/JLT.2021.3066203 [4] BOGAERTS W, DE HEYN P, VAN VAERENBERGH T, et al. Silicon microring resonators[J]. Laser & Photonics Reviews, 2012, 6(1): 47-73. doi: 10.1002/lpor.201100017 [5] YAO ZH SH, WU K Y, TAN B X, et al. Integrated silicon photonic microresonators: emerging technologies[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Quantum Electronics, 2018, 24(6): 5900324. [6] LI X Y, XIONG X Zh, SONG Y, et al. High-performance refractive index sensing based on Fano resonances in a subwavelength grating waveguide microring resonator[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2025, 43(15): 7407-7414. doi: 10.1109/JLT.2025.3569796 [7] ZHANG Q N, WU K Y, POON A W, et al. Polarization entanglement generation in silicon nitride waveguide-coupled dual microring resonators[J]. Optics Express, 2024, 32(13): 22804-22816. doi: 10.1364/OE.518985 [8] XIAO SH J, KHAN M H, SHEN H, et al. Multiple-channel silicon micro-resonator based filters for WDM applications[J]. Optics Express, 2007, 15(12): 7489-7498. doi: 10.1364/oe.15.007489 [9] DAI T G, SHEN A, WANG G CH, et al. Bandwidth and wavelength tunable optical passband filter based on silicon multiple microring resonators[J]. Optics Letters, 2016, 41(20): 4807-4810. doi: 10.1364/OL.41.004807 [10] CHAN D W U, WU X, ZHANG Z Y, et al. C-band 67-GHz silicon photonic microring modulator for dispersion-uncompensated 100-Gbaud PAM-4[J]. Optics Letters, 2022, 47(11): 2935-2938. doi: 10.1364/OL.460602 [11] CHAN D W U, TSANG H K. Sub-volt forward-biased silicon microring modulator at 210 Gb/s[J]. Optics Letters, 2024, 49(22): 6477-6480. doi: 10.1364/OL.535202 [12] YAN H, HUANG L J, XU X CH, et al. Unique surface sensing property and enhanced sensitivity in microring resonator biosensors based on subwavelength grating waveguides[J]. Optics Express, 2016, 24(26): 29724-29733. doi: 10.1364/OE.24.029724 [13] YANG M X, HAN SH SH, GAO H X, et al. High-sensitivity and wide-range refractive index sensing based on the envelope spectrum of the subwavelength grating waveguide racetrack microring resonator[J]. Optics Letters, 2024, 49(19): 5603-5606. doi: 10.1364/OL.536732 [14] PITRIS S, MITSOLIDOU C, MORALIS-PEGIOS M, et al. 400 Gb/s silicon photonic transmitter and routing WDM technologies for glueless 8-socket chip-to-chip interconnects[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2020, 38(13): 3366-3375. doi: 10.1109/JLT.2020.2977369 [15] XIA F N, ROOKS M, SEKARIC L, et al. Ultra-compact high order ring resonator filters using submicron silicon photonic wires for on-chip optical interconnects[J]. Optics Express, 2007, 15(19): 11934-11941. doi: 10.1364/oe.15.011934 [16] CHEN P X, CHEN S T, GUAN X W, et al. High-order microring resonators with bent couplers for a box-like filter response[J]. Optics Letters, 2014, 39(21): 6304-6307. doi: 10.1364/OL.39.006304 [17] XU Q F, SHAKYA J, LIPSON M. Direct measurement of tunable optical delays on chip analogue to electromagnetically induced transparency[J]. Optics Express, 2006, 14(14): 6463-6468. doi: 10.1364/oe.14.006463 [18] ZHOU X Y, ZHANG L, ARMANI A M, et al. An integrated photonic gas sensor enhanced by optimized Fano effects in coupled microring resonators with an athermal waveguide[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2015, 33(22): 4521-4530. doi: 10.1109/JLT.2015.2478137 [19] DOTAN I E, SCHEUER J. Fano resonances in vertically and horizontally coupled micro-resonators[J]. Optics Communications, 2012, 285(16): 3475-3482. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2012.04.004 [20] QIU CH, YU P, HU T, et al. Asymmetric Fano resonance in eye-like microring system[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2012, 101(2): 021110. doi: 10.1063/1.4735258 [21] YI H X, CITRIN D S, ZHOU ZH P. Highly sensitive silicon microring sensor with sharp asymmetrical resonance[J]. Optics Express, 2010, 18(3): 2967-2972. doi: 10.1364/OE.18.002967 [22] TU ZH R, GAO D SH, ZHANG M L, et al. High-sensitivity complex refractive index sensing based on Fano resonance in the subwavelength grating waveguide micro-ring resonator[J]. Optics Express, 2017, 25(17): 20911-20922. doi: 10.1364/OE.25.020911 [23] CHAO C Y, GUO L J. Biochemical sensors based on polymer microrings with sharp asymmetrical resonance[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2003, 83(8): 1527-1529. doi: 10.1063/1.1605261 [24] GU L P, FANG H L, LI J T, et al. A compact structure for realizing Lorentzian, Fano, and electromagnetically induced transparency resonance lineshapes in a microring resonator[J]. Nanophotonics, 2019, 8(5): 841-848. doi: 10.1515/nanoph-2018-0229 [25] HEEBNER J E, WONG V, SCHWEINSBERG A, et al. Optical transmission characteristics of fiber ring resonators[J]. IEEE Journal of Quantum Electronics, 2004, 40(6): 726-730. doi: 10.1109/JQE.2004.828232 [26] VLASOV Y A, MCNAB S J. Losses in single-mode silicon-on-insulator strip waveguides and bends[J]. Optics Express, 2004, 12(8): 1622-1631. doi: 10.1364/opex.12.001622 [27] XUAN Y, LIU Y, VARGHESE L T, et al. High-Q silicon nitride microresonators exhibiting low-power frequency comb initiation[J]. Optica, 2016, 3(11): 1171-1180. doi: 10.1364/OPTICA.3.001171 -





 下载:
下载: