-
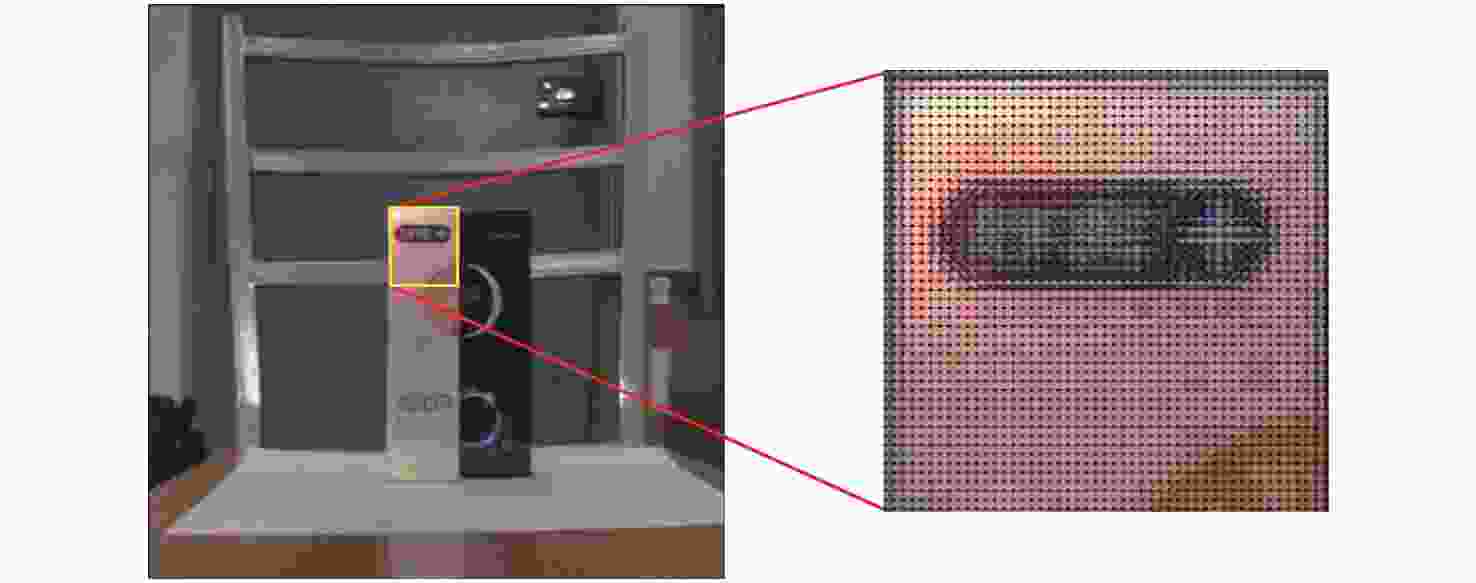
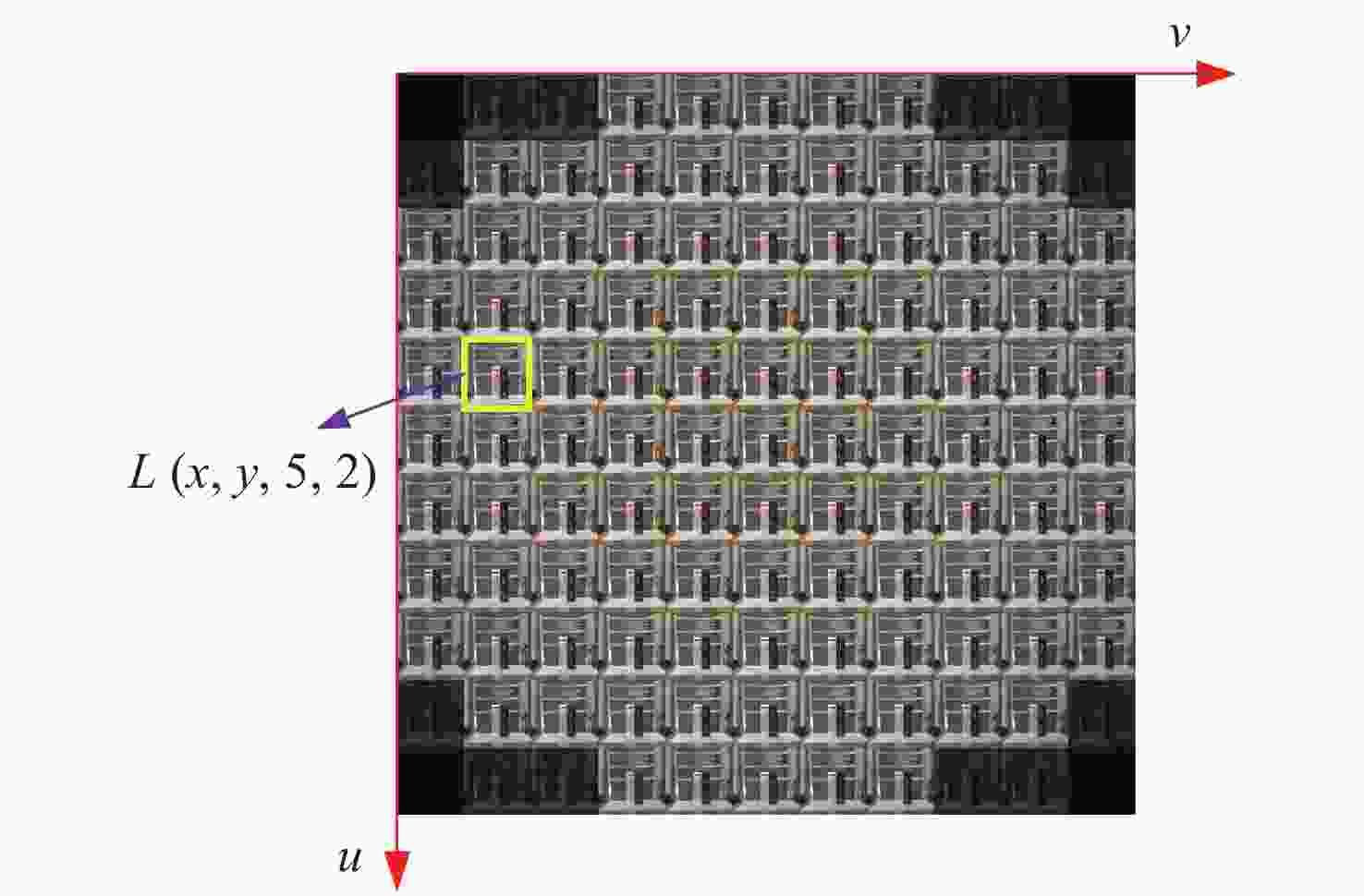
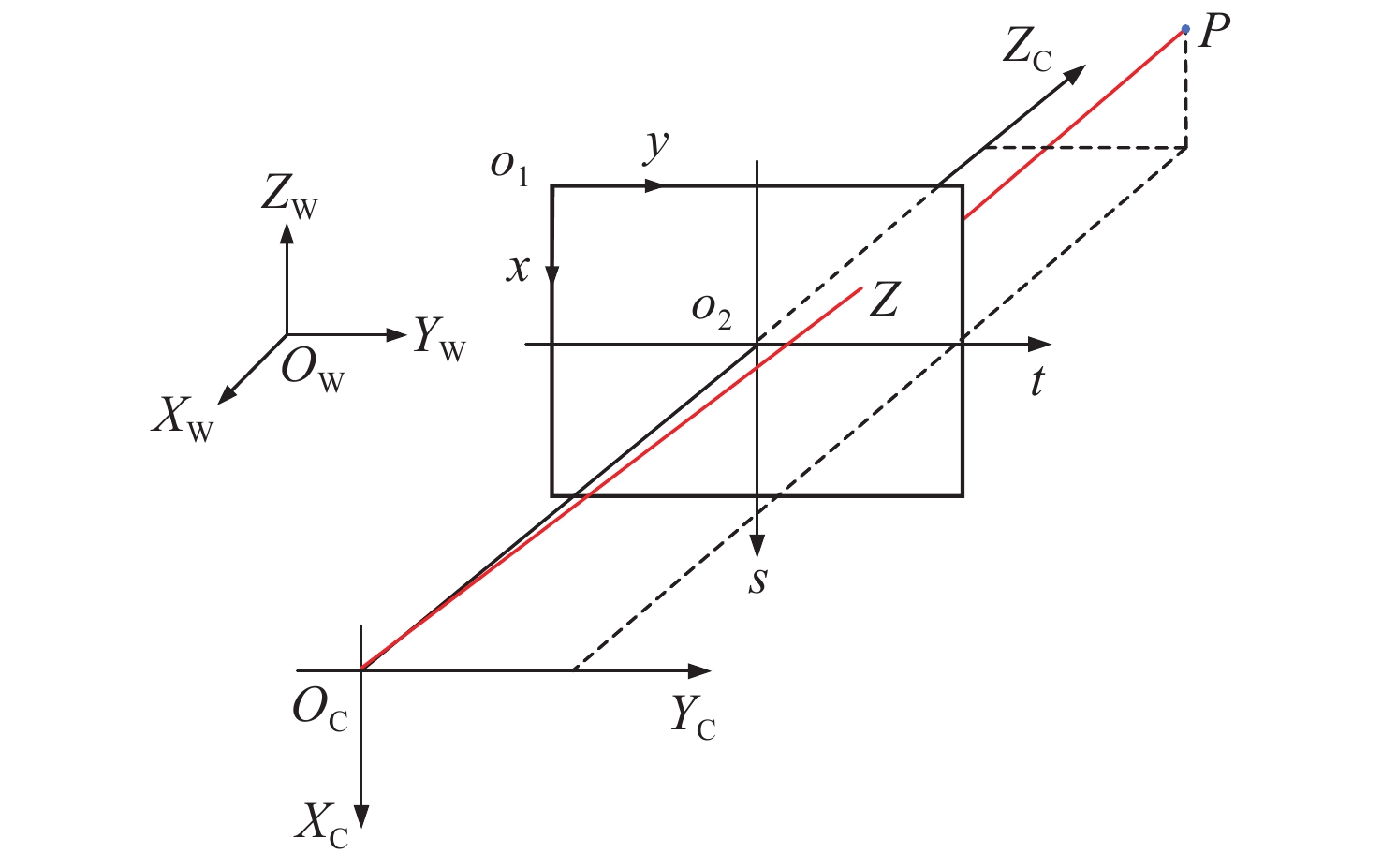
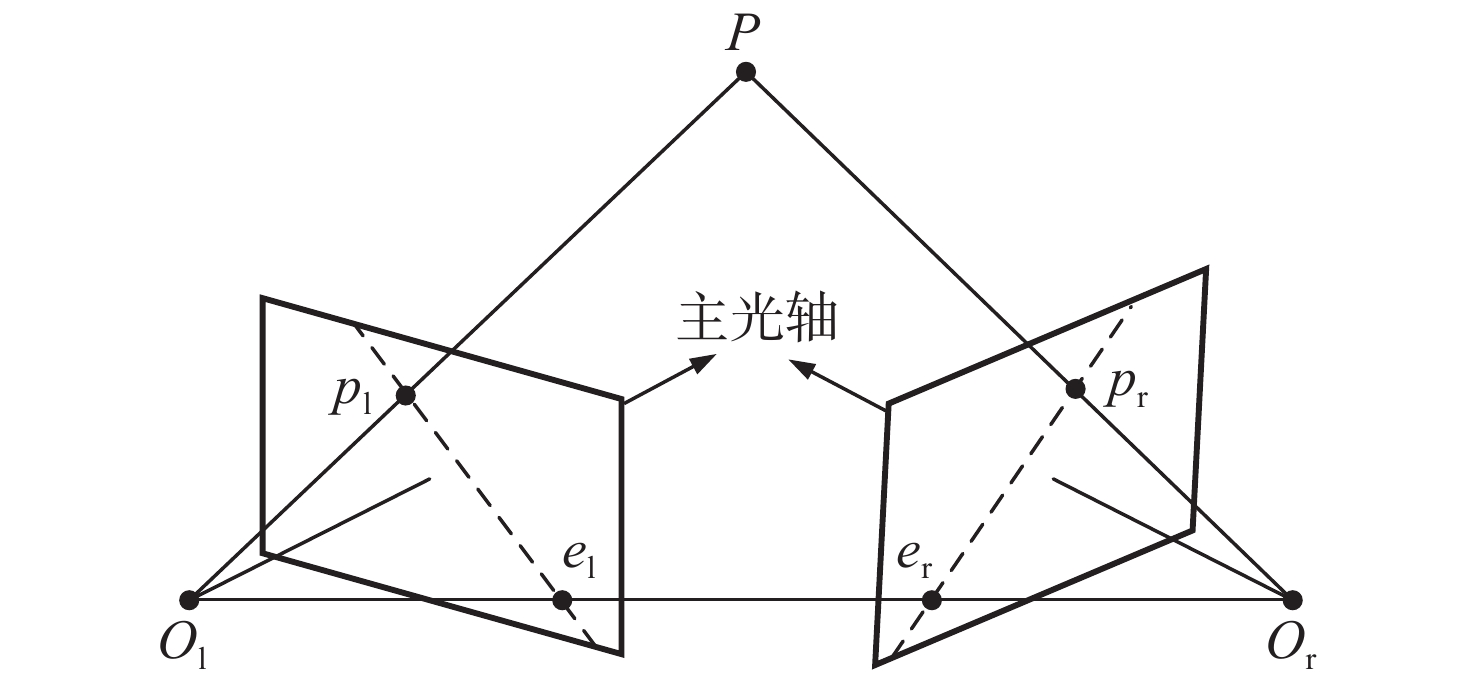
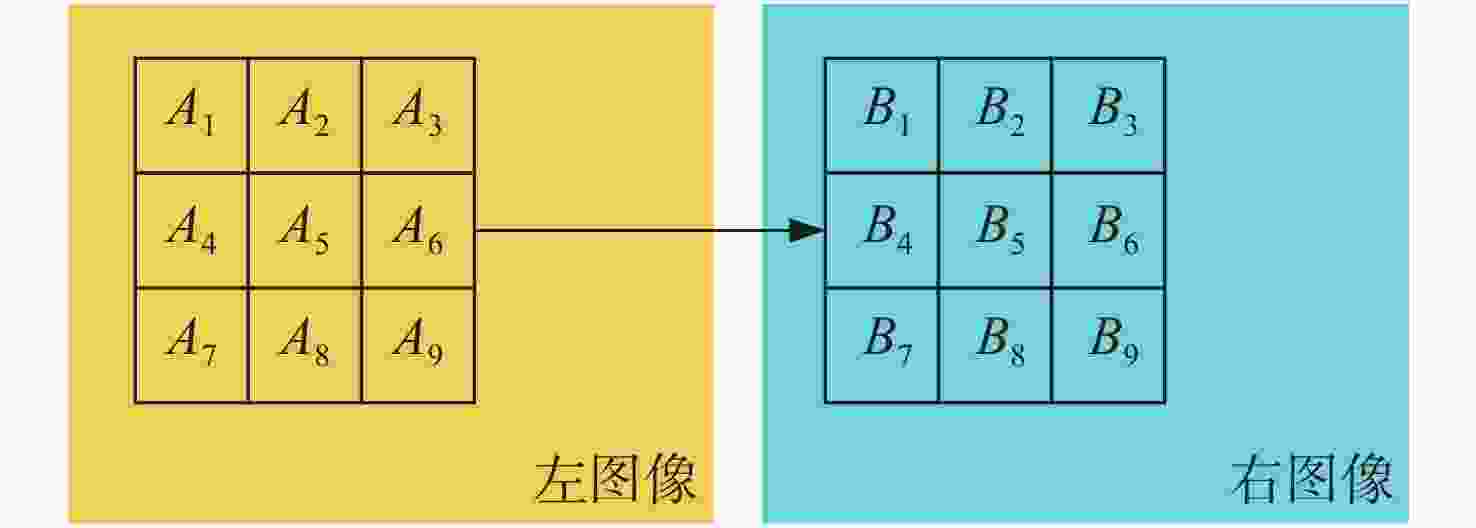
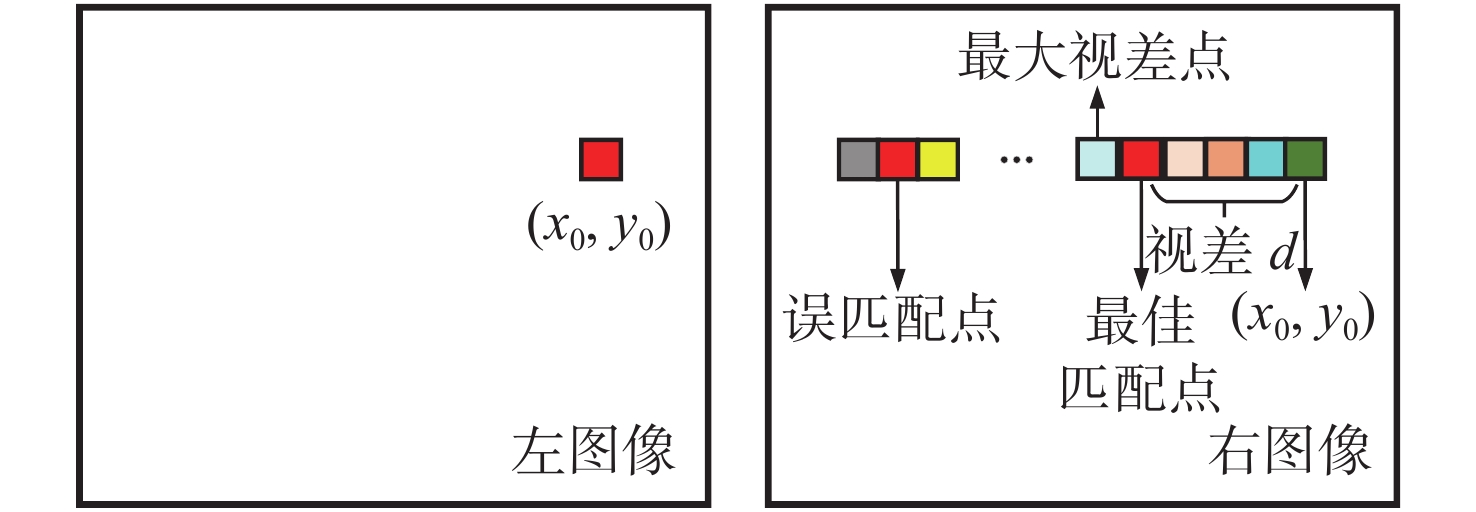
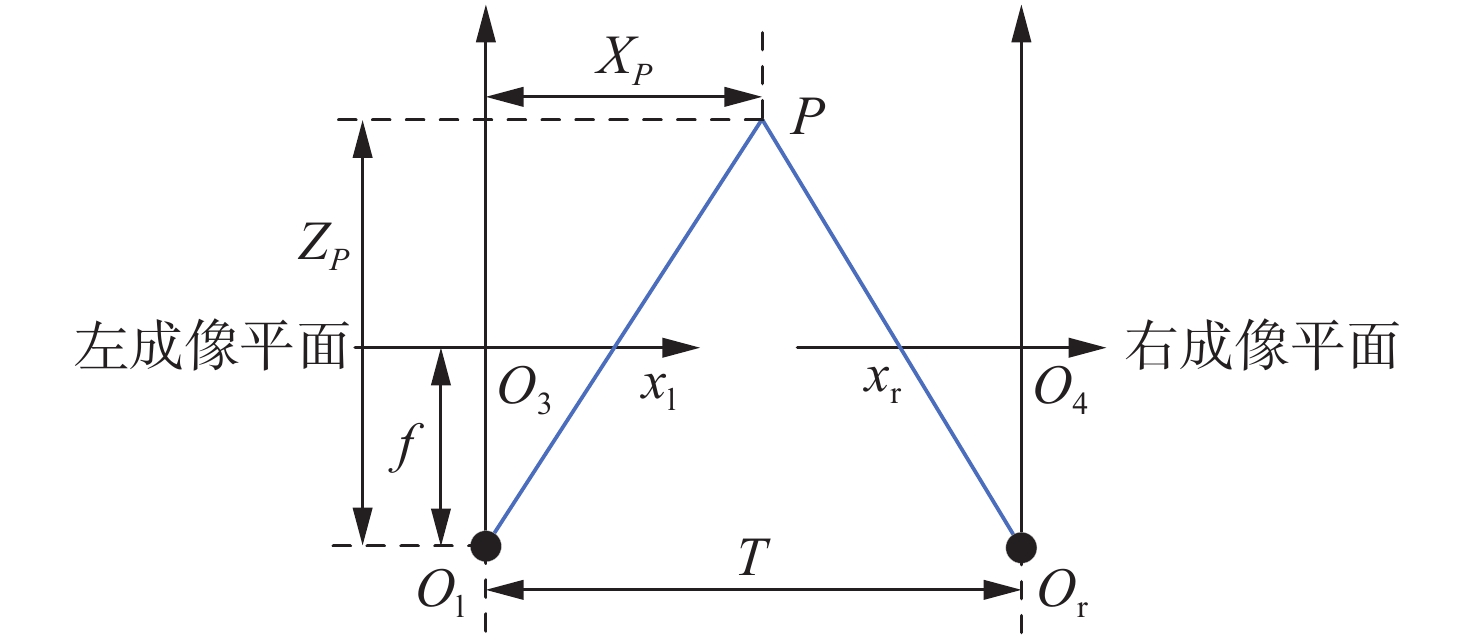
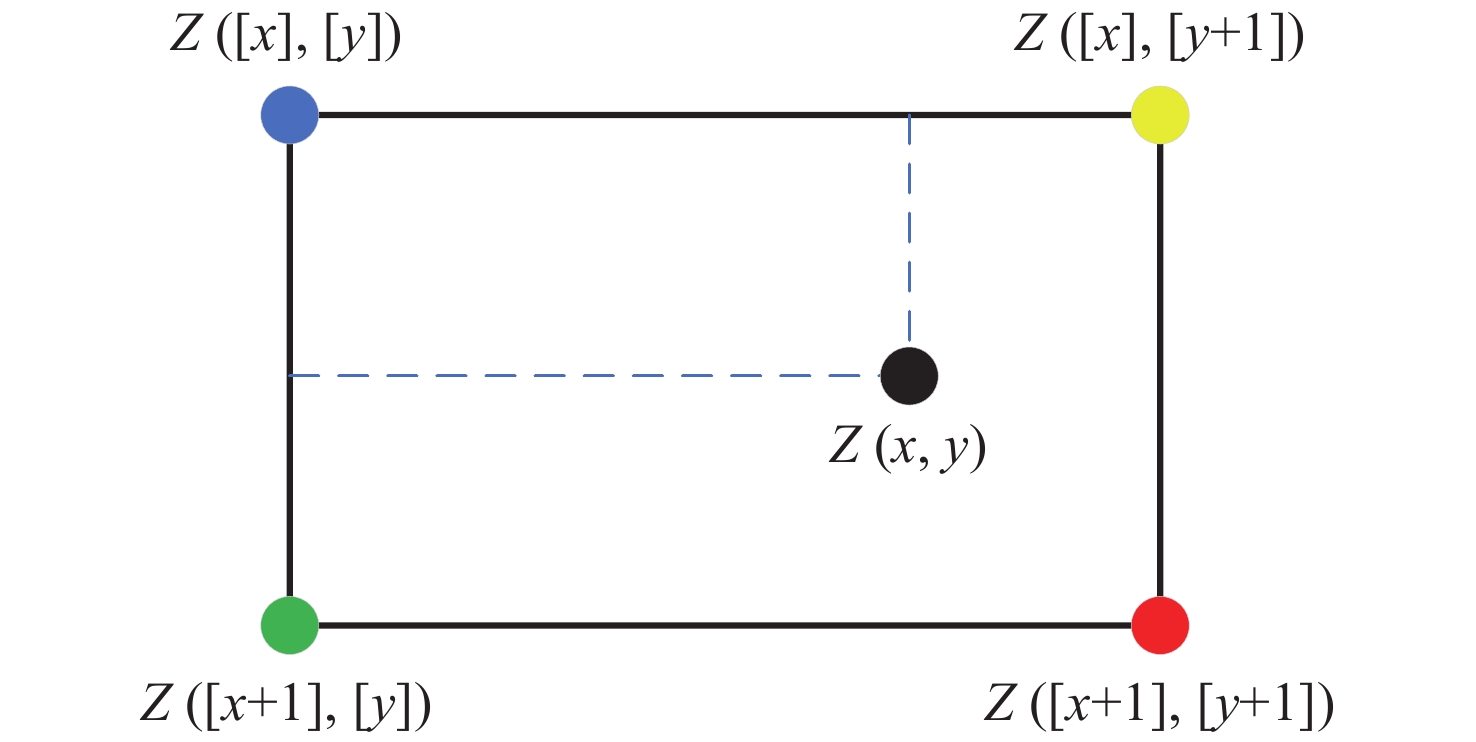
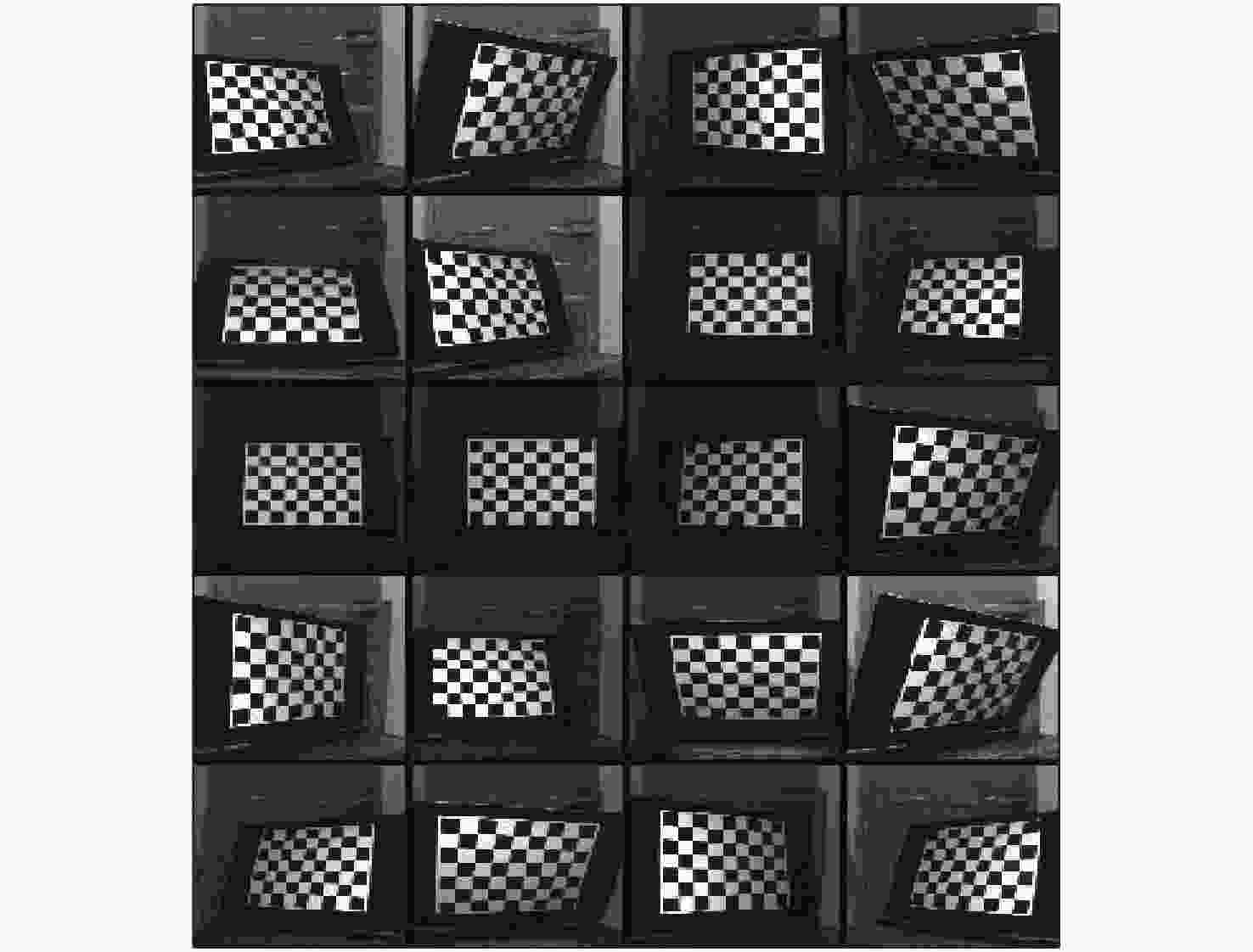
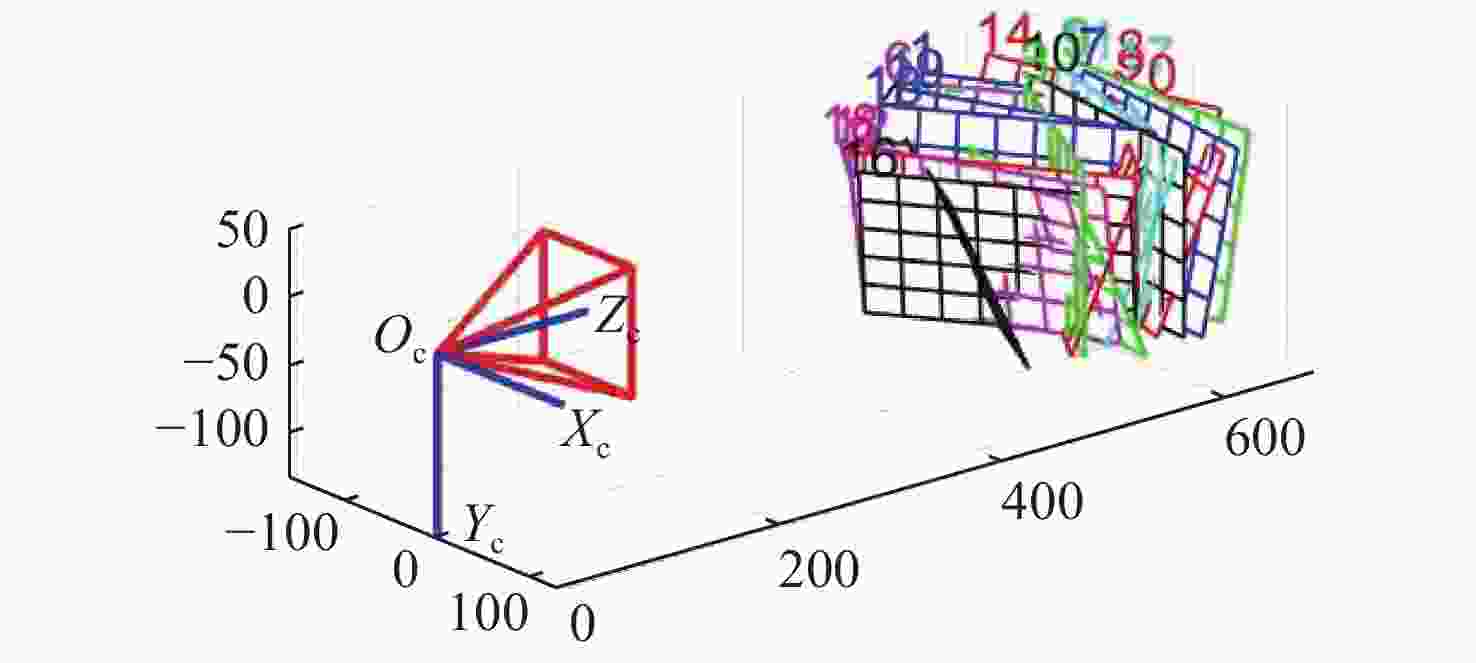
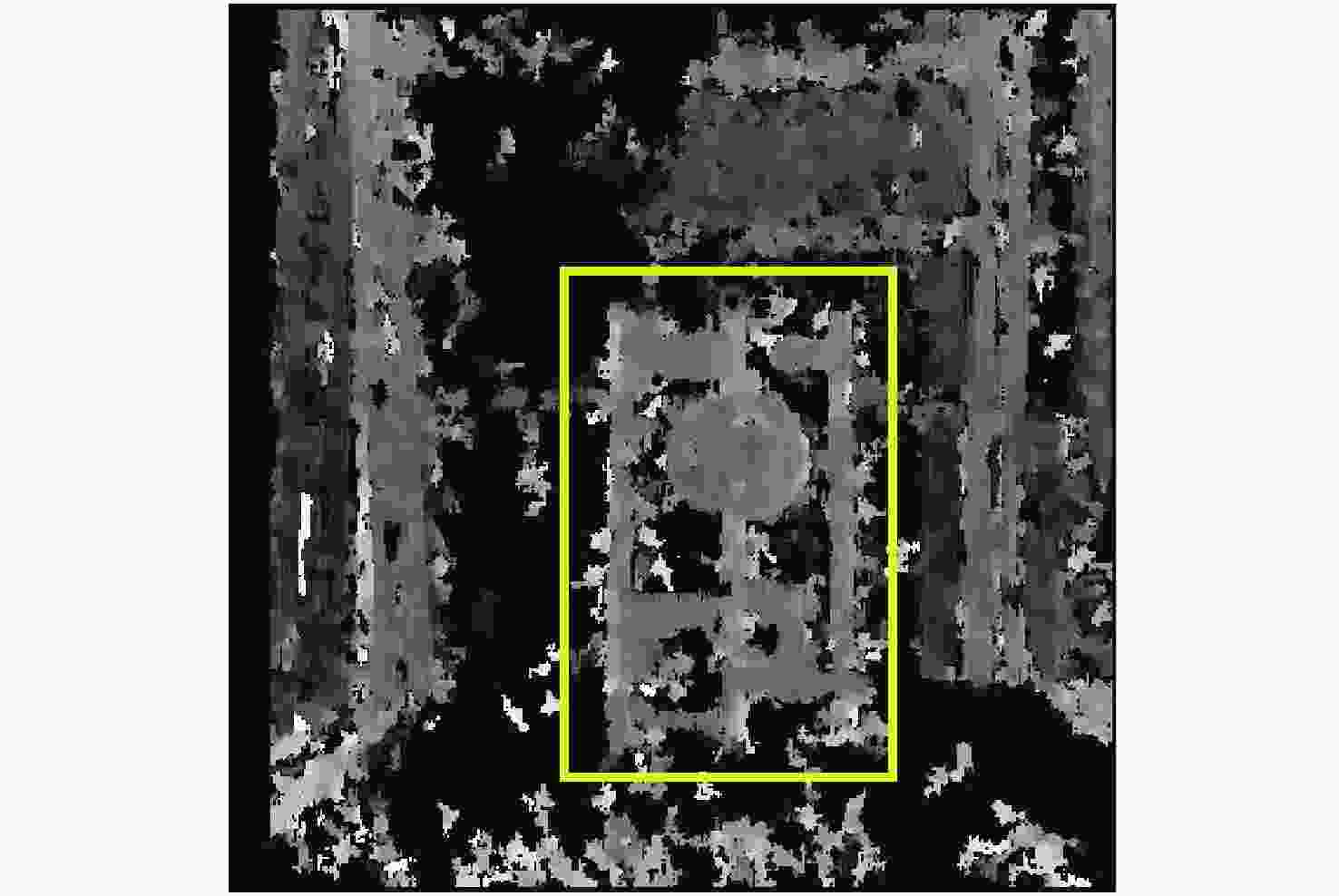
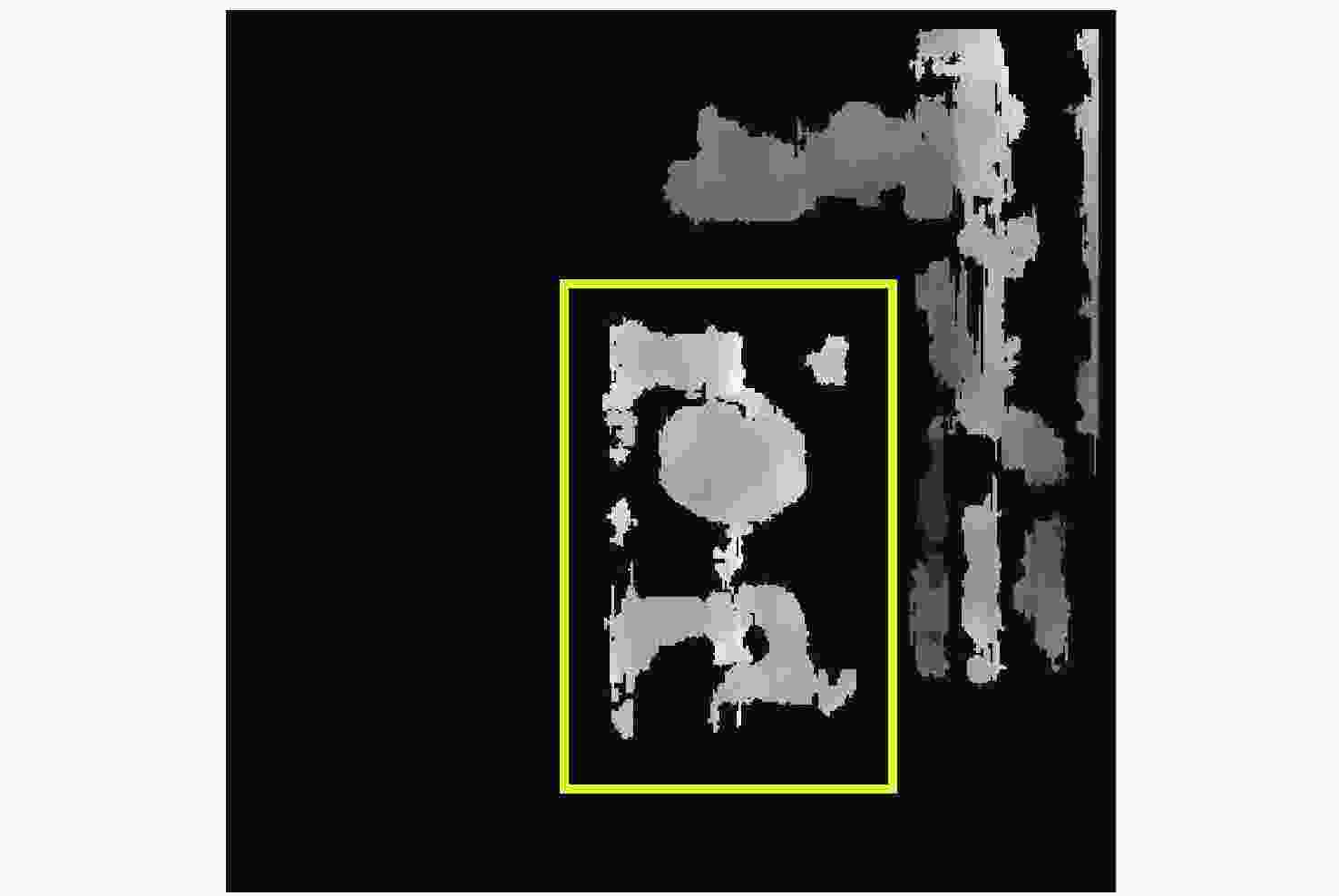
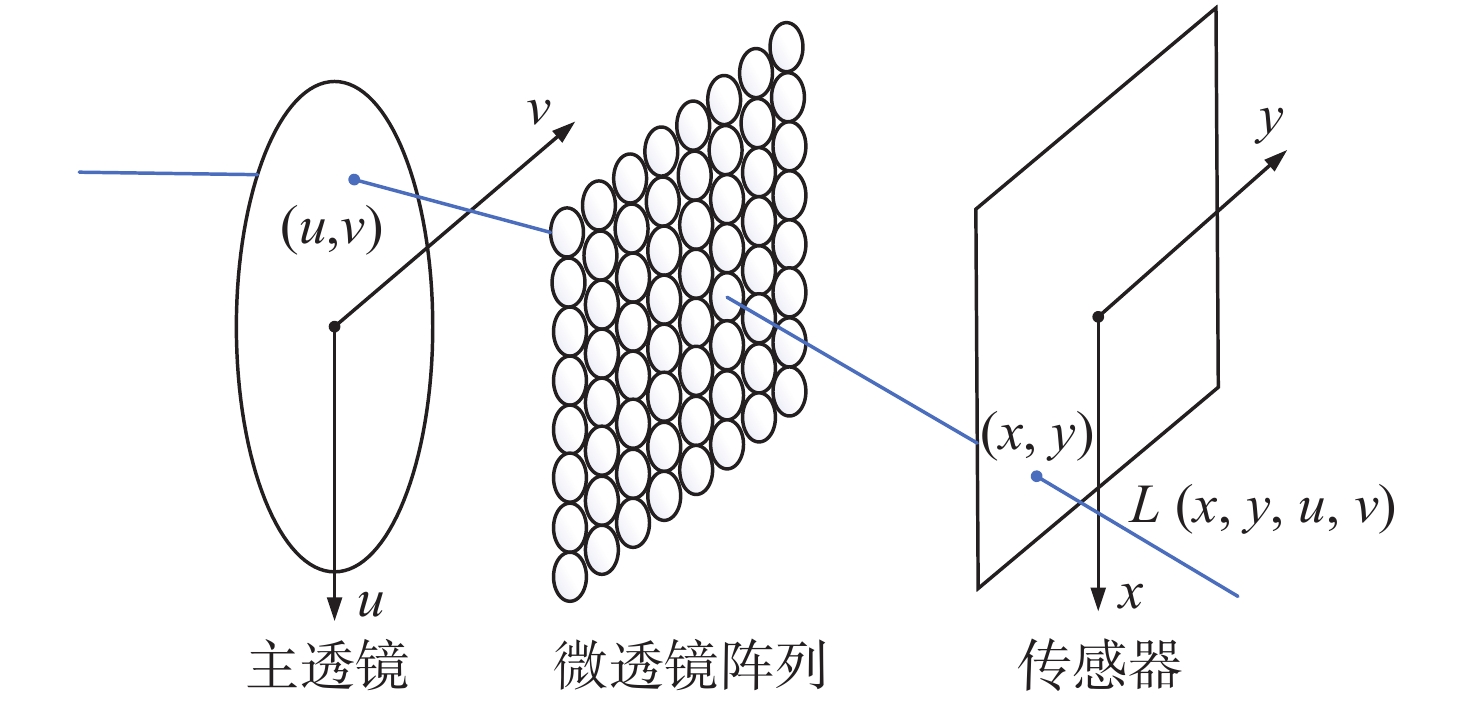
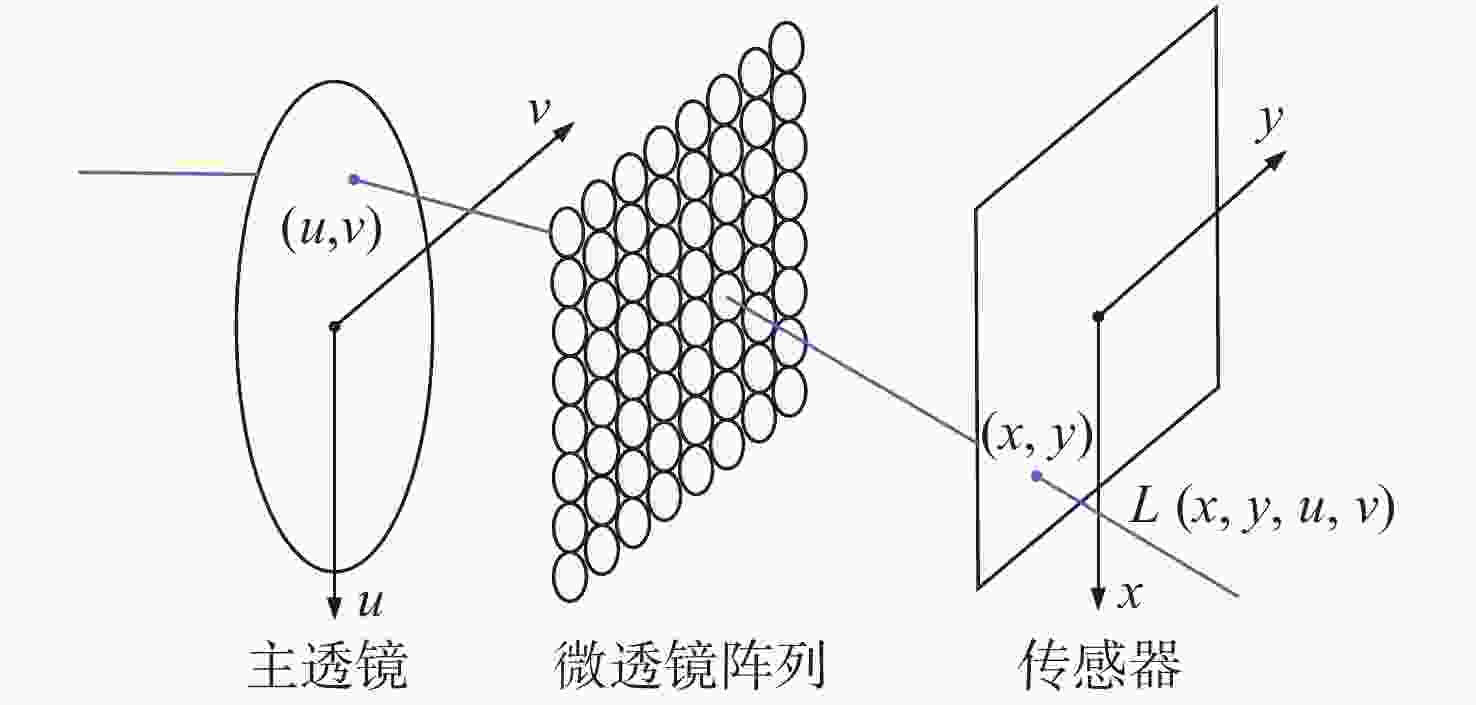
摘要: 为了使现代制导律能够在图像制导中得以应用,提高图像制导的性能,针对图像制导难以获取目标距离信息的问题,提出基于光场成像的目标测距算法。该算法首先对光场数据进行解码和整定,从原始图像中提取出子孔径图像;其次,对两张子孔径图像进行双线性插值,以提高图像的空间分辨率;之后,选取两张子孔径图像进行标定以获取对应的内参数和外参数,并利用这些参数校正子孔径图像,使其共面且行对准;最后,采用半全局匹配方法进行图像匹配,获取目标的视差值,将视差进行三维转换即可得到目标距离。实验结果表明,改进前、后算法的平均测量误差分别为28.54 mm和14.96 mm,距离测量精度得到有效提高,能够在较为复杂的场景中有效提取目标距离信息,具有一定的理论和应用价值。Abstract: At present, it is difficult to obtain target distance information in image guidance. In order to apply modern guidance laws to image guidance technology and improve its performance, a target ranging algorithm using light field imaging is proposed. The algorithm decodes and tunes light field data to extract sub-aperture images from an original image. Bilinear interpolation is then performed on the two sub-aperture images to improve the image’s spatial resolution, and two sub-aperture images are selected as calibration data to obtain the corresponding internal and external parameters. The parameters are used to correct the sub-aperture images, which aligns them and makes them coplanar. Finally, a semi-global matching method is used to match the images to obtain the disparity value of the target. Then, 3D transformation of parallax can be used to get the target distance. The experimental results show that the average measurement errors of the algorithm are 28.54 mm and 14.96 mm, respectively, before and after improvement. This algorithm can effectively extract target distance information in complex scenes, which has value in theoretical and real-world applications.
-
Key words:
- light field imaging /
- sub-aperture images /
- distance measurement
-
表 1 不同算法的测量结果
Table 1. Measurement results with different algorithms
距离测量/mm 有效像素点 初始算法 488.57 8051 双线性插值算法 480.59 21363 半全局匹配算法 483.10 16659 双重改进算法 466.55 57441 表 2 实验结果
Table 2. Experiment results
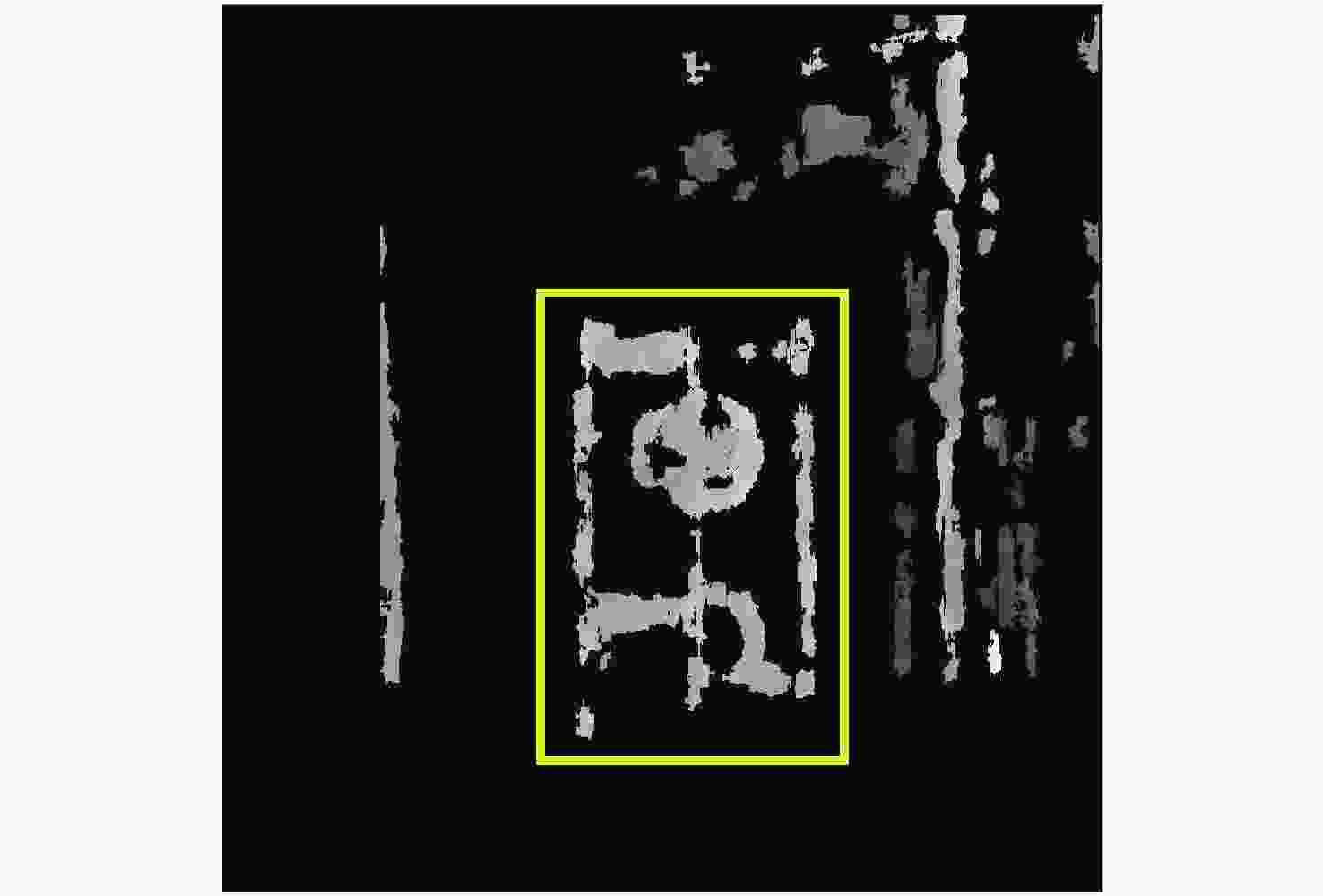
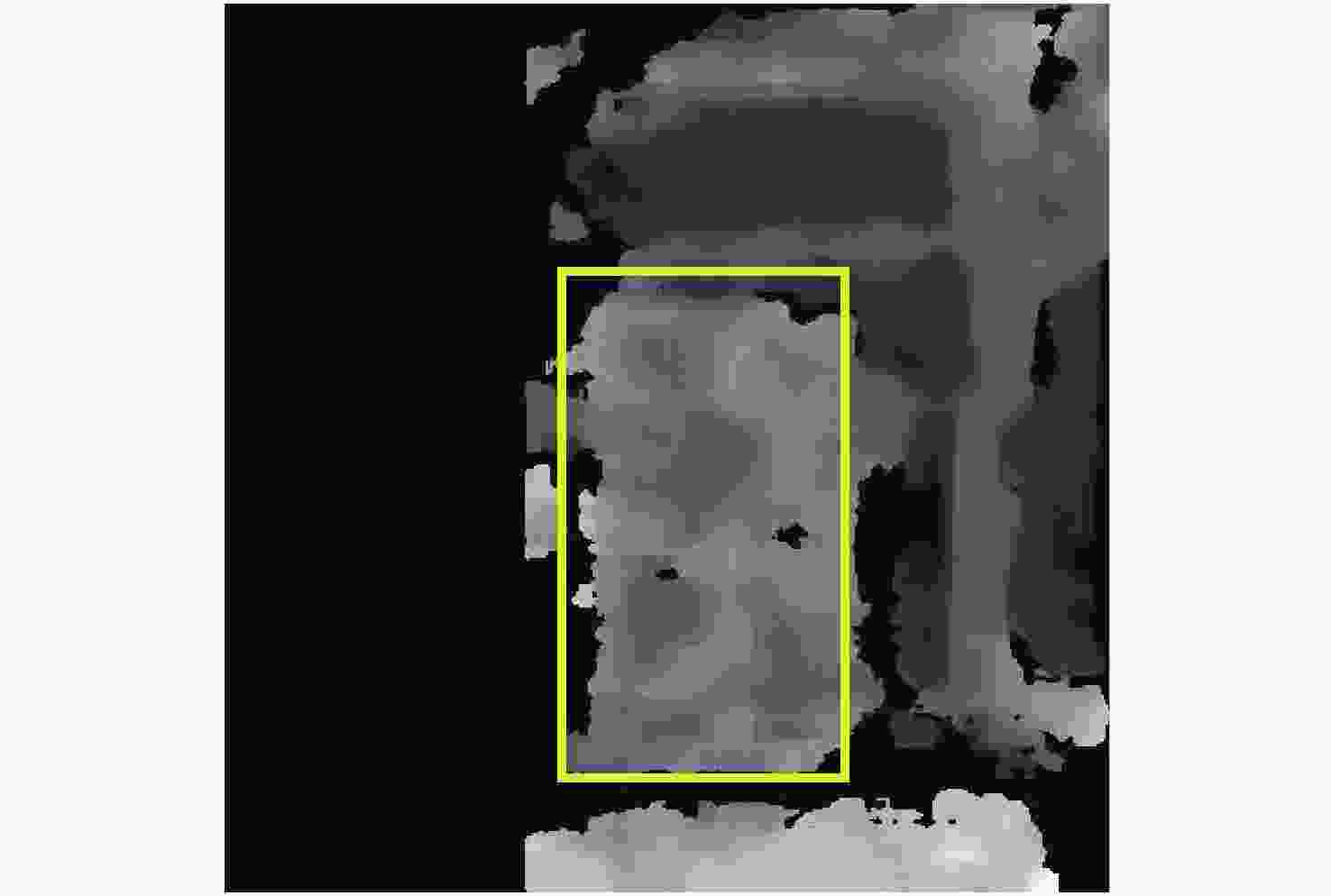
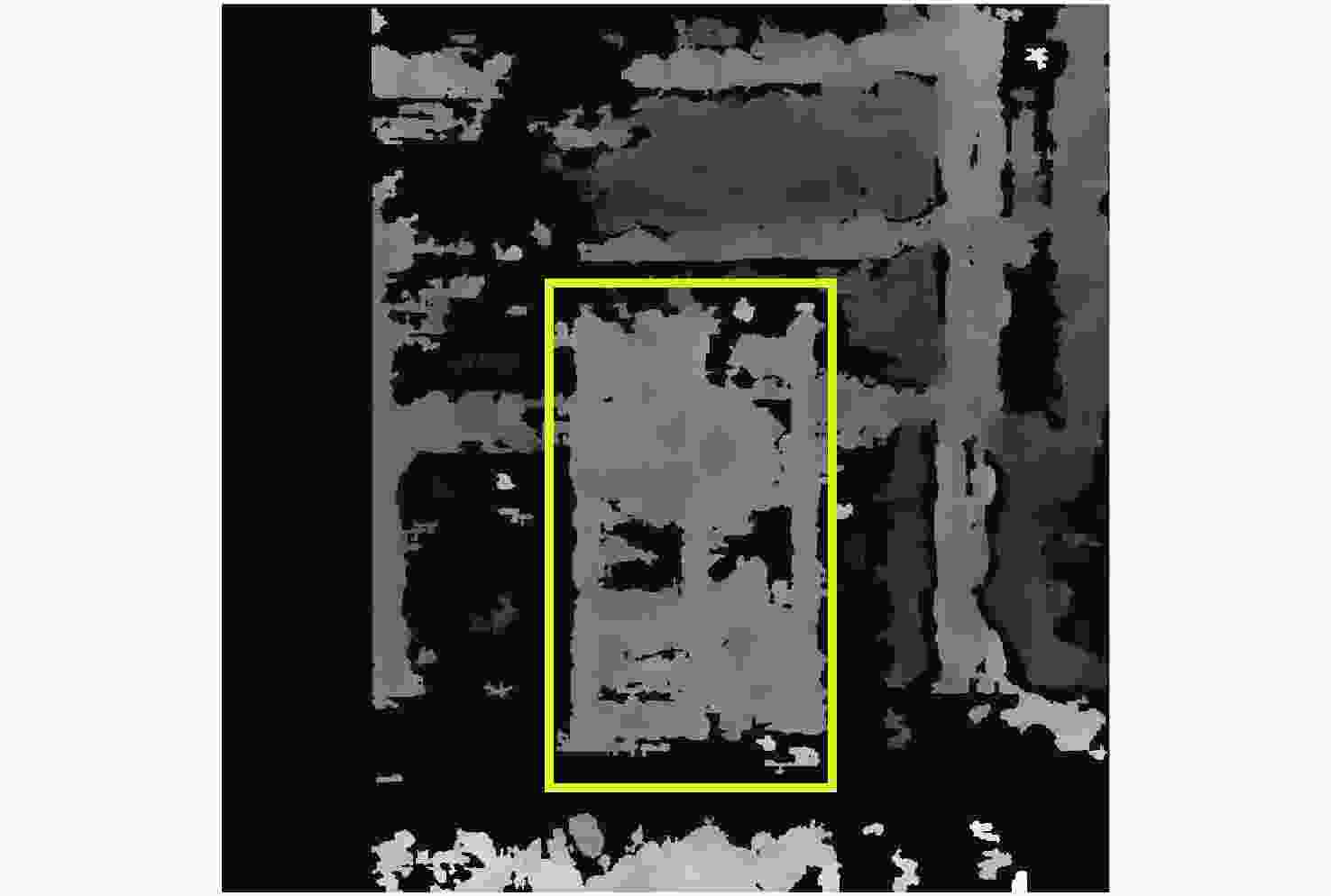
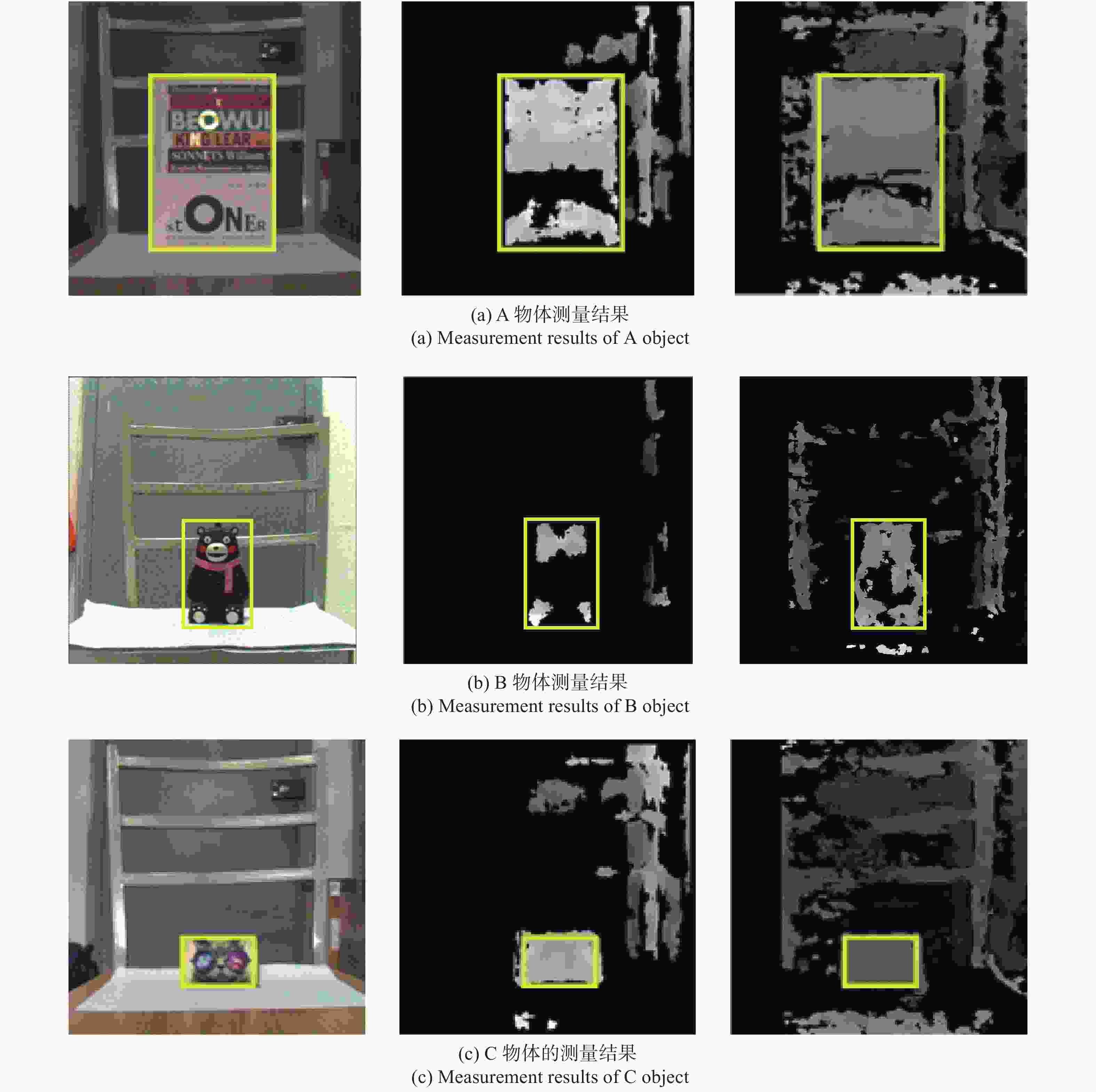
真实距离/mm 距离测量/mm 有效像素点 时间/s A-初始算法 400 442.83 17218 1.31 A-改进算法 400 431.14 111380 6.42 B-初始算法 400 372.50 3161 1.06 B-改进算法 400 392.54 28557 5.83 C-初始算法 450 465.28 4156 1.27 C-改进算法 450 443.72 14168 5.76 -
[1] 姚秀娟, 彭晓乐, 张永科. 几种精确制导技术简述[J]. 激光与红外,2006,36(5):338-340. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5078.2006.05.002YAO X J, PENG X L, ZHANG Y K. Brief descriptions of precision guidance technology[J]. Laser &Infrared, 2006, 36(5): 338-340. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5078.2006.05.002 [2] 胡林亭, 李佩军, 姚志军. 提高外场重频激光光斑测量距离的研究[J]. 液晶与显示,2006,31(12):1137-1142.HU L T, LI P J, YAO ZH J. Improvement of the measuring distance of repetitive-frequency laser spot in field[J]. Chinese Journal of Liquid Crystals and Displays, 2006, 31(12): 1137-1142. (in Chinese) [3] 黄继鹏, 王延杰, 孙宏海. 激光光斑位置精确测量系统[J]. 光学 精密工程,2013,21(4):841-848. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20132104.0841HUANG J P, WANG Y J, SUN H H. Precise position measuring system for laser spots[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2013, 21(4): 841-848. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/OPE.20132104.0841 [4] 谢艳新. 基于LatLRR和PCNN的红外与可见光融合算法[J]. 液晶与显示,2019,34(4):423-429. doi: 10.3788/YJYXS20193404.0423XIE Y X. Infrared and visible fusion algorithm based on latLRR and PCNN[J]. Chinese Journal of Liquid Crystals and Displays, 2019, 34(4): 423-429. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/YJYXS20193404.0423 [5] 赵战民, 朱占龙, 王军芬. 改进的基于灰度级的模糊C均值图像分割算法[J]. 液晶与显示,2020,35(5):499-507. doi: 10.3788/YJYXS20203505.0499ZHAO ZH M, ZHU ZH L, WANG J F. Improved fuzzy C-means algorithm based on gray-level for image segmentation[J]. Chinese Journal of Liquid Crystals and Displays, 2020, 35(5): 499-507. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/YJYXS20203505.0499 [6] 冯维, 吴贵铭, 赵大兴, 等. 多图像融合Retinex用于弱光图像增强[J]. 光学 精密工程,2020,28(3):736-744. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20202803.0736FENG W, WU G M, ZHAO D X, et al. Multi images fusion Retinex for low light image enhancement[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2020, 28(3): 736-744. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/OPE.20202803.0736 [7] YANG J C, EVERETT M, BUEHLER C. A real-time distributed light field camera[C]. Proceedings of the 13th Eurographics Workshop on Rendering, ACM, 2002: 77-86. [8] NG R. Digital light field photography[D]. California: Stanford University, 2006: 38-50. [9] 计吉焘, 翟雨生, 吴志鹏, 等. 基于周期性光栅结构的表面等离激元探测[J]. 光学 精密工程,2020,28(3):526-534. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20202803.0526JI J T, ZHAI Y SH, WU ZH P, et al. Detection of surface plasmons based on periodic grating structure[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2020, 28(3): 526-534. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/OPE.20202803.0526 [10] 于洁, 李鹏涛, 王春华, 等. RGBW液晶显示中的像素极性排布方式解析[J]. 液晶与显示,2020,35(5):444-448. doi: 10.3788/YJYXS20203505.0444YU J, LI P T, WANG CH H, et al. Pixel polarity arrangement analysis of RGBW LCD module[J]. Chinese Journal of Liquid Crystals and Displays, 2020, 35(5): 444-448. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/YJYXS20203505.0444 [11] 王江南, 丁磊, 倪婷, 等. 基于微结构阵列基板的高效顶发射OLED器件[J]. 液晶与显示,2019,34(8):725-732. doi: 10.3788/YJYXS20193408.0725WANG J N, DING L, NI T, et al. High-efficiency top-emitting OLEDs based on microstructure array substrate[J]. Chinese Journal of Liquid Crystals and Displays, 2019, 34(8): 725-732. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/YJYXS20193408.0725 [12] 解培月, 杨建峰, 薛彬, 等. 基于矩阵变换的光场成像及重聚焦模型仿真[J]. 光子学报,2017,46(5):0510001. doi: 10.3788/gzxb20174605.0510001XIE P Y, YANG J F, XUE B, et al. Simulation of light field imaging and refocusing models based on matrix transformation[J]. Acta Photonica Sinica, 2017, 46(5): 0510001. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/gzxb20174605.0510001 [13] 张春萍, 王庆. 光场相机成像模型及参数标定方法综述[J]. 中国激光,2016,43(6):0609004. doi: 10.3788/CJL201643.0609004ZHANG CH P, WANG Q. Survey on imaging model and calibration of light field camera[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2016, 43(6): 0609004. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/CJL201643.0609004 [14] LIN X, RIVENSON Y, YARDIMCI N T, et al. All-optical machine learning using diffractive deep neural networks[J]. Science, 2018, 361(6406): 1004-1008. doi: 10.1126/science.aat8084 [15] YAN T, WU J M, ZHOU T K, et al. Fourier-space diffractive deep neural network[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2019, 123(2): 023901. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.123.023901 [16] SHIN C, JEON H G, YOON Y, et al.. EPINET: a fully-convolutional neural network using epipolar geometry for depth from light field images[C]. Proceedings of 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE, 2018: 4748-4757. [17] PENG J Y, XIONG ZH W, LIU D, et al.. Unsupervised depth estimation from light field using a convolutional neural network[C]. Proceedings of 2018 International Conference on 3D Vision, IEEE, 2018: 295-303. [18] ZHOU T H, TUCKER R, FLYNN J, et al. Stereo magnification: learning view synthesis using multiplane images[J]. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2018, 37(4): 65. [19] YEUNG H W F, HOU J H, CHEN J, et al.. Fast light field reconstruction with deep coarse-to-fine modeling of spatial-angular clues[C]. Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision, Springer, 2018: 137-152. [20] ZHANG ZH Y. A flexible new technique for camera calibration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2000, 22(11): 1330-1334. doi: 10.1109/34.888718 -





 下载:
下载: