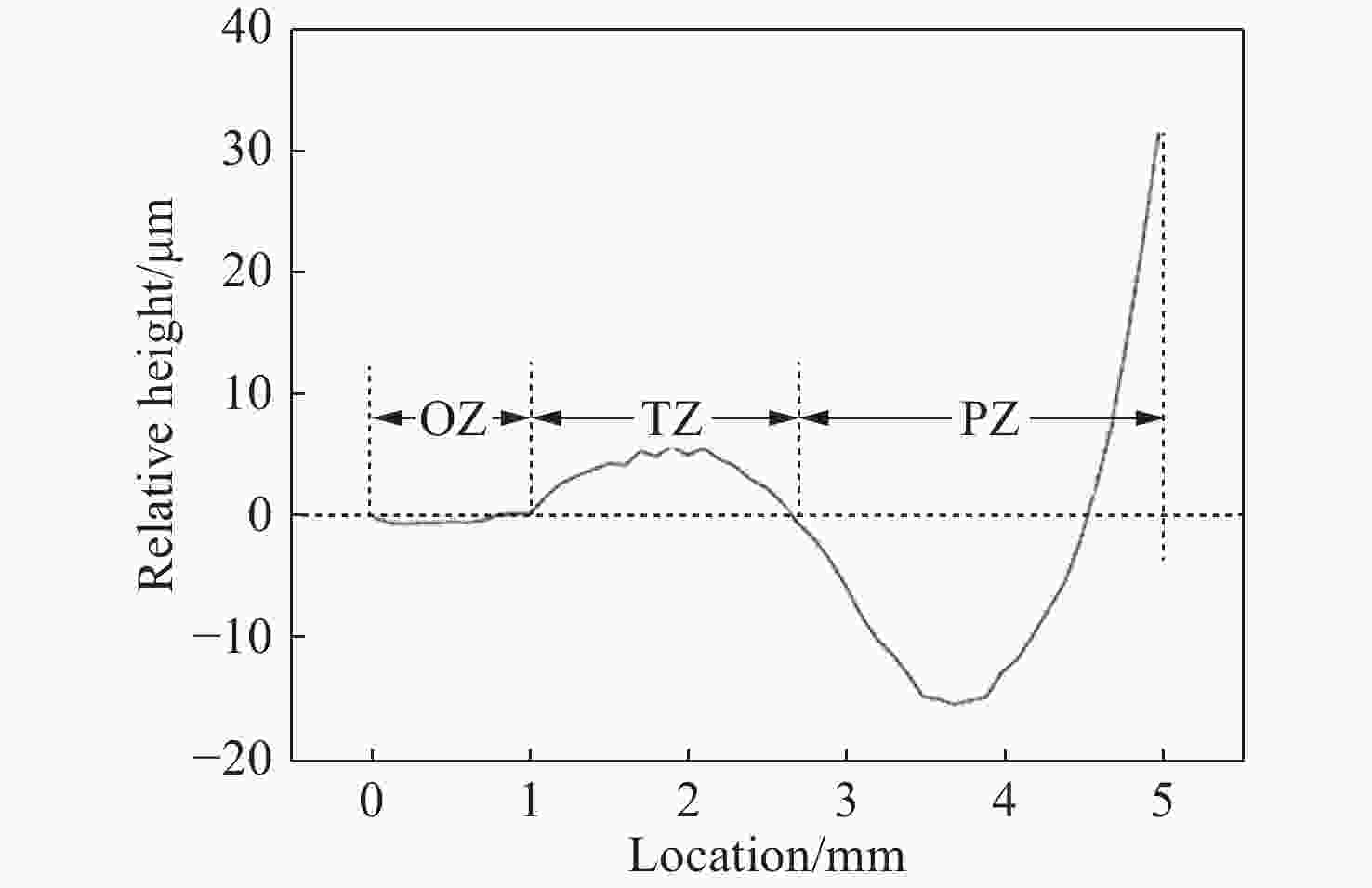
-
摘要: 本文提出了一种新的角膜面形分析方法,不仅消除了角膜本体厚度对塑形后角膜面形分析的影响,同时也能体现塑形后角膜的不对称性。在角膜前表面高度数据分析中引入基准参考面,以消除角膜本体厚度的影响,进而将塑形后的角膜前表面划分为光学区、转换区和边缘区。分析表明,角膜塑形后的光学区口径为(1.9±0.27) mm,曲率半径为(8.32±0.38) mm;转换区口径为(6.56±0.38) mm,曲率半径为(7.48±0.55) mm;边缘区的曲率半径为(10.49±1.83) mm。角膜塑形后的转换区水平方向屈光能力小于竖直方向的屈光能力,鼻侧屈光能力大于颞侧屈光能力,上侧屈光能力大于下侧屈光能力。利用所得参数建立半定制化的眼模型,对眼模型进行分析,结果表明:角膜塑形后周边呈近视性离焦,各方向的离焦呈非对称性分布,符合临床表现。Abstract: A new method of corneal shape analysis method is proposed. It not only eliminates the influence of corneal thickness on the shape of cornea after orthokeratology, but also reflects the asymmetry of a cornea. A reference surface is introduced into the analysis of the height data of the anterior surface of the cornea to eliminate the influence of corneal thickness. On the basis of above, anterior surface of the cornea is divided into the optical zone, transition zone and peripheral zone. The results show that the optical zone diameter is (1.9±0.27) mm, and the curvature radius is (8.32±0.38) mm; the transition zone diameter is (6.56±0.38) mm, and the curvature radius is (7.48±0.55) mm; the curvature radius of the peripheral zone is (10.49±1.83) mm. After orthokeratology, the horizontal refraction of the transition zone is lower than its vertical refraction. The refraction of the nasal side is greater than that of the temporal side and the refraction of the upper side is greater than that of the lower side. A semi-customized eye model is established based on the obtained parameters and the results show that its peripheral defocus is myopic after orthokeratology and its defocus is asymmetrical in each direction, which is consistent with clinical observations.
-
Key words:
- orthokeratology lens /
- division of cornea /
- peripheral defocus /
- partition algorithm /
- eye model
-
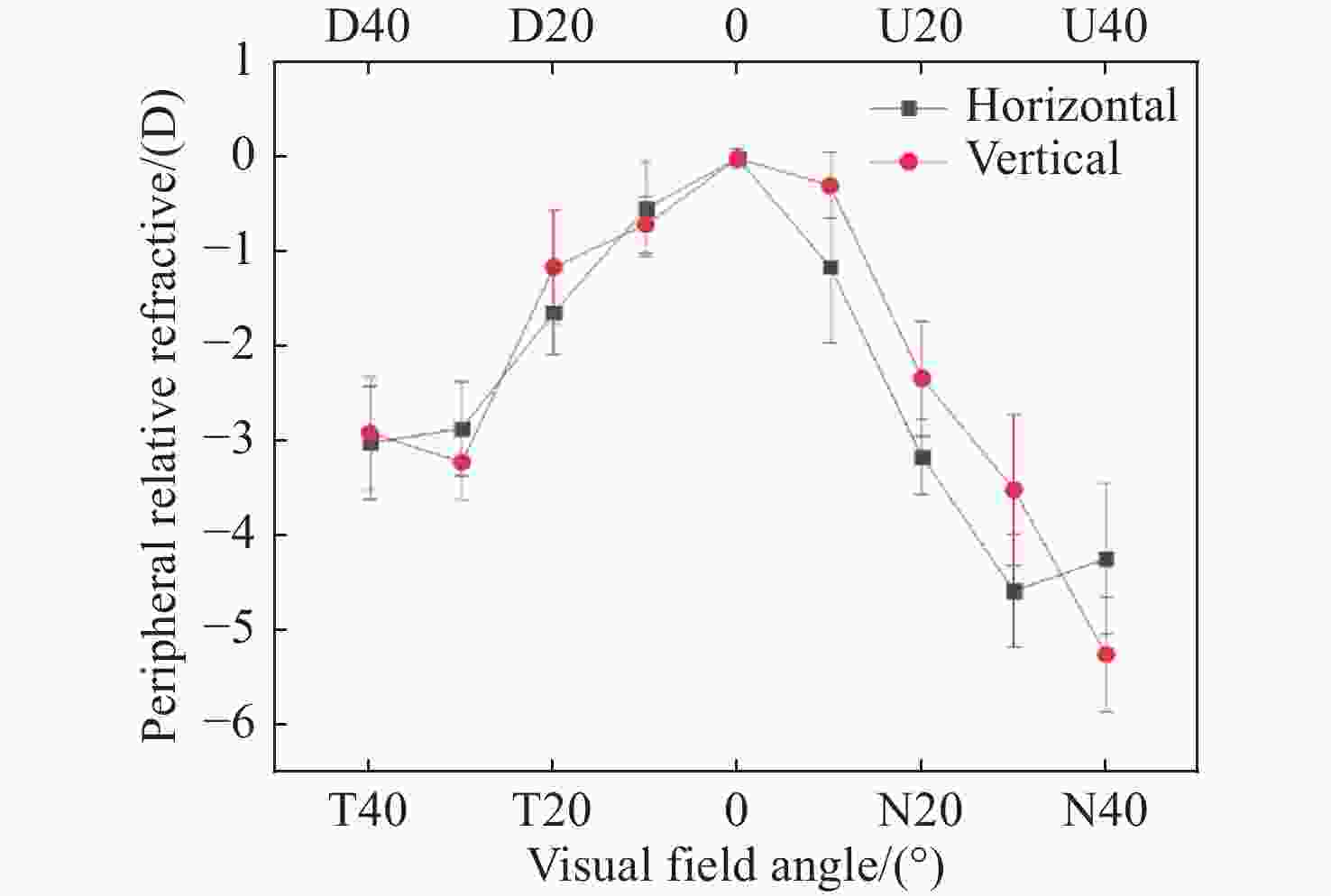
图 3 不同视场下的周边相对离焦。图中下侧水平轴表示水平视场,上侧水平轴表示竖直视场。N代表鼻侧,T代表颞侧,U代表上侧,D代表下侧。垂直的短线代表该点的标准差。
Figure 3. Peripheral relative refractions at different visual field angles. The lower and upper horizontal axes represent horizontal and vertical visual field of view respectively. N, T, U, D represents nasal, temporal, superior and inferior visual field of view respectively. The vertical bar represents the standard deviation at that point.
表 1 Navarro眼模型结构参数
Table 1. Parameters of the Navarro eye model
人眼 位置/mm 半径/mm 折射率 非球面系数 角膜 0 7.72 1.367 −0.26 0.55 6.5 1.337 4 0 晶状体 3.6 10.2 1.42 −3.131 6 7.6 −6 1.336 −1 视网膜 24 −12.5 − − 表 2 光学区,转换区和边缘区的平均分区口径、各区曲面曲率半径及分区平均圆心坐标
Table 2. The average zone diameter, radius of curvature and average center coordinates of the optical zone, the transition zone and the peripheral zone (mm)
光学区 转换区 边缘区 分区口径 1.90±0.27 6.56±0.38 >6.56 曲率半径 8.32±0.38 7.48±0.55 10.49±1.83 圆心坐标 Xo 0.01±0.05 0.14±0.14 −0.80±11.14 Yo 8.38±0.50 7.61±0.46 9.39±2.06 表 3 水平和竖直方向上的光学区、转换区及边缘区平均分区口径及各区曲面的曲率半径
Table 3. Zone diameter and curvature radius of the optical zone, the transition zone and the peripheral zone in the horizontal and vertical directions (mm)
光学区 转换区 边缘区 水平方向 分区口径 0.95±0.14 3.40±0.42 >3.40 曲率半径 8.47±0.30 7.67±0.33 10.67±1.25 竖直方向 分区口径 0.92±0.13 3.41±0.39 >3.41 曲率半径 8.15±0.28 7.56±0.73 11.00±1.58 表 4 鼻侧、颞侧、上侧和下侧角膜光学区、转换区及边缘的分区口径及曲率半径
Table 4. Zone diameter and curvature radius of the optical zone, the transition zone and the peripheral zone of the nasal,temporal,lower and upper cornea areas (mm)
光学区 转换区 边缘区 鼻侧 分区口径 0.94±0.14 3.41±0.42 >3.41 曲率半径 8.51±0.31 7.17±0.34 10.24±1.41 颞侧 分区口径 0.95±0.15 3.39±0.41 >3.39 曲率半径 8.42±0.27 7.62±0.33 11.11±1.14 上侧 分区口径 0.93±0.14 3.40±0.40 >3.40 曲率半径 8.13±0.48 7.72±0.76 10.59±1.27 下侧 分区口径 0.92±0.13 3.42±0.38 >3.42 曲率半径 8.18±0.16 7.40±0.70 11.01±1.85 -
[1] SWARBRICK H A. Orthokeratology review and update[J]. Clinical and Experimental Optometry, 2006, 89(3): 124-143. doi: 10.1111/j.1444-0938.2006.00044.x [2] KOFFLER B H, SEARS J J. Myopia control in children through refractive therapy gas permeable contact lenses: is it for real?[J]. American Journal of Ophthalmology, 2013, 156(6): 1076-1081. doi: 10.1016/j.ajo.2013.04.039 [3] CHO P, CHEUNG S W and EDWARDS M. The longitudinal orthokeratology research in children (LORIC) in Hong Kong: a pilot study on refractive changes and myopic control[J]. Current Eye Research, 2005, 30(1): 71-80. [4] WALLINE J J, JONES L A, SINNOTT L T. Corneal reshaping and myopia progression[J]. British Journal of Ophthalmology, 2009, 93(9): 1181-1185. doi: 10.1136/bjo.2008.151365 [5] VERKICHARLA P K, SUHEIMAT M, SCHMID K L, et al. Peripheral refraction, peripheral eye length, and retinal shape in myopia[J]. Optometry and Vision Science, 2016, 93(9): 1072-1078. doi: 10.1097/OPX.0000000000000905 [6] 李前, 何书喜. 周边屈光对近视的影响[J]. 国际眼科杂志,2013,13(9):1795-1798. doi: 10.3980/j.issn.1672-5123.2013.09.16LI Q, HE SH X. Influence of peripheral refraction on myopia[J]. International Eye Science, 2013, 13(9): 1795-1798. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3980/j.issn.1672-5123.2013.09.16 [7] ENDL M J, MARTINEZ C E, KLYCE S D, et al. Effect of larger ablation zone and transition zone on corneal optical aberrations after photorefractive keratectomy[J]. Archives of Ophthalmology, 2001, 119(8): 1159-1164. doi: 10.1001/archopht.119.8.1159 [8] QUEIRÓS A, GONZÁLEZ-MÉIJOME J M, VILLA-COLLAR C, et al. Local steepening in peripheral corneal curvature after corneal refractive therapy and LASIK[J]. Optometry and Vision Science, 2010, 87(6): 432-439. [9] REINSTEIN D Z, GOBBE M, ARCHER T J, et al. Epithelial, stromal, and corneal pachymetry changes during orthokeratology[J]. Optometry and Vision Science, 2009, 86(8): E1006-E1014. doi: 10.1097/OPX.0b013e3181b18219 [10] ALHARBI A, SWARBRICK H A. The effects of overnight orthokeratology lens wear on corneal thickness[J]. Investigative Ophthalmology &Visual Science, 2003, 44(6): 2518-2523. [11] 吕帆. 角膜塑形镜在控制近视进展中的作用[J]. 中国眼镜科技杂志,2018(21):92-93. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-6615.2018.21.043LU F. The role of keratoplasty in controlling the progression of myopia[J]. China Glasses Science-Technology Magazine, 2018(21): 92-93. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-6615.2018.21.043 [12] FARIA-RIBEIRO M, BELSUE R N, LÓPEZ-GIL N. Morphology, topography, and optics of the orthokeratology cornea[J]. Journal of Biomedical Optics, 2016, 21(7): 075011. doi: 10.1117/1.JBO.21.7.075011 [13] LU F H, SIMPSON T, SORBARA L, et al. The relationship between the treatment zone diameter and visual, optical and subjective performance in corneal refractive therapyTM lens wearers[J]. Ophthalmic and Physiological Optics, 2007, 27(6): 568-578. doi: 10.1111/j.1475-1313.2007.00520.x [14] ZHONG Y Y, CHEN ZH, XUE F, et al. Corneal power change is predictive of myopia progression in orthokeratology[J]. Optometry and Vision Science, 2014, 91(4): 404-411. doi: 10.1097/OPX.0000000000000183 [15] 张玉轩, 吴佳泽, 郑昌文. 基于Navarro示意眼模型的视觉真实感绘制[J]. 计算机应用研究,2011,28(8):3124-3127, 3130. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3695.2011.08.090ZHANG Y X, WU J Z, ZHENG CH W. Schematic eye model-based vision-realistic rendering[J]. Application Research of Computers, 2011, 28(8): 3124-3127, 3130. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3695.2011.08.090 [16] 陈浩, 宣丽, 胡立发, 等. 望远镜的紧凑型闭环液晶自适应光学系统设计[J]. 液晶与显示,2010,25(3):379-385. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2780.2010.03.017CHEN H, XUAN L, HU L F, et al. Design on compact type closed-loop liquid crystal adaptive optical system for telescope[J]. Chinese Journal of Liquid Crystals and Displays, 2010, 25(3): 379-385. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2780.2010.03.017 [17] 孔梅梅, 高志山, 陈磊, 等. 基于人眼光学模型建立的角膜模型[J]. 光学 精密工程,2009,17(4):707-712.KONG M M, GAO ZH SH, CHEN L, et al. Corneal model based on human eye optical models[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2009, 17(4): 707-712. (in Chinese) [18] 周峰, 闫海, 王晓莉, 等. 基于ZEMAX用户自定义操作数的波前编码成像系统优化设计[J]. 光学 精密工程,2010,18(3):528-535.ZHOU F, YAN H, WANG X L, et al. Optimization of wavefront coding imaging systems based on ZEMAX user defined operands[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2010, 18(3): 528-535. (in Chinese) [19] 李鹏飞, 许金凯, 胡立发, 等. 人眼像差校正仪成像CCD随动控制的设计与实现[J]. 液晶与显示,2010,25(5):733-737. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2780.2010.05.026LI P F, XU J K, HU L F, et al. Design and realization of focus auto adjustment for imaging CCD in retinal aberration correction setup[J]. Chinese Journal of Liquid Crystals and Displays, 2010, 25(5): 733-737. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2780.2010.05.026 [20] 曹正林, 廖文和, 沈建新. Zernike多项式拟合人眼波前像差的一种新算法[J]. 光学 精密工程,2006,14(2):308-314.CAO ZH L, LIAO W H, SHEN J X. A new algorithm for human eye's wave-front aberration fitting with Zernike polynomial[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2006, 14(2): 308-314. (in Chinese) [21] 王红波, 孙凤仙, 王敏婷. 降低远视离焦对儿童近视发展的影响[J]. 中国斜视与小儿眼科杂志,2014,22(2):22-24.WANG H B, SUN F X, WANG M T. Clinical study of reducing hyperopic optical defocus on children's development of myopia[J]. Chinese Journal of Strabismus &Pediatric Ophthalmology, 2014, 22(2): 22-24. (in Chinese) [22] 高稳生, 陈子林. 角膜塑形术在近视治疗中的作用机制[J]. 中国医药科学,2015,5(1):60-62.GAO W SH, CHEN Z L. The action mechanism of orthokeratology in the treatment of myopia[J]. China Medicine and Pharmacy, 2015, 5(1): 60-62. (in Chinese) [23] 陈明璿, 陈柏儒, 林怡欣. 基于液晶透镜的电控式光学影像缩放系统[J]. 液晶与显示,2015,30(3):375-380. doi: 10.3788/YJYXS20153003.0375CHEN M R, CHEN B R, LIN Y X. Electrically tunable optical zoom system based on liquid crystal lenses[J]. Chinese Journal of Liquid Crystals and Displays, 2015, 30(3): 375-380. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/YJYXS20153003.0375 [24] 余鑫鑫, 李大禹, 夏明亮, 等. 基于液体变焦透镜离焦补偿机构的设计[J]. 液晶与显示,2013,28(3):344-348. doi: 10.3788/YJYXS20132803.0344YU X X, LI D Y, XIA M L, et al. Design of defocus compensate mechanism based on liquid lens[J]. Chinese Journal of Liquid Crystals and Displays, 2013, 28(3): 344-348. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/YJYXS20132803.0344 [25] 黄德天, 刘雪超, 张红胜, 等. 基于人类视觉的快速自动调焦法[J]. 液晶与显示,2014,29(5):768-776. doi: 10.3788/YJYXS20142905.0768HUANG D T, LIU X CH, ZHANG H SH, et al. Fast auto-focusing method based on human visual system[J]. Chinese Journal of Liquid Crystals and Displays, 2014, 29(5): 768-776. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/YJYXS20142905.0768 [26] 周珺, 王肖, 吴晓璇, 等. 夜戴型角膜塑形镜矫正青少年近视疗效及其影响因素分析[J]. 中国实用眼科杂志,2017,35(2):136-142. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1006-4443.2017.02.009ZHOU J, WANG X, WU X X, et al. Clinic effect and relevant influencing factors of overninght orthokeratology in myopic adolescent[J]. Chinese Journal of Practical Ophthalmology, 2017, 35(2): 136-142. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1006-4443.2017.02.009 [27] QUEIRÓS A, GONZÁLEZ-MÉIJOME J M, JORGE J, et al. Peripheral refraction in myopic patients after orthokeratology[J]. Optometry and Vision Science, 2010, 87(5): 323-329. [28] MATHUR A, ATCHISON D A. Effect of orthokeratology on peripheral aberrations of the eye[J]. Optometry and Vision Science, 2009, 86(5): E476-E484. doi: 10.1097/OPX.0b013e31819fa5aa [29] SANKARIDURG P, HOLDEN B, SMITH Ⅲ E, et al. Decrease in rate of myopia progression with a contact lens designed to reduce relative peripheral hyperopia: one-year results[J]. Investigative Ophthalmology &Visual Science, 2011, 52(13): 9362-9367. [30] 陈志, 瞿小妹, 周行涛. 角膜塑形镜对周边屈光度的影响及其作用机制[J]. 中华眼视光学与视觉科学杂志,2012,14(2):74-78. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1674-845X.2012.02.003CHEN ZH, QU X M, ZHOU X T. Effects of orthokeratology on peripheral refraction and its mechanism[J]. Chinese Journal of Optometry Ophthalmology and Visual Science, 2012, 14(2): 74-78. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1674-845X.2012.02.003 -





 下载:
下载: