-
摘要:
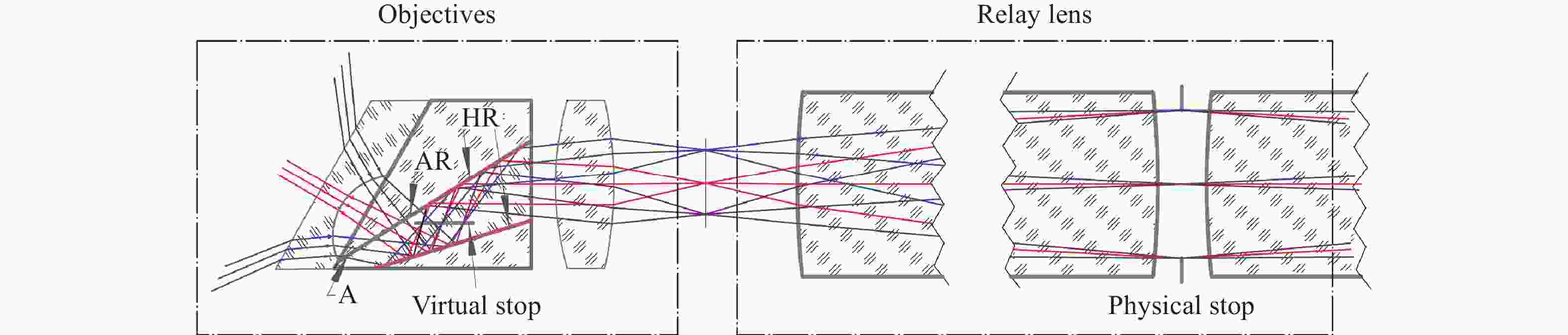
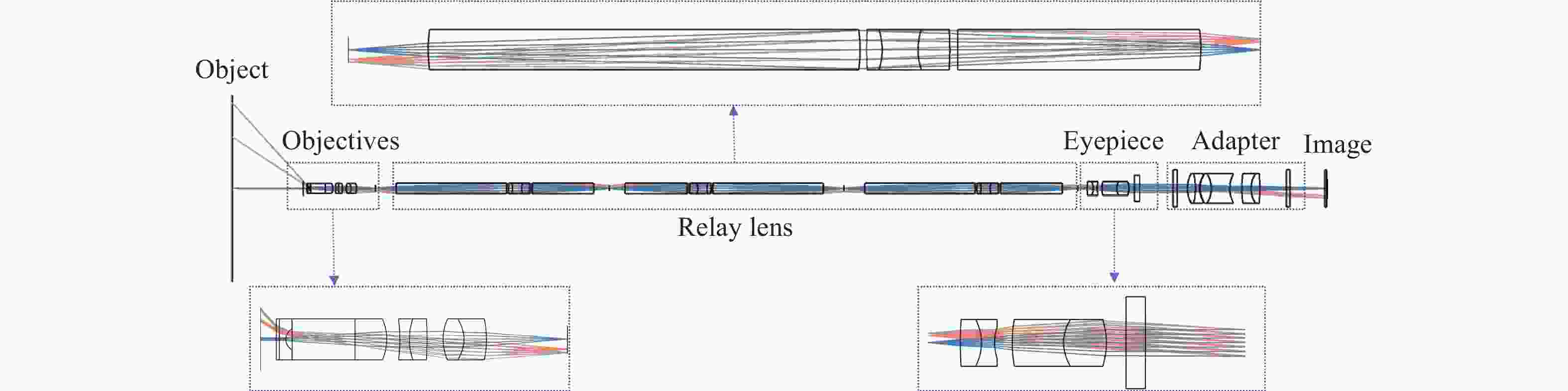
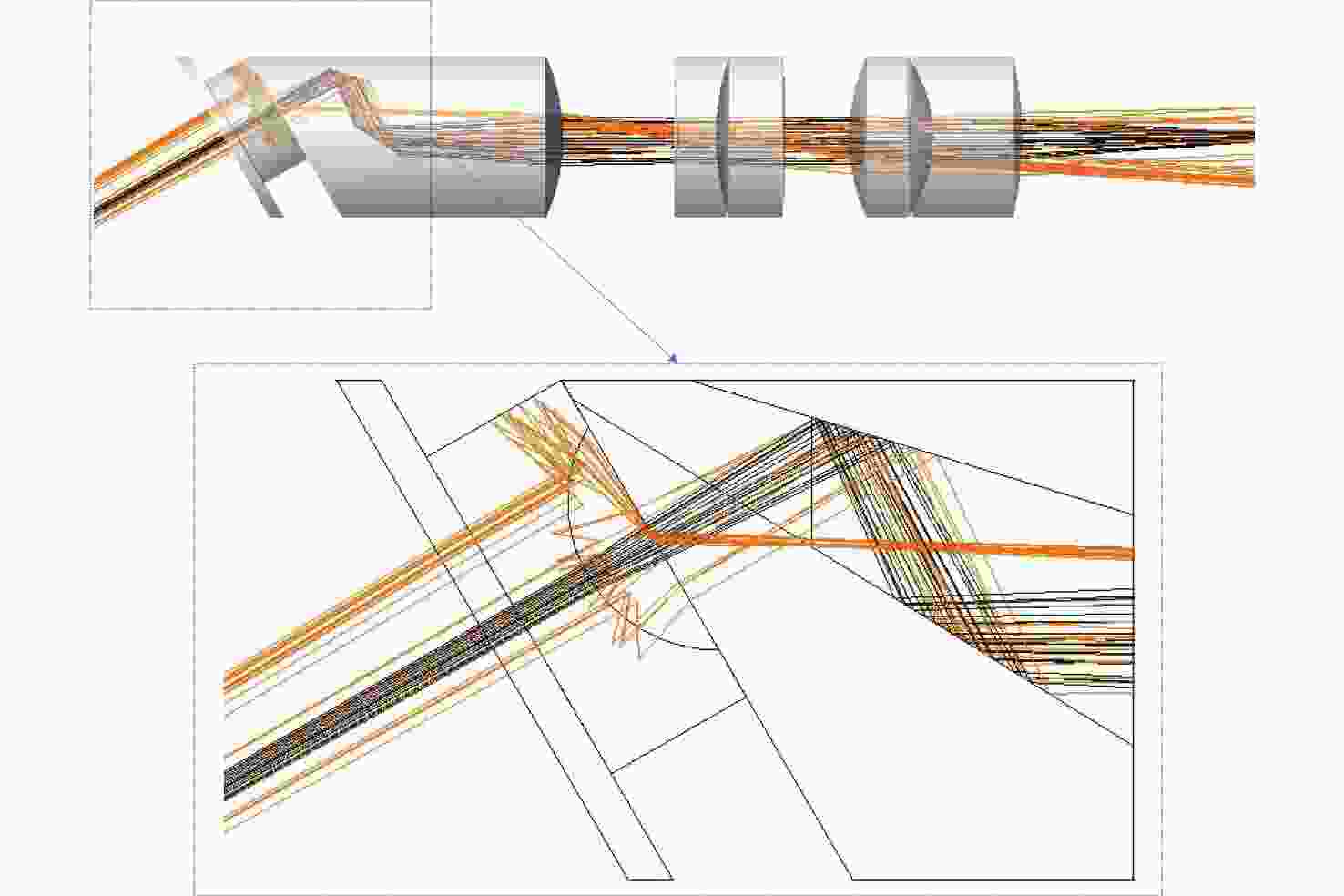
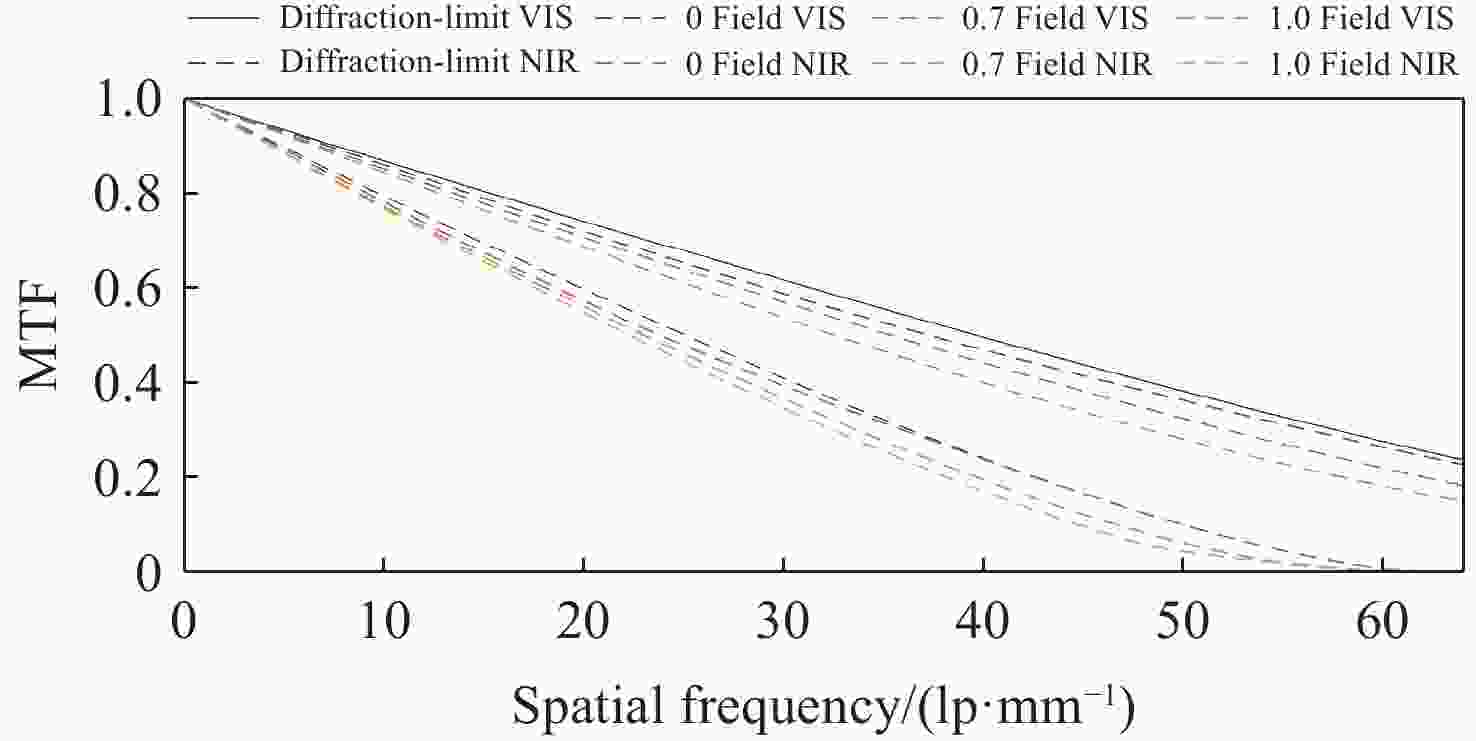
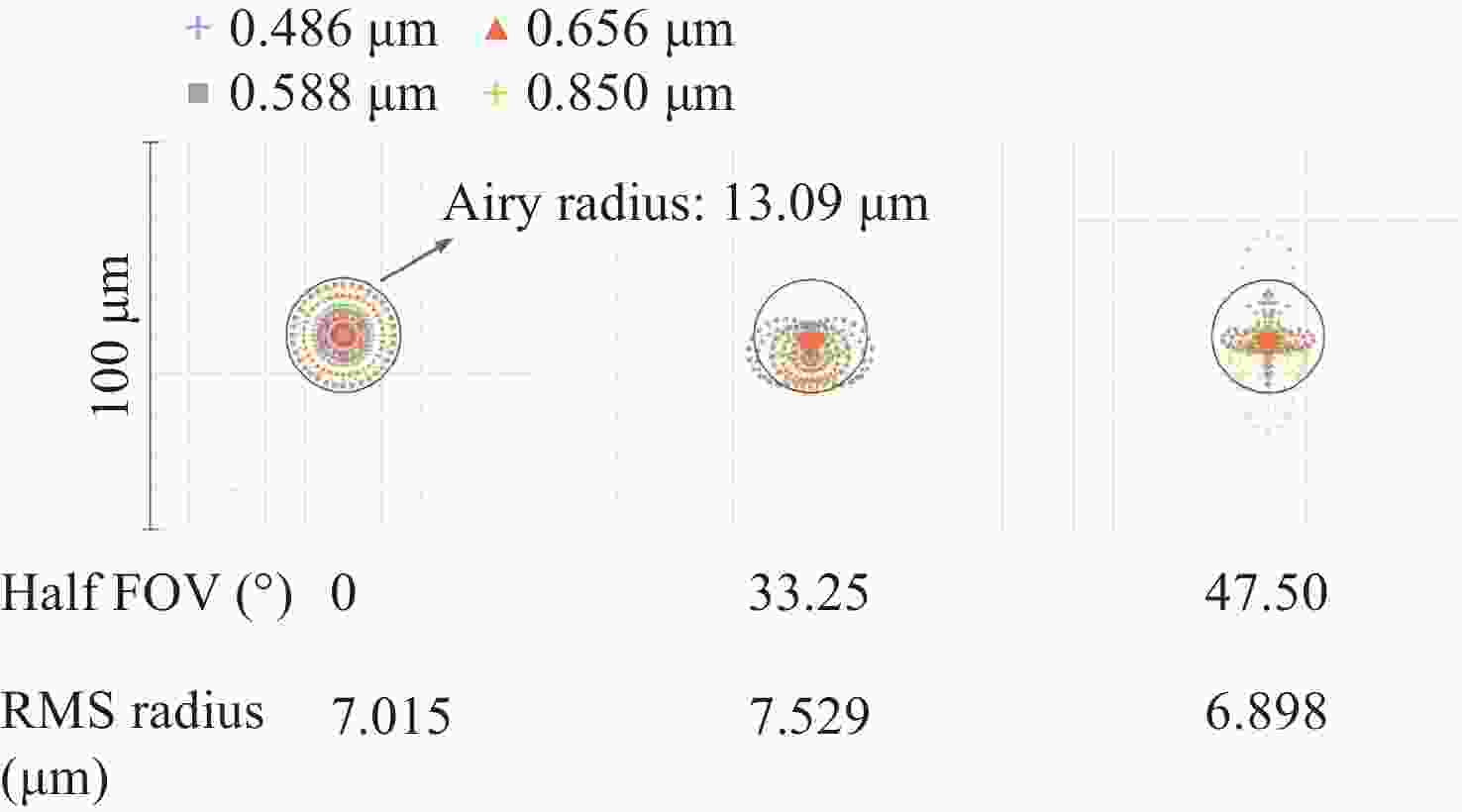
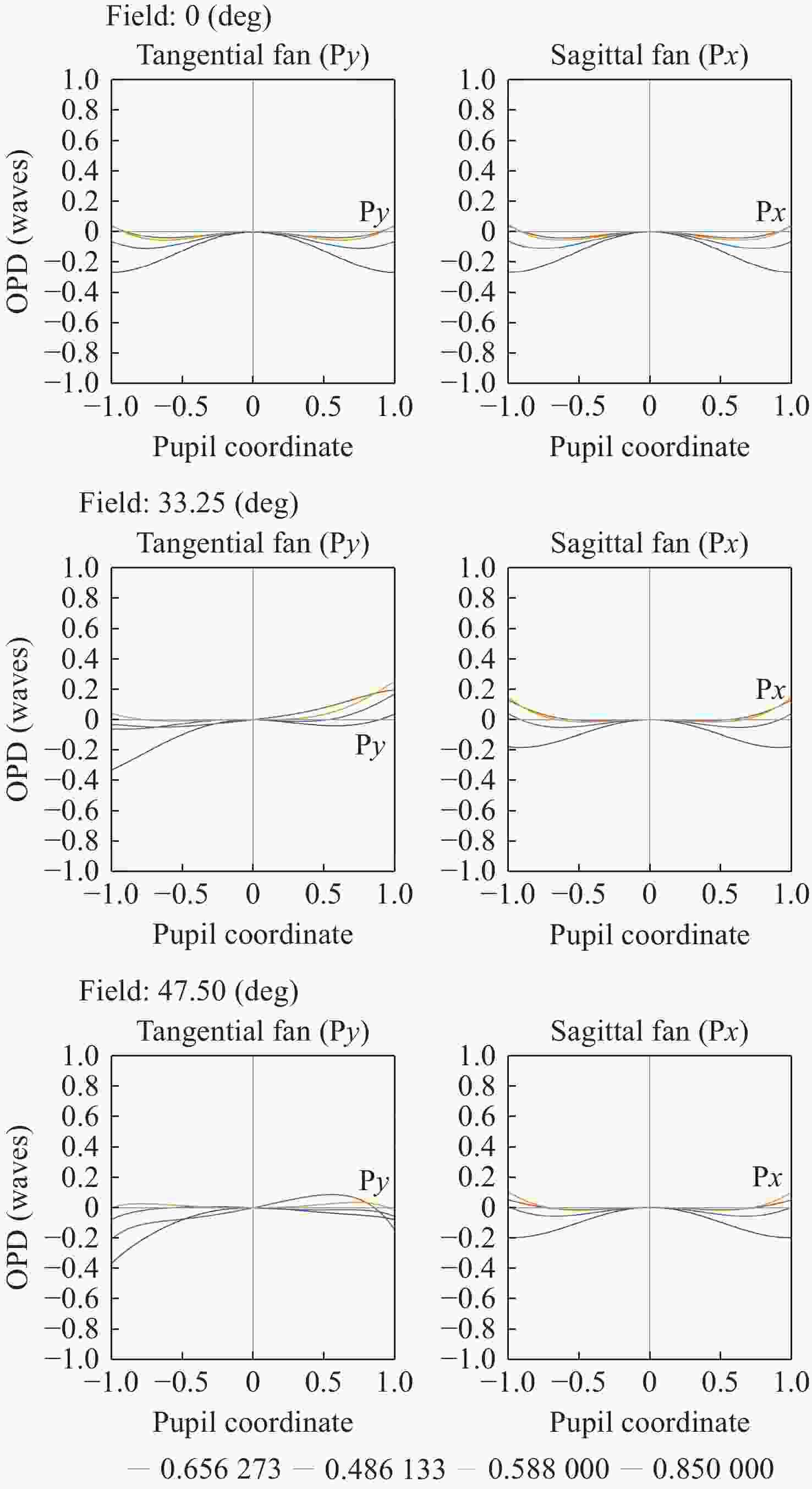
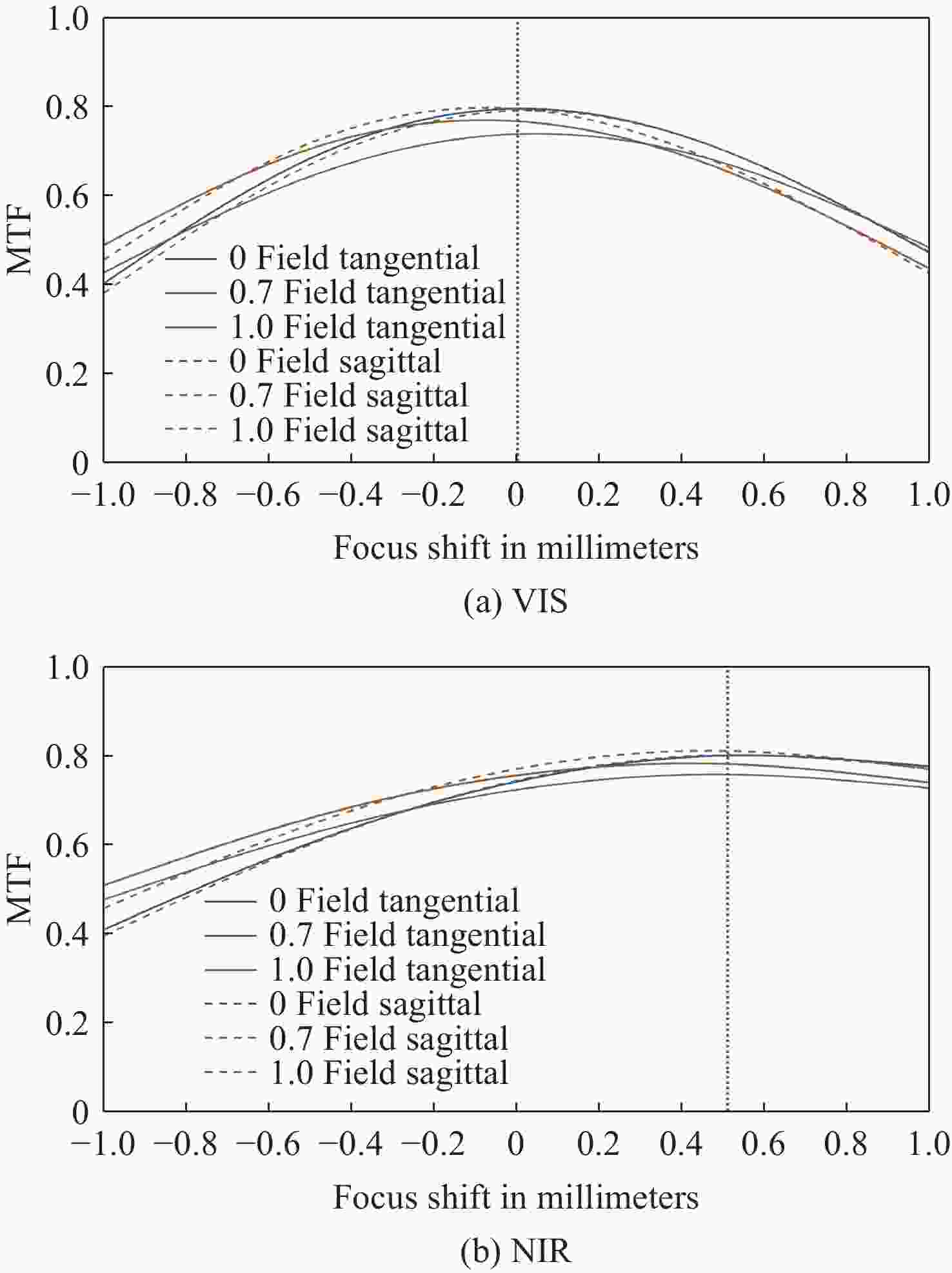
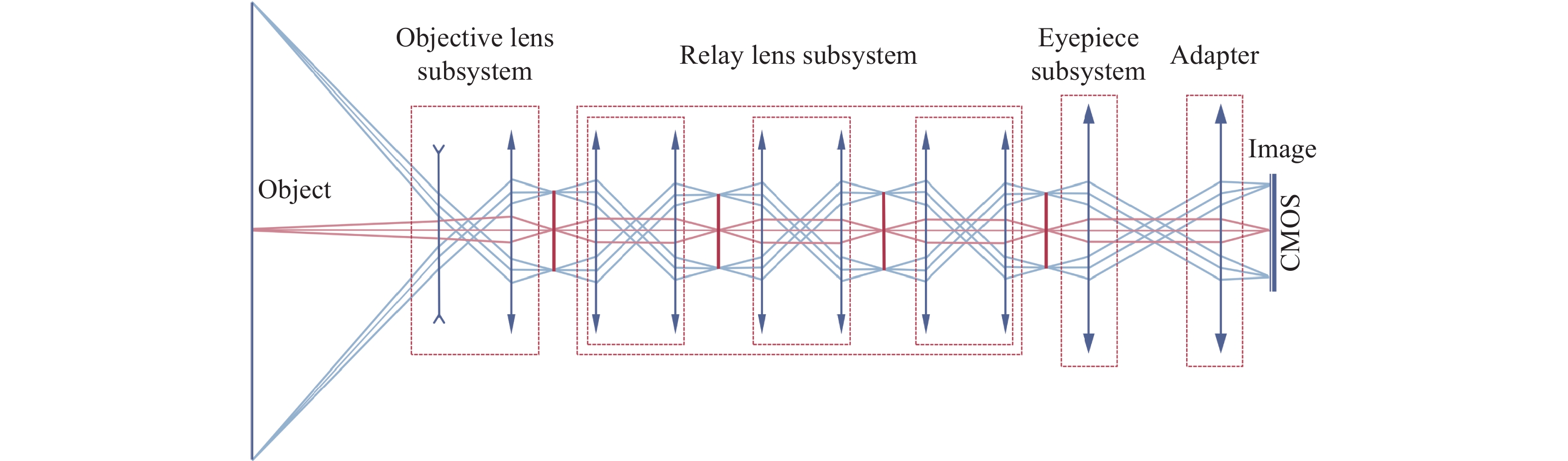
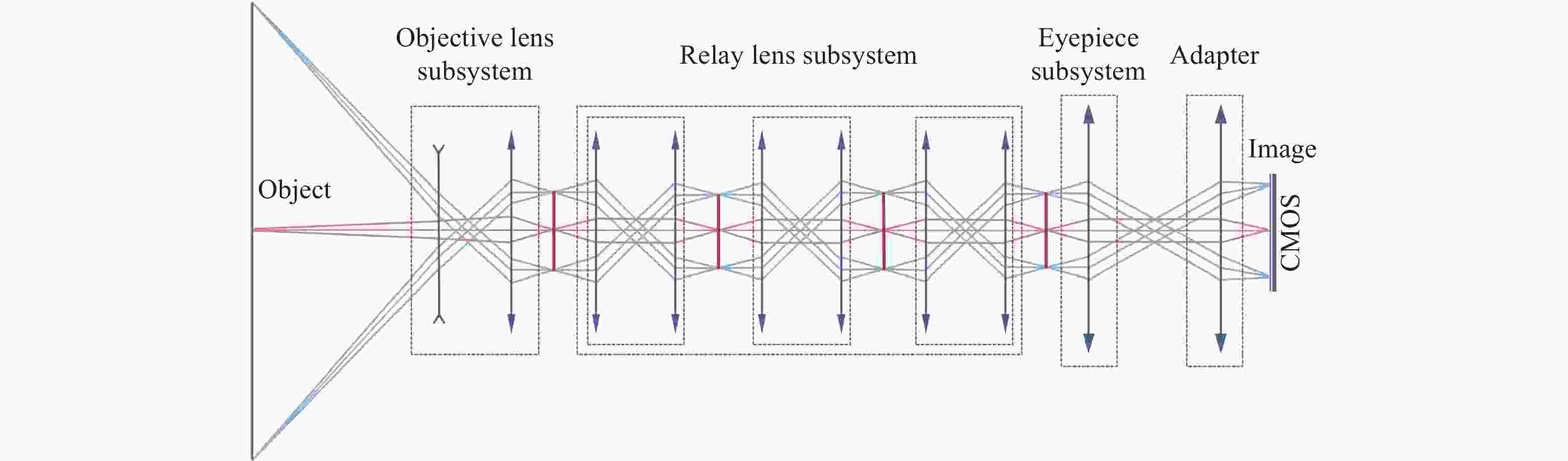
为提升关节内窥镜在临床手术中的成像性能并拓展其应用前景,设计了一种兼具大视场与高分辨率、可见光与近红外宽光谱齐焦成像特性的关节内窥镜光学系统。物镜通过大光焦度负透镜压缩主光线角度、减小轴外与轴上光线的光程差;并利用光阑共轭成像在转向棱镜内形成等效虚拟光阑,以在有限口径下兼顾大视场下的通光效率与高像质。中继镜采用三级近对称结构,通过光焦度与阿贝数分配有效抑制宽光谱传像过程中的轴向色差累积,从而实现齐焦成像。经公差分析表明,该系统具有良好制造与装调可实现性。实验结果验证了所设计的宽光谱关节内窥镜在95°视场角下可实现可见光与近红外波段齐焦成像,角分辨力分别为4.34 C/(°)和2.74 C/(°),光学系统为低成本实现高性能荧光内窥镜提供了可行方案,具备重要的应用价值。
Abstract:To enhance the imaging performance of arthroscopes in clinical surgery and broaden their potential for clinical applications, a wide-spectrum arthroscopic optical system featuring a large field of view, high resolution, and parfocal imaging capability in both visible and near-infrared bands was designed. The objective lens use a high optical power negative lens to compress the chief-ray angle and reduce the optical path difference between off-axis and on-axis rays. Through conjugate aperture imaging, an equivalent virtual stop is formed inside the turning prism, which allows the system to maintain both high transmission efficiency and high image quality under a limited aperture. The relay lens adopts a near-symmetric structure, and by distributing optical power and Abbe numbers appropriately, it effectively suppresses the accumulation of axial chromatic aberration across the broad spectral range, thereby achieving parfocal imaging. Tolerance analysis shows that the system has good manufacturability and assembly feasibility. Experimental results verify that the designed wide-spectrum arthroscope achieves parfocal imaging in the visible and near-infrared bands with a 95° field of view, and angular resolutions of 4.34 C/(°) and 2.74 C/(°), respectively. The optical system provides a feasible solution for achieving low-cost, high-performance fluorescence arthroscopy and has significant application value.
-
Key words:
- optical design and fabrication /
- wide-spectrum parfocality /
- turning prism /
- arthroscope
-
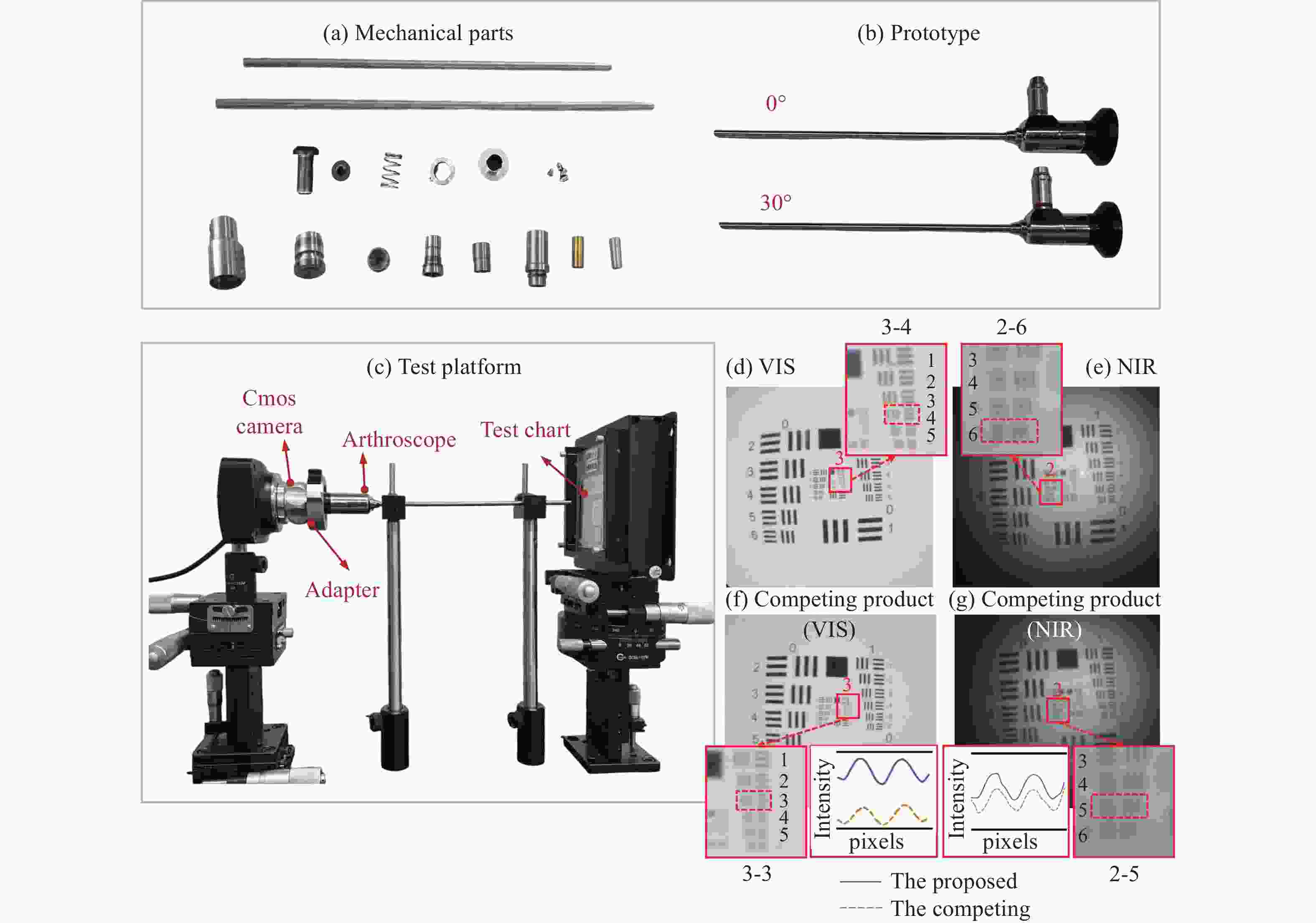
图 10 样机及物方分辨率检测。(a)机械件;(b)样机;(c)测试平台;(d)所设计的关节内窥镜在VIS下;(e)所设计的关节内窥镜在NIR下;(f)竞品关节内窥镜在VIS下;(g)竞品关节内窥镜在NIR下
Figure 10. Prototype and object space resolution measurement. (a) mechanical parts; (b) prototype; (c) test platform; (d) the proposed arthroscope in VIS; (e) the proposed arthroscope in NIR; (f) the competing product in VIS; (g) the competing product in NIR
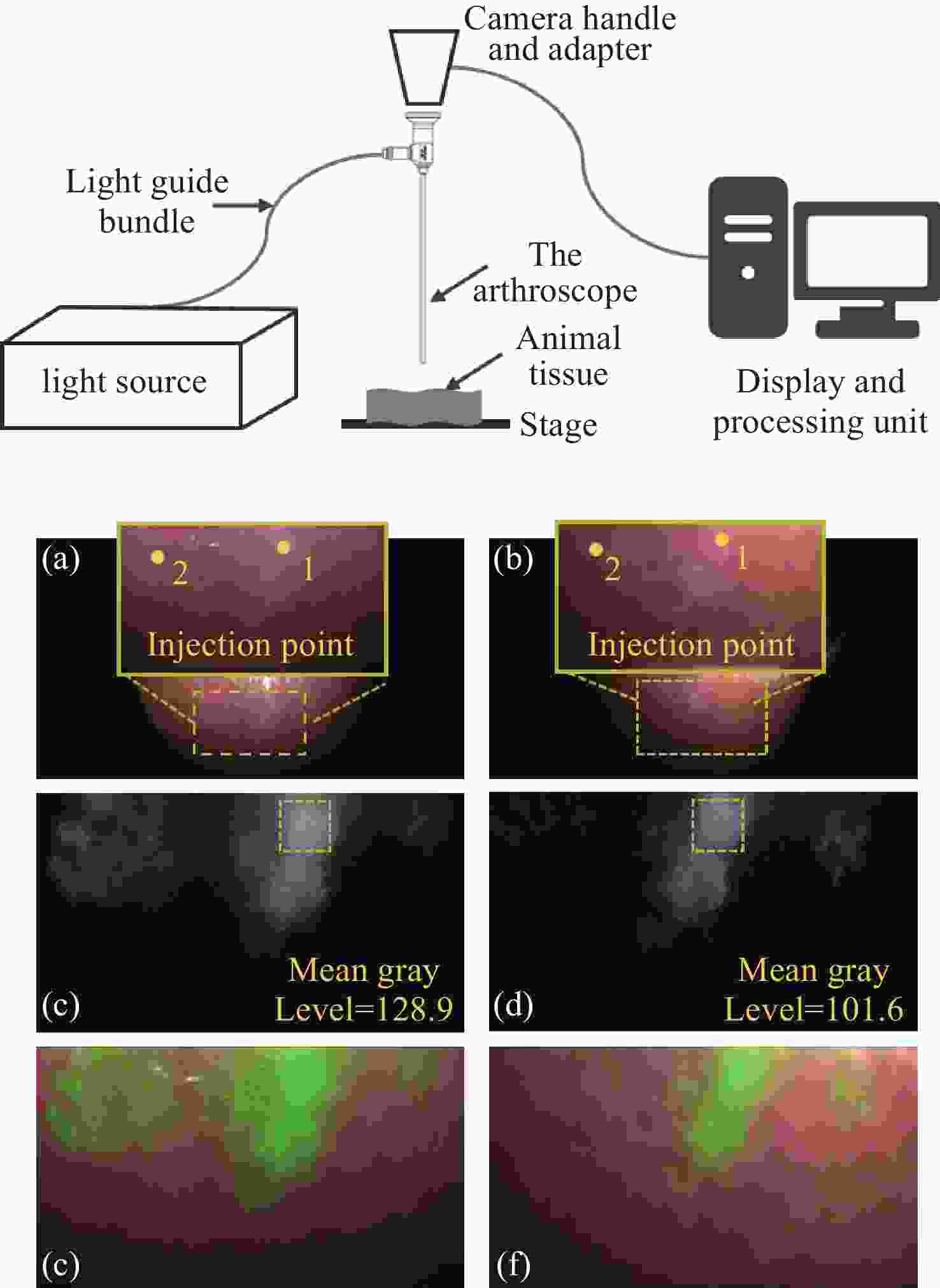
图 11 宽光谱关节内窥镜在动物组织上成像效果。(a)(b)所述关节内窥镜与竞品在白光模式下成像;(c)(d)所述关节内窥镜与竞品在荧光模式下成像;(e)(f)所述关节内窥镜与竞品在融合模式下成像
Figure 11. Performance of the wide-spectrum arthroscope on animal tissue. (a)(b) Imaging of the arthroscope and competing product in white light mode; (c)(d) Imaging of the arthroscope and competing product in fluorescence mode; (e)(f) Imaging of the arthroscope and competing product in fusion mode
表 1 宽光谱关节内窥镜整体参数
Table 1. Overall parameters of the wide spectrum arthroscope
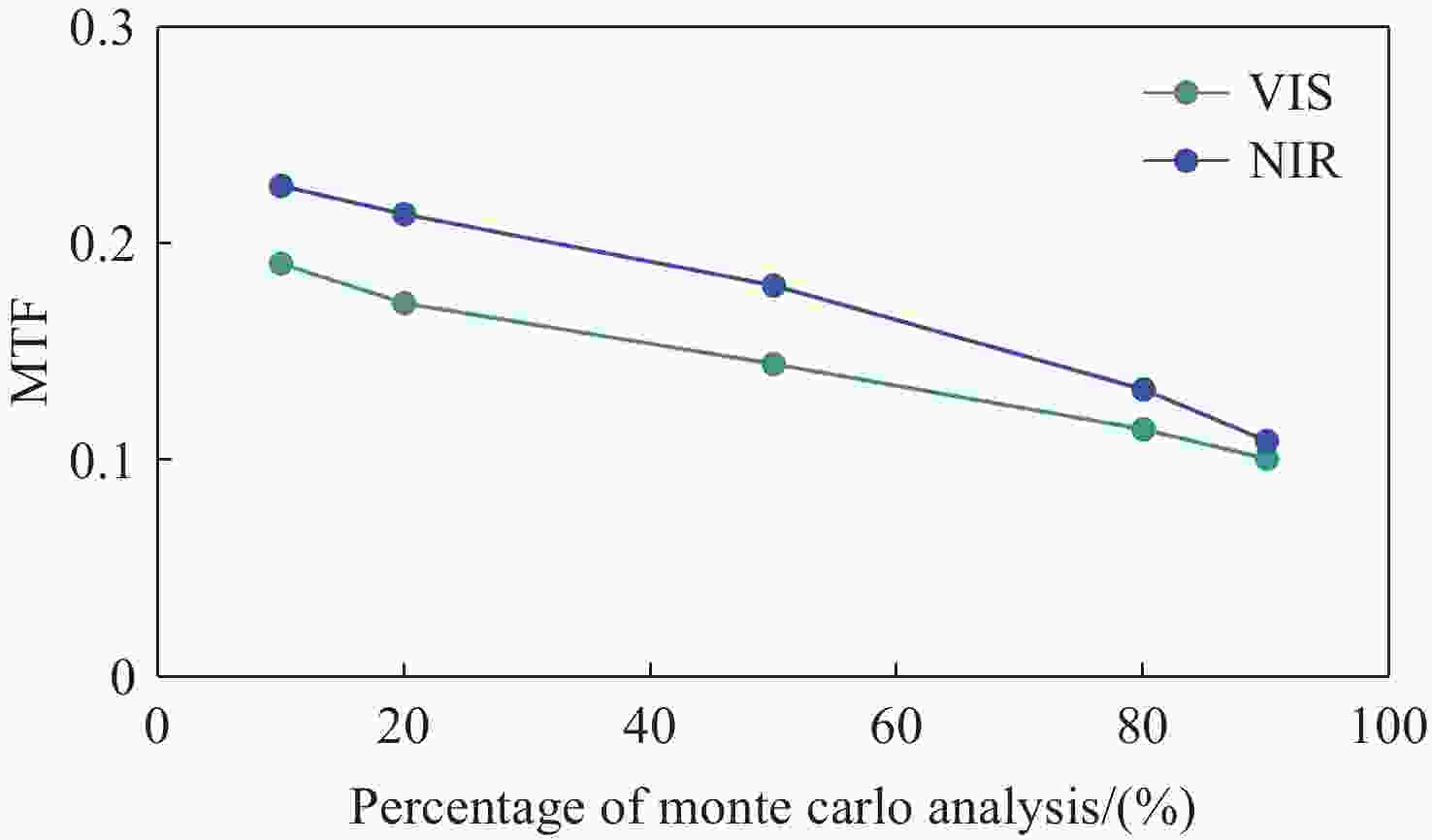
Design parameters Requirements Direction of view 0°/30° Field of view 95° Outer diameter/Clear aperture 4 mm/2.6 mm Entrance pupil diameter(De) 0.2 mm Working length 175 mm Working distance 20 mm Working wavelength(λ) 450-656 nm、800-900 nm 表 2 光学系统的公差分布
Table 2. Tolerance distribution of the optical system
Parameters Range(±) Radius (fringes) 2 Thickness (mm) 0.02 Surface decenter (mm) 0.02 Element decenter (mm) 0.02 Element tilt (°) 0.02 Refractive index 0.0005 Abbe number (%) 0.5 表 3 关键实测指标对比
Table 3. Comparison of key measured metrics
the proposed
arthroscopethe competing
productField of view 96° 101° Direction of view 28° 28° Diameter 4 mm 4 mm Angular resolution in VIS 4.34 C/(°) 3.88 C/(°) Angular resolution in NIR 2.74 C/(°) 2.46 C/(°) Parfocality √ × -
[1] 王宸, 陆军. 关节镜技术的发展与创新[J]. 中国骨伤, 2011, 24(9): 711-713.WANG CH, LU J. Development and innovation of arthroscopic techniques[J]. China Journal of Orthopaedics and Traumatology, 2011, 24(9): 711-713. (in Chinese). [2] 陈百成. 关节镜技术临床应用的现状与展望[J]. 中国骨伤, 2014, 27(8): 621-624.CHEN B CH. Development and great achievements on application of arthroscopy[J]. China Journal of Orthopaedics and Traumatology, 2014, 27(8): 621-624. (in Chinese). [3] 符荣松, 彭述娟. 内窥镜成像技术的发展现状分析[J]. 产业与科技论坛, 2023, 22(11): 37-39.FU R S, PENG SH J. Analysis of the current development status of endoscopic imaging technology[J]. Industrial & Science Tribune, 2023, 22(11): 37-39. (in Chinese) (查阅网上资料, 未找到对应的英文翻译, 请确认) [4] 上官佳伟, 李永亮, 冯海龙, 等. 大视场医用电子内窥镜光学成像系统研究综述[J]. 激光杂志, 2024, 45(8): 1-5. doi: 10.14016/j.cnki.jgzz.2024.08.001SHANGGUAN J W, LI Y L, FENG H L, et al. A review of the research on optical imaging systems of large-field medical electronic endoscopes[J]. Laser Journal, 2024, 45(8): 1-5. (in Chinese). doi: 10.14016/j.cnki.jgzz.2024.08.001 [5] 何旭舟, 林峰, 谢忠鑫, 等. 一种2k分辨率内窥镜光学系统设计[J]. 应用光学, 2024, 45(2): 276-281. doi: 10.5768/JAO202445.0201001HE X ZH, LIN F, XIE ZH X, et al. Design of endoscopic optical system with 2k resolution[J]. Journal of Applied Optics, 2024, 45(2): 276-281. (in Chinese). doi: 10.5768/JAO202445.0201001 [6] 王宏志, 冯大伟, 向阳. 椎间孔镜光学系统设计[J]. 长春理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2025, 48(1): 83-91. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9870.2025.01.010WANG H ZH, FENG D W, XIANG Y. Transforaminal endoscope optical system design[J]. Journal of Changchun University of Science and Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2025, 48(1): 83-91. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9870.2025.01.010 [7] 赵风萍. 视向角30°医用硬性电子内窥镜设计研究[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2024.ZHAO F P. Design of medical rigid electronic endoscope with 30° viewing angle[D]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology, 2024. (in Chinese). [8] KAMIMURA T. Indocyanine green fluorescence-guided knee arthroscopy: a technical note for investigating the microvasculature around the meniscus[J]. Arthroscopy Techniques, 2024, 13(3): 102878. doi: 10.1016/j.eats.2023.11.006 [9] STREETER S S, HEBERT K A, BATEMAN L M, et al. Current and future applications of fluorescence guidance in orthopaedic surgery[J]. Molecular Imaging and Biology, 2023, 25(1): 46-57. doi: 10.1007/s11307-022-01789-z [10] SHIBATA T, DOI N, SHIBATA Y, et al. Application of indocyanine green fluorescence angiography in evaluating blood flow in rotator cuff tears: a preliminary study[J]. Journal of Shoulder and Elbow Surgery, 2024, 33(10): 2149-2158. doi: 10.1016/j.jse.2024.04.027 [11] KAMIMURA T. Blood flow in the meniscus can be visualized arthroscopically using an intravenous Indocyanine green solution diluted 10× in a pig model[J]. Arthroscopy, Sports Medicine, and Rehabilitation, 2024, 6(3): 100932. doi: 10.1016/j.asmr.2024.100932 [12] 聂璞, 张志坚, 王淼, 等. 一款细径腹腔荧光内窥镜的光学系统设计[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2025, 62(9): 0917001. doi: 10.3788/LOP241736NIE P, ZHANG ZH J, WANG M, et al. Optical system design of a small-diameter abdominal fluorescence endoscope[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2025, 62(9): 0917001. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/LOP241736 [13] 刘钧, 陈阳. 可见光/红外双波段大视场共口径齐焦光学系统[J]. 西安工业大学学报, 2014, 34(2): 87-93.LIU J, CHEN Y. Visible/Infrared dual-band large field shared-aperture and parfocal optical system[J]. Journal of Xi’an Technological University, 2014, 34(2): 87-93. (in Chinese). [14] 李恩泽, 潘宇, 顾国超, 等. 单一透镜材料宽温度范围空间相机无热化设计[J]. 中国光学(中英文), 2025, 18(6): 1388-1398.LI E Z, PAN Y, GU G CH, et al. Athermal design of a space camera using a single lens material over a wide temperature range[J]. Chinese Optics, 2025, 18(6): 1388-1398. (in Chinese). [15] 张丽芝, 陆秋萍, 段帆琳, 等. 关键参数先验的车载雷达镜头杂散光抑制模型研究[J]. 中国光学(中英文), 2025, 18(6): 1399-1408.ZHANG L ZH, LU Q P, DUAN F L, et al. Stray light suppression model of vehicle LiDAR lens based on key parameter priors[J]. Chinese Optics, 2025, 18(6): 1399-1408. (in Chinese). [16] 国家食品药品监督管理局. YY 0068.1-2008 医用内窥镜 硬性内窥镜 第1部分: 光学性能及测试方法[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2009.National Medical Products Administration. YY 0068.1-2008 Medical endoscopes—rigid endoscope—Part 1: optical properties and test methods[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2009. (in Chinese). -





 下载:
下载: