-
摘要: 以新一代同步辐射光源和全相干X射线自由电子激光为代表的先进光源已成为众多学科领域中一种不可或缺的研究工具。先进光源技术不断进步,驱动超精密光学制造快速发展,先进光源中关键聚焦光学元件K-B镜的面形精度是影响光源性能的重要指标,要求其在几十纳弧度以下。然而,高精度K-B镜面形检测技术依然存在较大技术挑战,一直是国内外研究热点。本文介绍了反射式轮廓测量技术即长程轮廓仪(LTP)、纳米测量仪(NOM)以及拼接干涉检测技术等典型K-B镜面形检测技术的基本原理,对比分析了其技术特点,综述了国内外K-B镜面形检测技术的研究现状和最新进展,对发展趋势进行了展望。Abstract: The advanced light source represented by the new generation of the diffraction limit synchrotron radiation source and the full-coherent X-ray free-electron laser has become an indispensable research tool in many fields. The continuous development of advanced light sources drives the rapid progress of ultra-precision optical manufacturing. The surface precision of a K-B mirror, a key focusing optical element in advanced light sources, is an important factor, which should be less than tens of nano radians. However, high precision K-B mirror surface metrology still has great technical challenges and is now a research hotspot in the scientific community. This paper introduces typical K-B mirror surface metrology, including reflection profile measuring technology such as the Long Trace Profiler (LTP), the Nanometer Optical component Measuring (NOM), and stitching interference metrology. Current K-B mirror surface shape technologies are summarized and the upcoming research progress is prospected.
-
Key words:
- X-ray optics /
- K-B mirror /
- optical measurement /
- surface metrology /
- stitching interferometer
-
表 1 LTP/NOM技术典型参数
Table 1. Specifications of LTP/NOM
类型 LTP NOM 工作距离/mm 100~1100 300~1300 斜率/mrad ±5 ±5 扫描速率/(mm·s−1) 5~10 2~4 精度(RMS)/nrad 平面: ~50
曲面: ~250平面: ~50
曲面: ~500空间分辨率/mm ~1 2.5~5 表 2 国内外典型LTP/NOM技术参数
Table 2. Technical specifications of typical LTP/NOM technologies at home and abroad
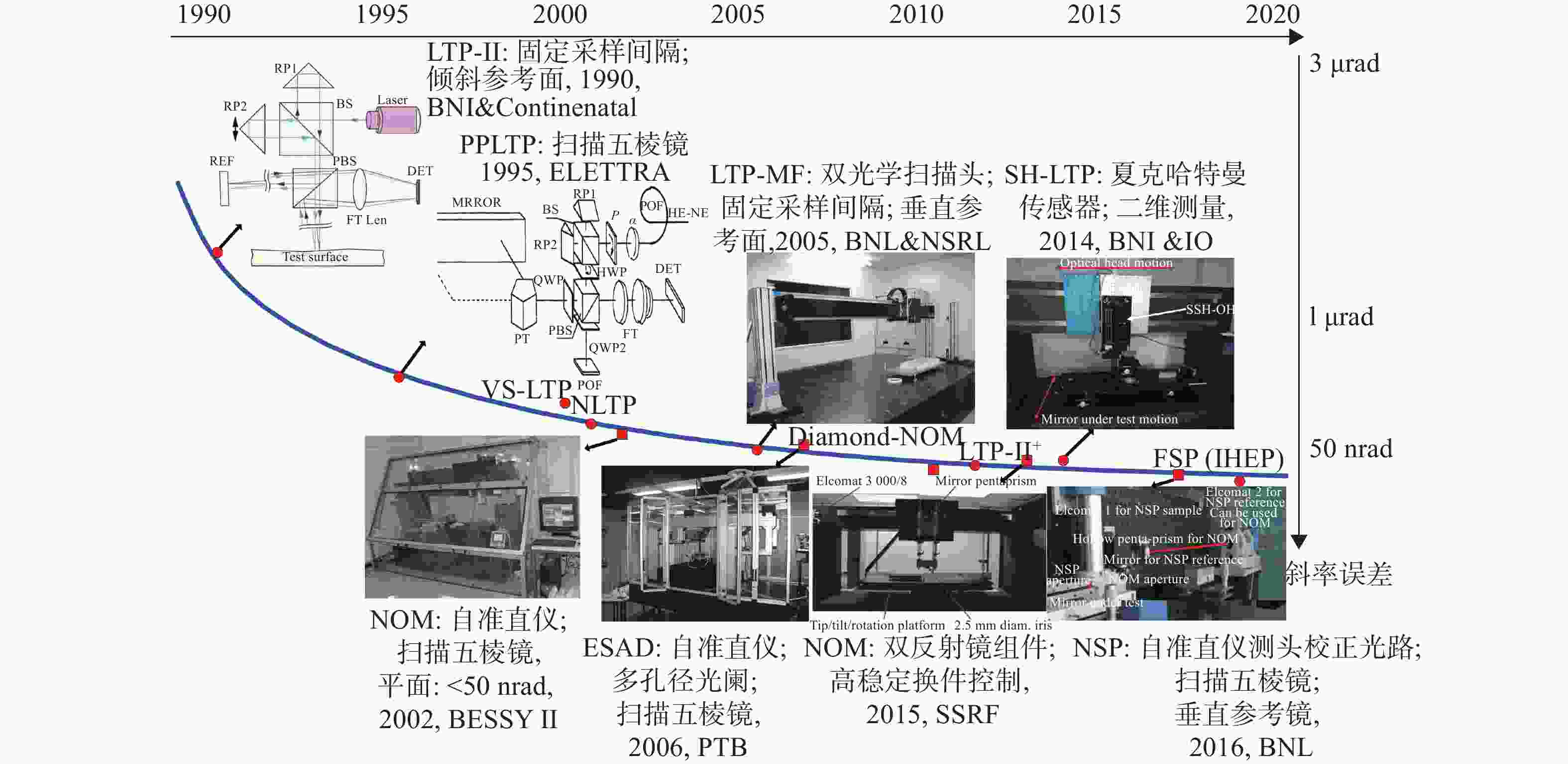
类型 机构/装置 设备 时间 测量范围 性能 备注 LTP 日本JASRI/SPring-8 Laser-LTP 2014 3.6 mrad 0.2 μrad
重复精度60 nrad激光校准测头误差
分辨率30 nradLTP 2016 ~1 m 5 nm 新型斜率传感器;
空间分辨率<1 mm美国LBNLALS LTP-II+ 2014 1 m
±2.5 mrad平面:<80 rad rms
曲面(>15 m): 250 nrad rms校正K-B位置误差 中国台湾NSRRC NLTP 2013 1.2 m 测量重复精度50 nrad 定位基准为衍射暗线;
光束定位精度高中国SSRF上海光源 LTP 2016 1 m 平面:<50 nrad
曲面(>38 m): 0.27μrad支持快速测量 中国IHEP高能所 FSP 2019 1 m 平面:25 nrad rms
曲面(3 mrad): 32 nrad rms空间分辨率优于1 mm NOM 巴西LNLS NOM 2017 1.5 m 平面:50 nrad rms 横向分辨率大 德国BESSY-II Diamond-NOM 2014 1.5 m
±5 mrad平面:50 nrad rms
曲面:200 nrad rms (±24μrad)
500 nrad rms (±5 mrad)曲率测量范围大 美国BNL DLTP 2014 1 m
±4.6 mrad平面:60 nrad rms
曲面(>15 m): 200 nrad rms曲面测量受限 OSMS 2017 1.2 m 平面:<50 nrad rms
曲面(>60 m): 100 nrad rms实现二维测量 日本JASRI/SPring-8 AC-NOM 2014 9.7 mrad ±1.2μrad ±0.24μrad (48μrad)
重复精度100 nrad rms校准扫描俯仰误差; 扫描速度慢分辨率24.2 nrad 中国SSRF上海光源 NOM 2015 1100 mm
±5 mrad0.08μrad rms (±50μrad)
0.25μrad rms (±5 mrad)空间采样频率在1~10 mm
重复精度50 nrad rms主动角控制拼接干涉仪
控制算法+精密转台测角拼接干涉仪
测角系统(RADSI)测角辅助拼接干涉仪
测角辅助装置+拼接算法





大口径、小曲率长焦K-B镜
300~1000 mm; <20 mrad小口径、大曲率短焦K-B镜
100~300 mm; >20 mrad平面镜、小曲率椭圆柱镜(探索阶段) 平面优于0.30 nm rms
曲面优于0.30 μrad rms
步进单孔径测量(干涉仪尺寸)平面优于0.2 nm rms
曲面优于2 nm rms
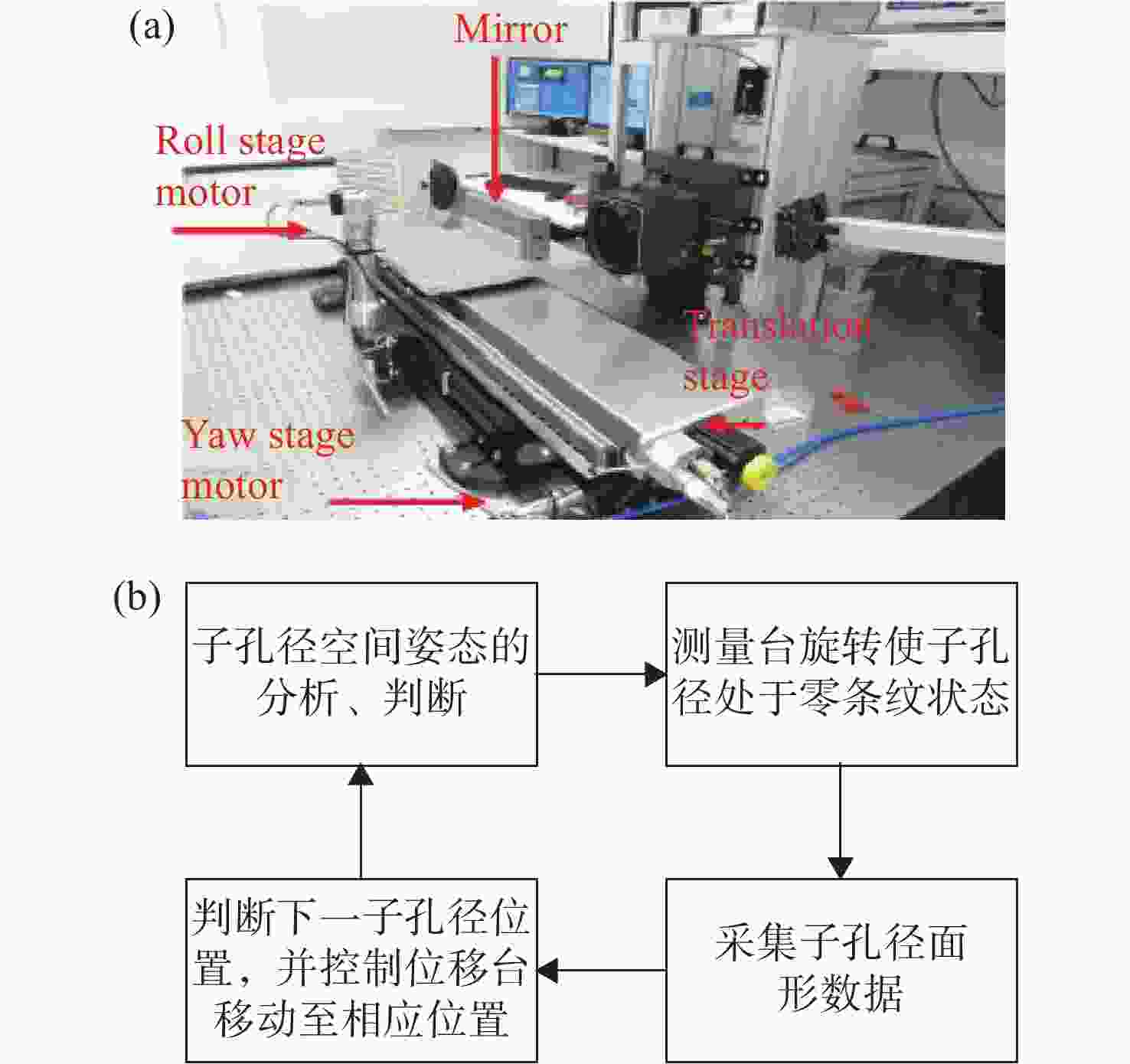
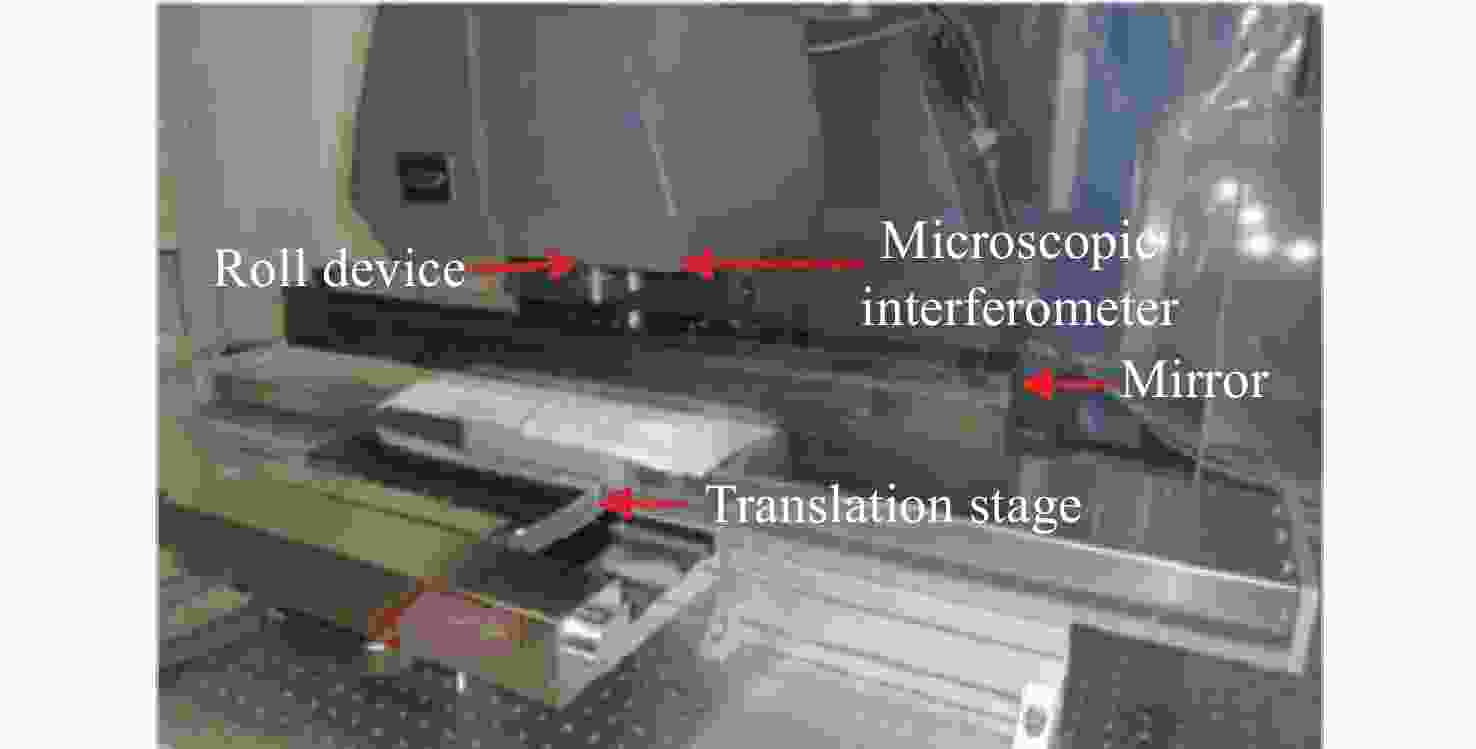
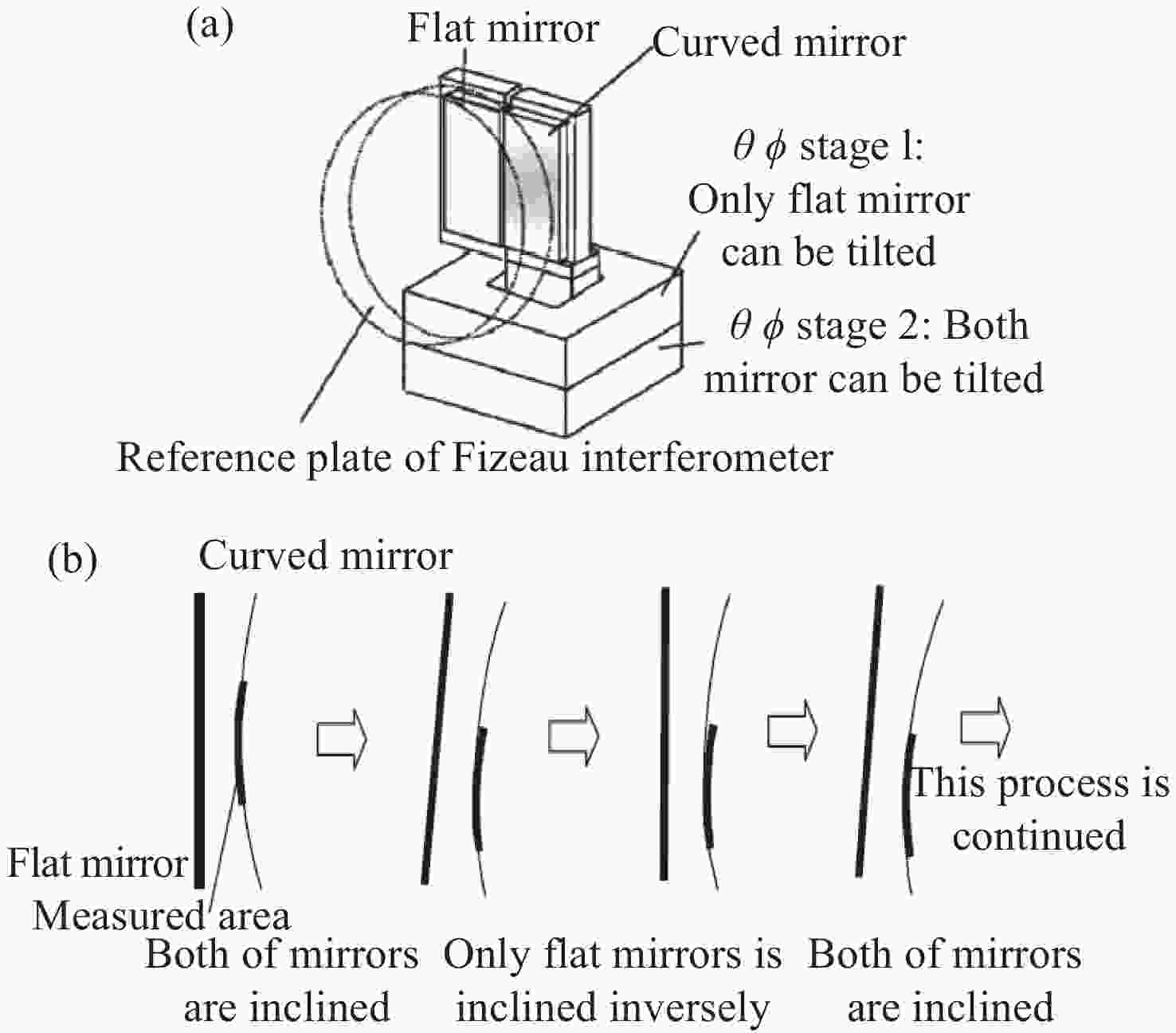
步进单孔径测量: 2 mm×2 mm重复精度1.5 nm rms
步进单孔径量: 2 mm×2 mm结构相对简单,测量口径范围大,
测量效率高 测量频段有限,
测量精度受待测面曲率影响大测量频段宽,测量精度高,
曲率测量范围大,结构复杂,
易受环境影响,测量口径范围受限结构简单,动态范围大,测量精度高
有待进一步完善具体结构表 4 国内外典型拼接干涉仪技术参数
Table 4. Technical parameters of typical stitching interferometer at home and abroad
机构/装置 设备 时间 技术性能 备注 欧洲ERSF Fizeau-SI 2019 平面镜:优于0.30 nm rms
椭面镜:优于0.30 μrad rms
球面镜:优于0.25 μrad rms主镜法校正参考误差需弥补球面低频信息空间分辨率: 80 μm MSI 2019 平面: 0.2 nm rms
横向分辨率: (2.5倍) 16 μm; (1倍) 40 μm适合于平面或强弯短镜;
存在拼接伪影美国BNL MSI 2017 残余斜率偏差: 2 μrad rms 采用曲率拼接技术 ASI-AMS 2018 平面:重复精度0.5 nm rms
椭球面:重复精度2 nm rms可以减小回程误差; 子孔径重叠
面积小,测量速度快日本大阪大学 MSI-RADSI 2016 面型高度误差:3 nm rms
重复精度:0.51 nm rms可测极端曲率面形以及椭面镜;
测量范围有限法国SOLEIL Mich-SI 2019 重复精度:0.2 nm rms 可测20 mm−1频段面形信息 复旦大学 RADSI 2017 平面镜:重复精度0.5 nm rms
球面镜:曲率偏差为2.3%验证了RADSI球面测量能力 国防科技大学 DST 2018 测量PV值8 nm;
重复精度达到1.5 nm rms一维测量;双扫描间隔; 减小回程
误差及参考误差 -
[1] KIRKPATRICK P, BAEZ A V. Formation of optical images by X-rays[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America, 1948, 38(9): 766-774. doi: 10.1364/JOSA.38.000766 [2] GIEWEKEMEYER K, WILKE R N, OSTERHOFF M, et al. Versatility of a hard X-ray kirkpatrick–baez focus characterized by ptychography[J]. Journal of Synchrotron Radiation, 2013, 20(3): 490-497. doi: 10.1107/S0909049513005372 [3] NAULLEAU P P, GOLDBERG K A, BATSON P J, et al. Tolerancing of diffraction-limited Kirkpatrick-Baez synchrotron beamline optics for extreme-ultraviolet metrology[J]. Applied Optics, 2001, 40(22): 3703-3709. doi: 10.1364/AO.40.003703 [4] MATSUYAMA S, YAMADA J, KOHMURA Y, et al. Full-field X-ray fluorescence microscope based on total-reflection advanced Kirkpatrick-Baez mirror optics[J]. Optics Express, 2019, 27(13): 18318-18328. doi: 10.1364/OE.27.018318 [5] KODAMA R, IKEDA N, KATO Y, et al. Development of an advanced Kirkpatrick-Baez microscope[J]. Optics Letters, 1996, 21(17): 1321-1323. doi: 10.1364/OL.21.001321 [6] HUDEC R, PINA L, VAN INNEMAN A, et al. Lightweight x-ray optics for future space missions[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2003, 4851: 656-665. doi: 10.1117/12.461590 [7] YUMOTO H, MIMURA H, KOYAMA T, et al. Focusing of X-ray free-electron laser pulses with reflective optics[J]. Nature Photonics, 2012, 7(1): 43-47. [8] SIEWERT F, BUCHHEIM J, BOUTET S, et al. Ultra-precise characterization of LCLS hard X-ray focusing mirrors by high resolution slope measuring deflectometry[J]. Optics Express, 2012, 20(4): 4525-4536. doi: 10.1364/OE.20.004525 [9] HEYNACHER E, REINHARDT D. Measuring equipment for testing the directrix of high-resolution wolter-type telescopes[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 1979, 184: 167-169. doi: 10.1117/12.957446 [10] COCCO D, IDIR M, MORTON D, et al. Advances in X-ray optics: from metrology characterization to wavefront sensing-based optimization of active optics[J]. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A:Accelerators,Spectrometers,Detectors and Associated Equipment, 2018, 907: 105-115. [11] QIAN S, TAKACS P. Nano-accuracy Surface Figure Metrology of Precision Optics[M]. COCCO L. Modern Metrology Concerns. Rijeka: Intech Open, 2012. [12] OWADA S, TOGAWA K, INAGAKI T, et al. A soft X-ray free-electron laser beamline at SACLA: the light source, photon beamline and experimental station[J]. Journal of Synchrotron Radiation, 2018, 25(1): 282-288. doi: 10.1107/S1600577517015685 [13] YANDAYAN T, GECKELER R D, SIEWERT F. Pushing the limits: latest developments in angle metrology for the inspection of ultra-precise synchrotron optics[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2014, 9206: 92060F. [14] TAKACS P Z, FENG S C K, CHURCH E L, et al. Long trace profile measurements on cylindrical aspheres[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 1989, 966: 354-364. doi: 10.1117/12.948082 [15] TAKACS P Z, QIAN SH N, COLBERT J. Design of a long trace surface profiler[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 1987, 749: 59-64. doi: 10.1117/12.939842 [16] SIEWERT F, LAMMERT H, NOLL T, et al. Advanced metrology: an essential support for the surface finishing of high performance x-ray optics[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2005, 5921: 592101. doi: 10.1117/12.622747 [17] SIEWERT F, ZESCHKE T, ARNOLD T, et al. Linear chirped slope profile for spatial calibration in slope measuring deflectometry[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2016, 87(5): 051907. doi: 10.1063/1.4950737 [18] OTSUBO M, OKADA K, TSUJIUCHI J. Measurement of large plane surface shapes by connecting small-aperture interferograms[J]. Optical Engineering, 1994, 33(2): 608-613. doi: 10.1117/12.152248 [19] IRICK S C, MCKINNEY W R, LUNT D L J, et al. Using a straightness reference in obtaining more accurate surface profiles from a long trace profiler[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 1992, 63(1): 1436-1438. doi: 10.1063/1.1143036 [20] QIAN SH N, LI H ZH, TAKACS P Z. Penta-Prism Long Trace Profiler (PPLTP) for measurement of grazing incidence space optics[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 1996, 2805: 108-114. doi: 10.1117/12.245083 [21] QIAN SH N, SOSTERO G, TAKACS P Z. Precision calibration and systematic error reduction in the long trace profiler[J]. Optical Engineering, 2000, 39(1): 304-310. doi: 10.1117/1.602364 [22] PEDREIRA P, NICOLAS J, ŠICS I, et al. Deflectometry encoding the measured angle in a time-dependent intensity signal[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2019, 90(2): 021707. doi: 10.1063/1.5057768 [23] QIAN SH N, TAKACS P Z. Design of multiple-function long trace profiler[J]. Optical Engineering, 2007, 46(4): 043602. doi: 10.1117/1.2724851 [24] FLORIOT J, LEVECQ X, BUCOURT S, et al. A Shack–Hartmann measuring head for the two-dimensional characterization of X-ray mirrors[J]. Journal of Synchrotron Radiation, 2008, 15(2): 134-139. doi: 10.1107/S0909049507066083 [25] IDIR M, KAZNATCHEEV K, DOVILLAIRE G, et al. A 2 D high accuracy slope measuring system based on a stitching shack hartmann optical head[J]. Optics Express, 2014, 22(3): 2770-2781. doi: 10.1364/OE.22.002770 [26] ALCOCK S G, SAWHNEY K J S, SCOTT S, et al. The Diamond-NOM: a non-contact profiler capable of characterizing optical figure error with sub-nanometre repeatability[J]. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A:Accelerators,Spectrometers,Detectors and Associated Equipment, 2010, 616(2-3): 224-228. doi: 10.1016/j.nima.2009.10.137 [27] QIAN SH N, IDIR M. Innovative nano-accuracy surface profiler for sub-50 nrad rms mirror test[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2016, 9687: 96870D. [28] GECKELER R D. ESAD shearing deflectometry: potentials for synchrotron beamline metrology[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2006, 6317: 63171H. doi: 10.1117/12.716301 [29] LACEY I, ADAM J, CENTERS G P, et al. Development of a high performance surface slope measuring system for two-dimensional mapping of x-ray optics[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2017, 10385: 103850G. [30] QIAN SH N, WANG Q P, HONG Y L, et al. Multiple Functions Long Trace Profiler (LTP-MF) for national synchrotron radiation laboratory of China[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2005, 5921: 592104. doi: 10.1117/12.618800 [31] ZENG D H, XIAO T Q, DU G H, et al. New long trace profiler based on phase plate diffraction for optical metrology of SSRF[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2006, 77(9): 093305. doi: 10.1063/1.2186253 [32] 李直, 赵洋, 李达成, 等. 衍射型长程大型非球面轮廓测量仪[J]. 光学学报,2002,22(10):1224-1228. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2239.2002.10.014LI ZH, ZHANG Y, LI D CH, et al. A diffractive long trace profiler for large aspherical optics[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2002, 22(10): 1224-1228. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2239.2002.10.014 [33] SHUN L, YAN G, WEI ZH, et al. Design of co-path scanning long trace profiler for measurement of x-ray space optical elements[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2010, 7544: 754421. doi: 10.1117/12.885415 [34] 澎湃新闻. 高能同步辐射光源验证装置通过国家验收, 最亮光源年中开建[OL]. https://www.thepaper.cn/newsDetail_forward_2935727. 2019-1-31.The Paper. The verification device of high energy synchrotron radiation light source has passed acceptance, and the brightest light source will be built in the middle of the year [OL]. https://www.thepaper.cn/newsDetail_forward_2935727. 2019-1-31. [35] 秦超.同步辐射椭圆柱面压弯镜机构的研究[D]. 北京: 中国科学院大学(中国科学院上海应用物理研究所), 2018.QIN CH. Research on synchrotron radiation elliptic cylinder mirror bender[D]. Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Shanghai Institute of Applied Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences), 2018. (in Chinese) [36] SIEWERT F, BUCHHEIM J, ZESCHKE T, et al. On the characterization of ultra-precise X-ray optical components: advances and challenges in ex situ metrology[J]. Journal of Synchrotron Radiation, 2014, 21(5): 968-975. doi: 10.1107/S1600577514016221 [37] ASSOUFID L, BRAY M, QIAN J, et al. 3D surface profile measurements of large x-ray synchrotron radiation mirrors using stitching interferometry[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2002: 4728. [38] VIVO A, LANTELME B, BAKER R, et al. Stitching methods at the European Synchrotron Radiation Facility (ESRF)[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2016, 87(5): 051908. doi: 10.1063/1.4950745 [39] VIVO A, BARRETT R. Fizeau stitching at the European Synchrotron Radiation Facility (ESRF)[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2017, 10385: 103850N. [40] VIVO A, BARRETT R, PERRIN F. Stitching techniques for measuring X-ray synchrotron mirror topography[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2019, 90(2): 021710. doi: 10.1063/1.5063339 [41] WIEGMANN A, STAVRIDIS M, WALZEL M, et al. Accuracy evaluation for sub-aperture interferometry measurements of a synchrotron mirror using virtual experiments[J]. Precision Engineering, 2011, 35(2): 183-190. doi: 10.1016/j.precisioneng.2010.08.007 [42] YAMAUCHI K, YAMAMURA K, MIMURA H, et al. Microstitching interferometry for x-ray reflective optics[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2003, 74(5): 2894-2898. doi: 10.1063/1.1569405 [43] OHASHI H, TSUMURA T, OKADA H, et al. Microstitching interferometer and relative angle determinable stitching interferometer for half-meter-long x-ray mirror[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2007, 6704: 670405. doi: 10.1117/12.733476 [44] GEVORKYAN G S, CENTERS G, POLONSKA K S, et al.. Surface slope metrology of highly curved x-ray optics with an interferometric microscope[C]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2017, 10385: 103850H. [45] ASSOUFID L, QIAN J, KEWISH C M, et al. A microstitching interferometer for evaluating the surface profile of precisely figured X-ray K-B mirrors[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2007, 6704: 670406. doi: 10.1117/12.736384 [46] ROMMEVEAUX A, BARRETT R. Micro-stitching interferometry at the ESRF[J]. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A:Accelerators,Spectrometers,Detectors and Associated Equipment, 2010, 616(2-3): 183-187. [47] POLACK F, THOMASSET M, BROCHET S, et al. Surface shape determination with a stitching Michelson interferometer and accuracy evaluation[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2019, 90(2): 021708. doi: 10.1063/1.5061930 [48] MIMURA H, YUMOTO H, MATSUYAMA S, et al.. Microstitching interferometry for nanofocusing mirror optics[C]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2004, 5533: 170-180. [49] KIMURA T, OHASHI H, MIMURA H, et al. A stitching figure profiler of large X-ray mirrors using RADSI for subaperture data acquisition[J]. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A:Accelerators,Spectrometers,Detectors and Associated Equipment, 2010, 616(2-3): 229-232. doi: 10.1016/j.nima.2009.11.014 [50] YUMOTO H, MIMURA H, KIMURA T, et al. Stitching interferometric metrology for steeply curved x-ray mirrors[J]. Surface and Interface Analysis, 2008, 40(6-7): 1023-1027. doi: 10.1002/sia.2807 [51] YUMOTO H, MIMURA H, HANDA S, et al. Stitching-angle measurable microscopic-interferometer: surface-figure metrology tool for hard X-ray nanofocusing mirrors with large curvature[J]. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A:Accelerators,Spectrometers,Detectors and Associated Equipment, 2010, 616(2-3): 203-206. [52] YUMOTO H, KOYAMA T, MATSUYAMA S, et al. Stitching interferometry for ellipsoidal x-ray mirrors[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2016, 87(5): 051905. doi: 10.1063/1.4950714 [53] EHRET G, LAUBACH S, SCHULZ M. Flatness metrology based on small-angle deflectometric procedures with electronic tiltmeters[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2017, 10326: 1032604. [54] MING L, SHANZHI T, FUGUI Y, et al.. Optical metrology at BSRF[C]. Advanced Optical Manufacturing and Testing Technologies, 2016. [55] XUE J P, HUANG L, GAO B, et al. One-dimensional stitching interferometry assisted by a triple-beam interferometer[J]. Optics Express, 2017, 25(8): 9393-9405. doi: 10.1364/OE.25.009393 [56] HUANG L, XUE J P, GAO B, et al. One-dimensional angular-measurement-based stitching interferometry[J]. Optics Express, 2018, 26(8): 9882-9892. doi: 10.1364/OE.26.009882 [57] HUANG L, IDIR M, ZUO CH, et al. Two-dimensional stitching interferometry based on tilt measurement[J]. Optics Express, 2018, 26(18): 23278-23286. doi: 10.1364/OE.26.023278 [58] 陈善勇. 非球面子孔径拼接干涉测量的几何方法研究[D]. 长沙: 国防科学技术大学, 2006.CHEN SH Y. Geometrical approach to subaperture stitching interferometry for aspheric surface[D]. Changsha: National University of Defense Technology, 2006. (in Chinese) [59] 侯溪, 伍凡, 杨力, 等. 环形子孔径拼接检测大口径非球面镜的规划模型及分析[J]. 光学 精密工程,2006,14(2):207-212.HOU X, WU F, YANG L, et al. Layout model and analysis of annular subaperture stitching technique for testing large aspheric mirror[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2006, 14(2): 207-212. (in Chinese) [60] 王孝坤, 王丽辉, 邓伟杰, 等. 用非零位补偿法检测大口径非球面反射镜[J]. 光学 精密工程,2011,19(3):520-528. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20111903.0520WANG X K, WANG L H, DENG W J, et al. Measurement of large aspheric mirrors by non-null testing[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2011, 19(3): 520-528. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/OPE.20111903.0520 [61] 李长春, 程国民, 曹永刚. 自动调焦系统速度评估与仿真[J]. 液晶与显示,2019,34(5):515-520. doi: 10.3788/YJYXS20193405.0515LI CH CH, CHENG G M, CAO Y G. Evaluation and simulation of auto-focus system speed[J]. Chinese Journal of Liquid Crystals and Displays, 2019, 34(5): 515-520. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/YJYXS20193405.0515 [62] ZHAI D D, CHEN SH Y, PENG X Q, et al. Absolute profile test by multi-sensor scanning system with relative angle measurement[J]. Measurement Science and Technology, 2018, 29(11): 115205. doi: 10.1088/1361-6501/aade0d [63] SHI Y N, XU X D, HUANG Q SH, et al. Development of relative angle determinable stitching interferometry for high-accuracy x-ray focusing mirrors[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2017, 10385: 103850M. [64] FREISCHLAD K R. Absolute Interferometric testing based on reconstruction of rotational shear[J]. Applied Optics, 2001, 40(10): 1637-1648. doi: 10.1364/AO.40.001637 [65] 张敏, 隋永新, 杨怀江. 用于子孔径拼接干涉系统的机械误差补偿算法[J]. 光学 精密工程,2015,23(4):934-940. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20152304.0934ZHANG M, SUI Y X, YANG H J. Mechanical error compensation algorithm for subaperture stitching interferometr[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2015, 23(4): 934-940. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/OPE.20152304.0934 [66] MURPHY P, FORBES G, FLEIG J, et al. Stitching interferometry: a flexible solution for surface metrology[J]. Optics and Photonics News, 2003, 14(5): 38-43. doi: 10.1364/OPN.14.5.000038 [67] NICOLAS J, NG M L, PEDREIRA P, et al. Completeness condition for unambiguous profile reconstruction by sub-aperture stitching[J]. Optics Express, 2018, 26(21): 27212-27220. doi: 10.1364/OE.26.027212 [68] ASSOUFID L, BRAY M, SHU D M. Development of a linear stitching interferometric system for evaluation of very large X-ray synchrotron radiation substrates and mirrors[J]. AIP Conference Proceedings, 2004, 705(1): 851-854. -






 下载:
下载: