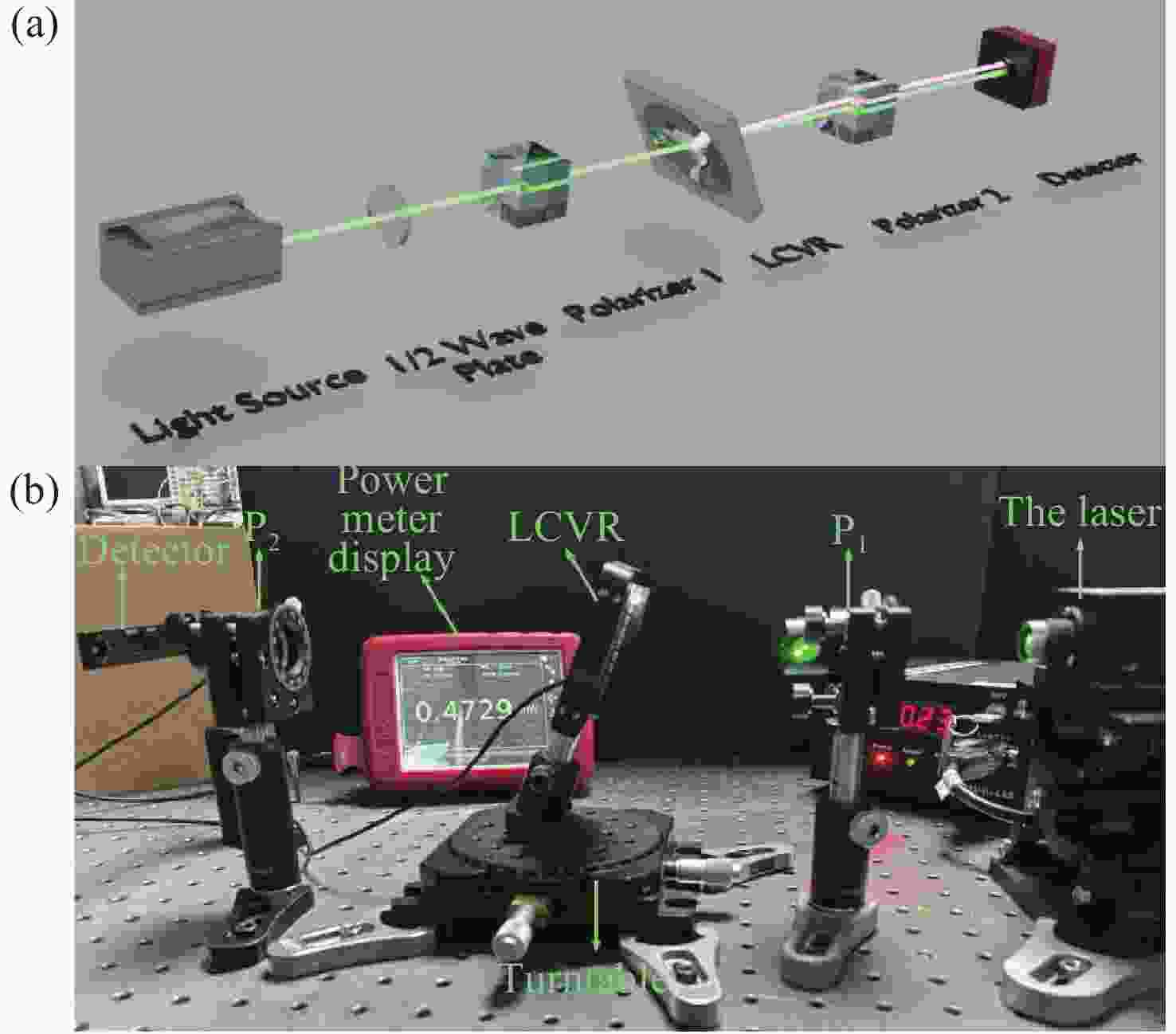
Precise calibration of liquid crystal variable retarder for various incident angles
doi: 10.37188/CO.EN-2025-0035
-
摘要:
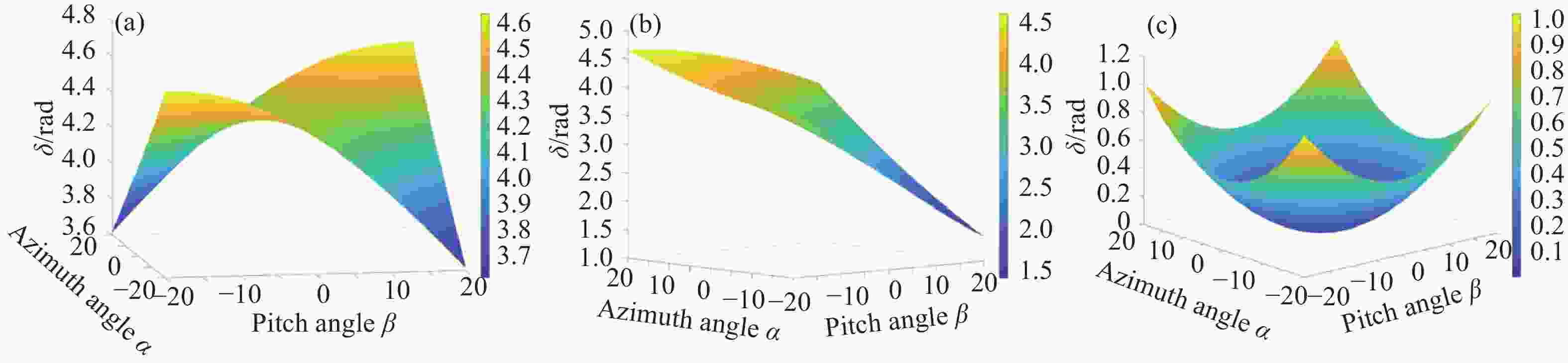
针对液晶可变相位延迟器(LCVR)入射角变化引起的偏振测量精度下降问题,本文探讨了液晶可变相位延迟器的相位延迟特性,重点分析了不同入射角对相位延迟量的影响。在垂直入射LCVR的延迟量标定基础上,推导了LCVR在不同入射角度和不同驱动电压下的相位延迟标定方程,建立相位延迟量与二维入射角(方位角
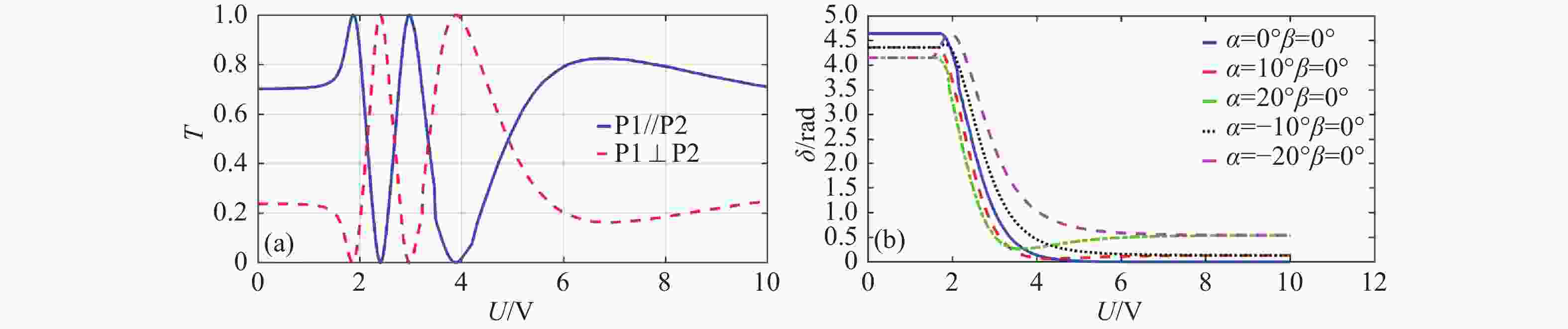
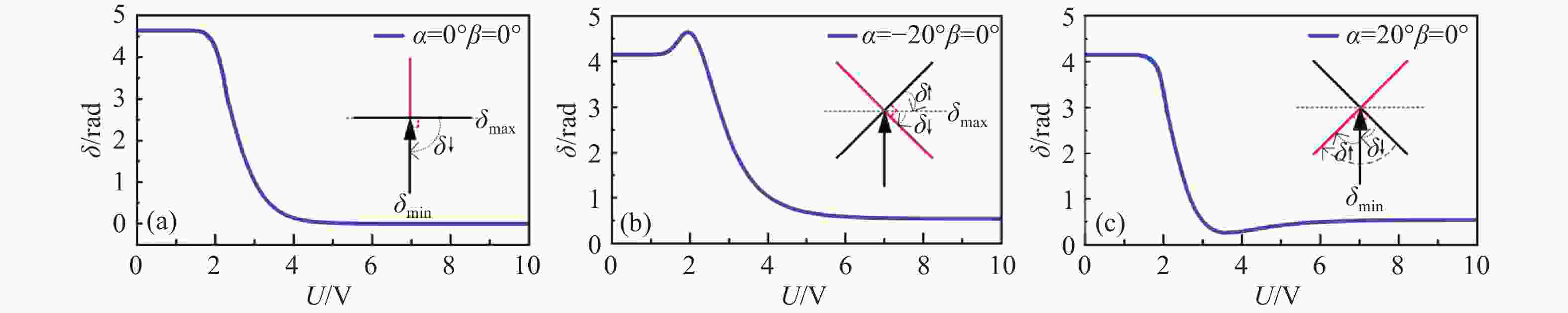
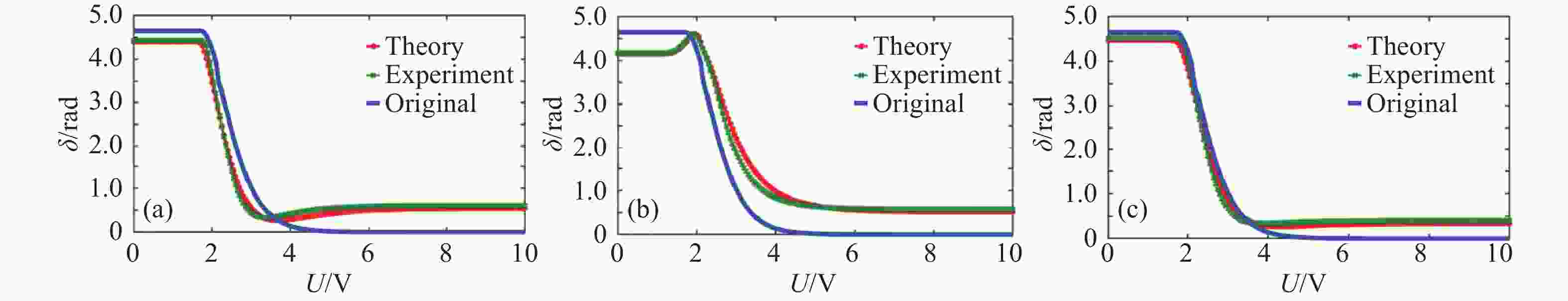
α 和俯仰角β )之间的关系。实验在α = 20°β = 0°,α = 0°β = 20°,及任意角度α = 15°β = 5°三种情况进行验证,结果表明,相位延迟量理论计算值与实验测量值之间的最大平均误差不超过0.059 rad,所提标定方法准确可行。本文所提方法为LCVR在偏振成像等光学应用中的参数标定及性能提升提供了有力的支撑。-
关键词:
- 液晶可变相位延迟器(LCVR) /
- 二维入射角 /
- 驱动电压 /
- 相位延迟标定
Abstract:This study investigates the reduction in polarization measurement accuracy caused by varying incident angles in a liquid crystal variable retarder (LCVR). The phase delay characteristics of the LCVR were examined, with particular emphasis on the influence of different two-dimensional incident angles on phase delay behavior. Building upon the calibration of phase delay under normal incidence, a phase delay calibration model was developed to account for variations in incident angle and driving voltage. A mathematical relationship was established between phase delay and the azimuth angle (
α ) and pitch angle (β ). Experimental validation was conducted under three conditions:α = 20°,β = 0°;α = 0°,β = 20°; and an arbitrary angle whereα = 5°,β = 15°. The results demonstrated that the maximum average deviation between theoretical predictions and experimental measurements did not exceed 0.059 rad. The proposed calibration method proved to be both accurate and practical. This approach offers robust support for LCVR parameter calibration and performance optimization in optical systems, particularly in polarization imaging applications. -
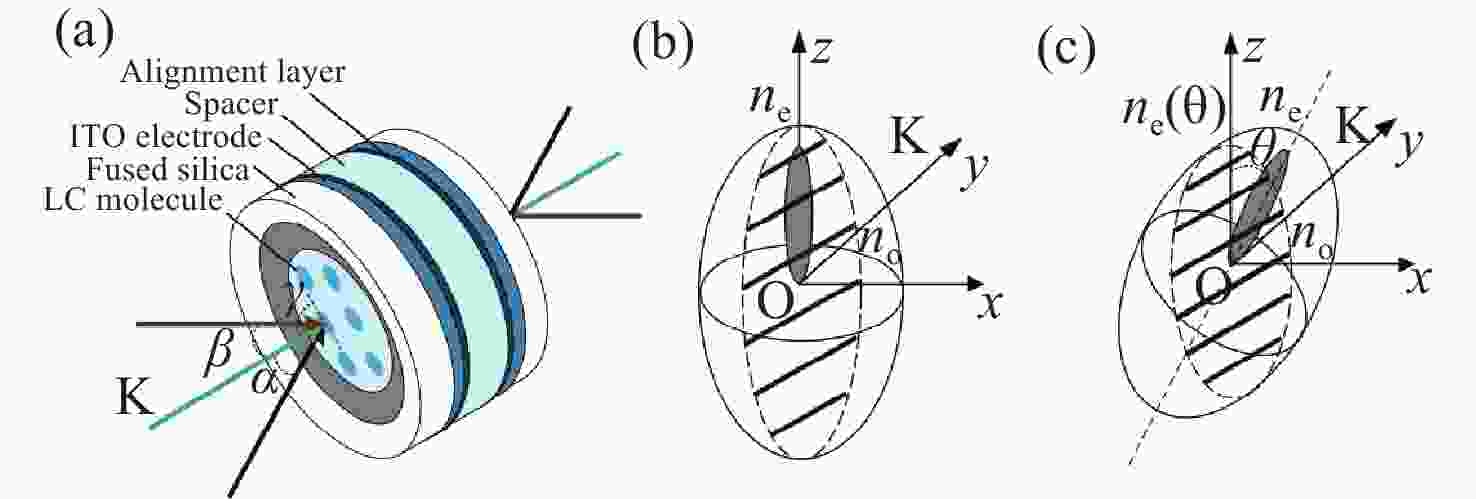
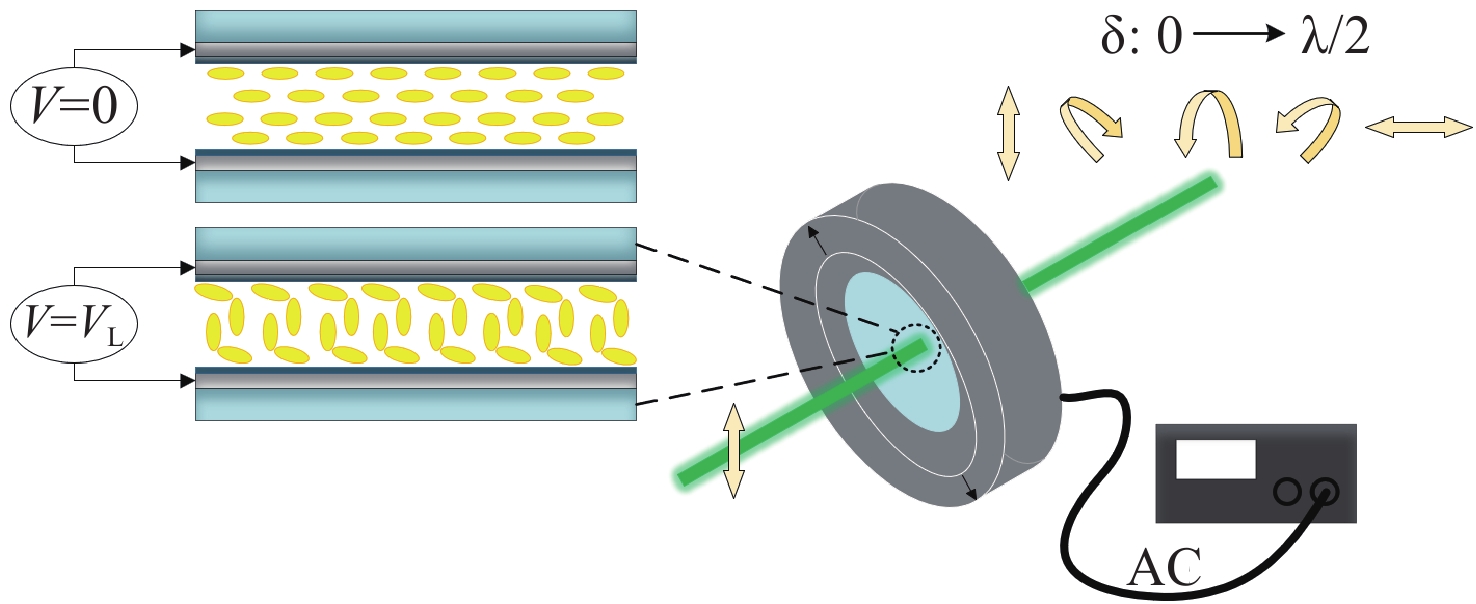
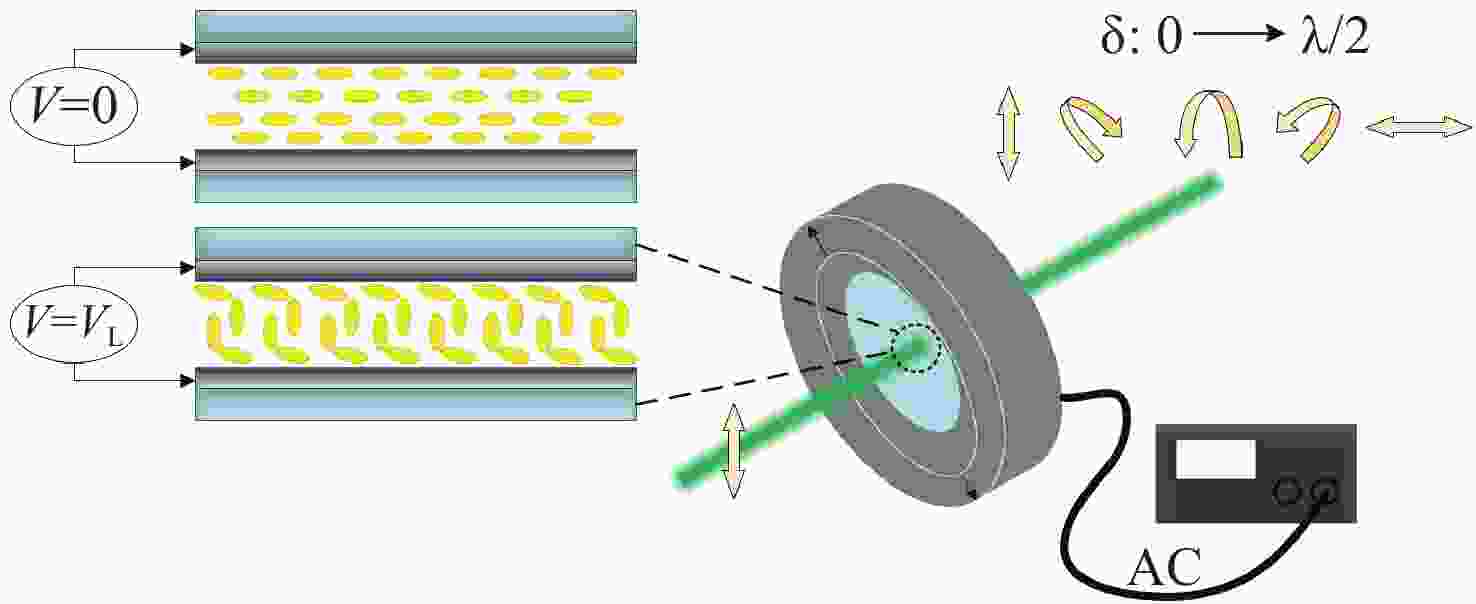
图 2 LCVR驱动电压与折射率椭球偏转角关系示意图 (a)二维角度入射LCVR原理图;(b) U≤UL的折射率椭球;(c) U>UL的折射率椭球
Figure 2. LCVR drive voltage and refractive index ellipsoid deflection angle diagram. (a) Schematic diagram of the two-dimensional angle incident LCVR. (b) Refractive index ellipsoid for U≤UL; (c) Refractive index ellipsoid for U>UL.
-
[1] WANG W, LI G H, XUE D. A study of voltage-dependent electric-control birefringence of liquid crystal[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2004, 24(7): 970-972. (in Chinese). [2] WEI P, GU H G, CHEN X G, et al. Characterization of a liquid crystal variable retarder by Mueller matrix ellipsometry[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2019, 11053: 110531Q. [3] LIU J M, ZHANG S, DENG B W, et al. Development and calibration of a vertical high-speed Mueller matrix ellipsometer[J]. Photonics, 2023, 10(9): 1064. doi: 10.3390/photonics10091064 [4] MA X, WU J X, HU Y J, et al. Fast and high-accuracy collinear reflection Mueller imaging polarimeter implemented with the compound calibration method[J]. Applied Optics, 2024, 63(13): 3381-3389. doi: 10.1364/AO.517955 [5] ZHOU Z Y, SITLER R, ODA Y, et al. Quantum crosstalk robust quantum control[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2023, 131(21): 210802. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.131.210802 [6] DE OLIVEIRA M, AMBROSIO A. Subcycle modulation of light’s orbital angular momentum via a Fourier space-time transformation[J]. Science Advances, 2025, 11(2): eadr6678. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adr6678 [7] LI Y T, ZHANG W F, YANG J Q, et al. Application and performance improvement of an optical power stabilization system based on MEMS-LCVR in a SERF atomic magnetometer[J]. Photonics, 2025, 12(6): 573. doi: 10.3390/photonics12060573 [8] 张瑞. 基于声光和液晶调制的高精度高光谱全偏振成像系统研究[D]. 太原: 中北大学, 2017.ZHANG R. The research on high-accuracy hyper-spectral full-polarization imaging based on acousto-optic and liquid crystal variable retarder[D]. Taiyuan: North University of China, 2017. (in Chinese). [9] CHEN L X, ZHANG SH Y, ZHENG W B, et al. High light efficiency spectral polarization imaging method based on mach–zehnder structured liquid crystal tunable filters and variable retarders[J]. Photonics, 2023, 10(7): 765. doi: 10.3390/photonics10070765 [10] GLADISH J C, DUNCAN D D. Alignment and temperature effects in liquid-crystal-based active polarimetry[J]. Applied Optics, 2014, 53(18): 3982-3992. doi: 10.1364/AO.53.003982 [11] CHEN Y, GAO J, XIAO Y, et al. Research of LCVR calibration method based on Stokes vector measurement[J]. Chinese Journal of Quantum Electronics, 2019, 36(1): 19-27. (in Chinese). [12] YANG R, MA F Y, DOU W T, et al. High-accuracy and high-efficiency calibration method for determining voltage-phase characteristics of LCVR based on a Wollaston prism[J]. Optics Communications, 2023, 546: 129771. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2023.129771 [13] WANG G, HOU J F, LIN J B, et al. Accurate and fast calibration of liquid crystal variable retarder phase delay-voltage curve[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2020, 28(4): 827-833. (in Chinese). [14] HU D M, SONG L, NIU G CH. New method to measure phase retardation of wave plates based on SVM[J]. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2016, 37(7): 1517-1523. (in Chinese). [15] LI K W, WANG ZH B, ZHANG R, et al. Study of birefringence dispersion based on liquid crystal variable retarder[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2015, 42(1): 0108001. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/CJL201542.0108001 [16] XUE P, WANG ZH B, ZHANG R, et al. Accurate calibration of phase retardation based on the liquid crystal variable retarder[J]. Journal of Optoelectronics · Laser, 2016, 27(8): 798-803. (in Chinese). [17] ZHANG Y, ZHAO H J, ZHOU P W, et al. Photoelectric characteristics of liquid crystal variable retarder[J]. Foreign Electronic Measurement Technology, 2009, 28(3): 17-20. (in Chinese). [18] ZHENG Q Q, WANG CH Y, WANG Z SH, et al. Research on diffraction characteristics of liquid crystal polarization grating under oblique incidence[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2022, 51(7): 20210511. (in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/IRLA20210511 [19] FANG Y X, JIANG L, PEI H Y, et al. Tilt error’s characteristic analysis of dual liquid crystal polarization grating system[J]. Chinese Optics, 2024, 17(6): 1387-1396. (in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/CO.2024-0041 [20] GLADISH J C, DUNCAN D D. Parameterizing liquid crystal variable retarder structural organization with a fractal-Born approximation model[J]. Optical Engineering, 2016, 55(5): 054104. doi: 10.1117/1.OE.55.5.054104 [21] CHANG L Y, WANG G R, WANG X Y, et al. Optimization of polarization parameters for an LCVR polarization spectrometer under non-oversampling[J]. Applied Optics, 2023, 62(16): 4150-4160. doi: 10.1364/AO.486941 [22] LEE S L, MAO C N, LIN Y H. Investigation of a polarizer-free liquid crystal phase modulation via nanometer size encapsulation of nematic liquid crystals[J]. Optical Materials Express, 2023, 13(12): 3531-3542. doi: 10.1364/OME.509266 [23] URIBE-PATARROYO N, ALVAREZ-HERRERO A. Determination of the molecular tilt profile of a liquid crystal under applied electric field by generalized transmission ellipsometry[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America B, 2009, 26(6): 1188-1195. doi: 10.1364/JOSAB.26.001188 [24] TIWARI V. Advances in polarization imaging: techniques and instrumentation[J]. Journal of Quantitative Spectroscopy and Radiative Transfer, 2025, 338: 109427. doi: 10.1016/j.jqsrt.2025.109427 [25] ZHANG Y M, CHEN Q, GAO Y, et al. High phase retardation polarization-independent liquid crystal devices[J]. Optics Communications, 2023, 531: 129244. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2022.129244 [26] 白林灵. 外场下液晶波片相位延迟量的研究[D]. 成都: 电子科技大学, 2012: 40-43.BAI L L. Study on phase retardation of liquid crystal waveplates under external fields[D]. Chengdu: University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2012: 40-43. (in Chinese)(查阅网上资料, 未找到本条文献英文翻译, 请确认). -





 下载:
下载: