Three-dimensional single-molecule localization microscopy imaging based on compressed sensing
-
摘要: 本文建立了一种三维压缩感知模型以实现对高密度荧光分子图像的快速三维定位。首先,根据荧光显微的三维点扩展函数成像理论,设计测量矩阵,并建立压缩感知模型。接着,对荧光显微成像过程进行了模拟,并采用凸优化方法(CVX)、正交匹配追踪(Orthogonal Matching Pursuit,OMP)算法和同伦算法对建立的压缩感知模型中模拟生成的图像进行了定位分析,分别从恢复率、定位精度、重构时间几方面进行了对比。最后,采用同伦算法对模拟的生物样品和实验室采集的细胞进行了三维定位,并获得了三维超分辨图像。对比结果表明:在重构密度和定位精度接近的情况下,同伦算法比CVX方法的重构速度快2个数量级。同伦算法较OMP算法的定位精度要高一倍。采用同伦算法来实现三维的超分辨荧光显微成像在节约计算时间、实现实时成像方面具有一定的意义。Abstract: In order to achieve fast three-dimensional localization of high-density fluorescent molecular images, a three-dimensional compressed sensing model was established and studied using the CVX method, the Orthogonal Matching Pursuit(OMP) algorithm and a homotopy algorithm. The models’ measurement matrix was then designed. Firstly, the system’s theory and design were both developed using the three-dimensional point-spread function imaging theory of fluorescence microscopy. Then, the process of fluorescence microscopic imaging was simulated, through which the images generated in the established compressed sensing model were analyzed using the CVX method, OMP algorithm and homotopy algorithm. The recall rate, localization accuracy and reconstruction time were compared. Finally, the simulated biological samples and the collected cells in the laboratory were analyzed using the homotopy algorithm, and thus three-dimensional super-resolution imaging was achieved. It can be seen from the comparative results that the homotopy algorithm is two orders of magnitude faster than the CVX method when the reconstruction density and localization accuracy have little deviation. The localization accuracy of the homotopy algorithm is twice higher than that of the OMP algorithm. The homotopy algorithm is meaningful for 3D super-resolution fluorescence microscopy imaging, which can save computing time and achieve real-time imaging.
-
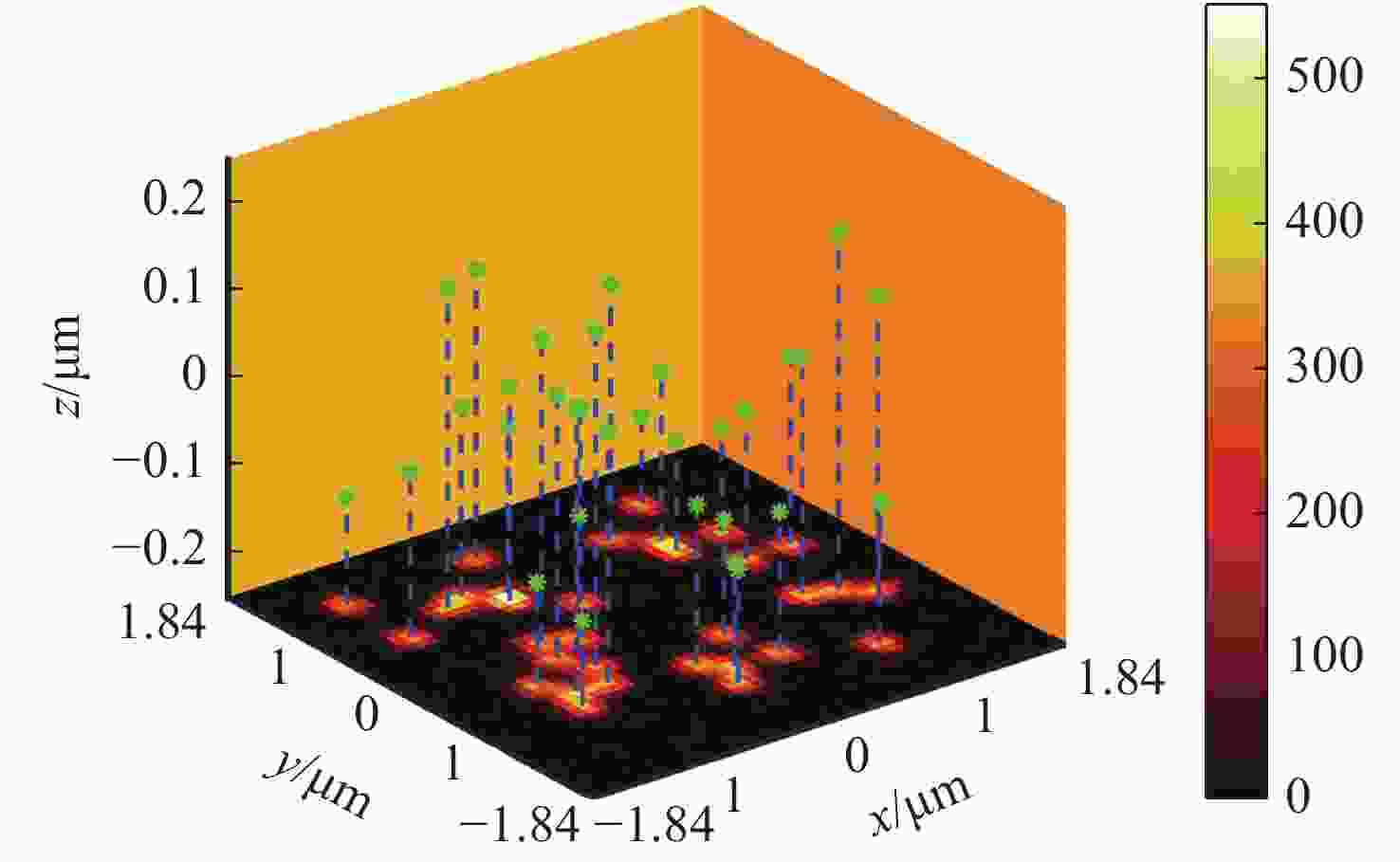
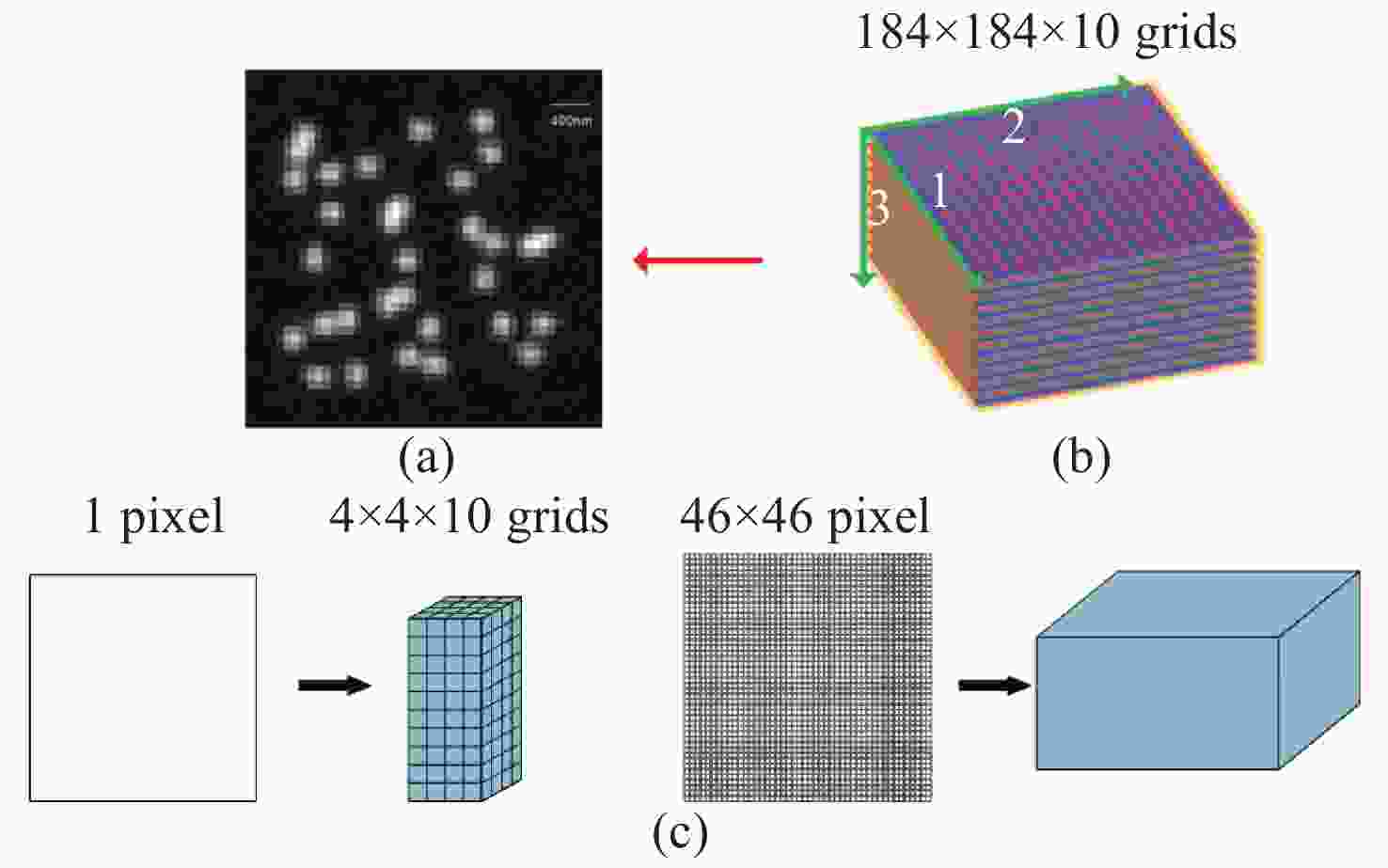
图 1 荧光图像对应样本进行三维网格细分图。 (a)模拟生成荧光分子成像;(b)荧光图像对应的荧光分子三维空间细分;(c)一个像素和整个图像对应网格细分数
Figure 1. 3D mesh subdivision process of fluorescence image corresponding sample. (a) Simulated fluorescence molecular image; (b) the three-dimensional subdivision of sample corresponding to fluorescent image; (c) the number of the subdivision corresponding to a pixel and the whole image
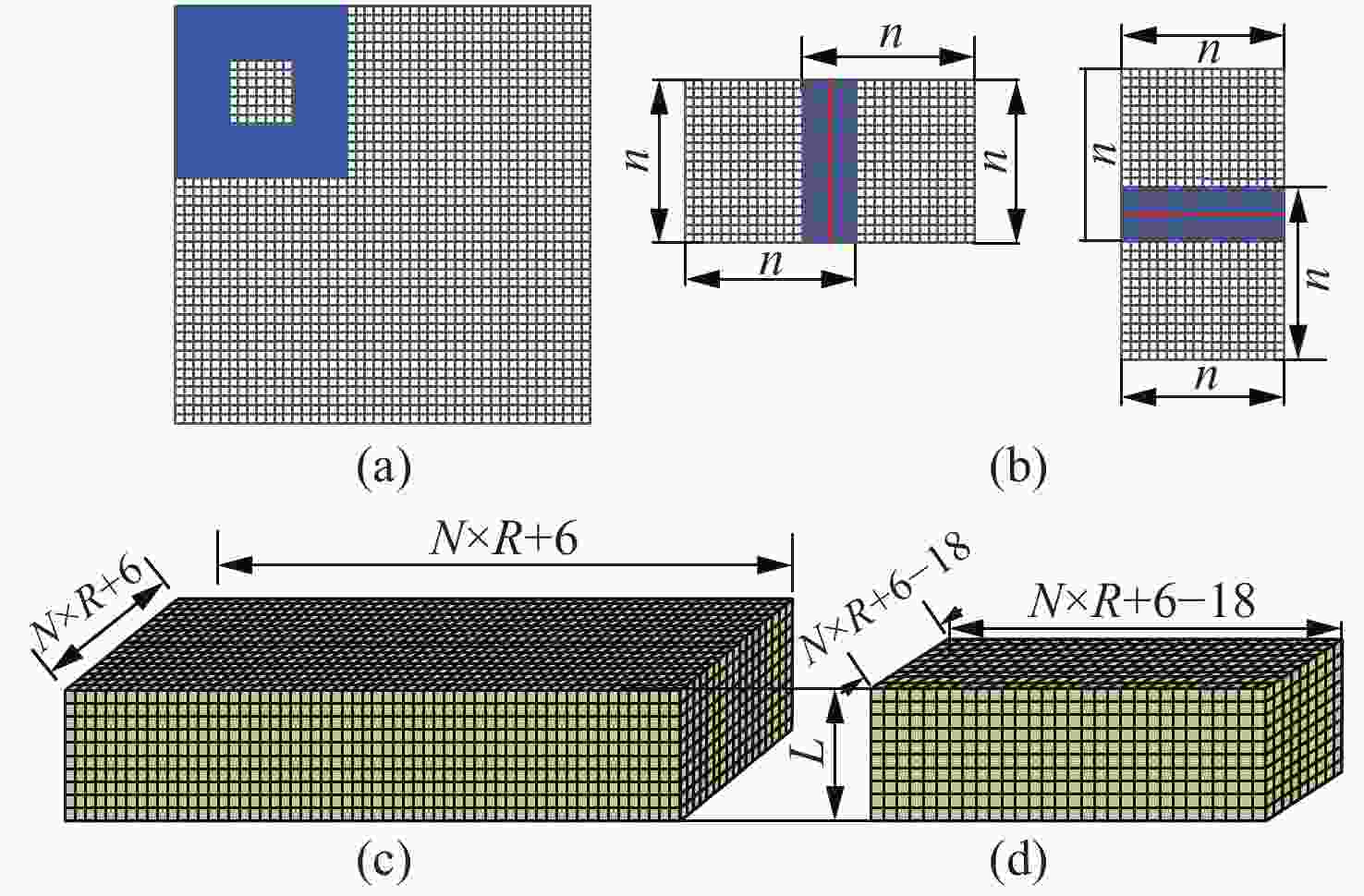
图 2 对整个图像进行分块处理。(a)从一帧图像里取一小块;(b)重合边缘;(c)对取出的小块图像进行边缘扩展;(d)对重构结果保留有效区域
Figure 2. The original image subdivided into smaller patches. (a) A small patch taken from one frame of image; (b) superposition edges; (c) edge expansion of the small block of image; (d) the retaining valid areas of reconstruction results
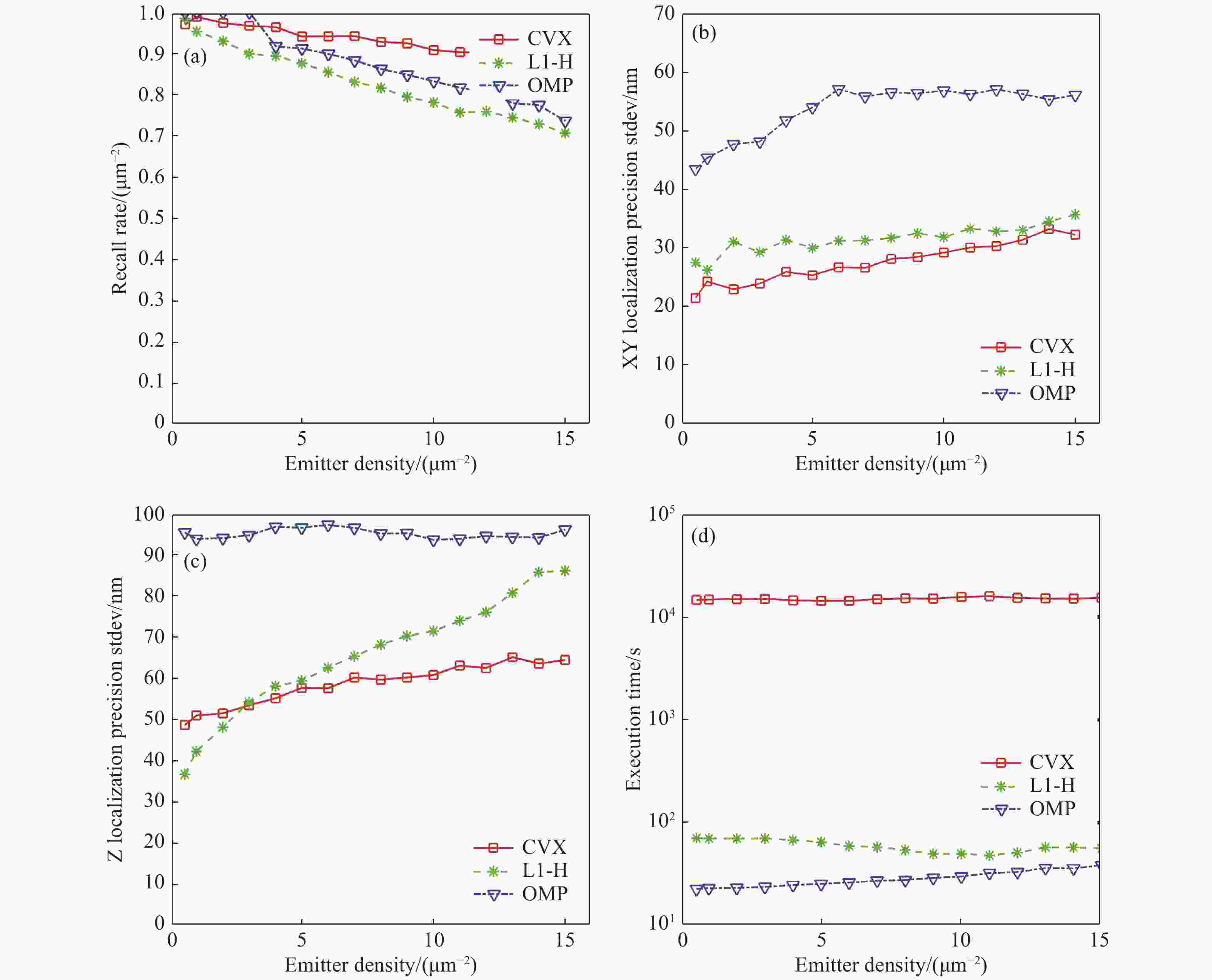
图 4 CVX,OMP和L1-H 三种算法对模拟生成的荧光分子图像的重构结果。(a)恢复率;(b)横向XY用标准差(Stdev)显示定位精度;(c)Z向用标准差显示定位精度;(d)算法运行时间
Figure 4. Reconstructed results of simulated fluorescence molecule image by three kinds of algorithms. (a) Recovery rate; (b) localization accuracy of horizontal XY shown with the standard deviation; (c) localization accuracy of axial Z shown with the standard deviation; (d) algorithm running time
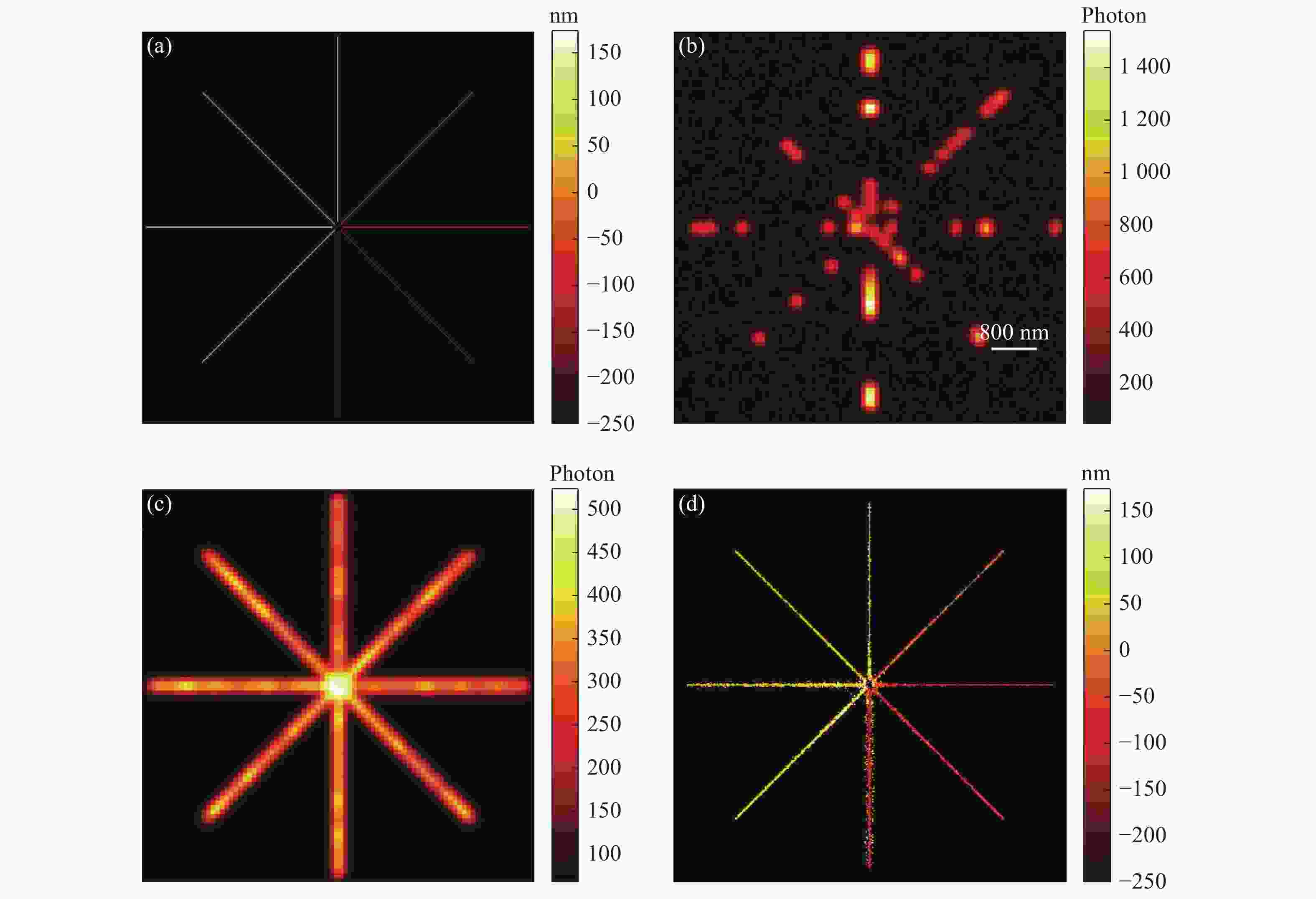
图 5 模拟生物实验的三维重构结果,图中的比例尺为800 nm。 (a)模拟生成随机分布的荧光分子累加结果,横向范围为6.9 μm × 6.9 μm,轴向范围为−200~200 nm;(b)随机生成一帧图像;(c)随机生成200幅图像进行累加的结果;(d)用算法分别对200帧图像进行重构定位出分子整合成的一张三维超分辨图像。
Figure 5. 3D reconstructed results of simulated bioexperiment (scale bar is 800 nm). (a) Accumulation results of randomly distributed fluorescent molecules with a transverse range of 6.9 μm×6.9 μm and an axial range from −200 nm to 200 nm. (b) A randomly generated frame of image. (c) Accumulation results of randomly generated 200 frames of images. (d) A 3D super-resolution image obtained by reconstructing 200 frames of images.
-
[1] 张颖, 朱爱美, 张迎秋, 等. 波长与能量色散复合式X射线荧光光谱技术测定海洋沉积物元素[J]. 分析化学,2019,47(7):1090-1097.ZHANG Y, ZHU A M, ZHANG Y Q, et al. Fast analysis of major and minor elements in marine sediments by wavelength and energy dispersive X-Ray fluorescence spectrometer[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2019, 47(7): 1090-1097. (in Chinese) [2] 王肖莉, 姚猛, 李引, 等. 新型比色荧光双通道探针用于硫化氢的检测[J]. 分析化学,2019,47(12):1915-1921.WANG X L, YAO M, LI Y, et al. A novel colorimetric and fluorescent probe for detection of hydrogen sulfide[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2019, 47(12): 1915-1921. (in Chinese) [3] 陈兆辉, 李媛媛, 韩娟, 等. 一种基于香豆素衍生物的铁离子水溶性荧光探针的合成及其应用[J]. 分析化学,2018,46(1):20-26. doi: 10.11895/j.issn.0253-3820.170114CHEN ZH H, LI Y Y, HAN J, et al. Synthesis and biological application of a water-soluble fluorescent probe based on coumarin derivatives for detection of ferric ion[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2018, 46(1): 20-26. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11895/j.issn.0253-3820.170114 [4] 杜晓辉, 刘霖, 张静, 等. 基于LBP纹理特征的白带显微图像中上皮细胞检测方法[J]. 液晶与显示,2019,34(9):871-878. doi: 10.3788/YJYXS20193409.0871DU X H, LIU L, ZHANG J, et al. Detection of epithelial cells in leucorrhea microscopic images based on LBP texture features[J]. Chinese Journal of Liquid Crystals and Displays, 2019, 34(9): 871-878. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/YJYXS20193409.0871 [5] 全廷伟, 曾绍群, 吕晓华. 超分辨成像中荧光分子定位算法性能比较[J]. 中国激光,2010,37(11):2714-2718. doi: 10.3788/CJL20103711.2714QUAN T W, ZENG S Q, LV X H. Comparison of algorithms for localization of single fluorescent molecule in super resolution imaging[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2010, 37(11): 2714-2718. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/CJL20103711.2714 [6] BETZIG E, PATTERSON GH, SOUGRAT R, et al. Imaging intracellular fluorescent proteins at nanometer resolution[J]. Science, 2006, 313(5793): 1642-1645. doi: 10.1126/science.1127344 [7] LOMMERSE P H M, BLAB G A, COGNET L, et al. Single-molecule imaging of the H-ras membrane-anchor reveals domains in the cytoplasmic leaflet of the cell membrane[J]. Biophysical Journal, 2004, 86(1): 609-616. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(04)74139-9 [8] JONES S A, SHIM S H, HE J, et al. Fast, three-dimensional super-resolution imaging of live cells[J]. Nature Methods, 2011, 8(6): 499-505. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.1605 [9] HUANG B, WANG W Q, BATES M, et al. Three-dimensional super-resolution imaging by stochastic optical reconstruction microscopy[J]. Science, 2008, 319(5864): 810-813. doi: 10.1126/science.1153529 [10] HOLTZER L, MECKEL T, SCHMIDT T. Nanometric three-dimensional tracking of individual quantum dots in cells[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2007, 90(5): 053902. doi: 10.1063/1.2437066 [11] PAVANI S R P, THOMPSON M A, BITEEN J S, et al. Three-dimensional, single-molecule fluorescence imaging beyond the diffraction limit by using a double-helix point spread function[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2009, 106(9): 2995-2999. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0900245106 [12] 李恒, 于斌, 陈丹妮, 等. 高效双螺旋点扩展函数相位片的设计与实验研究[J]. 物理学报,2013,62(12):124201. doi: 10.7498/aps.62.124201LI H, YU B, CHEN D N, et al. Design and experimental demonstration of high-efficiency double-helix point spread function phase plate[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2013, 62(12): 124201. (in Chinese) doi: 10.7498/aps.62.124201 [13] 武兴睿. 基于PSF重构和改进的最大后验估计的自适应光学图像复原算法[J]. 液晶与显示,2019,34(9):921-927. doi: 10.3788/YJYXS20193409.0921WU X R. Adaptive optical image restoration method based on PSF reconstruction and improved Maximum A Posteriori estimation[J]. Chinese Journal of Liquid Crystals and Displays, 2019, 34(9): 921-927. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/YJYXS20193409.0921 [14] RAM S, PRABHAT P, WARD E S, et al. Improved single particle localization accuracy with dual objective multifocal plane microscopy[J]. Optics Express, 2009, 17(8): 6881-6898. doi: 10.1364/OE.17.006881 [15] SHTENGEL G, GALBRAITH J A, GALBRAITH C G, et al. Interferometric fluorescent super-resolution microscopy resolves 3D cellular ultrastructure[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2009, 106(9): 3125-3130. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0813131106 [16] BABCOCK H, SIGAL Y M, ZHUANG X W. A high-density 3D localization algorithm for stochastic optical reconstruction microscopy[J]. Optical Nanoscopy, 2012, 1(1): 6. doi: 10.1186/2192-2853-1-6 [17] 谢斌, 黄安, 黄辉. 本征图像分解的稀疏表示彩色图像去噪算法[J]. 液晶与显示,2019,34(11):1104-1114. doi: 10.3788/YJYXS20193411.1104XIE B, HUANG A, HUANG H. Colorimage denoising algorithm based on intrinsic image decomposition and sparse representation[J]. Chinese Journal of Liquid Crystals and Displays, 2019, 34(11): 1104-1114. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/YJYXS20193411.1104 [18] BARSIC A, GROVER G, PIESTUN R. Three-dimensional super-resolution and localization of dense clusters of single molecules[J]. Scientific Reports, 2015, 4: 5388. doi: 10.1038/srep05388 [19] GU L S, SHENG Y, CHEN Y, et al. High-density 3D single molecular analysis based on compressed sensing[J]. Biophysical Journal, 2014, 106(11): 2443-2449. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2014.04.021 [20] ZHANG S W, CHEN D N, NIU H B. 3D localization of high particle density images using sparse recovery[J]. Applied Optics, 2015, 54(26): 7859-7864. doi: 10.1364/AO.54.007859 [21] SHUANG B, WANG W X, SHEN H, et al. Generalized recovery algorithm for 3D super-resolution microscopy using rotating point spread functions[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6: 30826. doi: 10.1038/srep30826 [22] 张赛文. 基于压缩感知的单分子定位显微超分辨图像重建方法研究[D]. 深圳: 深圳大学, 2018.ZHANG S W. Study on super-resolution image reconstruction algorithms based on compressed sensing for single-molecule localization microscopy[D]. Shenzhen: Shenzhen University, 2018. (in Chinese) [23] WADA A, OHTANI T, MIYAMOTO Y, et al. Propagation analysis of the Laguerre-Gaussian beam with astigmatism[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America A, 2005, 22(12): 2746-2755. doi: 10.1364/JOSAA.22.002746 [24] ZHU L, ZHANG W, ELNATAN D, et al. Faster STORM using compressed sensing[J]. Nature Methods, 2012, 9(7): 721-723. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.1978 [25] 张赛文, 于斌, 陈丹妮, 等. 基于压缩感知的高密度分子定位算法比较[J]. 中国激光,2018,45(3):0307014. doi: 10.3788/CJL201845.0307014ZHANG S W, YU B, CHEN D N. Comparison of algorithms of high-density molecule localization based on compressed sensing[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2018, 45(3): 0307014. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/CJL201845.0307014 [26] BABCOCK H P, MOFFITT J R, CAO Y L, et al. Fast compressed sensing analysis for super-resolution imaging using L1-homotopy[J]. Optics Express, 2013, 21(23): 28583-28596. doi: 10.1364/OE.21.028583 [27] HUGELIER S, DE ROOI J J, BERNEX R, et al. Sparse deconvolution of high-density super-resolution images[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6: 21413. doi: 10.1038/srep21413 -





 下载:
下载: