Method of enhancing the quality of in-line holographic images for micro-milling tool
-
摘要: 数字同轴全息对刀技术中,再现像中的零级项和离焦共轭像会形成一个强而复杂的背景噪声作用在实像上,严重降低了再现像的质量。针对全息应用中的干扰像问题,提出了一种基于改进自蛇模型滤波的全息图像增强方法,改进后的自蛇模型令每次扩散中只根据初始图像的梯度来选择扩散力度。实验结果表明,改进后的自蛇模型能够避免在扩散过程中由于受大梯度背景噪声影响而出现的“伪轮廓”和边缘锯齿化,弥补了自蛇模型在全息图像应用中的不足。此外,与相位恢复法和多重再现法去干扰像效果相比较,本文提出的改进自蛇模型滤波法不仅对干扰像有更好的抑制作用,还能够增强刀具边缘,有利于实现微铣刀的数字全息对刀。Abstract: When tool setting with digital in-line holography, the zero-order image and defocused twin-image can form strong and complex background noise, which gets superimposed on the real image and seriously reduces the quality of the reconstructed image. To improve quality of interferential images in digital in-line holography, a holographic image enhancement method using an improved self-snake model is proposed. The improved self-snake model selects a diffusion intensity according to the gradient of the initial image. The experimental results show that the improved self-snake model can avoid the appearance of jagged edges and “pseudo-contours” caused by large gradient background noise during the diffusion process. This improvement outweighs the shortcomings of the self-snake model in holographic imaging. In addition, compared with the phase retrieval and multi-plane reproduction approaches, the improved self-snake model filtering method proposed in this paper not only has better suppression for interferential images but also can enhance the edge of the tool, which is conducive to the actualization of tool-setting using on digital in-line holography.
-
Key words:
- digital holography /
- twin-image /
- self-snake model /
- image denoising
-
图 2 改进前后的自蛇模型处理结果。(a)原图;(b)改进前的自蛇模型扩散结果及局部放大图;(c)改进后的自蛇模型扩散结果及局部放大图
Figure 2. The diffusion results of self-snake model before and after improvement. (a) Original image; (b) diffusion result and local enlargement obtained by self-snake model; (c) diffusion result and local enlargement obtained by improved self-snake model
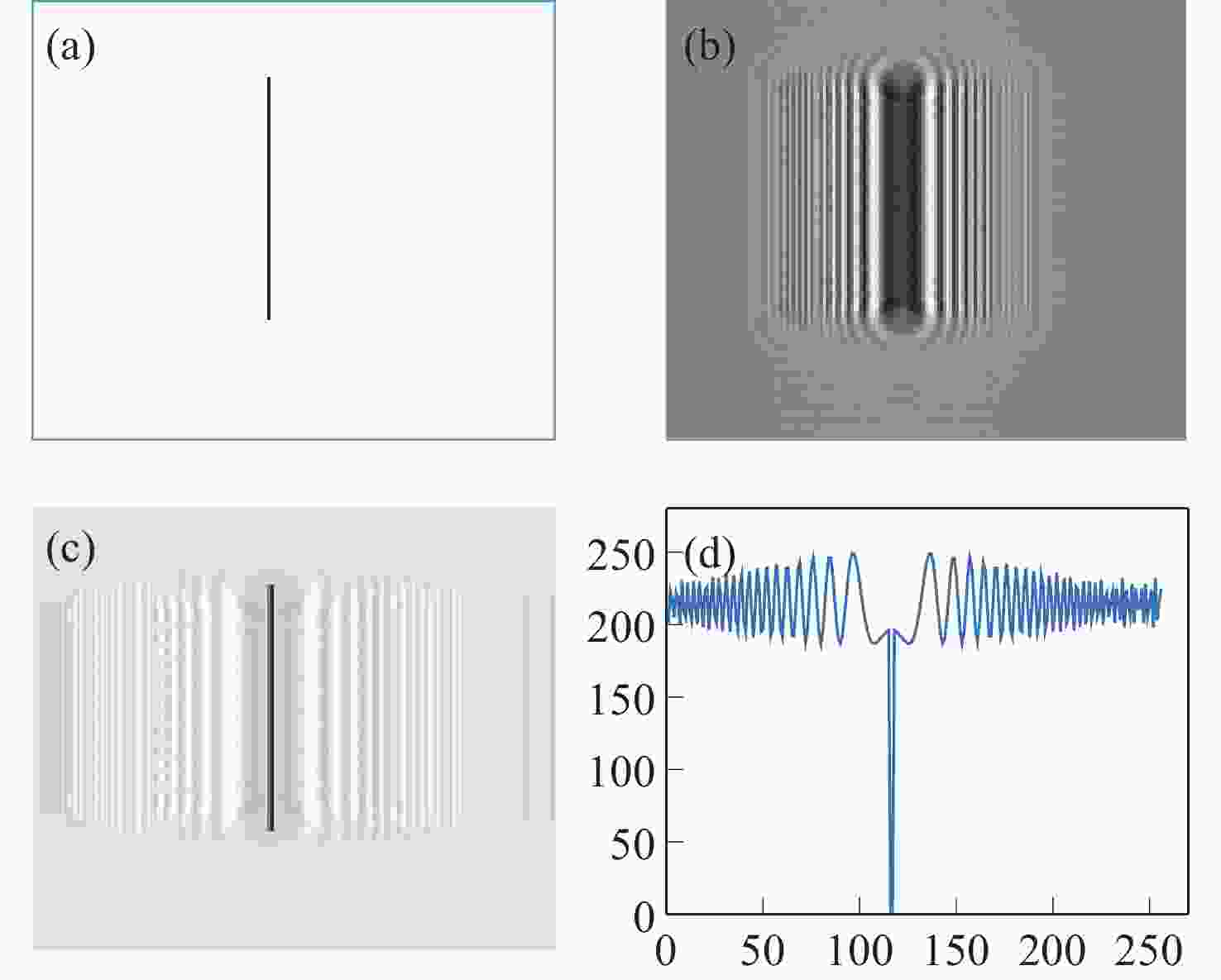
图 4 不同方法消除干扰像后的模拟物体再现像(左)及再现像第128行的强度分布(右)。(a)相位恢复法;(b)多重再现法;(c)自蛇模型滤波法;(d)改进自蛇模型滤波法
Figure 4. The reconstructed images of simulation object (left) that interferential image were eliminated by different approaches and corresponding intensity distributions in 128th line (right). (a) Phase retrieval approach; (b) multi-plane reproduction approach; (c) self-snake filtering approach; (d) improved self-snake filtering approach
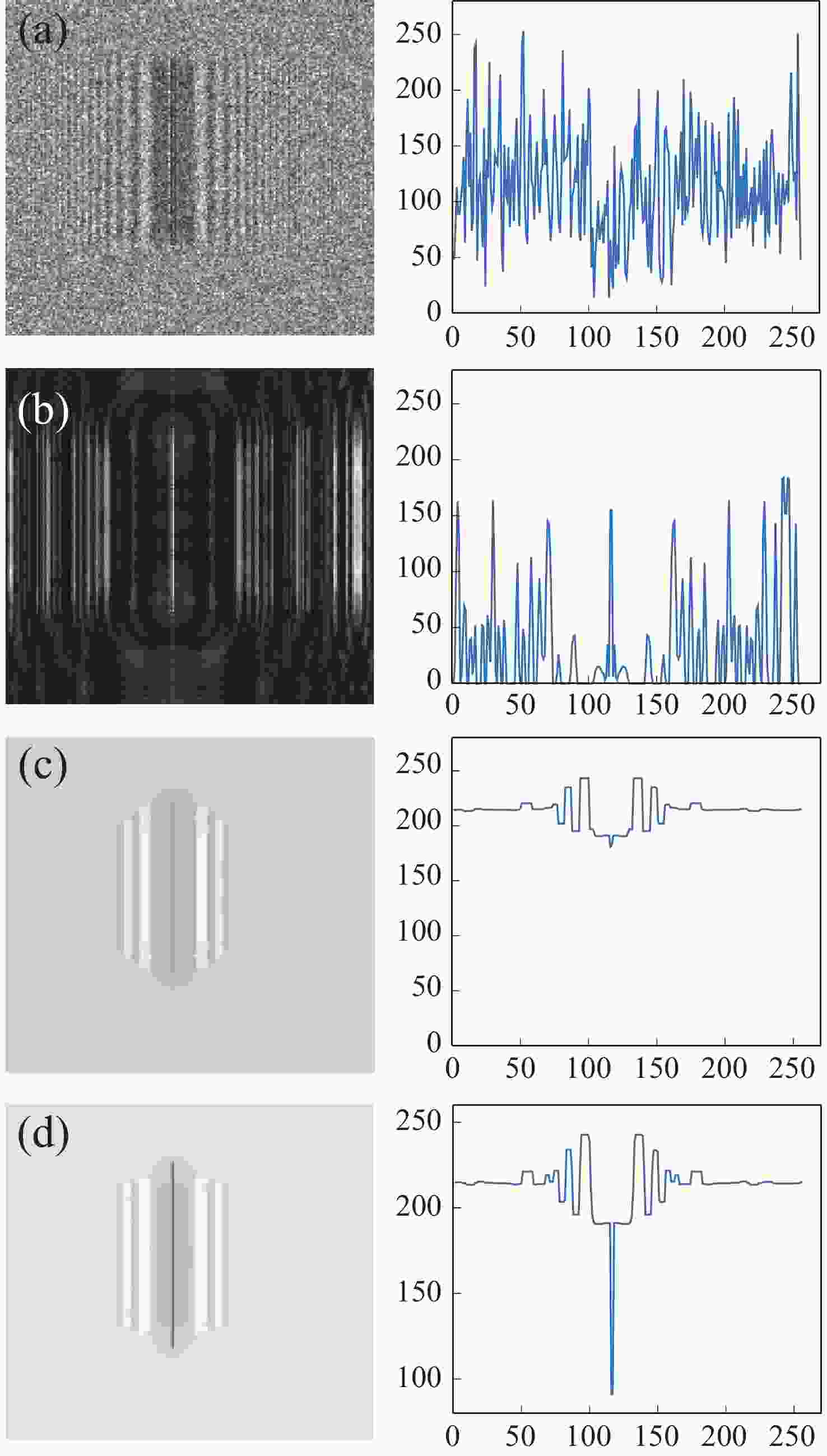
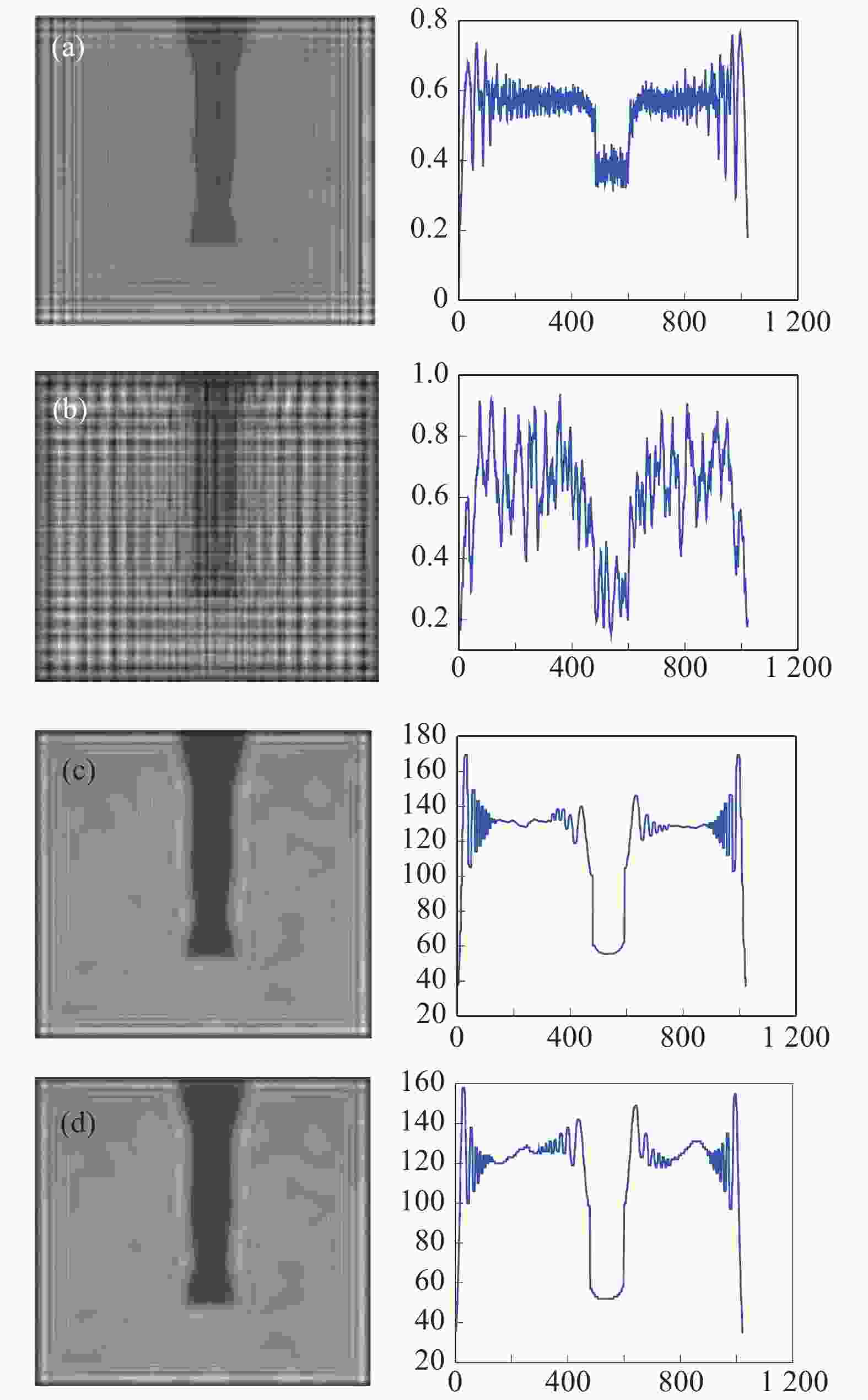
图 7 不同方法消除干扰像后的微铣刀再现像(左)及对应截面的强度分布(右)。(a)相位恢复法;(b)多重再现法;(c)自蛇模型滤波法;(d)改进自蛇模型滤波法
Figure 7. The reconstructed images of the micro-milling tool (left) that interferential image were eliminated by different approaches and their intensity distributions (right). (a) Phase retrieval approach; (b) multi-plane reproduction approach; (c) self-snake filtering approach; (d) improved self-snake filtering approach
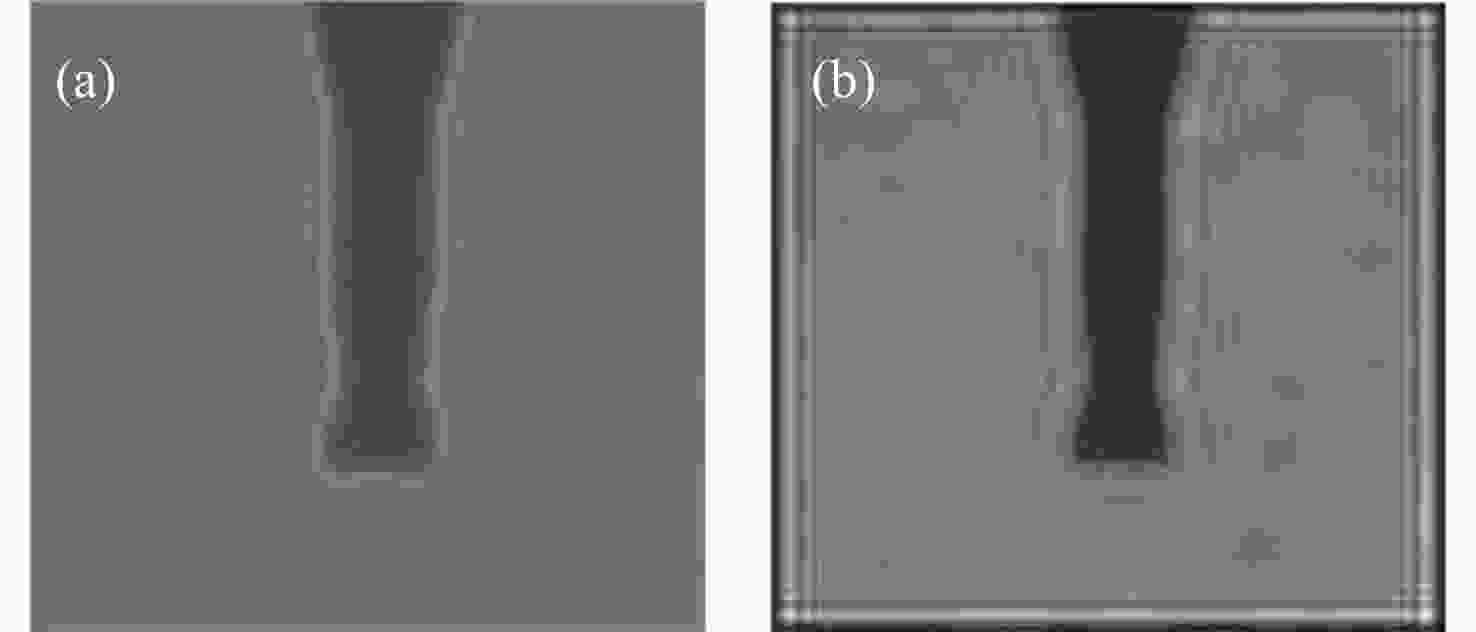
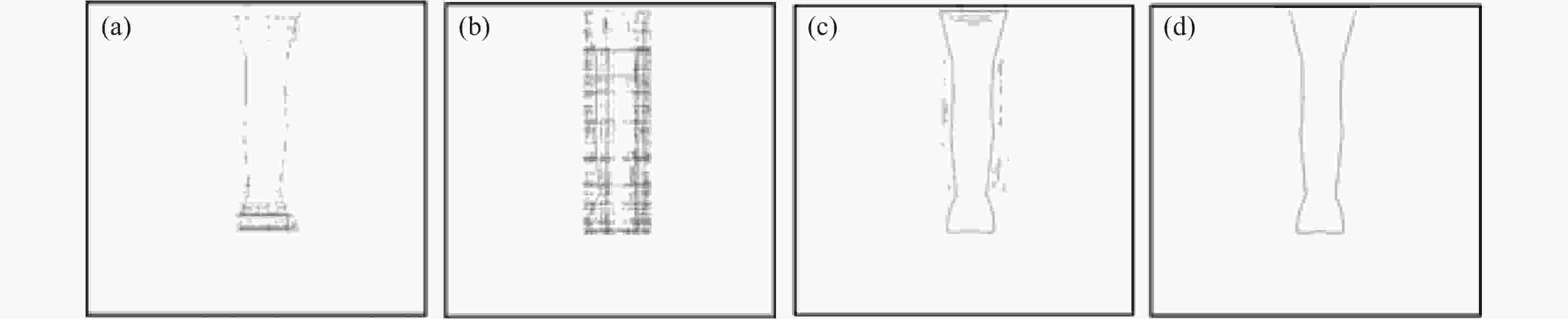
图 8 再现像轮廓提取结果。(a)相位恢复法;(b)多重再现法;(c)自蛇模型滤波法;(d)改进自蛇模型滤波法
Figure 8. Results of contour extraction from reconstructed images. (a), (b), (c), (d) are reconstructed images obtained by phase retrieval approach, multi-plane reproduction approach, self-snake filtering approach and improved self-snake filtering approach, respectively
表 1 各种去干扰像方法性能比较
Table 1. Performance comparison of different interference removal methods
Method SNR/dB PSNR/dB Phase retrieval 0.281 24.365 Multi-plane reproduction 0.019 24.103 Self-snake filtering 8.304 32.388 Improved self-snake filtering 8.433 32.517 -
[1] 于占江, 王晶东, 张留新, 等. 微小车床对刀间隙检测技术[J]. 光电工程,2012,39(10):122-127. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2012.10.020YU ZH J, WANG J D, ZHANG L X, et al. Detection method for tool setting gap of small lathe[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2012, 39(10): 122-127. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2012.10.020 [2] MATSUMURA T F D, SHINOZAKI S M. Method of trial cutting: EP, 0566750A1[P]. 1994-02-16. [3] 陈明涛, 李永强, 黄京岳. 一种接触式Z轴对刀仪: 中国, 209062685U[P]. 2019-07-05.CHEN M T, LI Y Q, HUANG J Y. A contact Z-axis tool-setting Instrument: CN, 209062685U[P]. 2019-07-05. (in Chinese) [4] SHI G F, ZHANG Y SH, ZHANG H, et al. Analysis of the influence of installation tilt error on the tool setting accuracy by laser diffraction[J]. Applied Optics, 2018, 57(12): 3012-3020. doi: 10.1364/AO.57.003012 [5] 刘力双. 电子摄像式刀具预调测量仪的研究[D]. 天津: 天津大学, 2006: 12-18.LIU L SH. Research of tool presetting and measuring machine based on CCD imaging[D]. Tianjin: Tianjin University, 2006: 12-18. (in Chinese) [6] BRAMLET C R. Tool presetting, shrinking and measuring-Zoller, booth 1551[J]. Modern Machine Shop, 2005. [7] 于化东, 张向辉, 于占江, 等. 一种微径铣刀高精度对刀装置及对刀方法: CN, 105345595A[P]. 2016-02-24.YU H D, ZHANG X H, YU ZH J, et al.. A high-precision tool-setting device and method for micro-milling tools: CN, 105345595A[P]. 2016-02-24. (in Chinese) [8] LIU G, SCOTT P D. Phase retrieval and twin-image elimination for in-line Fresnel holograms[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America A, 1987, 4(1): 159-165. doi: 10.1364/JOSAA.4.000159 [9] LIU G. Object reconstruction from noisy holograms: multiplicative noise model[J]. Optics Communications, 1990, 79(6): 402-406. doi: 10.1016/0030-4018(90)90471-5 [10] KOREN G, JOYEUX D, POLACK F. Twin-image elimination in in-line holography of finite-support complex objects[J]. Optics Letters, 1991, 16(24): 1979-1981. doi: 10.1364/OL.16.001979 [11] ZHANG Y, PEDRINI G, OSTEN W, et al. Whole optical wave field reconstruction from double or multi in-line holograms by phase retrieval algorithm[J]. Optics Express, 2003, 11(24): 3234-3241. doi: 10.1364/OE.11.003234 [12] LATYCHEVSKAIA T, FINK H W. Solution to the twin image problem in holography[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2007, 98(23): 233901. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.98.233901 [13] ZHAO J, WANG D Y, ZHANG F C, et al. Hybrid phase retrieval approach for reconstruction of in-line digital holograms without twin image[J]. Optical Engineering, 2011, 50(9): 091310. doi: 10.1117/1.3596203 [14] 戎路, 王大勇, 王云新, 等. 同轴数字全息中的相位恢复算法[J]. 中国激光,2014,41(2):0209006. doi: 10.3788/CJL201441.0209006RONG L, WANG D Y, WANG Y X, et al. Phase retrieval methods in in-line digital holography[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2014, 41(2): 0209006. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/CJL201441.0209006 [15] WANG Y Z, ZHEN Y K, ZHANG H J, et al. Study on digital holography with single phase-shifting operation[J]. Chinese Optics Letters, 2004, 2(3): 141-143. [16] LAI S C, KING B, NEIFELD M A. Wave front reconstruction by means of phase-shifting digital in-line holography[J]. Optics Communications, 2000, 173(1-6): 155-160. doi: 10.1016/S0030-4018(99)00625-2 [17] GUO P Y, DEVANEY A J. Digital microscopy using phase-shifting digital holography with two reference waves[J]. Optics Letters, 2004, 29(8): 857-859. doi: 10.1364/OL.29.000857 [18] KAKUE T, TAHARA T, ITO K, et al. Parallel phase-shifting color digital holography using two phase shifts[J]. Applied Optics, 2009, 48(34): H244-H250. doi: 10.1364/AO.48.00H244 [19] 杨绍光, 谢行恕, 赵永飞, 等. 高通滤波法数字重现同轴全息图[J]. 强激光与粒子束,1998,10(2):203-206.YANG SH G, XIE X SH, ZHAO Y F, et al. Digital reconstruction of in-line hologram with high-pass filter method[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 1998, 10(2): 203-206. (in Chinese) [20] YANG SH G, XIE X SH, ZHAO Y F, et al. Reconstruction of near-field in-line hologram[J]. Optics Communications, 1999, 159(1-3): 29-31. doi: 10.1016/S0030-4018(98)00346-0 [21] 刘迪, 王玉荣, 孟祥锋, 等. Gabor同轴数字全息的多重再现与自动聚焦[J]. 中国激光,2014,41(9):230-238.LIU D, WANG Y R, MENG X F, et al. Multi-plane reconstruction and auto-focus method of Gabor in-line digital holography[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2014, 41(9): 230-238. (in Chinese) [22] KREIS T M, JUEPTNER W P O. Suppression of the dc term in digital holography[J]. Optical Engineering, 1997, 36(8): 2357-2360. doi: 10.1117/1.601426 [23] 国承山, 王伟田, 李健, 等. 全息图数字再现中零级衍射斑的消除[J]. 光学学报,1998,18(8):1073-1076. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2239.1998.08.023GUO CH SH, WANG W T, LI J, et al. Elimination of zero-order diffraction spot in digital reconstruction of hologram[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 1998, 18(8): 1073-1076. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2239.1998.08.023 [24] 李俊昌. 衍射计算及数字全息[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2014: 81-84.LI J CH. Diffraction Calculation and Digital Holography[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2014: 81-84. (in Chinese) [25] CASELLES V, KIMMEL R, SAPIRO G. Geodesic active contours[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 1997, 22: 61-79. doi: 10.1023/A:1007979827043 [26] 王大凯, 侯榆青, 彭进业. 图像处理的偏微分方程方法[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2008: 88-95.WANG D K, HOU Y Q, PENG J Y. Partial Differential Equation Method for Image Processing[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2008: 88-95. (in Chinese) -





 下载:
下载: