Multi-Fano resonances sensing based on a non-through metal-insulator-metal waveguide coupling D-shaped cavity
doi: 10.37188/CO.EN-2025-0017
-
摘要:
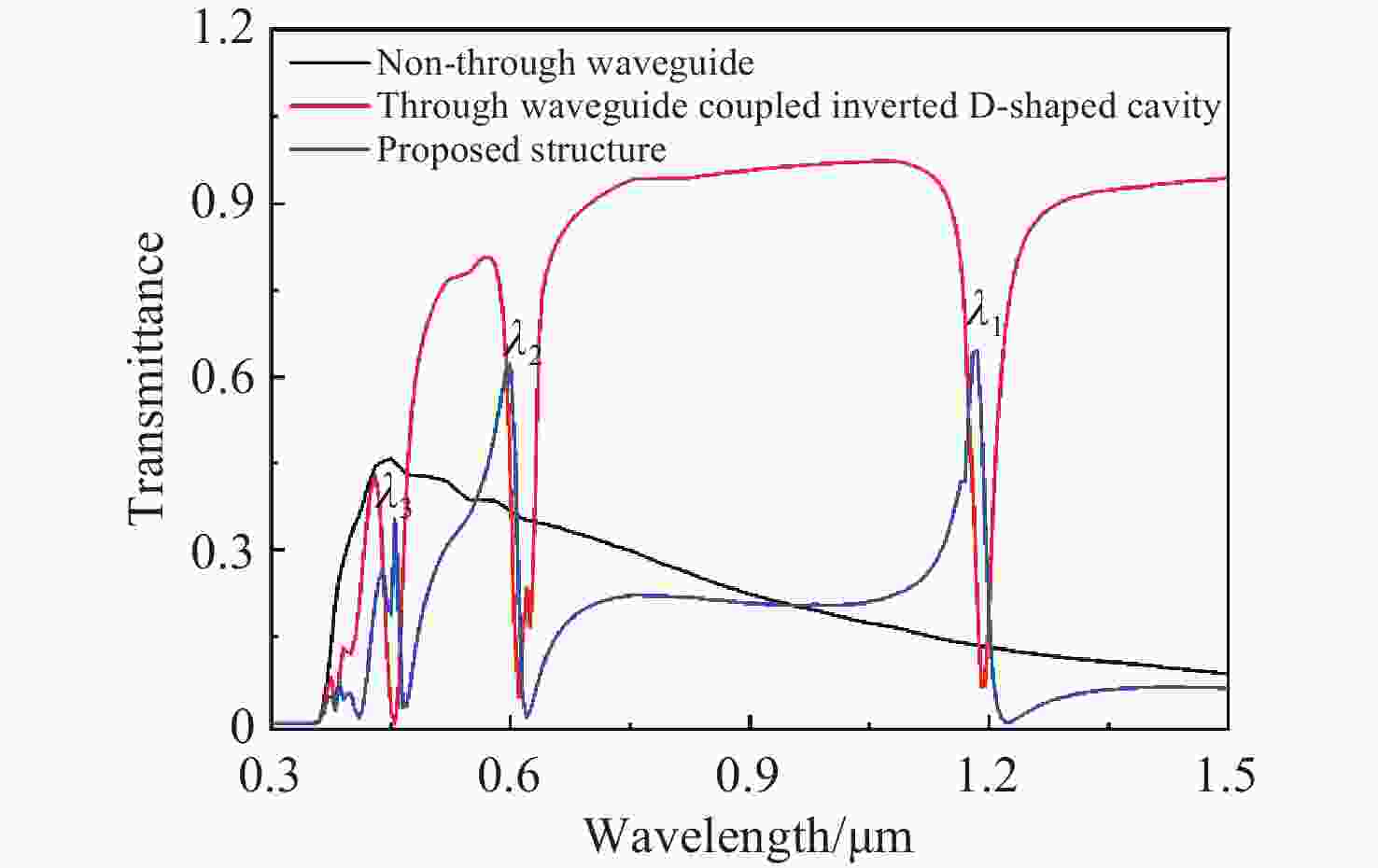
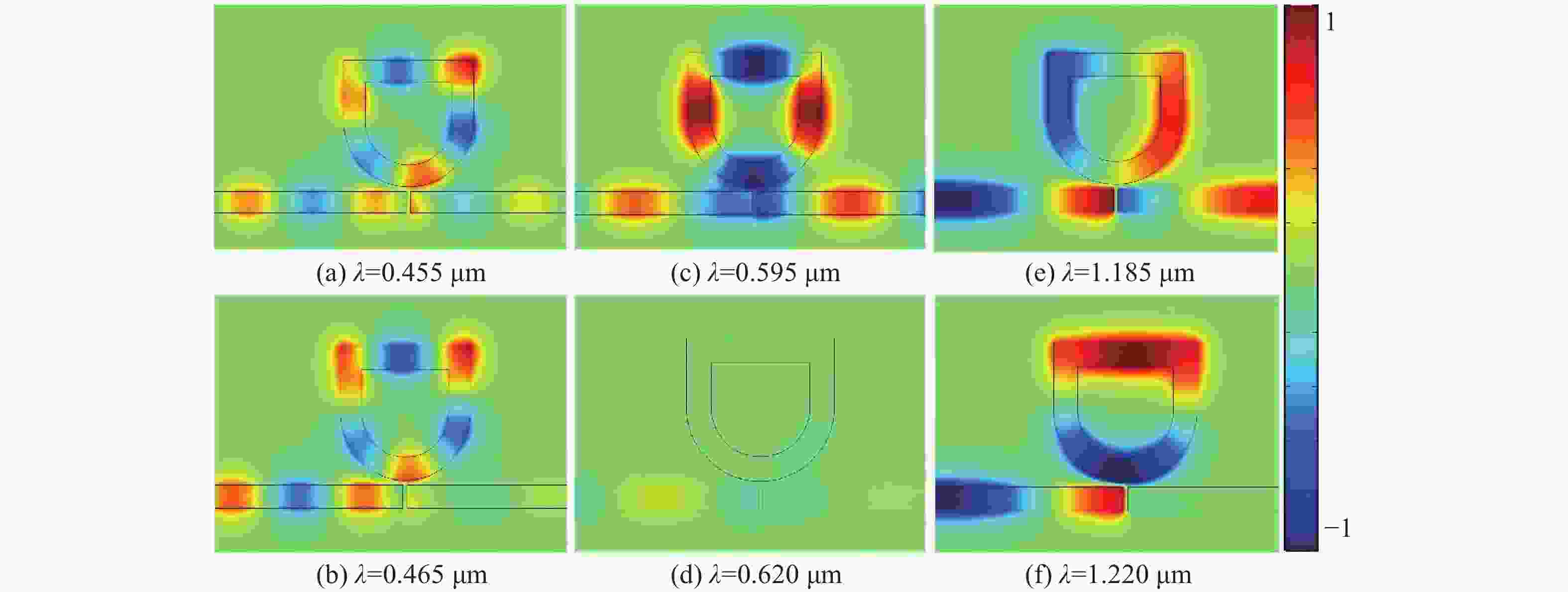
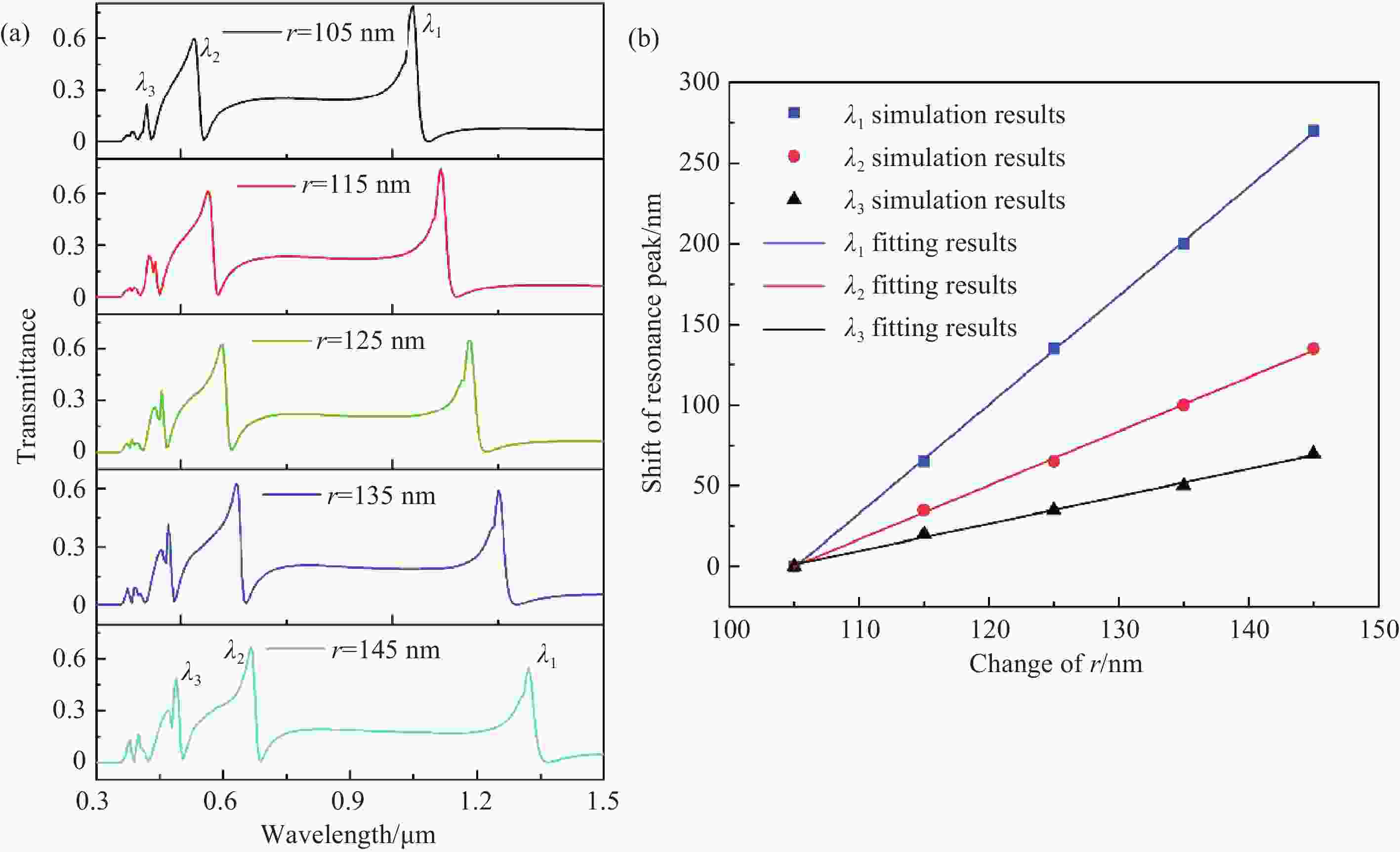
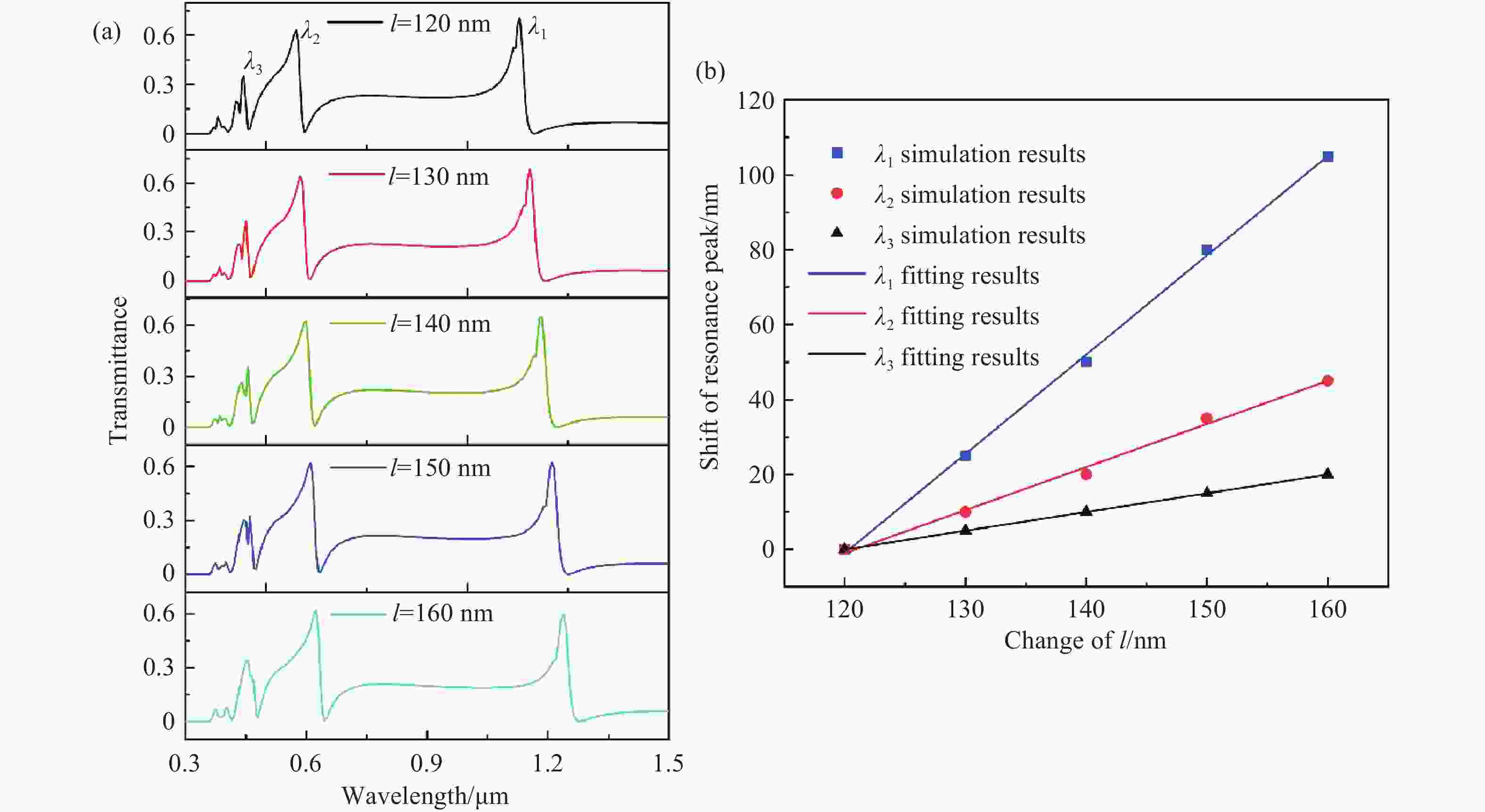
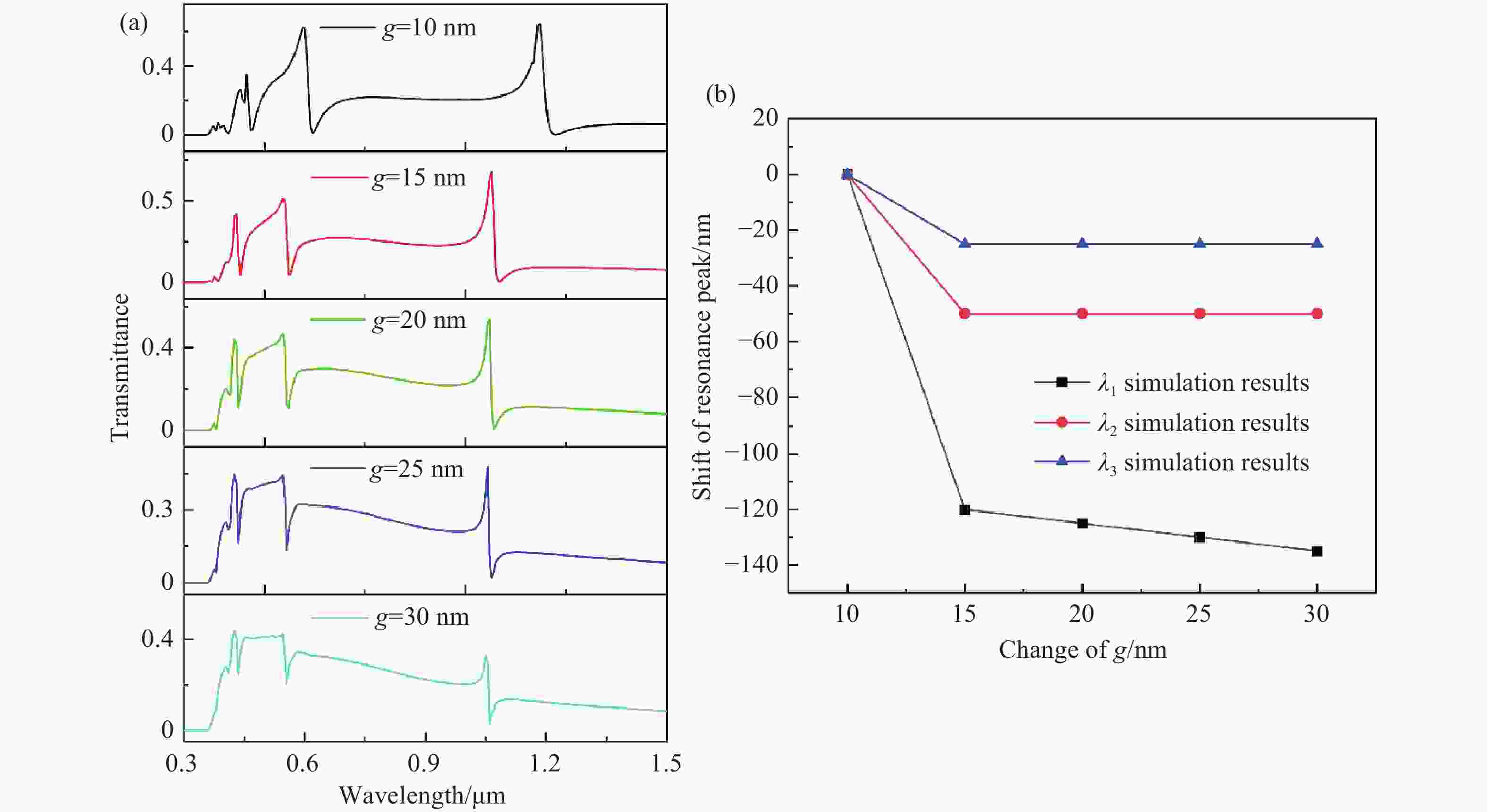
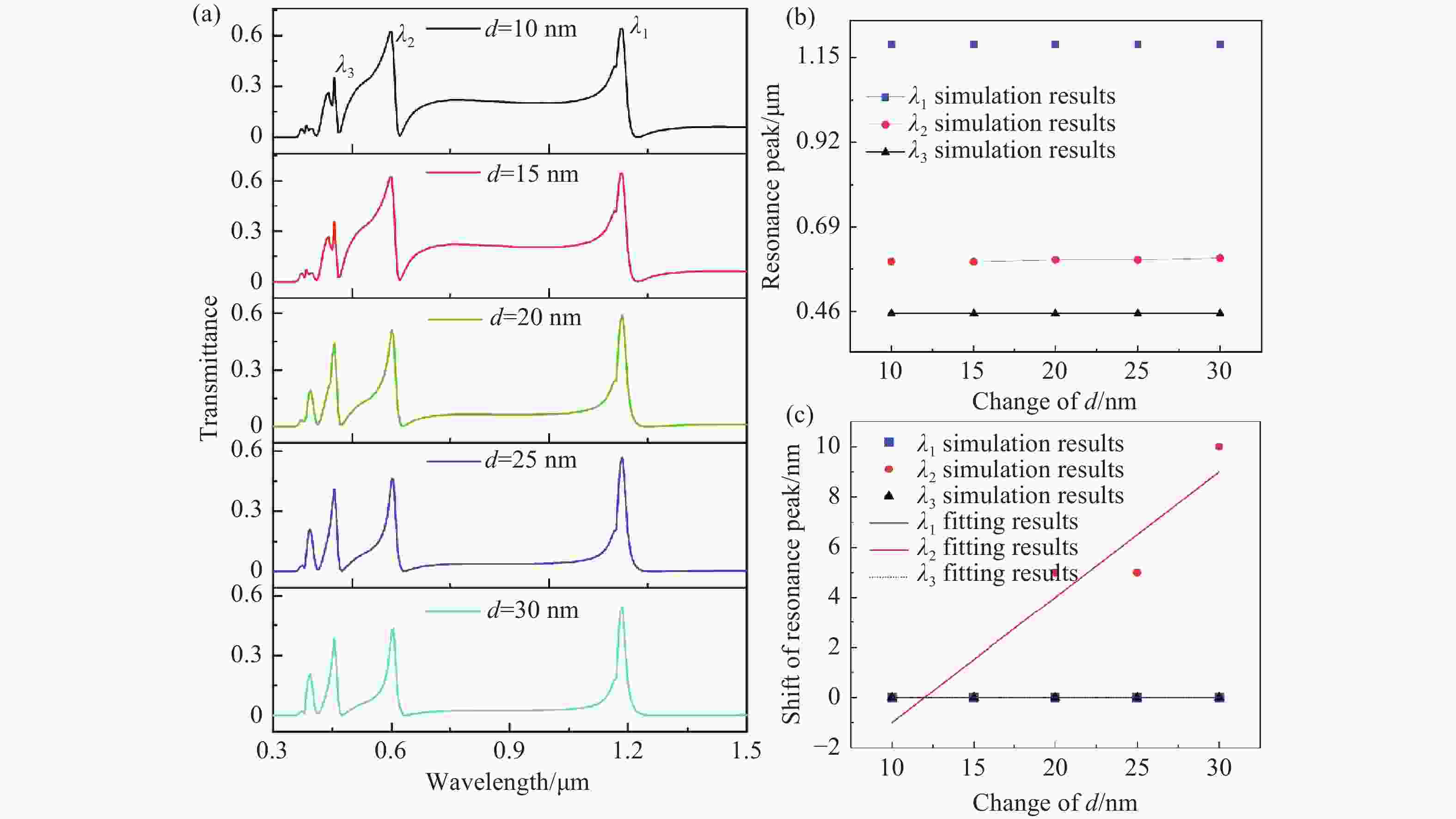
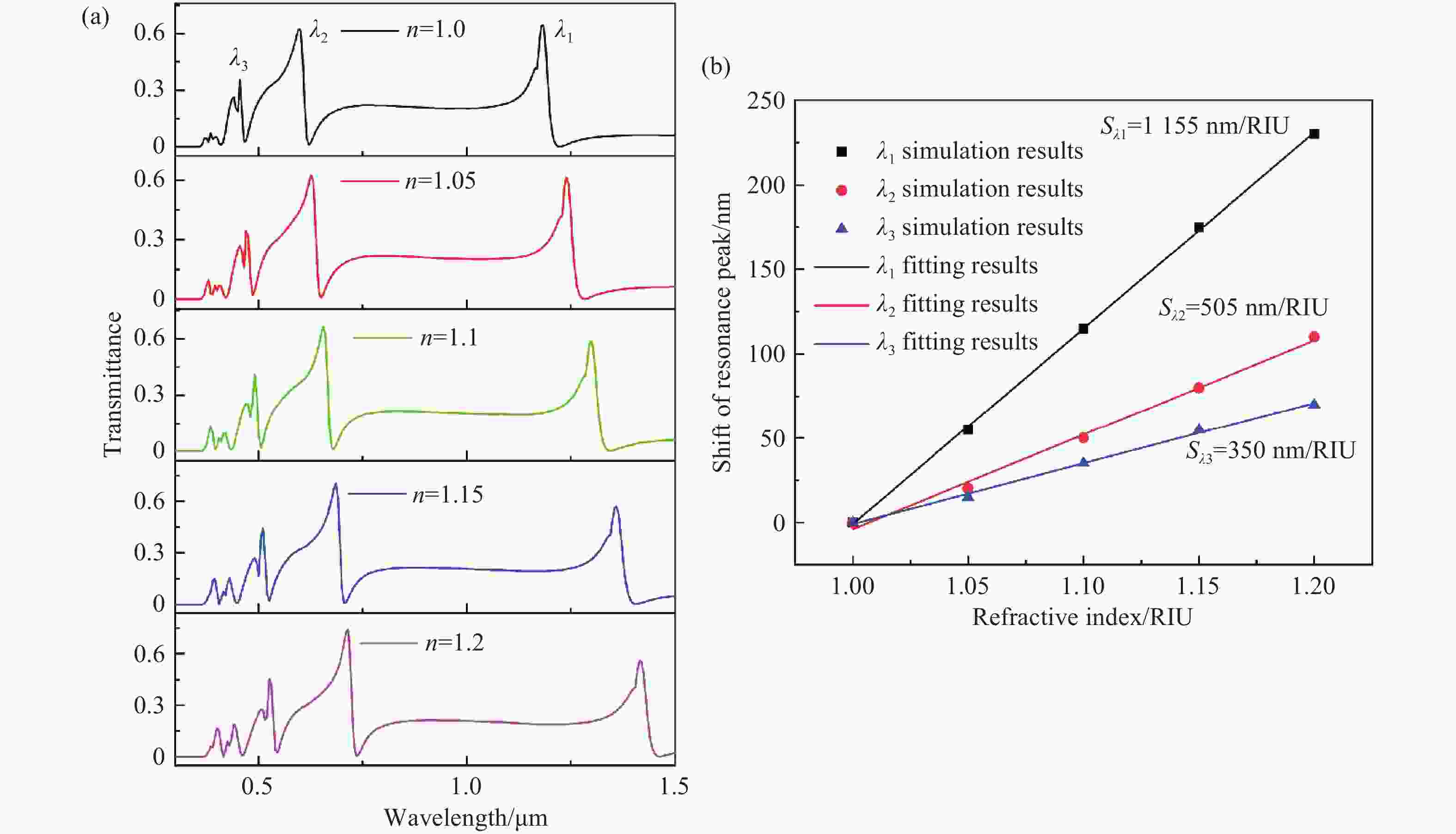
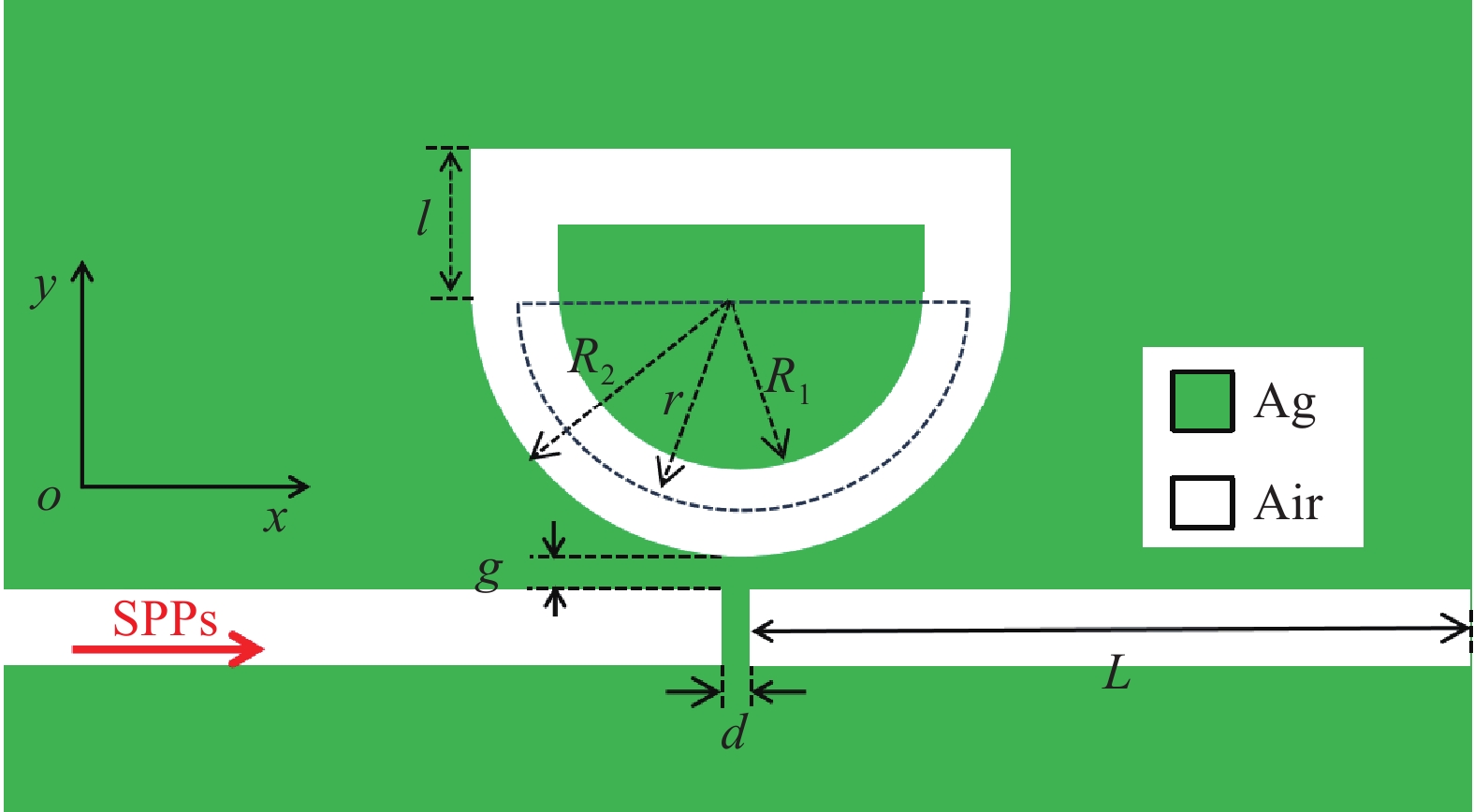
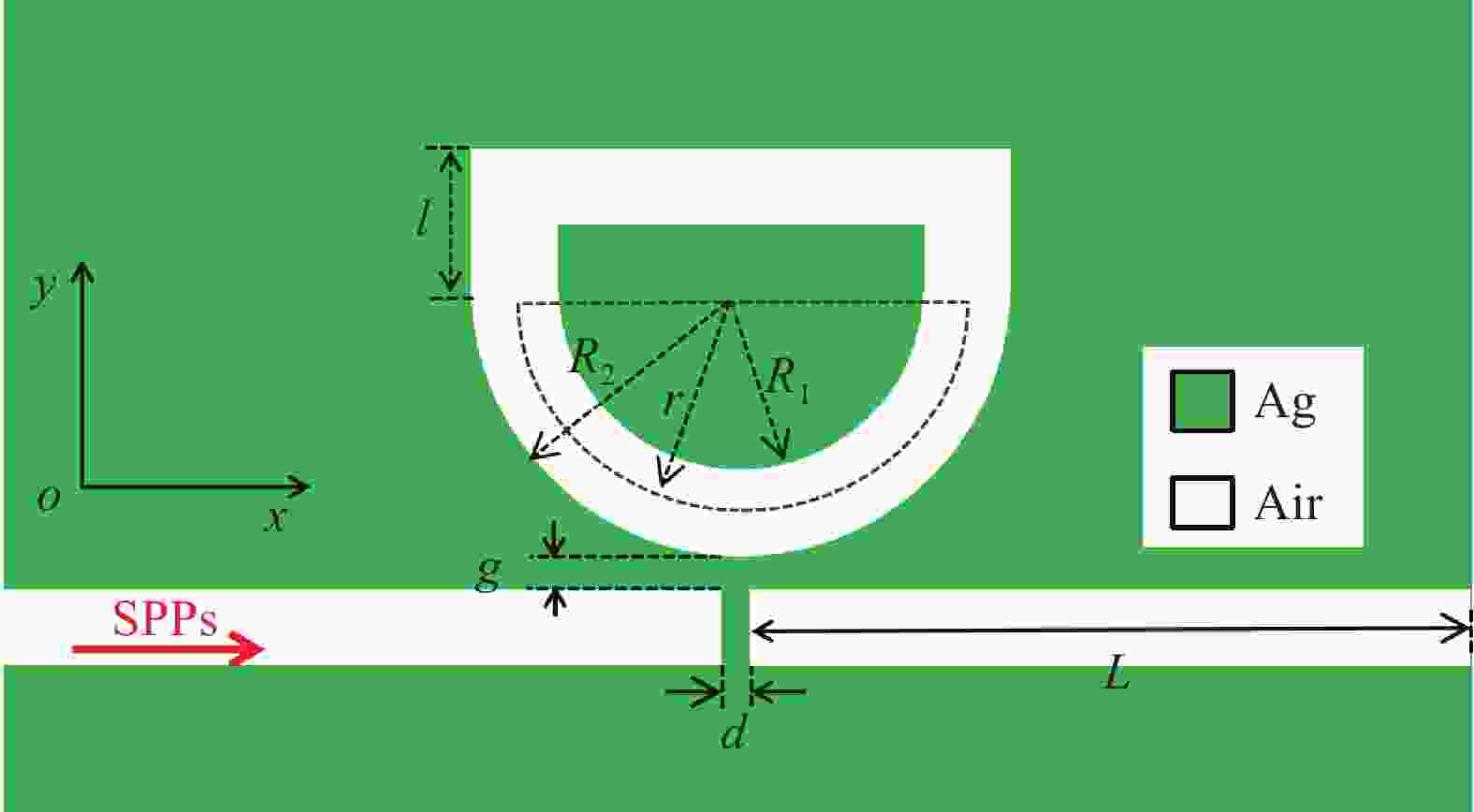
本文设计了一种由两个一端封堵的金属-绝缘体-金属(MIM)波导与一个D形腔耦合组成的表面等离激元波导结构。使用有限元方法(FEM)模拟了该结构的传输特性、磁场分布以及折射率传感特性。在透射光谱中可以明显观察到多Fano共振现象。这些Fano共振源于D形谐振腔产生的共振离散态与一端封堵的MIM波导产生的连续态之间的相互耦合。通过系统地调整结构参数,研究了其对Fano共振调制的影响。此外,通过改变MIM波导中绝缘层的折射率,研究了基于Fano共振折射率传感特性。结果表明,该结构实现的最大折射率灵敏度和品质因子(FOM)分别为
1155 RIU/nm和40。这些研究对高灵敏度光子器件、微型传感器、未来新型片上传感的设计和研究提供了新的途径。-
关键词:
- 表面等离激元 /
- 金属-绝缘体-金属波导 /
- D形谐振腔 /
- 双Fano共振 /
- 折射率传感器
Abstract:A plasmonics waveguide structure that consist of a non-through metal–insulator–metal (MIM) waveguide coupled with a D-shaped cavity was designed. And the transmission properties, magnetic field distribution, and refractive index sensing functionality were simulated using the finite element method (FEM). A multi-Fano resonance phenomenon was clearly observable in the transmission spectra. The Fano resonances observed in the proposed structure arise from the interaction between the discrete states of the D-shaped resonant cavity and the continuum state of the non-through MIM waveguide. The influence of structural parameters on Fano resonance modulation was investigated through systematic parameter adjustments. Additionally, the refractive index sensing properties, based on the Fano resonance, were investigated by varying the refractive index of the MIM waveguide's insulator layer. A maximum sensitivity and FOM of
1155 RIU/nm and 40 were achieved, respectively. This research opens up new possibilities for designing and exploring high-sensitivity photonic devices, micro-sensors, and innovative on-chip sensing architectures for future applications. -
-
[1] ZAYATS A V, SMOLYANINOV I I. Near-field photonics: surface plasmon polaritons and localized surface plasmons[J]. Journal of Optics A: Pure and Applied Optics, 2003, 5(4): S16-S50. [2] PEI J H , QI X H, ZOU M Q, et al. Advances in Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy for the Detection of Veterinary Drug Residues in Foods of Animal Origin[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Chemistry, 2024, 41(4): 459-471. (in Chinese). [3] LIU J, LIU J, WANG Y T, et al. Resonant properties of sub-wavelength metallic gratings[J]. Chinese Optics, 2011, 4(4): 363-368. (in Chinese). [4] CHEN S Y, ZHANG X Y, LIU B, et al. Classification and Application of Surface-enhanced Raman Spectroscopy Substrates[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2024, 52(7): 910-924. (in Chinese). [5] GONG H B, HU W Y, HUANG Q T, et al. Highly Sensitive Qualitative Analysis of Electronegative Molecules Based on Surface-enhanced Raman Spectroscopy[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2023, 51(7): 1213-1221. (in Chinese). [6] ZHU J, LI Z Q. Characteristics of transmission and attenuation of surface plasmon polaritons in Otto structure loaded MIM wave guide[J]. Chinese Journal of Luminescence, 2013, 34(11): 1533-1537. (in Chinese). [7] LI M, CUSHING S K, WU N Q. Plasmon-enhanced optical sensors: a review[J]. Analyst, 2015, 140(2): 386-406. [8] LEI J G, LIU T H, LIN J Q, et al. New applications of surface plasmon polaritons[J]. Chinese Journal of Optics and Applied Optics, 2010, 3(5): 432-439. (in Chinese). [9] YUE S Q, MO Z H, ZHAO J Q, et al. Detection of Haptoglobin by Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering Based on the Shift of Characteristic Peak[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2024, 52(2): 231-239. (in Chinese). [10] HONG L, DONG W N, WU Z N, et al. Application of Photoresponsive Behavior of Metal Nanoclusters in Biomedical Diagnostics and Therapy[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Chemistry, 2024, 41(9): 1238-1247. (in Chinese). [11] BUTT M A. Review of innovative cavity designs in metal–insulator-metal waveguide-based plasmonic sensors[J]. Plasmonics, 2024, 20(6): 4257-4276. doi: 10.1007/s11468-024-02562-4 [12] CHEN J J, GAN F Y, WANG Y J, et al. Plasmonic sensing and modulation based on fano resonances[J]. Advanced Optical Materials, 2018, 6(9): 1701152. [13] KONG Y, CAO J J, QIAN W C, et al. Multiple Fano resonance based optical refractive index sensor composed of micro-cavity and micro-structure[J]. IEEE Photonics Journal, 2018, 10(6): 6804410. [14] BORETTI A. A perspective on the use of perovskite luminophores for solar windows[J]. Advanced Sensor and Energy Materials, 2024, 3(1): 100060. [15] SHU Y, YANG M, LI Z H, et, al. MicroRNA Sensing Based on Gold Nanoparticle Aggregation and Hybridization Chain Amplification[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Chemistry, 2024, 41(1): 109-117. (in Chinese). [16] GUO H Y, FANG W J, PANG J L, et al. Multiple Fano resonances based on all-dielectric metastructure for refractive index sensing[J]. Infrared Physics & Technology, 2024, 139: 105284. [17] ROHIMAH S, TIAN H, WANG J F, et al. Fano resonance in the plasmonic structure of MIM waveguide with r-shaped resonator for refractive index sensor[J]. Plasmonics, 2022, 17(4): 1681-1689. [18] ZHANG Z D, ZHANG H N, LIANG J, et al. Double Fano resonance and refractive index sensors based on parallel-arranged Au nanorod dimer metasurface arrays[J]. Chinese Optics, 2023, 16(4): 961-971. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/CO.EN-2023-0008 [19] ZHU J, WU C S. Optical refractive index sensor with Fano resonance based on original MIM waveguide structure[J]. Results in Physics, 2021, 21: 103858. [20] RAHAD R, HOSSAIN N, HOSSAIN A. Enhanced alcohol detection using surface plasmon polariton dependent MIM plasmonic sensor[J]. Plasmonics, 2025, 20: 1331-1340. doi: 10.1007/s11468-024-02360-y [21] BUTT M A, KAZANSKIY N L, KHONINA S N. Tapered waveguide mode converters for metal-insulator-metal waveguide plasmonic sensors[J]. Measurement, 2023, 211: 112601. [22] BUTT M A, PIRAMIDOWICZ R. Orthogonal mode couplers for plasmonic chip based on metal–insulator–metal waveguide for temperature sensing application[J]. Scientific reports, 2024, 14(1): 3474. [23] BUTT M A. Plasmonic sensors based on a metal–insulator–metal waveguide—what do we know so far[J]. Sensors, 2024, 24(22): 7158. [24] XIANG X X, SUN H Y, CHAI H N, et al. Advances in smartphone-based visual biosensors for immediate detection[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2024(2): 145-156. (in Chinese). [25] ZHANG Z D, LUO L, XUE C Y, et al. Fano resonance based on metal-insulator-metal waveguide-coupled double rectangular cavities for plasmonic nanosensors[J]. Sensors, 2016, 16(5): 642. [26] ZHANG Z Y, WANG J D, ZHAO Y N, et al. Numerical investigation of a branch-shaped filter based on metal-insulator-metal waveguide[J]. Plasmonics, 2011, 6(4): 773-778. [27] KEKATPURE R D, HRYCIW A C, BARNARD E S, et al. Solving dielectric and plasmonic waveguide dispersion relations on a pocket calculator[J]. Optics Express, 2009, 17(26): 24112-24129. -





 下载:
下载: