Improved model and experimental study of laser-induced damage in multilayer dielectric films
-
摘要:目的
多层介质薄膜的结构会调制光场,因此在研究激光诱导损伤特性时,有必要考虑薄膜体系内部的能量分布以及由此引起的材料光学性质变化。
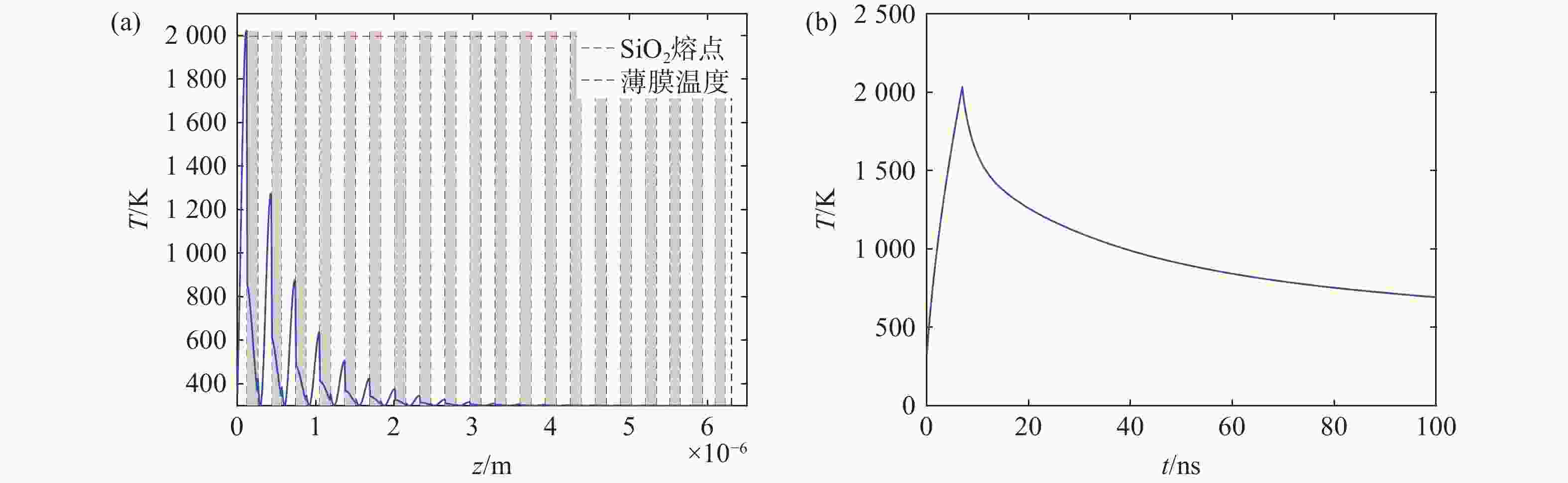
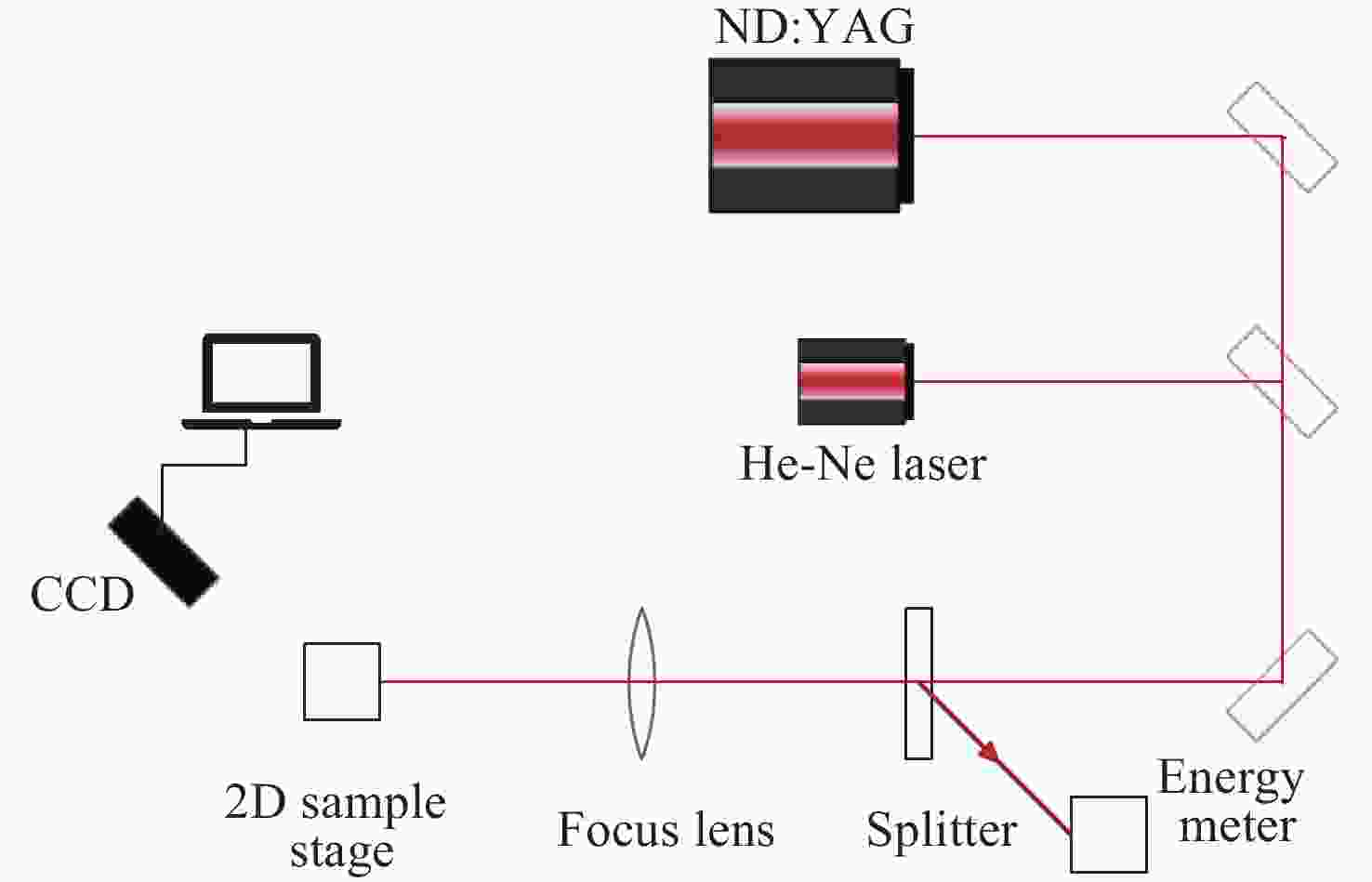
方法以 HfO2/SiO2多层介质薄膜结构为例,基于激光诱导电离/电子倍增过程,在光场计算中引入Drude模型,将膜层折射率由静态常数扩展为由自由电子密度驱动的动态复折射率。在此基础上耦合热传导(及热应力)模型,计算纳秒脉冲激光作用下薄膜内部的热效应演化,并求得相应的损伤阈值为13.65 J/cm2,同时开展实验研究其损伤特性。
结果验证实验观察到HfO2/SiO2多层介质薄膜的损伤形貌为圆孔状,属于典型的热熔融型损伤,测得的损伤阈值13.75 J/cm2略高于理论分析结果,与理论模型结论吻合。
结论本文建立的改进模型有助于从理论层面进一步分析强激光与多层介质薄膜的相互作用,并更好地研究光学薄膜的抗损伤能力。
-
关键词:
- HfO2/SiO2多层介质膜 /
- 场致效应 /
- Drude模型 /
- 热力耦合 /
- 损伤阈值
Abstract:ObjectiveThe structure of multilayer dielectric film will modulate the optical field, thus in the study of laser-induced damage characteristics, it is necessary to consider the energy distribution within the film system and the resulting changes in material optical properties.
MethodTaking the HfO2/SiO2 multilayer dielectric film structure as an example, and based on the laser-induced ionization/electron multiplication process, the Drude model is introduced into the optical field calculation, extending the film layer refractive index from a static constant to a dynamic complex refractive index driven by the free electron density. Based on this, a thermal conduction (and thermal stress) model is coupled to calculate the evolution of thermal effects inside the thin film under nanosecond pulsed laser irradiation, and the corresponding damage threshold is determined to be 13.65 J/cm2, and the damage characteristics of the film are studied experimentally.
ResultThe verification experiment observed that the damage appearance of the HfO2/SiO2 multilayer dielectric film is a round hole type, which is a typical thermal melting damage, and is consistent with the conclusion of the theoretical model. The measured damage threshold is 13.75 J/cm2, which is only higher than the theoretical analysis result.
ConclusionThe improved model established is helpful to further analyse the interaction between strong laser and multilayer dielectric film from the theoretical level, and to better study the damage resistance of optical thin film.
-
Key words:
- multilayer dielectric films /
- field effect /
- Drude model /
- thermal-stress coupling /
- damage threshold
-
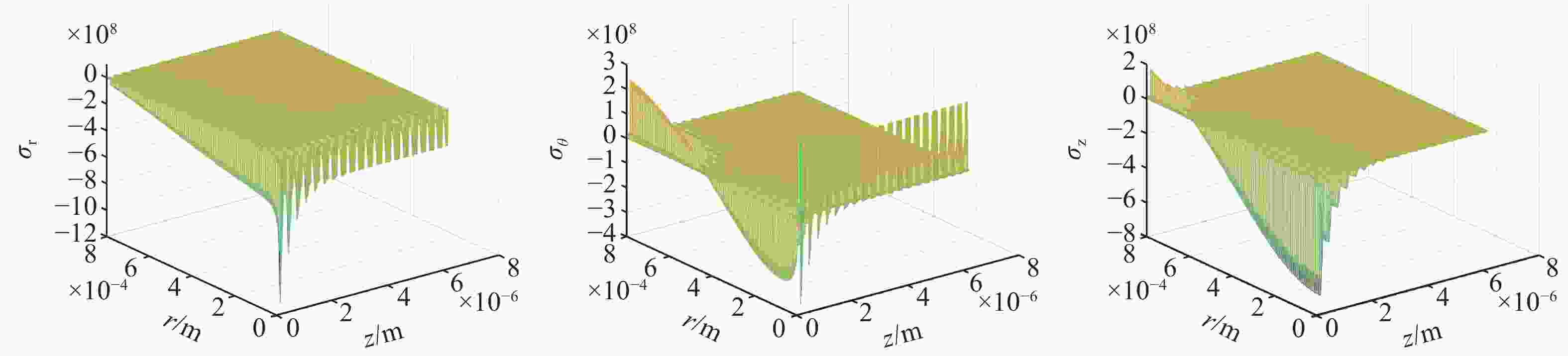
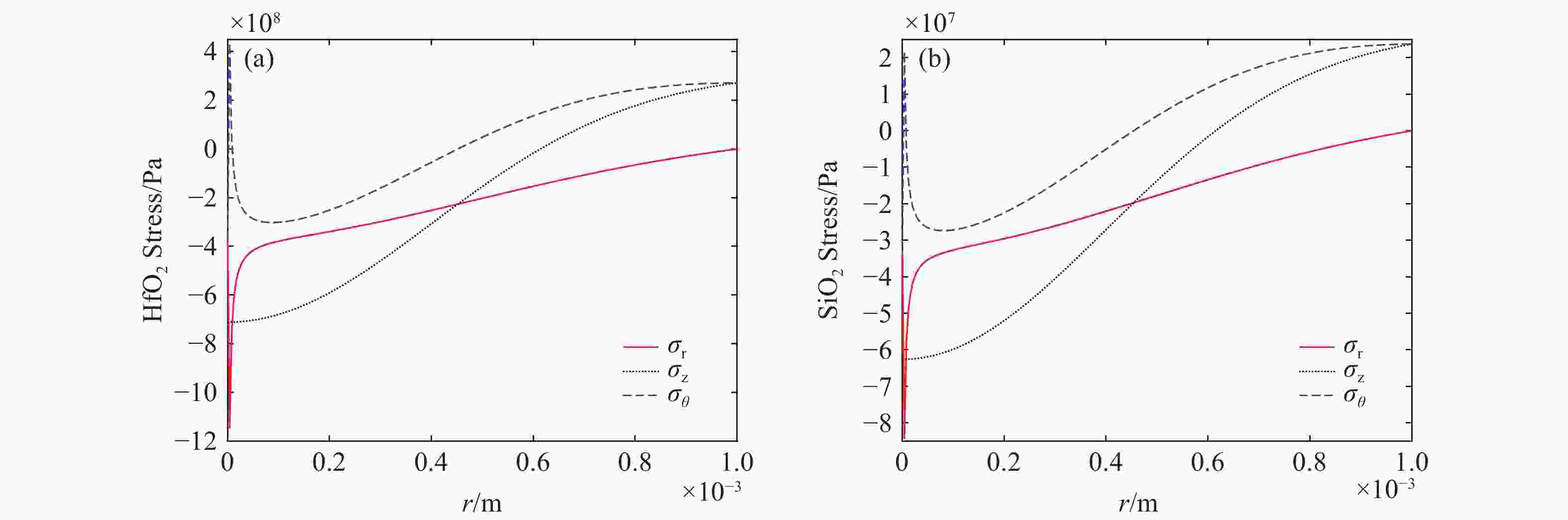
图 3 波长
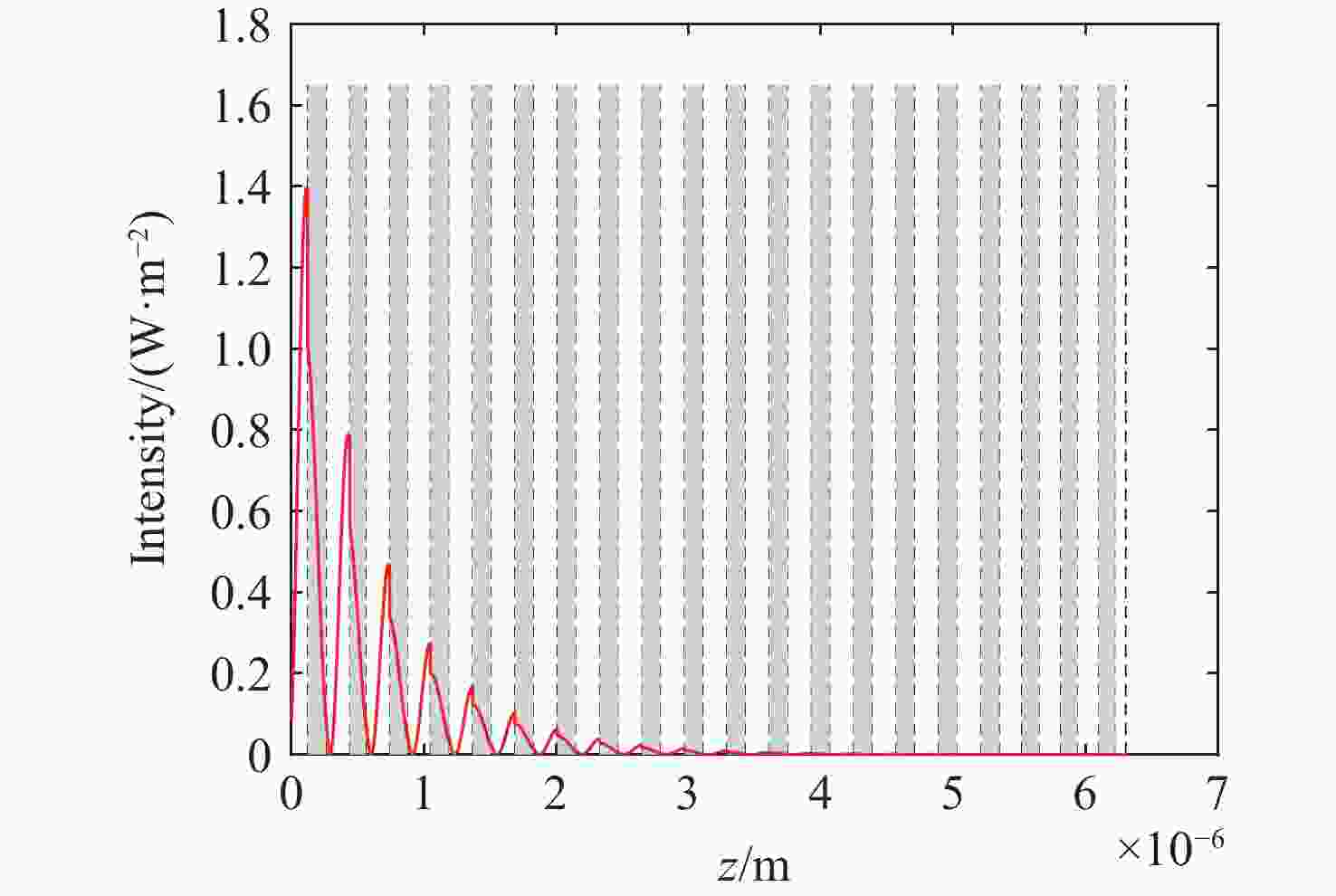
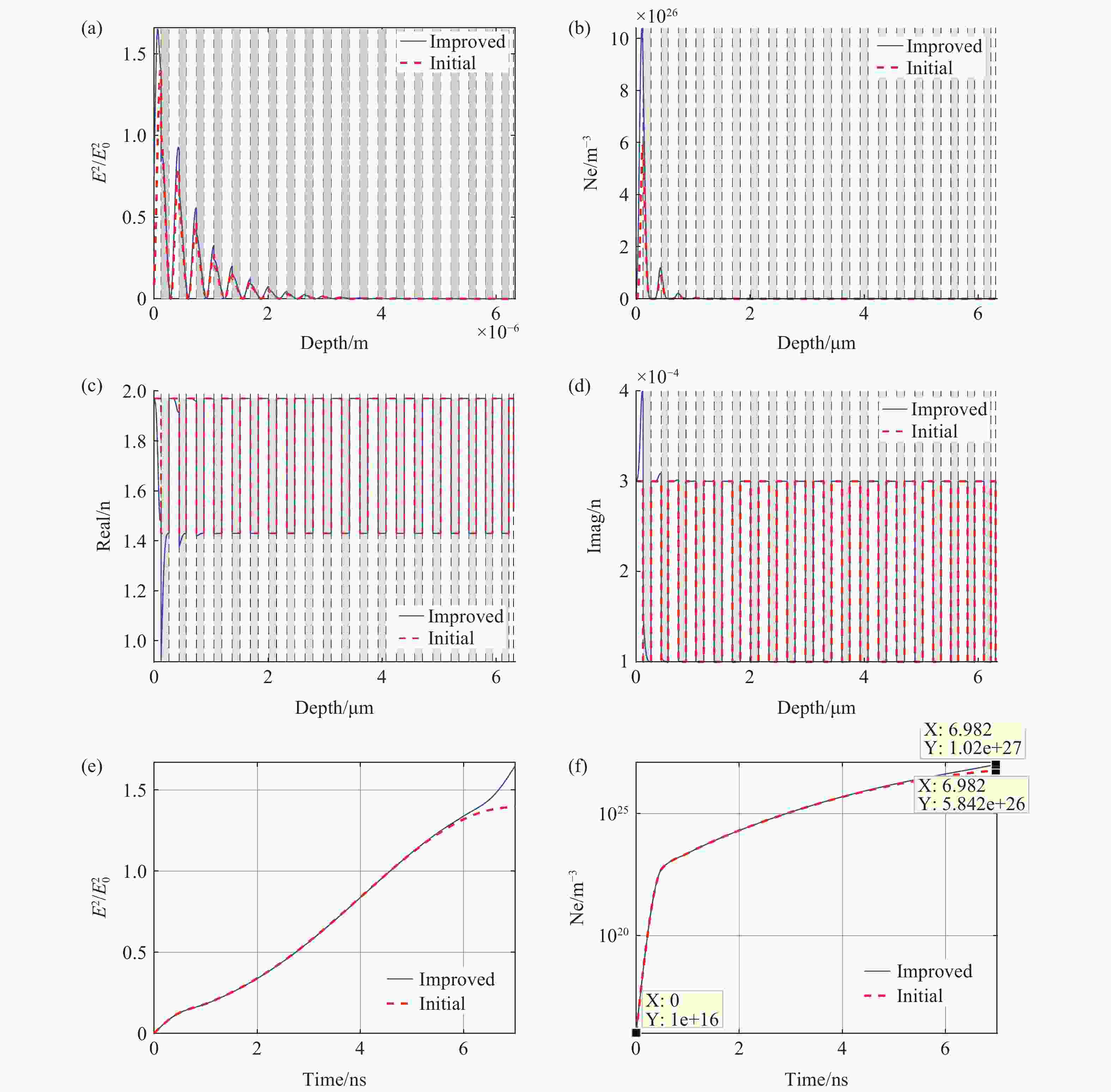
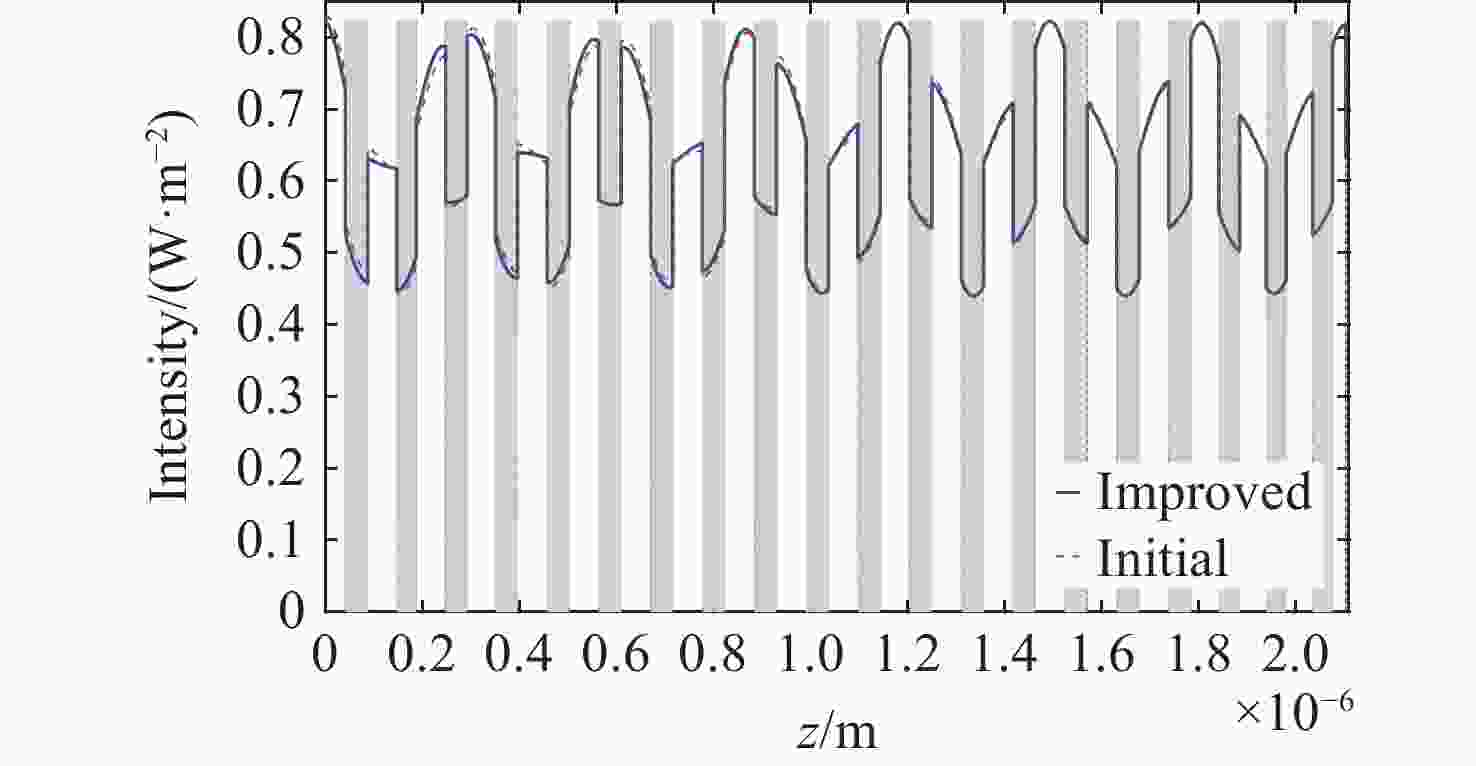
1064 nm激光辐照下膜内各参数变化趋势。(a) 电场沿深度分布;(b) 自由电子数密度沿深度分布;(c) 折射率实部沿深度分布;(d) 折射率虚部沿深度分布;(e) 电场随时间变化;(f) 自由电子数密度随时间变化Figure 3. Variation of film parameters under
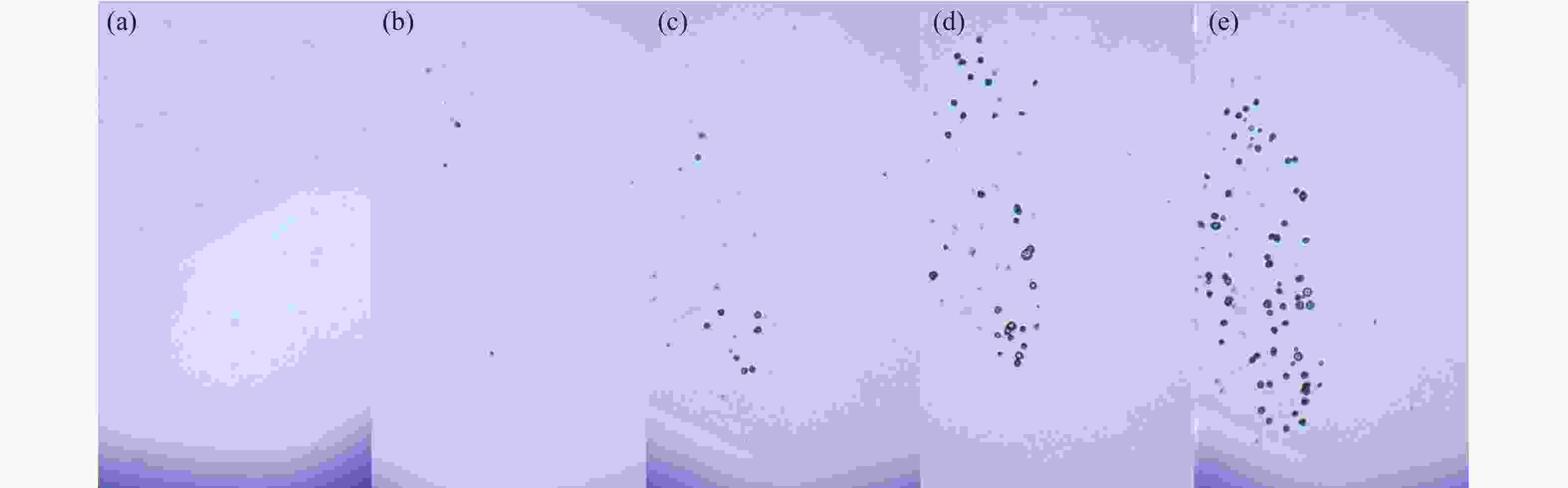
1064 nm laser irradiation. (a) Electric field distribution along depth; (b) Free electron density distribution along depth; (c) Real refractive index distribution along depth; (d) Imaginary refractive index distribution along depth; (e) Electric field variation over time; (f) Free electron density variation over time.图 9 不同激光能量辐照后膜层的损伤形貌。(a)激光能量密度12.5 J/cm2;(b)激光能量密度14.5 J/cm2;(c)激光能量密度20.0 J/cm2;(d)激光能量密度5.0 J/cm2;(e)激光能量密度30.0 J/cm2
Figure 9. Damage morphology within the film after irradiation with different laser energies (a) Laser energy density 12.5 J/cm2; (b) Laser energy density 14.5 J/cm2; (c) Laser energy density 20.0 J/cm2; (d) Laser energy density 5.0 J/cm2; (e) Laser energy density 30.0 J/cm2
Parameter Symbol HfO2 SiO2 Band gap $ {E}_{g}/({\mathrm{eV}}) $ 5.5 7.8 Effective electron mass $ m/({10}^{-31}{\mathrm{kg}}) $ 0.39×9.11 0.50×9.11 Electron saturated drift velocity $ {v}_{s}/({10}^{5}\;{\mathrm{m}}\cdot {{\mathrm{s}}}^{-1}) $ 2.0 2.0 Refractive index $ {n}_{0} $ 1.97 1.45 Heat capacity*Density $ \rho c/({10}^{6}\;{\mathrm{J}}\cdot {{\mathrm{m}}}^{-3}\cdot {{\mathrm{K}}}^{-1}) $ 4.65 2.10 Thermal conductivity $ K/({\mathrm{W}}\cdot {{\mathrm{m}}}^{-1}\cdot {{\mathrm{K}}}^{-1}) $ 2.0 1.19 Melting point $ T/({\mathrm{K}}) $ 3073 1997 Young’s modulus $ \gamma /({10}^{10}\;{\mathrm{Pa}}) $ 24.0 8.7 Thermal coefficient of expansion $ \beta /({10}^{-6}\;{{\mathrm{K}}}^{-1}) $ 5.6 0.5 Poisson’s ratio $ \nu $ 0.27 0.17 -
[1] KOZLOWSKI M R, THOMAS I M, CAMPBELL J H, et al. High-power optical coatings for a megajoule class ICF laser[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 1993, 1780: 17802L. doi: 10.1117/12.983267 [2] 毛思达, 邹永刚, 范杰, 等. 离子后处理对TiO2光学薄膜及损伤特性的影响[J]. 光学 精密工程, 2019, 27(7): 1451-1457. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20192707.1451MAO S D, ZOU Y G, FAN J, et al. Influence of plasma treatment on optical and damage properties of TiO2 thin films[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2019, 27(7): 1451-1457. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/OPE.20192707.1451 [3] 刘瑞斌, 殷允嵩. 激光诱导击穿光谱技术相关物理机制研究进展[J]. 中国光学(中英文), 2024, 17(1): 19-37. doi: 10.37188/CO.2023-0019LIU R B, YIN Y S. Research progress on the related physical mechanism of laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy[J]. Chinese Optics, 2024, 17(1): 19-37. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/CO.2023-0019 [4] 陈斐, 王树青, 程年恺, 等. 高重频声光门控自吸收免疫激光诱导击穿光谱技术分析研究[J]. 中国光学(中英文), 2024, 17(2): 253-262.CHEN F, WANG SH Q, CHENG N K, et al. Study and analysis of self-absorption-free laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy with high-repetition rate acousto-optic gating[J]. Chinese Optics, 2024, 17(2): 253-262. (in Chinese). [5] 钱方, 彭佳琦, 许永博. 脉冲激光辐照背照式CMOS图像传感器损伤机理研究[J]. 中国光学(中英文), 2025, 18(2): 256-265. doi: 10.37188/CO.2024-0139QIAN F, PENG J Q, XU Y B. Damage mechanism of back-illuminated CMOS image sensor irradiated by pulsed laser[J]. Chinese Optics, 2025, 18(2): 256-265. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/CO.2024-0139 [6] 杨艳, 张慧敏, 张旭霖, 等. TiO2/PSS薄膜对Kretschmann型传感器光谱的调制[J]. 中国光学(中英文), 2025, 18(2): 297-306. doi: 10.37188/CO.2024-0125YANG Y, ZHANG H M, ZHANG X L, et al. Modulation of a Kretschmann-type sensor’s spectra using TiO2/PSS thin films[J]. Chinese Optics, 2025, 18(2): 297-306. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/CO.2024-0125 [7] 辛亚武, 彭永超, 张宇翔, 等. 可见/近红外多波段激光滤光膜的研制[J]. 中国光学(中英文), 2026, 19(1): 239-249.XIN Y W, PENG Y CH, ZHANG Y X, et al. Development of visible/near-infrared multiband laser filter film[J]. Chinese Optics, 2026, 19(1): 239-249. (in Chinese). [8] DU L F, ZHU X B, ZHANG R ZH. The thermal-stress accumulation in anti-reflective coatings with multi-pulse laser irradiation[J]. Optics Communications, 2015, 350: 263-269. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2015.04.009 [9] CAI Y, ZHOU M L, MA ZH L, et al. Spectrum method for laser induced damage in dielectric thin films[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2015, 9543: 95430C. doi: 10.1117/12.2181798 [10] WU SH J, SU J H, LI D J, et al. The effect of the applied electric field on laser-induced damage of dielectric thin films[J]. Materials Research Express, 2017, 4(1): 016403. doi: 10.1088/2053-1591/4/1/016403 [11] ZHOU Q, MA P, QIU F M, et al. Material ejection and layer peeling-off in HfO2/SiO2 thin-film beam splitters induced by 1ω and 3ω lasers[J]. Optical Materials, 2022, 125: 111894. doi: 10.1016/j.optmat.2021.111894 [12] 郑梦珂, 李杰, 张蓉竹, 等. 激光诱导多层光学薄膜损伤分析与仿真[J]. 光学学报, 2022, 42(1): 0131001. doi: 10.3788/AOS202242.0131001ZHENG M K, LI J, ZHANG R ZH, et al. Analysis and simulation on damage characteristics of multilayer optical film by pulsed laser[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2022, 42(1): 0131001. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/AOS202242.0131001 [13] GROSSO G, PARRAVICINI G P. Solid State Physics[M]. 2nd ed. Amsterdam: Academic Press, 2013. [14] LI F Y, LIU G D, DU L F, et al. Comparisons and analyses of the properties of laser-induced damage to SiO2 and ZnS[J]. Journal of Modern Optics, 2014, 61(14): 1158-1163. doi: 10.1080/09500340.2014.924597 [15] MANSURIPUR M, CONNELL G A N, GOODMAN J W. Laser-induced local heating of multilayers[J]. Applied Optics, 1982, 21(6): 1106-1114. doi: 10.1364/AO.21.001106 [16] WANG ZH, ZHANG R ZH, CHEN M. Analysis of composite wavelength multilayer dielectric film damage based on the field-thermal effect[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America B, 2024, 41(11): 2589-2598. doi: 10.1364/JOSAB.534813 [17] WANG F, CHEN K J, GAO F, et al. Analysis of laser-induced damage in optical thin film based on ANSYS[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2018, 10964: 109642M. doi: 10.1117/12.2505819 [18] WEBER M J. Handbook of Optical Materials[M]. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 2002. [19] WAKAKI M. Optical Materials and Applications[M]. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 2017. -





 下载:
下载: