Effects of spot size on the temperature response of an aluminum alloy irradiated by a continuous laser
-
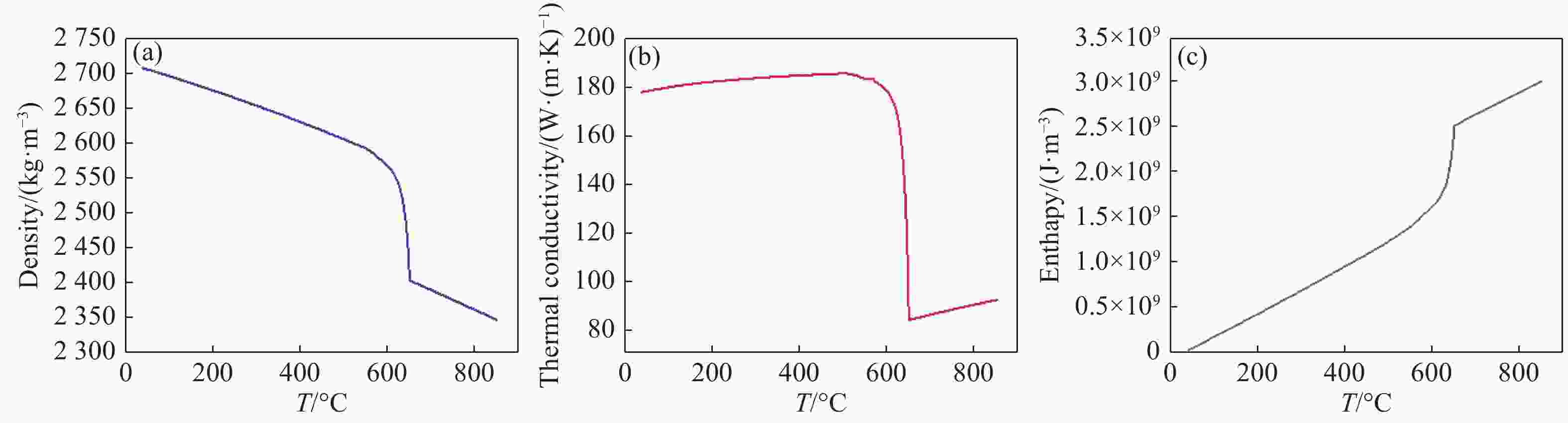
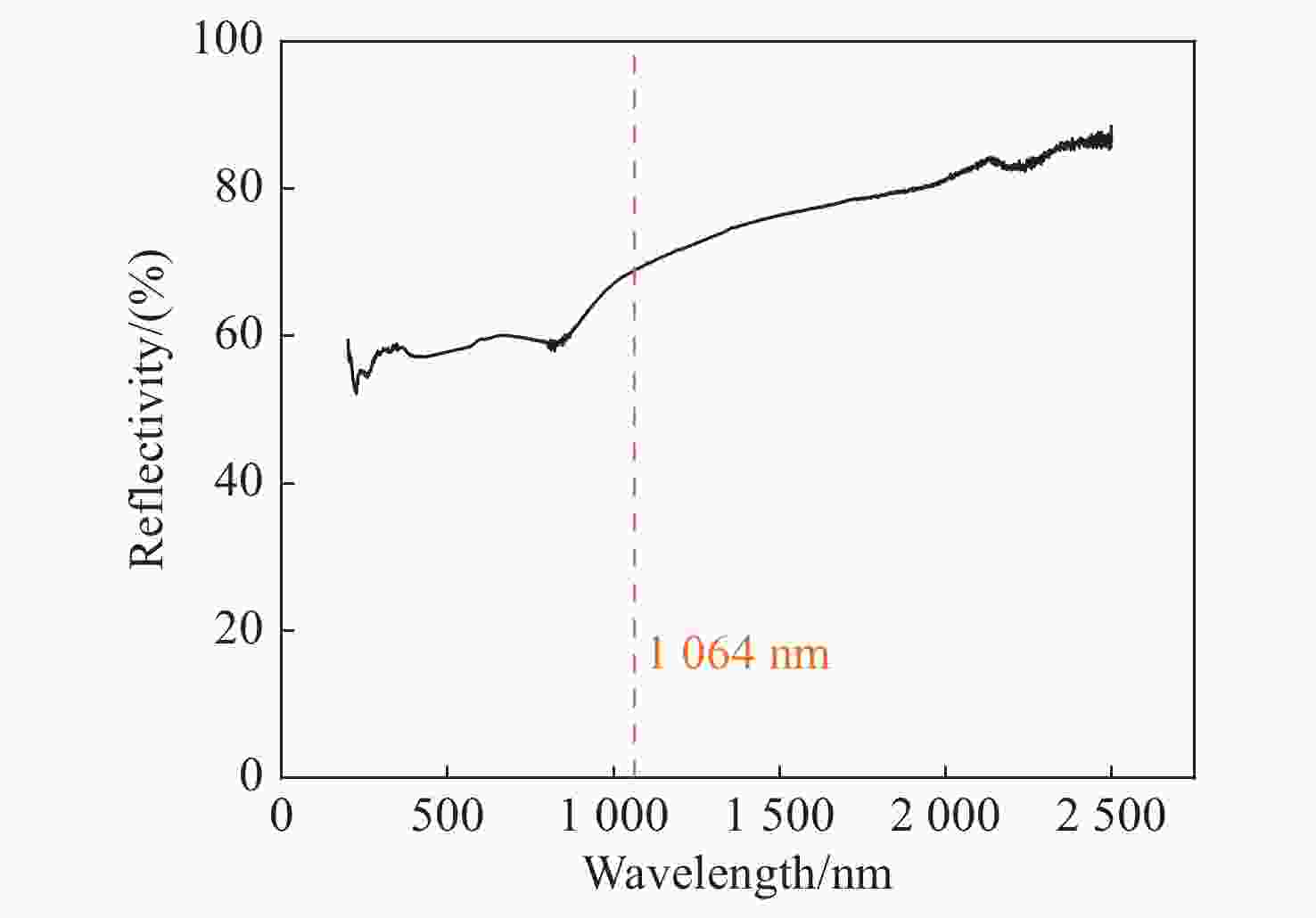
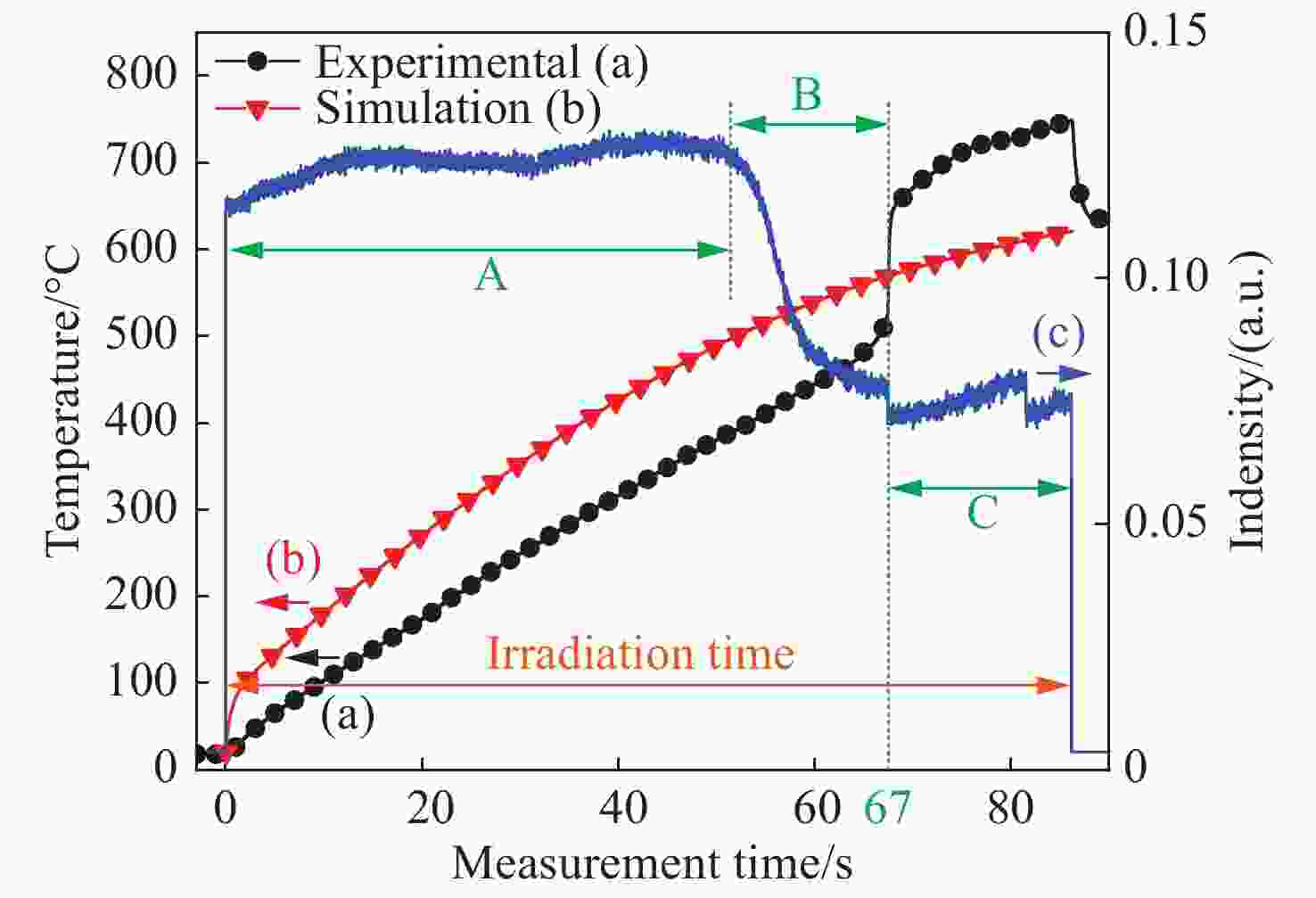
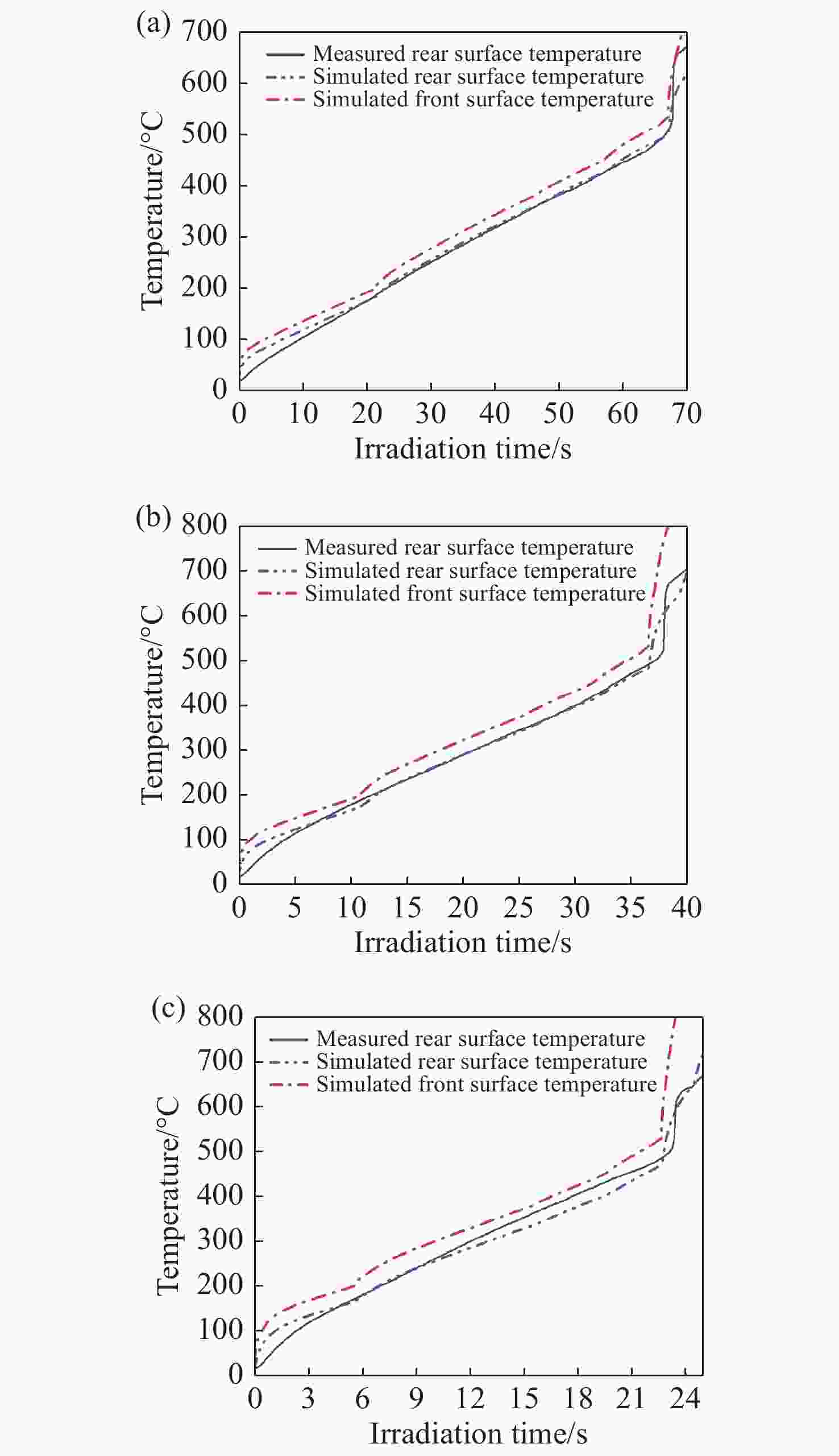
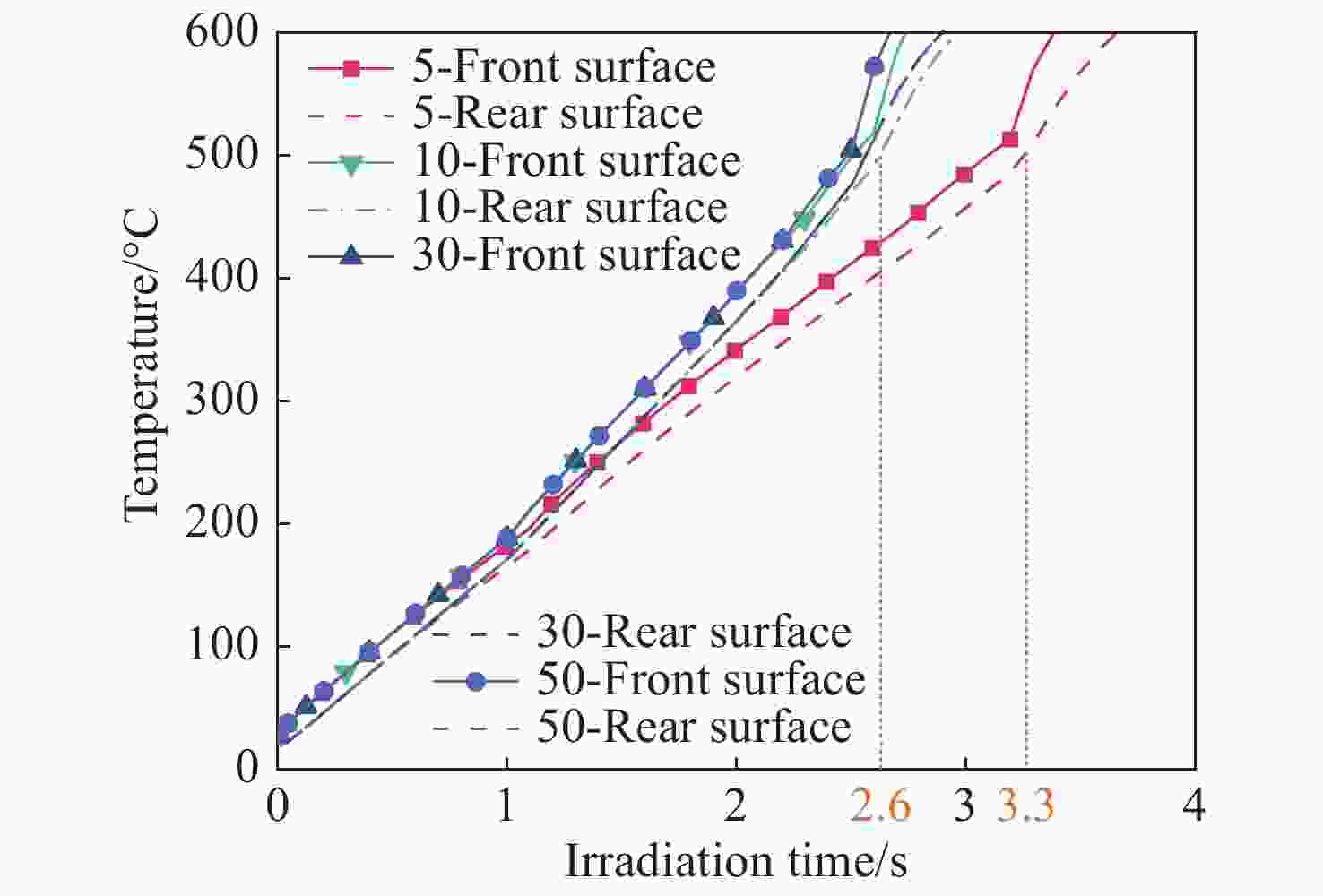
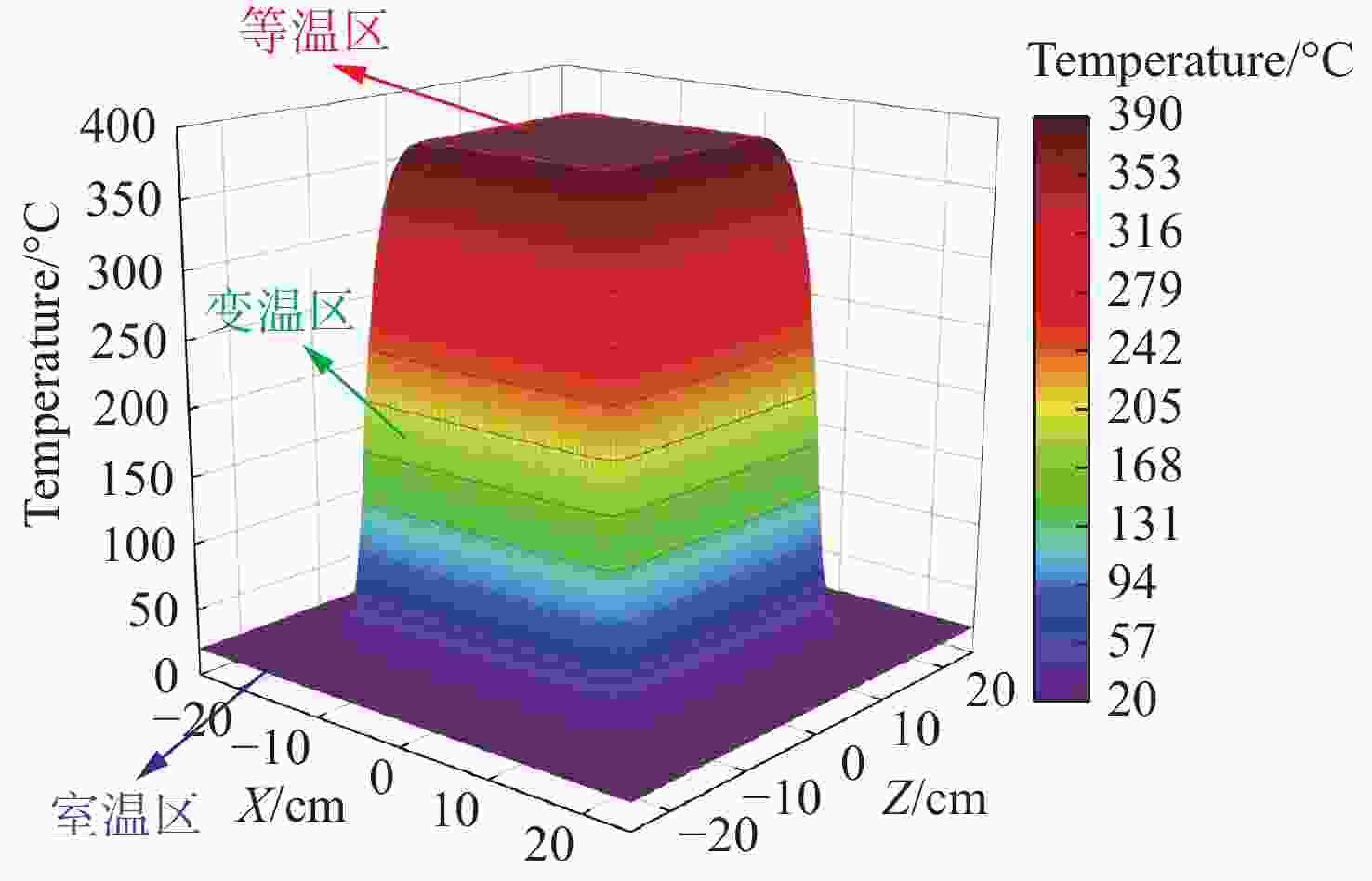
摘要: 为了探究不同光斑尺寸连续激光辐照6061铝合金的温度响应及热致损伤问题,基于ANSYS有限元软件建立了激光辐照下的三维物理模型;使用不同的激光参数进行激光辐照实验,根据所采集的温度和前表面散射光强度数据,反演计算了靶材在激光辐照过程中吸收率的动态变化;最后,利用优化后的模型分析了不同光斑尺寸下,激光辐照靶材的温升特点。研究结果表明:在1000 W/cm2的激光辐照条件下,材料的吸收率随着温度的升高而升高;由于激光加载的局域化特征,横向热扩散影响纵向温升,光斑足够大时该影响变小,这与其热扩散长度有关;对于4 mm厚的6061铝合金材料,当光斑尺寸大于10 cm时,光斑影响可以忽略,靶材背表面发生熔融损伤时间阈值保持2.6 s不变。Abstract: In order to investigate the temperature response and thermal damage of a 6061 aluminum alloy after variations in spot size of continuous laser irradiation, a three-dimensional physical model under laser irradiation was established based on ANSYS finite element software. First, we used different laser parameters to carry out laser irradiation experiments, and then, based on the collected temperature and front surface scattered light intensity data, we calculated the dynamic changes in the absorptivity of the target during laser irradiation. Finally, the optimized model was used to analyze the temperature rise characteristics of the target irradiated by lasers at different spot sizes. The research results show that the absorption rate of the material increases with an increase in temperature under 1000 W/cm2 laser irradiation. Due to the localized characteristics of laser loading, lateral thermal diffusion affects the longitudinal temperature rise, and its effect becomes smaller when the spot is larger, as related with the alloy’s thermal diffusion length. For the 6061 aluminum alloy material with a thickness of 4 mm, when the spot size is greater than 10 cm, the effect of the spot’s size is negligible, and the time threshold of fusion damage on the back surface of the target remains unchanged at 2.6 s.
-
Key words:
- Laser irradiation /
- Numerical simulation /
- Temperature field /
- Spot size
-
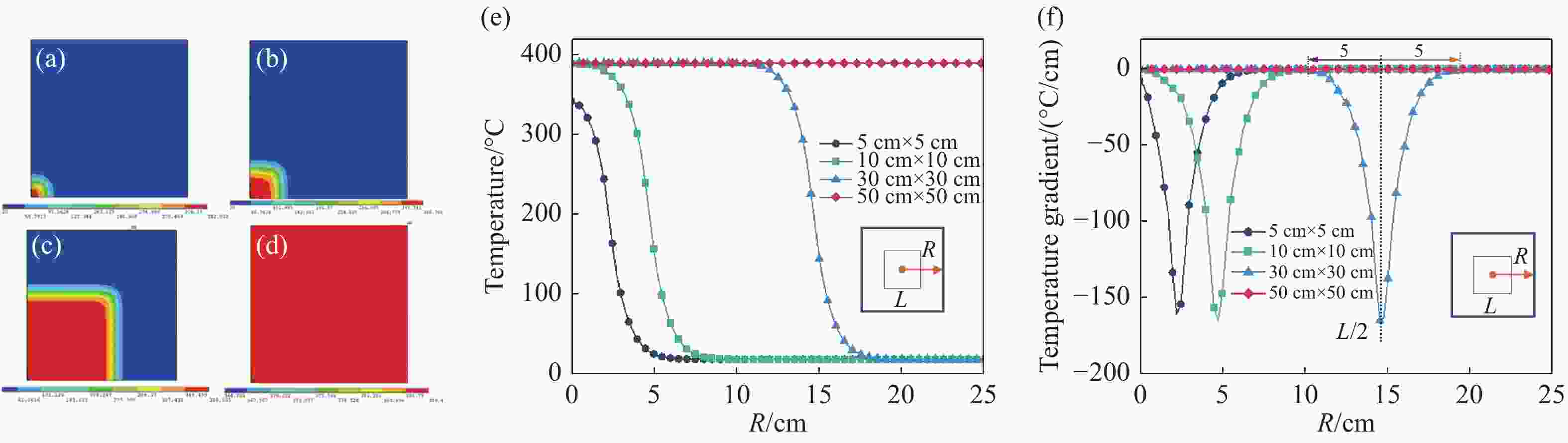
图 8 不同尺寸光斑激光辐照下铝合金前表面温度分布。(a)5 cm×5 cm;(b)10 cm×10 cm;(c)30 cm×30 cm;(d)50 cm×50 cm;(e)温度随R的变化图;(f)温度梯度随R的变化图
Figure 8. Temperature distribution in the front surface of aluminum alloy under laser irradiation with different spot sizes. (a) 5 cm×5 cm; (b) 10 cm×10 cm; (c) 30 cm×30 cm; (d) 50 cm×50 cm; (e) graph of temperature vs
$R$ ; (f) graph of temperature gradient vs$R$ 表 1 6061铝合金成分[19]
Table 1. Composition of 6061 aluminum alloy
(%) $w({\rm{Mg}})$ $w({\rm{Si}})$ $w({\rm{Mn}})$ $w({\rm{Fe}})$ $w({\rm{Cr}})$ $w({\rm{Cu}})$ $w({\rm{Zn}})$ $w({\rm{Al}})$ 1.06 0.53 0.43 0.38 0.17 0.33 0.16 余量 表 2 不同温度下6061铝合金表面换热系数[22]
Table 2. Surface heat transfer coefficients of 6061 aluminum alloy at different temperatures
$T$/(℃) 20 100 200 300 400 500 600 700 $h$/( W/m2·℃) 8.22 11.0 13.7 23.2 33.4 46.8 58.0 68.5 表 3 6061铝合金激光吸收率参数设置
Table 3. Parameter settings of laser absorptivity of 6061 aluminum alloy
Temperature
range/ (℃)0~200 200~380 380~450 450~525 525~800 α 0.19 0.25 0.27 0.32 0.74 -
孟献丰, 陆春华, 倪亚茹, 等. 激光技术的应用与防护[J]. 红外与激光工程,2005,34(2):136-141. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2276.2005.02.003MENG X F, LU CH H, NI Y R, et al. Application and protection of laser technology[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2005, 34(2): 136-141. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2276.2005.02.003 罗曦, 陈培锋, 王英, 等. 新型高功率激光加工用激光光束展宽方法的探索性研究[J]. 中国激光,2011,38(4):0403003. doi: 10.3788/CJL201138.0403003LUO X, CHEN P F, WANG Y, et al. An exploratory investigation of wide-band beam shaping for high power laser processing[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2011, 38(4): 0403003. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/CJL201138.0403003 刘友强, 曹银花, 李景, 等. 激光加工用5 kW光纤耦合半导体激光器[J]. 光学 精密工程,2015,23(5):1279-1287. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20152305.1279LIU Y Q, CAO Y H, LI J, et al. 5 kW fiber coupling diode laser for laser processing[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2015, 23(5): 1279-1287. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/OPE.20152305.1279 王立军, 宁永强, 秦莉, 等. 大功率半导体激光器研究进展[J]. 发光学报,2015,36(1):1-19.WANG L J, NING Y Q, QIN L, et al. Development of high power diode laser[J]. Chinese Journal of Luminescence, 2015, 36(1): 1-19. (in Chinese) 陈军燕, 卢慧玲, 杨春才. 美军海上激光武器发展研究[J]. 飞航导弹,2014(11):67-72.CHEN J Y, LU H L, YANG CH C. Research on the development of US marine laser weapons[J]. Aerodynamic Missile Journal, 2014(11): 67-72. (in Chinese) 刘铭. 国外激光武器技术的发展[J]. 舰船电子工程,2011,31(4):18-23. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1627-9730.2011.04.005LIU M. Development of the laser weapon technology abroad[J]. Ship Electronic Engineering, 2011, 31(4): 18-23. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1627-9730.2011.04.005 黄勇, 刘杰. 高能激光武器的杀伤机理及主要特性分析[J]. 光学与光电技术,2004,2(5):20-23. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3392.2004.05.007HUANG Y, LIU J. Analysis on kill mechanism and characteristics of high energy laser weapon[J]. Optics &Optoelectronic Technology, 2004, 2(5): 20-23. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3392.2004.05.007 乔相信, 成艺光, 唐恩凌, 等. 飞秒脉冲激光辐照FRAM诱发的毁伤效应及热演化[J]. 发光学报,2019,40(6):815-825. doi: 10.3788/fgxb20194006.0815QIAO X X, CHENG Y G, TANG E L, et al. Damage effects and thermal evolution of FRAM irradiated by femtosecond pulsed laser[J]. Chinese Journal of Luminescence, 2019, 40(6): 815-825. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/fgxb20194006.0815 张江华. 高能激光武器毁伤机理及其防护技术[J]. 中国科技信息,2008(20):37, 39.ZHANG J H. Damage mechanism and protection technology of high energy laser weapon[J]. China Science and Technology Information, 2008(20): 37, 39. (in Chinese) READY J F. Effects of High-power Laser Radiation[M]. New York: Academic Press, 1971. 陈彦北, 陆建, 倪晓武. 激光作用金属板材的温度场和热应力场[J]. 华中科技大学学报(自然科学版),2007,35(S1):129-132.CHEN Y B, LU J, NI X W. Temperature and thermal stress fields during the laser irradiating a metal plate[J]. Journal of Huazhong University of Science &Technology (Natural Science Edition) , 2007, 35(S1): 129-132. (in Chinese) 钱秋冬, 汪庆桃, 钱浩勇. 激光辐照过程中材料吸收率的理论研究[C]. 第28届全国结构工程学术会议论文集(第Ⅲ册), 中国力学学会结构工程专业委员会, 2019: 459-464.QIAN Q D, WANG Q T, QIAN H Y. Theoretical study on absorption rate of materials during laser irradiation[C]. Proceedings of the 28th National Conference on Structural Engineering (Volume Ⅲ), Structural Engineering Committee of Chinese Society of Mechanics, 2019: 459-464. (in Chinese) 张英聪, 沈华, 朱日宏. 连续激光辐照材料的三维温度场[J]. 中国激光,2013,40(8):0806002. doi: 10.3788/CJL201340.0806002ZHANG Y C, SHEN H, ZHU R H. Three-dimensional temperature field of material irradiated by continuous wave laser[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2013, 40(8): 0806002. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/CJL201340.0806002 蒙文, 张文杰, 李云霞, 等. 切向气流作用下激光辐照对尼龙材料的热烧蚀规律[J]. 光学 精密工程,2017,25(2):351-357. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20172502.0351MENG W, ZHANG W J, LI Y X, et al. Thermal ablation law of laser irradiation on nylon materials under tangential airflow[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2017, 25(2): 351-357. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/OPE.20172502.0351 LEE K C, BAEK W K, KWON H, et al. Analysis of melt-through process of 1.07 μm continuous wave high power laser irradiation on metal[J]. Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology, 2013, 27(6): 1745-1752. doi: 10.1007/s12206-013-0425-z SIHN S, CHILDERS L B, WALTERS C T, et al. Computational and experimental study on laser heating of a Ni-based metal alloy[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2016, 102: 1034-1043. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2016.06.061 宋乃秋. 高能激光武器多物理场仿真建模[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2016.SONG N Q. Multiple Physical Modeling and Simulation of High Energy Laser Weapon[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2016. (in Chinese) 王振宝, 吴勇, 杨鹏翎, 等. 强激光辐照铝靶温度分布数值模拟及实验研究[J]. 红外与激光工程,2014,43(7):2061-2065. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2276.2014.07.002WANG ZH B, WU Y, YANG P L, et al. Numerical simulation and experiment on temperature fields distribution of aluminum target under intensive laser[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2014, 43(7): 2061-2065. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2276.2014.07.002 王宇, 张腾, 叶晓凤, 等. 6061铝合金搅拌摩擦焊接温度场及性能分析[J]. 电焊机,2014,44(10):152-157.WANG Y, ZHANG T, YE X F, et al. Research in the temperature field and mechanical properties of 6061 Aluminum FSW joint[J]. Electric Welding Machine, 2014, 44(10): 152-157. (in Chinese) 张鹏波. 1064 nm重频激光辐照复合金属温度场的研究[D]. 长春: 长春理工大学, 2019.ZHANG P B. Temperature field of composite metal irradiated by 1064 nm repetitive laser[D]. Changchun: Changchun University of Science and Technology, 2019. (in Chinese) DENG A Y, ZHONG ZH, WANG E G, et al.. Stress behavior of incoloy 800 superalloy in slab continuous casting process[C]. MARQUIS F. Proceedings of the 8th Pacific Rim International Congress on Advanced Materials and Processing. Cham: Springer, 2013: 2651-2658. 吴圣川. 铝合金激光—电弧复合焊研究及其温度场的数值模拟[D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2005.WU SH CH. A study on laser-arc hybrid welding for aluminum alloy and numerical simulation for the temperature field[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 2005. (in Chinese) 巩水利. 先进激光加工技术[M]. 北京: 航空工业出版社, 2016.GONG SH L. Advanced Laser Materials Processing Technology[M]. Beijing: Aviation Industry Press, 2016. (in Chinese) 王贵兵, 罗飞, 刘仓理. 大气环境下重复频率激光辐照45#钢反射率变化分析[J]. 强激光与粒子束,2006,18(2):181-183.WANG G B, LUO F, LIU C L. Reflectance change of 45# steel irradiated by laser in atmosphere[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2006, 18(2): 181-183. (in Chinese) -





 下载:
下载: