Influence of turbulent atmosphere on the effect of coherent beam combining
doi: 10.37188/CO.2019-0197
-
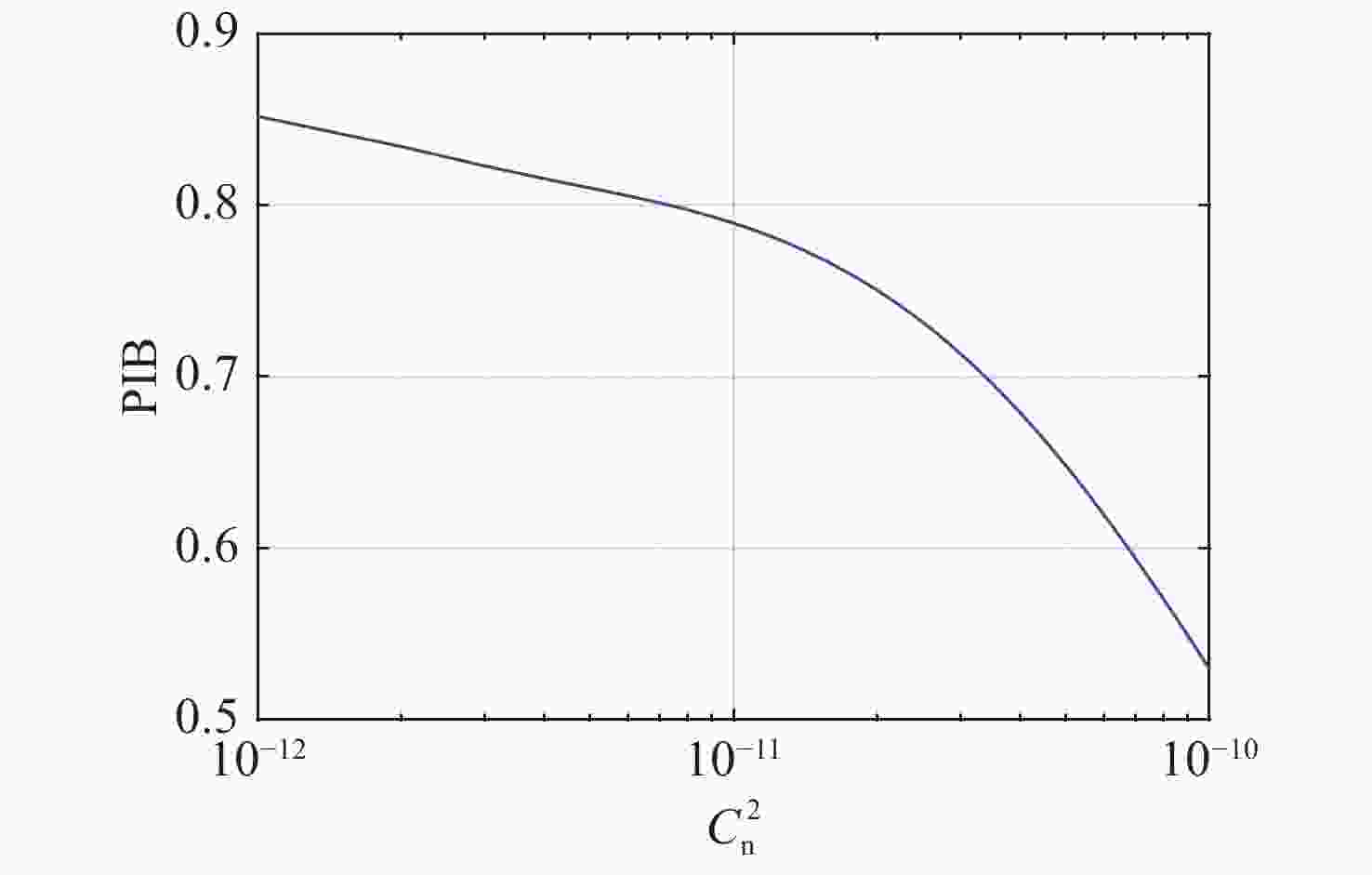
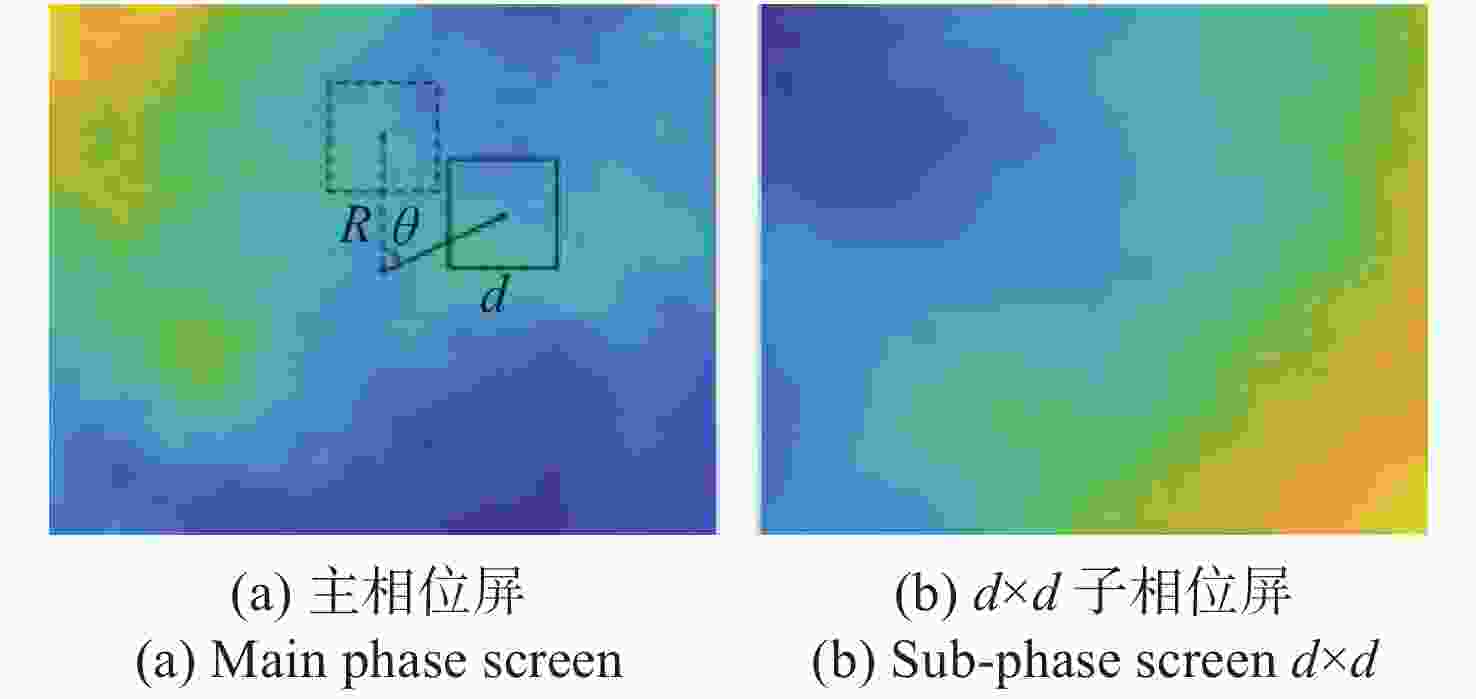
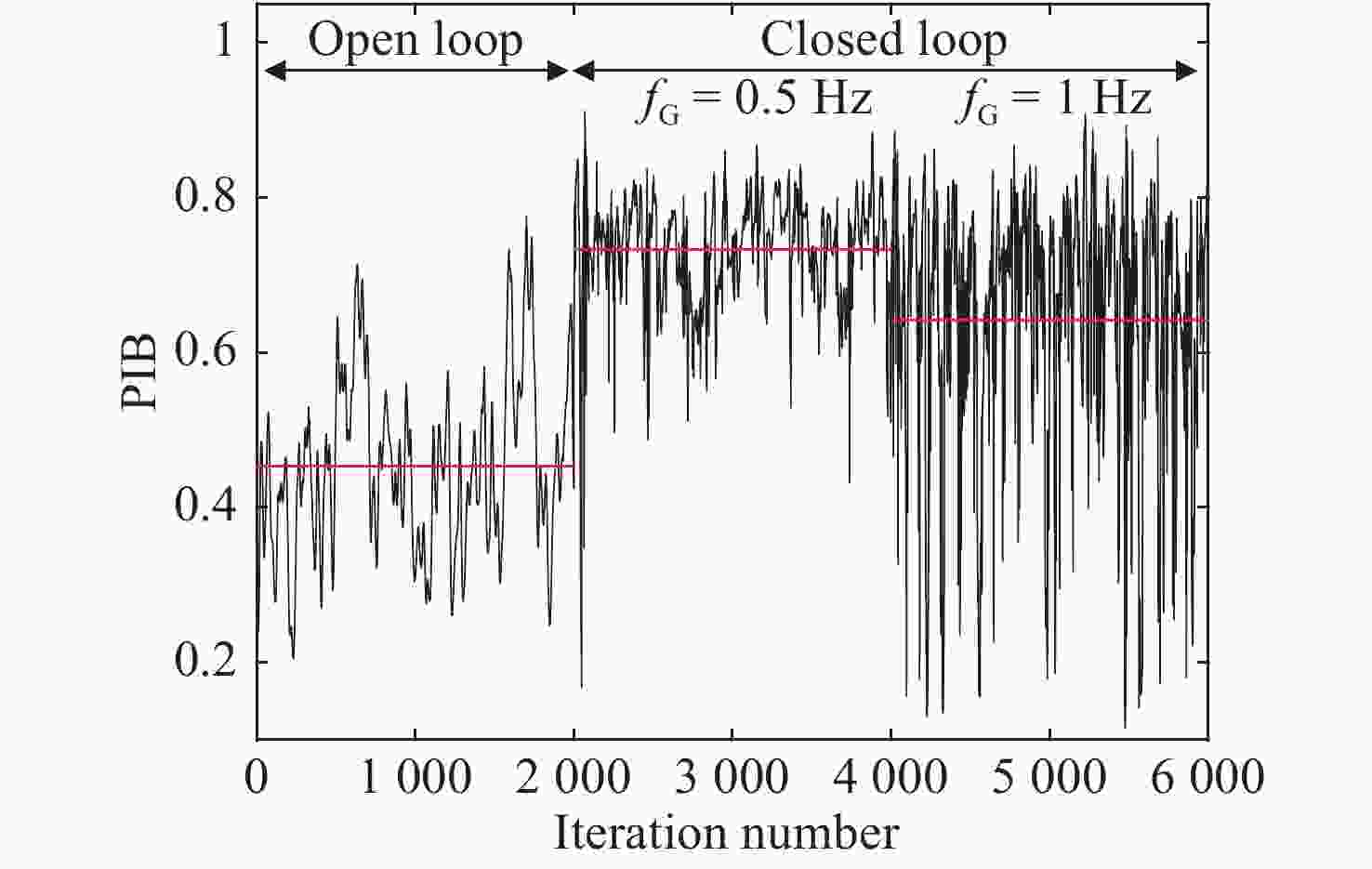
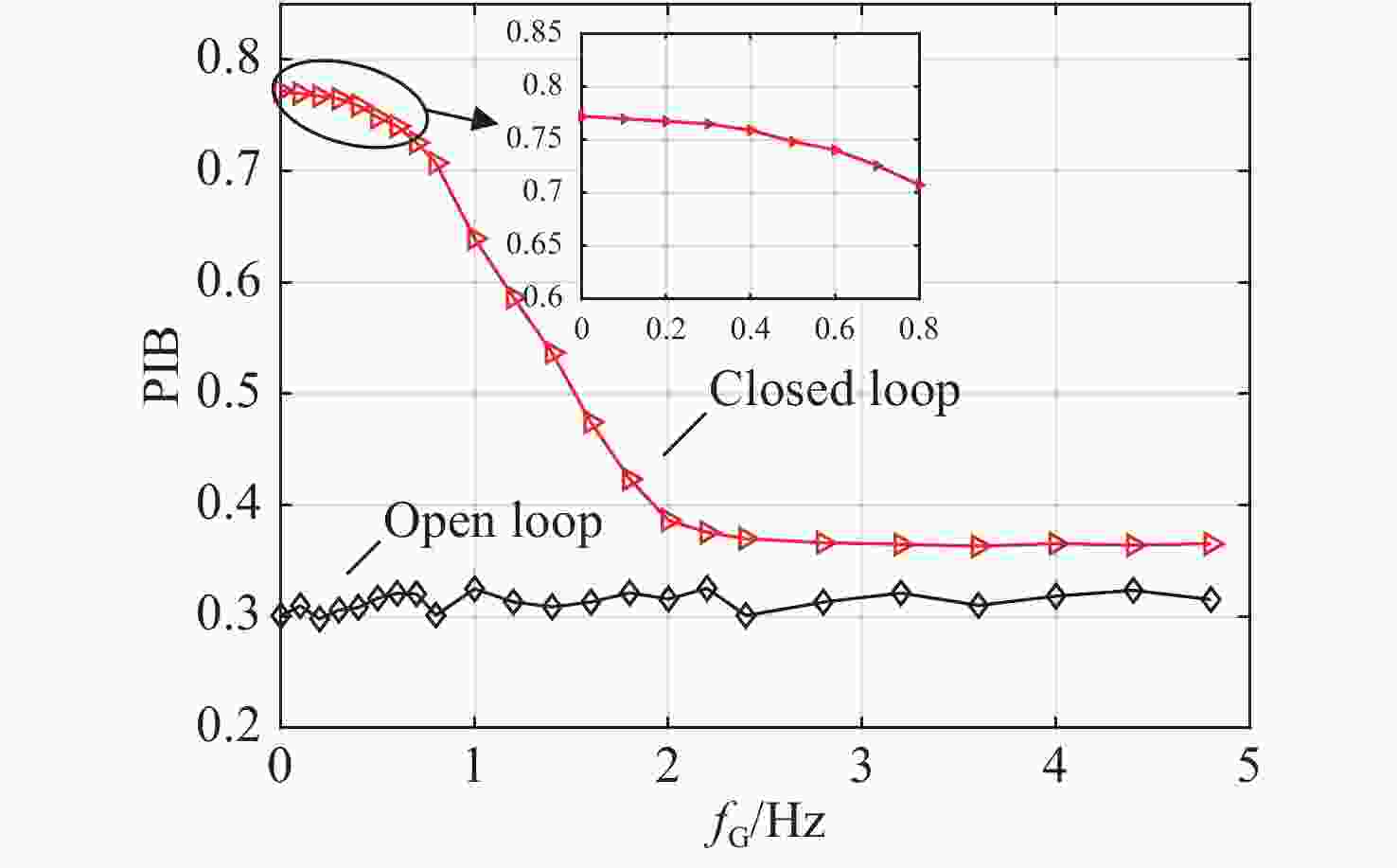
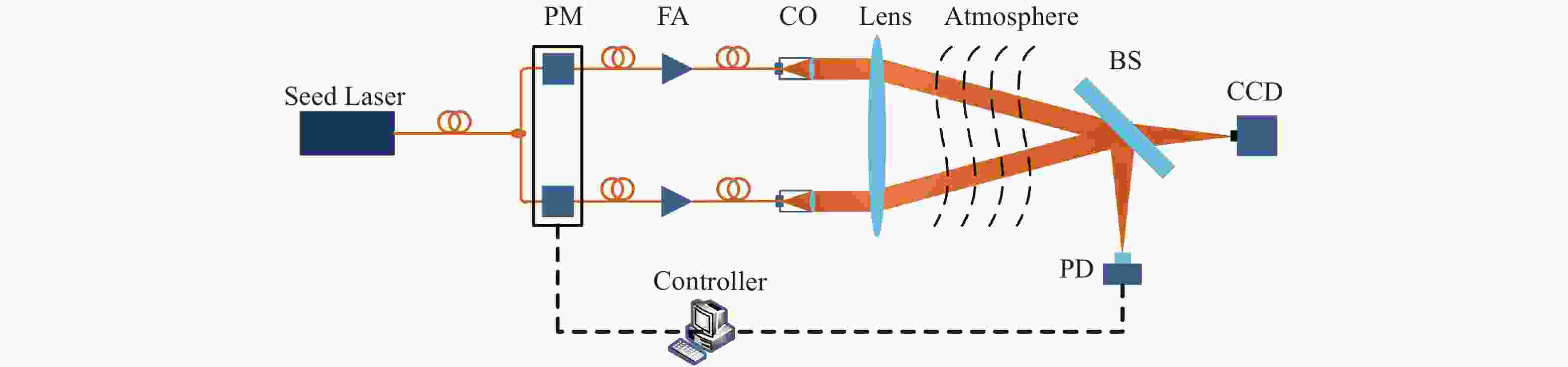
摘要: 光纤激光相干合成是获得高功率高光束质量输出较为有效的途径,而湍流大气是制约其应用与发展的关键因素之一。本文重点研究了大气格林伍德频率对基于随机并行梯度下降算法(SPGD)相干合成系统校正效果的影响。首先,在静态大气条件下,分析了不同湍流强度对相干合成系统校正效果的影响;然后,利用数值计算生成一组旋转的符合Kolmogorov统计规律的相位屏模拟湍流大气,对在不同大气格林伍德频率下相干合成系统的校正效果进行研究;最后,搭建两路光纤激光相干合成实验平台,进行实验验证。仿真和实验结果表明,在系统的控制算法迭代频率(350 Hz)一定时,随着大气格林伍德频率的增加,湍流大气对光束的相位和光强的扰动加剧,使得相干合成系统的合成效果变得越来越差。Abstract: Coherent beam combining is a promising technology for achieving a high-power laser beam with good beam quality. However, turbulent atmosphere is one of the key factors that restrict its application and development. This paper focuses on the influence of atmospheric Greenwood frequency on the correction effect of the coherent combination system based on Stochastic Parallel Gradient Descent (SPGD) algorithm. At first, the influence of different turbulence intensities on the correction effect of coherent combination systems is analyzed by numerical simulation under static atmospheric conditions. Then, a set of rotating phase screens that meet Kolmogorov’s statistical law are generated by numerical calculation to simulate the turbulent atmosphere and study the correction effect of coherent combination system at different atmospheric Greenwood frequencies. Finally, an experimental platform is established to demonstrate the coherent combination effect of two laser beams. The simulated and experimental results show that when the system's control algorithm iteration frequency (350 Hz) is constant, the disturbance of turbulent atmosphere to the phase and light intensity of laser beams will increase with atmospheric Greenwood frequency, making the effect of coherent combination worse.
-
Key words:
- coherent beam combining /
- SPGD algorithm /
- turbulent atmosphere /
- phase screen
-
表 1 System parameters used for simulation
Table 1. System parameters used for simulation
Parameter Value Distance: L/m 2 Wavelength: λ/m 1 064 × 10−9 Beam radius: w0/m 2.5 × 10−3 Number of samples: 256 -
[1] WANG X L, ZHOU P, SU R T, et al. Current situation, tendency and challenge of coherent combining of high power fiber lasers[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2017, 44(2): 3-28. (in Chinese) [2] LIU Z J, ZHOU P, XU X J, et al. Coherent beam combining of high power fiber lasers: progress and prospect[J]. Science China Technological Sciences, 2013, 56(7): 1597-1606. doi: 10.1007/s11431-013-5260-z [3] ZENG H M, LI S, ZHANG ZH Y, et al. Risley-prism-based beam scanning system for mobile lidar[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2019, 27(7): 1444-1450. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/OPE.20192707.1444 [4] WANG H Q, SONG L H, CAO M H, et al. Compressed sensing detection of optical spatial modulation signal in turbulent channel[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2018, 26(11): 2669-2674. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/OPE.20182611.2669 [5] CHEN X, WANG J L, LIU CH H. Beam combining of high energy fibre lasers[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2018, 47(1): 0103011. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/IRLA201847.0103011 [6] WANG X L, ZHOU P, MA Y X, et al. Active phasing a nine-element 1.14 kW all-fiber two-tone MOPA array using SPGD algorithm[J]. Optics Letters, 2011, 36(16): 3121-3123. doi: 10.1364/OL.36.003121 [7] GOODNO G D, KOMINE H, MCNAUGHT S J, et al. Coherent combination of high-power, zigzag slab lasers[J]. Optics Letters, 2006, 31(9): 1247-1249. doi: 10.1364/OL.31.001247 [8] MA Y X, ZHOU P, WANG X L, et al. Coherent beam combination with single frequency dithering technique[J]. Optics Letters, 2010, 35(9): 1308-1310. doi: 10.1364/OL.35.001308 [9] ZHOU P, MA Y X, WANG X L, et al. Coherent beam combining of fiber amplifiers based on stimulated annealing algorithm[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2010, 22(5): 973-977. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/HPLPB20102205.0973 [10] ZHOU P, LIU Z J, WANG X L, et al. Coherent beam combining of two fiber amplifiers using stochastic parallel gradient descent algorithm[J]. Optics &Laser Technology, 2009, 41(7): 853-856. [11] ZHOU P, MA Y X, WANG X L, et al. Coherent beam combination of three two-tone fiber amplifiers using stochastic parallel gradient descent algorithm[J]. Optics Letters, 2009, 34(19): 2939-2941. doi: 10.1364/OL.34.002939 [12] VORONTSOV M A, CARHART G W, RICKLIN J C. Adaptive phase-distortion correction based on parallel gradient-descent optimization[J]. Optics Letters, 1997, 22(12): 907-909. doi: 10.1364/OL.22.000907 [13] VORONTSOV M. Adaptive Photonics Phase-Locked Elements (APPLE): system architecture and wavefront control concept[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2005, 5895: 589501. doi: 10.1117/12.617390 [14] WEYRAUCH T, VORONTSOV M, CARHART G, et al. Experimental demonstration of coherent beam combining over a 7 km propagation path[J]. Optics Letters, 2011, 36(22): 4455-4457. doi: 10.1364/OL.36.004455 [15] VORONTSOV M, FILIMONOV G, OVCHINNIKOV V, et al. Comparative efficiency analysis of fiber-array and conventional beam director systems in volume turbulence[J]. Applied Optics, 2016, 55(15): 4170-4185. doi: 10.1364/AO.55.004170 [16] GENG CH, YANG Y, LI F, et al. Research progress of fiber laser coherent combining[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2018, 45(3): 170692. (in Chinese) doi: 10.12086/oee.2018.170692 [17] SU R T, MA Y X, XI J CH, et al. 60-channel large array element fiber laser high efficiency coherent synthesis[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2019, 48(1): 331. (in Chinese) [18] ZHI D, MA Y X, MA P F, et al. Efficient coherent beam combining of fiber laser array through km-scale turbulent atmosphere[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2019, 48(10): 1005007. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/IRLA201948.1005007 [19] LIU L, GUO J, ZHAO SH, et al. Application of stochastic parallel gradient descent algorithm in laser beam shaping[J]. Chinese Optics, 2014, 7(2): 260-266. (in Chinese) [20] LI D, NING Y, WU W M, et al. Numerical simulation and validation method of atmospheric turbulence of phase screen in rotation[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2017, 46(12): 1211003. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/IRLA201746.1211003 -





 下载:
下载: