基于超表面的整数阶和分数阶涡旋拓扑电荷的高精度检测
High-precision detection of topological charge of integral and fractional vortices based on metasurface
doi: 10.37188/CO.EN-2025-0037
-
摘要:
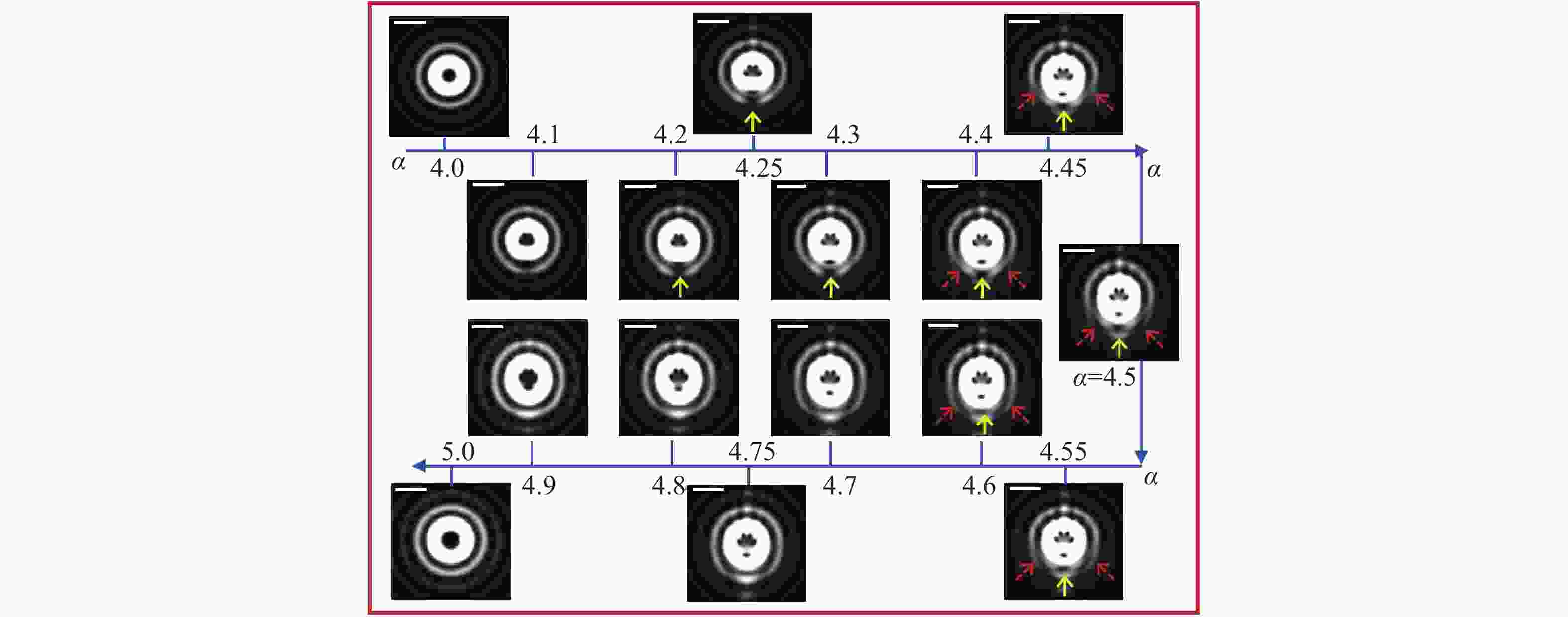
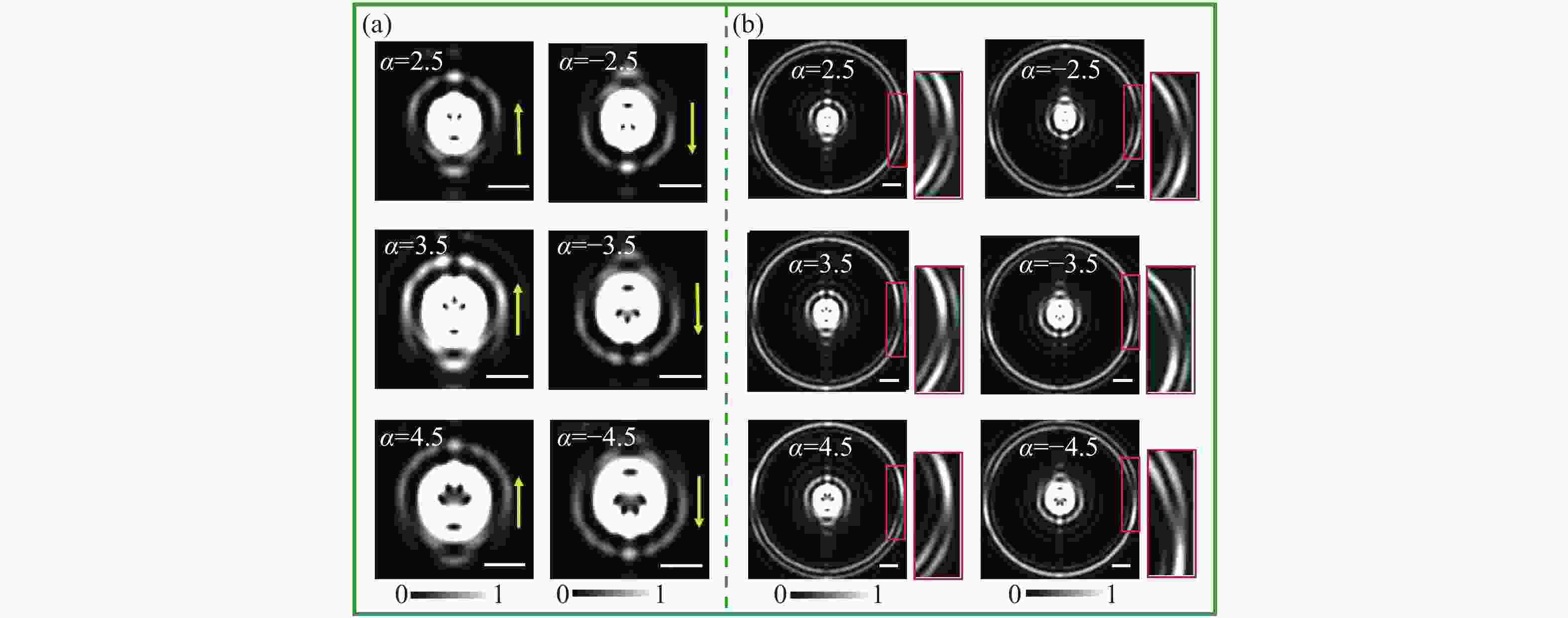
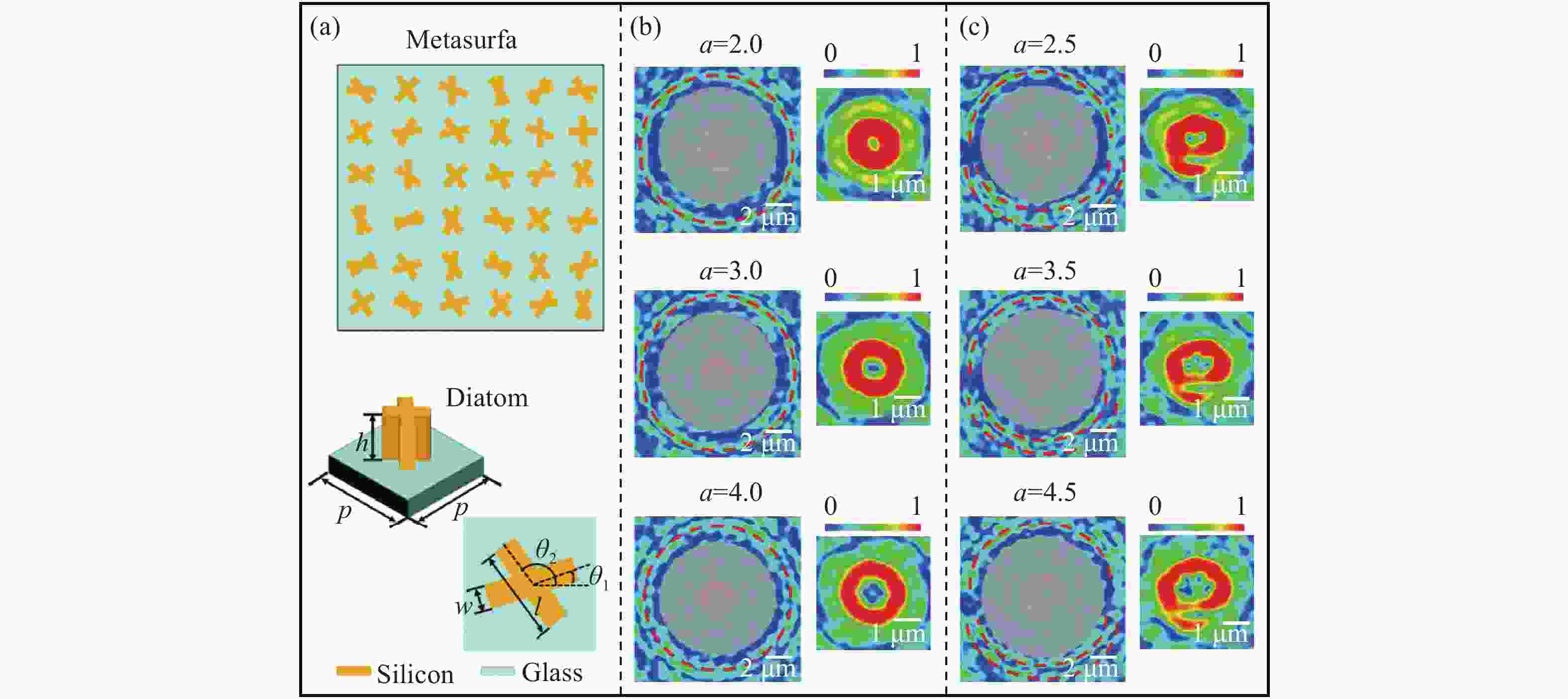
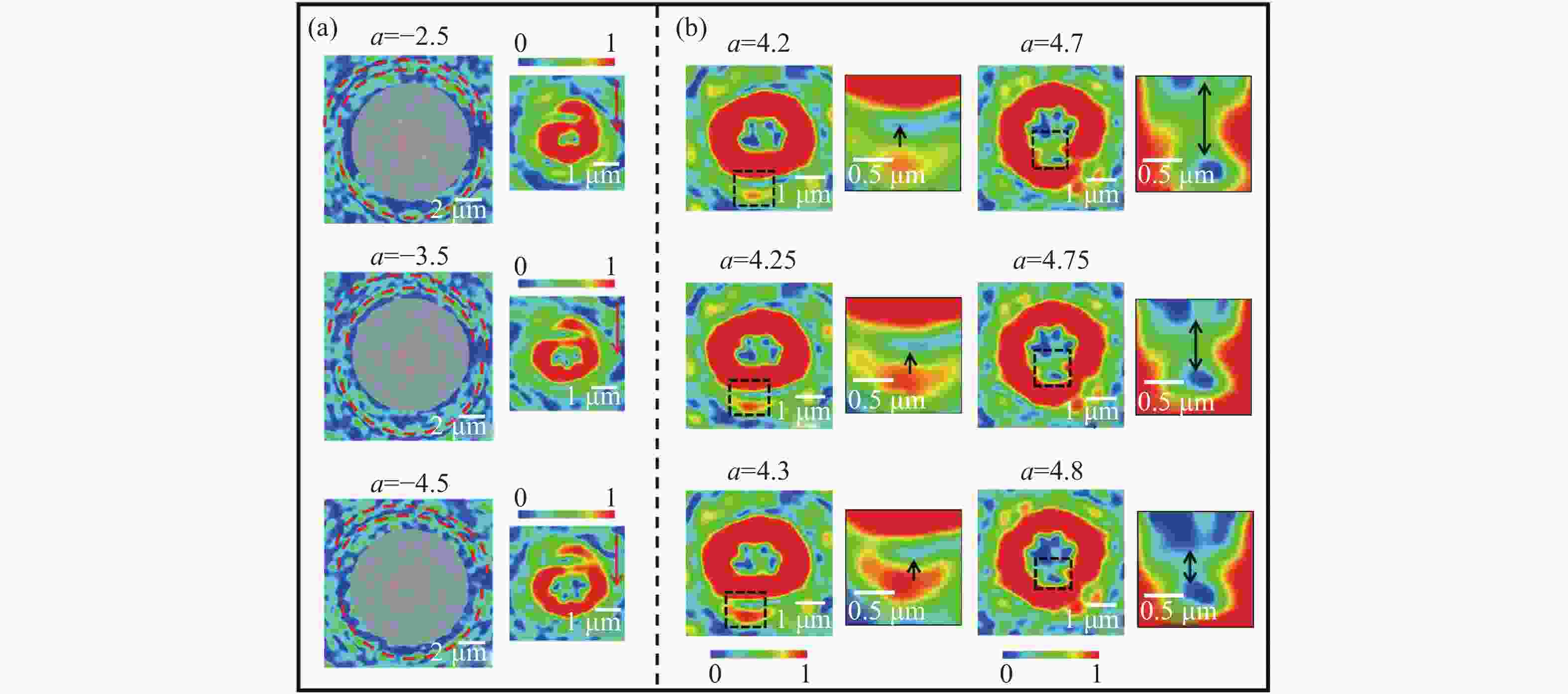
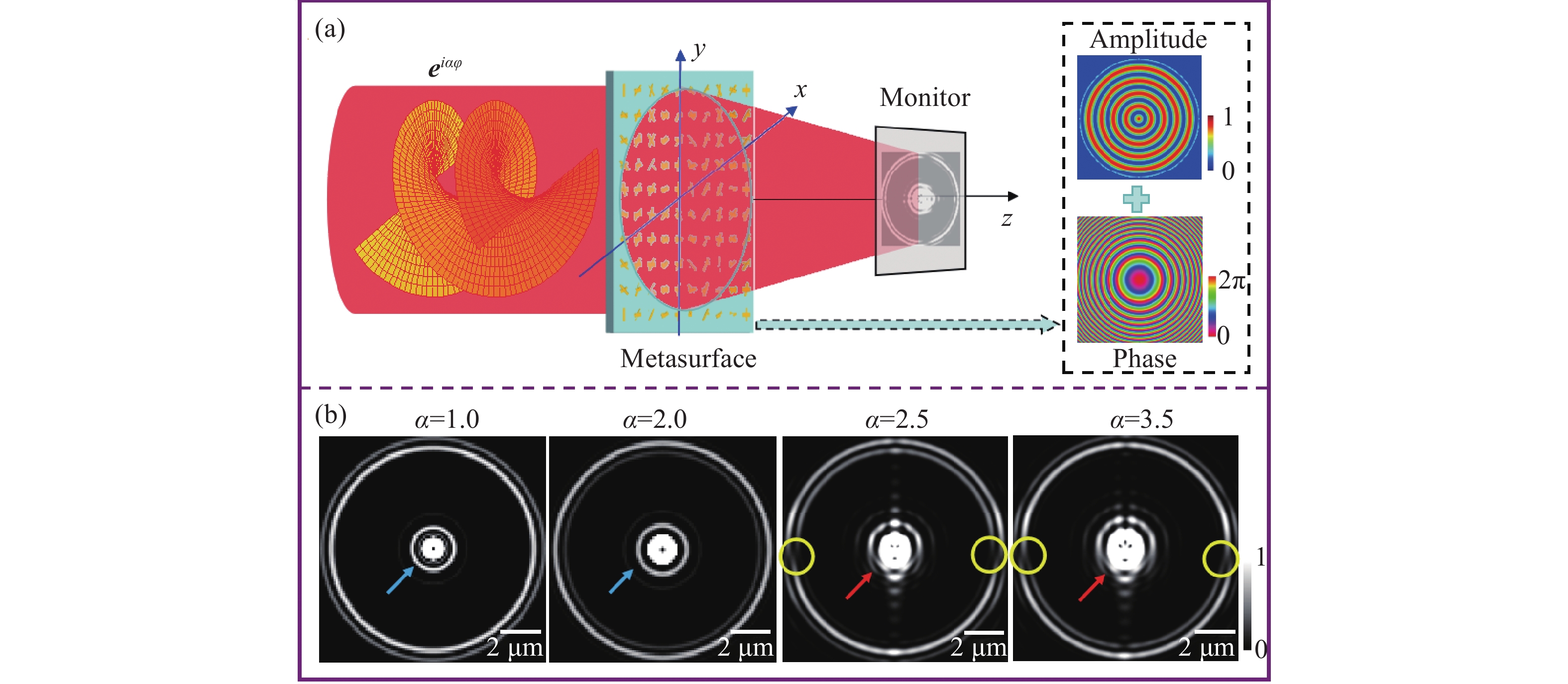
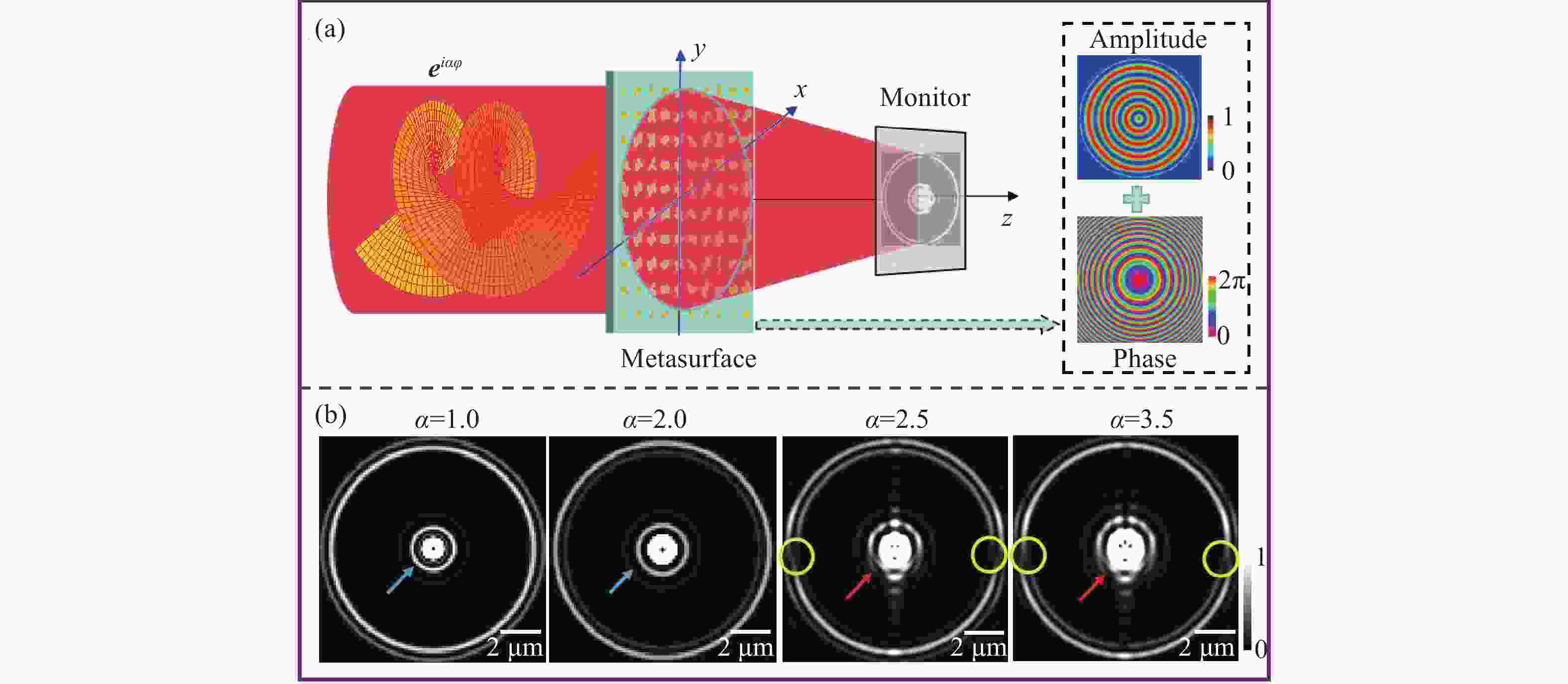
在涡旋光束的实际应用中,拓扑荷的高精度检测具有重要意义。针对现有拓扑荷检测方法存在分辨率低、难以同时判别整数阶与分数阶拓扑荷的问题,本文从理论上提出并通过数值模拟验证了一种基于设计超表面的拓扑荷双重判别方法。该超表面产生的内外衍射图样可分别用于判别拓扑荷的数值与符号,且所提方法的检测精度可达0.05。理论分析与仿真结果充分验证了该方法的有效性。与现有方法相比,该方法具有显著优势:采用平面结构设计,无需额外光学元件;无需数据处理,可直接判别;检测精度高。我们认为,此项工作有助于推动拓扑荷检测技术的发展及光学涡旋的实际应用。
Abstract:High-precision detection of topological charge is significant for the practical applications of vortex beams. In view of the existing evaluation with low resolution of topological charge and more complexity to judge simultaneously integer and fraction, this paper theoretically proposes and numerically verifies the double judgment method for topological charge based on the designed metasurface. The inner and outer diffraction patterns of metasurface can judge the value and sign of topological charge. The detection precision of the proposed method reaches 0.05. The theoretic and simulated results give the solid verification for the effectiveness of the proposed method. This method has outstanding advantages including planar structure design without additional elements, direct judgment without data processing and high precision over the existing methods. We think this work is beneficial to the detection of topological charge and the applications of optical vortices.
-
Key words:
- optical vortex /
- topological charge /
- metasurface
-
Table 1. Comparison of works for detecting topological charge of vortex
Works Principle and Method Complexity Precision Dehnoei Sf et al[17] Cross-blade diffraction Simple 0.1 Shikder A et al[18] Hybrid digital-optical correlation Complex 0.05 Hu Z et al[19] Rotational Doppler effect Additional devices 0.1 Liu Z et al[20] Fraunhofer diffraction Deep learning Additional lens Time-consuming 0.01 This paper Fresnel diffraction Metasurface Simple 0.05 -
[1] PADGETT M J. Orbital angular momentum 25 years on [Invited][J]. Optics Express, 2017, 25(10): 11265-11274. doi: 10.1364/OE.25.011265 [2] ZHANG H, ZENG J, LU X Y, et al. Review on fractional vortex beam[J]. Nanophotonics, 2022, 11(2): 241-273. doi: 10.1515/nanoph-2021-0616 [3] ŘEHÁČEK J, HRADIL Z, BOUCHAL Z, et al. Tomographic analysis of vortex information content[J]. Journal of Modern Optics, 2006, 53(5-6): 689-697. doi: 10.1080/09500340500259920 [4] BOUGOUFFA S, BABIKER M. Atom trapping and dynamics in the interaction of optical vortices with quadrupole-active transitions[J]. Physical Review A, 2020, 101(4): 043403. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.101.043403 [5] SUCIU Ş, BULZAN G A, ISDRAILĂ T A, et al. Quantum communication networks with optical vortices[J]. Physical Review A, 2023, 108(5): 052612. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.108.052612 [6] TAO SH H, YUAN X C, LIN J, et al. Fractional optical vortex beam induced rotation of particles[J]. Optics Express, 2005, 13(20): 7726-7731. doi: 10.1364/OPEX.13.007726 [7] HUANG K, LIU H, RESTUCCIA S, et al. Spiniform phase-encoded metagratings entangling arbitrary rational-order orbital angular momentum[J]. Light: Science & Applications, 2018, 7(3): 17156. [8] ZHANG X H, XIA T, CHENG SH B, et al. Free-space information transfer using the elliptic vortex beam with fractional topological charge[J]. Optics Communications, 2019, 431: 238-244. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2018.09.035 [9] LIU H Y, WANG Y, WANG J Q, et al. Electromagnetic vortex enhanced imaging using fractional OAM beams[J]. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 2021, 20(6): 948-952. doi: 10.1109/LAWP.2021.3067914 [10] VAITY P, BANERJI J, SINGH R P. Measuring the topological charge of an optical vortex by using a tilted convex lens[J]. Physics Letters A, 2013, 377(15): 1154-1156. doi: 10.1016/j.physleta.2013.02.030 [11] WU L X, FENG X K, LIN ZH ZH, et al. Spiral fractional vortex beams[J]. Optics Express, 2023, 31(5): 7813-7824. doi: 10.1364/OE.482361 [12] WANG H, LIU L X, ZHOU CH D, et al. Vortex beam generation with variable topological charge based on a spiral slit[J]. Nanophotonics, 2019, 8(2): 317-324. doi: 10.1515/nanoph-2018-0214 [13] MOU ZH, ZHOU CH D, LU P Y, et al. Structured vortices generated by metasurface holography[J]. Photonics Research, 2021, 9(10): 2125-2131. doi: 10.1364/PRJ.427745 [14] ZHOU J, ZHANG W H, CHEN L X. Experimental detection of high-order or fractional orbital angular momentum of light based on a robust mode converter[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2016, 108(11): 111108. doi: 10.1063/1.4944463 [15] ZHENG SH, WANG J. Measuring orbital angular momentum (OAM) states of vortex beams with annular gratings[J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7(1): 40781. doi: 10.1038/srep40781 [16] DENG D, CHU Y H, LIU Y, et al. Measurement of multiplexed fractional vortices with integer mode interval[J]. Results in Physics, 2021, 29: 104699. doi: 10.1016/j.rinp.2021.104699 [17] DEHNOEI S F, SABOURI S G. Measurement of the integer and fractional topological charge of optical vortex beams by using crossed blades[J]. Applied Optics, 2023, 62(13): 3409-3415. doi: 10.1364/AO.487898 [18] SHIKDER A, MOHAPATRA J B, NISHCHAL N K. Fractional topological charge measurement through optical correlation[J]. Optics Letters, 2024, 49(8): 2017-2020. doi: 10.1364/OL.523154 [19] HU ZH Q, ZHU J N, ZHANG H, et al. . Quantitative determination of fractional topological charge based on the rotational Doppler effect[J]. Optics Express, 2024, 32(17): 29057-29067. (不确定标黄作者拼写是否正确, 请确认).HU ZH Q, ZHU J N, ZHANG H, et al. Quantitative determination of fractional topological charge based on the rotational Doppler effect[J]. Optics Express, 2024, 32(17): 29057-29067. (不确定标黄作者拼写是否正确, 请确认). [20] LIU ZH W, YAN SH, LIU H G, et al. Superhigh-resolution recognition of optical vortex modes assisted by a deep-learning method[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2019, 123(18): 183902. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.123.183902 [21] WU R, JIANG K, JIANG X Q, et al. Metasurface-based circular polarizer with a controllable phase and its application in holographic imaging[J]. Optics Letters, 2024, 49(3): 774-777. doi: 10.1364/OL.511135 [22] JIANG K, JIANG X Q, WU R, et al. Generation of structural colors with wide gamut based on stretchable transmission metasurfaces[J]. Photonics Research, 2025, 13(2): 257-262. doi: 10.1364/PRJ.538645 [23] JIANG X Q, WU R, JIANG K, et al. Phase compensation enables the generation of near-field perfect structured light[J]. Optics Letters, 2025, 50(14): 4574-4577. doi: 10.1364/OL.562378 [24] FANG J, WANG R X, NING X L, et al. KCUNET: multi-focus image fusion via the parallel integration of KAN and convolutional layers[J]. Entropy, 2025, 27(8): 785. doi: 10.3390/e27080785 [25] MA J Y, LE ZH L, TIAN X, et al. SMFuse: multi-focus image fusion via self-supervised mask-optimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computational Imaging, 2021, 7: 309-320. doi: 10.1109/TCI.2021.3063872 [26] JIANG X W, YAN T H, ZHU J J, et al. Densely connected deep extreme learning machine algorithm[J]. Cognitive Computation, 2020, 12(5): 979-990. doi: 10.1007/s12559-020-09752-2 -





 下载:
下载: