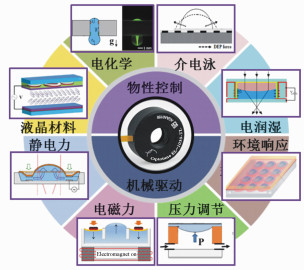
-
摘要: 相比于传统的机械变焦镜头,液体变焦镜头具有体积小、响应快、成本低和集成度高等特点,被广泛应用于图像采集、目标追踪和特征识别等领域。焦距调节方式决定了液体镜头的性能和应用,本文概括了基于液晶材料、介电泳、电化学、电润湿原理的物性控制式变焦镜头和基于静电力、电磁力、压力调节和环境响应的机械驱动式变焦镜头的研究现状,介绍了液体变焦镜头在光流控芯片内的集成应用,并指出当前面临的主要问题和解决方案。最后,对液体变焦镜头的发展前景和研究方向进行了展望和总结。Abstract: Compared with the traditional mechanical zoom lens, the variable-focus liquid lens has a smaller lens, faster response time, lower cost and higher integration capabilities. These lenses are widely used in image acquisition, target tracking and feature recognition. The performance and applications of liquid lenses are determined by the focal length adjustment method. This paper summarizes the progress of liquid crystals, dielectrophoresis, electrochemistry, electrowetting principle-based function control variable-focus lenses, electrostatic force, electromagnetic force, pressure regulation, and environmental-response-technology-based mechanical driven variable-focus lenses. The integrated applications of variable-focus liquid lenses in optofluidic chips are introduced. Also, the major obstacles and the settlement are described. Furthermore, the development potential and future research direction of the variable-focus liquid lens are also predicted and summarized.
-
Key words:
- liquid lens /
- focus tunable /
- function control /
- mechanical driven
-
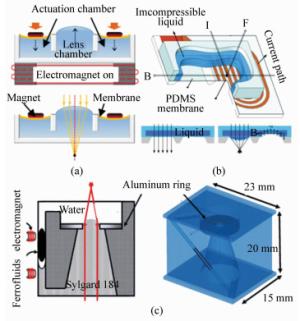
图 8 3种常见的电磁驱动液体镜头结构[49-51]。(a)基于电磁吸引的液体变焦镜头;(b)基于通电线圈洛伦兹力驱动的液体变焦镜头;(c)基于铁磁流体流动的液体变焦镜头
Figure 8. Structure of three common electromagnetically driven liquid lenses[49-51]. (a) Electromagnetic attraction varifocal liquid lens. (b) Electric coil Lorentz force driven varifocal liquid lens. (c) Ferrofluid-based fluid varifocal liquid lens
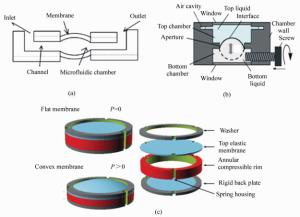
图 9 压力调节液体镜头结构[54-56]。(a)基于液压控制的液体变焦镜头;(b)基于手动操纵的液体变焦镜头;(c)基于形状记忆合金变形的液体变焦镜头
Figure 9. Structures of pressure adjusted liquid lenses[54-56].(a)Variable-focus liquid lens based on hydraulic control.(b)Variable-focus liquid lens based on manual actuation. (c)Variable-focus liquid lens based on shape memory alloy deformation
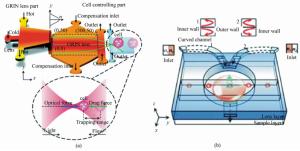
图 12 基于液体变焦镜头集成的光流控芯片[61-62]。(a)用于流动环境中生物细胞捕捉的热梯度折射率液体镜头;(b)三维液-液双凸凹变焦镜头用于生物细胞成像
Figure 12. Varifocal liquid lens integrated optofluidic chip[61-62].(a)Thermal gradient refractive index liquid lens for trapping single living cell in flowing environments. (b)Switchable 3D liquid-liquid biconvex lens for biological cell image
表 1 4种介质层的实验结果
Table 1. Experimental results obtained with four kinds of dielectric layers
介电层 填充液 击穿电压/V 工作电压/V Parylene C D.I water 95 10 SDS 20 2 Parylene C+Al2O3 D.I water 125 50 SDS 22 6 Parylene C+SiO2 D.I water 120 40 SDS 20 2 Parylene C+SiO2+Al2O3 D.I water 135 65 SDS 24 8 -
[1] 顾寄南, 尚正阳, 唐仕喜, 等.当前智能制造若干关键技术综述[J].机械设计与制造工程, 2017, 46(9):11-15. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-509X.2017.09.002GU J N, SHANG ZH Y, TANG SH X, et al.. The symposium on some key technologies of intelligent manufacturing[J]. Machine Design and Manufacturing Engineering, 2017, 46(9):11-15.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-509X.2017.09.002 [2] 阮晋蒙.机器视觉:让中国制造2025"看"得更远[J].新经济导刊, 2017(z1):80-83. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yygx200605025RUAN J M. Machine vision:let made in China 2025 "see" farther[J]. New Economy Weekly, 2017(z1):80-83.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yygx200605025 [3] 王耀南, 陈铁健, 贺振东, 等.智能制造装备视觉检测控制方法综述[J].控制理论与应用, 2015, 32(3):273-286. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/kzllyyy201503001WANG Y N, CHEN T J, HE ZH D, et al.. Review on the machine vision measurement and control technology for intelligent manufacturing equipment[J]. Control Theory & Applications, 2015, 32(3):273-286.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/kzllyyy201503001 [4] SUN J W, MENG Y, TAN J Y, et al.. A vision-based perception framework for outdoor navigation tasks applicable to legged robots[C]. 2017 Chinese Automation Congress, IEEE, 2017: 2894-2899. [5] ZHANG H, LI X L, ZHONG H, et al.. Automated machine vision system for liquid particle inspection of pharmaceutical injection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2018, 67(6):1278-1297. doi: 10.1109/TIM.2018.2800258 [6] JOSHI K D, CHAUHAN V, SURGENOR B. A flexible machine vision system for small part inspection based on a hybrid SVM/ANN approach[J]. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 2018:1-23. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=cc7d18cf9b623ee3ef57a5d6c9919d9a&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [7] 童季刚, 廖菲, 罗良传.一种机器视觉的瓶罐缺陷检测系统设计[J].机电工程技术, 2016, 45(8):28-31. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9492.2016.08.009TONG J G, LIAO F, LUO L CH. Design of bottle cap encapsulation testing based on machine vision[J]. Mechanical & Electrical Engineering Technology, 2016, 45(8):28-31.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9492.2016.08.009 [8] 刘明周, 马靖, 张淼, 等.基于机器视觉的机械产品装配系统在线作业方法[J].计算机集成制造系统, 2015, 21(9):2343-2353. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/jsjjczzxt201509009LIU M ZH, MA J, ZHANG M, et al.. Online operation method for assembly system of mechanical products based on machine vision[J]. Computer Integrated Manufacturing Systems, 2015, 21(9):2343-2353.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/jsjjczzxt201509009 [9] 李丽丽, 熊倍华, 贾海龙.高速机器人分拣系统机器视觉技术的应用[J].装备制造技术, 2016(11):11-12, 31. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-545X.2016.11.004LI L L, XIONG B H, JIA H L. Application of high-speed sorting systems robot machine vision technology[J]. Equipment Manufacturing Technology, 2016(11):11-12, 31.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-545X.2016.11.004 [10] ZHONG Y H, GAO J Y, LEI Q L, et al.. A vision-based counting and recognition system for flying insects in intelligent agriculture[J]. Sensors, 2018, 18(5):1489. doi: 10.3390/s18051489 [11] 李铮, 戴明, 李嘉全.步进电机驱动的直线变倍成像系统研究[J].中国光学, 2018, 11(5):779-789. http://www.chineseoptics.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract9516.shtmlLI ZH, DAI M, LI J Q. Continuous zooming imaging system driven by stepping motors[J]. Chinese Optics, 2018, 11(5):779-789.(in Chinese) http://www.chineseoptics.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract9516.shtml [12] 王潇枫, 石岩, 庄一, 等.变焦结构光成像系统的光学设计[J].应用光学, 2018, 39(1):22-27. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yygx201801004WANG X F, SHI Y, ZHUANG Y, et al.. Optical design of zoom structured light imaging system[J]. Journal of Applied Optics, 2018, 39(1):22-27.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yygx201801004 [13] 李零印, 王一凡.液体变焦技术的发展与展望[J].中国光学, 2012, 5(6):578-582. http://www.chineseoptics.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract8907.shtmlLI L Y, WANG Y F. Development and prospect of varifocal-liquid technique[J]. Chinese Optics, 2012, 5(6):578-582.(in Chinese) http://www.chineseoptics.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract8907.shtml [14] 石广丰, 杨彬, 史国权, 等.高速变焦液体透镜的发展动态综述[J].红外技术, 2014, 36(10):777-781, 786. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hwjs201410002SHI G F, YANG B, SHI G Q, et al.. A review of the development of high-speed liquid lens[J]. Infrared Technology, 2014, 36(10):777-781, 786.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hwjs201410002 [15] 贾书海, 唐振华, 董君, 等.柔性变焦透镜发展现状[J].中国光学, 2015, 8(4):535-547. http://www.chineseoptics.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract9291.shtmlJIA SH H, TANG ZH H, DONG J, et al.. Recent advances in flexible variable-focus lens[J]. Chinese Optics, 2015, 8(4):535-547.(in Chinese) http://www.chineseoptics.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract9291.shtml [16] SHAHINI A, JIN H, ZHOU ZH X, et al.. Toward individually tunable compound eyes with transparent graphene electrode[J]. Bioinspiration & Biomimetics, 2017, 12(4):046002. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=034fd352a03d26640cc551b253a986f3&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [17] LIANG D, WANG X Y. A bio-inspired optical system with a polymer membrane and integrated structure[J]. Bioinspiration & Biomimetics, 2016, 11(6):066008. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=IOP_9304489 [18] KONG M M, CHEN D, CHEN X, et al.. Research of the human eye model with variable-focus liquid lens[J]. Microfluidics and Nanofluidics, 2017, 21(3):40. doi: 10.1007/s10404-017-1857-z [19] CHENG Y, CAO J, MENG L T, et al.. Reducing defocus aberration of a compound and human hybrid eye using liquid lens[J]. Applied Optics, 2018, 57(7):1679-1688. doi: 10.1364/AO.57.001679 [20] 潘逸君, 李湘宁, 李强, 等.双液体透镜变焦系统的高斯光学分析[J].应用光学, 2016, 37(2):198-202. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yygx201602009PAN Y J, LI X N, LI Q, et al.. Gauss optical analysis of double liquid lens zoom system[J]. Journal of Applied Optics, 2016, 37(2):198-202.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yygx201602009 [21] 张鹰, 张新, 史广维, 等.液体透镜在变焦系统中的应用[J].中国光学, 2013, 6(1):46-56. http://www.chineseoptics.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract8854.shtmlZHANG Y, ZHANG X, SHI G W, et al.. Applications of liquid lenses in zoom systems[J]. Chinese Optics, 2013, 6(1):46-56.(in Chinese) http://www.chineseoptics.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract8854.shtml [22] BEZRUCHENKO V S, MURAVSKY A A, MURAUSKI A A, et al.. Tunable liquid crystal lens based on pretilt angle gradient alignment[J]. Molecular Crystals and Liquid Crystals, 2016, 626(1):222-228. doi: 10.1080/15421406.2015.1106890 [23] LI H, PAN F, WU Y T, et al.. Improvement in imaging contrast feature of liquid crystal lens with the dopant of multi-walled carbon nanotubes[J]. Applied Optics, 2017, 56(23):6655-6662. doi: 10.1364/AO.56.006655 [24] LI H, PENG J, PAN F, et al.. Focal stack camera in all-in-focus imaging via an electrically tunable liquid crystal lens doped with multi-walled carbon nanotubes[J]. Optics Express, 2018, 26(10):12441-12454. doi: 10.1364/OE.26.012441 [25] 吕文明, 张红霞, 宋晓敏, 等.梯形凸起电极液晶变焦透镜[J].液晶与显示, 2018, 33(1):30-37. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yjyxs201801004LV W M, ZHANG H X, SONG X M, et al.. Tunable liquid crystal lens with raised trapezoidal electrodes[J]. Chinese Journal of Liquid Crystals and Displays, 2018, 33(1):30-37.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yjyxs201801004 [26] GIDEN I H, ETI N, REZAEI B, et al.. Adaptive graded index photonic crystal lens design via nematic liquid crystals[J]. IEEE Journal of Quantum Electronics, 2016, 52(10):6400607. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ffbe87d373e872eaf73bcf1596a5e589 [27] CHANG K H, VARANYTSIA A, CHIEN L C. Electrically tunable liquid crystal lens with suppressed axial chromatic aberration[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2017, 111(3):2401-2410. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=490f41f71da2c84861d17d4f5c595ade [28] DOU H, CHU F, GUO Y Q, et al.. Large aperture liquid crystal lens array using a composited alignment layer[J]. Optics Express, 2018, 26(7):9254-9262. doi: 10.1364/OE.26.009254 [29] LÓPEZ C A, LEE C C, HIRSA A H. Electrochemically activated adaptive liquid lens[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2005, 87(13):134102. doi: 10.1063/1.2058209 [30] LU Y SH, TU H E, XU Y, et al.. Tunable dielectric liquid lens on flexible substrate[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2013, 103(26):261113. doi: 10.1063/1.4858616 [31] JIN B Y, REN H W, CHOI W K. Dielectric liquid lens with chevron-patterned electrode[J]. Optics Express, 2017, 25(26):32411-32419. doi: 10.1364/OE.25.032411 [32] ALMOALLEM Y D, JIANG H R. Double-sided design of electrodes driving tunable dielectrophoretic miniature lens[J]. Journal of Microelectromechanical Systems, 2017, 26(5):1122-1131. doi: 10.1109/JMEMS.2017.2711966 [33] LIAO K W, WANG W J, LUO R C, et al.. Development of portable microscope with tunable working distance by using dielectric liquid lens[C]. 2014 International Conference on Optical MEMS and Nanophotonics, IEEE, 2014: 153-154. [34] LI L, LIU CH, REN H W, et al.. Optical switchable electrowetting lens[J]. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 2016, 28(14):1505-1508. doi: 10.1109/LPT.2016.2555991 [35] BERGE B, PESEUX J. Variable focal lens controlled by an external voltage:An application of electrowetting[J]. The European Physical Journal E, 2000, 3(2):159-163. doi: 10.1007/s101890070029 [36] BERGE B. Liquid lens technology: principle of electrowetting based lenses and applications to imaging[C]. Proceedings of the 18th IEEE International Conference on Micro Electro Mechanical Systems, IEEE, 2005. [37] KOPP D, BRENDER T, ZAPPE H. All-liquid dual-lens optofluidic zoom system[J]. Applied Optics, 2017, 56(13):3758-3763. doi: 10.1364/AO.56.003758 [38] WEI X, KAWAMURA G, MUTO H, et al.. Fabrication on low voltage driven electrowetting liquid lens by dip coating processes[J]. Thin Solid Films, 2016, 608:16-20. doi: 10.1016/j.tsf.2016.04.006 [39] LI L, WANG J H, WANG Q H, et al.. Displaceable and focus-tunable electrowetting optofluidic lens[J]. Optics Express, 2018, 26(20):25839-25848. doi: 10.1364/OE.26.025839 [40] HAO CH L, LIU Y H, CHEN X M, et al.. Electrowetting on liquid-infused film(EWOLF):Complete reversibility and controlled droplet oscillation suppression for fast optical imaging[J]. Scientific Reports, 2014, 4:6846. [41] SATO S. Liquid-crystal lens-cells with variable focal length[J]. Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 1979, 18(9):1679-1684. doi: 10.1143/JJAP.18.1679 [42] NOSE T, MASUDA S, SATO S. A liquid crystal microlens with hole-patterned electrodes on both substrates[J]. Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 1992, 31(5B):1643-1646. [43] REN H W, WU S T. Introduction to Adaptive Lenses[M]. Hoboken:Wiley, 2012:181-183. [44] HAWKINS B G, SMITH A E, SYED Y A, et al.. Continuous-flow particle separation by 3D insulative dielectrophoresis using coherently shaped, DC-biased, AC electric fields[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2007, 79(19):7291-7300. doi: 10.1021/ac0707277 [45] 韩春光, 郭隐彪.基于电润湿技术的液体微透镜研究进展[J].机械设计与制造, 2010(9):247-249. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3997.2010.09.103HAN CH G, GUO Y B. Current development in liquid micro-lens based on electrowetting technology[J]. Machinery Design & Manufacture, 2010(9):247-249.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3997.2010.09.103 [46] MUGELE F, BARET J C. Electrowetting:from basics to applications[J]. Journal of Physics:Condensed Matter, 2005, 17(28):R705-R774. doi: 10.1088/0953-8984/17/28/R01 [47] POUYDEBASQUE A, BRIDOUX C, JACQUET F, et al.. Varifocal liquid lenses with integrated actuator, high focusing power and low operating voltage fabricated on 200 mm wafers[J]. Sensors and Actuators A:Physical, 2011, 172(1):280-286. doi: 10.1016/j.sna.2011.05.005 [48] POUYDEBASQUE A, BOLIS S, BRIDOUX C, et al.. Process optimization and performance analysis of an electrostatically actuated varifocal liquid lens[C]. 201116th international Solid-state Sensors, Actuators and Microsystems Conference, IEEE, 2011. [49] OH S H, RHEE K, CHUNG S K. Electromagnetically driven liquid lens[J]. Sensors and Actuators A:Physical, 2016, 240:153-159. doi: 10.1016/j.sna.2016.01.048 [50] LEE S W, LEE S S. Focal tunable liquid lens integrated with an electromagnetic actuator[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2007, 90(12):121129. doi: 10.1063/1.2716213 [51] CHENG H CH, XU S, LIU Y F, et al.. Adaptive mechanical-wetting lens actuated by ferrofluids[J]. Optics Communications, 2011, 284(8):2118-2121. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2010.12.073 [52] YU H, ZHOU G, CHAU F S, et al.. Tunable electromagnetically actuated liquid-filled lens[J]. Sensors and Actuators A:Physical, 2011, 167(2):602-607. doi: 10.1016/j.sna.2011.03.005 [53] XIAO W J, HARDT S. An adaptive liquid microlens driven by a ferrofluidic transducer[J]. Journal of Micromechanics and Microengineering, 2010, 20(5):055032. doi: 10.1088/0960-1317/20/5/055032 [54] 吴雯婷, 梁忠诚, 仉乐.可调微流控光学变焦透镜[J].发光学报, 2015, 36(6):718-723. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/fgxb201506020WU W T, LIANG ZH CH, ZHANG L. Optofluidic varifocal microlens[J]. Chinese Journal of Luminescence, 2015, 36(6):718-723.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/fgxb201506020 [55] PATRA R, AGARWAL S, KONDARAJU S, et al.. Membrane-less variable focus liquid lens with manual actuation[J]. Optics Communications, 2017, 389:74-78. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2016.12.021 [56] HASAN N, KIM H, MASTRANGELO C H. Large aperture tunable-focus liquid lens using shape memory alloy spring[J]. Optics Express, 2016, 24(12):13334-13342. doi: 10.1364/OE.24.013334 [57] ZHAO P P, ATAMAN C, ZAPPE H. Gravity-immune liquid-filled tunable lens with reduced spherical aberration[J]. Applied Optics, 2016, 55(28):7816-7823. doi: 10.1364/AO.55.007816 [58] LIANG D, LIANG D T, WANG X Y, et al.. Flexible fluidic lens with polymer membrane and multi-flow structure[J]. Optics Communications, 2018, 421:7-13. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2018.03.062 [59] MALYUK A Y, IVANOVA N A. Varifocal liquid lens actuated by laser-induced thermal Marangoni forces[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2018, 112(10):103701. doi: 10.1063/1.5023222 [60] SHIMIZU Y, KOYAMA D, FUKUI M, et al.. Ultrasound liquid crystal lens[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2018, 112(16):161104. doi: 10.1063/1.5027131 [61] LIU H L, SHI Y, LIANG L, et al.. A liquid thermal gradient refractive index lens and using it to trap single living cell in flowing environments[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2017, 17(7):1280-1286. doi: 10.1039/C7LC00078B [62] LIANG L, ZHU X Q, LIU H L, et al.. A switchable 3D liquid-liquid biconvex lens with enhanced resolution using Dean flow[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2017, 17(19):3258-3263. doi: 10.1039/C7LC00598A [63] WEE D, HWANG S H, SONG Y S, et al.. Tunable optofluidic birefringent lens[J]. Soft Matter, 2016, 12(17) 3868-3876. doi: 10.1039/C5SM02782A [64] SONG CH L, LUONG T D, KONG T F, et al.. Disposable flow cytometer with high efficiency in particle counting and sizing using an optofluidic lens[J]. Optics Letters, 2011, 36(5):657-659. doi: 10.1364/OL.36.000657 [65] CHEN Q M, LI T G, ZHU Y J, et al.. Dielectrophoresis-actuated in-plane optofluidic lens with tunability of focal length from negative to positive[J]. Optics Express, 2018, 26(6):6532-6541. doi: 10.1364/OE.26.006532 [66] CHEN Q M, LI T H, LI ZH H, et al.. Dielectrophoresis-actuated liquid lenses with dual air/liquid interfaces tuned from biconcave to biconvex[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2018, 18(24):3849-3854. doi: 10.1039/C8LC00999F [67] CHEN Q M, LI T H, LI ZH H, et al.. Optofluidic tunable lenses for in-plane light manipulation[J]. Micromachines, 2018, 9(3):97. doi: 10.3390/mi9030097 [68] 闵伶俐, 陈松月, 盛智芝, 等.仿生微流控的发展与应用[J].物理学报, 2016, 65(17):178301. doi: 10.7498/aps.65.178301MIN L L, CHEN S Y, SHENG ZH ZH, et al.. Development and application of bio-inspired and biomimetic microfluidics[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2016, 65(17):178301.(in Chinese) doi: 10.7498/aps.65.178301 [69] YE M, WANG B, SATO S. Realization of liquid crystal lens of large aperture and low driving voltages using thin layer of weakly conductive material[J]. Optics Express, 2008, 16(6):4302-4308. doi: 10.1364/OE.16.004302 [70] BEECKMAN J, YANG T H, NYS I, et al.. Multi-electrode tunable liquid crystal lenses with one lithography step[J]. Optics Letters, 2018, 43(2):271-274. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=7f6ab91091a7ada0f1cd67d0388cdd83 [71] 胡水兰, 彭润玲, 李一凡, 等.双层介电薄膜结构双液体变焦透镜的研究[J].光子学报, 2014, 43(2):0223003. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gzxb201402012HU SH L, PENG R L, LI Y F, et al.. Research on the double-liquid lens with double-layer dielectric films[J]. Acta Photonica Sinica, 2014, 43(2):0223003.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gzxb201402012 [72] 魏茂炜, 彭润玲, 汤征洋, 等.低压双液体变焦透镜的理论及工艺研究[J].光子学报, 2015, 44(5):36-40. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gzxb201505007WEI M W, PENG R L, TANG ZH Y, et al.. Study on theory and technology of low voltage variable-focus double liquid lens[J]. Acta Photonica Sinica, 2015, 44(5):36-40.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gzxb201505007 [73] LEE J, KIM J, KIM D, et al.. Low voltage electrowetting lenticular lens by using multilayer dielectric structure[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2017, 10116:1011609. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=01f7efa0bdddfd1424fd6ce0729614f6&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [74] SUN W, YANG F Q. Evaporation of a volatile liquid lens on the surface of an immiscible liquid[J]. Langmuir, 2016, 32(24):6058-6067. doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.6b01471 [75] HU X D, ZHANG SH G, LIU Y, et al.. Electrowetting based infrared lens using ionic liquids[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2011, 99(21):213505. doi: 10.1063/1.3663633 [76] BAE J W, SHIN E J, JEONG J, et al.. High-performance PVC gel for adaptive micro-lenses with variable focal length[J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7(1):2068. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-02324-9 [77] SHI L, YANG R S, LU SH Y, et al.. Dielectric gels with ultra-high dielectric constant, low elastic modulus, and excellent transparency[J]. NPG Asia Materials, 2018, 10(8):821-826. doi: 10.1038/s41427-018-0077-7 [78] WANG SH M, WU P C, SU V C, et al.. A broadband achromatic metalens in the visible[J]. Nature Nanotechnology, 2018, 13(3):227-323. doi: 10.1038/s41565-017-0052-4 [79] SHE A, ZHANG SH Y, SHIAN S, et al.. Adaptive metalenses with simultaneous electrical control of focal length, astigmatism, and shift[J]. Science Advances, 2018, 4(2):eaap9957. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aap9957 [80] WATSON A M, DEASE K, TERRAB S, et al.. Focus-tunable low-power electrowetting lenses with thin parylene films[J]. Applied Optics, 2015, 54(20):6224-6229. doi: 10.1364/AO.54.006224 [81] VAFAEI S, PODOWSKI M Z. Theoretical analysis on the effect of liquid droplet geometry on contact angle[J]. Nuclear Engineering and Design, 2005, 235(10-12):1293-1301. doi: 10.1016/j.nucengdes.2005.02.026 [82] REN H W, XU S, WU S T. Effects of gravity on the shape of liquid droplets[J]. Optics Communications, 2010, 283(17):3255-3258. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2010.04.045 [83] LI L, WANG Q H, JIANG W. Liquid lens with double tunable surfaces for large power tunability and improved optical performance[J]. Journal of Optics, 2011, 13(11):115503. doi: 10.1088/2040-8978/13/11/115503 [84] ZHANG W, LIU P F, WEI X N, et al.. The analysis of the wavefront aberration caused by the gravity of the tunable-focus liquid-filled membrane lens[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2010, 7849:78491W. doi: 10.1117/12.869866 [85] POKORN P, MEJKAL F, KULMON P, et al.. Calculation of nonlinearly deformed membrane shape of liquid lens caused by uniform pressure[J]. Applied Optics, 2017, 56(21):5939-5947. doi: 10.1364/AO.56.005939 [86] DING Z Q, WANG CH H, HU ZH X, et al.. Surface profiling of an aspherical liquid lens with a varied thickness membrane[J]. Optics Express, 2017, 25(4):3122-3132. doi: 10.1364/OE.25.003122 [87] 朱凌峰, 孔梅梅, 宋驰, 等.电润湿双液体透镜的界面面型分析[J].光电工程, 2016, 43(12):65-71. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2016.12.011ZHU L F, KONG M M, SONG CH, et al.. Analysis on the interface shape of double liquid lens based on electro-wetting technology[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2016, 43(12):65-71.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2016.12.011 [88] ZOHRABI M, CORMACK R H, MCCULLOUGH C, et al.. Numerical analysis of wavefront aberration correction using multielectrode electrowetting-based devices[J]. Optics Express, 2017, 25(25):31451-31461. doi: 10.1364/OE.25.031451 [89] MISHRA K, MURADE C, CARREEL B, et al.. Optofluidic lens with tunable focal length and asphericity[J]. Scientific Reports, 2014, 4:6378. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=22af7772312360fd77f20793ddc4a5ff&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [90] BEGEL L, GALSTIAN T. Liquid crystal lens with corrected wavefront asymmetry[J]. Applied Optics, 2018, 57(18):5072-5078. doi: 10.1364/AO.57.005072 [91] 郭鑫, 张薇, 速晋辉, 等.可调焦胶囊内窥镜光学系统设计[J].光子学报, 2015, 44(5):179-183. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gzxb201505031GUO X, ZHANG W, SU J H, et al.. Design of a focus-tunable capsule endoscope system[J]. Acta Photonica Sinica, 2015, 44(5):179-183.(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gzxb201505031 [92] XIONG K D, YANG S H, LI X W, et al.. Autofocusing optical-resolution photoacoustic endoscopy[J]. Optics Letters, 2018, 43(8):1846-1849. doi: 10.1364/OL.43.001846 [93] 张祥翔.基于液体透镜的显微镜自动调焦技术[J].光电工程, 2015, 42(10):37-42. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2015.10.007ZHANG X X. Autofocus technology based on liquid lens in microscopic imaging system[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2015, 42(10):37-42.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2015.10.007 [94] LI L, YUAN R Y, WANG J H, et al.. Electrically optofluidic zoom system with a large zoom range and high-resolution image[J]. Optics Express, 2017, 25(19):22280-22291. doi: 10.1364/OE.25.022280 [95] REZA S A, RIZA N A. A liquid lens-based broadband variable fiber optical attenuator[J]. Optics Communications, 2009, 282(7):1298-1303. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2008.12.029 [96] AMIRSOLAIMANI B, PEYMAN G, SCHWIEGERLING J, et al.. A new low-cost, compact, auto-phoropter for refractive assessment in developing countries[J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7(1):13990. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-14507-5 [97] XU CH L, ZHAO W CH, HU J H, et al.. Liquid lens-based optical sectioning tomography for three-dimensional flame temperature measurement[J]. Fuel, 2017, 196:550-563. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2017.01.115 -





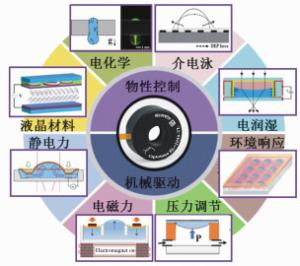
 下载:
下载: