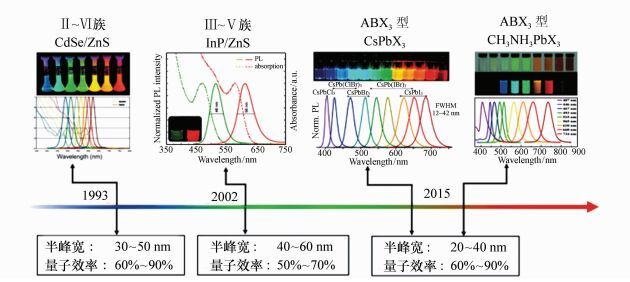
-
摘要: 量子点材料兼具极高的色纯度、发光颜色可调以及的荧光量子产率高等特点,已成为显示领域中的明星材料,在提升显示器件的色域方面具有巨大潜力。基于量子点材料的液晶显示背光技术是目前量子点材料在显示器件中的主流应用方向,引起了学术界和工业界的广泛关注。本文将综述量子点液晶显示背光技术的研究进展,主要包括量子点材料的选择、背光结构的应用以及材料复合与封装技术的发展现状,重点介绍了目前产业界广泛关注的量子点光学膜技术,特别是国内自主知识产权的低成本钙钛矿量子点光学膜技术,由于其具备广色域(124% NTSC)、易加工、低成本等特点,已成为具有成长潜力的技术路线。Abstract: Quantum dots are rising as suitable candidates in the field of display application due to their extremely high color purity, tunable emission spectra and high photoluminescence efficiency, especially for their contribution to the expanded color gamut in display technology. Motivated by the commercialization in the market, quantum dots based backlights have drawn great deal of attentions from both the scientific and industrial circles. In this paper, the research progress of quantum dot liquid crystal display backlight technology is reviewed, including the selection of quantum dots materials, the application of backlight structure and the development of composite materials and encapsulation technology. In addition, this paper also introduces the low-cost perovskite quantum dot optical film technology, which is widely concerned by industrial circle, especially the low-cost perovskite quantum dot optical film technology with independent intellectual property rights. This technology has the advantages of wide color gamut(124% NTSC), easy processing, and low cost with a great development potential.
-
Key words:
- quantum dot /
- backlight technology /
- wide color gamut /
- display /
- perovskite /
- optical film
-
图 2 量子点背光结构示意图:(a)“芯片封装型”结构,量子点发光材料封装在蓝光LED贴片上; (b) “侧管封装型”结构,量子点与基质形成的复合材料置于蓝光LED与导光板的侧边; (c) “光学膜集成型”结构,量子点与基质形成的量子点光学膜置于导光板的正上方[26]
Figure 2. Schematic of quantum dots based backlight: (a)"On-chip" structure, in which the quantum dot light emitting material is encapsulated on the blue LED chip. (b)"On-edge" structure, where the quantum dot based composite material is placed on the side between the blue LED and the light guide plate. (c)"On-surface" structure, where the quantum dots based optical film is directly placed above the light guide plate[26]
图 3 (a)CdSe/ZnS量子点与NaCl无机盐晶体形成的复合发光材料[39];(b)CdSe/CdS/ZnS量子点与二氧化硅通过溶胶-凝胶缩合反应形成的复合发光玻璃[42];(c)复合发光玻璃与有机硅胶树脂基复合发光材料的热稳定性对比[42]
Figure 3. (a)Composite formed by embedding CdSe/ZnS quantum dots in NaCl crystals[39]. (b)Inorganic silica-based glass formed by embedding CdSe/CdS/ZnS quantum dots in silica monolith[42]. (c)Thermal stability of inorganic silica-based glass and organic silicone resin-based composite material[42]
图 4 (a)InP/ZnS量子点与PMMA基质复合得到的大面积量子点光学膜[48]; (b)CdSe/ZnS量子点与PVA基质复合得到的透明量子点光学膜[50]; (c)CdSe/ZnS量子点与氧化聚乙烯基质形成的复合材料结构示意图[53]; (d)量子点光学膜两侧的阻隔膜结构示意图[60]
Figure 4. (a)Quantum dot based optical film with large area [48]. (b)Quantum dots based optical films with high transparency[50]. (c)Quantum dots based optical films with stable structure[53]. (d)Quantum dots based optical films with barriers[60]
图 5 (a)引发量子点表面的可聚合单体发生原位聚合反应,制备所需的聚合物基量子点复合材料[74];(b)采用量子点在聚合物基质中原位形核与生长的方式来制备聚合物基量子点复合薄膜材料[76]
Figure 5. (a)Quantum dots based composite fabricated by in-situ polymerization of the surface monomers[74]; (b)Quantum dots based composite film fabricated by in situ nucleation and growth of the quantum dot in the polymer matrix[76]
图 6 (a)“原位制备技术”制备的大面积钙钛矿量子点光学膜; (b)基于钙钛矿量子点光学膜的背光源和显示器样机在CIE色度图中的色域三角形; (c)集成有钙钛矿量子点光学膜的显示器样机与苹果笔记本显示器的显示效果对比
Figure 6. (a)Perovskite quantum dots based optical film prepared by "in-situ fabrication technique". (b)The color triangle of obtained backlight and LCD prototype in CIE 1931 diagram. (c)Comparison of a colorful picture display on the LCD prototype and Apple MacBook Air
表 1 量子点光学膜的系列优化方法及其应用效果
Table 1. A series of optimization methods for quantum dot based optical films and corresponding effects
大面积 稳定性好 制备工艺简单 透明性高 发光效率高 基质选择 √ × × × √ 界面相容性 × × × √ √ 聚合物结构 × √ × × √ 阻隔膜技术 × √ × × √ 商品化技术 √ √ × × √ 原位聚合 × × × √ × 原位生长 × × √ × × 原位制备技术 √ ? √ √ √ -
[1] MOROVIČ J. Color Gamut Mapping[M]. New York:John Wiley & Sons Inc., 2008. [2] SMITH A R. Color gamut transform pairs[J]. ACM Siggraph Computer Graphics, 1978, 12(3):12-19. doi: 10.1145/965139 [3] ZHU R, LUO Z, CHEN H, et al.. Realizing Rec. 2020 color gamut with quantum dot displays[J]. Optics Express, 2015, 23(18):23680-23693. doi: 10.1364/OE.23.023680 [4] BOURZAC K. Quantum dots go on display[J]. Nature, 2013, 493(7432):283. doi: 10.1038/493283a [5] JANG E, JUN S, JANG H, et al.. White-light-emitting diodes with quantum dot color converters for display backlights[J]. Advanced Materials, 2010, 22(28):3076-3080. doi: 10.1002/adma.v22:28 [6] CHEN B K, ZHONG H Z, ZHANG W, et al.. Highly emissive and color-tunable CuInS2-based colloidal semiconductor nanocrystals:off-stoichiometry effects and improved electroluminescence performance[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2012, 22(10):2081-2088. doi: 10.1002/adfm.201102496 [7] ZHONG H Z, BAI Z L, ZOU B S. Tuning the luminescence properties of colloidal Ⅰ-Ⅲ-Ⅵ semiconductor nanocrystals for optoelectronics and biotechnology applications[J]. J. Physical Chemistry Letters, 2012, 3(21):3167-3175. doi: 10.1021/jz301345x [8] KAMAT P V, SCHOLES G D. Quantum dots continue to shine brightly[J]. J. Physical Chemistry Letters, 2016, 7(3):584-585. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.6b00077 [9] 周忠伟, 孟长军, 王磊, 等.液晶显示器广色域技术的研究[J].发光学报, 2015, 36(9):1071-1075. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FGXB201509019.htmZHOU ZH W, MENG CH J, WANG L, et al. Research of wide color gamut technology for liquid crystal display[J]. Chinese J. Luminescence, 2015, 36(9):1071-1075.(in Chinese) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FGXB201509019.htm [10] MURRAY C B, NORRIS D J, BAWENDI M G. Synthesis and characterization of nearly monodisperse CdE(E=sulfur, selenium, tellurium) semiconductor nanocrystallites[J]. J. American Chemical Society, 1993, 115(19):8706-8715. doi: 10.1021/ja00072a025 [11] ZHONG X, FENG Y, KNOLL W, et al.. Alloyed ZnxCd1-xS nanocrystals with highly narrow luminescence spectral width[J]. J. American Chemical Society, 2003, 125(44):13559-13563. doi: 10.1021/ja036683a [12] PENG X, SCHLAMP M C, KADAVANICH A V, et al.. Epitaxial growth of highly luminescent CdSe/CdS core/shell nanocrystals with photostability and electronic accessibility[J]. J. American Chemical Society, 1997, 119(30):7019-7029. doi: 10.1021/ja970754m [13] BAILEY R E, NIE S. Alloyed semiconductor quantum dots:tuning the optical properties without changing the particle size[J]. J. American Chemical Society, 2003, 125(23):7100-7106. doi: 10.1021/ja035000o [14] CHEN Y, VELA J, HTOON H, et al.. "Giant" multishell CdSe nanocrystal quantum dots with suppressed blinking[J]. J. American Chemical Society, 2008, 130(15):5026-5027. doi: 10.1021/ja711379k [15] 政策法规司. 电器电子产品有害物质限制使用管理办法[EB/OL]. [2016-1-21]. http://www.miit.gov.cn/n1146285/n1146352/n3054355/n3057254/n3057260/c4608532/content.html. [16] BATTAGLIA D, PENG X. Formation of high quality InP and InAs nanocrystals in a noncoordinating solvent[J]. Nano Letters, 2002, 2(9):1027-1030. doi: 10.1021/nl025687v [17] LEE S H, LEE K H, JO J H, et al.. Remote-type, high-color gamut white light-emitting diode based on InP quantum dot color converters[J]. Optical Materials Express, 2014, 4(7):1297-1302. doi: 10.1364/OME.4.001297 [18] ZHANG F, ZHONG H Z, CHEN C, et al.. Brightly luminescent and color-tunable colloidal CH3NH3PbX3(X=Br, I, Cl) quantum dots:potential alternatives for display technology[J]. ACS Nano, 2015, 9(4):4533-4542. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.5b01154 [19] HUANG H L, ZHAO F C, LIU L G, et al.. Emulsion synthesis of size-tunable CH3NH3PbBr3 quantum dots:an alternative route toward efficient light-emitting diodes[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2015, 7(51):28128-28133. http://www.academia.edu/21157609/In_Coatings_Adhesives_and_Laminates [20] YANG G L, FAN Q S, CHEN B K, et al.. Reprecipitation synthesis of luminescent CH3NH3PbBr3/NaNO3 nanocomposites with enhanced stability[J]. J. Materials Chemistry C, 2016, 4(48):11387-11391. doi: 10.1039/C6TC04069A [21] LIU L G, HUANG S, PAN L F, et al.. Colloidal synthesis of CH3NH3PbBr3 nanoplatelets with polarized emission through self-organization[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2017. DOI: 10.1002/anie.201610619. [22] BAI Z L, ZHONG H Z. Halide perovskite quantum dots:potential candidates for display technology[J]. Science Bulletin, 2015, 18(60):1622-1624. doi: 10.1007/s11434-015-0884-y?slug=full%20text [23] YANG G L, ZHONG H Z. Organometal halide perovskite quantum dots:synthesis, optical properties, and display applications[J]. Chinese Chemical Letters, 2016, 27(8):1124-1130. doi: 10.1016/j.cclet.2016.06.047 [24] PROTESESCU L, YAKUNIN S, BODNARCHUK M I, et al.. Nanocrystals of cesium lead halide perovskites(CsPbX3, X=Cl, Br, and I):novel optoelectronic materials showing bright emission with wide color gamut[J]. Nano Letter, 2015, 15(6):3692-3696. doi: 10.1021/nl5048779 [25] WANG H C, LIN S Y, TANG A C, et al.. Mesoporous silica particle integrated with all-inorganic CsPbBr3 perovskite quantum-dot nanocomposite(MP-PQDs) with high stability and wide color gamut used for backlight display[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2016, 55(28):7924-7929. doi: 10.1002/anie.201603698 [26] COE-SULLIVAN S, LIU W, ALLEN P, et al.. Quantum dots for LED downconversion in display applications[J]. ECS J. Solid State Science and Technology, 2013, 2(2):R3026-R3030. https://ecs.confex.com/ecs/224/webprogram/Abstract/Paper24945/J3-2729.pdf [27] 周青超, 柏泽龙, 鲁路, 等.白光LED远程荧光粉技术研究进展与展望[J].中国光学, 2015, 8(3):313-328. http://www.chineseoptics.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract9292.shtmlZHOU Q CH, BAI Z L, LU L, et al.. Remote phosphor technology for white LED applications:advances and prospects[J]. Chinese Optics, 2015, 8(3):313-328.(in Chinese) http://www.chineseoptics.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract9292.shtml [28] 谢洪波, 李韬, 李富琳, 等.LED背光源中侧发光导光管长度与出光性能的关系[J].发光学报, 2011, 32(9):934-938. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FGXB201109018.htmXIE H B, LI T, LI F L, et al.. Relationship between the length and emitted light property of side-emitting light pipe in LED back light source[J]. Chinese J. Luminescence, 2011, 32(9):934-938.(in Chinese) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FGXB201109018.htm [29] NICK R J, BREEN C A, DENTON C M, et al.. Method of making components including quantum dots, methods, and products:US, 13762354[P]. 2013-02-07. [30] 3M. Expericence color transformed:3M color from 3M OSD[EB/OL].http://solutions.3m.com/wps/portal/3M/en_US/NA_Optical/Systems/QDEF/ [31] TSUJIMURA T. OLED Display Fundamentals and Applications[M]. New York:John Wiley & Sons Inc., 2012. [32] IWASAKI T. Recent progress and challenges of OLED technologies toward next-generation lighting[C]. Optical Instrumentation for Energy and Environmental Applications. Optical Society of America, 2014:JTh1A. 1. [33] STECKEL J S, HO J, HAMILTON C, et al.. Quantum dots:the ultimate down-conversion material for LCD displays[J]. J. Society for Information Display, 2015, 23(7):294-305. doi: 10.1002/jsid.313 [34] WANG Y, HE J, CHEN H, et al.. Ultrastable, highly luminescent organic-inorganic perovskite-polymer composite films[J]. Advanced Materials, 2016, 28(48):10710-10717. doi: 10.1002/adma.201603964 [35] CHEN B, ZHONG H, WANG M, et al.. Integration of CuInS2-based nanocrystals for high efficiency and high colour rendering white light-emitting diodes[J]. Nanoscale, 2013, 5(8):3514-3519. doi: 10.1039/c3nr33613a [36] SONG H, LEE S. Photoluminescent(CdSe) ZnS quantum dots polymethylmethacrylate polymer composite thin films in the visible spectral range[J]. Nanotechnology, 2007, 18(5):055402. doi: 10.1088/0957-4484/18/5/055402 [37] LEE J, SUNDAR V C, HEINE J R, et al.. Full Color emission from Ⅱ~Ⅵ semiconductor quantum dot-polymer composites[J]. Advanced Materials, 2000, 12(15):1102-1105. doi: 10.1002/1521-4095(200008)12:15<>1.0.CO;2-V [38] SONG W S, KIM J H, YANG H. Silica-embedded quantum dots as downconverters of light-emitting diode and effect of silica on device operational stability[J]. Materials Letter, 2013, 111:104-107. doi: 10.1016/j.matlet.2013.08.091 [39] OTTO T, M LLER M, MUNDRA P, et al.. Colloidal nanocrystals embedded in macrocrystals:robustness, photostability, and color purity[J]. Nano Letter, 2012, 12(10):5348-5354. doi: 10.1021/nl3027444 [40] DUBOIS F, MAHLER B, DUBERTRET B, et al.. A versatile strategy for quantum dot ligand exchange[J]. J. American Chemical Society, 2007, 129(3):482-483. doi: 10.1021/ja067742y [41] ADAM M, ERDEM T, STACHOWSKI G M, et al.. Implementation of high-quality warm-white light-emitting diodes by a model-experimental feedback approach using quantum dot salt mixed crystals[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2015, 7(41):23364-23371. doi: 10.1002/adfm.201500552/abstract [42] JUN S, LEE J, JANG E. Highly Luminescent and photostable quantum dot-silica monolith and its application to light-emitting diodes[J]. ACS Nano, 2013, 7(2):1472-1477. doi: 10.1021/nn3052428 [43] KHANNA P K, SINGH N. Light emitting CdS quantum dots in PMMA:synthesis and optical studies[J]. J. Luminescence, 2007, 127(2):474-482. doi: 10.1016/j.jlumin.2007.02.037 [44] KIM J H, SONG W S, YANG H. Color-converting bilayered composite plate of quantum-dot-polymer for high-color rendering white light-emitting diode[J]. Optics Letters, 2013, 38(15):2885-2888. doi: 10.1364/OL.38.002885 [45] WANG H, SHAO Z, CHEN B, et al.. Transparent, flexible and luminescent composite films by incorporating CuInS2 based quantum dots into a cyanoethyl cellulose matrix[J]. RSC Advances, 2012, 2(7):2675-2677. doi: 10.1039/c2ra01359b [46] COSGUN A, FU R, JIANG W, et al.. Flexible quantum dot-PVA composites for white LEDs[J]. J. Materials Chemistry C, 2015, 3(2):257-264. doi: 10.1039/C4TC02256D [47] ZHU L, HUO P, WANG Q, et al.. Photoluminescent poly(ether ether ketone)-quantum dot composite films[J]. Chemical Communications, 2013, 49(46):5283-5285. doi: 10.1039/c3cc42074d [48] MUTLUGUN E, HERNANDEZ-MARTINEZ P L, EROGLU C, et al.. Large-Area(Over 50 cm×50 cm) freestanding films of colloidal InP/ZnS quantum dots[J]. Nano Letter, 2012, 12(8):3986-3993. doi: 10.1021/nl301198k [49] CHO S, KWAG J, JEONG S, et al.. Highly fluorescent and stable quantum dot-polymer-layered double hydroxide composites[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2013, 25(7):1071-1077. doi: 10.1021/cm3040505 [50] LIANG R, YAN D, TIAN R, et al.. Quantum dots-based flexible films and their application as the phosphor in white light-emitting diodes[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2014, 26(8):2595-2600. doi: 10.1021/cm404218y [51] XU H, PANG X, HE Y, et al.. An unconventional route to monodisperse and intimately contacted semiconducting organic-inorganic nanocomposites[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2015, 127(15):4719-4723. http://www.nature.com/cited/cited.html?doi=10.1038/nmat3032 [52] GAI Y, LIN Y, SONG D P, et al.. Strong ligand-block copolymer interactions for incorporation of relatively large nanoparticles in ordered composites[J]. Macromolecules, 2016, 49(9):3352-3360. doi: 10.1021/acs.macromol.5b02609 [53] PARK S Y, KIM H S, YOO J, et al.. Long-term stability of CdSe/CdZnS quantum dot encapsulated in a multi-lamellar microcapsule[J]. Nanotechnology, 2015, 26(27):275602. doi: 10.1088/0957-4484/26/27/275602 [54] ZHU M, PENG X, WANG Z, et al.. Highly transparent and colour-tunable composite films with increased quantum dot loading[J]. J. Materials Chemistry C, 2014, 2(46):10031-10036. [55] BOBROVSKY A, SHIBAEV V, ELYASHEVITCH G, et al.. Polyethylene-based composites containing high concentration of quantum dots[J]. Colloid and Polymer Science, 2015, 293(5):1545-1551. doi: 10.1007/s00396-015-3551-6 [56] VAIDYA S V, COUZIS A, MALDARELLI C. Reduction in aggregation and energy transfer of quantum dots incorporated in polystyrene beads by kinetic entrapment due to cross-linking during polymerization[J]. Langmuir, 2015, 31(10):3167-3179. doi: 10.1021/la503251s [57] JANG J W, KIM J S, KWON O H, et al.. UV-curable silicate phosphor planar films printed on glass substrate for white light-emitting diodes[J]. Optics Letters, 2015, 40(16):3723-3726. doi: 10.1364/OL.40.003723 [58] YANG X, SHAO Q, YANG L, et al.. Preparation and performance of high refractive index silicone resin-type materials for the packaging of light-emitting diodes[J]. J. Applied Polymer Science, 2013, 127(3):1717-1724. doi: 10.1002/app.37897 [59] CHEN W, WANG K, HAO J, et al.. High efficiency and color rendering quantum dots white light emitting diodes optimized by luminescent microspheres incorporating[J]. Nanophotonics, 2016, 5(4):565-572. [60] JANG E P, SONG W S, LEE K H, et al.. Preparation of a photo-degradation-resistant quantum dot-polymer composite plate for use in the fabrication of a high-stability white-light-emitting diode[J]. Nanotechnology, 2013, 24(4):045607. doi: 10.1088/0957-4484/24/4/045607 [61] LIEN J Y, CHEN C J, CHIANG R K, et al.. High color-rendering warm-white lamps using quantum-dot color conversion films[J]. Optics Express, 2016, 24(14):A1021-A1032. doi: 10.1364/OE.24.0A1021 [62] WOO J Y, LEE J, HAN C S. Alumina/polymer-coated nanocrystals with extremely high stability used as a color conversion material in LEDs[J]. Nanotechnology, 2013, 24(50):505714. doi: 10.1088/0957-4484/24/50/505714 [63] CHEN G H, YEH C W, YEH M H, et al.. Wide gamut white light emitting diodes using quantum dot-silicone film protected by an atomic layer deposited TiO2 barrier[J]. Chemical Communications, 2015, 51(79):14750-14753. doi: 10.1039/C5CC05299H [64] KIM E, SHIM H W, UNITHRATTIL S, et al.. Effective heat dissipation from color-converting plates in high-power white light emitting diodes by transparent graphene wrapping[J]. ACS Nano, 2015, 10(1):238-245. http://jglobal.jst.go.jp/public/201702254088490007 [65] SONG Y H, HAN G S, MANG S R, et al.. Design of a thermally stable rGO-embedded remote phosphor for applications in white LEDs[J]. J. Materials Chemistry C, 2015, 3(2):235-238. doi: 10.1039/C4TC02403F [66] CHEN W, HAO J, LU R, et al.. P-93:High performance of quantum dot based light emitting diodes optimized by graphene sheets[C]. SID Symposium Digest of Technical Papers, 2016, 47(1):1472-1475. [67] LEE S, HONG J Y, JANG J. Multifunctional graphene sheets embedded in silicone encapsulant for superior performance of light-emitting diodes[J]. ACS Nano, 2013, 7(7):5784-5790. doi: 10.1021/nn4024587 [68] NELSON E W, ECKERT K L, KOLB W B, et al., Quantum dot film:US, 14/762, 173[P]. 2014-01-16. [69] DUBROW R S, FREEMAN W P, LEE E, et al.. Quantum dot films, lighting devices, and lighting methods:US, 9199842[P]. 2015-12-01. [70] MIN S Y, BANG J, PARK J, et al.. Electrospun polymer/quantum dot composite fibers as down conversion phosphor layers for white light-emitting diodes[J]. RSC Advances, 2014, 4(23):11585-11589. doi: 10.1039/c3ra46809g [71] KIM N, NA W, YIN W, et al.. CuInS2/ZnS quantum dot-embedded polymer nanofibers for color conversion films[J]. J. Materials Chemistry C, 2016, 4(13):2457-2462. doi: 10.1039/C5TC03967C [72] GALEOTTI F, MR Z W, CATELLANI M, et al.. Tailorable perylene-loaded fluorescent nanostructures:a multifaceted approach enabling their application in white hybrid LEDs[J]. J. Materials Chemistry C, 2016, 4(23):5407-5415. doi: 10.1039/C6TC00486E [73] DI BENEDETTO F, CAMPOSEO A, PERSANO L, et al.. Light-emitting nanocomposite CdS-polymer electrospun fibres via in situ nanoparticle generation[J]. Nanoscale, 2011, 3(10):4234-4239. doi: 10.1039/c1nr10399g [74] ZHANG H, CUI Z, WANG Y, et al.. From water-soluble CdTe nanocrystals to fluorescent nanocrystal-polymer transparent composites using polymerizable surfactants[J]. Advanced Materials, 2003, 15(10):777-780. doi: 10.1002/adma.200304521 [75] ANTOLINI F, PENTIMALLI M, DI LUCCIO T, et al.. Structural characterization of CdS nanoparticles grown in polystyrene matrix by thermolytic synthesis[J]. Materials Letters, 2005, 59(24):3181-3187. [76] ZHOU Q, BAI Z, LU W, et al.. In situ fabrication of halide perovskite nanocrystal-embedded polymer composite films with enhanced photoluminescence for display backlights[J]. Advanced Materials, 2016, 28(41):9163-9168. doi: 10.1002/adma.201602651 -






 下载:
下载: