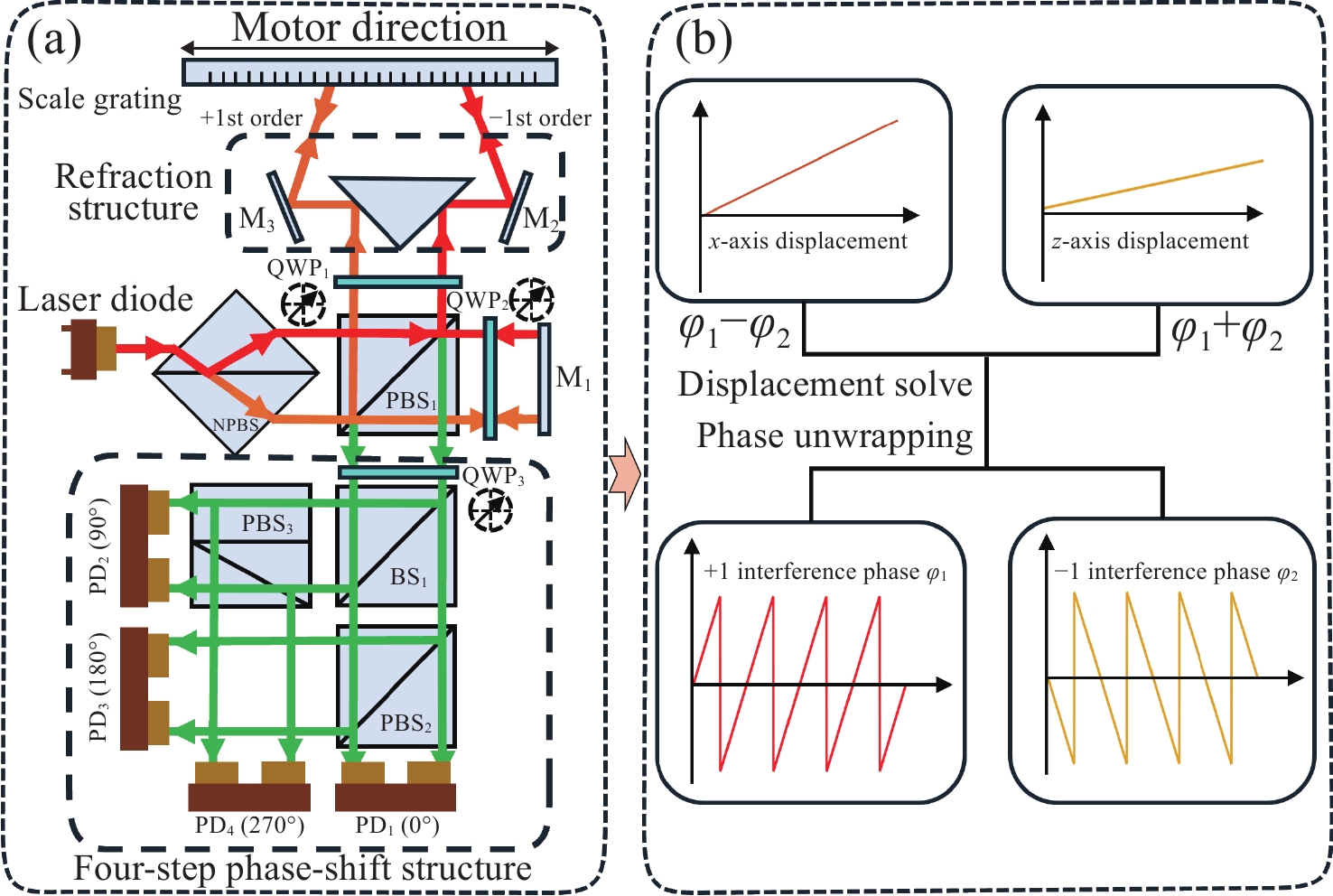
零差利特罗光栅双轴干涉仪
Homodyne Littrow grating interferometer for two-degrees-of-freedom measurement
doi: 10.37188/CO.EN-2025-0019
-
摘要:
针对目前先进制造设备对于高精度平面位移测量的需求,本文提出了一种
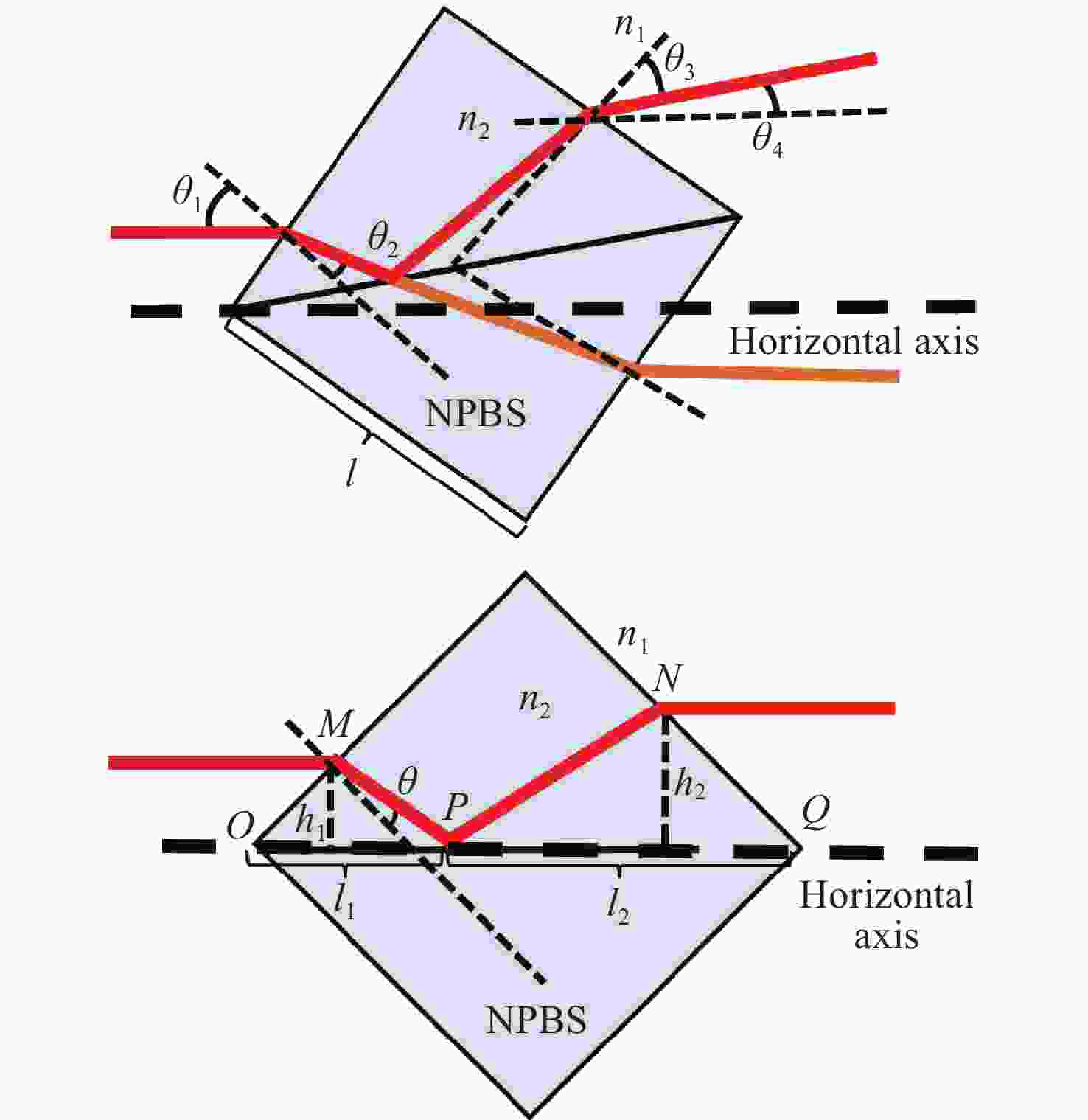
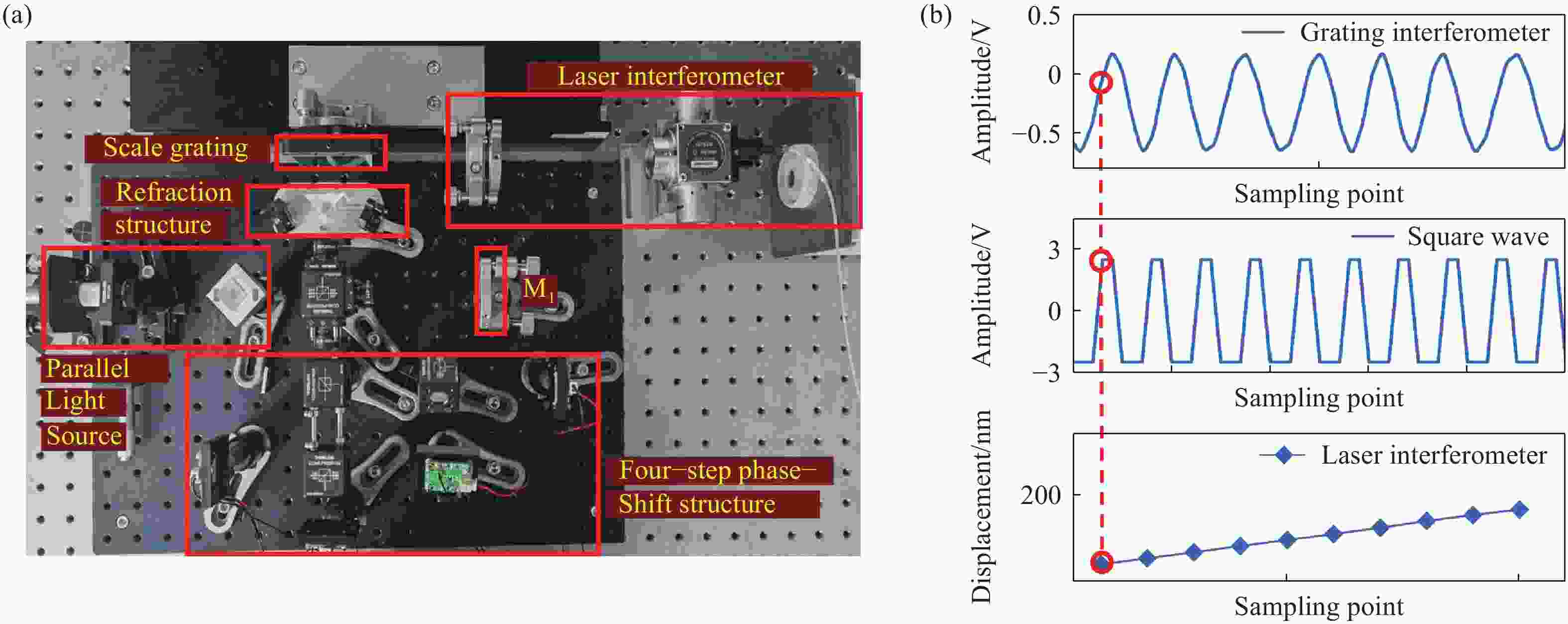
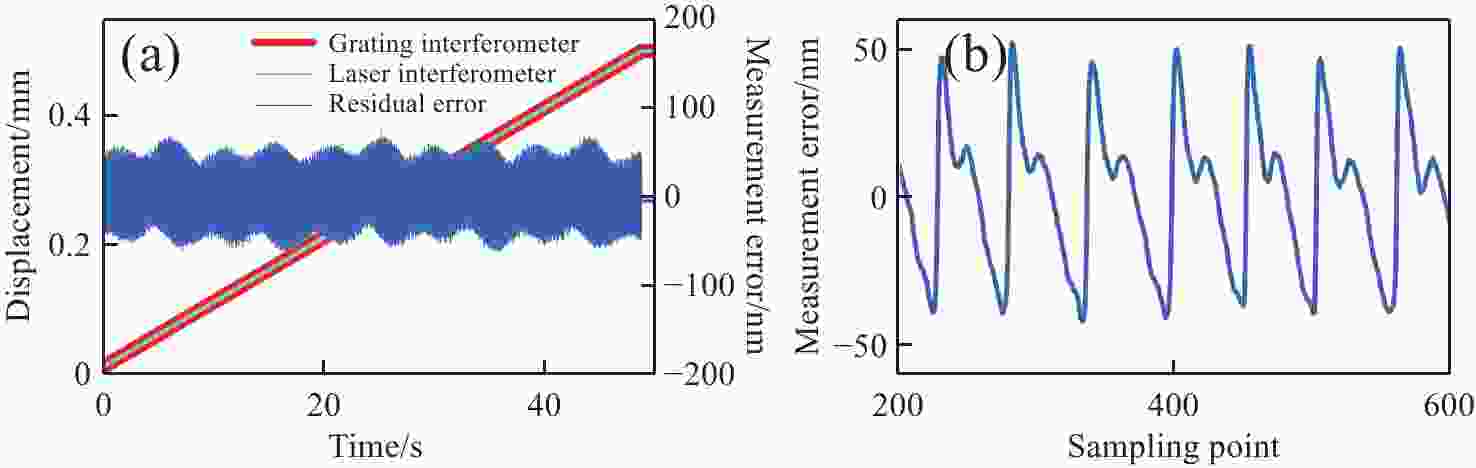
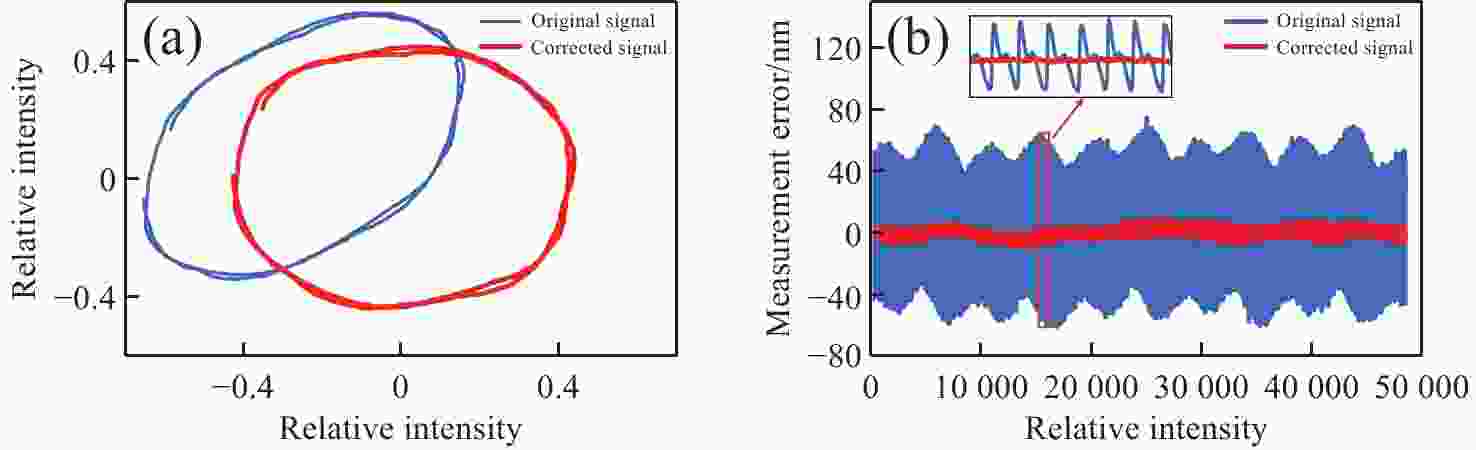
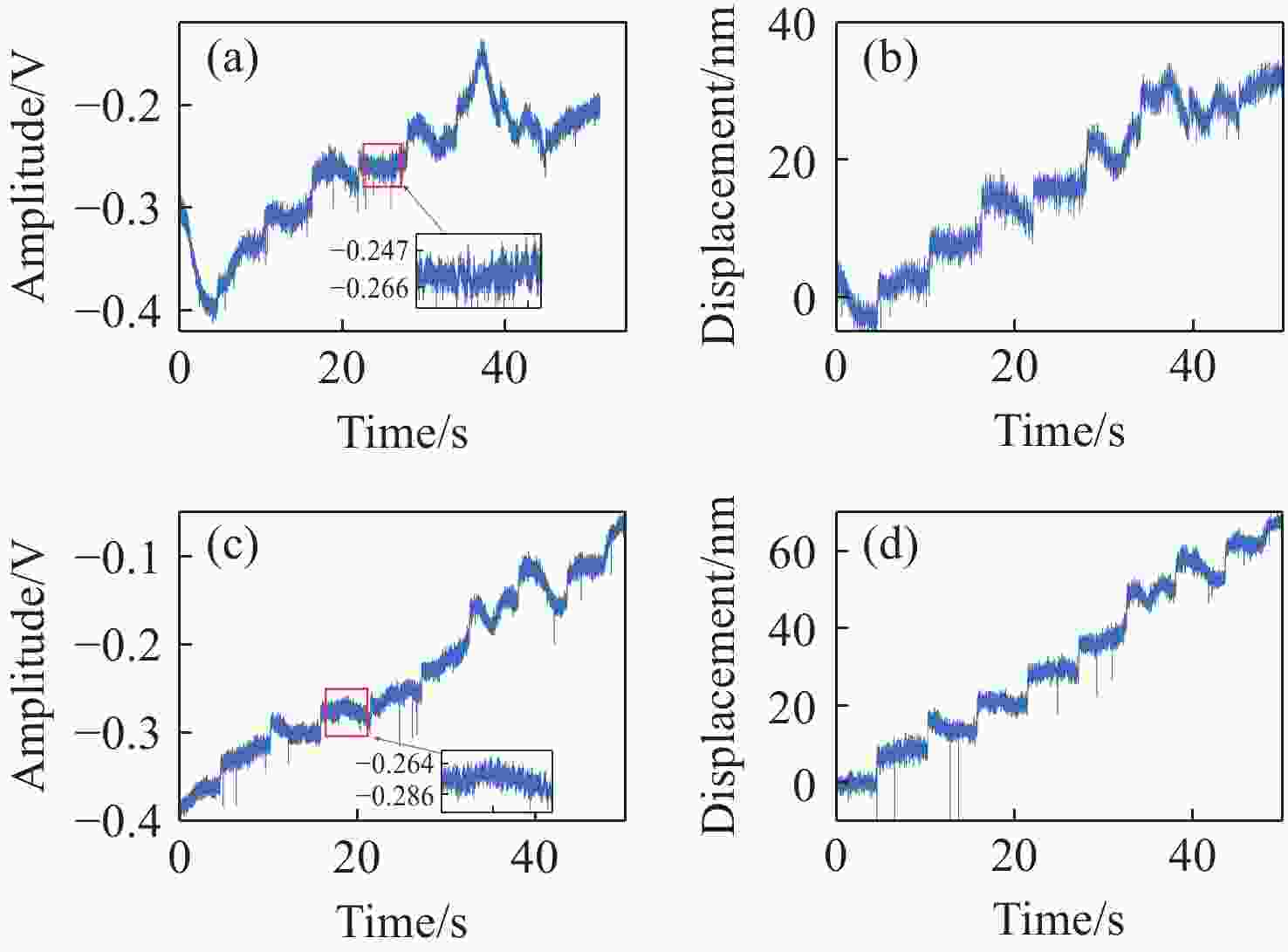
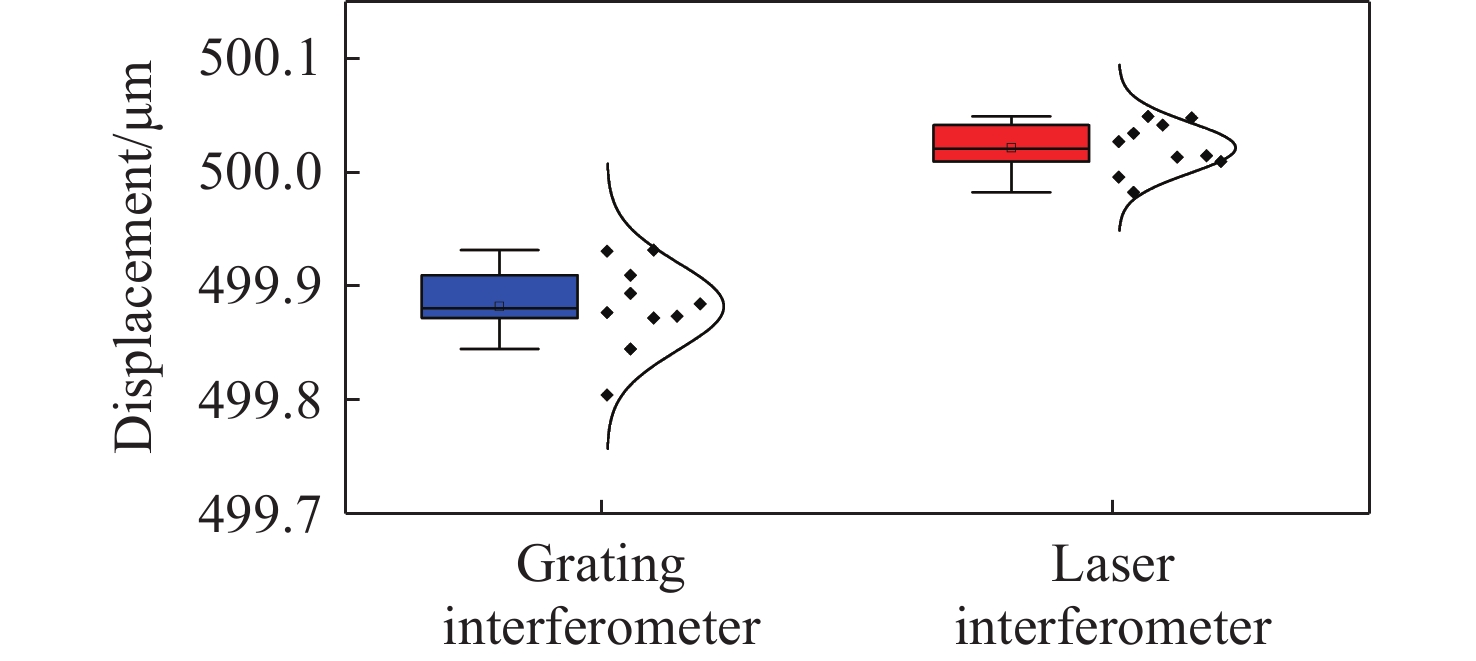
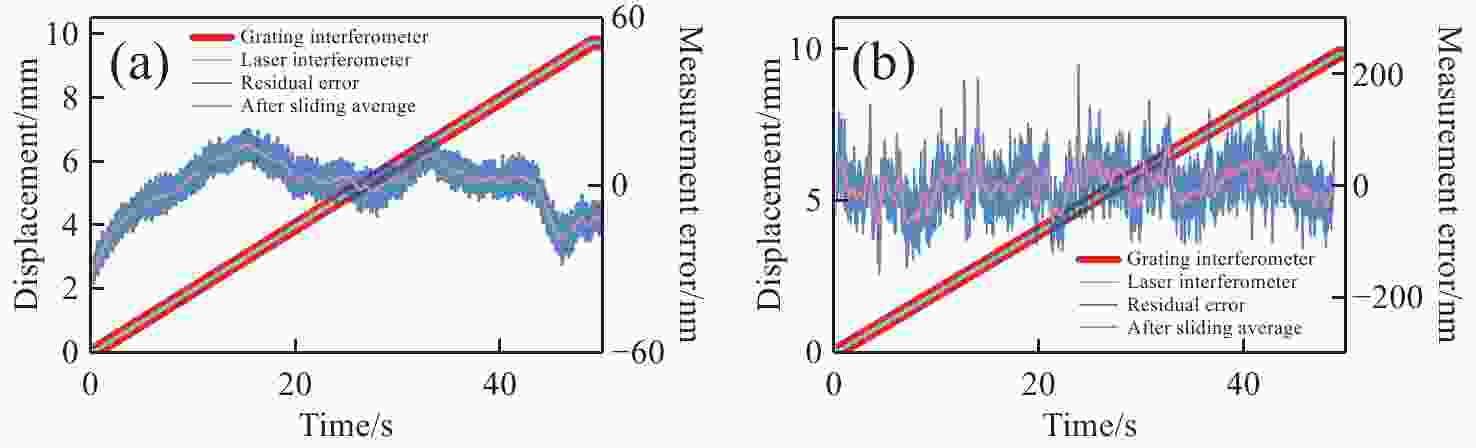
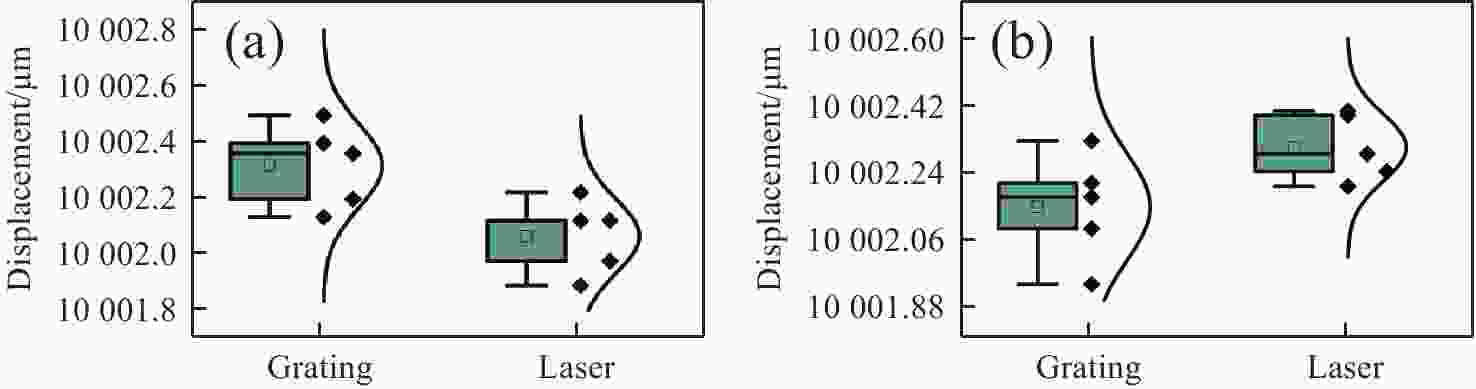
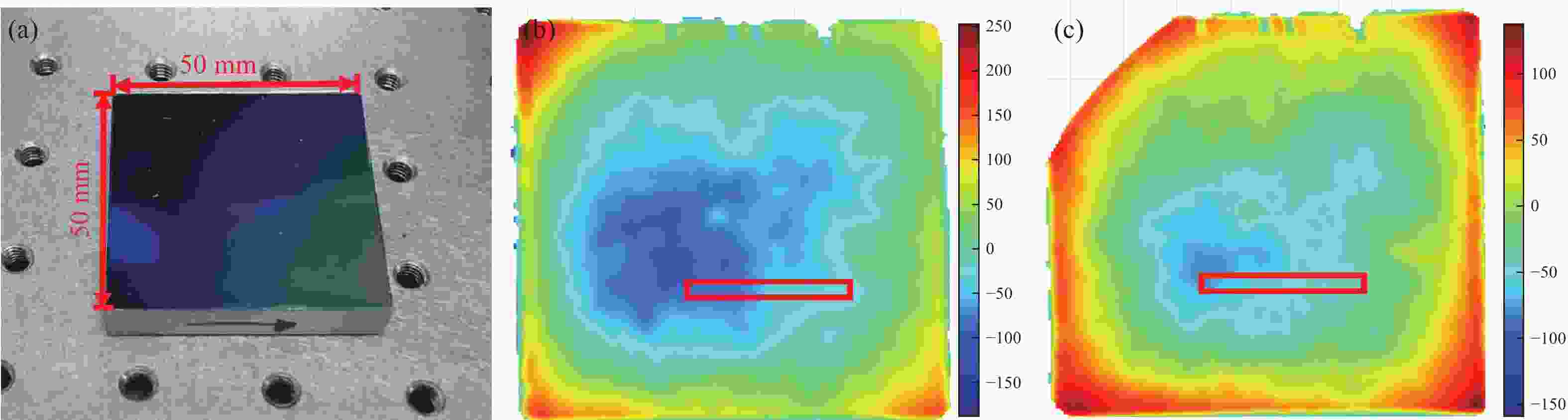
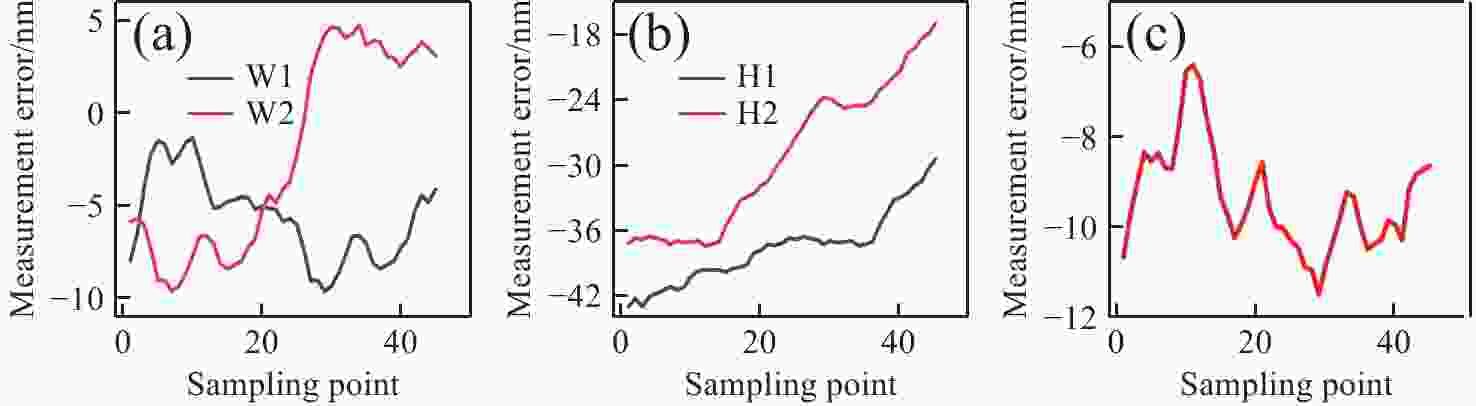
xz 双轴光栅干涉仪,通过偏置分束镜配合直角棱镜反射镜搭建双侧Littrow入射光路结构。分析了出射光束平行性、光束间距与入射光位置、角度之间的关系。实验验证了提出干涉仪的可行性和测量性能,光栅干涉仪在x 轴和z 轴上分别实现4 nm、7 nm的位移分辨率,经海德曼算法修正后,将周期非线性误差抑制至±5 nm以内。10 mm行程范围内,x 轴和z 轴分别获得±30 nm和±100 nm的测量精度。最后讨论了由于非共点入射结构所引入的面型误差对测量结果的影响。Abstract:In response to the current demand for high-precision planar displacement measurements in advanced manufacturing equipment, this paper proposes an xz dual-axis grating interferometer. The system adopts a biaxial Littrow incident light path structure, established using a biaxial beam splitter mirror and right-angled prism mirror. The relationship between the parallelism of the outgoing beam, the beam spacing, and the position and angle of the incident light is analyzed. Experimental results verify the feasibility and measurement performance of the proposed interferometer. The grating interferometer achieves a displacement resolution of 5 nm along the x-axis and 7 nm along the z-axis. After correction using the Heydemann algorithm, the periodic nonlinear error is reduced to ±5 nm. Over a travel range of 10 mm, the measurement accuracies are ±30 nm along the x-axis and ±100 nm along the z-axis, respectively. Finally, the influence of the surface error introduced by the non-coincident incident structure on the measurement results is discussed.
-
-
[1] LI M, CHEN T T, CHENG R, et al. Dual-loop iterative learning control with application to an ultraprecision wafer stage[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2022, 69(11): 11590-11599. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2021.3120481 [2] LI X C, ZHU H Y, MA J, et al. Data-driven multi-objective controller optimization for a magnetically-levitated nanopositioning system[J]. arXiv: 2007.02593, 2020. (查阅网上资料, 不确定文献类型及格式是否正确, 请确认). [3] SCHMIDT R H M. Ultra-precision engineering in lithographic exposure equipment for the semiconductor industry[J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 2012, 370(1973): 3950-3972. doi: 10.1098/rsta.2011.0054 [4] CASTENMILLER T, VAN DE MAST F, DE KORT T, et al. Towards ultimate optical lithography with NXT: 1950i dual stage immersion platform[C]. Proceedings of the SPIE 7640, Optical Microlithography XXIII, SPIE, 2010: 76401N. [5] CIDDOR P E. Refractive index of air: new equations for the visible and near infrared[J]. Applied Optics, 1996, 35(9): 1566-1573. doi: 10.1364/AO.35.001566 [6] MA T CH, LI Z CH, CAO H L, et al. A parallel denoising model for dual-mass MEMS gyroscope based on PE-ITD and SA-ELM[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 169979-169991. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2951612 [7] SHIBAZAKI Y, KOHNO H, HAMATANI M. An innovative platform for high-throughput high-accuracy lithography using a single wafer stage[C]. Proceedings of the SPIE 7274, Optical Microlithography XXII, SPIE, 2009: 72741I. [8] TEIMEL A. Technology and applications of grating interferometers in high-precision measurement[J]. Precision Engineering, 1992, 14(3): 147-154. doi: 10.1016/0141-6359(92)90003-F [9] ZHOU W Y, SUN Y J, LIU ZH W, et al. A random angle error interference eliminating method for grating interferometry measurement based on symmetry littrow structure[J]. Laser & Photonics Reviews, 2025, 19(11): 2401659. doi: 10.1002/lpor.202401659 [10] LI W H, WANG X Y, BAYANHESHIG, et al. Controlling the wavefront aberration of a large-aperture and high-precision holographic diffraction grating[J]. Light: Science & Applications, 2025, 14(1): 112. [11] BAI Y, HU P CH, LU Y F, et al. A six-axis heterodyne interferometer system for the joule balance[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2017, 66(6): 1579-1585. doi: 10.1109/TIM.2016.2634758 [12] ZHOU W Y, LI W H, LIU L, et al. Bidirectional two-degree-of-freedom grating interferometer with biased Littrow configuration[J]. Optics Communications, 2024, 557: 130333. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2024.130333 [13] ZHU Y, ZHANG M, WANG L J, et al. Two-degree-of-freedom heterodyne grating interferometry measurement system: US, 11307018B2[P]. 2022-04-19. [14] ZHOU W Y, LIU ZH W, SUN Y J, et al. Bidirectional Littrow double grating interferometry for quadruple optical interpolation[J]. Optics & Laser Technology, 2024, 175: 110751. doi: 10.1016/j.optlastec.2024.110751 [15] ZHOU W Y, SUN Y J, LI W H, et al. Polarization-folding ultra-wide spectral chromatic confocal line displacement sensor based on a binary lens[J]. Optics & Laser Technology, 2024, 177: 111152. doi: 10.1016/j.optlastec.2024.111152 [16] HORI Y, GONDA S, BITOU Y, et al. Periodic error evaluation system for linear encoders using a homodyne laser interferometer with 10 picometer uncertainty[J]. Precision Engineering, 2018, 51: 388-392. doi: 10.1016/j.precisioneng.2017.09.009 [17] HSIEH H L, PAN S W. Development of a grating-based interferometer for six-degree-of-freedom displacement and angle measurements[J]. Optics Express, 2015, 23(3): 2451-2465. doi: 10.1364/OE.23.002451 [18] LI X H, SHIMIZU Y, ITO T, et al. Measurement of six-degree-of-freedom planar motions by using a multiprobe surface encoder[J]. Optical Engineering, 2014, 53(12): 122405. doi: 10.1117/1.OE.53.12.122405 [19] GAO W, SAITO Y, MUTO H, et al. A three-axis autocollimator for detection of angular error motions of a precision stage[J]. CIRP Annals, 2011, 60(1): 515-518. doi: 10.1016/j.cirp.2011.03.052 [20] HSIEH H L, PAN S W. Three-degree-of-freedom displacement measurement using grating-based heterodyne interferometry[J]. Applied Optics, 2013, 52(27): 6840-6848. doi: 10.1364/AO.52.006840 [21] LI X H, WANG H H, NI K, et al. Two-probe optical encoder for absolute positioning of precision stages by using an improved scale grating[J]. Optics Express, 2016, 24(19): 21378-21391. doi: 10.1364/OE.24.021378 [22] SHI Y P, NI K, LI X H, et al. Highly accurate, absolute optical encoder using a hybrid-positioning method[J]. Optics Letters, 2019, 44(21): 5258-5261. doi: 10.1364/OL.44.005258 [23] ZHU J H, WANG G CH, WANG S T, et al. A reflective-type heterodyne grating interferometer for three-degree-of-freedom subnanometer measurement[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2022, 71: 7007509. doi: 10.1109/tim.2022.3213005 [24] KIMURA A, GAO W, ARAI Y, et al. Design and construction of a two-degree-of-freedom linear encoder for nanometric measurement of stage position and straightness[J]. Precision Engineering, 2010, 34(1): 145-155. doi: 10.1016/j.precisioneng.2009.05.008 [25] KIMURA A, GAO W, ZENG L J. Position and out-of-straightness measurement of a precision linear air-bearing stage by using a two-degree-of-freedom linear encoder[J]. Measurement Science and Technology, 2010, 21(5): 054005. doi: 10.1088/0957-0233/21/5/054005 [26] KIMURA A, HOSONO K, KIM WJ, et al. A two-degree-of-freedom linear encoder with a mosaic scale grating[J]. International Journal of Nanomanufacturing, 2011, 7(1): 73-91. doi: 10.1504/ijnm.2011.039964 [27] WANG L J, ZHANG M, ZHU Y, et al. A novel heterodyne grating interferomter system for in-plane and out-of-plane displacement measurement with nanometer resolution[C]. Proceedings of the 29th Annual Meeting of the American Society for Precision Engineering, ASPE, 2014: 173-177. [28] LI S M, WANG J K, ZHANG W T, et al. Real-time direction judgment system of sub-nanometer scale grating ruler[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 74939-74948. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3081152 [29] ZENG Q L, ZHAO ZH Y, DU H, et al. Separation and compensation of nonlinear errors in sub-nanometer grating interferometers[J]. Optics Express, 2022, 30(26): 46259. doi: 10.1364/OE.471714 [30] SHIBAZAKI Y, KANAYA Y. Movable body drive method and movable body drive system, pattern formation method and apparatus, exposure method and apparatus, and device manufacturing method for continuous position measurement of moveable body before and after switching between sensor heads: US, 20120293788[P]. 2012-11-22. [31] GUAN J, KÖCHERT P, WEICHERT C, et al. A high performance one-dimensional homodyne encoder and the proof of principle of a novel two-dimensional homodyne encoder[J]. Precision Engineering, 2013, 37(4): 865-870. doi: 10.1016/j.precisioneng.2013.05.003 [32] (查阅网上资料, 本条文献没有内容, 请确认). [33] LEE C K, WU C C, CHEN S J, et al. Design and construction of linear laser encoders that possess high tolerance of mechanical runout[J]. Applied Optics, 2004, 43(31): 5754-5762. doi: 10.1364/AO.43.005754 [34] DE GROOT P J, BADAMI V G, LIESENER J. Concepts and geometries for the next generation of precision heterodyne optical encoders[C]. Proceedings of the 31st Annual Meeting of the American Society for Precision Engineering, ASPE, 2016: 146-149. [35] WANG L J, GUO Z W, YE W N, et al. Ultra-precision spatial-separated heterodyne Littrow grid encoder displacement measurement system[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2022, 30(5): 499-509. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/OPE.20223005.0499 [36] LIN J, GUAN J, WEN F, et al. Grating encoder for wide range three-axis displacement measurement[C]. Proceedings of the SPIE 9446, 9th International Symposium on Precision Engineering Measurements and Instrumentation (ISPEMI), SPIE, 2014: 944602. [37] LIN J, GUAN J, WEN F, et al. High-resolution and wide range displacement measurement based on planar grating[J]. Optics Communications, 2017, 404: 132-138. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2017.03.012 [38] LI X T, BAYANHESHIG, QI X D, et al. Two-dimensional fast fourier transform method of analyzing the influence of plane grating′s line error and surface error on grating′s spectral performance[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2012, 32(11): 1105001. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/AOS201232.1105001 [39] MAO X Y, ZENG L J. Design and fabrication of crossed gratings with multiple zero-reference marks for planar encoders[J]. Measurement Science and Technology, 2018, 29(2): 025204. doi: 10.1088/1361-6501/aa9d5e -





 下载:
下载: