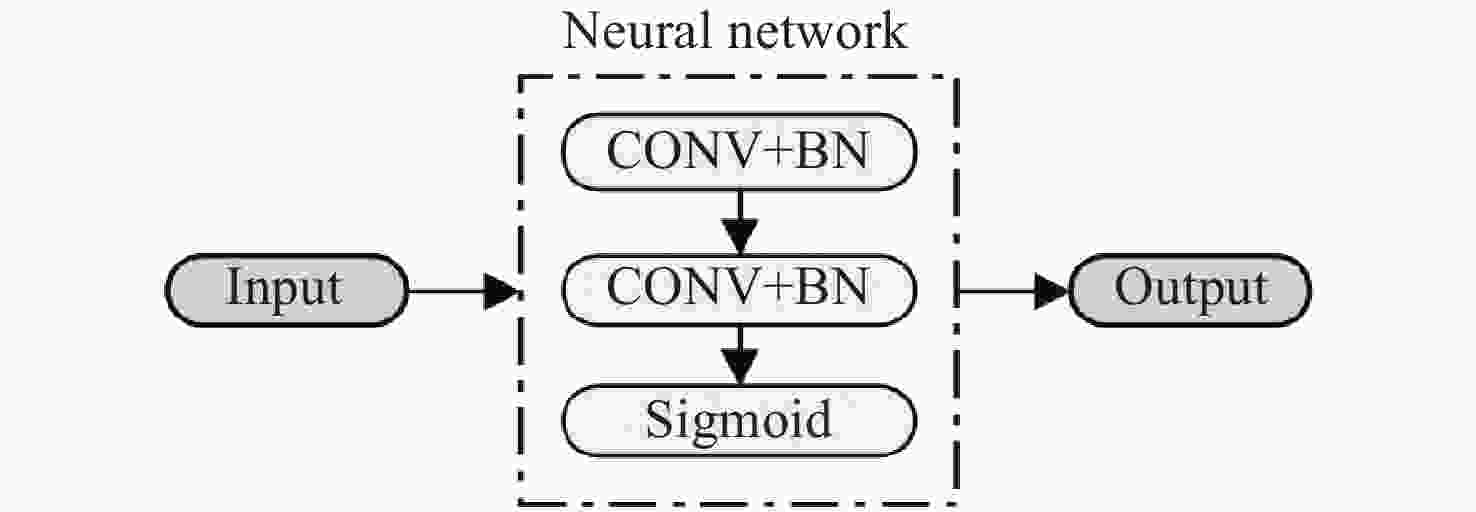
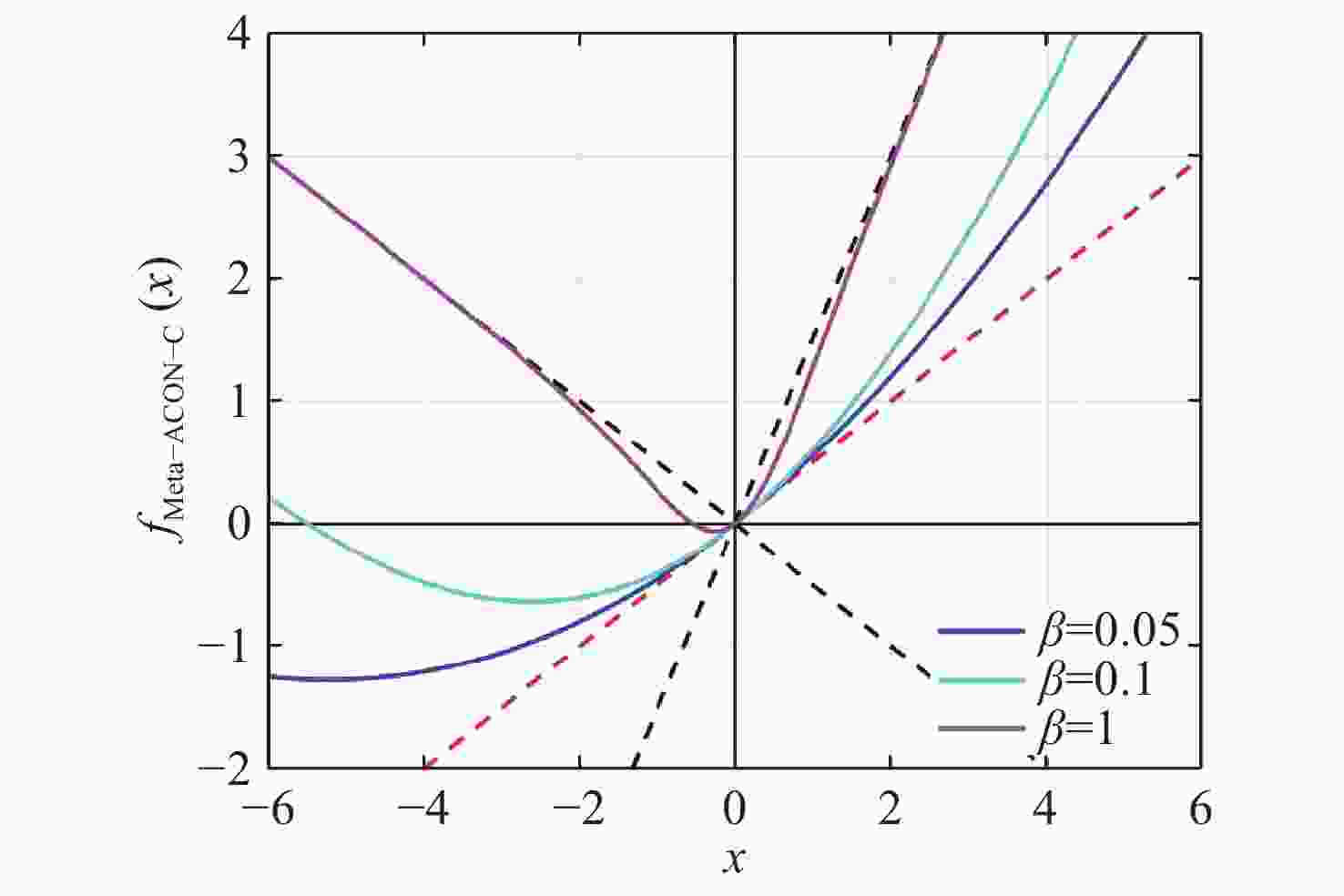
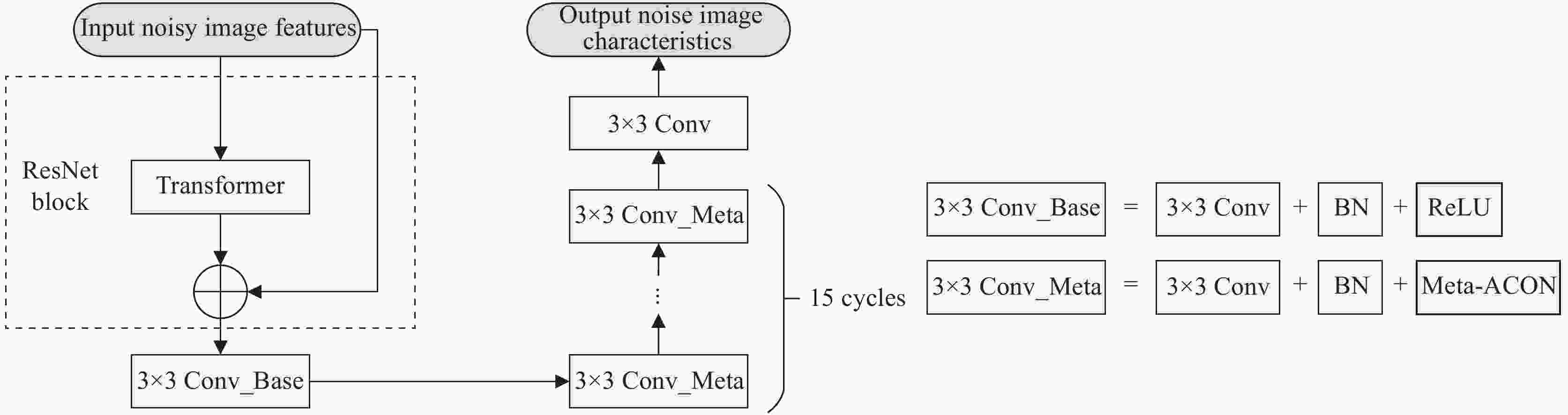
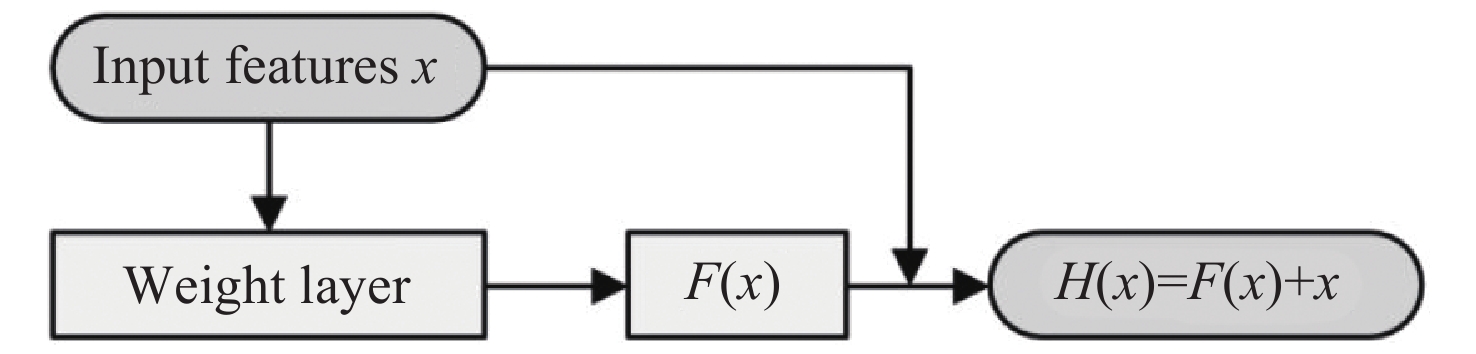
DnCNN-RM: an adaptive SAR image denoising algorithm based on residual networks
doi: 10.37188/CO.EN-2024-0028
-
摘要:
在图像处理领域,合成孔径雷达(SAR)图像的应用很广泛,因而分析SAR图像具有重要意义。然而,这些图像常常受到相干斑噪声的干扰,显著降低了图像质量。传统的去噪方法,通常基于滤波器技术,往往存在效率低和适应性差的局限性。为了克服这些不足,本文提出了一种基于增强残差网络架构的SAR图像去噪算法,旨在提升SAR图像在复杂电磁环境中的应用效果。该算法结合了残差网络模块,直接对含噪输入图像进行处理,生成去噪输出。这种方法不仅有效降低了计算复杂度,还缓解了模型训练过程中遇到的困难。通过将Transformer模块与残差块相结合,显著提高了网络对全局特征的提取能力。相较于基于卷积神经网络(CNN)的残差模块,该方法具有更强的特征提取能力。此外,算法引入了自适应激活函数Meta-ACON,能够动态调整神经元的激活模式,从而进一步提升了网络的特征提取效率。通过在RSOD数据集上的实验证明,所提出的去噪方法在EPI、SSIM和ENL等指标上表现出色,同时在PSNR方面也取得了显著的提升。与传统的去噪算法及深度学习算法相比,该算法的PSNR性能提高了两倍以上。进一步在MSTAR SAR数据集上进行测试,得到的PSNR值为
25.2021 ,验证了该算法在SAR去噪领域的良好泛化性。上述结果表明,所提出的算法不仅能够有效降低相干斑噪声,还能有效保留SAR图像中的关键信息特征,从而在实际应用中显著提高图像质量和可用性。Abstract:In the field of image processing, the analysis of Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) images is crucial due to its broad range of applications. However, SAR images are often affected by coherent speckle noise, which significantly degrades image quality. Traditional denoising methods, typically based on filter techniques, often face challenges related to inefficiency and limited adaptability. To address these limitations, this study proposes a novel SAR image denoising algorithm based on an enhanced residual network architecture, with the objective of enhancing the utility of SAR imagery in complex electromagnetic environments. The proposed algorithm integrates residual network modules, which directly process the noisy input images to generate denoised outputs. This approach not only reduces computational complexity but also mitigates the difficulties associated with model training. By combining the Transformer module with the residual block, the algorithm enhances the network's ability to extract global features, offering superior feature extraction capabilities compared to CNN-based residual modules. Additionally, the algorithm employs the adaptive activation function Meta-ACON, which dynamically adjusts the activation patterns of neurons, thereby improving the network's feature extraction efficiency. The effectiveness of the proposed denoising method is empirically validated using real SAR images from the RSOD dataset. The proposed algorithm exhibits remarkable performance in terms of EPI, SSIM, and ENL, while achieving a substantial enhancement in PSNR when compared to traditional and deep learning-based algorithms. The PSNR performance is enhanced by over twofold. Moreover, the evaluation of the MSTAR SAR dataset substantiates the algorithm's robustness and applicability in SAR denoising tasks, with a PSNR of
25.2021 being attained. These findings underscore the efficacy of the proposed algorithm in mitigating speckle noise while preserving critical features in SAR imagery, thereby enhancing its quality and usability in practical scenarios.-
Key words:
- SAR images /
- image denoising /
- residual networks /
- adaptive activation function
-
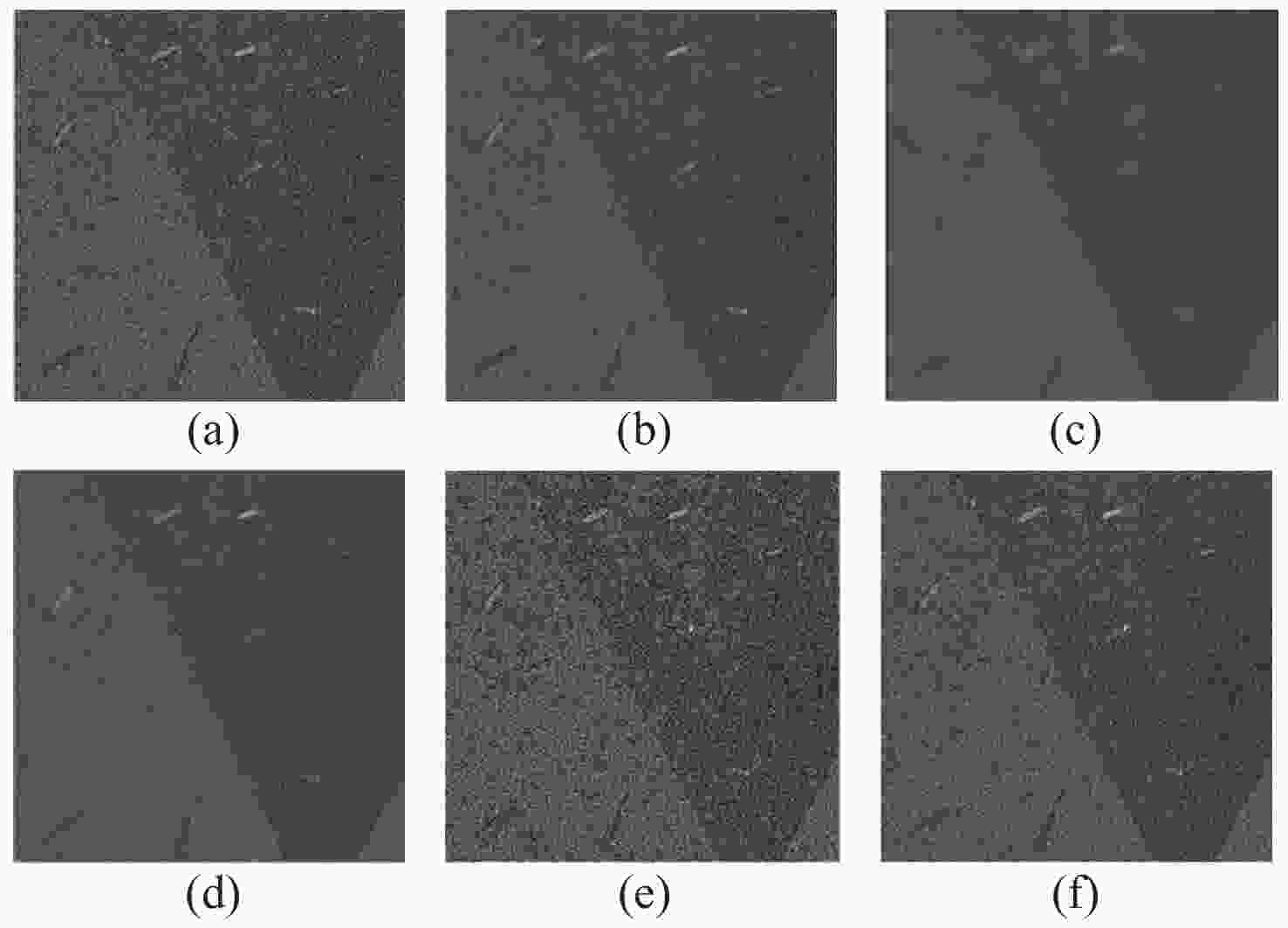
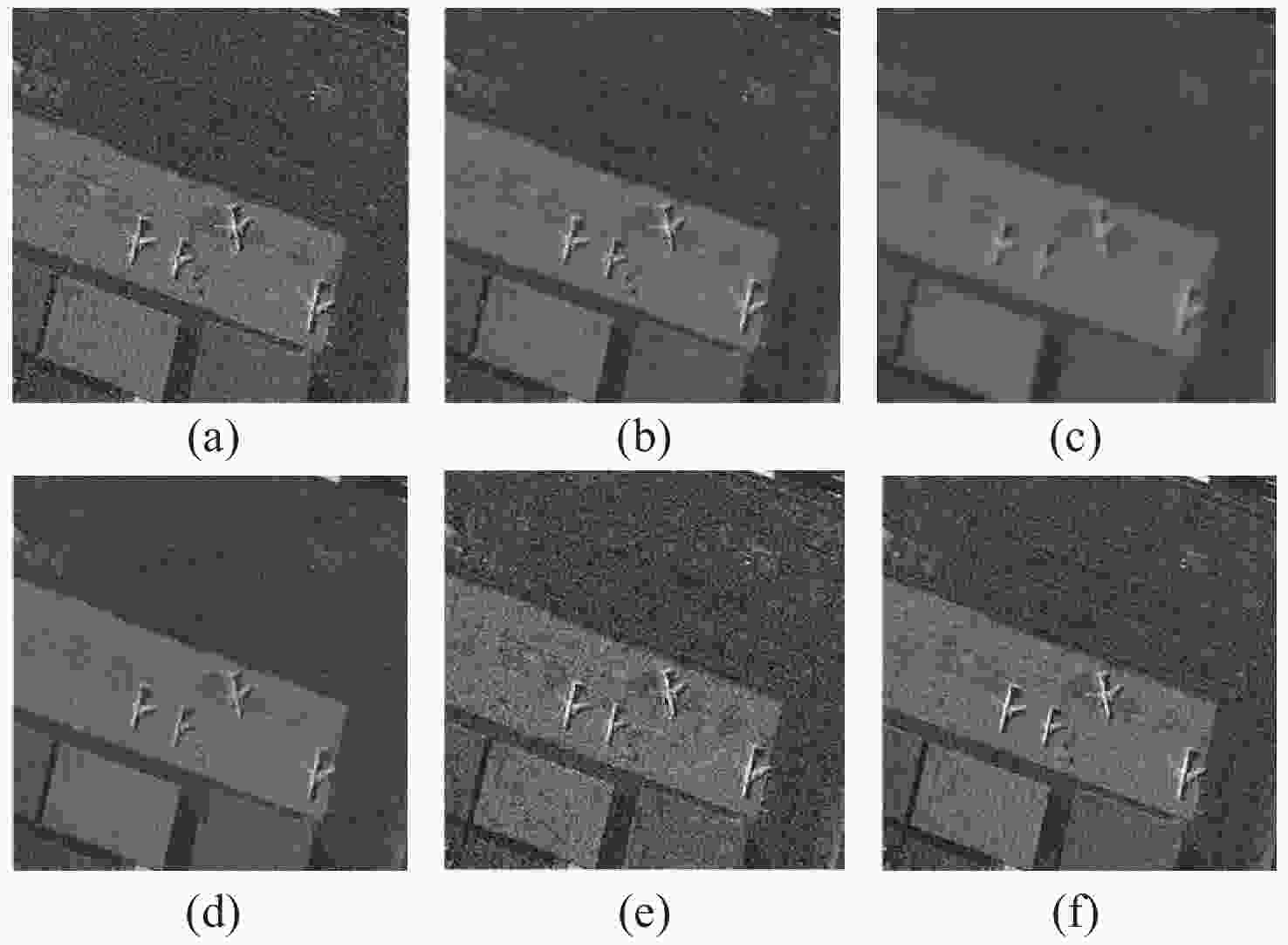
Table 1. Denoising results of SAR1 by different SAR image denoising algorithms
Method Mean Std PNSR EPI SSIM ENL Lee 118.44 13.73 14.74 0.987 0.996 0.999 Frost 115.32 10.74 12.49 0.833 0.979 0.999 SAR-BM3D 292.84 17.11 51.74 0.992 0.992 0.999 DnCNN 607.76 25.38 22.56 1.000 0.988 0.999 DnCNN-RM 697.12 25.22 59.011 1.000 0.999 0.999 Table 2. Denoising results of SAR2 by different SAR image denoising algorithms
Method Mean Std PNSR EPI SSIM ENL Lee 556.73 23.38 18.38 0.989 0.995 0.999 Frost 409.82 20.24 24.55 0.735 0.978 0.999 SAR-BM3D 595.95 24.41 21.45 1.000 0.997 0.999 DnCNN 1180.49 34.36 23.40 1.000 0.987 0.999 DnCNN-RM 1150.26 35.65 39.78 0.999 0.999 0.999 Table 3. Denoising results of various denoising algorithms in ablation study
Method PSNR DnCNN 15.5135 DnCNN+ ResNet Block (CNN) 24.5698 DnCNN + ResNet Block (Transformer) 24.8080 DnCNN + Meta-ACON 24.5833 DnCNN+ ResNet Block (CNN) + Meta-ACON 24.5888 DnCNN + ResNet Block (Transformer) + Meta-ACON 25.2021 -
[1] THEODOSIOU A, LÓPEZ-DEKKER P. On the sensitivity to height and motion of bistatic SAR interferometry: a spectral view[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2024, 62: 5212212. [2] WU Y M, SUO Y X, MENG Q B, et al. FAIR-CSAR: a benchmark dataset for fine-grained object detection and recognition based on single-look complex SAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2025, 63: 5201022. [3] ZHAO CH H, LI K Y, WANG L, et al. A rapid SAR image simulation method for ship wakes coupled with sea waves using fluid velocity potential[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2025, 32: 271-275. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2024.3514804 [4] GOU SH P, LI D B, HAI D, et al. Spectral clustering with eigenvalue similarity metric method for POL-SAR image segmentation of land cover[J]. Journal of Geographic Information System, 2018, 10: 150-164. doi: 10.4236/jgis.2018.101007 [5] PETTINATO S, SANTI E, PALOSCIA S, et al. Large area robust identification of snow cover from multitemporal COSMO-SkyMed images[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2015, 9642: 964204. [6] LI CH D, LI G Y, SONG Y CH, et al. Fast forest fire detection and segmentation application for UAV-assisted mobile edge computing system[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2024, 11(16): 26690-26699. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2023.3311950 [7] QIN CH, ZHANG L P, WANG X Q, et al. RDB-DINO: an improved end-to-end transformer with refined de-noising and boxes for small-scale ship detection in SAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2025, 63: 5200517. [8] JOSHI G P, ALENEZI F, THIRUMOORTHY G, et al. Ensemble of deep learning-based multimodal remote sensing image classification model on unmanned aerial vehicle networks[J]. Mathematics, 2021, 9(22): 2984. doi: 10.3390/math9222984 [9] SUN Y X, FENG SH SH, YE Y M, et al. Multisensor fusion and explicit semantic preserving-based deep hashing for cross-modal remote sensing image retrieval[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 60: 5219614. [10] THAKUR R S, YADAV R N, GUPTA L. State-of-art analysis of image denoising methods using convolutional neural networks[J]. IET Image Processing, 2019, 13(13): 2367-2380. doi: 10.1049/iet-ipr.2019.0157 [11] DUAN Y P, TAO X M, HAN C Y, et al. Multi-scale convolutional neural network for SAR image semantic segmentation[C]. 2018 IEEE Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM), IEEE, 2018: 1-6. [12] WANG CH, YIN ZH X, MA X SH, et al. SAR image despeckling based on block-matching and noise-referenced deep learning method[J]. Remote Sensing, 2022, 14(4): 931. doi: 10.3390/rs14040931 [13] GUO Q, LIU J N, KALIUZHNYI M. YOLOX-SAR: high-precision object detection system based on visible and infrared sensors for SAR remote sensing[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2022, 22(17): 17243-17253. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2022.3186889 [14] WANG P Y, ZHANG H, PATEL V M. SAR image despeckling using a convolutional neural network[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2017, 24(12): 1763-1767. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2017.2758203 [15] ZHANG Q, YUAN Q Q, LI J, et al. Learning a dilated residual network for SAR image despeckling[J]. Remote Sensing, 2018, 10(2): 196. doi: 10.3390/rs10020196 [16] 王曦. 基于深度学习的SAR图像目标识别方法研究[D]. 成都: 电子科技大学, 2022.WANG X. Research on SAR image target recognition method based on deep learning[D]. Chengdu: University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2022. (in Chinese). -





 下载:
下载: