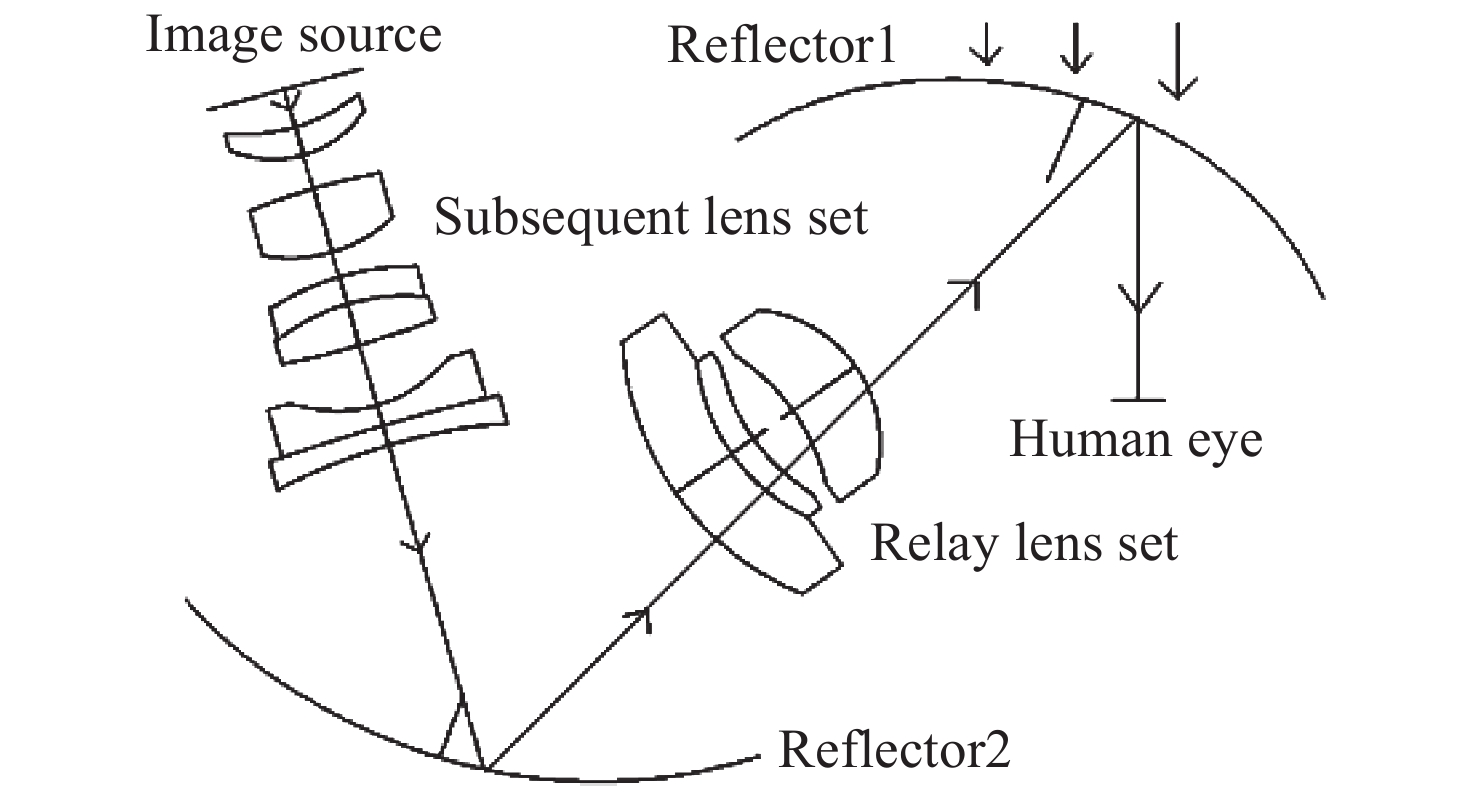
-
摘要: 针对非对称光学系统视场范围和出瞳直径较窄、光学结构复杂、制造成本昂贵、装配调整麻烦等问题,本文采用在系统中加入自由曲面反射镜的设计方法。首先,论述了双反射镜非对称光学系统的设计要求和工作原理。然后,分析了三反射镜非对称光学系统的离轴结构控制方法。最后,采用XY多项式自由曲面反射镜折叠光路、消除遮拦、扩大视场、校正离轴像差,设计出一款适用于头盔显示器的非对称光学系统。设计的双反射镜非对称光学系统的视场为60°×30°,出瞳直径为8 mm。在截止频率52 lp/mm处,全视场的调制传递函数值大于0.25,系统畸变小于5%,单目系统重量约为190 g。设计结果表明,该非对称光学系统的视场大小和成像质量均有所提升,实现了小型轻量化,可应用于头盔显示器。Abstract: In non-symmetric optical systems, the field of view is narrow, the diameter of their exit pupil is narrow, their optical structure is complicated, their cost of manufacturing is high, and assembly adjustment is troublesome. To address these problems, free-form mirror is applied in the system. The design requirements and working principle of the dual mirror non-symmetrical optical system are firstly discussed. Then, the off-axis structure control method of the three-mirror non-symmetric optical system is analyzed. Finally, the XY polynomial free-form mirror is used to fold the optical path, eliminating the obstruction, enlarging the field of view, correcting the off-axis aberration, and a non-symmetrical optical system is designed suitable for Helmet-Mounted Display(HMD). The designed dual mirror non-symmetrical optical system has a field of view of 60° × 30° and a pupil diameter of 8 mm. At a cutoff frequency of 52 lp/mm, the full field of view Modulation Transfer Function(MTF) value is greater than 0.25 and system distortion is less than 5%. This monocular system’s weight is about 190 g. The design results show that the non-symmetrical optical system has an improved field of view and image quality, it is compact and lightweight, and can be applied to a HMD.
-
Key words:
- optical design /
- non-symmetrical /
- helmet-mounted display /
- lightweight design /
- free-form surface
-
表 1 三反射镜非对称光学系统的结构控制宏语言与注解
Table 1. Control macro language and annotation of non-symmetric optical system structure with three mirror
ZPL annotation !threemirror.zpl ZPLXX.zpl ! nfield=NFLD () Number of fields maxfield=MAXF () Maximum half angle of view IF(Maxfield==0.0)
THEN Maxfield=1.0;Avoid errors that divide by zero ! 面的个数 n==pvhx () Take the value of Hx to n ! field i=pvhy () Take the value of Hy to i ! 子午或弧矢 j=pvpy () Take the value of Py to j hx=FLDX(i)/maxfield Hx= field of view (x direction) / maximum field of view hy=FLDY(i)/Maxfield Hy= field of view (y direction) / maximum field of view PRINT “Field number”, i RAYTRACE hx, hy, 0, j, PWAV () Ray tracing PRINT “X-field angle:”, FLDX(i),
“Y-field angle:”, FLDY(i)PRINT “X-chief ray:”, RAGX(n),
“Y-chief ray:”, RAGY(n),
“Z-chief ray:”, RAGZ(n)Spherical coordinate position at the ray cutoff PRINT OPTRETURN 0, RAGY(n) OPTRETURN 1, RAGZ(n) Return value PRINT “All Done!” 表 2 三反射镜非对称光学系统的部分ZPL调用方式
Table 2. Partial ZPL calling method of three mirror asymmetric optical system
Oper# Op1 Op2 Hx Hy Px Py Target Weight 1 BLNK 1 field of view meridian upper edge of the intersection of light and face 1 2 ZPLM 11 0 1 1 0 1 0 0 3 ZPLM 11 1 4 BLNK 1 field of view meridian upper edge of the intersection of light and face 2 5 ZPLM 12 0 3 1 0 1 0 0 6 ZPLM 12 1 7 BLNK 1 field of view meridian edge light and face 3 intersection 8 ZPLM 12 0 6 1 0 −1 0 0 9 ZPLM 12 1 10 BLNK Solving straight line 11 DIFF 6 3 12 DIFF 5 2 13 BLNK Solving slope k0 14 DIVI 12 11 15 BLNK The distance between the line and the light on the meridian of the field of view 16 PROD 14 9 17 PROD 14 3 18 DIFF 16 17 19 SUMM 2 18 20 DIFF 8 19 21 OPLT 20 250 0.1 22 OPGT 20 25 0.1 表 3 eMagin公司的AMOLED规格参数
Table 3. Specifications of AMOLED produced by eMagin
Item Parameter Pixel size/μm 9.6×9.6 Resolution ratio 1 920×1 200 Visible area/mm 18.7×11.75 (0.856 inch) The white light brightness/(cd·m−2) >150 Contrast >1000:1 Refresh rate/Hz 30~85 Power consumption <350 mW(150 cd/m2) Weight/g <3 -
[1] 夏振平, 胡伏原, 程成, 等. 基于视觉空间定向理论的虚拟现实空间重构[J]. 液晶与显示, 2019, 34(2): 215-219.XIA ZH P, HU F P, CHENG CH, et al. Virtual reality space reconstruction based on visual space orientation theory[J]. Chinese Journal of Liquid Crystals and Displays, 2019, 34(2): 215-219. (in Chinese) [2] 王士铭, 程德文, 黄一帆, 等. 大视场高分辨率光学拼接头盔显示器的设计[J]. 激光与光电子学进展,2018,55(6):364-369.WANG SH M, CHENG D W, HUANG Y F, et al. Design of wide FOV optical-tiled head-mounted display with high-resolution[J]. Laser &Optoelectronics Progress, 2018, 55(6): 364-369. (in Chinese) [3] 程德文, 王涌天, 常军, 等. 轻型大视场自由曲面棱镜头盔显示器的设计[J]. 红外与激光工程,2007,36(3):309-311. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2276.2007.03.006CHENG D W, WANG Y T, CHANG J, et al. Design of a lightweight and wide field-of-view HMD system with free-form-surface prism[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2007, 36(3): 309-311. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2276.2007.03.006 [4] 徐越, 范君柳, 孙文卿, 等. 基于全息波导的增强现实头盔显示器研究进展[J]. 激光杂志,2019,40(1):11-17.XU Y, FAN J L, SUN W Q, et al. Research progress of augmented reality head-mounted display based on holographic waveguide[J]. Laser Journal, 2019, 40(1): 11-17. (in Chinese) [5] 刘奡, 张宇宁, 沈忠文, 等. 全息波导显示系统的实现与优化[J]. 光学学报,2017,37(5):0523003. doi: 10.3788/AOS201737.0523003LIU A, ZHANG Y N, SHEN ZH W, et al. Realization and optimization of holographic waveguide display system[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2017, 37(5): 0523003. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/AOS201737.0523003 [6] 相广鑫, 郭岩, 李文强, 等. L型全息波导构型设计[J]. 电光与控制,2017,24(3):89-92.XIANG G X, GUO Y, LI W Q, et al. Design of a holographic waveguide with L configuration[J]. Electronics Optics &Control, 2017, 24(3): 89-92. (in Chinese) [7] 何丽鹏, 曾振煌, 林峰. 折/反射式离轴头盔显示器光学系统设计[J]. 激光与光电子学进展,2017,54(12):122201.HE L P, ZENG ZH H, LIN F. Optical design of catadioptric off-axis helmet-mounted display[J]. Laser &Optoelectronics Progress, 2017, 54(12): 122201. (in Chinese) [8] 刘军, 黄玮. 反射式自由曲面头盔显示器光学系统设计[J]. 红外与激光工程,2016,45(10):1018001. doi: 10.3788/IRLA201645.1018001LIU J, HUANG W. Optical system design of reflective head mounted display using freeform surfaces[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2016, 45(10): 1018001. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/IRLA201645.1018001 [9] 何子清, 葛超, 王春阳. 基于最小二乘配置的光学镜头畸变校正方法[J]. 液晶与显示, 2019, 34(3): 302-308.HE Z Q, GE CH, WANG CH Y. Optical lens distortion correction method based on least square configuration[J]. Chinese Journal of Liquid Crystals and Displays, 2019, 34(3): 302-308. (in Chinese) [10] 周鑫, 肖锡晟, 孙胜利. 自由曲面在离轴光学系统中的应用[J]. 红外,2017,38(3):6-11, 16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-8785.2017.03.002ZHOU X, XIAO X SH, SUN SH L. Application of free-form surface in off-axis optical systems[J]. Infrared, 2017, 38(3): 6-11, 16. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-8785.2017.03.002 [11] 庞志海, 樊学武, 马臻, 等. 自由曲面校正光学系统像差的研究[J]. 光学学报,2016,36(5):0522001. doi: 10.3788/AOS201636.0522001PANG ZH H, FAN X W, MA ZH, et al. Free-form optical elements corrected aberrations of optical system[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2016, 36(5): 0522001. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/AOS201636.0522001 [12] TSOU B H. System design considerations for a visually coupled system[J]. The Infrared and Electro-Optics Systems Handbook, 1993, 8: 515-540. [13] 孟祥翔, 刘伟奇, 张大亮, 等. 双自由曲面大视场头盔显示光学系统设计[J]. 红外与激光工程,2016,45(4):0418004. doi: 10.3788/irla201645.0418004MENG X X, LIU W Q, ZHANG D L, et al. Design of wide field-of-view head-mounted display optical system with double freeform surfaces[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2016, 45(4): 0418004. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/irla201645.0418004 [14] 李华. 头盔显示器光学系统关键技术研究[D]. 长春: 中国科学院研究生院(长春光学精密机械与物理研究所), 2015.LI H. Research on key technologies of optical system of helmet-mounted display[D]. Changchun: Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2015. (in Chinese) [15] 张春燕, 陈文栋, 季渊, 等. 基于OLED微显示器的原子扫描控制器设计[J]. 液晶与显示, 2019, 34(4): 395-401.ZHANG CH Y, CHEN W D, JI Y, et al. Design of atomic scan controller based on OLED microdisplay[J]. Chinese Journal of Liquid Crystals and Displays, 2019, 34(4): 395-401. (in Chinese) [16] 解红军, 张小宝. 一种针对AMOLED器件劣化的电学补偿技术[J]. 液晶与显示, 2019, 34(4): 335-341.XIE H J, ZHANG X B. Electronic-compensation technique for improving the degradation of AMOLED Devices[J]. Chinese Journal of Liquid Crystals and Displays, 2019, 34(4): 335-341. (in Chinese) -






 下载:
下载: