Ionizing Particle Discrimination and Extraction Based on Morphological Imaging Features
-
摘要:
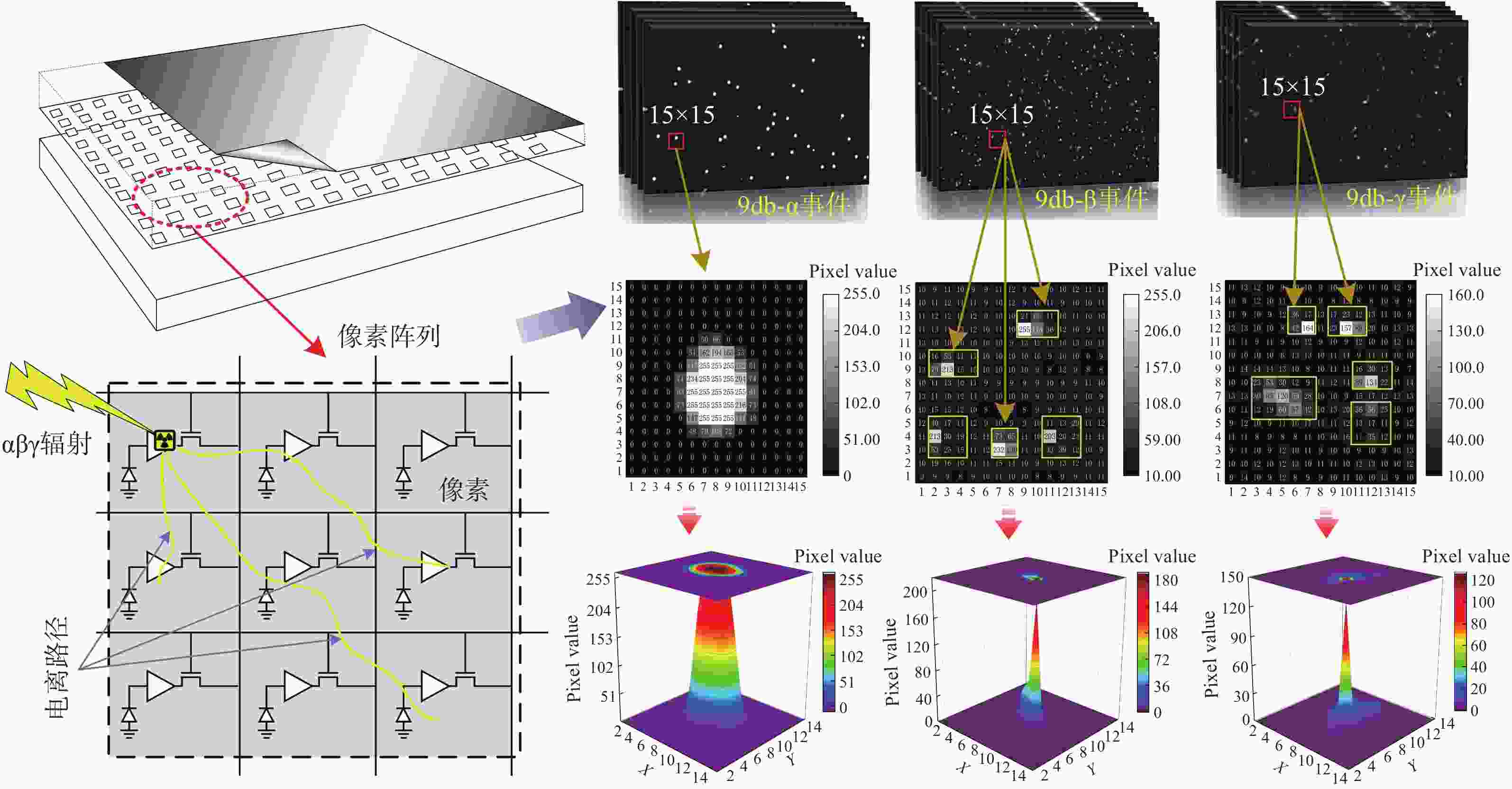
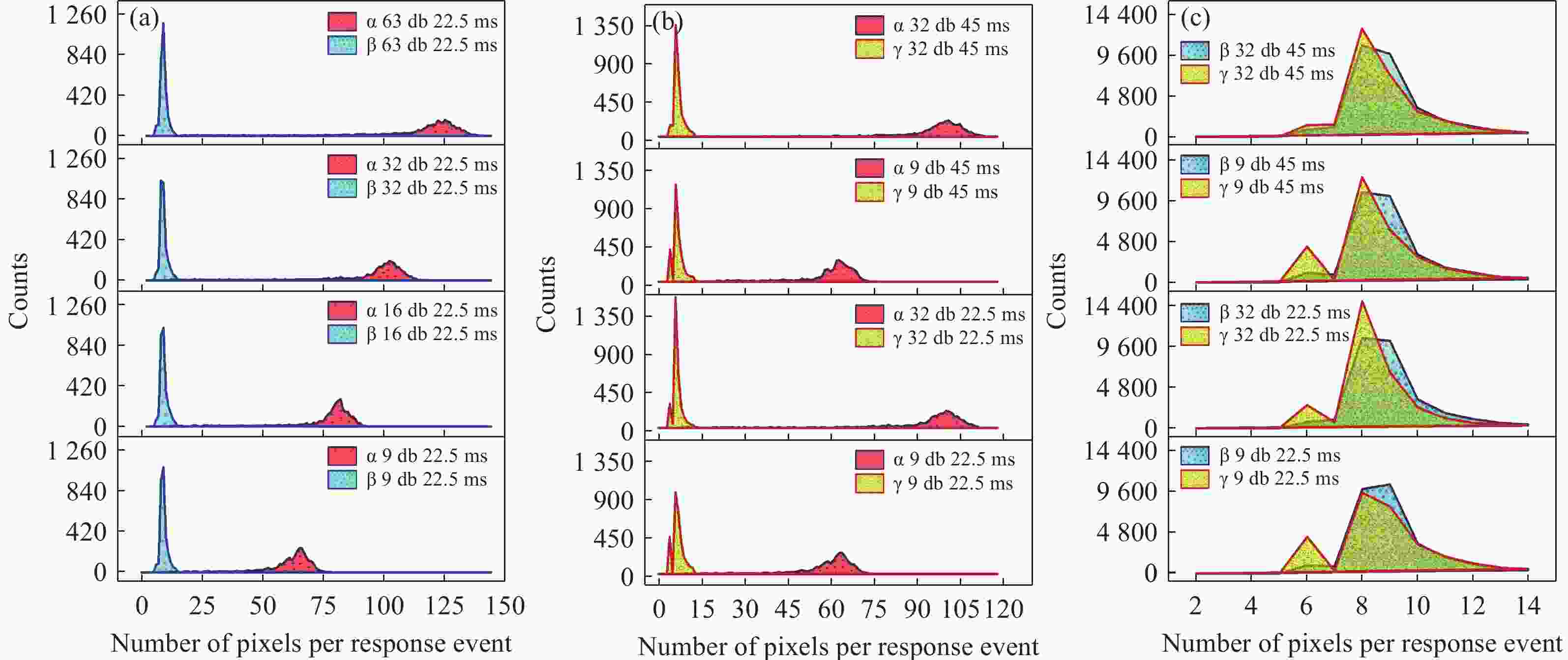
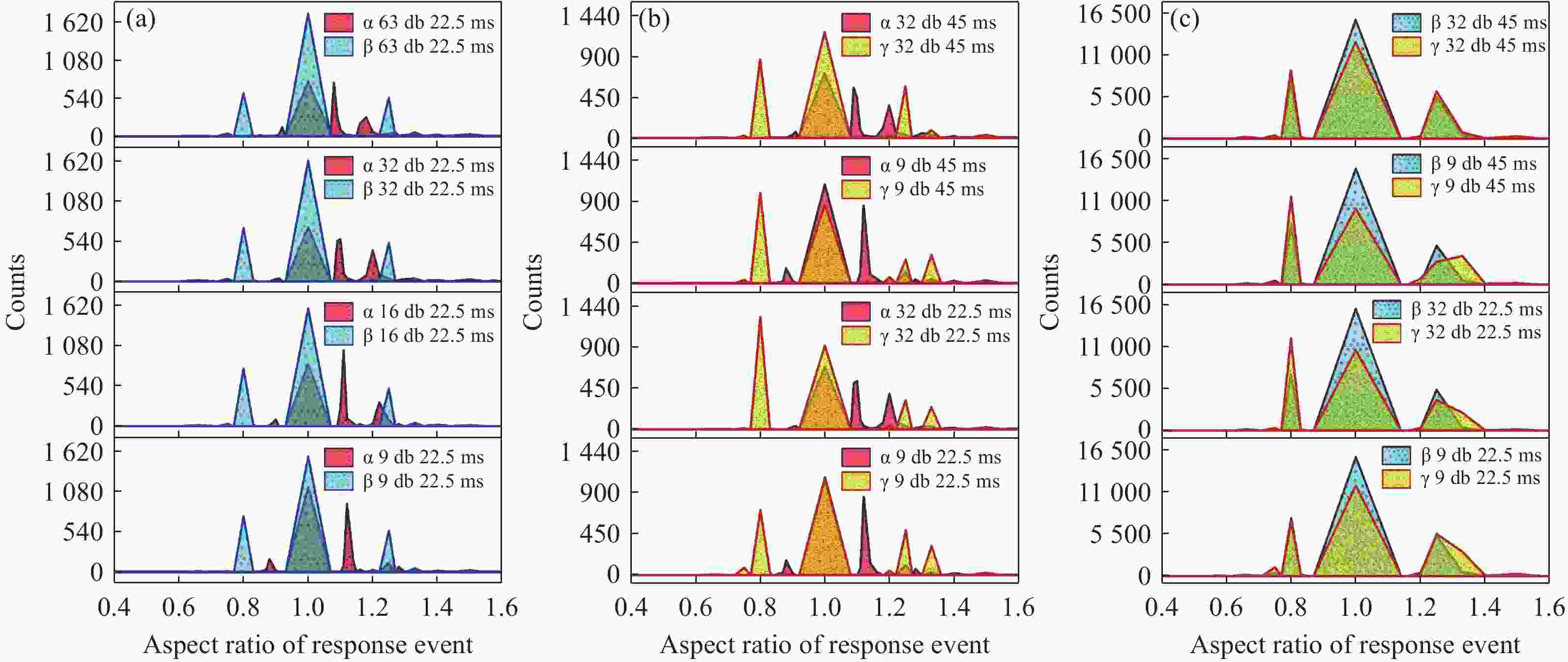
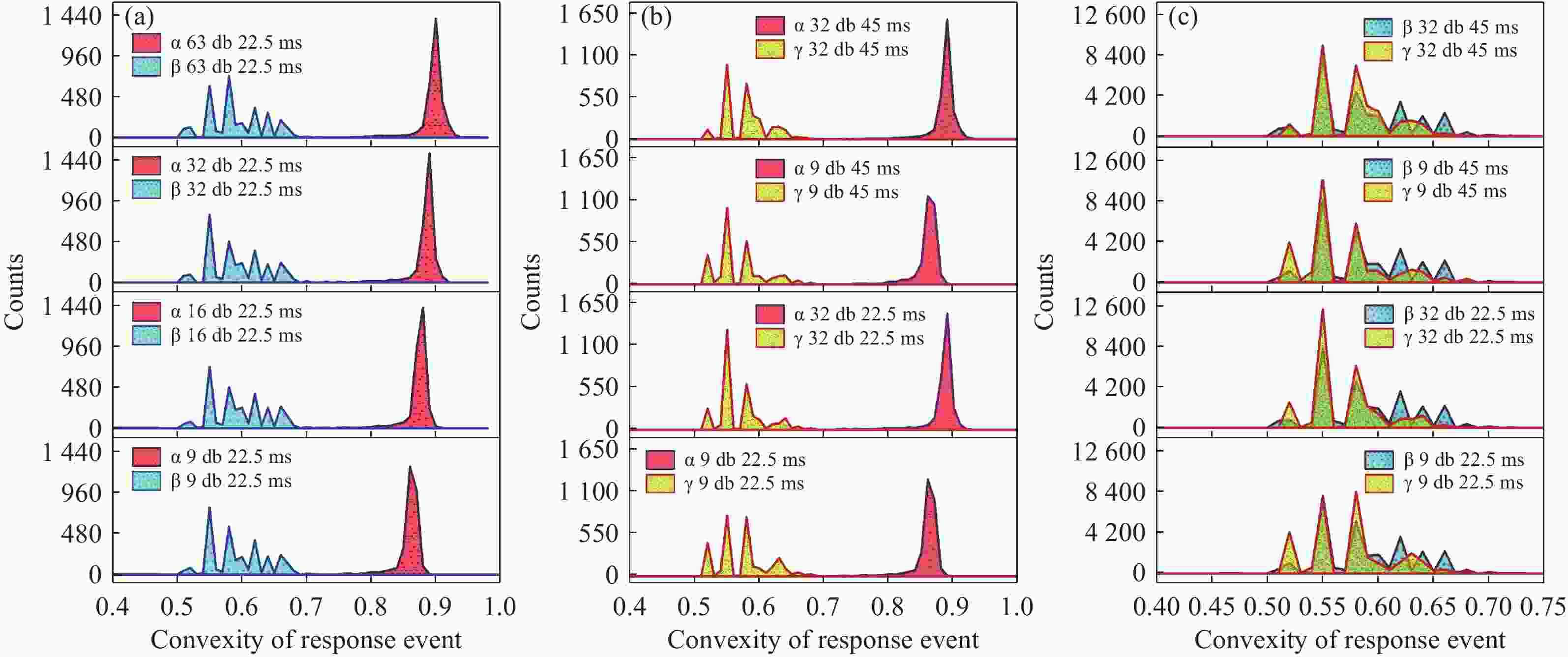
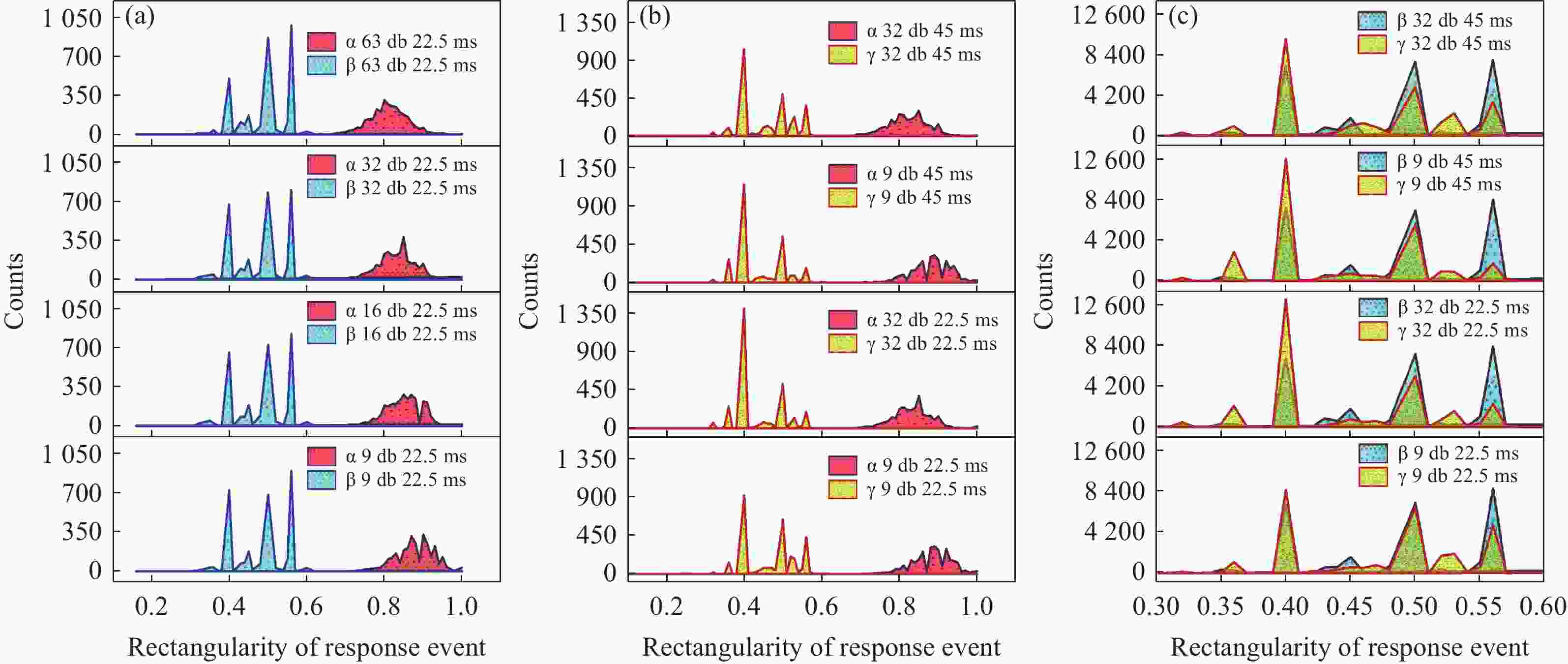
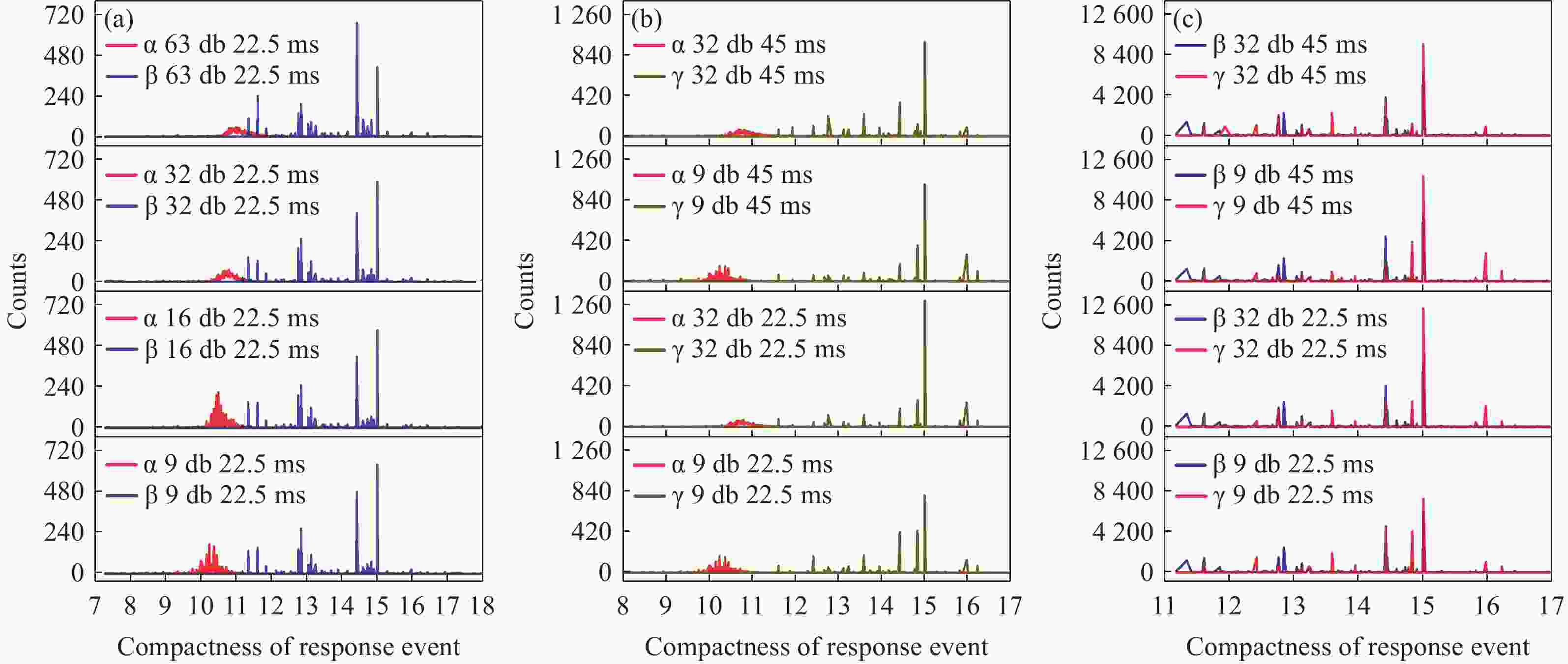
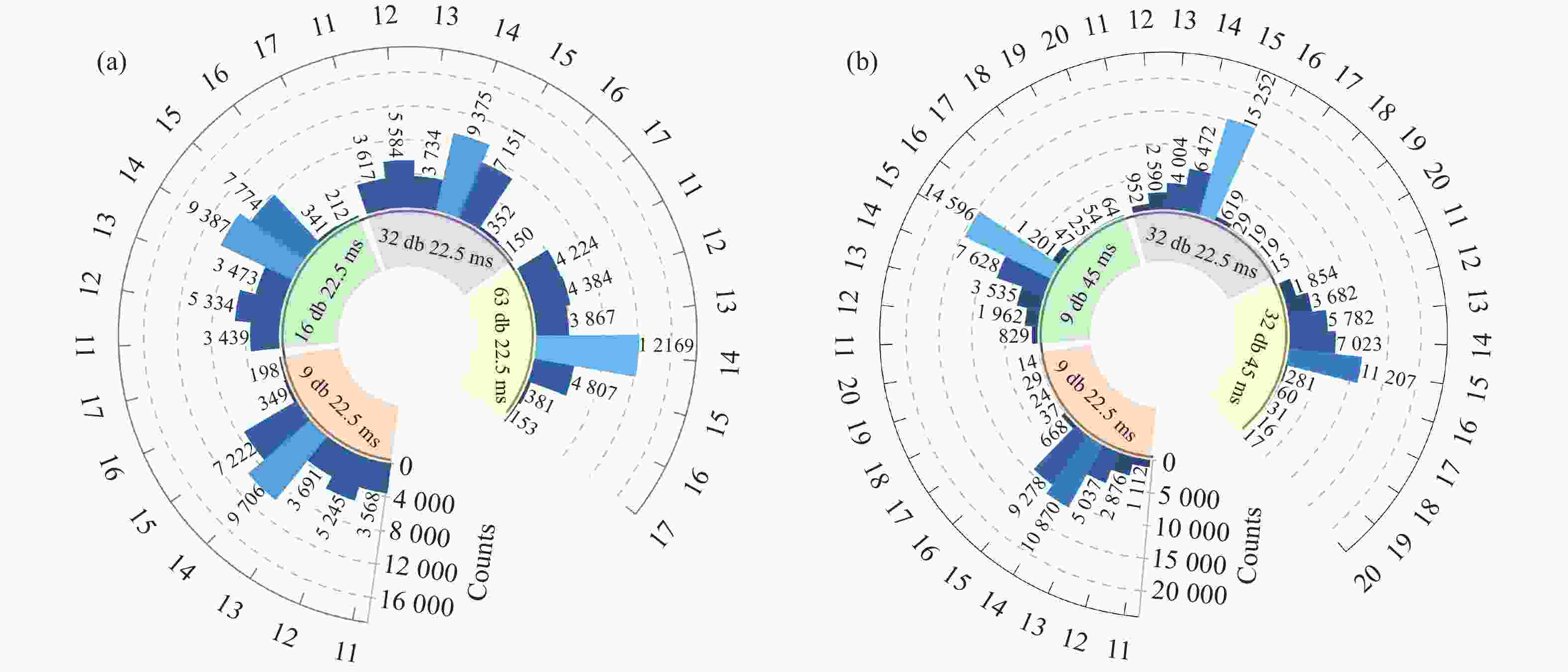
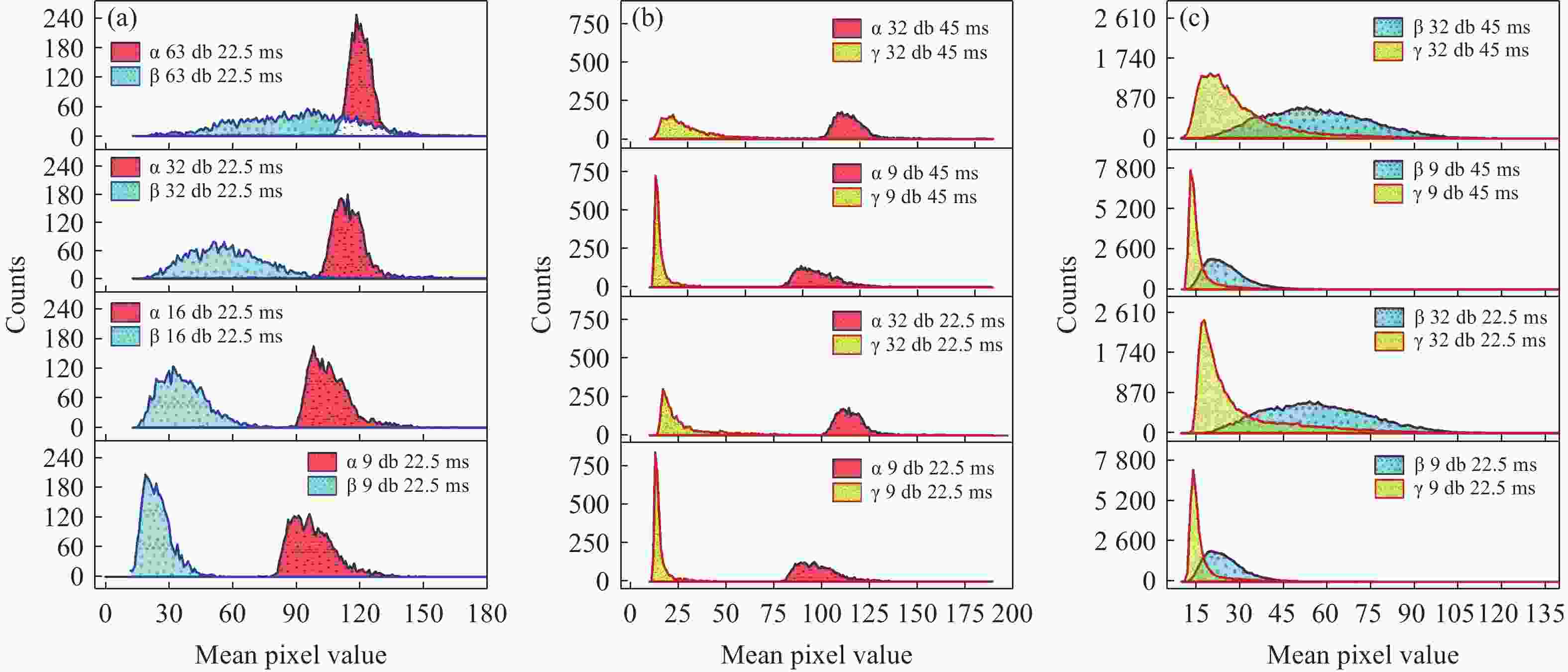
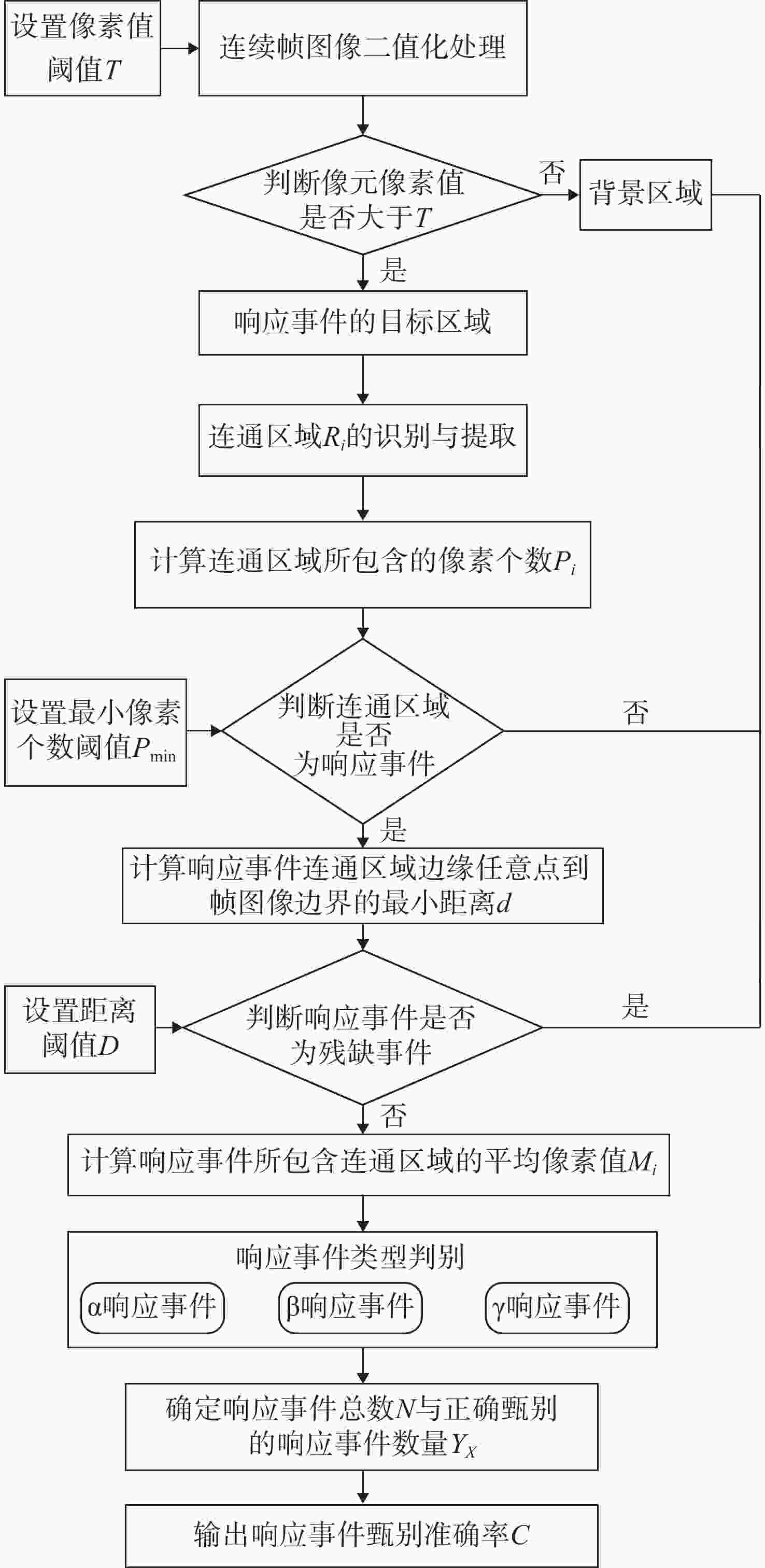
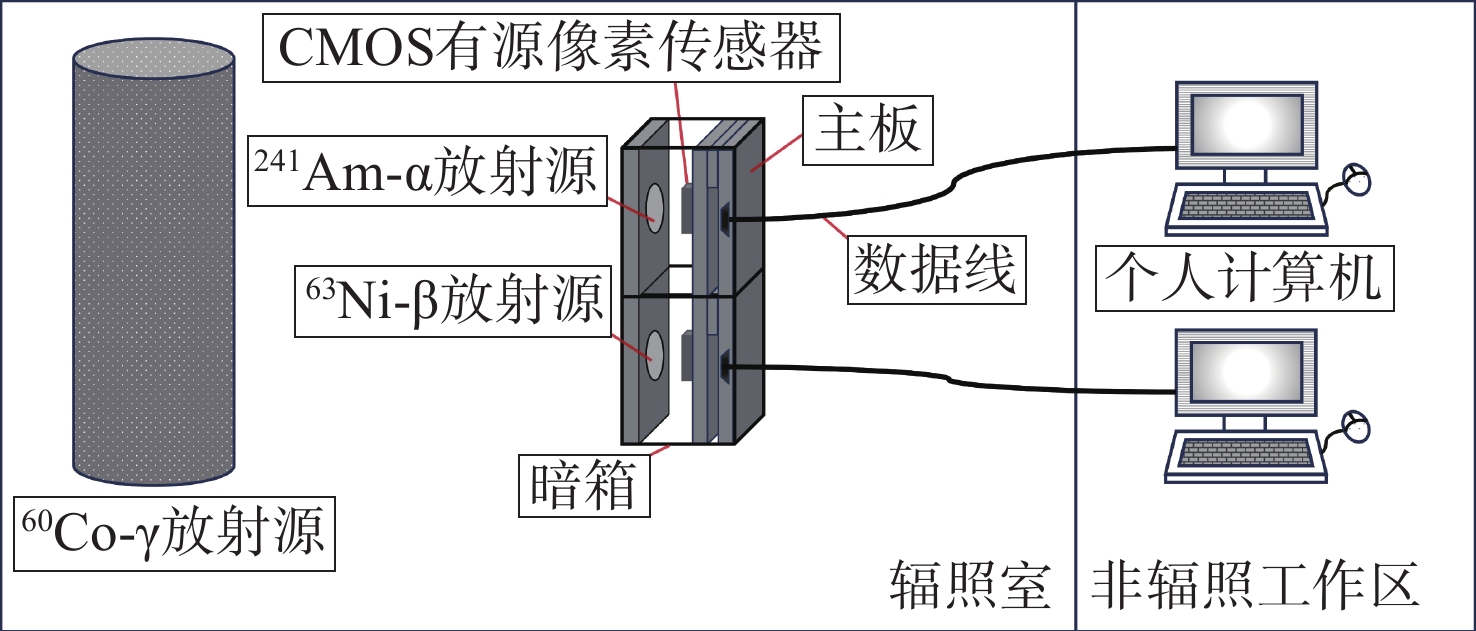
为避免脉冲堆积效应,改善辐射电离粒子甄别效率。本文利用 CMOS 有源像素传感器对电离粒子的光学响应特性,提出了一种基于成像形态学特征的粒子甄别方法。通过分析对比不同电离粒子响应事件特征,阐明其受增益及积分时间的调控机制,并对甄别效果进行验证。研究结果表明,α粒子响应事件的像素个数、平均像素值、矩形度、凸度与紧致度等5个特征参数相较于β和γ粒子响应事件存在显著差异。β和γ粒子响应事件在像素个数、矩形度和凸度等特征参数上相似,但可通过对比平均像素值或紧致度加以区分。利用响应事件所包含的像素个数来甄别α事件的准确率大于99%,利用平均像素值甄别β、γ事件的准确率大于82%。本文研究成果为混合辐射场的电离粒子甄别提供了新的方法和研究基础,为发展核环境电离粒子甄别技术,以及抗辐射噪声干扰技术提供新的路径与理论支撑。
-
关键词:
- 电离粒子甄别 /
- 成像形态学特征 /
- CMOS 有源像素传感器 /
- 混合辐射场
Abstract:To reduce pulse pile-up and improve ionizing particle discrimination efficiency. This study uses a CMOS active pixel sensor to analyze ionizing particle optical responses and propose morphology-based discrimination. Particle response features were compared to reveal gain and integration effects, and discrimination effectiveness was validated. Results show α events differ significantly from β and γ events in pixel count, mean pixel value, rectangularity, convexity, and compactness. β and γ events are similar in pixel count, rectangularity, and convexity, but differ in mean pixel value or compactness. Using pixel count, α events were identified with over 99% accuracy. β and γ events were discriminated by mean pixel value with over 82% accuracy. The results provide a new method and basis for ionizing particle identification in mixed radiation fields. It supports nuclear particle discrimination and noise mitigation, providing new approaches and theoretical guidance.
-
表 1 实验样品参数
Table 1. Parameters of experimental samples
实验样品 参数 传感器像素尺寸 2.2 μm × 2.2 μm 传感器分辨率 2592 (水平) × 1944 (垂直)α 放射源活度 2.9× 104 Bq (241Am) β 放射源活度 7.4 × 107 Bq (63Ni) γ 放射源活度 9 × 1014 Bq (60Co) 表 2 响应事件的甄别效果
Table 2. Identification performance of response events
混合辐射场类型 甄别事件总数 准确率 α/β 10000 > 99.9% α/γ 10000 > 99.9% β/γ 10000 > 82.5% -
[1] HADFIELD R H, LEACH J, FLEMING F, et al. Single-photon detection for long-range imaging and sensing[J]. Optica, 2023, 10(9): 1124-1141. doi: 10.1364/OPTICA.488853 [2] DUTTON N A W, GYONGY I, PARMESAN L, et al. A SPAD-based QVGA image sensor for single-photon counting and quanta imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, 2016, 63(1): 189-196. doi: 10.1109/TED.2015.2464682 [3] MADONINI F, SEVERINI F, ZAPPA F, et al. Single photon avalanche diode arrays for quantum imaging and microscopy[J]. Advanced Quantum Technologies, 2021, 4(7): 2100005. doi: 10.1002/qute.202100005 [4] MA J J, ZHANG D X, ROBLEDO D, et al. Ultra-high-resolution quanta image sensor with reliable photon-number-resolving and high dynamic range capabilities[J]. Scientific Reports, 2022, 12(1): 13869. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-17952-z [5] GUO X D, HE P, LV X J, et al. Material decomposition of spectral CT images via attention-based global convolutional generative adversarial network[J]. Nuclear Science and Techniques, 2023, 34(3): 45. doi: 10.1007/s41365-023-01184-5 [6] YANG J ZH, LI M F, CHEN X X, et al. Single-photon quantum imaging via single-photon illumination[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2020, 117(21): 214001. doi: 10.1063/5.0021214 [7] CHENG Q Q, MA CH W, YUAN Y ZH, et al. X-ray detection based on complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor sensors[J]. Nuclear Science and Techniques, 2019, 30(1): 9. doi: 10.1007/s41365-018-0528-4 [8] HE R, NIU X Y, WANG Y, et al. Advances in nuclear detection and readout techniques[J]. Nuclear Science and Techniques, 2023, 34(12): 205. doi: 10.1007/s41365-023-01359-0 [9] CHAKRABORTY A, PARASHAR N, PANDEY D K, et al. Radiological complexity of nuclear facilities: an information complexity approach to workplace monitoring[J]. Journal of Radiological Protection, 2024, 44(2): 021511. doi: 10.1088/1361-6498/ad42a5 [10] 罗智文, 冯婕, 郭旗, 等. 质子辐照下动态星敏感器质心定位[J]. 光学 精密工程, 2025, 33(13): 2089-2107.LUO ZH W, FENG J, GUO Q, et al. Centroid localization of dynamic star sensors under proton irradiation[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2025, 33(13): 2089-2107. (in Chinese). [11] LUO D W, WU H Y, LI ZH H, et al. Performance of digital data acquisition system in gamma-ray spectroscopy[J]. Nuclear Science and Techniques, 2021, 32(8): 79. doi: 10.1007/s41365-021-00917-8 [12] GU Z, PROUT D L, TASCHEREAU R, et al. A new pulse pileup rejection method based on position shift identification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, 2016, 63(1): 22-29. doi: 10.1109/TNS.2015.2495169 [13] LIU X H, LIU B Q, LIU M ZH, et al. An optimized SVR algorithm for pulse pile-up correction in pulse shape discrimination[J]. Sensors, 2024, 24(23): 7545. doi: 10.3390/s24237545 [14] NEUBÜSER C, CORRADINO T, DALLA BETTA G F, et al. ARCADIA FD-MAPS: simulation, characterization and perspectives for high resolution timing applications[J]. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment, 2023, 1048: 167946. doi: 10.1016/j.nima.2022.167946 [15] YOO S, PARK S, YUN S, et al. Impact of the fiber-optic faceplate on the imaging performance of a CMOS X-ray detector[J]. Journal of Instrumentation, 2024, 19(12): P12003. doi: 10.1088/1748-0221/19/12/P12003 [16] ALMEIDA B D, AMARO F D, ANTONIETTI R, et al. Noise assessment of CMOS active pixel sensors for the CYGNO Experiment[J]. Measurement Science and Technology, 2023, 34(12): 125145. doi: 10.1088/1361-6501/acf7e1 [17] 刘塔拉, 任同阳, 于勇, 等. 地基大型光学望远镜大靶面相机成像电路设计[J]. 光学 精密工程, 2025, 33(21): 3373-3382. doi: 10.37188/OPE.20253321.3373LIU T L, REN T Y, YU Y, et al. Design of imaging circuit for large-format camera of ground-based large optical telescope[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2025, 33(21): 3373-3382. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/OPE.20253321.3373 [18] ZHOU ZH, ZHOU SH Q, WANG D, et al. Low-noise and low-power pixel sensor chip for gas pixel detectors[J]. Nuclear Science and Techniques, 2024, 35(3): 58. doi: 10.1007/s41365-024-01418-0 [19] LIU SH H, GAO C S, ZHANG X, et al. CMOS direct conversion X-ray detector coupled with fluorinated liquid[J]. Nuclear Science and Techniques, 2025, 36(1): 1. doi: 10.1007/s41365-024-01529-8 [20] XU R, HSU C K, KALANI S, et al. Single-event upset responses of metal-oxide-metal capacitors and diodes used in bulk 65-nm CMOS analog circuits[J]. IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, 2020, 67(4): 698-707. doi: 10.1109/TNS.2020.2974229 [21] HU M D, PADGETT F, MCCURDY M W, et al. Probing the single-event sensitivity of a COTS 3D-integrated imager with alpha particle irradiation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, 2023, 70(4): 410-417. doi: 10.1109/TNS.2022.3222099 [22] XU SH L, ZOU SH L, HAN Y C, et al. Study on the availability of 4T-APS as a video monitor and radiation detector in nuclear accidents[J]. Sustainability, 2018, 10(7): 2172. doi: 10.3390/su10072172 [23] PÉREZ M, LIPOVETZKY J, HARO M S, et al. Particle detection and classification using commercial off the shelf CMOS image sensors[J]. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment, 2016, 827: 171-180. doi: 10.1016/j.nima.2016.04.072 [24] BAR O, BIBRZYCKI Ł, NIEDŹWIECKI M, et al. Zernike moment based classification of cosmic ray candidate hits from CMOS sensors[J]. Sensors, 2021, 21(22): 7718. doi: 10.3390/s21227718 [25] HARO M S, BESSIA F A, PÉREZ M, et al. Soft X-rays spectroscopy with a commercial CMOS image sensor at room temperature[J]. Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 2020, 167: 108354. doi: 10.1016/j.radphyschem.2019.108354 [26] XUE Y Y, WANG Z J, MA W Y, et al. Comparison of displacement damage effects on the dark signal in CMOS image sensors induced by CSNS back-n and XAPR neutrons[J]. Nuclear Science and Techniques, 2024, 35(10): 169. doi: 10.1007/s41365-024-01513-2 [27] LIU J, ZHOU ZH, WANG D, et al. Prototype of single-event effect localization system with CMOS pixel sensor[J]. Nuclear Science and Techniques, 2022, 33(11): 136. doi: 10.1007/s41365-022-01128-5 [28] LIANG B, LIU J H, ZHANG X P, et al. Total ionizing dose effect modeling method for CMOS digital-integrated circuit[J]. Nuclear Science and Techniques, 2024, 35(2): 26. doi: 10.1007/s41365-024-01378-5 [29] TIWARI M K, DIWAN J, SINGH S K, et al. Study of TID & dose rate effect of gamma radiation on COTS CMOS camera[J]. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section B: Beam Interactions with Materials and Atoms, 2025, 563: 165700. doi: 10.1016/j.nimb.2025.165700 [30] 任同群, 曹润嘏, 张国锐, 等. 星敏感器CMOS电路板靶面自动装调系统[J]. 光学 精密工程, 2024, 32(16): 2513-2522.REN T Q, CAO R G, ZHANG G R, et al. Automatic assembly and adjustment system for target surface of CMOS circuit board of star sensor[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2024, 32(16): 2513-2522. [31] YANG M Y, QIAN Y, PU T L, et al. Edims: an event-driven internal memory synchronized readout prototype ASIC chip developed for HFRS-TPC[J]. Nuclear Science and Techniques, 2023, 34(12): 196. doi: 10.1007/s41365-023-01341-w [32] INAGAKI Y, MATSUYA Y. A method for detecting timing of photodiode saturation without in-pixel TDC for high-dynamic-range CMOS image sensor[J]. IEICE Transactions on Electronics, 2021, E104. C(10): 607-616. -






 下载:
下载: