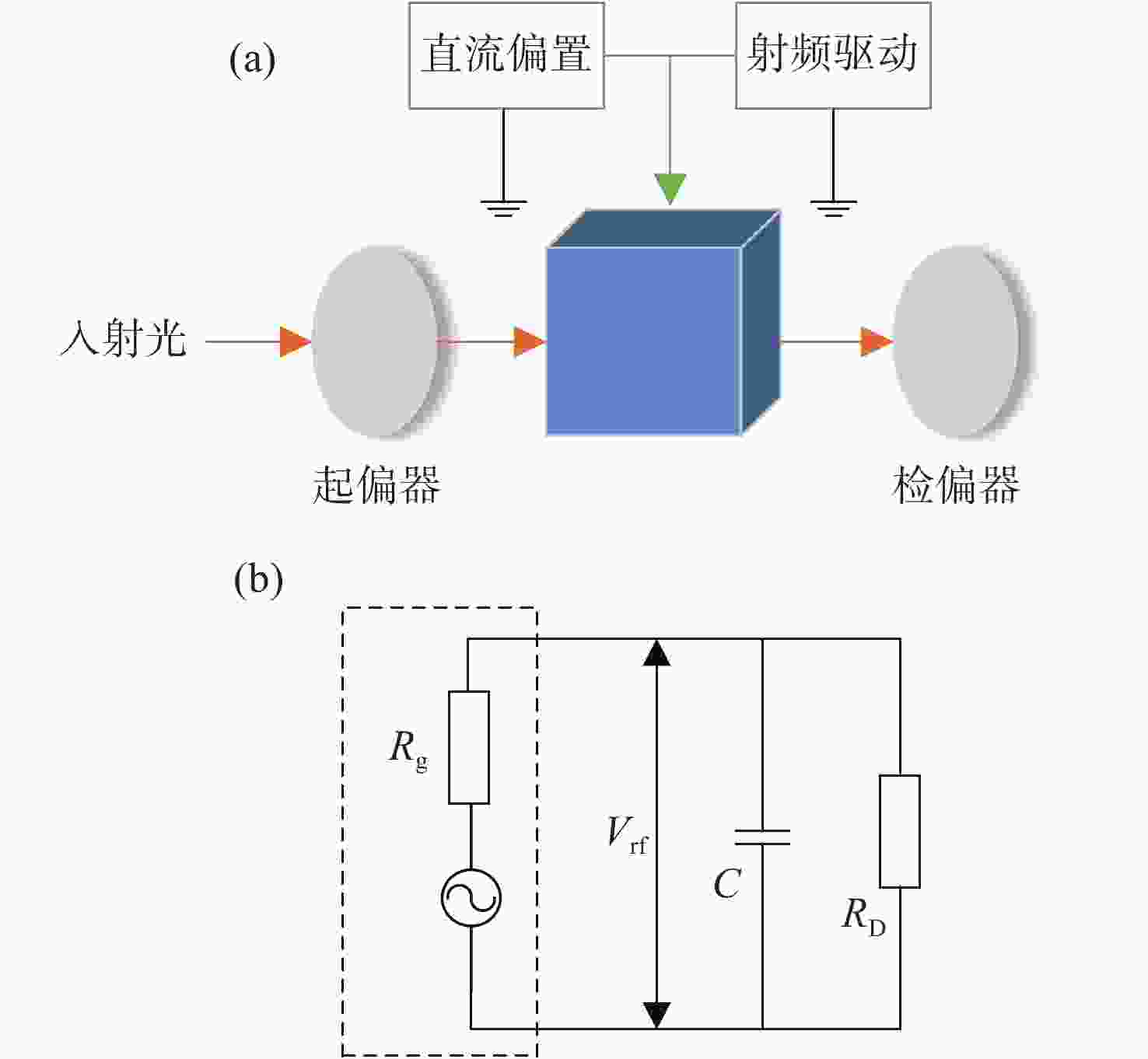
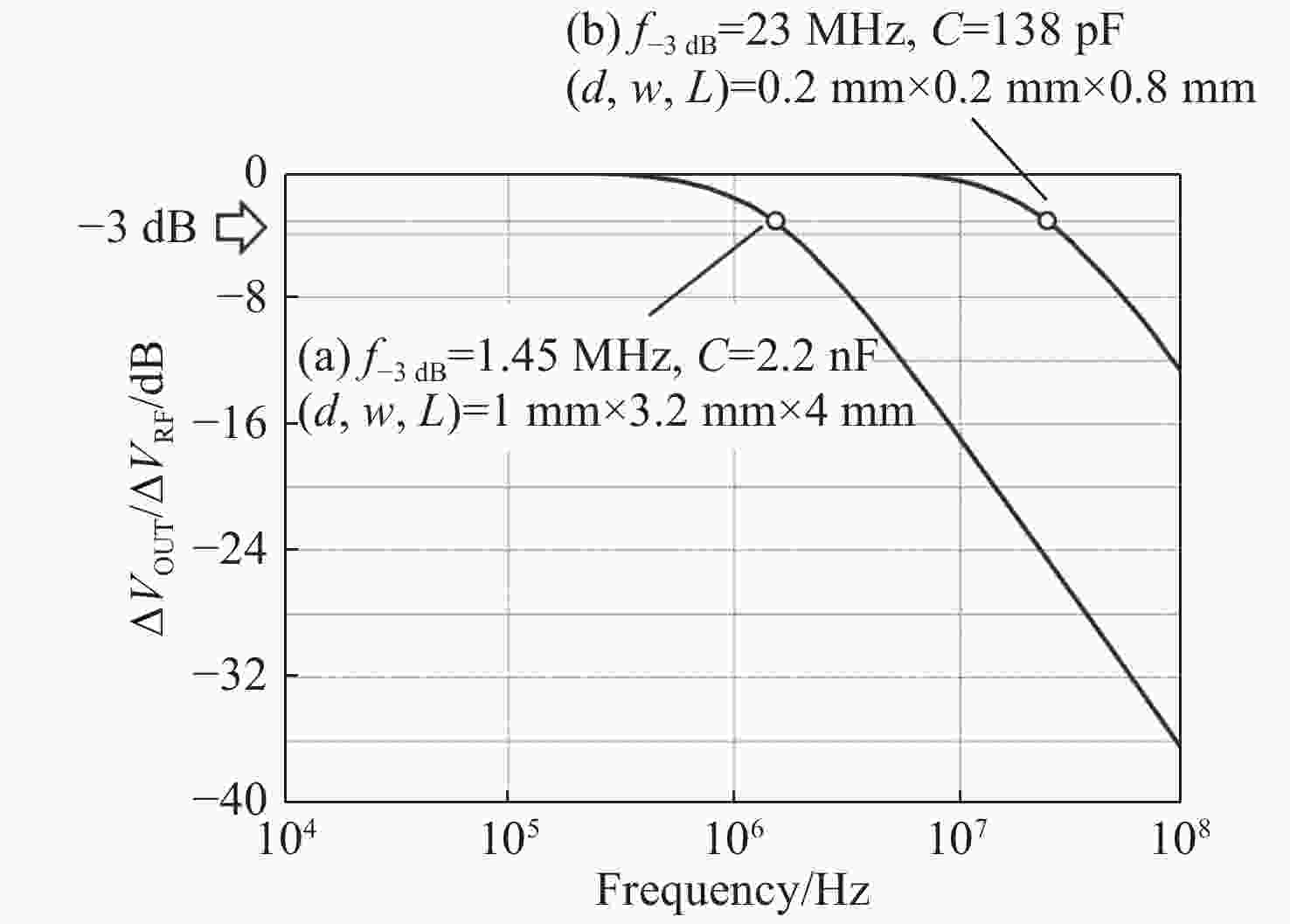
-
摘要: 基于电光晶体的偏振调制技术在激光三维成像领域起着越来越重要的作用。受限于铌酸锂(LN)材料的低视场和高半波电压,采用传统电光调制技术难以进一步提升三维成像性能。随着钙钛矿结构电光材料制备工艺的日趋成熟,基于新型材料的电光调制技术将成为突破激光三维成像探测精度的最佳手段,铌镁酸铅-钛酸铅(PMNT)、锆钛酸镧铅(PLZT)和钽铌酸钾(KTN)3种典型材料具有优良的电光性能和介电性质;能够突破视场和半波电压的限制,但应用到电光调制领域时存在PMNT调制带宽较低、PLZT透过性能较差、KTN实际应用带宽较低等难题。未来的研究将着眼于将该调制技术的实用性,一方面通过掺杂改性等手段提升电光调制性能,另一方面通过建立性能表征模型优化系统的信噪比。Abstract: Polarization modulation technology based on electro-optic crystals is playing an increasingly important role in the field of three-dimensional laser imaging. Due to the low field of view and high half-wave voltage of LiNiO3 (LN) materials, it is difficult for traditional electro-optic modulation technology to further improve 3D imaging performance. As the preparation technology of perovskite-structured electro-optical materials becomes more mature, electro-optic modulation technology based on new materials will become an excellent means to create a breakthrough in the detection accuracy of laser 3D imaging. PMNT, PLZT and KTaxNb1-xO3 (KTN) three typical materials have excellent electro-optical properties and dielectric properties that might surpass the field of view and half-wave voltage limitation. However, their applications in electro-optic modulation has lead to difficulties such as a low modulation bandwidth for PMNT, poor transmission performance for PLZT, and low practical application bandwidth for KTN. Future research will focus on the practicality of this modulation technology. The electro-optic modulation performance can be improved by doping and the signal-to-noise ratio of the system can be optimized by establishing performance characterization models.
-
图 3 Bridgman方法生长的PMNT单晶[25]
Figure 3. PMNT single crystal grown with the Bridgman method
图 4 锆钛酸镧铅(PLZT)光电陶瓷材料[36]
Figure 4. PLZT optoelectronic ceramic material
图 5 钽铌酸钾(KTa1-xNbxO3, KTN)晶体材料[50]
Figure 5. KTN crystal material
表 1 室温下632.5 nm波长测得PMNT材料的二次电光系数和1 kHz电场下的介电常数
Table 1. The secondary electro-optic coefficient of the PMNT material measured at a wavelength of 632.5 nm at room temperature and the dielectric constant under an electric field of 1 kHz
表 2 室温下在632.5 nm波长测得PLZT材料的二次电光系数和1 kHz电场下的介电常数
Table 2. The secondary electro-optic coefficient of the PLZT material measured at a wavelength of 632.5 nm at room temperature and the dielectric constant under an electric field of 1 kHz
PLZT材料La/Ti/Zr QEO系数10-16 m2/V2 文献 PLZT材料La/Ti/Zr 介电常数 文献 8/65/35 PLZT(λ=532 nm) 25 [35] 9/65/35PLZT+0.15 mol% Li+Bi(T=348 K) 7819 [37] 8.8/65/35 PLZT(T=258 K) 2.8 [33] 9/65/35PLZT+0.25 mol% Bi2O3+CuO(T=373 K) 11290 [38] 9/65/35 PLZT(λ=532 nm) 3.7 [35] 9/65/35PLZT(T=373 K) 10539 [39] 9.4/65/35 PLZT(T=244 K) 1.48 [33] 7/65/35PLZT+0.08 wt% Cr2O3(T=427 K) 13985 [40] 10/65/35PLZT(λ=532 nm) 1.3 [35] 薄膜PLZT+2%La(f=100 Hz) 1502.59 [42] 11/40/60PLZT+0.1 mol%Dy(T=385 K) 5.59 [34] PLZT+1.50 mol%Al(T=385 K) 16000 [45] 表 3 KTN材料二次电光系数对比分析
Table 3. Comparative analysis of quadratic electro-optic coefficient of KTN materials
单位 KTN(Ta/Nb) QEO系数/(10−16 m2/V2) 测量条件 备注 NTT公司 —— 224 T=314 K λ=685 nm 山东科学院 0.75/0.25 65 λ=633 nm 调研已经达到10−14量级 0.63/0.37 86 室温λ=633 nm 美国宾夕法尼亚大学 0.7/0.3 20 T=299 K λ=532 nm Kovacs前 694 0.45 K/s降温 Kovacs后 哈尔滨工业大学 0.61/0.39 59.6 T=296 K λ=632.8 nm 表 4 PMNT、PLZT和KTN电光调制可行性分析(附LN作为比较)
Table 4. Feasibility analysis of electro-optic modulation by PMNT, PLZT and KTN (with LN for comparison)
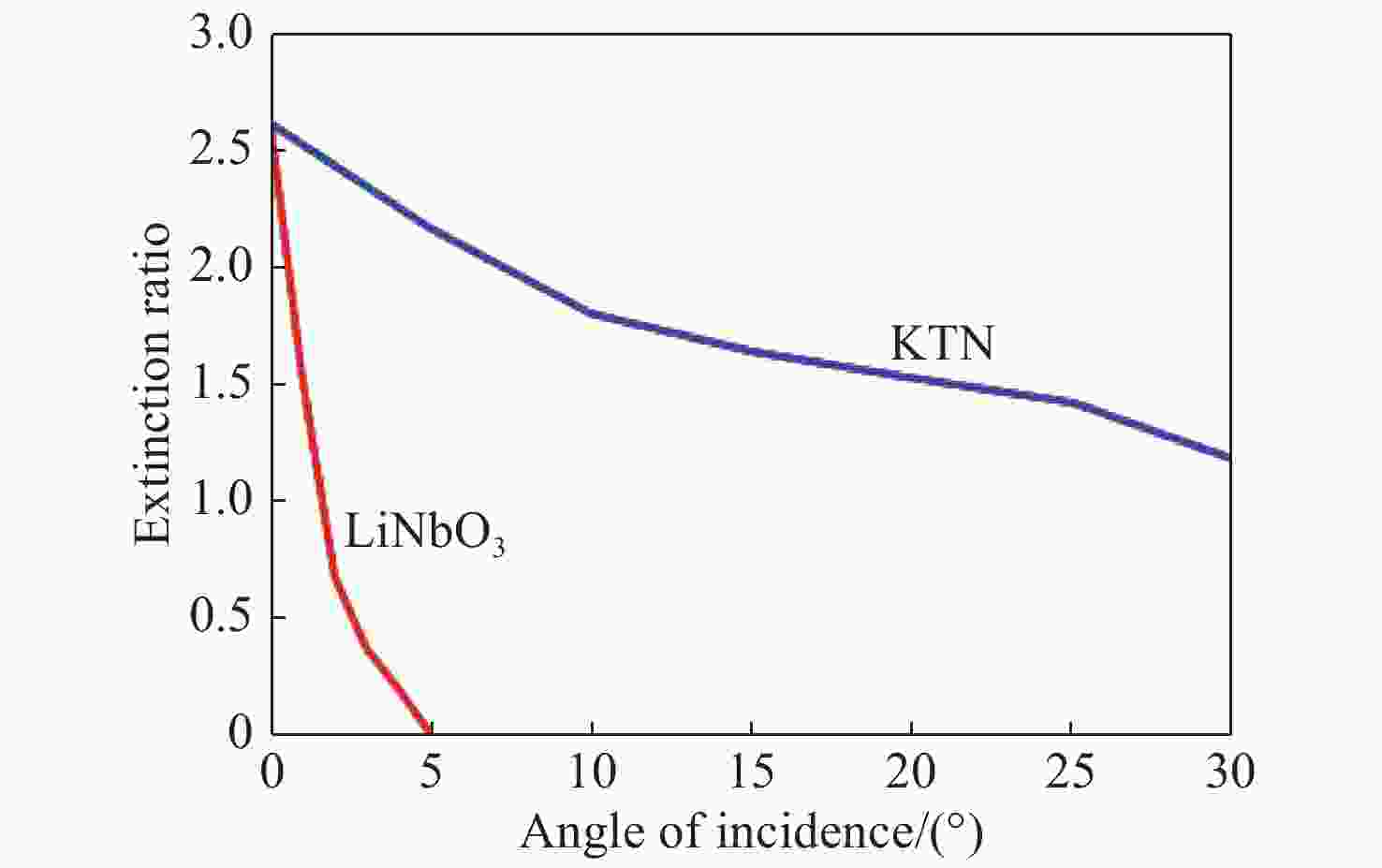
材料名称 有效电光系数/(m2·V−2) 半波电压/V 调制电压/V 视场 产品成熟度 LN 6.8×10−12 1 900 ~600 <5° 非常成熟 PMNT ~4×10−15 ~60 ~20 较成熟(硅酸盐所) PLZT ~5×10−16 ~160 ~50 较成熟(硅酸盐所) KTN 0.2×10−15 ~260 ~80 ~30° 较成熟(宾夕法尼亚) 4~9×10−15 ~50 ~16 较成熟(山东科学院) 2.24×10−14 ~24 ~8 较成熟(NTT公司) 表 5 PMNT、PLZT和KTN电光调制适用性分析
Table 5. Applicability analysis of different electro-optic modulations
调制器
类型调制性能 衍生难题 解决方式及效果 低电压调制 大视场 LN × × PMNT √ √ 响应速度慢、
光散射严重难以应用于高速
电光调制PLZT √ √ 半波电压高 Dy掺杂使二次电光
性能明显提高透过率低 Dy掺杂和Al掺杂使
透过率明显提高,
但无法突破65%KTN √ √ 实际应用调制
带宽低通过优化系统结构,理论上可以达到ns级响应及数百兆赫兹调制带宽,但实际仍未实现 -
[1] 赵炜渝, 邢宁. 美国航天创新项目发展分析[J]. 中国航天,2015(3):23-27.ZHAO W Y, XING N. Analysis of the development of US space innovation projects[J]. Aerospace China, 2015(3): 23-27. (in Chinese) [2] 王雪瑶, 宋博. 美国国防高级研究计划局启动“地球同步轨道卫星自主服务”项目[J]. 国际太空,2016(11):33-38.WANG X Y, SONG B. U.S. DARPA started the RSGS program[J]. Space International, 2016(11): 33-38. (in Chinese) [3] TICKER R L, CEPOLLINA F, REED B B. NASA’s in-space robotic servicing[C]. Proceedings of the AIAA SPACE 2015 Conference and Exposition, AAIA, 2015: 4644. [4] STRUBE M, HENRY R, SKELETON E, et al.. Raven: an on-orbit relative navigation demonstration using international space station visiting vehicles[C]. American Astronautical Society Guidance and Control Conference, American Astronautical Society, 2015. [5] GALANTE J M, VAN EEPOEL J, D’SOUZA C, et al.. Fast Kalman filtering for relative spacecraft position and attitude estimation for the raven ISS hosted payload[R]. AAS 16-045, 2016. [6] FORSHAW J L, AGLIETTI G S, NAVARATHINAM N, et al. Remove DEBRIS: An in-orbit active debris removal demonstration mission[J]. Acta Astronautica, 2016, 127: 448-463. doi: 10.1016/j.actaastro.2016.06.018 [7] MCMANAMON P F, BANKS P S, BECK J D, et al. Comparison of flash lidar detector options[J]. Optical Engineering, 2017, 56(3): 031223. doi: 10.1117/1.OE.56.3.031223 [8] ECKERSLEY S, SAUNDERS C, LOBB D, et al.. Future rendezvous and docking missions enabled by low-cost but safety compliant Guidance Navigation and Control (GNC) architectures[C]. Proceedings of The 15th Reinventing Space Conference, British Interplanetary Society, 2017. [9] 陈臻. 基于偏振调制的激光三维成像方法研究[D]. 北京: 中国科学院大学, 2017.CHEN ZH. Research on three-dimensional active imaging with polarization -modulated method[D]. Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2017. (in Chinese) [10] CHEN ZH, LIU B, LIU E H, et al. Electro-optic modulation methods in range-gated active imaging[J]. Applied Optics, 2016, 55(3): A184-A190. doi: 10.1364/AO.55.00A184 [11] ZHANG P, DU X P, ZHAO J G, et al. High resolution flash three-dimensional LIDAR systems based on polarization modulation[J]. Applied Optics, 2017, 56(13): 3889-3894. doi: 10.1364/AO.56.003889 [12] JO S, KONG H J, BANG H, et al. High resolution three-dimensional flash LIDAR system using a polarization modulating Pockels cell and a micro-polarizer CCD camera[J]. Optics Express, 2016, 24(26): A1580-A1585. doi: 10.1364/OE.24.0A1580 [13] 何子清, 葛超, 王春阳. 基于最小二乘配置的光学镜头畸变校正方法[J]. 液晶与显示,2019,34(3):302-309. doi: 10.3788/YJYXS20193403.0302HE Z Q, GE CH, WANG CH Y. Optical lens distortion correction method based on least square configuration[J]. Chinese Journal of Liquid Crystals and Displays, 2019, 34(3): 302-309. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/YJYXS20193403.0302 [14] 于国栋. 靶场光学镜头畸变校正方法研究[J]. 液晶与显示,2017,32(3):227-233. doi: 10.3788/YJYXS20173203.0227YU G D. Distortion correction method for optical lens of the range[J]. Chinese Journal of Liquid Crystals and Displays, 2017, 32(3): 227-233. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/YJYXS20173203.0227 [15] 李新娥, 班皓, 沙巍, 等. 一种大视场TDICCD相机的多传感器图像配准方法[J]. 液晶与显示,2014,29(4):644-648. doi: 10.3788/YJYXS20142904.0644LI X E, BAN H, SHA W, et al. Registration method of large field view and multi-sensor images of TDICCD cameras[J]. Chinese Journal of Liquid Crystals and Displays, 2014, 29(4): 644-648. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/YJYXS20142904.0644 [16] 王越, 蒋毅坚. 3 m点群晶体纵向压电性能的研究[J]. 人工晶体学报,2004,33(3):399-402.WANG Y, JIANG Y J. Crystal orientation dependence of longitudinal piezoelectric properties for 3 m point group crystals[J]. Journal of Synthetic Crystals, 2004, 33(3): 399-402. (in Chinese) [17] BU Y M, ZENG Z Y, DU X P, et al. Theoretical research on new photoelectric mixing technology based on electro-optical modulation[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2018, 10964: 109640I. [18] CHANG Y C, WANG CH, YIN SH ZH, et al. Kovacs effect enhanced broadband large field of view electro-optic modulators in nanodisordered KTN crystals[J]. Optics Express, 2013, 21(15): 17760-17768. doi: 10.1364/OE.21.017760 [19] 王菲菲, 邵喜斌. 负型液晶在ADS广视角技术中的应用[J]. 液晶与显示,2016,31(8):760-767. doi: 10.3788/YJYXS20163108.0760WANG F F, SHAO X B. Application of negative LC in ADS wide view technology[J]. Chinese Journal of Liquid Crystals and Displays, 2016, 31(8): 760-767. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/YJYXS20163108.0760 [20] YADA M, ISHIHARA Y, NAOE T, et al.. Noise reduction method for electro-optic measurement system using variable gain amplifier[C]. Proceedings of 2017 IEEE Region 10 Conference, IEEE, 2017: 1969-1972. [21] ZHANG J, NELSON J S, CHEN ZH P. Removal of a mirror image and enhancement of the signal-to-noise ratio in Fourier-domain optical coherence tomography using an electro-optic phase modulator[J]. Optics Letters, 2015, 30(2): 147-149. [22] PAN X J, CAI Y, ZENG X K, et al. A terahertz EO detector with large dynamical range, high modulation depth and signal-noise ratio[J]. Optics Communications, 2017, 391: 135-140. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2017.01.021 [23] 卜禹铭, 杜小平, 曾朝阳, 等. 无扫描激光三维成像雷达研究进展及趋势分析[J]. 中国光学,2018,11(5):711-727. doi: 10.3788/CO.20181105.0711BU Y M, DU X P, ZENG ZH Y, et al. Research progress and trend analysis of non-scanning laser 3D imaging radar[J]. Chinese Optics, 2018, 11(5): 711-727. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/CO.20181105.0711 [24] SHINAGAWA M, KOBAYASHI J, YAGI S, et al. Sensitive electro-optic sensor using KTa1−xNbxO3 crystal[J]. Sensors and Actuators A:Physical, 2013, 192: 42-48. doi: 10.1016/j.sna.2012.12.003 [25] 罗豪甦, 徐海清, 王评初, 等. 新型压电单晶PMNT的生长和性能研究[J]. 哈尔滨理工大学学报,2002,7(6):98-99, 104.LUO H S, XU H Q, WANG P CH, et al. Growth and properties of a new typical piezoelectric sircgle crystal PMNT[J]. Journal of Harbin University of Science and Technology, 2002, 7(6): 98-99, 104. (in Chinese) [26] LIN Y T, REN B, ZHAO X Y, et al. Large quadratic electro-optic properties of ferroelectric base 0.92Pb(Mg1/3Nb2/3)O3-0.08PbTiO3 single crystal[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2010, 507(2): 425-428. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2010.06.068 [27] KAMZINA L S, WEI R, ZENG J T, et al. Effect of the La concentration on the dielectric and optical properties of the transparent ferroelectric ceramics 75PbMg1/3Nb2/3O3-25PbTiO3[J]. Physics of the Solid State, 2011, 53(8): 1608-1613. doi: 10.1134/S1063783411080142 [28] KAMZINA L S, RUAN W, LI G R, et al. Transparent ferroelectric ceramics PbMg1/3Nb2/3O3-xPbZr0.53Ti0.47O3: Dielectric and electro-optical properties[J]. Physics of the Solid State, 2012, 54(10): 2024-2029. doi: 10.1134/S1063783412100174 [29] LIU A Y, HAN H L, WEI L L, et al. Microstructure and electrical properties of PMNT thin films prepared by a modified sol-gel process[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2013, 9068: 90680R. [30] 李国柱. PMN-PT单晶及薄膜的光电转换性能研究[D]. 上海: 上海师范大学, 2015.LI G ZH. Photoelectric conversion properties of PMN-PT single crystals and thin films[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Normal University, 2015. (in Chinese) [31] EL HOSINY ALI H, JIMéNEZ R, RAMOS R, et al. The role of PbTiO3 layers in piezoelectric multilayer composite films based on Pb(Mg1/3Nb2/3)O3-PbTiO3[J]. Thin Solid Films, 2017, 636: 730-736. doi: 10.1016/j.tsf.2017.07.011 [32] 张德强. 溶胶凝胶法制备PMNT薄膜及性能研究[D]. 西安: 西安工业大学, 2018.ZHANG D Q. Synthesis and properties of PMNT thin films prepared by sol-gel method[D]. Xi’an: Xi’an Technological University, 2018. (in Chinese) [33] 孙荣明, 郑芝凤, 祝炳和. 用氧化物原料制备大尺寸PLZT透明陶瓷[J]. 硅酸盐,1981(3):16-20.SUN R M, ZHENG ZH F, ZHU B H. Preparation of large-size PLZT transparent ceramics from oxide raw materials[J]. Chinese Journal of Ceramics, 1981(3): 16-20. (in Chinese) [34] 何夕云, 张勇, 郑鑫森, 等. 镝掺杂锆钛酸铅镧透明陶瓷的结构和电光性能[J]. 光学学报,2009,29(6):1601-1604. doi: 10.3788/AOS20092906.1601HE X Y, ZHANG Y, ZHENG X S, et al. Structure and electro-optical property of the Dy3+ doped lanthanum zirconate-titanate ceramics[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2009, 29(6): 1601-1604. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/AOS20092906.1601 [35] KNIAZKOV A V. Electro-optic study of PZT ferroelectric ceramics using modulation of reflected light[J]. Technical Physics, 2016, 61(4): 631-634. doi: 10.1134/S1063784216040125 [36] 中国科学院上海硅酸盐研究所. 锆钛酸镧铅(PLZT)光电陶瓷材料[EB/OL]. (2018-07-12)[2020-02-27]. http://www.sic.ac.cn/glbm/kjfzb/sdhzc/xmzs/201202/t20120220_3442451.html. [37] LIMPICHAIPANIT A, NGAMJARUROJANA A. Effect of Li and Bi co-doping and sintering temperature on dielectric properties of PLZT 9/65/35 ceramics[J]. Ceramics International, 2017, 43(5): 4450-4455. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2016.12.094 [38] SOMWAN S, NGAMJARUROJANA A, LIMPICHAIPANIT A. Dielectric, ferroelectric and induced strain behavior of PLZT 9/65/35 ceramics modified by Bi2O3 and CuO co-doping[J]. Ceramics International, 2016, 42(9): 10690-10696. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2016.03.181 [39] FUNSUEB N, NGAMJARUROJANA A, TUNKASIRI T, et al. Effect of composition and grain size on dielectric, ferroelectric and induced strain behavior of PLZT/ZrO2 composites[J]. Ceramics International, 2018, 44(6): 6343-6353. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.01.025 [40] SELVAMANI R, SINGH G. TIWARI V S, et al. Dielectric and piezoelectric properties of Cr2O3-doped PLZT (7/65/35) hot pressed ceramics[J]. Materials Today Communications, 2018, 15: 100-104. doi: 10.1016/j.mtcomm.2018.03.002 [41] HUANG C, XU J M, FANG ZH, et al. Effect of preparation process on properties of PLZT (9/65/35) transparent ceramics[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2017, 723: 602-610. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.06.271 [42] 许文才. 锆钛酸铅压电薄膜的制备和表征[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2017.XU W C. Fabrication and characterization of lead zirconate titanate piezoelectric thin films[D]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology, 2017. (in Chinese) [43] 郭有文. PLZT陶瓷的制备及其掺杂改性研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2018.GUO Y W. Preparation and doping modification research of PLZT ceramics[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2018. (in Chinese) [44] 刘宇锋. PLZT压电陶瓷的弛豫特性和压电特性研究[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2018.LIU Y F. Studies of relaxation and piezoelectric properties of PLZT ceramics[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2018. (in Chinese) [45] ZHU B, CAO ZH D, HE X Y, et al.. The effect of Al doping on ferroelectric and dielectric properties of PLZT transparent electro-optical ceramics[C]. Proceedings of 2018 Chinese Materials Conference on Physics and Techniques of Ceramic and Polymeric Materials, Springer, 2018: 205-211. [46] NAKAMURA K, MIYAZU J, SASAURA M, et al. Wide-angle, low-voltage electro-optic beam deflection based on space-charge-controlled mode of electrical conduction in KTa1− xNbxO3[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2006, 89(13): 131115. doi: 10.1063/1.2357335 [47] IMAI T, SASAURA M, NAKAMURA K, et al. Crystal growth and electro-optic properties of KTa1-xNbxO3[J]. NTT Technical Review, 2007, 5(9): 1-8. [48] 王旭平. KTN系列晶体的生长及其性能研究[D]. 济南: 山东大学, 2008.WANG X P. Growth and properties investigation of KTN series crystals[D]. Ji’nan: Shandong University, 2008. (in Chinese) [49] DI GERONIMO E, BORNAND V, PAPET P. Elaboration and characterization of potassium niobate tantalate ceramics[J]. Ceramics International, 2017, 43(1): 953-960. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2016.10.025 [50] 山东省科学院新材料研究所. 钽铌酸钾(KTa1-XNbXO3, KTN)晶体[EB/OL].[2020-02-27]. http://crystcn.51sole.com/companyproductdetail_7677292.htm. [51] DELRE E, SPINOZZI E, AGRANAT A J, et al. Scale-free optics and diffractionless waves in nanodisordered ferroelectrics[J]. Nature Photonics, 2011, 5(1): 39-42. doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2010.285 [52] DELRE E, PARRAVICINI J, PARRAVICINI G, et al.. Wavelength-insensitive negative optical permittivity without nanofabrication in transparent nonlinear dipolar glasses[C]. Proceedings of 2012 Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics (CLEO), IEEE, 2012: 1-2. [53] PARRAVICINI J, AGRANAT A J, CONTI C, et al. Equalizing disordered ferroelectrics for diffraction cancellation[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2012, 101(11): 111104. doi: 10.1063/1.4751847 [54] PARRAVICINI J, CONTI C, AGRANAT A J, et al. Programming scale-free optics in disordered ferroelectrics[J]. Optics Letters, 2012, 37(12): 2355-2357. doi: 10.1364/OL.37.002355 [55] PIERANGELI D, PARRAVICINI J, DI MEI F, et al. Photorefractive light needles in glassy nanodisordered KNTN[J]. Optics Letters, 2014, 39(6): 1657-1660. doi: 10.1364/OL.39.001657 [56] DI MEI F, FALSI L, FLAMMINI M, et al. Giant broadband refraction in the visible in a ferroelectric perovskite[J]. Nature Photonics, 2018, 12(12): 734-738. doi: 10.1038/s41566-018-0276-3 [57] TIAN H, YAO B, WANG L, et al. Dynamic response of polar nanoregions under an electric field in a paraelectric KTa0.61Nb0.39O3 single crystal near the para-ferroelectric phase boundary[J]. Scientific Reports, 2015, 5(1): 13751. doi: 10.1038/srep13751 [58] 王磊. 相界附近钽铌酸钾晶体的电光响应特性及其机理研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2015.WANG L. The study of electro-optic response and mechanism in potassium tantalat niobate near the phase boundary[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2015. (in Chinese) [59] TAN P, TIAN H, HU CH P, et al. Temperature field driven polar nanoregions in KTa1−xNbxO3[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2016, 109(25): 252904. doi: 10.1063/1.4972783 [60] 姚博. 钽铌酸钾晶体居里温度附近临界特性研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2016.YAO B. Critical properties of potassium tantalate niobate crystal near the curie temperature[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2016. (in Chinese) [61] 毛晨阳. 相变温度附近钽铌酸钾晶体的电光响应研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2017.MAO CH Y. The study of electro-optical response of potassium tantalate niobate crystal near phase transition temperature[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2017. (in Chinese) [62] TAN P, TIAN H, MAO CH Y, et al. Field-driven electro-optic dynamics of polar nanoregions in nanodisordered KTa1−xNbxO3 crystal[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2017, 111(1): 012903. doi: 10.1063/1.4991357 [63] TAN P, TIAN H, WANG Y, et al. Impact of dipolar clusters on electro-optic effects in KTa1−xNbxO3 crystal[J]. Optics Letters, 2018, 43(20): 5009-5012. doi: 10.1364/OL.43.005009 [64] ZHANG X J, YE Q, CAI H W, et al. Polarization-independent electro-optic modulator based on PMNT electrically-controlled birefringence effect and Sagnac interferometer[J]. Optics &Laser Technology, 2014, 57: 5-8. [65] ZHANG X J, YE Q, QU R H, et al. High-power electro-optic switch technology based on novel transparent ceramic[J]. Chinese Physics B, 2016, 25(3): 034202. doi: 10.1088/1674-1056/25/3/034202 [66] 宋益澄, 何晓明, 郭乃健. PLZT电光调制器[J]. 光电子·激光,1984(4):37-40.SONG Y CH, HE X M, GUO N J. PLZT electro-optic modulator[J]. Journal of Optoelectronics·Laser, 1984(4): 37-40. (in Chinese) [67] CHEN F S, GEUSIC J E, KURTZ S K, et al. Light modulation and beam deflection with potassium tantalate-niobate crystals[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 1966, 37(1): 388-398. doi: 10.1063/1.1707846 [68] ITOH T, SASAURA M, TOYODA S, et al.. High-frequency response of electro-optic single crystal KTaxNb1-xO3 in paraelectric phase[C]. Proceedings of 2005 Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics/Quantum Electronics and Laser Science and Photonic Applications Systems Technologies, Optical Society of America, 2005: JTuC36. [69] CHANG Y C, YIN SH ZH, HOFFMAN R C, et al. Broadband large field of view electro-optic modulators using potassium tantalate niobate (KTN) crystals[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2013, 8847: 88470L. doi: 10.1117/12.2025529 [70] GUMENNIK A, KURZWEIL-SEGEV Y, AGRANAT A J. Electrooptical effects in glass forming liquids of dipolar nano-clusters embedded in a paraelectric environment[J]. Optical Materials Express, 2011, 1(3): 332-343. doi: 10.1364/OME.1.000332 [71] KABESSA Y, YATIV A, ILAN H E, et al. Electro-optical modulation with immunity to optical damage by bipolar operation in potassium lithium tantalate niobate[J]. Optics Express, 2015, 23(4): 4348-4356. doi: 10.1364/OE.23.004348 [72] 王骁乾, 沈冬, 郑致刚, 等. 液晶光控取向技术进展[J]. 液晶与显示,2015,30(5):737-751. doi: 10.3788/YJYXS20153005.0737WANG X Q, SHEN D, ZHEN ZH G, et al. Review on liquid crystal photoalignment technologies[J]. Chinese Journal of Liquid Crystals and Displays, 2015, 30(5): 737-751. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/YJYXS20153005.0737 -





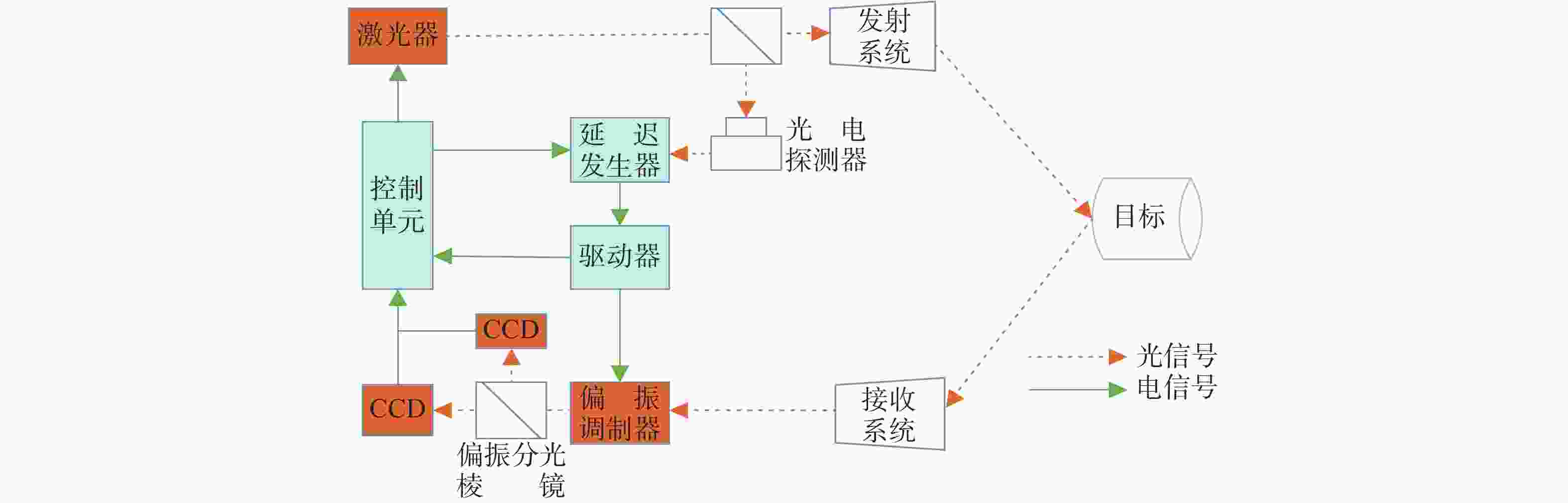
 下载:
下载: