-
摘要: 基于激光散斑的目标探测技术是一种长期以来被人们忽略的激光探测技术,该技术将传统激光探测技术中视为噪声的激光散斑视为新的信息来源,通过分析激光散斑形成机理探究散斑统计特性与目标物理特性间的关系,并结合行之有效的分析反演方法来获得包括目标形状、尺寸、表面粗糙度以及动力学参数等信息。与传统激光探测技术相比,基于激光散斑的目标探测技术具有结构简单,对光学系统要求低,对目标表面物理特性及微动特性敏感等特点,目前已广泛应用于航天、医学、工业、军事等多个领域。本文对近年来各类基于激光散斑的目标探测技术进行了分类总结,对各类探测方法的用途和优缺点以及适用环境进行了对比分析,对未来基于激光散斑的目标探测方法的发展趋势加以分析。Abstract: Target detection technology based on laser speckles is a kind of laser detection technology that has been ignored for a long time. In this technology, the laser speckle, which is regarded as noise in the traditional laser detection technology, is used as a new source of information. By analyzing the formation mechanism of a laser speckle pattern, the relationship between the statistical characteristics and the physical characteristics of the target is explored, and the effective analysis and inversion methods are combined to obtain the target’s shape, size, surface roughness and dynamic parameters. Compared with traditional laser detection technology, target detection technology based on laser speckles has a simple structure, has low optical system requirements, is sensitive to the physical and fretting characteristics of the target’s surface, and has been widely used in aerospace, medicine, industry, military and other fields. This paper classifies and summarizes the various kinds of speckle-based target detection technologies from recent years, compares and analyzes their applications, advantages and disadvantages, as well as the environmental restrictions. Finally, this paper prospects the trend for the future development of target detection methods based on laser speckles.
-
Key words:
- laser speckle /
- target detection /
- three-dimensional imaging /
- target recognition
-
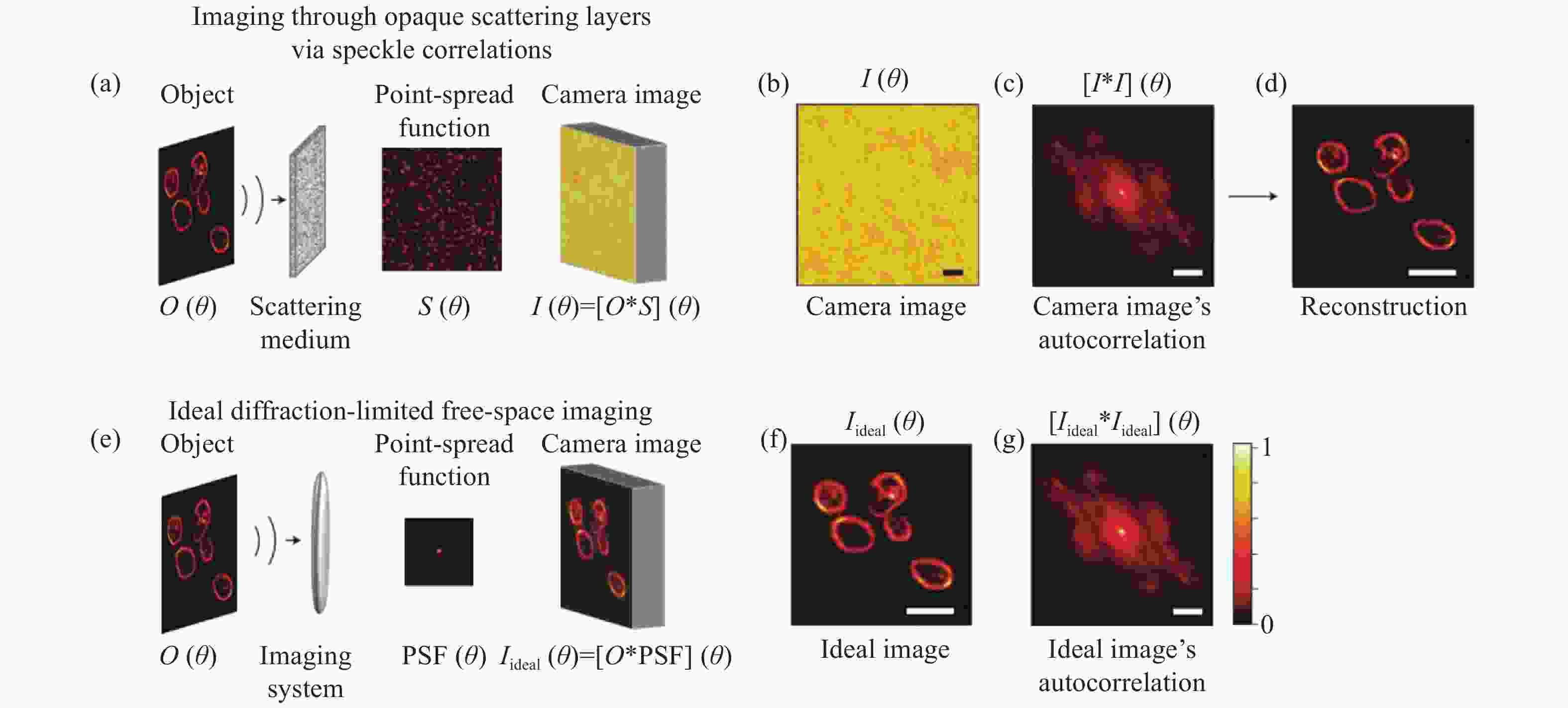
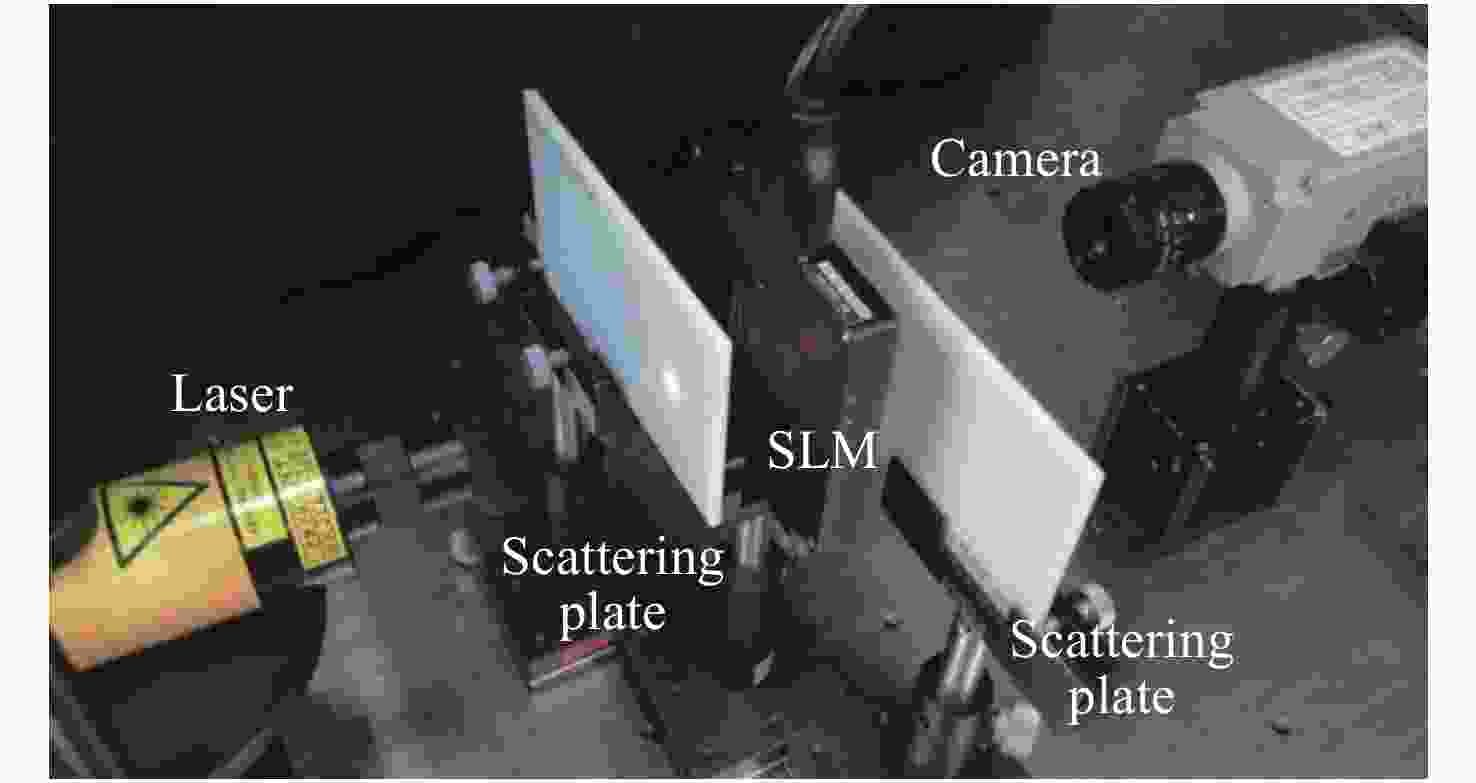
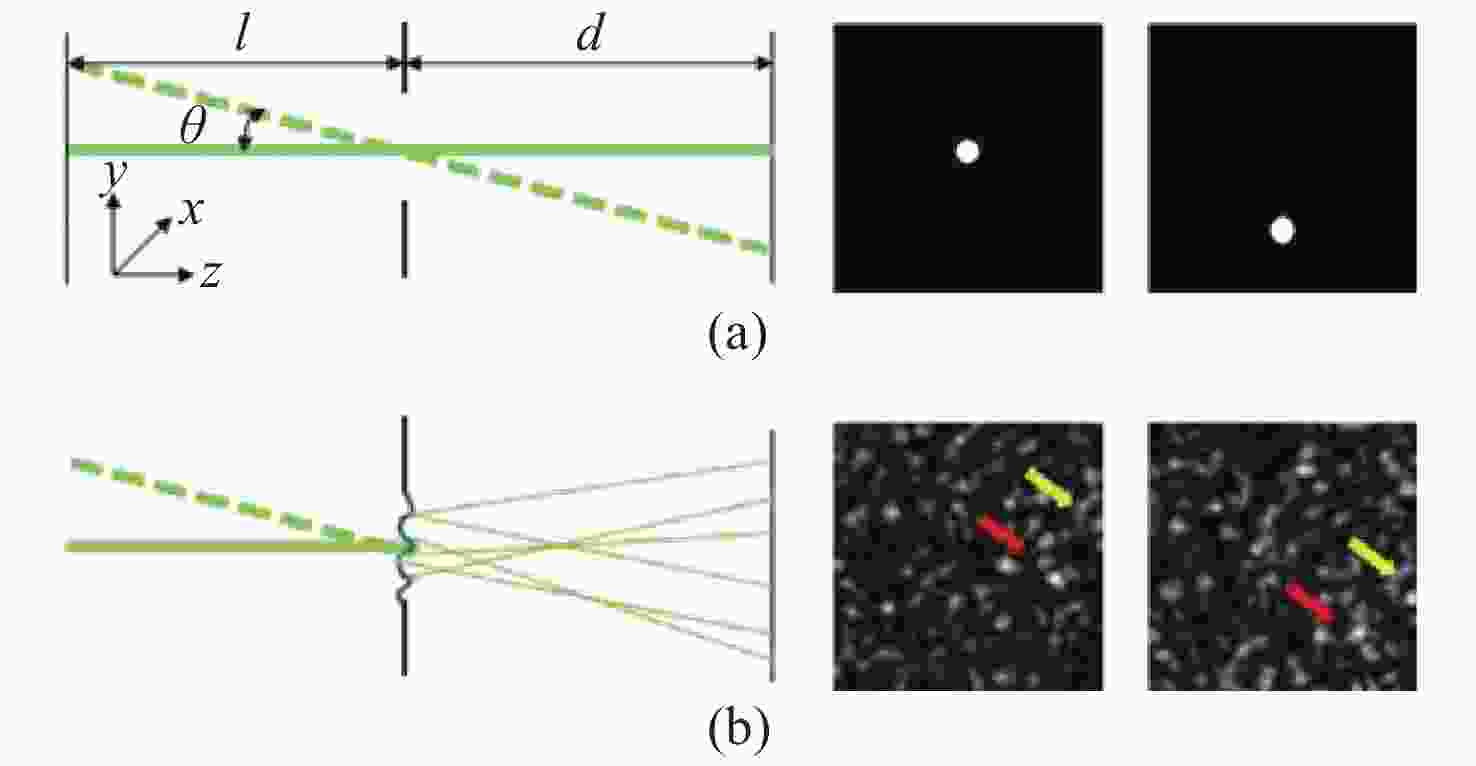
图 5 基于散斑相关的透过强散射介质的非侵入成像[48] 。(a)实验原理示意图;(b)初始散斑图像;(c)初始散斑图像的自相关;(d)重构图像;(e-g)理想的衍射极限自由空间成像
Figure 5. Non-invasive imaging through strong scattering media based on speckle correlation[48]. (a) Schematic diagram of experimental principle; (b) raw speckle image; (c) autocorrelation of raw speckle image; (d) reconstructed image; (e-g) ideal diffraction-limited free-space imaging
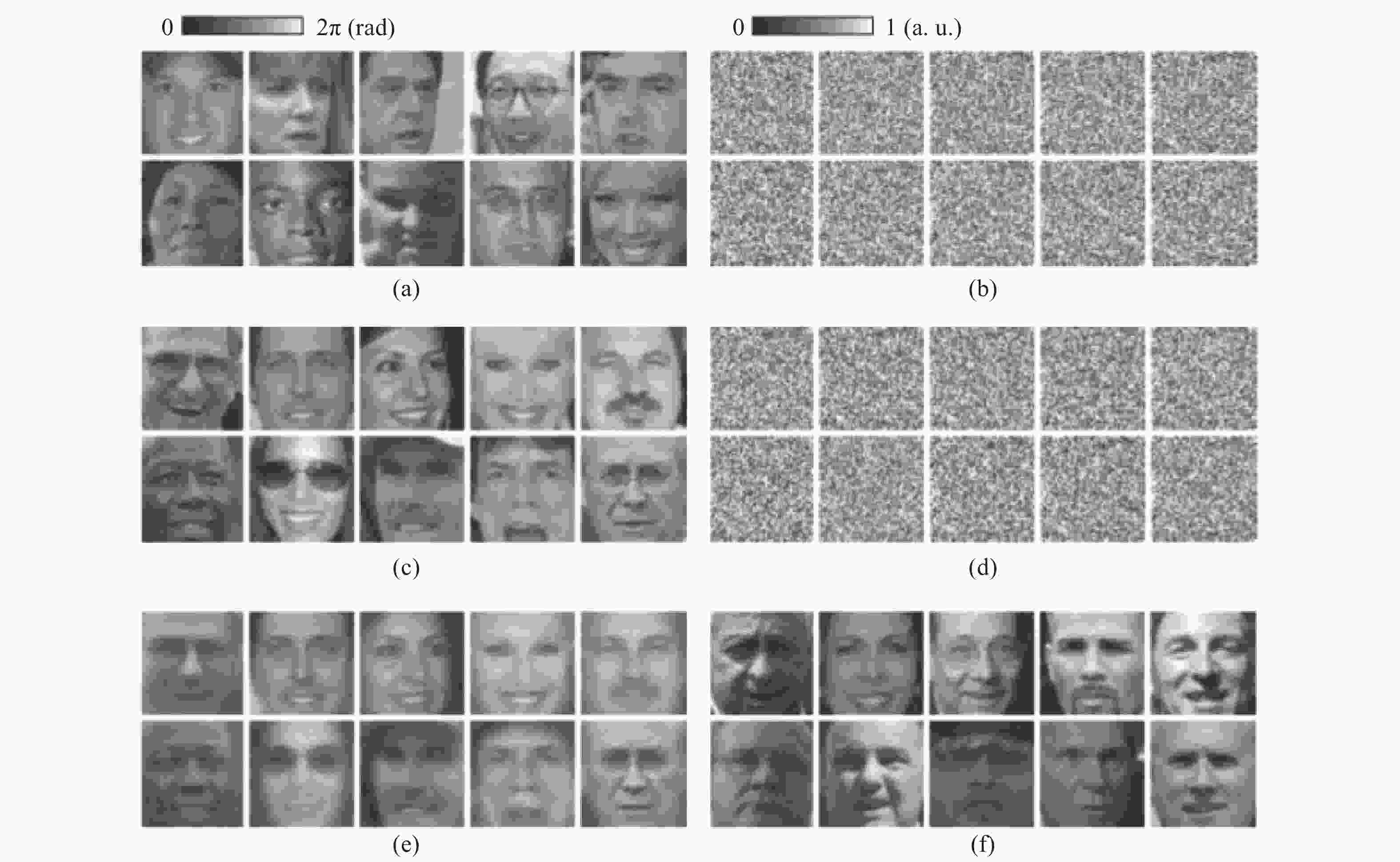
图 7 10个训练对象的(a)原始图像[51]及(b)对应的散斑图案。10个测试图像的(c)原始图像及(d)对应的散斑图案。基于(e)SVR方法和(f)模式匹配方法重构的目标像。
Figure 7. (a) Object images and (b) their measured speckle patterns for ten training examples. (c) Object images and (d) their measured speckle patterns for ten test examples. Reconstruction images obtained by (e) the SVR method and (f) the pattern matching method.
表 1 基于散斑的表面粗糙度探测方法对比
Table 1. Comparison of the surface roughness detection methods based on speckles
方法 优势 特点 缺陷 散斑对比度法 ------- 快速,非接触,非破坏性,光学装置简单,
可在线测量测量精度受限于被测表面的相关长度 镜像强度分量法 克服了对比度方法中
存在的精度极限问题更快的速度,更高的精度,依赖于镜像光分量 仅适用于测量有镜像回波的微粗糙表面 相关方法(角度相关和
光谱相关)更高的测量精度 更高的测量精度,对角度变化敏感 需要精确的角度校准,在非合作情况以及有机加工振动情况下探测精度差 散斑分形 更少的计算资源需求,
更简洁的光学装置对机加工过程敏感,可用于对材料和
机加工方式的识别探测精度还不能满足现有需求 -
[1] 郭冠军, 邵芸. 地面对激光雷达信号散射的统计研究[J]. 物理学报,2001,51(2):228-234.GUO G J, SHAO Y. Statistical properties of the back-scattered signals from ground in laser radar applications[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2001, 51(2): 228-234. (in Chinese) [2] 李自勤, 王骐, 李琦, 等. 激光成像雷达系统中散斑像的乘法模型及其滤除[J]. 中国激光,2003,30(8):717-720.LI Z Q, WANG Q, LI Q, et al. Multiplication model of speckle image and speckle suppression in imaging lidar[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2003, 30(8): 717-720. (in Chinese) [3] 郭冠军, 邵芸. 激光散斑效应对激光雷达探测性能的影响[J]. 物理学报,2004,53(7):2089-2093.GUO G J, SHAO Y. Rough surfaces induced speckle effects on detection performance of pulsed laser radar[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2004, 53(7): 2089-2093. (in Chinese) [4] LAURENZIS M, LUTZ Y, CHRISTNACHER F, et al. Homogeneous and speckle-free laser illumination for range-gated imaging and active polarimetry[J]. Optical Engineering, 2012, 51(6): 061302. doi: 10.1117/1.OE.51.6.061302 [5] 王锐, 史瑞新. 基于多光束照明的回波光场散斑抑制机理[J]. 光学 精密工程,2017,25(9):2333-2338. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20172509.2333WANG R, SHI R X. Suppression mechanics of returning wave speckle with multibeams illumination[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2017, 25(9): 2333-2338. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/OPE.20172509.2333 [6] 任淑艳, 张琢, 刘国栋, 等. 精密测量中激光成像系统散斑的抑制因素[J]. 光学 精密工程,2007,15(3):331-336.REN SH Y, ZHANG ZH, LIU G D, et al. Restraining speckle of laser imaging system in accurate measurement[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2007, 15(3): 331-336. (in Chinese) [7] 宋少华, 仝召民. 用于激光背光源电视的扫描分光与消散斑系统[J]. 光学 精密工程,2019,27(2):271-278. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20192702.0271SONG SH H, TONG ZH M. Scanning beam splitting and speckle reduction system for laser backlight TV[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2019, 27(2): 271-278. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/OPE.20192702.0271 [8] 王锐. 多束部分相干光抑制光强闪烁效应的仿真实验研究[J]. 发光学报,2014,35(7):835-839. doi: 10.3788/fgxb20143507.0835WANG R. Simulation experiment of using multiple partially coherent beams to limit laser intensity scintillation effect[J]. Chinese Journal of Luminescence, 2014, 35(7): 835-839. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/fgxb20143507.0835 [9] FUJII H, ASAKURA T. Effect of surface roughness on the statistical distribution of image speckle intensity[J]. Optics Communications, 1974, 11(1): 35-38. doi: 10.1016/0030-4018(74)90327-7 [10] GEORGE N, JAIN A. Space and wavelength dependence of speckle intensity[J]. Applied Physics, 1974, 4(3): 201-212. doi: 10.1007/BF00884230 [11] GOODMAN J W. Dependence of image speckle contrast on surface roughness[J]. Optics Communications, 1975, 14(3): 324-327. doi: 10.1016/0030-4018(75)90328-4 [12] ERDMANN J C, GELLERT R I. Speckle field of curved, rotating surfaces of Gaussian roughness illuminated by a laser light spot[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America, 1976, 66(11): 1194-1204. doi: 10.1364/JOSA.66.001194 [13] GEORGE N. Speckle from rough, moving objects[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America, 1976, 66(11): 1182-1194. doi: 10.1364/JOSA.66.001182 [14] YOSHIMURA T. Statistical properties of dynamic speckles[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America A, 1986, 3(7): 1032-1054. doi: 10.1364/JOSAA.3.001032 [15] 武颖丽, 吴振森. 旋转粗糙圆柱的激光散射功率谱分析[J]. 光学 精密工程,2012,20(12):2654-2660. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20122012.2654WU Y L, WU ZH S. Analysis of power spectra for laser scattering intensity on rotating cylinder targets[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2012, 20(12): 2654-2660. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/OPE.20122012.2654 [16] FUJI H, ASAKURA T, SHINDO Y. Measurement of surface roughness properties by means of laser speckle techniques[J]. Optics Communications, 1976, 16(1): 68-72. doi: 10.1016/0030-4018(76)90052-3 [17] 张耿. 粗糙目标激光散斑统计特性及微运动特征分析[D]. 西安: 西安电子科技大学, 2013.ZHANG G. Statistical properties of laser speckle from rough objects and analysis on micro-motion characteristic[D]. Xi’an: Xidian University, 2013. (in Chinese) [18] TCHVIALEVA L, MARKHVIDA I, ZENG H SH, et al. Surface roughness measurement by speckle contrast under the illumination of light with arbitrary spectral profile[J]. Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 2010, 48(7-8): 774-778. doi: 10.1016/j.optlaseng.2010.03.004 [19] LOUIE D C, TCHVIALEVA L, ZENG H SH, et al. Findings toward the miniaturization of a laser speckle contrast device for skin roughness measurements[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2017, 10037: 100370J. [20] LEHMANN P. Surface-roughness measurement based on the intensity correlation function of scattered light under speckle-pattern illumination[J]. Applied Optics, 1999, 38(7): 1144-1152. doi: 10.1364/AO.38.001144 [21] NIPPOLAINEN E, SEMENOV D V, KAMSHILIN A A, et al. Fast distance sensing by use of the speckle effect[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2005, 5856: 691-697. doi: 10.1117/12.612576 [22] GAO ZH, ZHAO X Z. On-line surface roughness measurement based on specular intensity component of speckle patterns[C]. Proceedings of 2008 International Conference on Information and Automation, IEEE, 2008: 1050-1055. [23] 赵博华, 王伯雄, 张金, 等. 粗糙金属表面光条中心提取方法[J]. 光学 精密工程,2011,19(9):2138-2145. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20111909.2138ZHAO B H, WANG B X, ZHANG J, et al. Extraction of laser stripe center on rough metal surface[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2011, 19(9): 2138-2145. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/OPE.20111909.2138 [24] ZHAO X Z, GAO ZH. Surface roughness measurement using spatial-average analysis of objective speckle pattern in specular direction[J]. Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 2009, 47(11): 1307-1316. doi: 10.1016/j.optlaseng.2009.04.012 [25] GAO ZH, ZHAO X Z. Roughness measurement of moving weak-scattering surface by dynamic speckle image[J]. Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 2012, 50(5): 668-677. doi: 10.1016/j.optlaseng.2011.11.014 [26] PRABHATHAN P, SONG CH L, HARIDAS A, et al. Intensity and contrast based surface roughness measurement approaches for rough and shiny surfaces[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2017, 10449: 1044912. [27] PATZELT S, STÖBENER D, FISCHER A. Laser light source limited uncertainty of speckle-based roughness measurements[J]. Applied Optics, 2019, 58(23): 6436-6445. doi: 10.1364/AO.58.006436 [28] BERLASSO R G, QUINTIAN F P, REBOLLO M A, et al. Speckle size of light scattered from slightly rough cylindrical surfaces[J]. Applied Optics, 2002, 41(10): 2020-2027. doi: 10.1364/AO.41.002020 [29] DEV K, A. S. G P, ASWIN H, et al. Surface roughness measurement of additive manufactured samples using angular speckle correlation[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2017, 10449: 104492W. [30] PRABHATHAN P, SONG CH L, HARIDAS A, et al. Experimental investigations and parametric studies of surface roughness measurements using spectrally correlated speckle images[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2017, 10449: 1044913. [31] PATZELT S, STÖBENER D, STRÖBEL G, et al. Uncertainty of scattered light roughness measurements based on speckle correlation methods[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2017, 10329: 103291P. [32] HARIDAS A, CRIVOI A, PRABHATHAN P, et al. Fractal speckle image analysis for surface characterization of aerospace structures[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2017, 10449: 104491T. [33] XU D, YANG Q, DONG F, et al. Evaluation of surface roughness of a machined metal surface based on laser speckle pattern[J]. The Journal of Engineering, 2018, 2018(9): 773-778. doi: 10.1049/joe.2018.5057 [34] GEORGE N, LIVANOS A, ROTH J, et al. Remote sensing of large roughened spheres[J]. Optica Acta:International Journal of Optics, 1976, 23(5): 367-387. doi: 10.1080/713819273 [35] MARRON J C. Wavelength decorrelation of laser speckle from three-dimensional diffuse objects[J]. Optics Communications, 1992, 88(4-6): 305-308. doi: 10.1016/0030-4018(92)90046-T [36] CRIMMINS T R, FIENUP J R, THELEN B J. Improved bounds on object support from autocorrelation support and application to phase retrieval[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America A, 1990, 7(1): 3-13. doi: 10.1364/JOSAA.7.000003 [37] PAXMAN R G, MARRON J C. System and method for three-dimensional imaging of opaque objects using frequency diversity and an opacity constraint: US, 5627363[P]. 1997-05-06. [38] SHIRLEY L G, ARIEL E D, HALLERMAN G R, et al. Advanced techniques for target discrimination using laser speckle[J]. The Lincoln Laboratory Journal, 1992, 5(3): 367-440. [39] SHIRLEY L G, HALLERMAN G R. Applications of tunable lasers to laser radar and 3D imaging[R]. Lexington Massachusetts: MIT Lincoln Laboratory, 1996. [40] SHIRLEY L G, HALLERMAN G R. Nonconventional 3D imaging using wavelength-dependent speckle[J]. The Lincoln Laboratory Journal, 1996, 9(2): 153-186. [41] SHIRLEY L G, LO P A. Bispectral analysis of the wavelength dependence of speckle: remote sensing of object shape[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America A, 1994, 11(3): 1025-1046. doi: 10.1364/JOSAA.11.001025 [42] FINI J M. Three dimensional image reconstruction from fourier magnitude measurements[D]. Cambridge, MA: Massachusetts Institute of Technology, 1997. [43] SHIRLEY L G. Method and apparatus for remote sensing of objects utilizing radiation speckle: US, 8265375[P]. 2012-09-11. [44] SHIRLEY L G. Method and apparatus for remote sensing of objects utilizing radiation speckle: US, 20170138722[P]. 2017-05-18. [45] SHIRLEY L G. Method and apparatus for remote sensing of objects utilizing radiation speckle: US, 10281257[P]. 2019-05-07. [46] 朱磊, 邵晓鹏. 散射成像技术的研究进展[J]. 光学学报,2020,40(1):0111005. doi: 10.3788/AOS202040.0111005ZHU L, SHAO X P. Research progress on scattering imaging technology[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2020, 40(1): 0111005. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/AOS202040.0111005 [47] BERTOLOTTI J, VAN PUTTEN E G, BLUM C, et al. Non-invasive imaging through opaque scattering layers[J]. Nature, 2012, 491(7423): 232-234. doi: 10.1038/nature11578 [48] KATZ O, HEIDMANN P, FINK M, et al. Non-invasive single-shot imaging through scattering layers and around corners via speckle correlations[J]. Nature Photonics, 2014, 8(10): 784-790. doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2014.189 [49] WU T F, KATZ O, SHAO X P, et al. Single-shot diffraction-limited imaging through scattering layers via bispectrum analysis[J]. Optics Letters, 2016, 41(21): 5003-5006. doi: 10.1364/OL.41.005003 [50] ANDO T, HORISAKI R, TANIDA J. Speckle-learning-based object recognition through scattering media[J]. Optics Express, 2015, 23(26): 33902-33910. doi: 10.1364/OE.23.033902 [51] HORISAKI R, TAKAGI R, TANIDA J. Learning-based imaging through scattering media[J]. Optics Express, 2016, 24(13): 13738-13743. doi: 10.1364/OE.24.013738 [52] TAKAGI R, HORISAKI R, TANIDA J. Object recognition through a multi-mode fiber[J]. Optical Review, 2017, 24(2): 117-120. doi: 10.1007/s10043-017-0303-5 [53] 万剑华, 韩仲志. 多模式融合下的海洋溢油高光谱成像油种识别方法[J]. 发光学报,2016,37(4):473-480. doi: 10.3788/fgxb20163704.0473WAN J H, HAN ZH ZH. Oil spills identification using hyperspectral imaging based on multi-pattern method[J]. Chinese Journal of Luminescence, 2016, 37(4): 473-480. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/fgxb20163704.0473 [54] 丁佳兴, 杨晓玉. 可见/近红外高光谱成像技术对鸡蛋种类无损判别[J]. 发光学报,2018,39(3):394-402. doi: 10.3788/fgxb20183903.0394DING J X, YANG X Y. Non-destructive discrimination of different kinds egg by Vis/NIR hyperspectral imaging technique[J]. Chinese Journal of Luminescence, 2018, 39(3): 394-402. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/fgxb20183903.0394 [55] VALENT E, SILBERBERG Y. Scatterer recognition via analysis of speckle patterns[J]. Optica, 2018, 5(2): 204-207. doi: 10.1364/OPTICA.5.000204 [56] LYU M, WANG H, LI G W, et al. Learning-based lensless imaging through optically thick scattering media[J]. Advanced Photonics, 2019, 1(3): 036002. [57] LEI X, HE L Y, TAN Y X, et al.. Direct object recognition without line-of-sight using optical coherence[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE, 2019: 11729-11738. -





 下载:
下载: