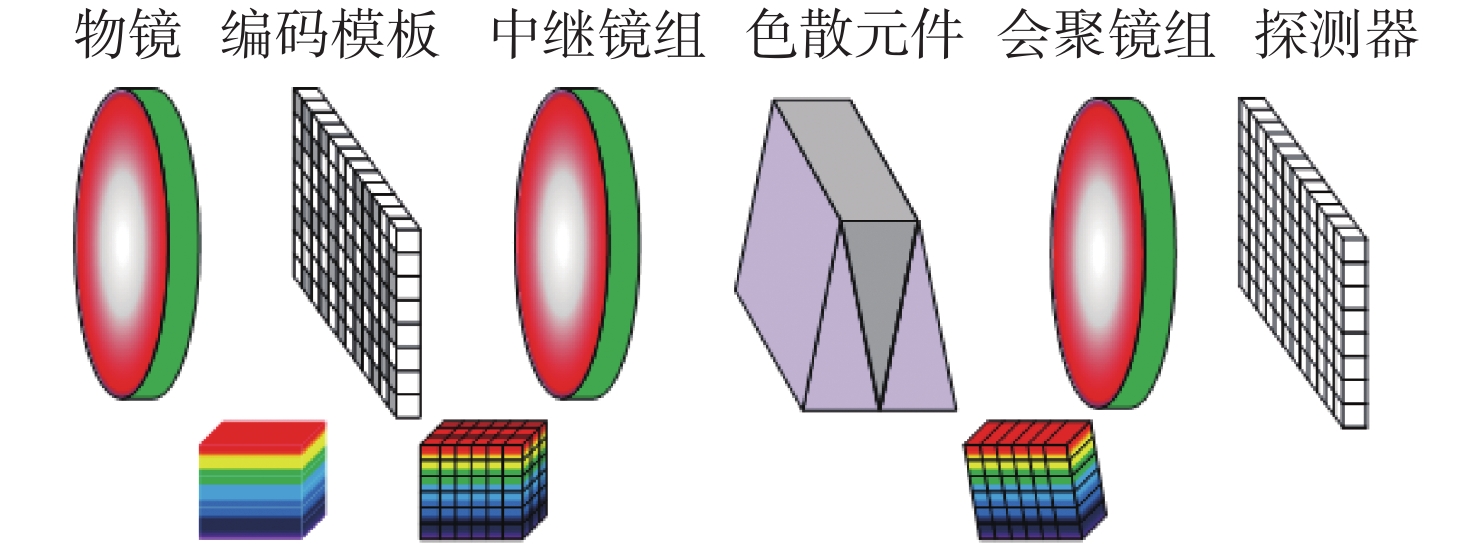
-
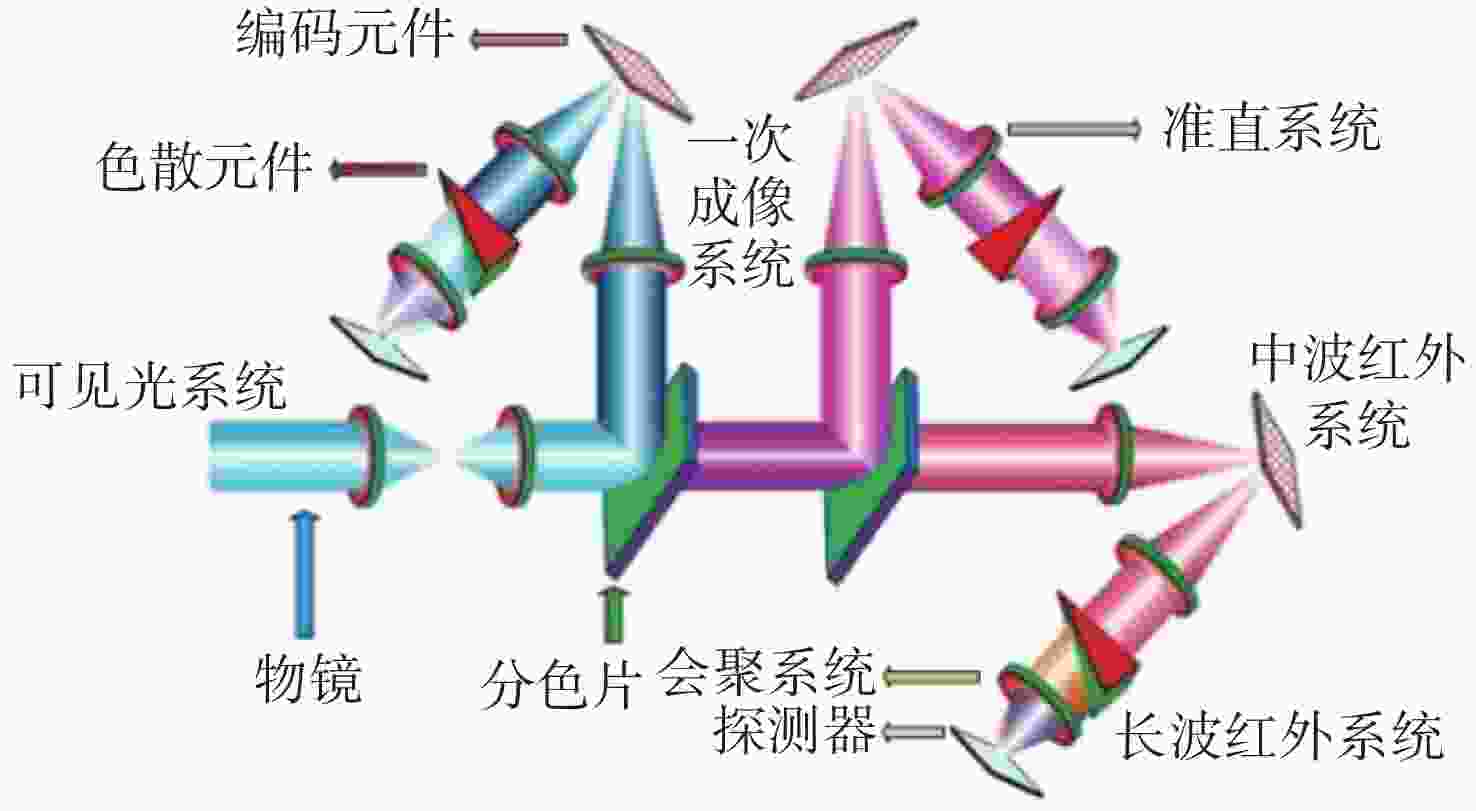
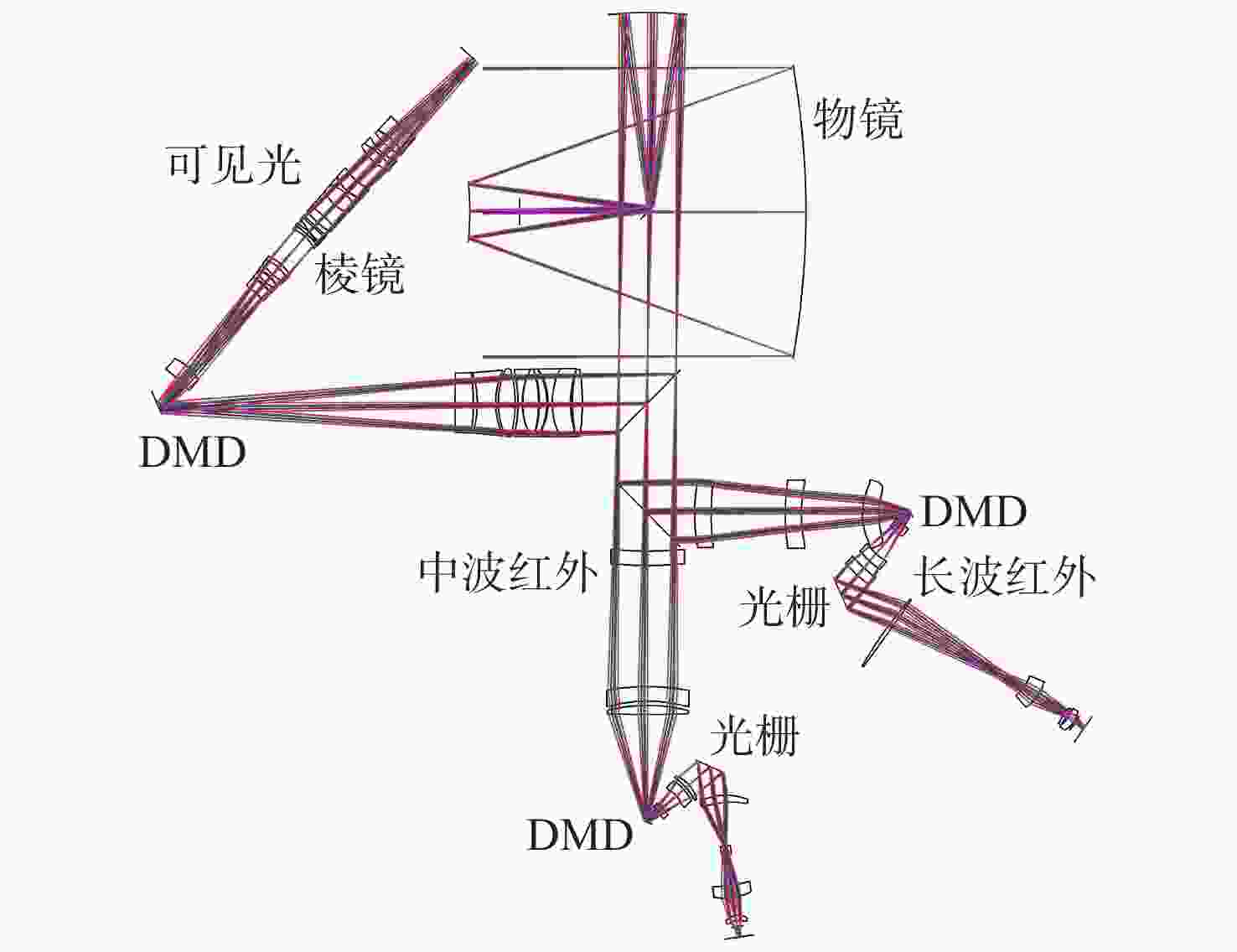
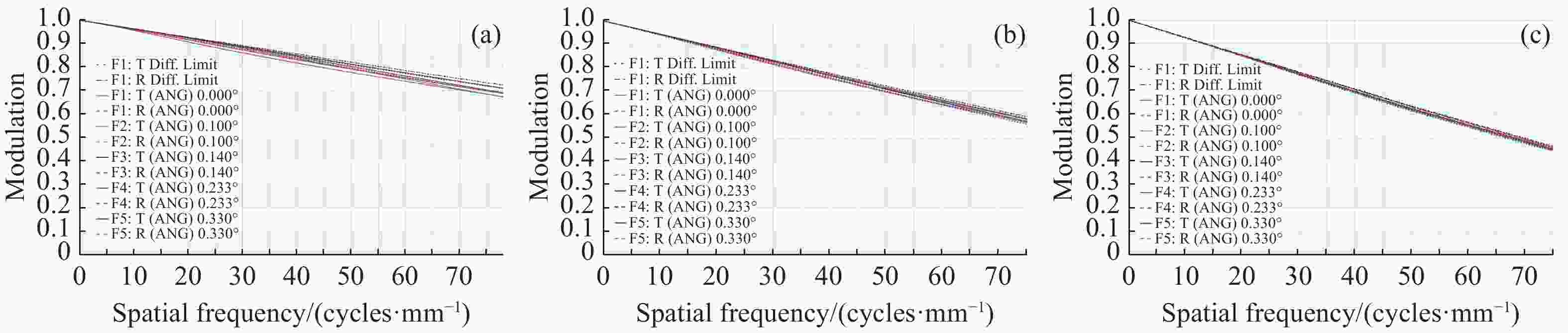
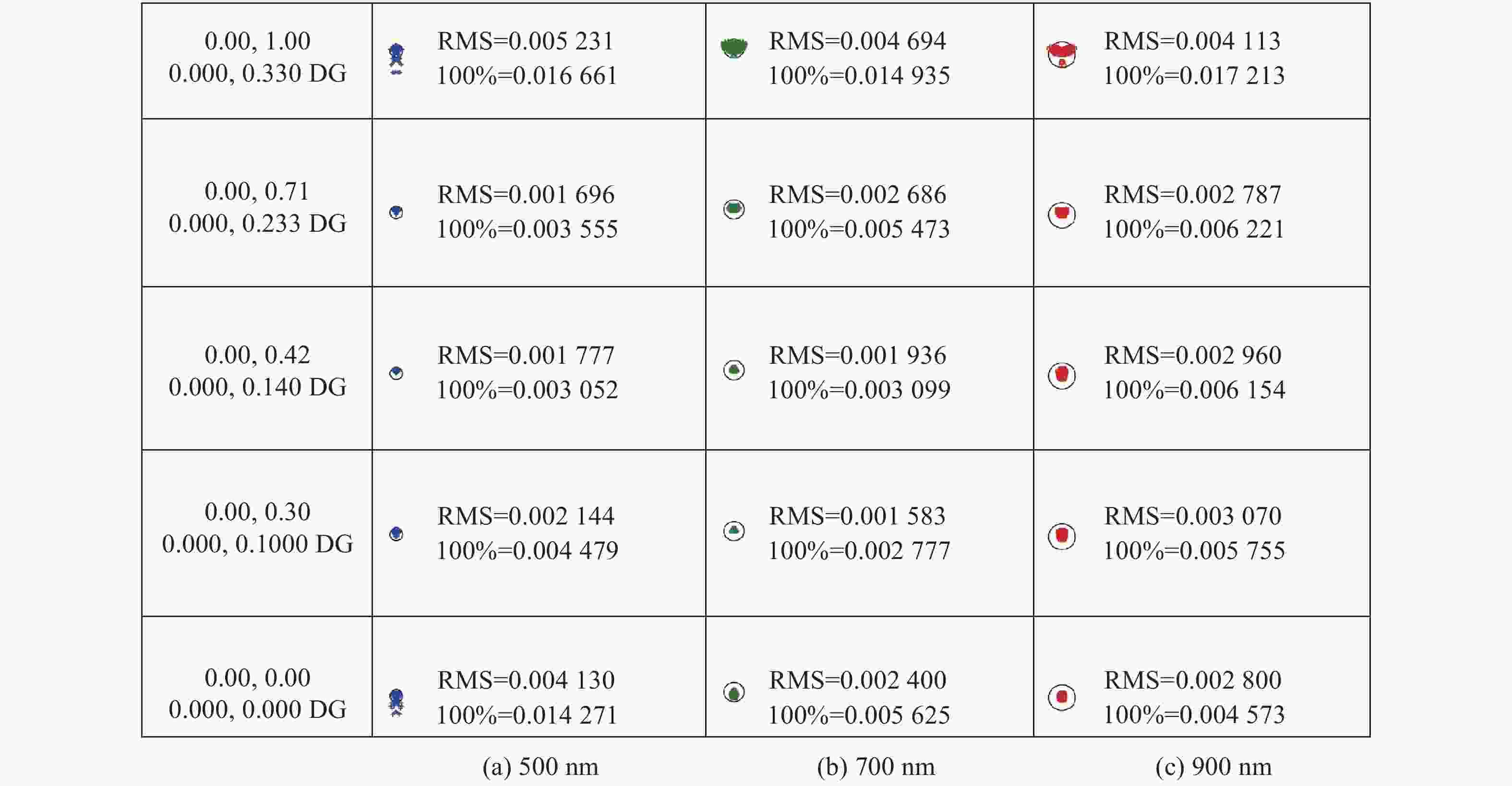
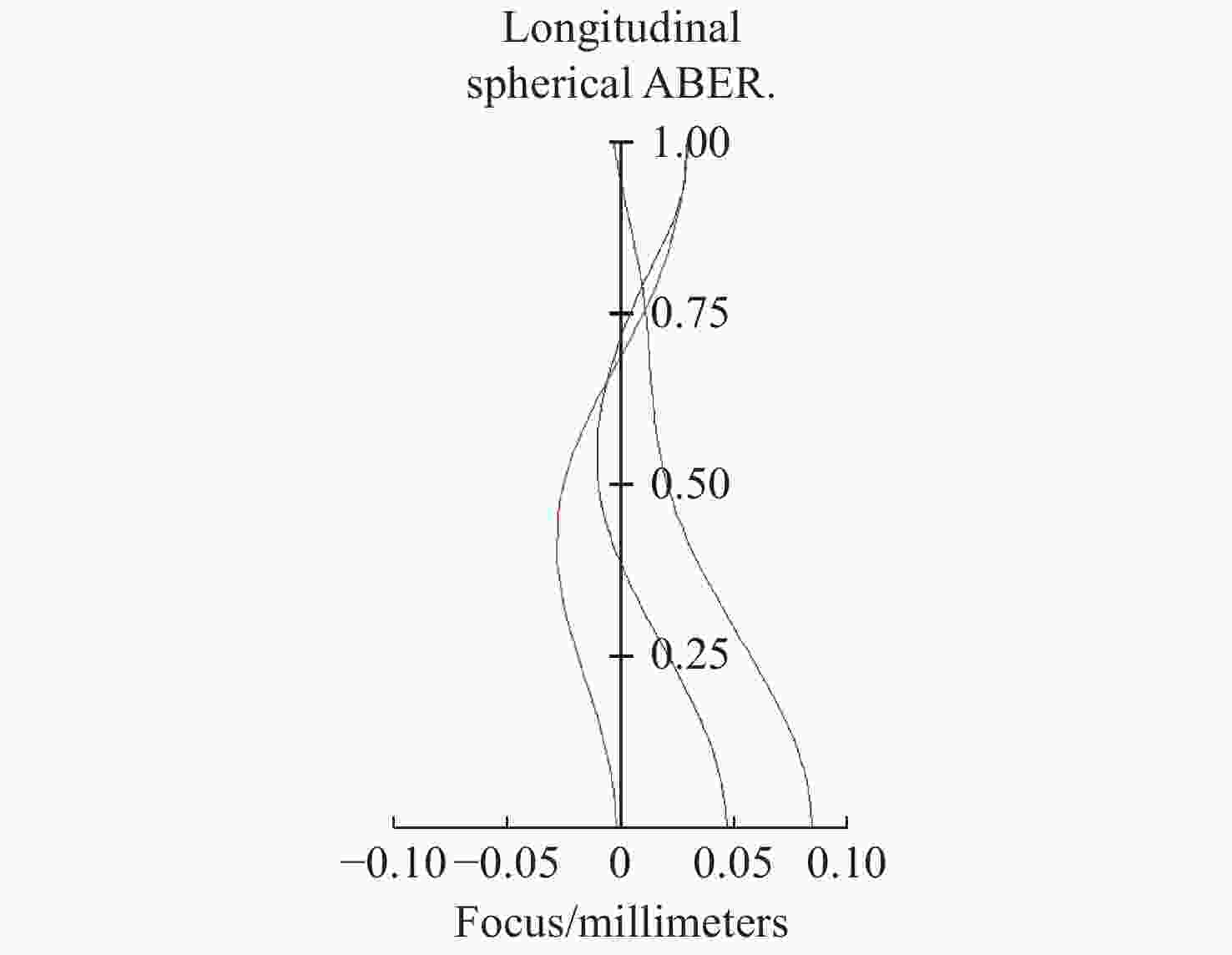
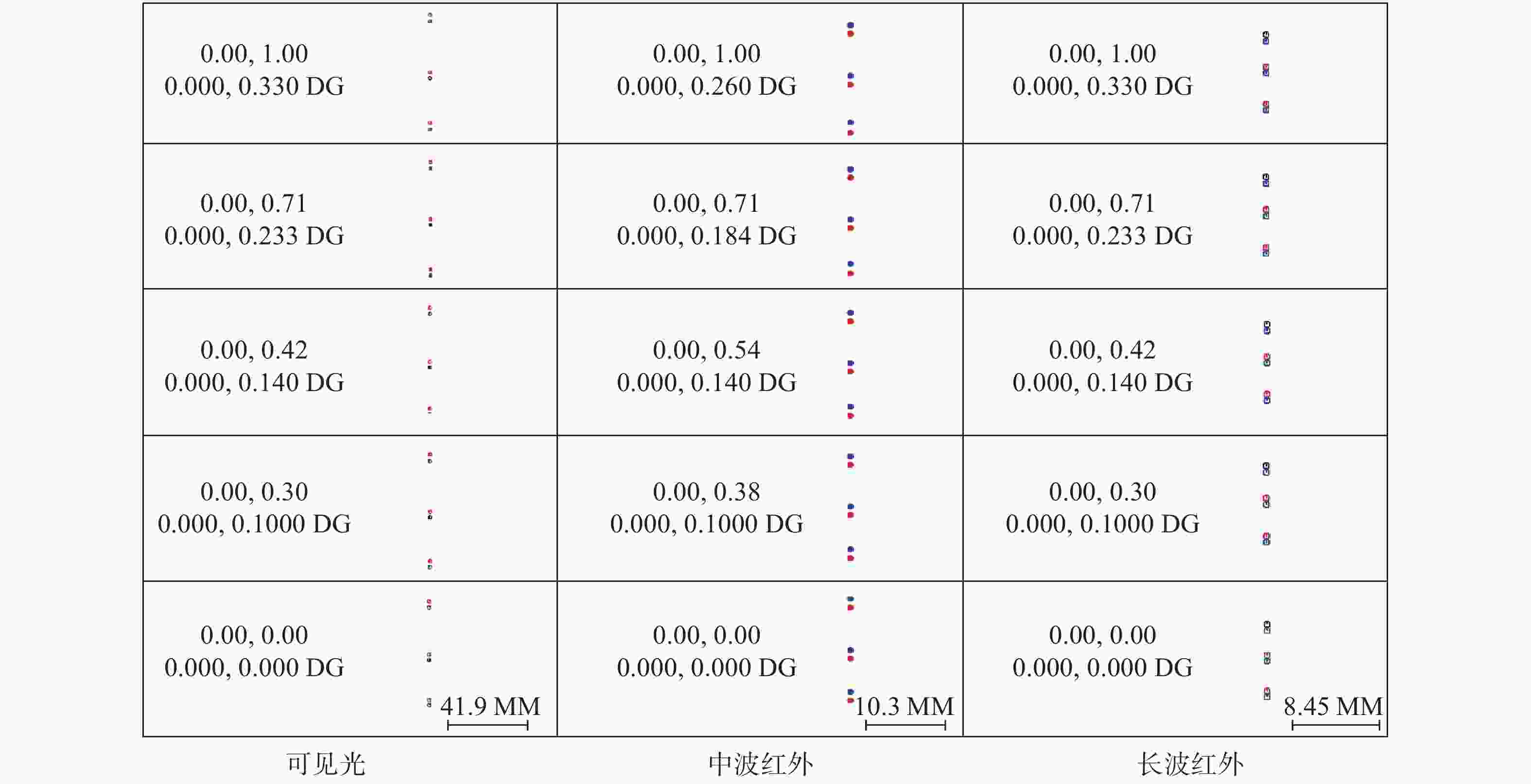
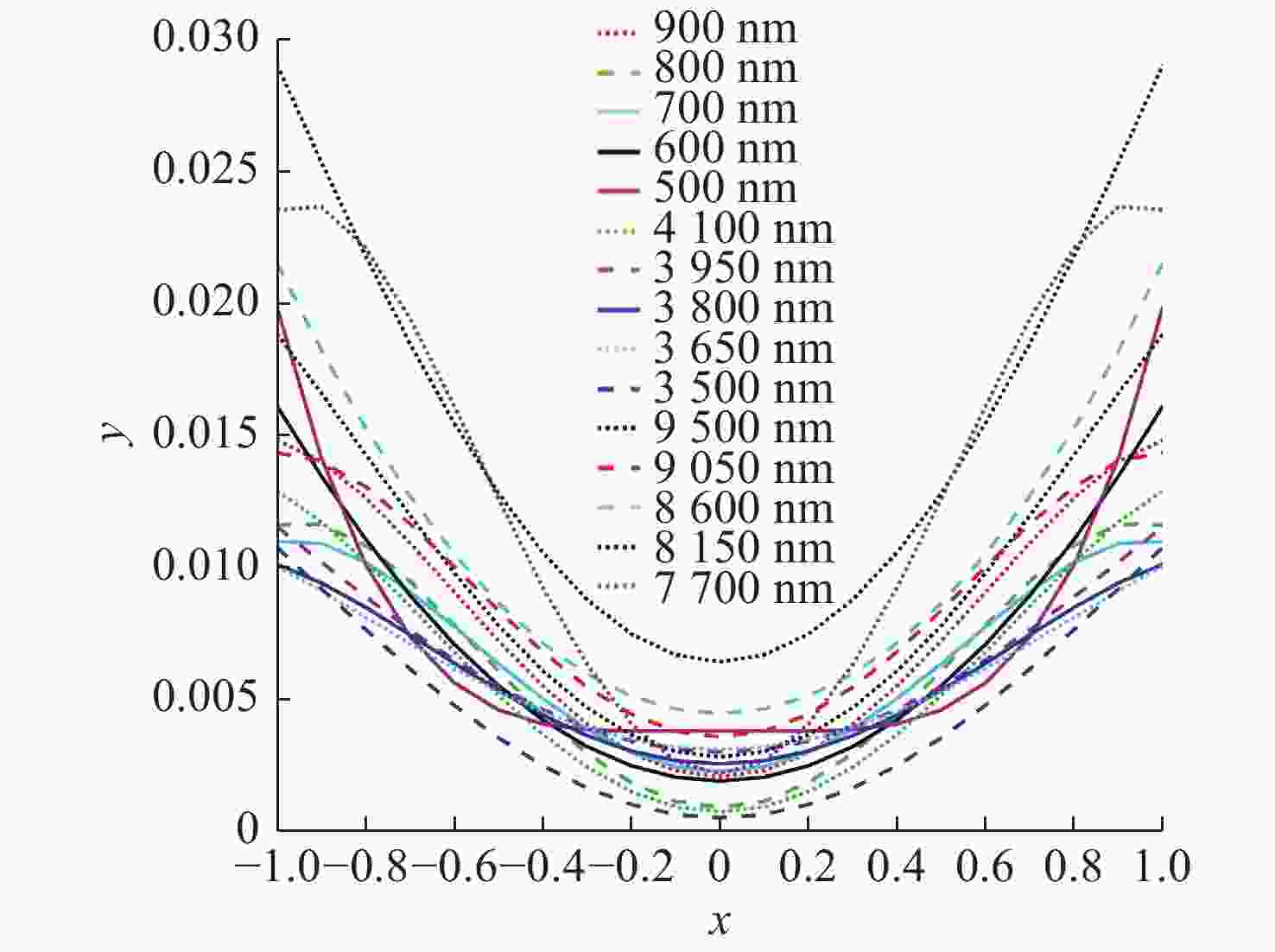
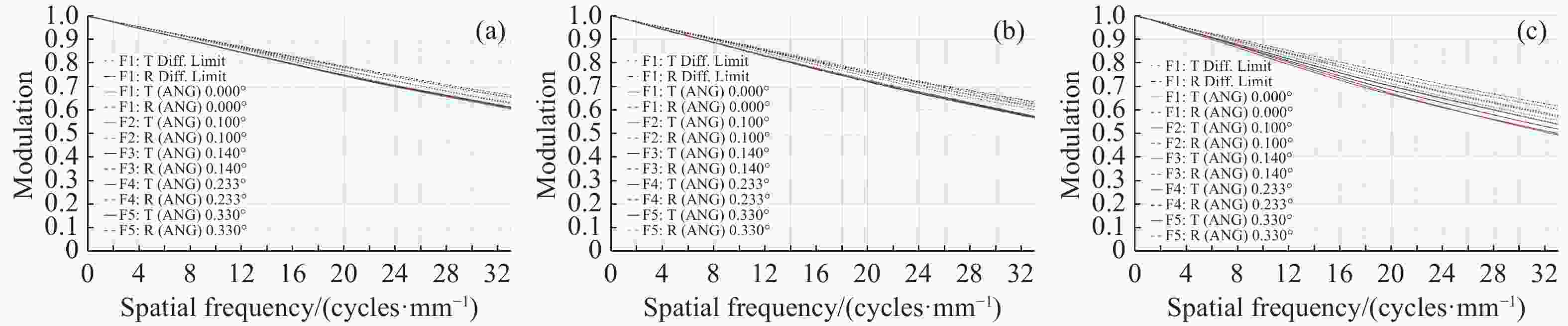
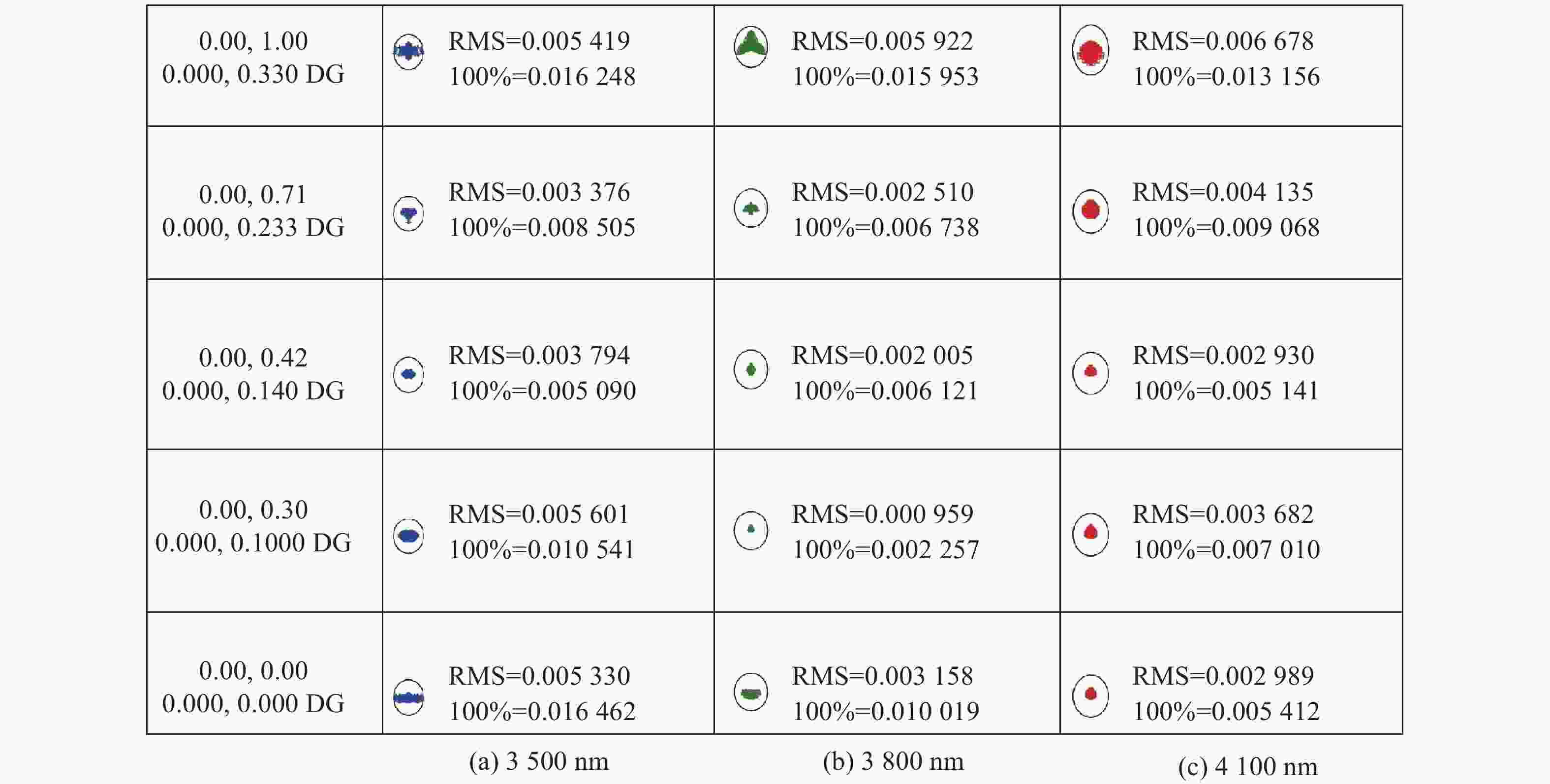
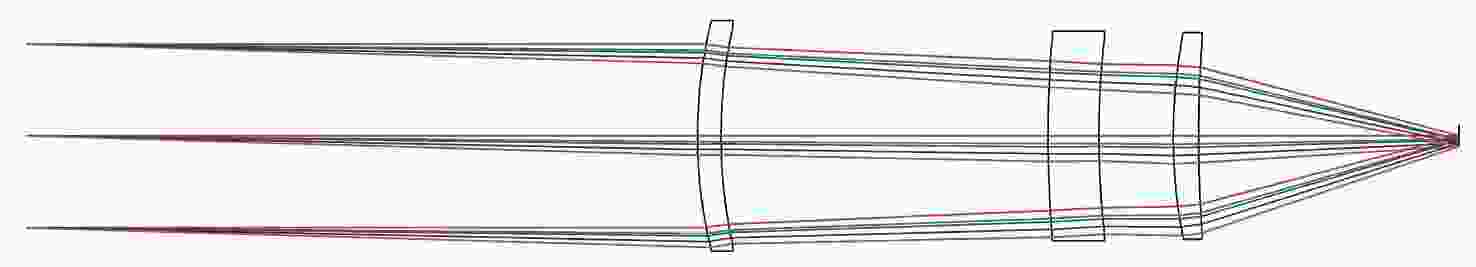
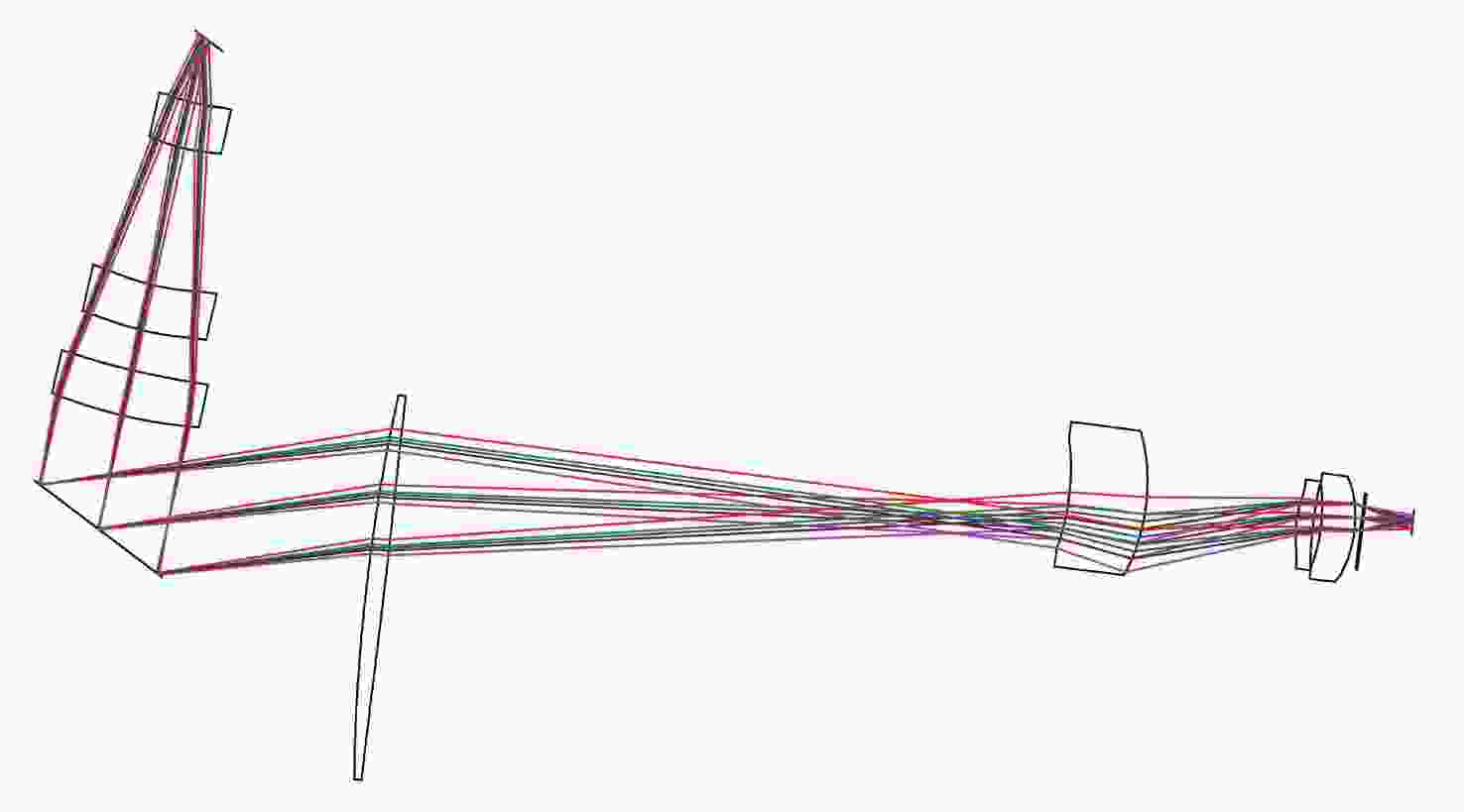
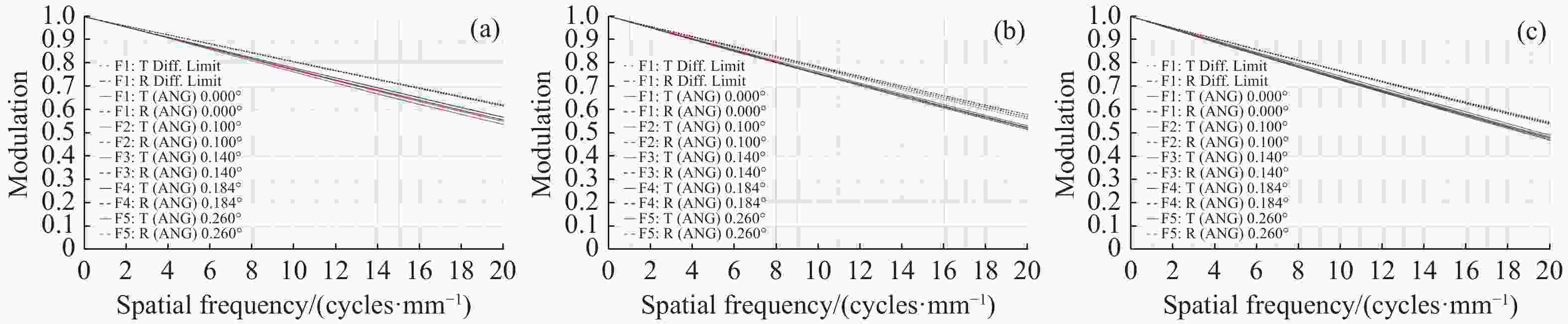
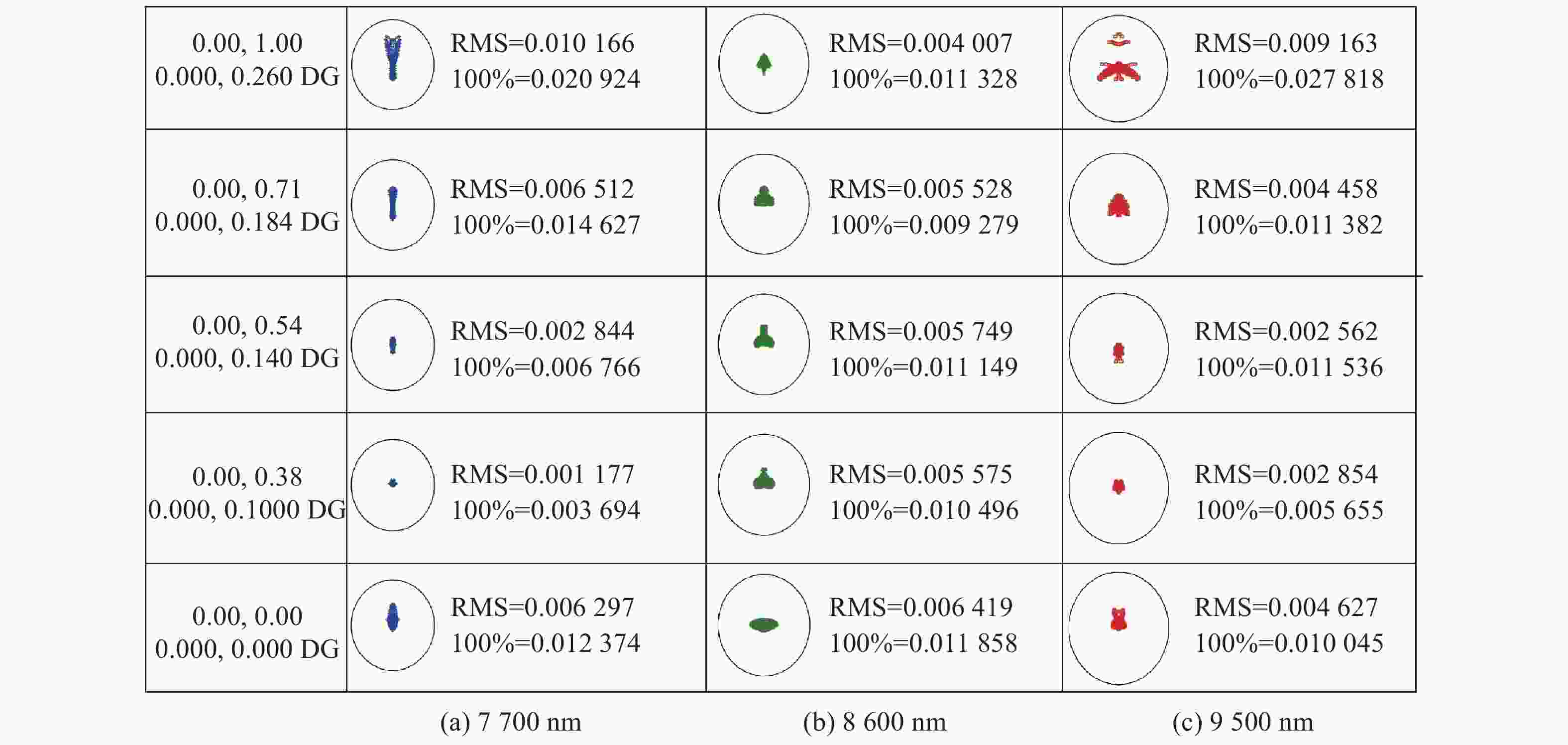
摘要: 针对用于地球静止轨道卫星的遥感面阵快照式成像光谱仪传输数据量过大引起的数据传输困难、信号采集处理时间长的问题,利用地球静止轨道平台可以长期驻留固定区域上空的特点,提出采用压缩感知的大口径宽谱段快照式光谱仪方案,对其光学系统结构进行设计,并对相关参数进行了计算。物镜采用同轴三反式无焦系统,用分色片对系统分光,经过对各系统进行优化处理,最终获得了幅宽为400 km×400 km,可见光地面像元分辨率为50 m、中波红外地面像元分辨率为400 m、长波红外地面像元分辨率为625 m的光学系统。该设计中,可见光路在78.125 lp/mm的MTF高于0.455,中波红外的光谱分辨率为光路在33.3 lp/mm处的MTF高于0.518,长波红外光路在20.8 lp/mm处的MTF高于0.498;可见光光谱分辨率为20 nm、中波红外的光谱分辨率为50 nm、长波红外的光谱分辨率为150 nm;可见光路二级光谱小于0.05 mm,设计结果具有良好的成像质量,各部分光学系统成像质量接近衍射极限,设计结果满足应用和指标需求。Abstract: Due to the excessive data transmission of the geostationary orbit array staring spectrometer, the data transmission is difficulty and signal acquisition and processing time is long. According to the characteristic that geostationary orbit platform can stay over the fixed area for a long time, a scheme of large aperture visual and infrared snapshot spectrometer based on compressive sensing was proposed. The physical model of compressive sensing spectral imaging was analyzed, the structure of the optical system was designed, and the relevant parameters were calculated. A coaxial three-mirror afocal optical system was used in objective lens, and dichroic films were used to split the spectrum. After optimization, the optical system was shown with a width of 400 km×400 km, 50 m Ground Sample Distance (GSD) in visible part, 400 m GSD in Middle Wave Infrared (MWIR) part and 625 m GSD in Long Wave Infrared (LWIR) part. The results show that the MTF in the visible part is higher than 0.455 at 78.125 lp/mm, the MTF in mid-wave infrared region is higher than 0.518 at 33.3 lp/mm, and the MTF is higher than 0.498 at 20.8 lp/mm in long-wave infrared region. The spectral resolutions are 20 nm, 50 nm, and 150 nm in the visible part, the mid-wave infrared region, and the long-wave infrared region, respectively. The second-order spectrum of the visual part is less than 0.05 mm. The optical system has good imaging performance, and the imaging quality of each part of the optical system is close to the diffraction limit, which meets the needs of applications and indicators.
-
表 1 光学系统设计要求
Table 1. Requirements for optical system design
可见光系统 中波红外系统 长波红外系统 空间分辨率/m 50 400 625 幅宽/km 400×400 400×400 320×320 光谱分辨率/nm 20 50 150 表 2 光学系统探测器参数
Table 2. Parameters of the optical system’s detector
可见光系统 中波红外系统 长波红外系统 像元数/pixel 8000×8000 1024×1024 512×512 像元尺寸/μm 6.4×6.4 15×15 24×24 表 3 光学系统最终设计参数
Table 3. Parameters of the designed optical system
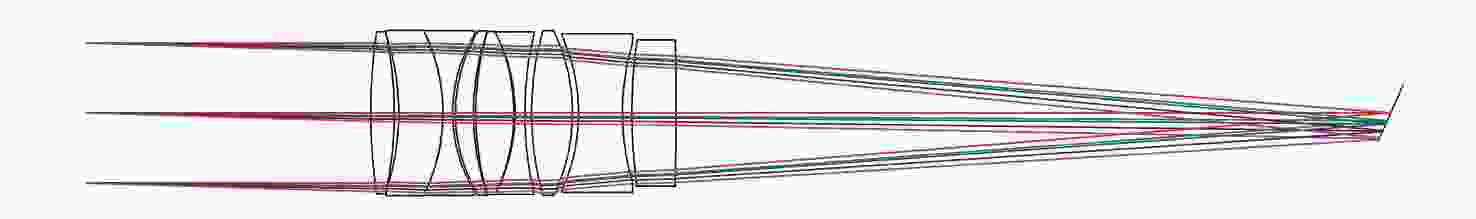
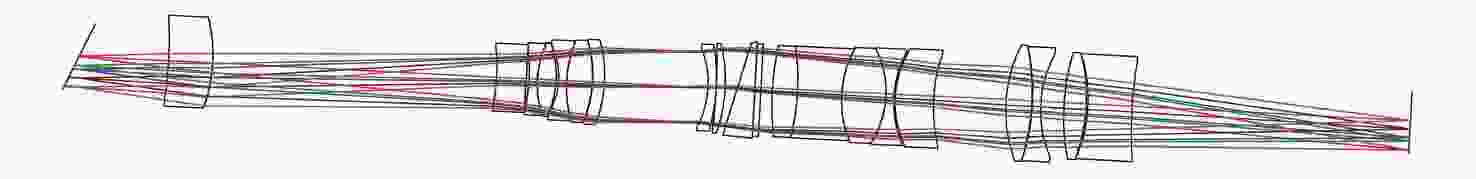
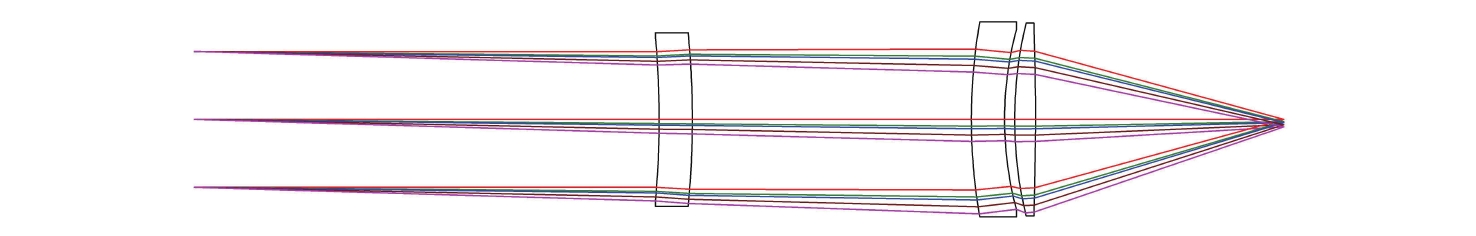
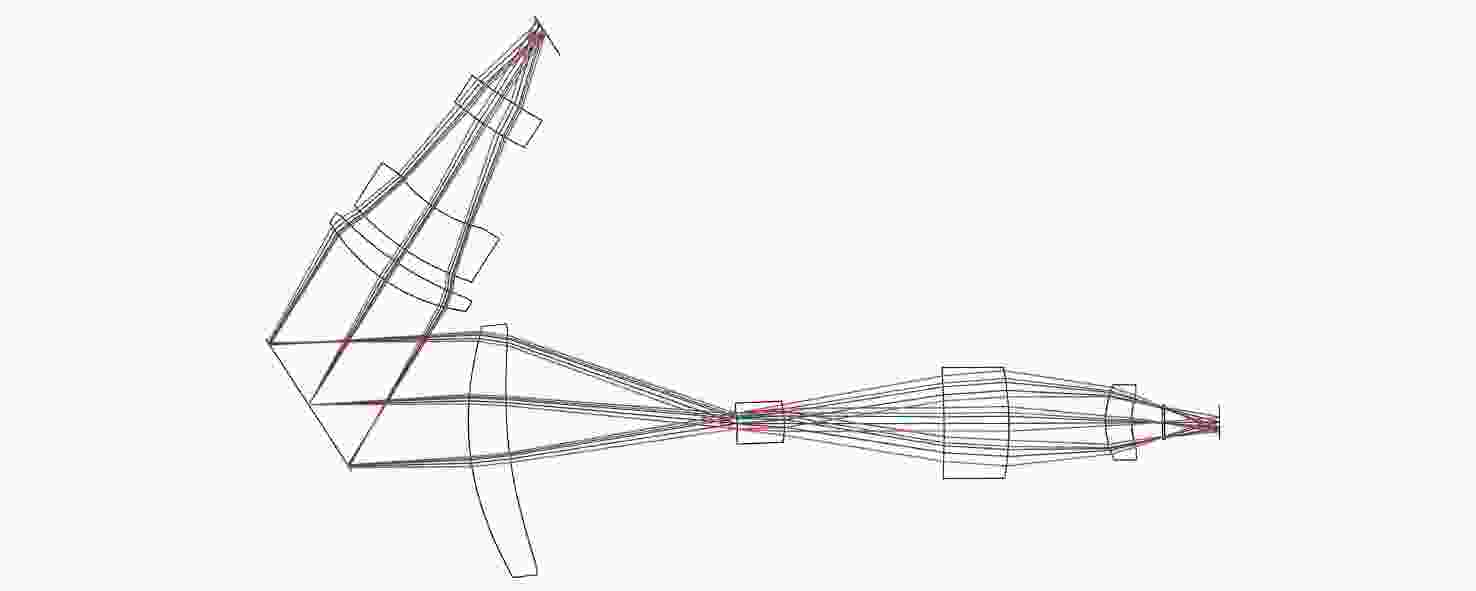
可见光系统 中波红外系统 长波红外系统 系统孔径/mm 700 视场角2ω/(°) 0.66×0.66 0.66×0.66 0.52×0.52 系统焦距/mm 4500 1350 1375 表 4 子系统参数
Table 4. Parameters of the sub-optical system
可见光一次会聚
光路/准直光路中波红外一次会聚
光路/准直光路长波红外一次会聚
光路/准直光路系统焦距/
mm900/534 270/137 275/124 光栅线对数/
(lp·mm−1)170 50 45 -
[1] 戴立群, 唐绍凡, 徐丽娜, 等. 从可见光到热红外全谱段探测的星载多光谱成像仪器技术发展概述[J]. 红外技术,2019,41(2):107-117. [2] 马文坡, 练敏隆. “高分四号”卫星凝视相机的技术特点[J]. 航天返回与遥感,2016,37(4):26-31. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-8518.2016.04.004MA W P, LIAN M L. Technical Characteristics of the Staring Camera on Board GF-4 Satellite[J]. Spacecraft Recovery&Remote Sening, 2016, 37(4): 26-31. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-8518.2016.04.004 [3] 陶家生, 孙治国, 孙英华, 等. 静止轨道高分辨率光学遥感探索[J]. 光电工程,2012,39(6):1-6.TAO J SH, SUN ZH G, SUN Y H, et al. Exploration of High Resolution Optical Remote Sensing of the Geostationary Orbit[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering., 2012, 39(6): 1-6. (in Chinese) [4] 罗秀娟, 刘辉, 张羽, 等. 地球同步轨道暗弱目标地基光学成像技术综述[J]. 中国光学,2019,12(4):753-766. [5] 黄思婕. 地球静止轨道大动态范围信息获取技术研究[D]. 上海: 中国科学院上海技术物理研究所. 2015.HUANG S J. Research on the technology of geosynchonous orbit high dynamic range information acquisition. Shanghai: Shanghai Institute of Technical Physics. 2015. (in Chinese) [6] 刘铭鑫.基于压缩感知的编码孔径光谱成像技术研究[D]. 长春: 中国科学院长春光学精密机械与物理研究所. 2019.Liu M X. Research on coded aperture spectral imaging technology based on compressed sensing[D]. Changchun: Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2019. (in Chinese) [7] 钱路路.计算光谱成像技术研究[D]. 安徽: 中国科学技术大学. 2013.Qian L L. Research on computational imaging spectroscopy[D]. Anhui: University of science and Technology of China. 2013. (in Chinese) [8] 闫歌, 许廷发, 马旭, 等. 动态测量的高光谱图像压缩感知[J]. 中国光学,2018,11(4):550-559. doi: 10.3788/co.20181104.0550YAN G, XU T F, MA X, et al. Hyperspectral image compression sensing based on dynamic measurement[J]. Chinese Optics, 2018, 11(4): 550-559. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/co.20181104.0550 [9] 韩庆, 王健, 熊峥, 等. 用于长波红外目标模拟器的 DMD衍射特性分析[J]. 红外激光与工程,2017,46(5).HAN Q, WANG J, XIONG J. et al. Diffraction characteristics analysis for DMD-based scene projectors in the long-wave infrared[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2017, 46(5). (in Chinese) [10] 吕伟振, 刘伟奇, 魏忠伦, 等. 基于DMD的高动态范围成像光学系统设计[J]. 红外与激光工程,2014,43(4).LV W ZH, LIU W Q, WEI ZH L, et al. Design of high dynamic range imaging optical system based on DMD[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2014, 43(4). (in Chinese) [11] 孙永强, 胡源, 王月旗, 等. 数字微镜器件在会聚成像光路中的像差分析[J]. 光学学报,2019,39(3).SUN Y Q, HU Y, WANG Y Q, et al. Analysis on Aberration of Digital Micromirror Device in Convergent Imaging[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2019, 39(3). (in Chinese) [12] 刑振冲.灵巧型长焦多波段共口径光学系统的研究[D]. 长春: 中国科学院长春光学精密机械与物理研究所. 2018.Xing ZH CH. Research on miniature telefocal multiband common aperture optical system[D]. Changchun: Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2018. (in Chinese) [13] 张天一, 朱永田, 候永辉, 等. LAMOST高分辨率光谱仪研制[J]. 中国光学,2019,12(1):148-155. doi: 10.3788/co.20191201.0148Zhang T Y, ZHU Y T, Hou Y H, et al. Construction of a LAMOST high resolution spectrograph[J]. Chinese Optics, 2019, 12(1): 148-155. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/co.20191201.0148 [14] 曹佃生, 林冠宇, 杨小虎, 等. 紫外双光栅光栅仪结构设计与波长精度分析[J]. 中国光学,2018,11(2):219-230.CAO T SH, LIN G Y, YANG X H, et al. Structure design and wavelength accuracy analysis of ultraviolet double grating spectrometer[J]. Chinese Optics, 2018, 11(2): 219-230. (in Chinese) [15] 潘君骅. 光学非球面的设计、加工与检验[M]. 苏州: 苏州大学出版社2004.PAN J H. Design, Fabrication and Testing of Optical Asphere[M]. Suzhou: Suzhou University Press, 2004. LUO X J, LIU H, ZHANG Y, et al. . Review of ground-based optical imaging techniques for dim GEO objects[J]. Chinese Optics, 2019, 12(4): 753-766. (in Chinese) [16] 孙武, 韩诚山, 吕恒毅, 等. 推扫式多光谱遥感相机动态范围拓展方法[J]. 中国光学,2019,12(4):906-913.SUN W, HAN CH SH, LV H Y, et al. Dynamic range extending method for push-broom multispectral remote sensing cameras[J]. Chinese Optics, 2019, 12(4): 906-913. (in Chinese) [17] 袁立银, 谢佳楠, 候佳, 等. 紧凑型红外成像光谱仪光学设计[J]. 红外激光与工程,2018,47(4).YUAN L Y, XIE J N, HOU J, et al. Optical design of compact infrared imaging spectrometer[J]. Ingrared and Laser Engineering, 2018, 47(4). (in Chinese) [18] 胡斌, 黄颖, 马永利, 等. 高分辨率红外成像仪五反无焦主系统设[J]. 红外与激光工程,2016,45(5).HU B, HUANG Y, MA Y L, et al. Design of five-mirror afocal principal system for high spatial resolution infrared imager[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2016, 45(5). (in Chinese) [19] 张营.长波红外高光谱成像仪光学技术研究[D]. 上海: 中国科学院上海技术物理研究所. 2016.ZHANG Y. Optical Technology of Long-wave Infrared Hyperspectral Imaging[D]. Shanghai: shanghai Institute of Technical Physics. 2016. [20] 韩军, 李珣, 吴玲玲, 等. 一种光栅型成像光谱仪光学系统设计[J]. 应用光学,2012,33(2):233-239.HAN J, LI X, WU L L. Optical system design of grating-based imaging spectrometer[J]. Journal of applied Optics, 2012, 33(2): 233-239. (in Chinese) -





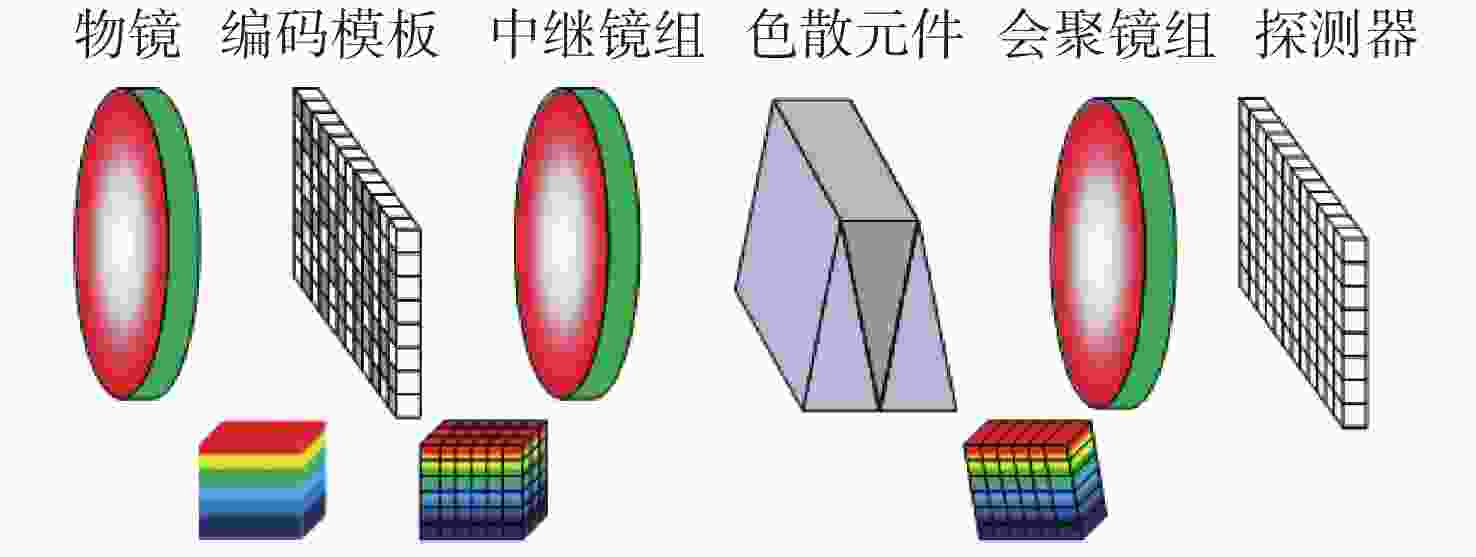
 下载:
下载: