Identification of opto-electronic fine tracking systems based on an improved differential evolution algorithm
-
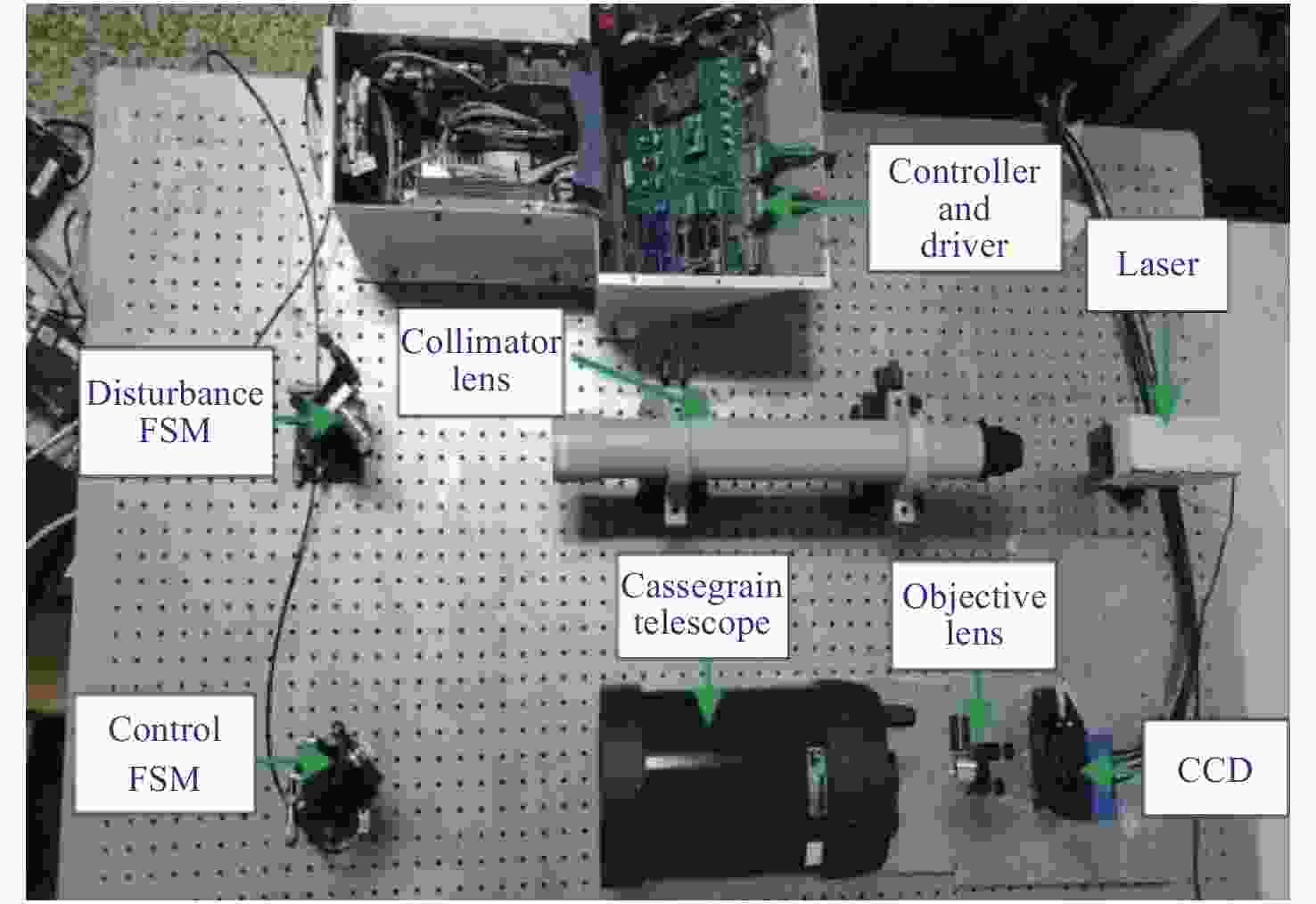
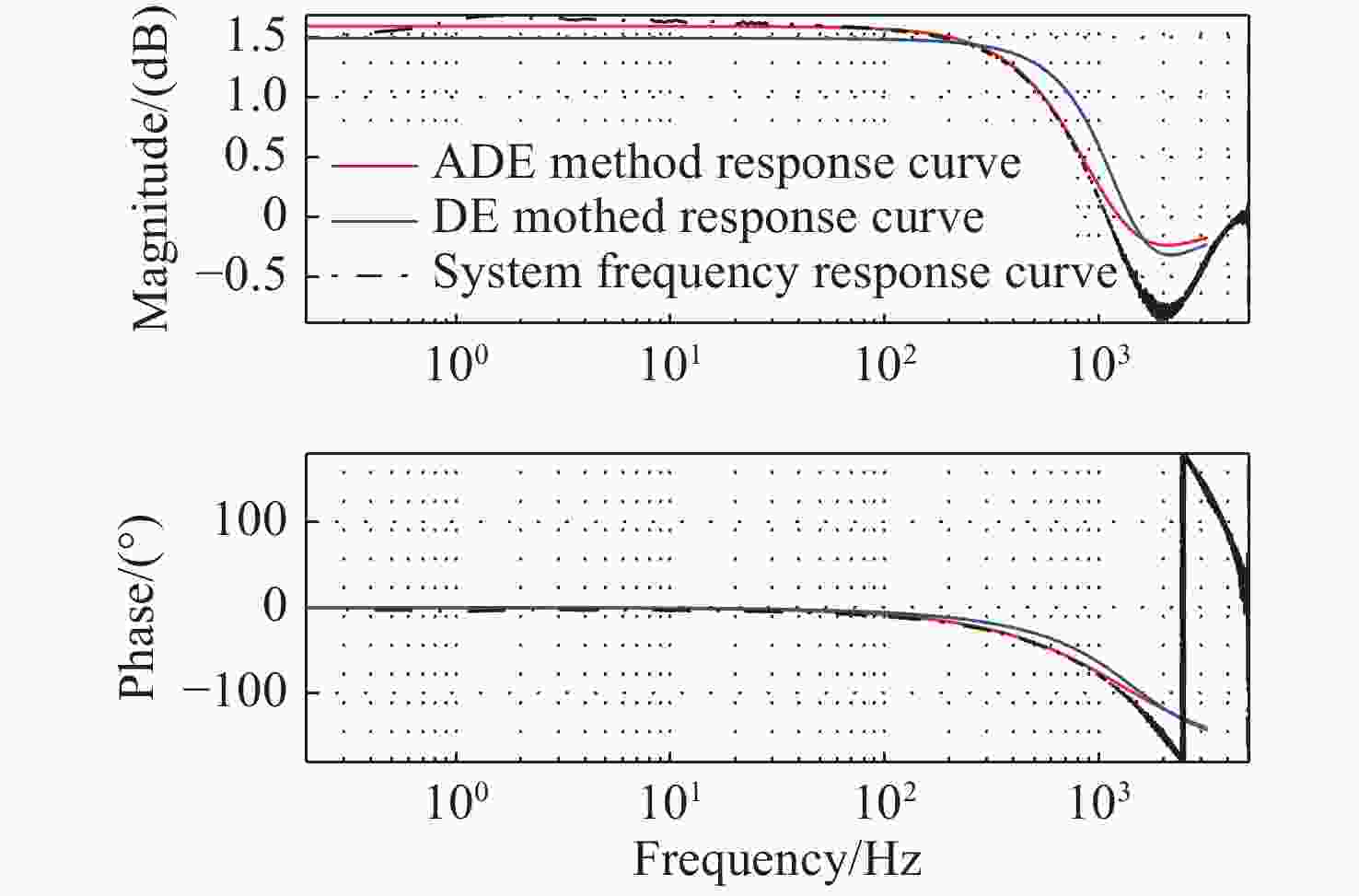
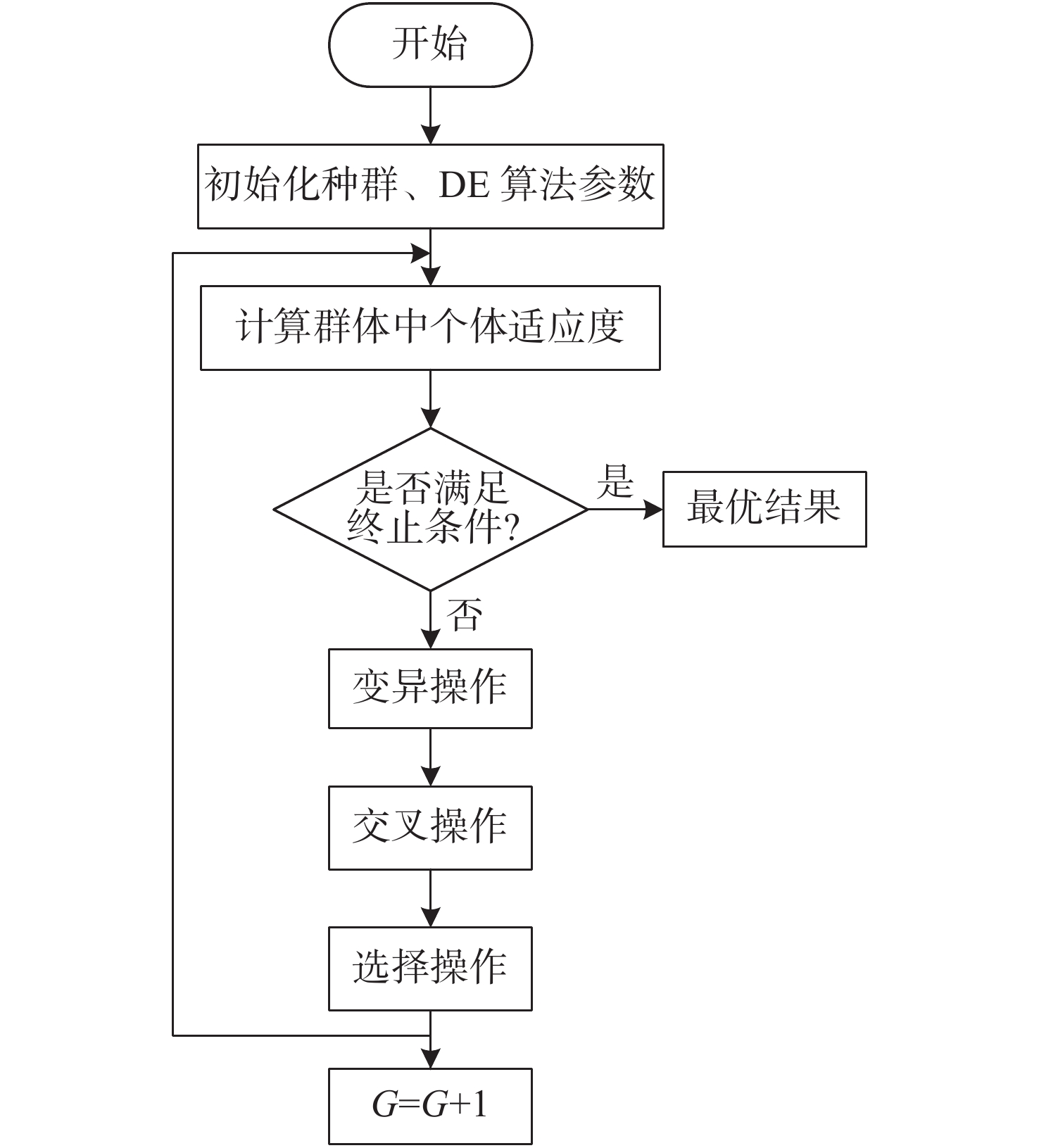
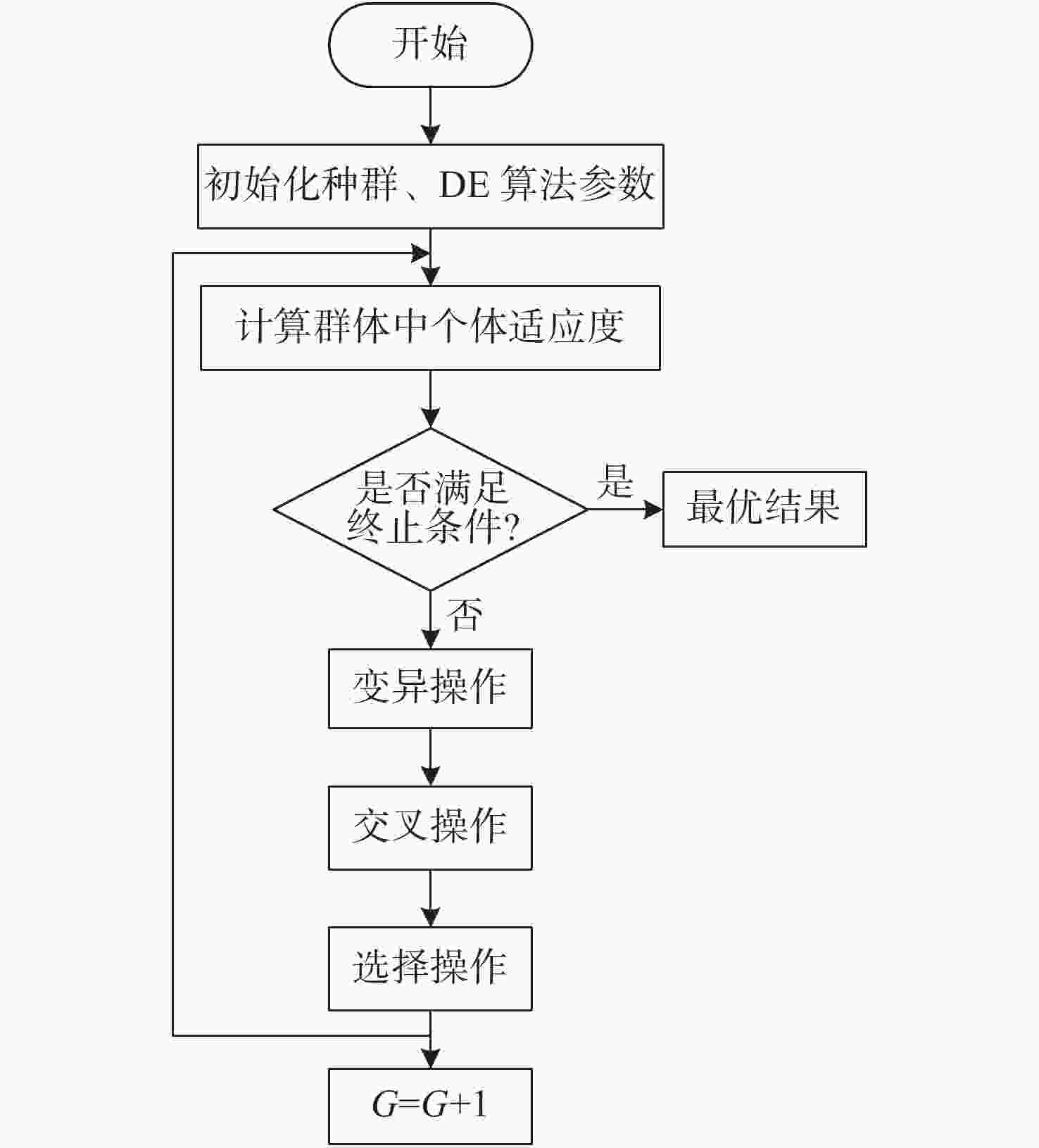
摘要: 针对激光通信精跟踪系统,提出一种基于改进差分进化算法的辨识方法。首先,介绍了标准差分进化算法的基本原理和算法流程,基于此提出一种改进的差分进化算法,并对算法中的参数进行优化;其次,通过扫频信号激励精跟踪系统分析被控对象的动态特性,同时采集CCD相机的位置反馈信息;最后,根据实验数据采用差分进化算法对系统进行辨识,获得精跟踪系统的控制模型。实验结果表明:采用改进差分进化算法后,辨识方法的收敛速度更快,辨识结果准确,该方法在光电跟踪领域有一定工程价值。Abstract: In this paper, an identification method based on an improved differential evolution algorithm is proposed for laser communication fine tracking systems. Firstly, the basic principle and calculation steps of the traditional differential evolution algorithm are introduced. Based on this, an improved algorithm is proposed, and the algorithm’s parameters are optimized . Then, the dynamic characteristics of a controlled object in the fine tracking system are simulated by a sweep signal, and the positional feed back information of the camera is collected. Finally, based on the experimental data, the differential evolution algorithm is used to identify the system, and the control model of the fine tracking system is obtained. The experimental results show that the improved differential evolution algorithm has faster convergence speed and accurate identification results. In general, this method has engineering value in the field of optoelectronic tracking.
-
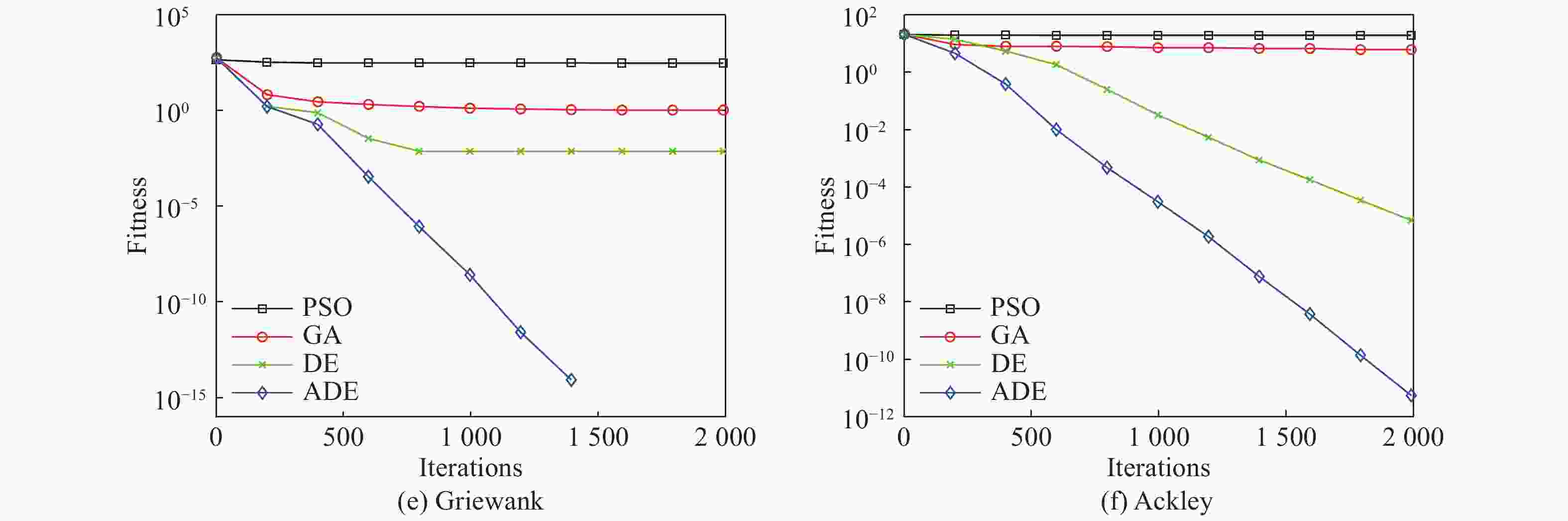
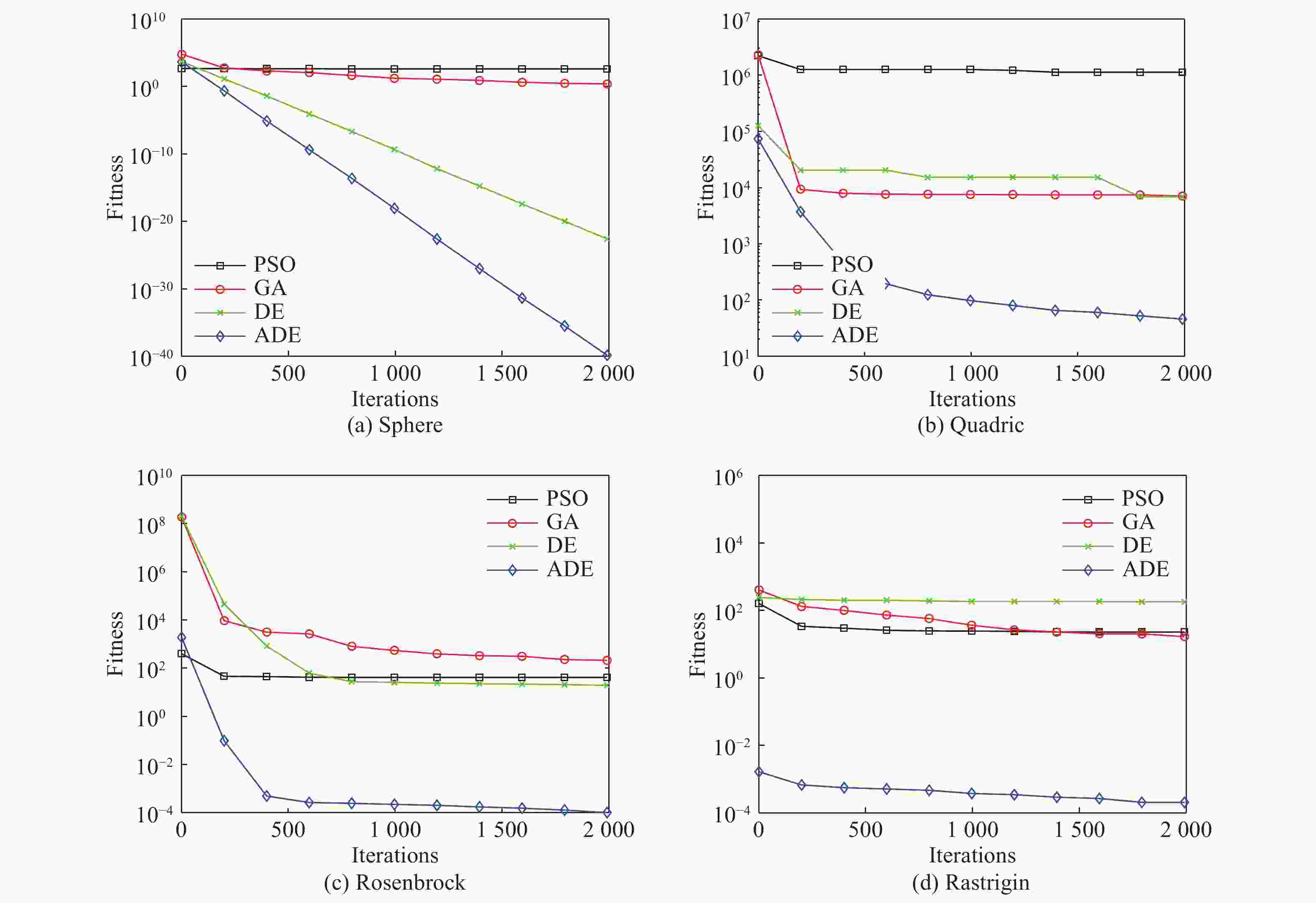
表 1 6个Benchmark函数
Table 1. Six kinds of Benchmark test functions
函数 公式 最优解 取值范围 Sphere $\displaystyle\sum\limits_{i = 1}^D { {x_i}^2}$ 0 [−100, 100] Quadric ${\displaystyle\sum\limits_{i = 1}^D {\left( {\sum\limits_{j = 1}^i { {x_i} } } \right)} ^2}$ 0 [−100, 100] Rosenbrock $\displaystyle\sum\limits_{i = 1}^D {\left[ {100{ {\left( {x{}_{i + 1} - {x_i}^2} \right)}^2} + { {\left( {1 - {x_i} } \right)}^2} } \right]}$ 0 [−30, 30] Rastrigin $\displaystyle\sum\limits_{i = 1}^D {\left[ { {x_i}^2 - 10\cos \left( {2{\text{π}} {x_i} } \right) + 10} \right]}$ 0 [−5.12, 5.12] Griewank $\dfrac{1}{ {4\;000} }\displaystyle\sum\limits_{i = 1}^D { {x_i}^2 - \mathop \prod \limits_{i = 1}^D } \cos \left( {\frac{ { {x_i} } }{ {\sqrt i } } } \right) + 1$ 0 [−600, 600] Ackley $- 20\exp \left( { - 0.2\sqrt {\dfrac{1}{n}\displaystyle\sum\limits_{i = 1}^D { {x_i}^2} } } \right) - \exp \left( {\dfrac{1}{D}\displaystyle\sum\limits_{i = 1}^D {\cos \left( {2{\text{π}} {x_i} } \right) + 20 + e} } \right)$ 0 [−32, 32] 表 2 算法精度测试结果
Table 2. Accuracy of the algorithm’s test results
函数 PSO GA DE ADE Mean Std Mean Std Mean Std Mean Std Sphere 48.9 25.7 0.25 0.13 4.82e-22 8.78e-23 3.9e-40 5.9e-41 Quadric 3.56e+6 3.05e+6 7.7e+4 3.23e+4 7.3e+4 8.62e+3 5.31e-3 3.42e-3 Rosenbrock 88.7 55.6 3.36e+3 1.32e+3 78.3 36.7 1.65e-4 1.23e-4 Rastrigin 9.75 6.96 8.65 3.94 4.36e+2 2.32e+2 2.32e-3 6.78e-4 Griewank 76.5 36.4 1.36 0.61 3.36e-3 1.32e-3 4.56e-15 6.23e-15 Ackley 60.2 40.5 46.6 33.8 8.65e-5 5.41e-5 1.65e-12 5.65e-13 表 3 两种算法的辨识结果比较
Table 3. Comparison of identification results by using two algorithms
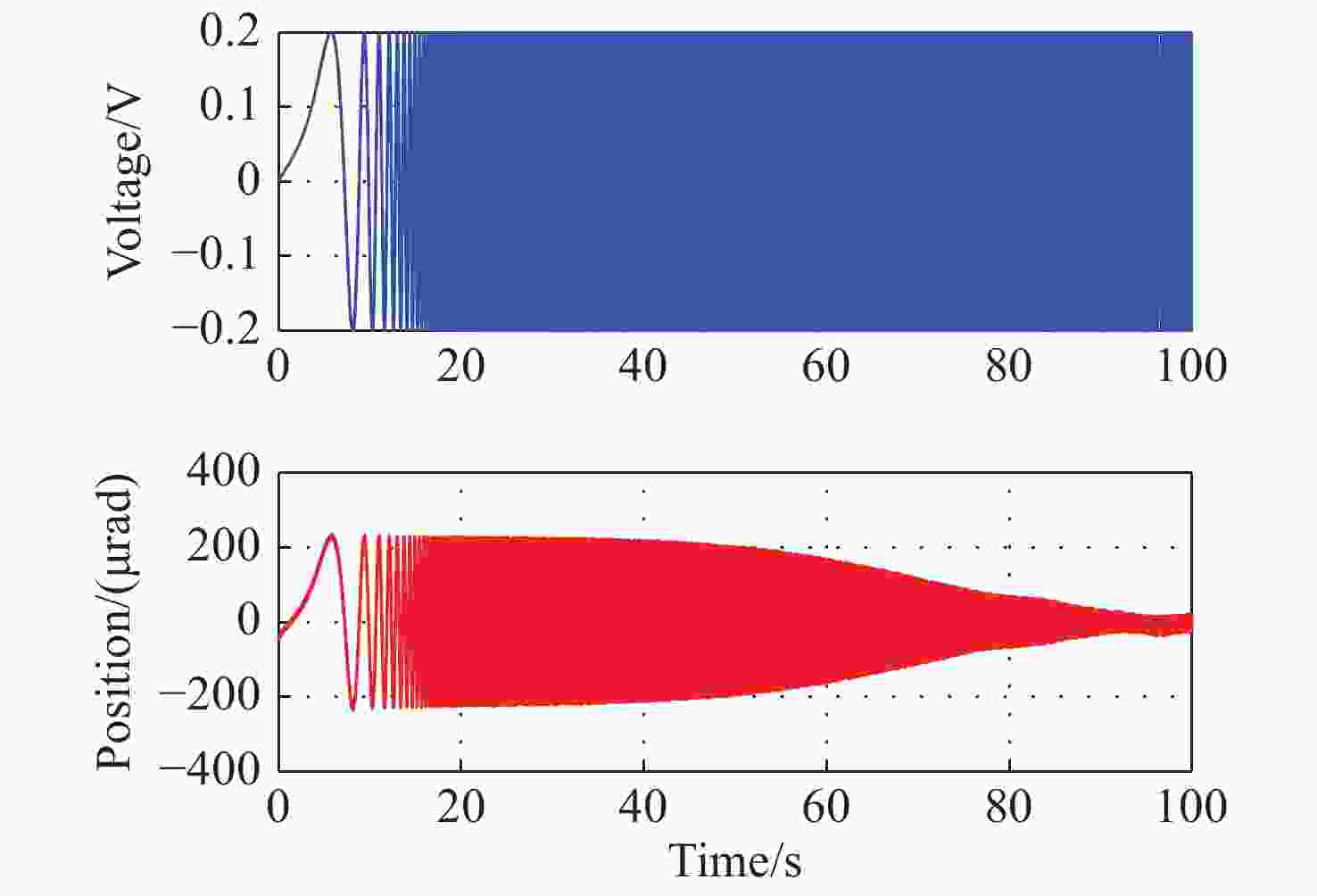
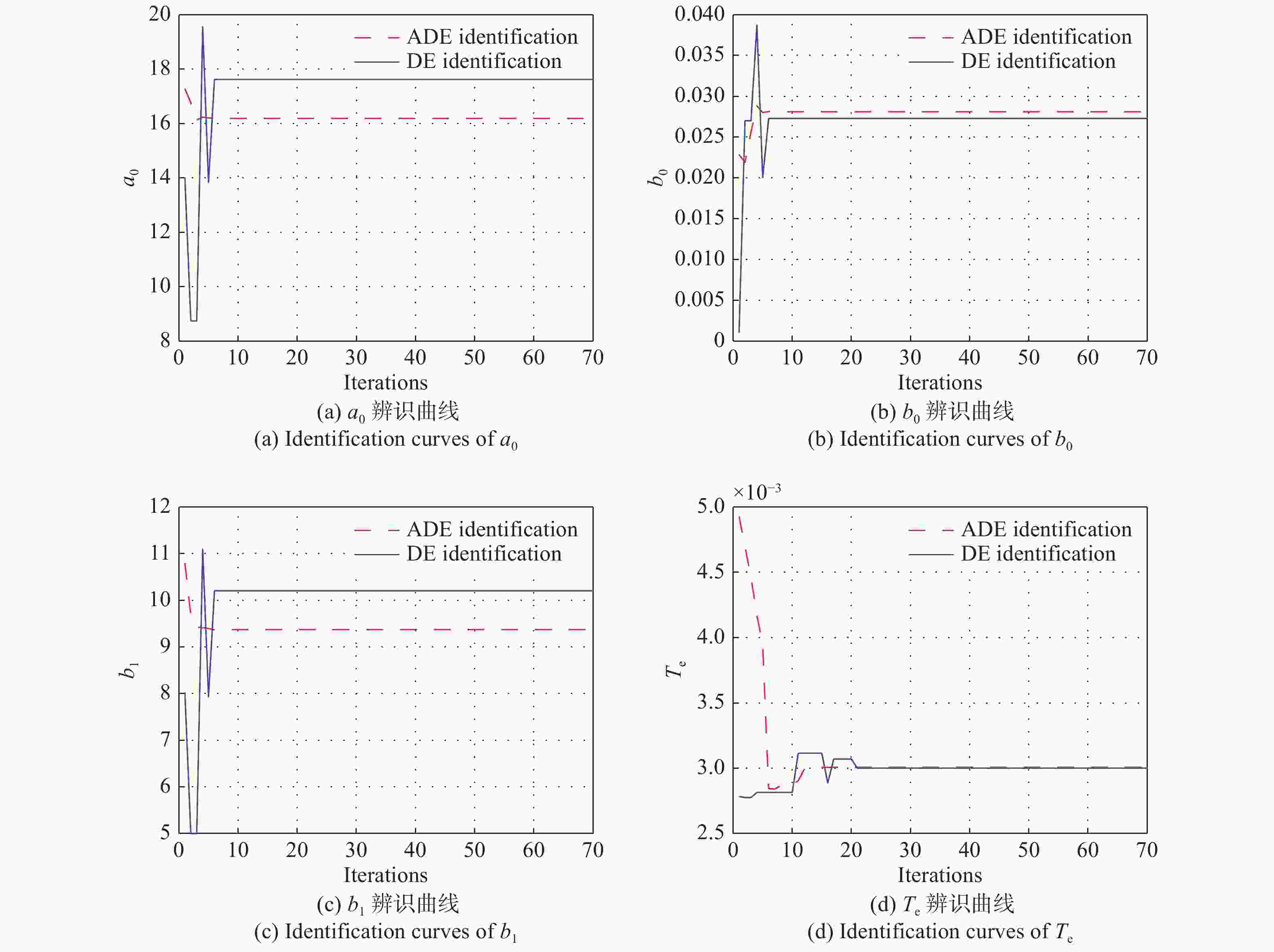
辨识方法 标准差分进化算法 改进差分进化算法 a0 17.62 16.18 b0 0.027 0.028 b1 10.2 9.37 Te 0.003 0.003 RMS 4.21×104 1.93×104 -
[1] 董全睿, 陈涛, 高世杰, 等. 星载激光通信技术研究进展[J]. 中国光学,2019,12(6):1260-1270. doi: 10.3788/co.20191206.1260DONG Q R, CHEN T, GAO SH J, et al. Progress of research on satellite-borne laser communication technology[J]. Chinese Optics, 2019, 12(6): 1260-1270. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/co.20191206.1260 [2] 张政江, 孙优贤. 基于阶跃响应的非自衡对象预测控制[J]. 控制与决策,2001,16(3):378-379.ZHANG ZH J, SUN Y X. Predictive control algorithm of integrating plant based on step-response[J]. Control and Decision, 2001, 16(3): 378-379. (in Chinese) [3] YIN H H, ZHU ZH F, DING F. Model order determination using the Hankel matrix of impulse responses[J]. Applied Mathematics Letters, 2011, 24(5): 797-802. doi: 10.1016/j.aml.2010.12.046 [4] 陈恒杰, 薛航, 李邵雄, 等. 一种通过约瑟夫森结非线性频率响应确定微波耗散的方法[J]. 物理学报,2019,68(11):118501.CHEN H J, XUE H, LI SH X, et al. A method of determining microwave dissipation of Josephson junctions with non-linear frequency response[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2019, 68(11): 118501. (in Chinese) [5] 唐志荣, 刘明哲, 蒋悦, 等. 基于典型相关分析的点云配准算法[J]. 中国激光,2019,46(4):0404006. doi: 10.3788/CJL201946.0404006TANG ZH R, LIU M ZH, JIANG Y, et al. Point cloud registration algorithm based on canonical correlation analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2019, 46(4): 0404006. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/CJL201946.0404006 [6] 李红云, 云利军, 高银. 基于边界限制加权最小二乘法滤波的雾天图像增强算法[J]. 中国激光,2019,46(3):0309002. doi: 10.3788/CJL201946.0309002LI H Y, YUN L J, GAO Y. Fog image enhancement algorithm based on boundary-limited weighted least squares filtering[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2019, 46(3): 0309002. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/CJL201946.0309002 [7] 周向阳, 朱军, 时延君. 轻小型无人机云台机电多目标优化[J]. 光学 精密工程,2018,26(11):2754-2763. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20182611.2754ZHOU X Y, ZHU J, SHI Y J. Multi-objective optimization on mechatronic system of a light and small pan-tilt system for unmanned aerial vehicle application[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2018, 26(11): 2754-2763. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/OPE.20182611.2754 [8] XIA X W, GUI L, YU F, et al. Triple archives particle swarm optimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2019. doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2019.2943928 [9] BENSINGH R J, MACHAVARAM R, BOOPATHY S R, et al. Injection molding process optimization of a Bi-aspheric lens using hybrid Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs) and Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO)[J]. Measurement, 2019, 134: 359-374. doi: 10.1016/j.measurement.2018.10.066 [10] 张泉, 尹达一, 张茜丹. 压电执行器动态迟滞建模与LQG最优控制器设计[J]. 光学 精密工程,2018,26(11):2744-2753. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20182611.2744ZHANG Q, YIN D Y, ZHANG X D. Dynamic hysteresis modeling and LQG optimal controller design of piezoelectric actuators[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2018, 26(11): 2744-2753. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/OPE.20182611.2744 [11] MALLIPEDDI R, SUGANTHAN P N, PAN Q K, et al. Differential evolution algorithm with ensemble of parameters and mutation strategies[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2011, 11(2): 1679-1696. doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2010.04.024 [12] MOHANTY B, PANDA S, HOTA P K, et al. Controller parameters tuning of differential evolution algorithm and its application to load frequency control of multi-source power system[J]. International Journal of Electrical Power &Energy Systems, 2014, 54: 77-85. [13] DEMERTZIS K, ILIADIS L. Adaptive elitist differential evolution extreme learning machines on big data: intelligent recognition of invasive species[C]. Proceedings of the 2nd INNS Conference on Big Data, Springer, 2016: 333-345. [14] DENG CH SH, ZHAO B Y, YANG Y L, et al.. Novel binary differential evolution without scale factor F[C]. Proceedings of the 3rd International Workshop on Advanced Computational Intelligence, IEEE, 2010: 250-253. [15] 骆晨钟, 邵惠鹤. 采用混沌变异的进化算法[J]. 控制与决策,2000,15(5):557-560.LUO CH ZH, SHAO H H. Evolutionary algorithms with chaotic mutations[J]. Control and Decision, 2000, 15(5): 557-560. (in Chinese) [16] QU B Y, SUGANTHAN P N, LIANG J J. Differential evolution with neighborhood mutation for multimodal optimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2012, 16(5): 601-614. doi: 10.1109/TEVC.2011.2161873 [17] AL-GHANIMI A, ZHENG J, MAN Z. A fast non-singular terminal sliding mode control based on perturbation estimation for piezoelectric actuators systems[J]. International Journal of Control, 2017, 90(3): 480-491. doi: 10.1080/00207179.2016.1185157 -





 下载:
下载: