Orthogonal luminescence properties of a single rare-earth activator ion doped upconversion nanoparticles
doi: 10.37188/CO.2020-0020
-
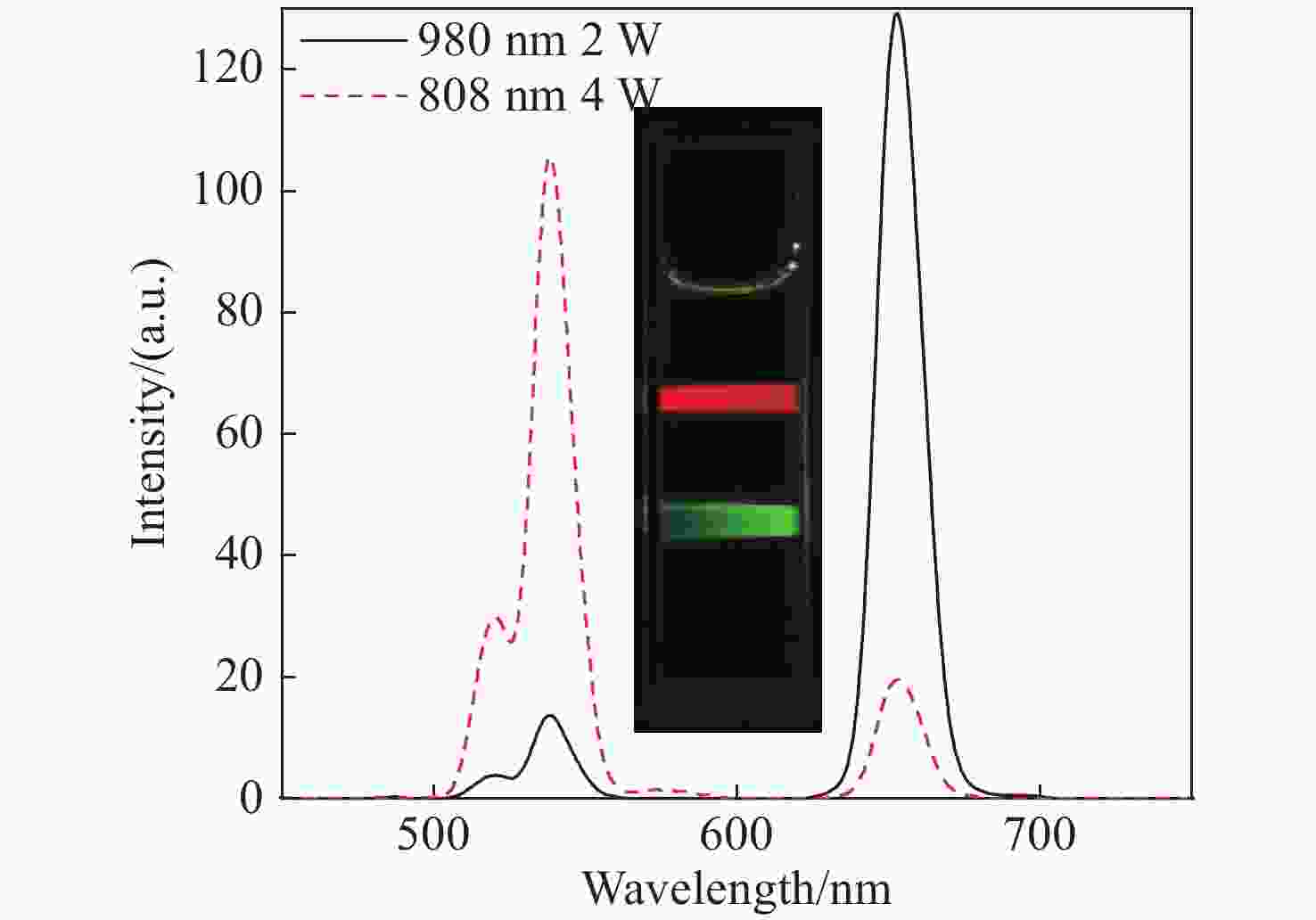
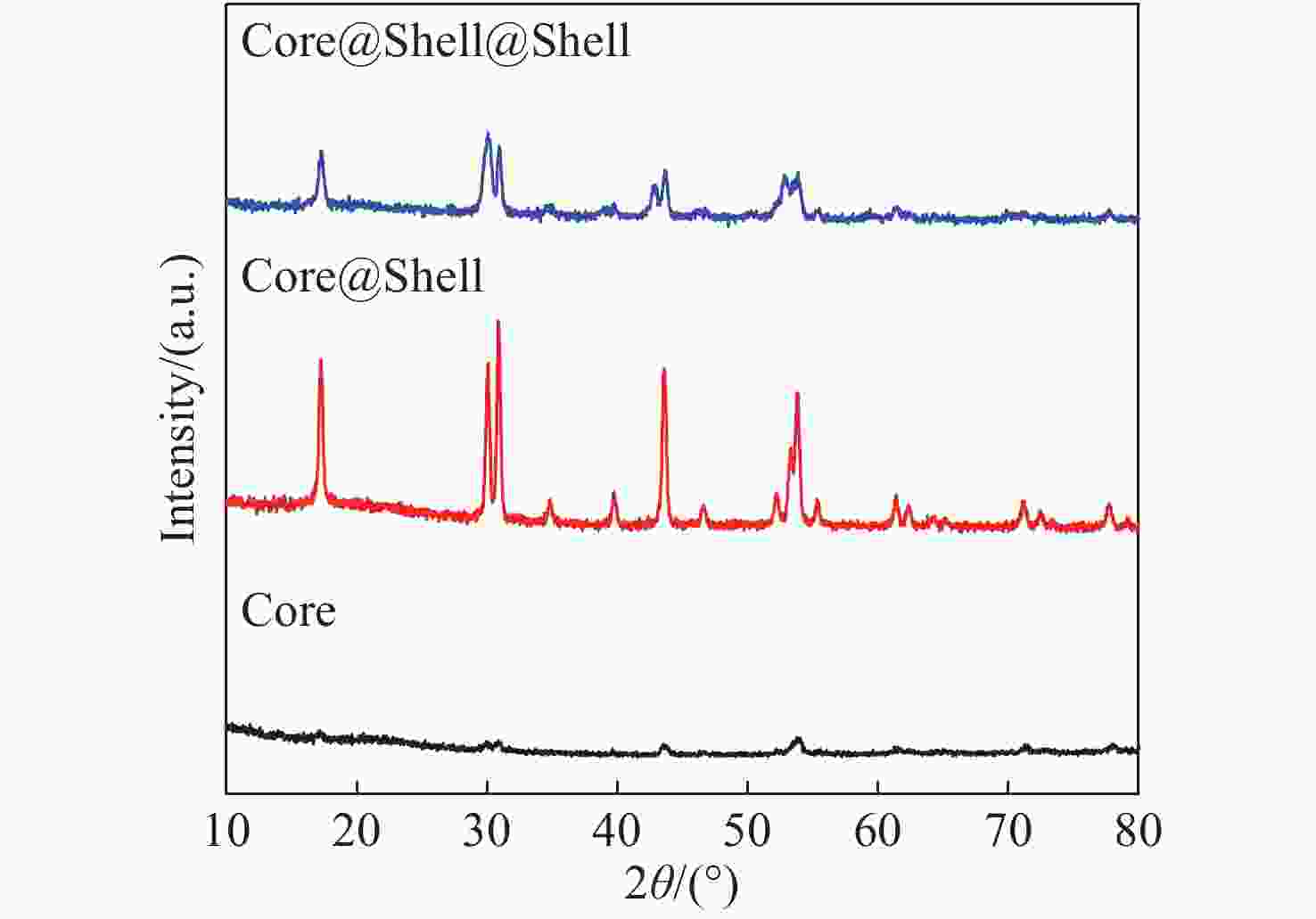
摘要: 上转换发光纳米材料由于其特有的光学性质而一直备受关注,但常见的上转换发光纳米材料多为单色发光,为了实现上转换多色正交发光,同时避免多种掺杂剂离子的合成复杂性以及相互间的干扰性,利用Er3+的2H11/2,4S3/2→4I15/2能级跃迁产生的绿色发光和4F9/2→4I15/2能级跃迁产生的红色发光,设计出由Er3+单个激活剂离子掺杂的双激发上转换纳米颗粒。通过热分解法一步步合成出NaErF4:Yb(19.5%)/Tm(0.5%)@NaYF4:Yb(10%)@NaNdF4:Yb(10%)三层结构的上转换纳米颗粒。此方法合成出来的颗粒大小均一、结构稳定、分散性好。该双激发纳米颗粒能够在980 nm和808 nm的激发光下实现红色和绿色的正交发射光,且其单独发光不受影响。在980 nm激发下,红色光中650 nm处的发射峰强度大约能达到540 nm处发射峰的9.46倍;在808 nm激发下,绿色光中540 nm处发射峰强度大约能达到650 nm处发射峰强度的5.39倍。Abstract: Upconversion luminescence nanomaterials have attracted widespread attention owing to their special optical properties, while most of them emit single color luminescence. In order to achieve multicolor orthogonal upconversion luminescence and avoid the synthesis complexity and interference between multiple dopant ions, herein, we reported a novel orthogonal emissive upconversion nanoparticle, NaErF4:Yb(19.5%)/Tm(0.5%)@NaYF4:Yb(10%)@NaNdF4:Yb(10%), through thermal decomposition strategy step by step. This novel nanoparticle can give out green luminescence and red luminescence by the energy level transition of Er3+ from 2H11/2,4S3/2→4I15/2 and 4F9/2→4I15/2 under the excitation light of 980 nm and 808 nm, respectively. The particles demonstrated uniform size, stable structure and excellent dispersibility. Under the excitation of 980 nm, the emission intensity at 650 nm of red luminescence was approximately 9.46 times more than the emission intensity at 540 nm. Under the excitation of 808 nm, the emission intensity at 540 nm of green luminescence was about 5.39 times more than the emission intensity at 650 nm.
-
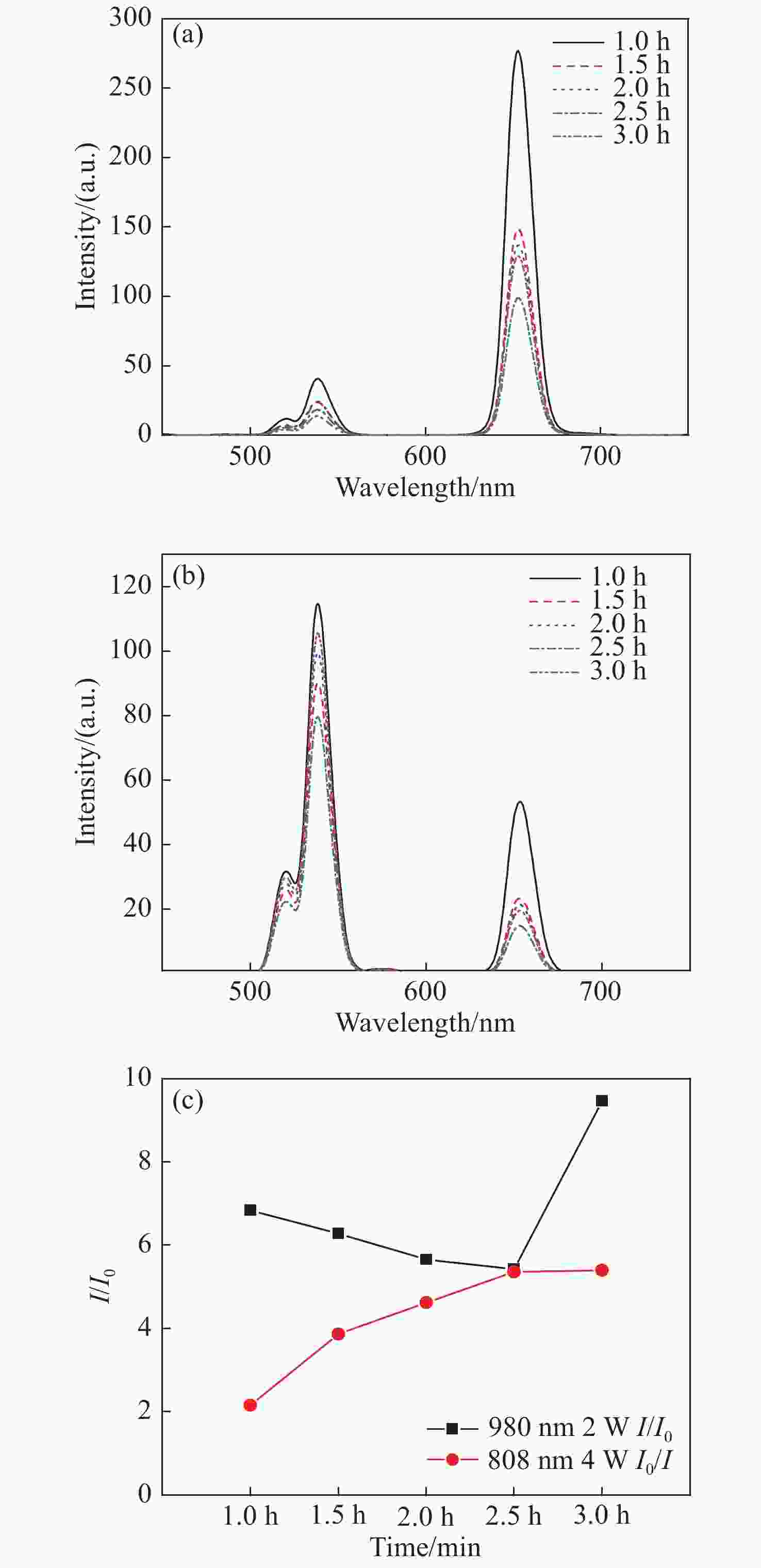
图 4 在(a)980 nm和(b)808 nm激光激发下的纳米颗粒荧光光谱变化图。(c)不同激发波长下纳米颗粒随时间变化的荧光比率的变化图(I和I0分别表示在650 nm和540 nm处发光峰强度)。
Figure 4. The luminescence spectrum variations of NPs under (a) 980 nm excitation and (b) 808 nm excitation . (c) The luminescence ratio variations of NPs with different synthesis time at different excitation wavelengths (I and I0 represent the luminescence peak intensities at 650 nm and 540 nm, respectively).
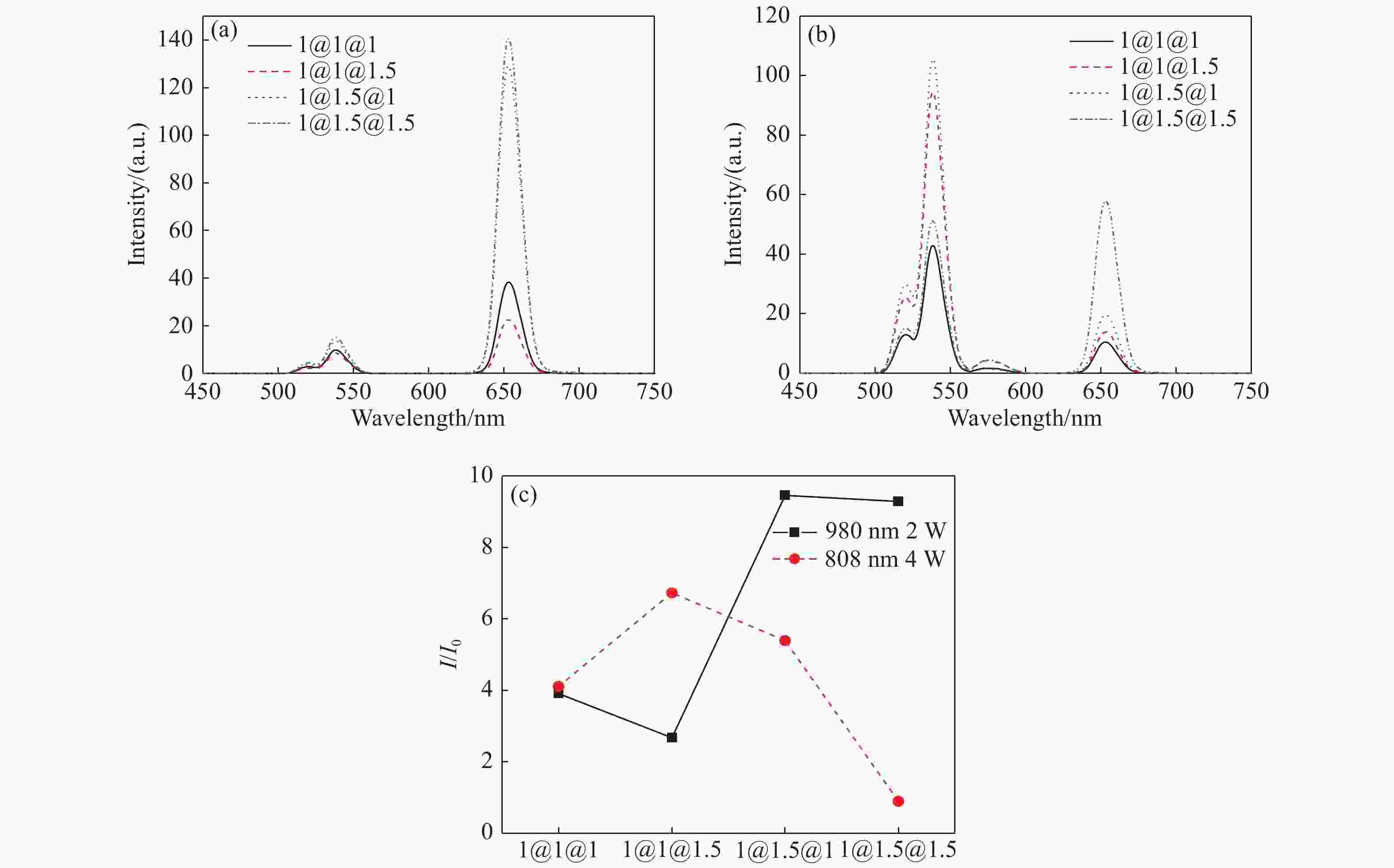
图 5 在(a)980 nm和(b)808 nm激发下的中间层和外层不同摩尔量的纳米颗粒荧光光谱变化图。(c)对应的荧光比率的变化图(I和I0分别表示在650 nm和540 nm处的发光峰强度)。
Figure 5. The luminescence spectrum variations of NPs with different molar weights in the middle and outer layers under (a) 980 nm excitation, and (b) 808 nm excitation. (c) The luminescence ratio variations of the corresponding NPs under different excitation wavelengths (I and I0 represent the luminescence intensities at 650 nm and 540 nm, respectively).
-
HUA J T, CHEN B J, SUN J SH, et al. Introduction to up-conversion luminescence of rare earth doped materials[J]. Chinese Journal of Optics and Applied Optics, 2010, 3(4): 301-309. (in Chinese) CHEN J, MENG W CH, LING X, et al. Multicolor fluorescent emission of graphene oxide and its application in fluorescence imaging[J]. Chinese Optics, 2018, 11(3): 377-391. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/co.20181103.0377 LIU Y CH, LI Y Y, PENG Y K, et al. Non-destructive rapid detection of rice amylose content by near-infrared diffuse transmission optical compensation method[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2019, 47(5): 785-793. (in Chinese) LIU J H, WANG L, ZHANG T Q, et al. Facile synthesis of biocompatible Fe3O4-based nanoparticles for pH-responsive dual-model magnetic resonance imaging-guided tumour eradication by photothermal therapy[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2019, 47(5): 678-685. (in Chinese) doi: 10.1016/S1872-2040(19)61158-8 WANG ZH R, QI F P, LUO M, et al. A turn-on near-infrared fluorescent probe for determination of Fe3+ and antioxidant capacity of dark teas[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2019, 47(1): 112-118. (in Chinese) FOWLEY C, NOMIKOU N, MCHALE A P, et al. Extending the tissue penetration capability of conventional photosensitisers: a carbon quantum dot–protoporphyrin IX conjugate for use in two-photon excited photodynamic therapy[J]. Chemical Communications, 2013, 49(79): 8934-8936. doi: 10.1039/c3cc45181j LI J, LIU L, GUO H Q, et al. An upconversion fluorescent method for rapid detection of perfluorooctane sulfonate in water samples based on fluorine-fluorine interaction[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2019, 47(3): 380-387. (in Chinese) SHAO SH, DING B B, ZHU ZH L, et al. Preparation of water-soluble up-conversion nano-drug by host-guest chemistry and its application in tumor diagnosis and treatment[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2019, 47(6): 823-831. (in Chinese) LIU X L, GUO Y Y, MI X Y, et al. Synthesis and luminescence properties of Er3+ doped and Er3+-Yb3+ co-doped Ca12Al14O32F2[J]. Chinese Journal of Luminescence, 2019, 40(5): 589-594. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/fgxb20194005.0589 SHIKHA S, SALAFI T, CHENG J T, et al. Versatile design and synthesis of nano-barcodes[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2017, 46(22): 7054-7093. doi: 10.1039/C7CS00271H SUN T Y, AI F J, ZHU G Y, et al. Upconversion in nanostructured materials: from optical tuning to biomedical applications[J]. Chemistry-An Asian Journal, 2018, 13(4): 373-385. doi: 10.1002/asia.201701660 DENG Y J, NIU CH H. Up-conversion luminescence properties of Ho3+/Yb3+ co-doped glass ceramic[J]. Chinese Journal of Luminescence, 2019, 40(7): 857-864. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/fgxb20194007.0857 CHENG L. Upconversion nanoparticles used in Nanomedicine[D]. Suzhou: Soochow University, 2012. (in Chinese) LI X X, LI Y Q, WANG X, et al. Highly sensitive down-conversion optical temperature-measurement material: NaGd(WO4)2: Yb3+/Er3+[J]. Chinese Optics, 2019, 12(3): 596-605. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/co.20191203.0596 YANG R B, LI Y, XU N, et al. Effects of alkali metal ions on upconversion of rare earth doped fluorides[J]. Chinese Journal of Luminescence, 2019, 40(1): 1-8. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/fgxb20194001.0001 ZHENG K ZH, QIN W P. Upconversion luminescence of Mn2+ in Yb3+-Mn2+ codoped CaF2 materials[J]. Chinese Journal of Luminescence, 2019, 40(11): 1321-1326. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/fgxb20194011.1321 WEN SH H, ZHOU J J, ZHENG K ZH, et al. Advances in highly doped upconversion nanoparticles[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9: 2415. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-04813-5 XIE X J, LI ZH J, ZHANG Y W, et al. Emerging ≈800 nm excited lanthanide-doped upconversion nanoparticles[J]. Small, 2017, 13(6): 1602843. doi: 10.1002/smll.201602843 WANG L X, TUO J, YE Y, et al. Preparation and luminescence properties of Li+, Zn2+, Mg2+ doped Lu2O3: Er3+ phosphors[J]. Chinese Optics, 2019, 12(1): 112-121. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/co.20191201.0112 DENG R R, QIN F, CHEN R F, et al. Temporal full-colour tuning through non-steady-state upconversion[J]. Nature Nanotechnology, 2015, 10(2): 237-242. ZHOU B, SHI B Y, JIN D Y, et al. Controlling upconversion nanocrystals for emerging applications[J]. Nature Nanotechnology, 2015, 10(11): 924-936. doi: 10.1038/nnano.2015.251 LAI J P, ZHANG Y X, PASQUALE N, et al. An upconversion nanoparticle with orthogonal emissions using dual NIR excitations for controlled two-way photoswitching[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2014, 53(52): 14419-14423. doi: 10.1002/anie.201408219 LI X M, GUO ZH ZH, ZHAO T C, et al. Filtration shell mediated power density independent orthogonal excitations-emissions upconversion luminescence[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2016, 55(7): 2464-2469. doi: 10.1002/anie.201510609 DONG H, SUN L D, FENG W, et al. Versatile spectral and lifetime multiplexing nanoplatform with excitation orthogonalized upconversion luminescence[J]. ACS Nano, 2017, 11(3): 3289-3297. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.7b00559 WEN H L, ZHU H, CHEN X, et al. Upconverting near-infrared light through energy management in core-shell-shell nanoparticles[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2013, 52(50): 13419-13423. doi: 10.1002/anie.201306811 CHEN X, PENG D F, JU Q, et al. Photon upconversion in core-shell nanoparticles[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2015, 44(6): 1318-1330. doi: 10.1039/C4CS00151F MEI Q S, BANSAL A, JAYAKUMAR M K G, et al. Manipulating energy migration within single lanthanide activator for switchable upconversion emissions towards bidirectional photoactivation[J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10(1): 4416. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-12374-4 -





 下载:
下载: