X-ray security inspection images classification combined octave convolution and bidirectional GRU
-
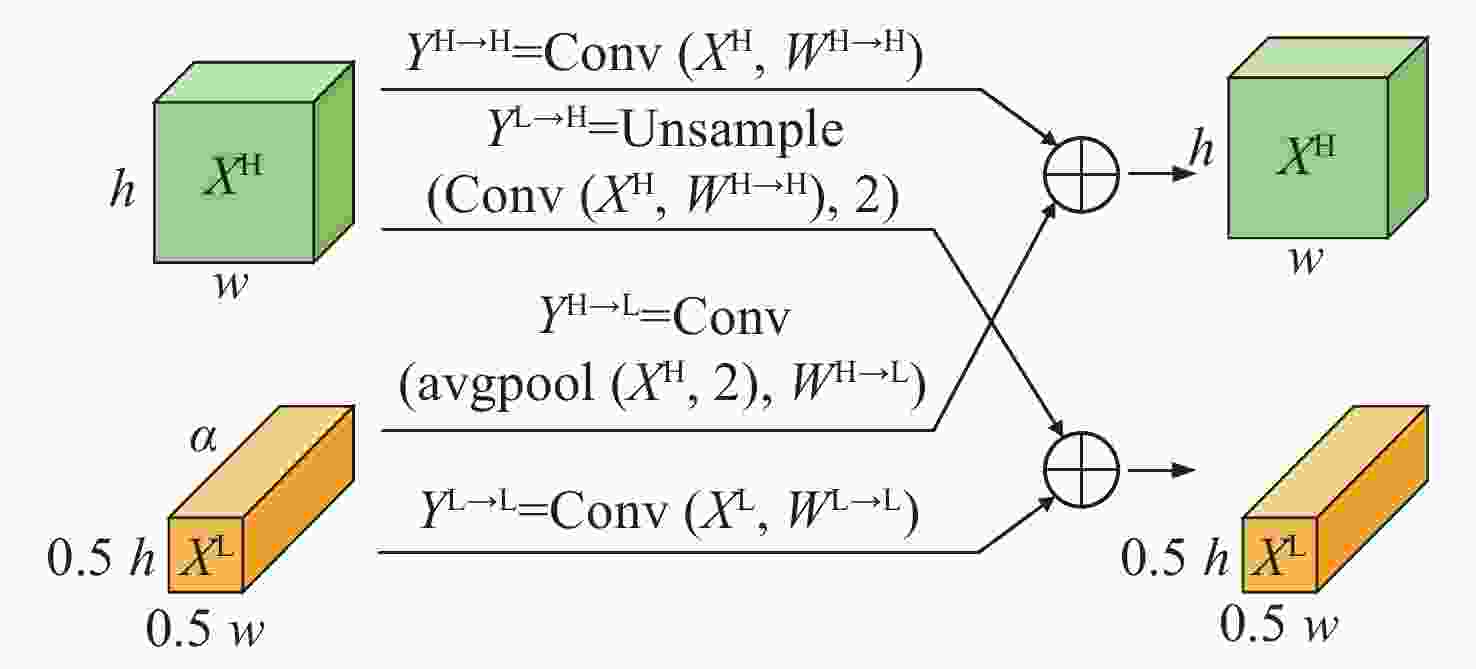
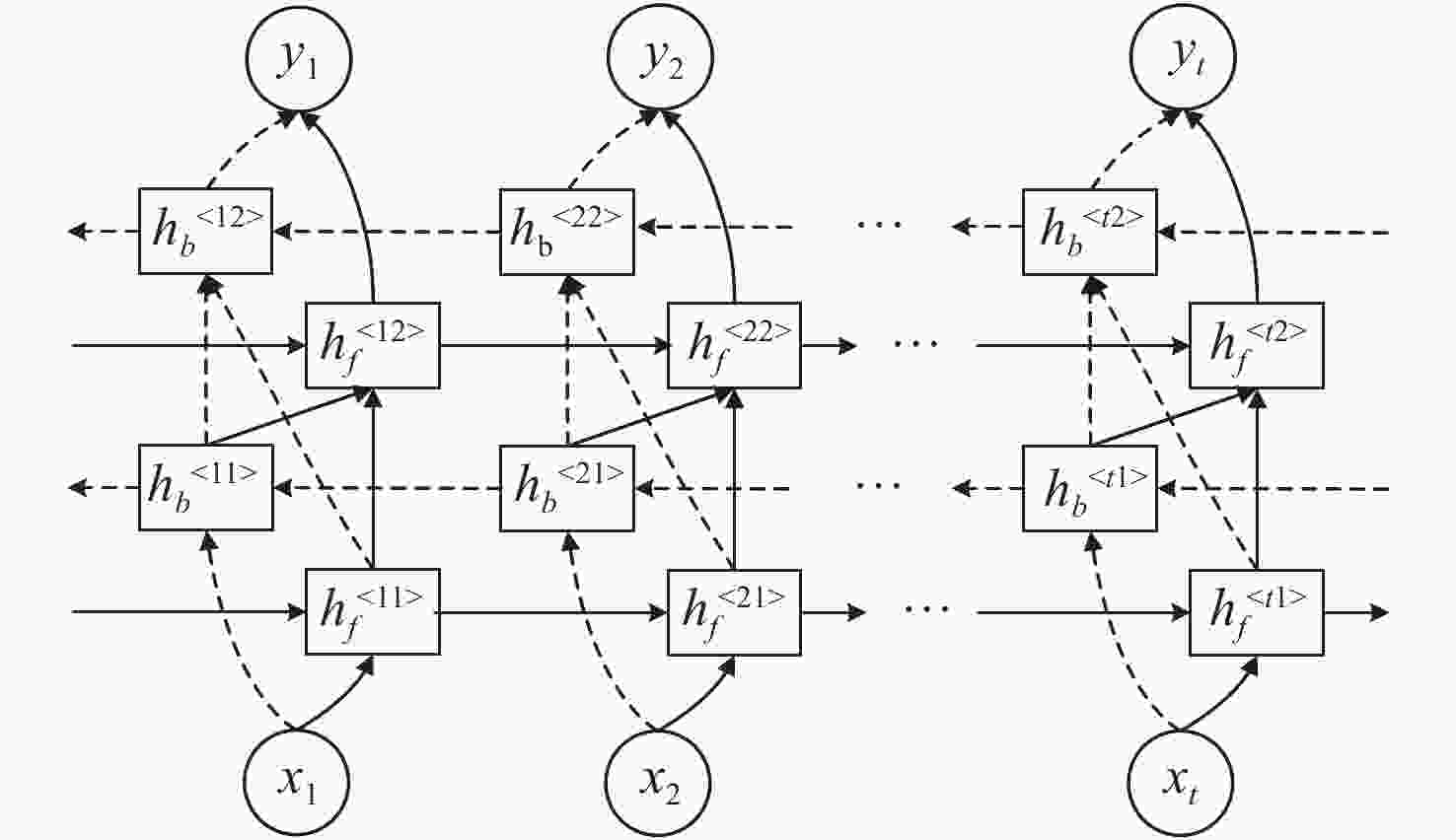
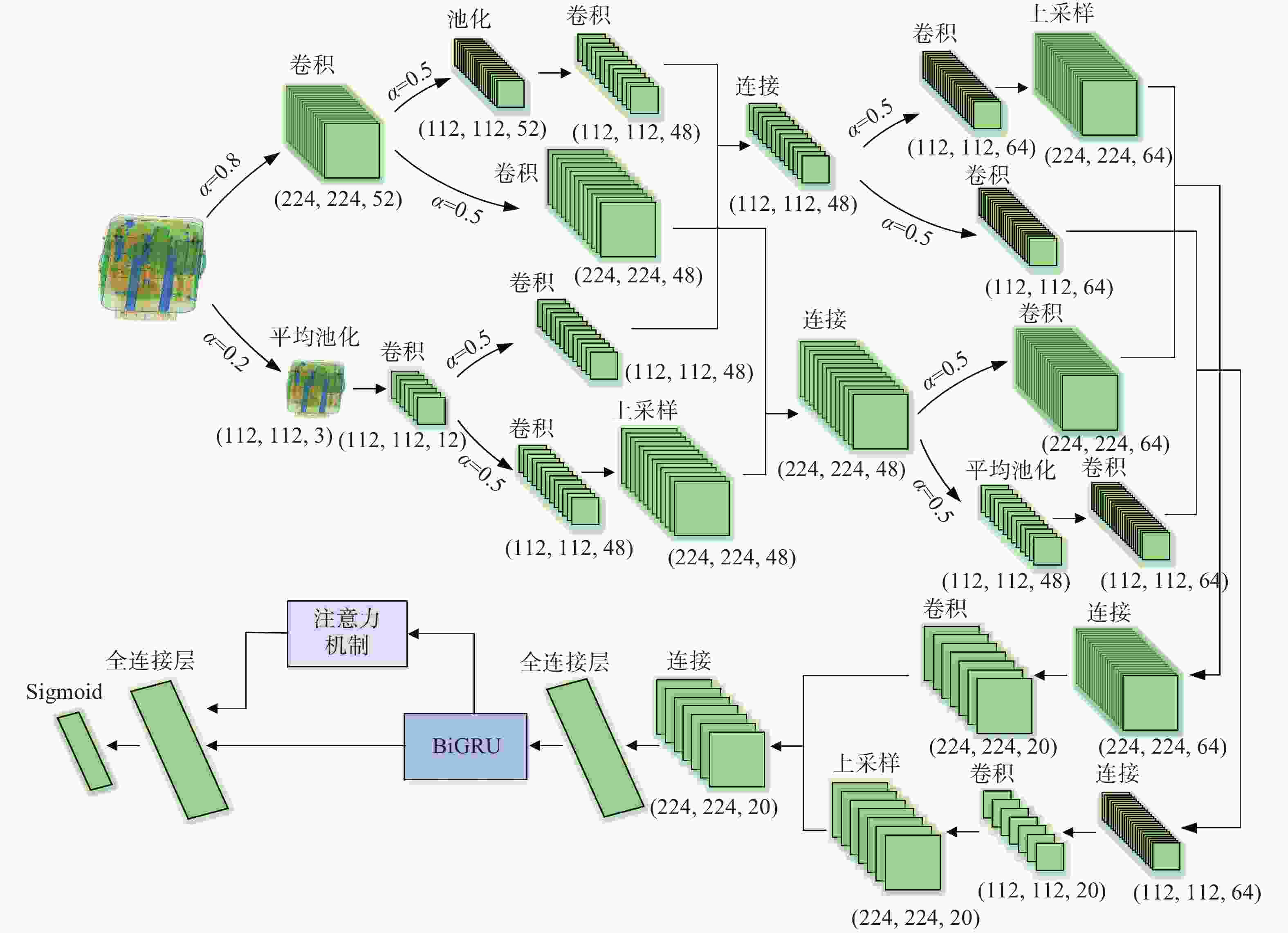
摘要: 针对主动视觉安检方法准确率低、速度慢,不适用于实时交通安检的问题,提出了八度卷积(OctConv)和注意力机制双向门控循环单元(GRU)神经网络相结合的X光安检图像分类方法。首先,利用八度卷积代替传统卷积,对输入的特征向量进行高低分频,并降低低频特征的分辨率,在有效提取X光安检图像特征的同时,减少了空间冗余。其次,通过注意力机制双向GRU,动态学习调整特征权重,提高危险品分类准确率。最后,在通用SIXRay数据集上的实验表明,对8000幅测试样本的整体分类准确率(ACC)、特征曲线下方面积(AUC)、正类分类准确率(PRE)分别为98.73%、91.39%、85.44%,检测时间为36.80 s。相对于目前主流模型,本文方法有效提高了X光安检图像危险品分类的准确率和速度。Abstract: Due to the disadvantages of low accuracy and slow speed in the active vision security inspection method, it is not suitable for real-time security inspection. Aiming at this problem, we propose an x-ray inspection image classification algorithm combining octave convolution (OctConv) with attention-based bidirectional Gate Recurrent Unit (GRU). Firstly, OctConv is introduced to replace the traditional convolution operation to divide the input feature vector into high and low frequency, and reduce the resolution of low frequency features, effectively extracting the features of security image and reducing the spatial redundancy. Then, the feature weight can be adjusted by dynamic learning through attention-based bidirectional GRU to improve the classification accuracy of threat objects. Finally, a lot of experimental results on SIXRay dataset show that the classification accuracy, AUC value and PRE of 8000 test samples are 98.73%, 91.39% and 85.44%, respectively, with a time of 36.80 seconds. Compared with the current mainstream model, the proposed algorithm can improve the performance and speed of threat objects recognition in X-ray security images.
-
Key words:
- X-ray inspection images /
- octave convolution /
- bidirectional GRU /
- attention mechanism
-
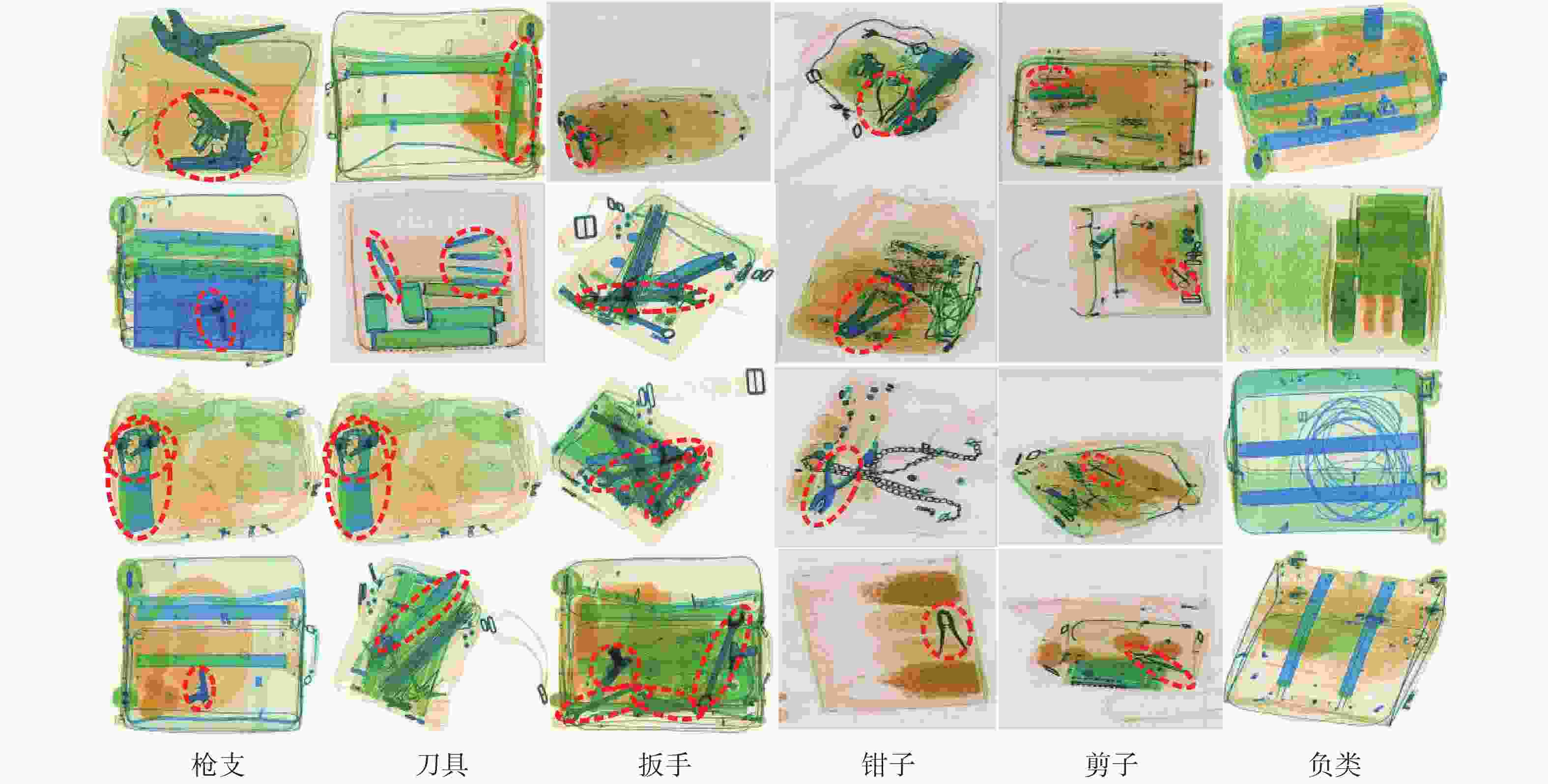
表 1 SIXray数据集样本分布
Table 1. Sample distribution in SIXray dataset
正类样本 (8929) 负类样本 枪支 刀具 扳手 钳子 剪子 3131 1943 2199 3961 983 1050302 表 2 不同类别数据增强前后对比结果
Table 2. Comparison results of different types of data before and after data augmentation
种类 增强前后 负类样本数 正类样本数 不平衡比率 枪支 增强前 72255 2705 26.27 增强后 89672 12659 7.08 刀具 增强前 73212 1748 41.88 增强后 93723 8608 10.89 扳手 增强前 72948 2012 36.26 增强后 92380 9951 9.28 钳子 增强前 71524 3436 20.82 增强后 85574 16757 5.10 剪子 增强前 74153 807 91.89 增强后 99760 2571 38.80 表 3 不同模型的ACC (%)比较
Table 3. Comparison of ACC (%) for different network modules
方法 枪支 刀具 扳手 钳子 剪子 平均 InceptionV3 94.63 87.52 88.97 80.50 96.95 89.71 VGG19 97.88 98.36 97.48 96.03 97.33 97.42 ResNet 98.36 99.20 98.16 96.10 97.80 97.92 DenseNet 98.69 99.25 98.18 96.16 97.65 97.99 STN-DenseNet 99.15 98.73 97.52 96.32 98.46 98.03 OnlyBiGRU 98.77 99.40 97.73 94.37 99.14 97.88 CNN-ABiGRU 98.89 99.42 98.89 97.07 98.96 98.65 OctConv-ABiGRU 98.60 99.25 99.10 97.50 99.20 98.73 表 4 不同模型的AUC (%) 比较
Table 4. Comparison of AUC (%) for different network modules
方法 枪支 刀具 扳手 钳子 剪子 平均 InceptionV3 63.34 54.57 51.33 52.92 50.74 54.57 VGG19 93.34 89.03 77.49 76.57 71.08 81.50 ResNet 94.06 88.68 76.00 73.92 60.45 78.64 DenseNet 93.91 90.37 72.59 74.65 61.08 78.52 STN-DenseNet 95.69 93.58 75.60 76.98 65.09 81.39 OnlyBiGRU 92.73 93.90 68.03 73.33 89.42 83.48 CNN-ABiGRU 93.96 93.94 82.22 80.09 87.99 87.65 OctConv-ABiGRU 91.53 94.59 87.84 86.15 96.70 91.39 表 5 不同网络用时比较
Table 5. Comparison of detection time for different network modules
方法 参数量(百万) 模型大小(MB) 检测时间(s) VGG19 45.12 344 41.56 DenseNet 57.22 437 24.91 CNN-ABiGRU 14.42 108 75.14 OctConv-ABiGRU 121.47 1382 36.80 表 6 不同方法的分类精度比较
Table 6. Comparison of PRE (%) for different network modules
方法 枪支 刀具 扳手 钳子 剪子 平均 VGG19 87.20 86.40 56.60 55.20 46.20 66.32 DenseNet 88.20 82.18 51.25 54.50 38.50 62.93 CNN-ABiGRU 88.50 87.20 63.00 61.20 76.40 75.26 OctConv-ABiGRU 86.78 92.22 77.44 76.22 94.56 85.44 -
陈志强, 张丽, 金鑫. X射线安全检查技术研究新进展[J]. 科学通报,2017,62(13):1350-1365. doi: 10.1360/N972016-00698CHEN ZH Q, ZHANG L, JIN X. Recent progress on X-ray security inspection technologies[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2017, 62(13): 1350-1365. (in Chinese) doi: 10.1360/N972016-00698 CAO S S, LIU Y H, SONG W W, et al.. Toward human-in-the-loop prohibited item detection in X-ray baggage images[C]. Proceedings of 2019 Chinese Automation Congress (CAC), IEEE, 2019: 4360-4364. LYU SH J, TU X, LU Y. X-Ray image classification for parcel inspection in high-speed sorting line[C]. Proceedings of the 2018 11th International Congress on Image and Signal Processing, BioMedical Engineering and Informatics (CISP-BMEI), IEEE, 2018: 1-5. 费彬, 孙京阳, 张俊举, 等. 基于稀疏处理的多能X射线分离成像[J]. 光学 精密工程,2017,25(4):1106-1111. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20172504.1106FEI B, SUN J Y, ZHANG J J, et al. Separation of multi-energy X-ray imaging based on sparse processing[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2017, 25(4): 1106-1111. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/OPE.20172504.1106 王旖旎. 基于Inception V3的图像状态分类技术[J]. 液晶与显示,2020,35(4):389-394. doi: 10.3788/YJYXS20203504.0389WANG Y N. Image classification technology based on inception V3[J]. Chinese Journal of Liquid Crystals and Displays, 2020, 35(4): 389-394. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/YJYXS20203504.0389 CHOUAI M, MERAH M, SANCHO-GOMEZ J L, et al. Supervised feature learning by adversarial autoencoder approach for object classification in dual X-Ray image of luggage[J]. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 2020, 31(5): 1101-1112. doi: 10.1007/s10845-019-01498-5 张万征, 胡志坤, 李小龙. 基于LeNet-5的卷积神经图像识别算法[J]. 液晶与显示,2020,35(5):486-490. doi: 10.3788/YJYXS20203505.0486ZHANG W ZH, HU ZH K, LI X L. Convolutional neural image recognition algorithm based on LeNet-5[J]. Chinese Journal of Liquid Crystals and Displays, 2020, 35(5): 486-490. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/YJYXS20203505.0486 刘恋秋. 基于深度卷积生成对抗网络的图像识别算法[J]. 液晶与显示,2020,35(4):383-388. doi: 10.3788/YJYXS20203504.0383LIU L Q. Image recognition algorithms based on deep convolution generative adversarial network[J]. Chinese Journal of Liquid Crystals and Displays, 2020, 35(4): 383-388. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/YJYXS20203504.0383 龚希, 吴亮, 谢忠, 等. 融合全局和局部深度特征的高分辨率遥感影像场景分类方法[J]. 光学学报,2019,39(3):0301002. doi: 10.3788/AOS201939.0301002GONG X, WU L, XIE ZH, et al. Classification method of high-resolution remote sensing scenes based on fusion of global and local deep features[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2019, 39(3): 0301002. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/AOS201939.0301002 贠卫国, 史其琦, 王民. 基于深度卷积神经网络的多特征融合的手势识别[J]. 液晶与显示,2019,34(4):417-422. doi: 10.3788/YJYXS20193404.0417YUN W G, SHI Q Q, WANG M. Multi-feature fusion gesture recognition based on deep convolutional neural network[J]. Chinese Journal of Liquid Crystals and Displays, 2019, 34(4): 417-422. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/YJYXS20193404.0417 LIU J Y, LENG X X, LIU Y. Deep convolutional neural network based object detector for X-Ray baggage security imagery[C]. Proceedings of 2019 IEEE 31st International Conference on Tools with Artificial Intelligence (ICTAI), IEEE, 2019: 1757-1761. AKCAY S, KUNDEGORSKI M E, WILLCOCKS C G, et al. Using deep convolutional neural network architectures for object classification and detection within X-ray baggage security imagery[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2018, 13(9): 2203-2215. doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2018.2812196 ZHU Y, ZHANG H G, AN J Y, et al. GAN-based data augmentation of prohibited item X-ray images in security inspection[J]. Optoelectronics letters, 2020, 16(3): 225-229. AKÇAY S, ATAPOUR-ABARGHOUEI A, BRECKON T P. Skip-GANomaly: skip connected and adversarially trained encoder-decoder anomaly detection[C]. Proceedings of 2019 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), IEEE, 2019. AYDIN I, KARAKOSE M, AKIN E. A new approach for baggage inspection by using deep convolutional neural networks[C]. Proceedings of 2018 International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Data Processing (IDAP), IEEE, 2018: 1-6. MERY D, SVEC E, ARIAS M, et al. Modern computer vision techniques for X-Ray testing in baggage inspection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems,Man,and Cybernetics:Systems, 2017, 47(4): 682-692. doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2016.2628381 GALVEZ R L, DADIOS E P, BANDALA A A, et al.. Threat object classification in X-ray images using transfer learning[C]. Proceedings of 2018 IEEE 10th International Conference on Humanoid, Nanotechnology, Information Technology, Communication and Control, Environment and Management (HNICEM), IEEE, 2018: 1-5. HOWARD A G, ZHU M L, CHEN B, et al.. MobileNets: efficient convolutional neural networks for mobile vision applications[C]. Proceedings of 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), IEEE, 2017. IANDOLA F N, HAN S, MOSKEWICZ M W, et al.. SqueezeNet: AlexNet-level accuracy with 50x fewer parameters and <0.5MB model size[C]. Proceedings of 2017 International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), Toulon, France, 2017. CHEN Y P, FAN H Q, XU B, et al.. Drop an octave: reducing spatial redundancy in convolutional neural networks with octave convolution[C]. Proceedings of 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, IEEE, 2019: 3434-3443. CHO K, VAN MERRIËNBOER B, GULCEHRE C, et al.. Learning phrase representations using RNN encoder-decoder for statistical machine translation[C]. Proceedings of the 2014 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), Association for Computational Linguistics, 2014: 1724-1734. 董潇潇, 何小海, 吴晓红, 等. 基于注意力掩模融合的目标检测算法[J]. 液晶与显示,2019,34(8):825-833. doi: 10.3788/YJYXS20193408.0825DONG X X, HE X H, WU X H, et al. Object detection algorithm based on attention mask fusion[J]. Chinese Journal of Liquid Crystals and Displays, 2019, 34(8): 825-833. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/YJYXS20193408.0825 MIAO C J, XIE L X, WAN F, et al.. SIXray: a large-scale security inspection X-ray benchmark for prohibited item discovery in overlapping images[C]. Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), IEEE, 2019: 2119-2128. SZEGEDY C, VANHOUCKE V, IOFFE S, et al.. Rethinking the inception architecture for computer vision[C]. Proceedings of 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), IEEE, 2016: 2818-2826. SIMONYAN K, ZISSERMAN A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition[C]. Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations, 2014. HE K M, ZHANG X Y, REN SH Q, et al.. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]. Proceedings of 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), IEEE, 2016. HUANG G, LIU ZH, VAN DER MAATEN L, et al.. Densely connected convolutional networks[C]. Proceedings of 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), IEEE, 2017. WANG A L, WANG M H, JIANG K Y, et al.. A novel lidar data classification algorithm combined densenet with STN[C]. Proceedings of 2019 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, IEEE, 2019: 2483-2486. -





 下载:
下载: