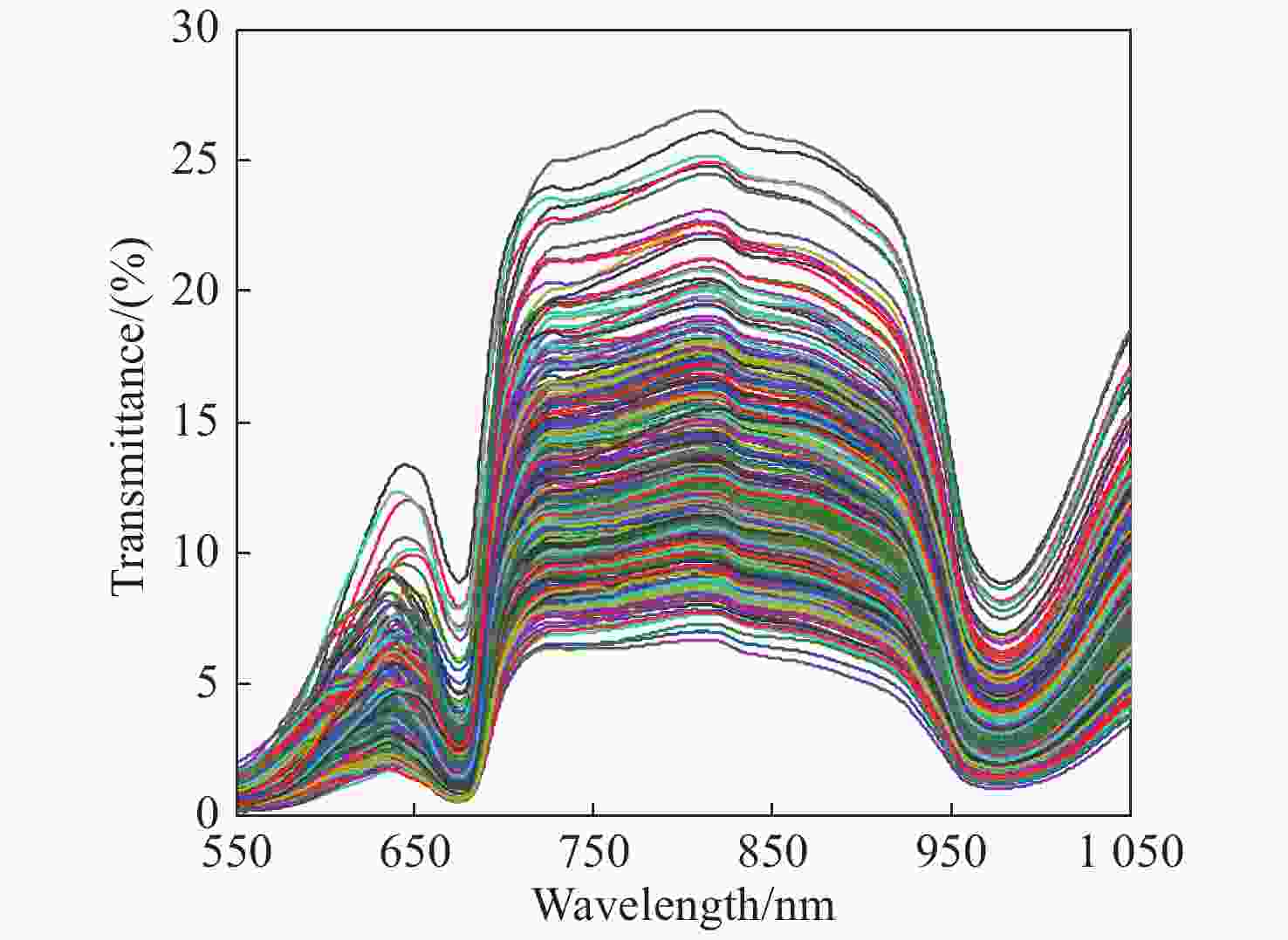
Non-destructive testing of red globe grape sugar content and moisture content based on visible/near infrared spectroscopy transmission technology
-
摘要: 本文研究基于可见/近红外透射光谱技术的红提糖度和含水率的无损检测方法。采集360个红提样本,并分别利用标准正态变量变换(Standard Normal Variable transformation,SNV)、SavitZky-Golay卷积平滑处理法(SavitZky-Golay,S_G)等光谱预处理方法处理后的数据建立PLSR模型,分别采用一次降维(GA、SPA、CARS、UVE)和二次降维组合(CARS-SPA、UVE-SPA、GA-SPA)7种数据降维方法对光谱进行特征变量提取,分别建立红提糖度和含水率的偏最小二乘回归算法(Partial Least Squares Regression,PLSR)和最小二乘支持向量机(Least Squares Support Vector Machine,LSSVM)含量检测模型并对比分析模型的优劣。结果表明:红提糖度和含水率的最优PLSR模型波长提取方法为GA-SPA-PLSR,最优模型的预测集相关系数分别为0.958、0.938;红提糖度和含水率的最优LSSVM模型波长提取方法分别为CARS-SPA-LSSVM、UVE-SPA-LSSVM,最优模型的预测集相关系数分别为0.969、0.942;LSSVM所建模型的效果好于PLSR所建模型,但模型的运算时间较长。研究结果表明:基于可见/近红外技术无损检测红提糖度和含水率的方法可行,两种最优检测模型的预测精度均较高,都能满足检测要求。在不同应用下,可酌情选择不同模型,PLSR所建最优模型的运算时间较短,适合在线快速检测;LSSVM的检测性能最佳,可更加准确地检测红提糖度和含水率。Abstract: In this paper, a non-destructive detection method for the sugar and moisture content of red globe grapes based on visible/near-infrared spectroscopy transmission technology is studied. The PLSR model is established by collecting 360 red globe grape samples by using spectral data processed by spectral preprocessing methods such as Standard Normal Variable transformation (SNV), SavitZky-Golay(S_G) and other spectral preprocessing methods respectively to determine the best spectral preprocessing method. Seven data dimensionality reduction methods of primary dimensionality reduction (GA, SPA, CARS, UVE) and secondary dimensionality reduction combinations (CARS-SPA, UVE-SPA, GA-SPA) are used to identify characteristic variables of spectra. PLSR and LSSVM detection models of sugar content and moisture content of red globe grape are established respectively, and the advantages and disadvantages of each model are compared and analyzed. The results show that the optimal PLSR model wavelength extraction method for red globe grape sugar content and moisture content is GA-SPA-PLSR, and the correlation coefficients of the optimal model are 0.958 and 0.938, respectively. The optimal LSSVM model wavelength extraction methods for red globe grape sugar and moisture content are CARS-SPA-LSSVM and UVE-SPA-LSSVM, respectively. The correlation coefficients of the optimal model are 0.969 and 0.942, respectively. The model built using LSSVM is better than that built using PLSR, but its operation time is longer. The results also show that the non-destructive detection method of red globe grape sugar and moisture content based on visible/near-infrared technology is feasible, and the detection accuracy of both two optimal detection models is high, which can meet detection requirements. Different models can be selected for different applications. The optimal model built by PLSR has shorter computation time and is suitable for online rapid detection. LSSVM has the best detection performance and can accurately detect red globe grape sugar and moisture content.
-
表 1 原始光谱及采用不同预处理方法后建立的的全波长PLSR检测模型
Table 1. Original spectra and full-wavelength PLSR detection model established by different pretreatment methods
指标 预处理 LVs主因子数 校正集 预测集 Rc RMSEC Rp RMSEP 糖度 原始光谱 15 0.927 0.498 0.933 0.493 SNV 19 0.954 0.412 0.907 0.468 S_G 14 0.793 0.809 0.808 0.759 Nor 20 0.957 0.401 0.878 0.516 含水率 原始光谱 15 0.901 0.549 0.868 0.780 SNV 15 0.892 0.583 0.842 0.731 Nor 15 0.893 0.603 0.832 0.719 表 2 利用KS算法划分样本集的数据统计
Table 2. Data statistics of sample sets partitioned by KS algorithm
样本数量 指标 最小值 最大值 平均值 标准差S.D 变异系数C.V 校正集(270个) 糖度 16.8(°Brix) 24.0(°Brix) 20.2(°Brix) 1.334 6.595% 含水率 76.689% 84.327% 80.746% 1.268 1.570% 预测集(90个) 糖度 17.8(°Brix) 22.7(°Brix) 20.2(°Brix) 1.275 6.293% 含水率 76.635% 83.621% 80.582% 1.450 1.780% 表 3 不同放置模式的全波长PLSR检测模型
Table 3. Full-wavelength PLSR detection models of samples with different placement modes
放置模式 指标 LVs主因子数 校正集 预测集 Rc RMSEC Rp RMSEP 竖放 糖度 16 0.922 0.503 0.907 0.589 含水率 15 0.897 0.567 0.861 0.812 横放 糖度 15 0.908 0.576 0.890 0.614 含水率 15 0.884 0.629 0.811 0.921 平均光谱 糖度 15 0.927 0.498 0.933 0.493 含水率 15 0.901 0.549 0.868 0.780 表 4 基于特征波长建立的红提糖度和含水率PLSR检测模型
Table 4. PLSR detection models of red globe grape′s sugar and moisture content based on wavelength characteristics
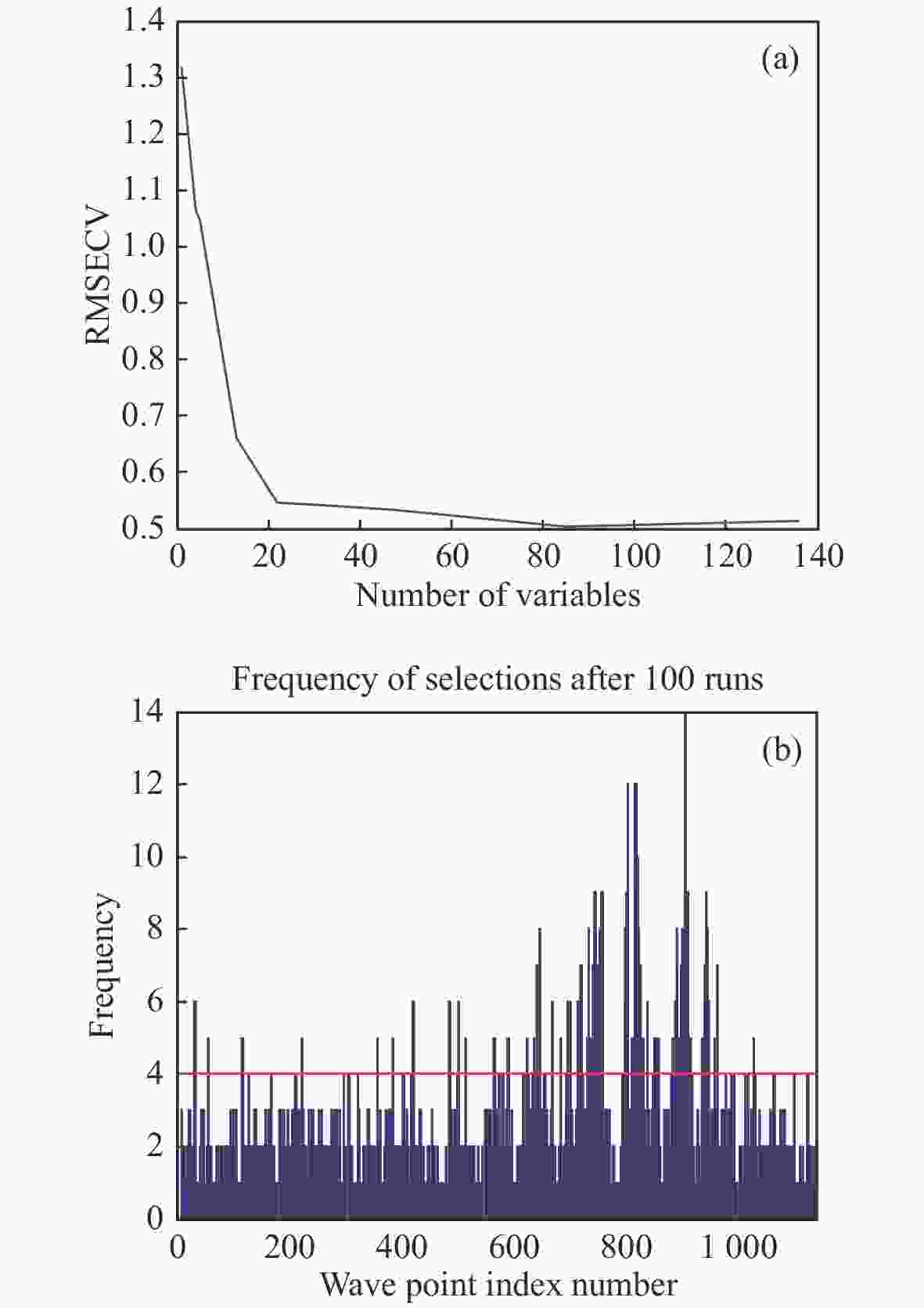
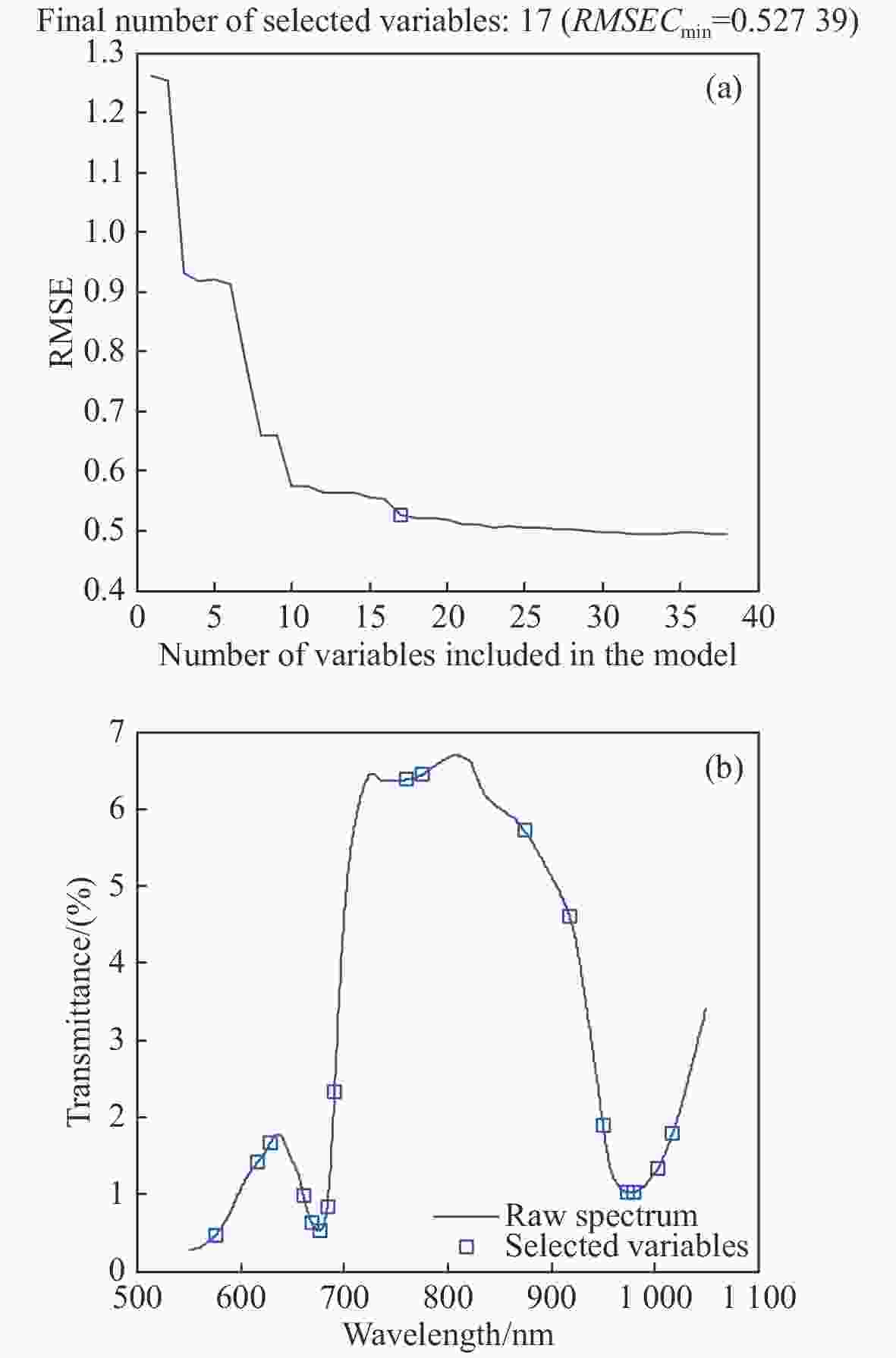
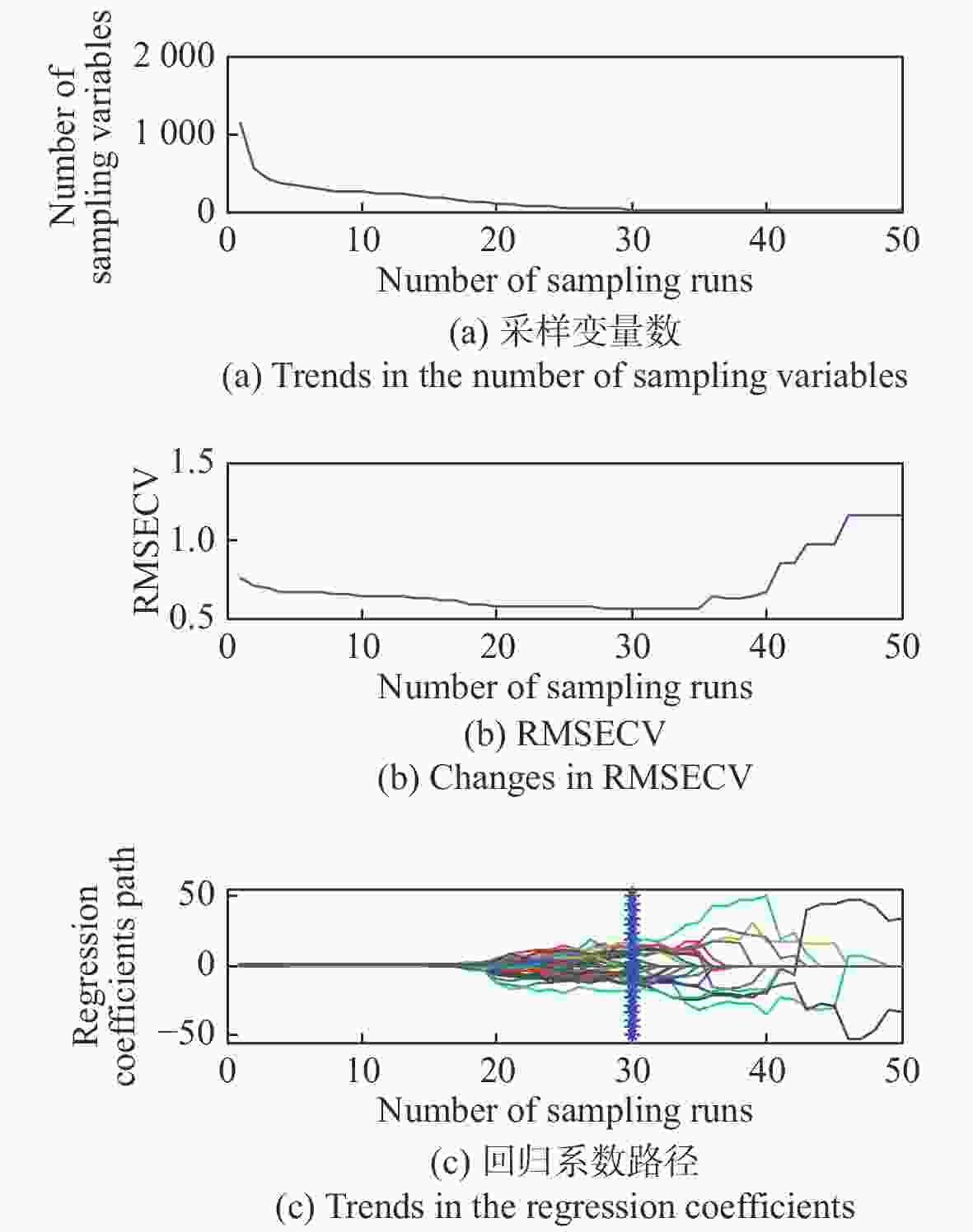
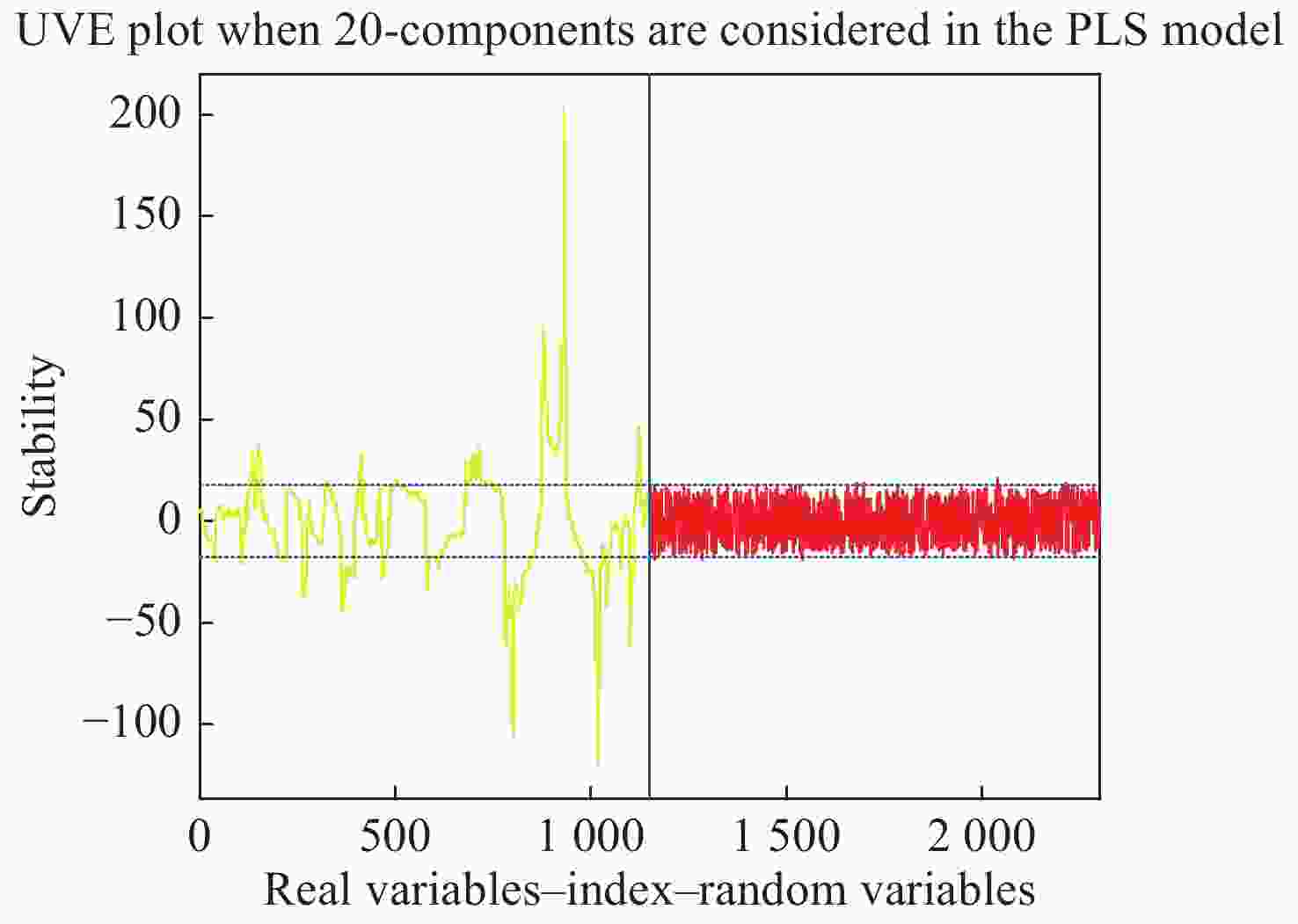
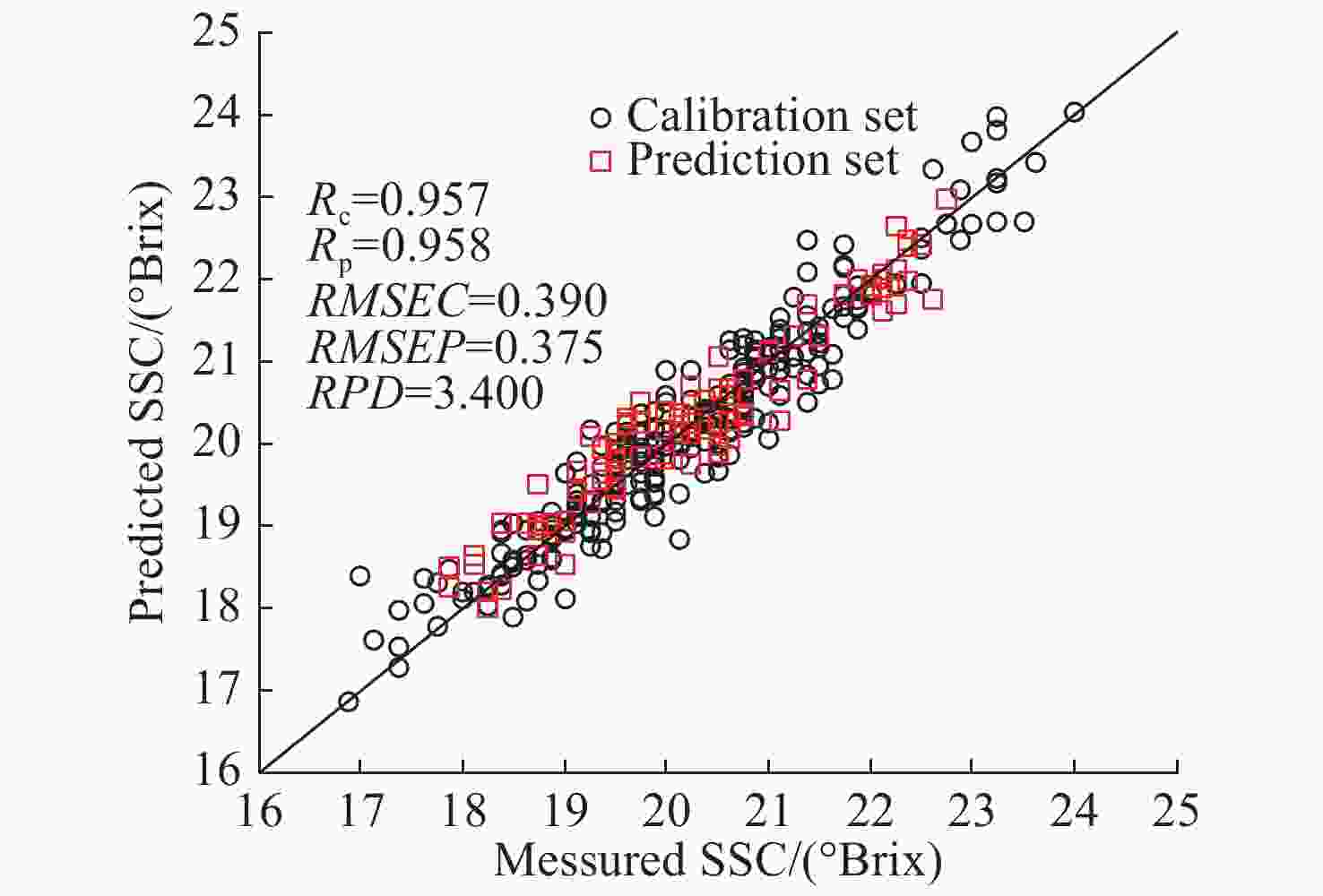
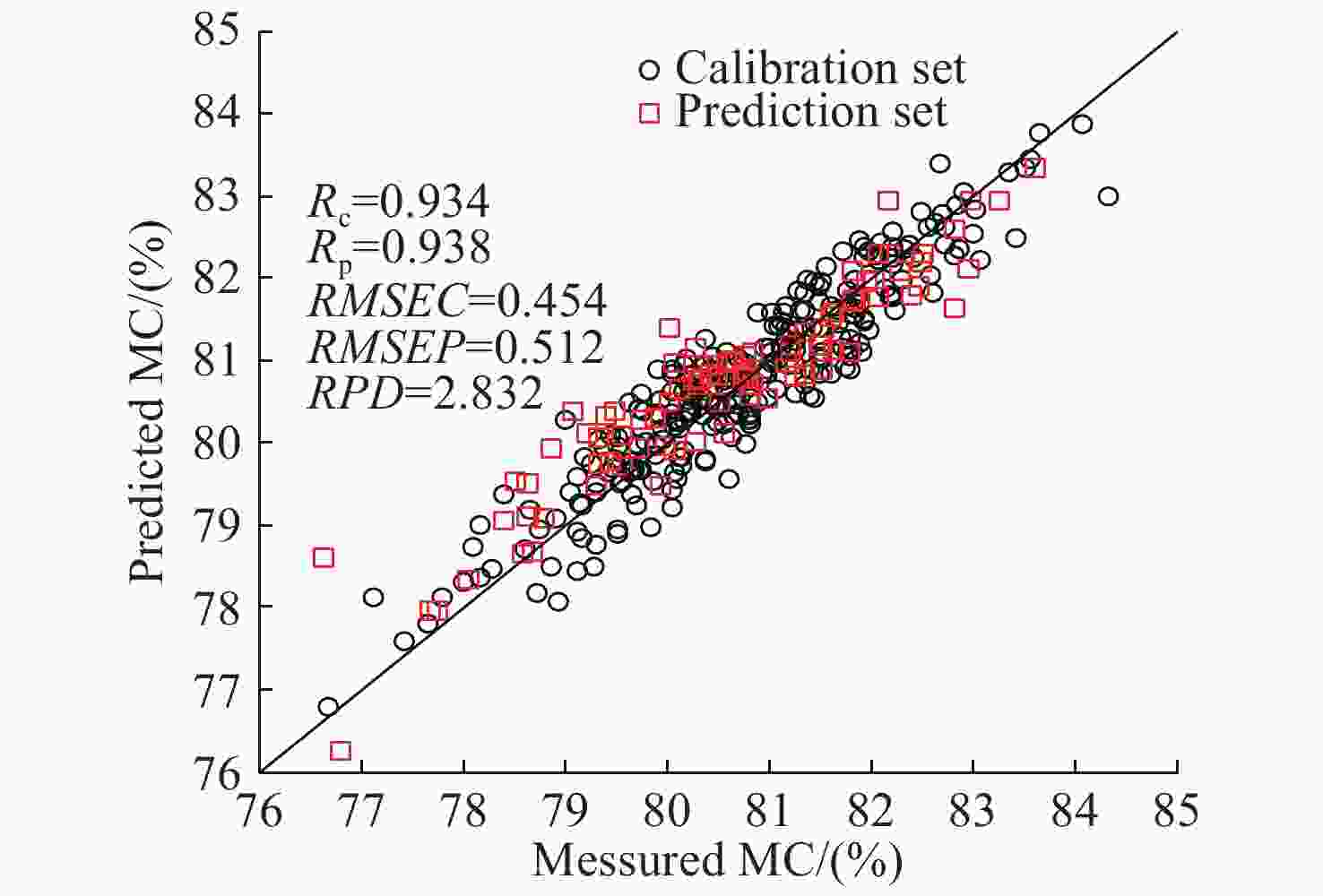
指标 特征波长提取方法 波点个数 LVs主因子数 校正集 预测集 RPD Rc RMSEC Rp RMSEP 糖度 原始光谱 1150 15 0.927 0.498 0.933 0.493 2.586 GA 85 13 0.941 0.450 0.929 0.499 2.555 SPA 17 15 0.889 0.610 0.921 0.527 2.419 CARS 27 15 0.915 0.537 0.926 0.502 2.540 糖度 UVE 437 13 0.912 0.547 0.925 0.510 2.500 CARS-SPA 9 5 0.896 0.592 0.919 0.529 2.410 UVE-SPA 15 10 0.898 0.585 0.917 0.531 2.401 GA-SPA 15 10 0.957 0.390 0.958 0.375 3.400 含水率 原始光谱 1150 15 0.901 0.549 0.868 0.780 1.860 GA 78 10 0.900 0.551 0.892 0.728 1.992 SPA 12 11 0.840 0.687 0.838 0.833 1.741 CARS 27 15 0.901 0.549 0.868 0.780 1.859 UVE 615 13 0.891 0.574 0.874 0.758 1.913 CARS-SPA 11 11 0.819 0.726 0.848 0.858 1.690 UVE-SPA 19 14 0.882 0.597 0.867 0.770 1.884 GA-SPA 13 7 0.934 0.454 0.938 0.512 2.832 表 5 红提糖度和含水率PLSR检测模型的最优特征波点列表
Table 5. List of optimal wave point characteristics of the sugar and moister content of PLSR detection model for red globe grapes
指标 建模方法 波长/nm 糖度(15个) GA-SPA-PLSR 722.35、774.15、802.39、813.39、867.92、882.13、904.45、910.44、929.67、943.31、950.11、954.36、968.36、975.57、1002.59 含水率(13个) GA-SPA-PLSR 750.06、799.03、825.98、835.52、859.73、863.61、869.64、878.26、904.02、909.58、913.01、947.56、967.09 表 6 基于特征波长建立的红提糖度和含水率LSSVM检测模型
Table 6. LSSVM detection models of sugar and moisture content for red globe grapes based on wavelength characteristics
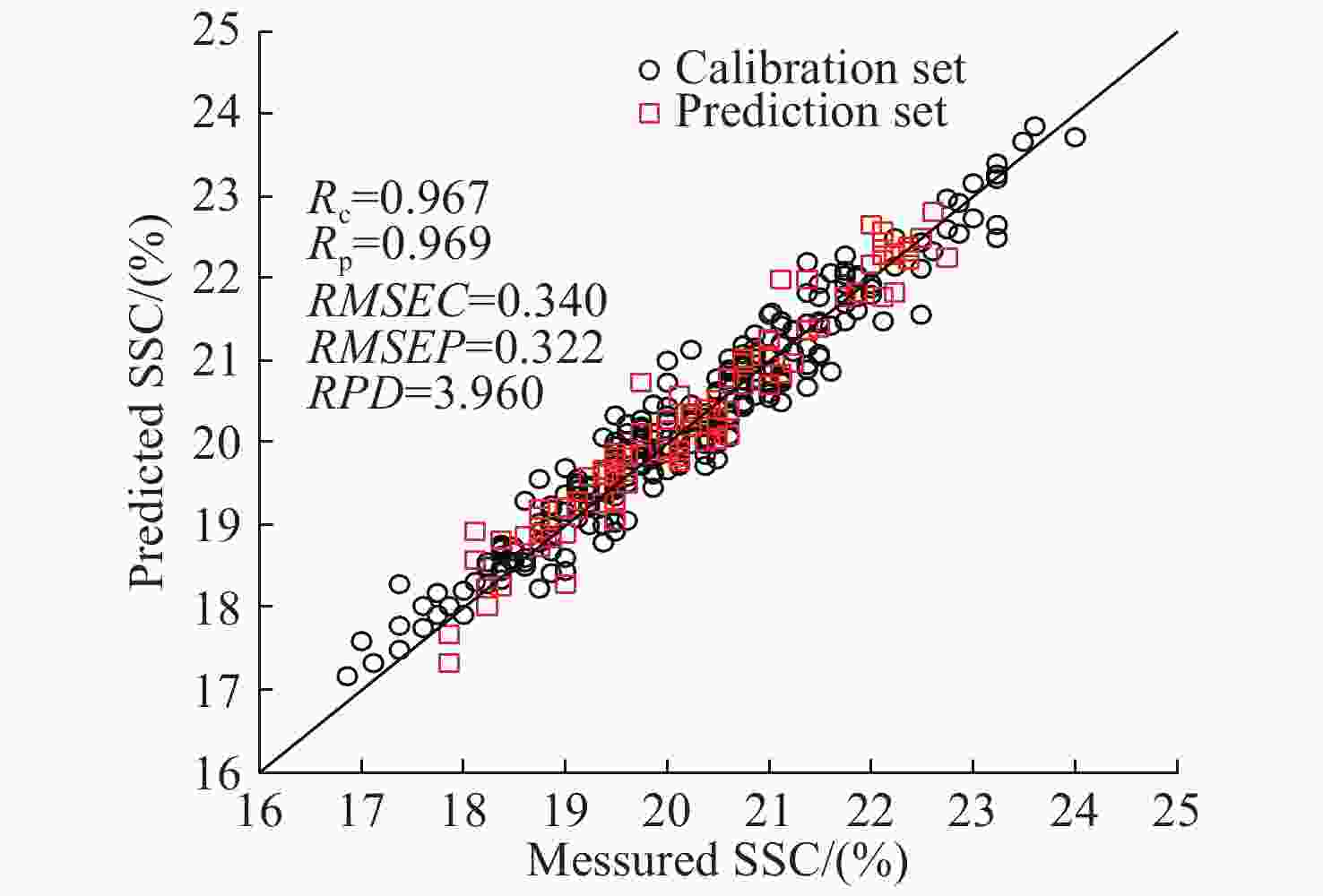
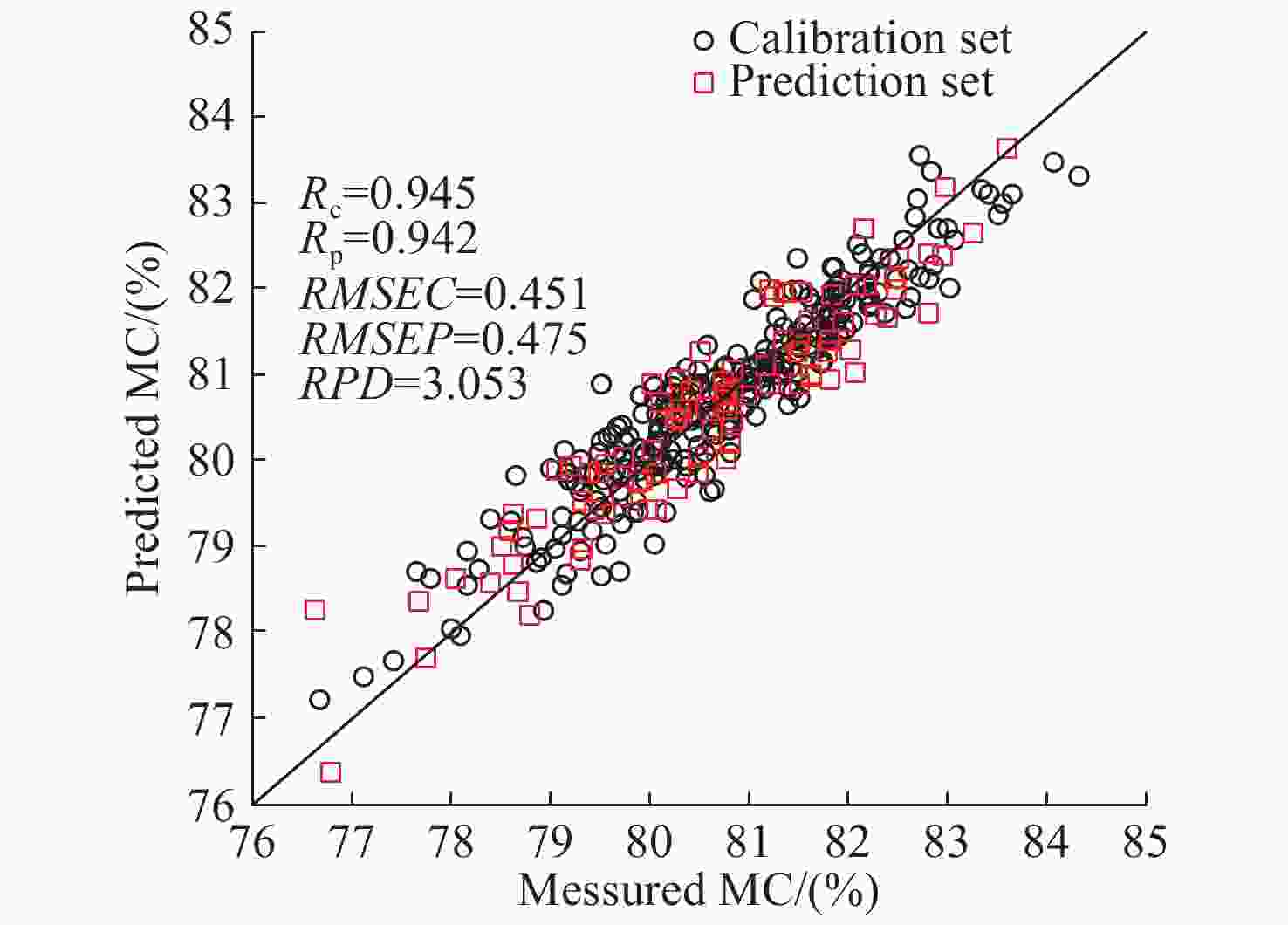
指标 特征波长提取方法 波点个数 γ σ2 校正集 预测集 RPD Rc RMSEC Rp RMSEP 糖度 原始光谱 1150 606877.813 27698.587 0.976 0.296 0.937 0.451 2.827 GA 85 486007.978 1715.475 0.964 0.354 0.940 0.441 2.891 SPA 17 255631.106 269.184 0.946 0.436 0.905 0.544 2.344 CARS 27 352524.566 442.091 0.944 0.442 0.941 0.434 2.938 UVE 437 709628.506 8410.785 0.968 0.338 0.942 0.431 2.958 CARS-SPA 9 493958.299 187.240 0.967 0.340 0.969 0.322 3.960 UVE-SPA 15 394145.82 282.089 0.935 0.472 0.925 0.485 2.629 GA-SPA 15 347263.829 384.322 0.935 0.473 0.937 0.449 2.839 含水率 原始光谱 1150 54302.715 46313.338 0.949 0.405 0.888 0.711 2.040 GA 78 351395.906 2351.707 0.931 0.465 0.899 0.683 2.124 含水率 SPA 12 224241.827 258.227 0.873 0.620 0.844 0.806 1.800 CARS 27 454665.452 23000.299 0.962 0.350 0.891 0.686 2.114 UVE 615 647436.819 22685.185 0.947 0.412 0.896 0.684 2.120 CARS-SPA 11 751032.167 865.070 0.883 0.595 0.843 0.820 1.769 UVE-SPA 19 606836.672 365.462 0.945 0.451 0.942 0.475 3.053 GA-SPA 13 3888528.517 496.001 0.908 0.531 0.889 0.728 1.992 表 7 红提糖度和含水率LSSVM检测模型的最优特征波点列表
Table 7. List of optimal wave point characteristics of the sugar and moisture content of LSSVM detection model for red globe grape
指标 建模方法 波长/nm 糖度(9个) CARS-SPA-LSSVM 826.41、874.38、880.84、904.45、910.44、915.15、944.16、950.96、974.30 含水率(19个) UVE-SPA-LSSVM 644.83、647.94、711.77、726.76、768.90、781.14、803.82、815.56、825.98、863.61、876.53、888.14、909.16、914.72、959.03、965.40、995.85、997.96、1032.01 -
[1] 国家统计局. 中国统计年鉴[M]. 北京: 中国统计出版社, 2018.National Bureau of Statistics. China Statistical Yearbook[M]. Beijing: China Statistics Press, 2018. (in Chinese). [2] 刘燕德, 徐海, 孙旭东, 等. 不同产地苹果糖度可见近红外光谱在线检测[J]. 中国光学,2020,13(3):482-491.LIU Y D, XU H, SUN X D, et al. On-line detection of soluble solids content of apples from different origins by visible and near-infrared spectroscopy[J]. Chinese Optics, 2020, 13(3): 482-491. (in Chinese) [3] ZHANG D Y, XU L, WANG Q Y, et al. The optimal local model selection for robust and fast evaluation of soluble solid content in melon with thick peel and large size by vis-NIR spectroscopy[J]. Food Analytical Methods, 2019, 12(1): 136-147. doi: 10.1007/s12161-018-1346-3 [4] 朱丹实, 张巧曼, 曹雪慧, 等. 湿度条件对巨峰葡萄贮藏过程中水分及质构变化的影响[J]. 食品科学,2014,35(22):340-345. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201422066ZHU D SH, ZHANG Q M, CAO X H, et al. Effect of relative humidity on the changes in water and texture of Kyoho grape during storage[J]. Food Science, 2014, 35(22): 340-345. (in Chinese) doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201422066 [5] 王凡, 李永玉, 彭彦昆, 等. 基于可见/近红外透射光谱的番茄红素含量无损检测方法研究[J]. 分析化学,2018,46(9):1424-1431.WANG F, LI Y Y, PENG Y K, et al. Nondestructive determination of Lycopene content based on visible/near infrared[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2018, 46(9): 1424-1431. (in Chinese) [6] 孙静涛, 马本学, 董娟, 等. 高光谱技术结合特征波长筛选和支持向量机的哈密瓜成熟度判别研究[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析,2017,37(7):2184-2191.SUN J T, MA B X, DONG J, et al. Study on maturity discrimination of Hami melon with hyperspectral imaging technology combined with characteristic wavelengths selection methods and SVM[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2017, 37(7): 2184-2191. (in Chinese) [7] 陈欣欣, 郭辰彤, 张初, 等. 高光谱成像技术的库尔勒梨早期损伤可视化检测研究[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析,2017,37(1):150-155.CHEN X X, GUO CH T, ZHANG CH, et al. Visual detection study on early bruises of Korla pear based on hyperspectral imaging technology[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2017, 37(1): 150-155. (in Chinese) [8] 王转卫, 迟茜, 郭文川, 等. 基于近红外光谱技术的发育后期苹果内部品质检测[J]. 农业机械学报,2018,49(5):348-354. doi: 10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2018.05.041WANG ZH W, CHI Q, GUO W CH, et al. Internal quality detection of apples during late developmental period based on near-infrared spectral technology[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2018, 49(5): 348-354. (in Chinese) doi: 10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2018.05.041 [9] 彭彦昆, 赵芳, 白京, 等. 基于图谱特征的番茄种子活力检测与分级[J]. 农业机械学报,2018,49(2):327-333. doi: 10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2018.02.042PENG Y K, ZHAO F, BAI J, et al. Detection and classification of tomato seed vitality based on image processing[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2018, 49(2): 327-333. (in Chinese) doi: 10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2018.02.042 [10] 高升, 王巧华, 李庆旭, 等. 基于近红外光谱的红提维生素C含量、糖度及总酸含量无损检测方法[J]. 分析化学,2019,47(6):941-949.GAO SH, WANG Q H, LI Q X, et al. Non-destructive detection of vitamin c, sugar content and total acidity of red globe grape based on near-infrared spectroscopy[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2019, 47(6): 941-949. (in Chinese) [11] 路皓翔, 徐明昌, 张卫东, 等. 基于压缩自编码融合极限学习机的柑橘黄龙病鉴别方法[J]. 分析化学,2019,47(5):652-660.LU H X, XU M CH, ZHANG W D, et al. Identification of citrus Huanglongbing based on contractive auto-encoder combined extreme learning machine[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2019, 47(5): 652-660. (in Chinese) [12] 付丹丹, 王巧华, 高升, 等. 不同品种鸡蛋贮期S-卵白蛋白含量分析及其可见/近红外光谱无损检测模型研究[J]. 分析化学,2020,48(2):289-297.FU D D, WANG Q H, GAO SH, et al. Analysis of S-ovalbumin content of different varieties of eggs during storage and its nondestructive testing model by visible-near infrared spectroscopy[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2020, 48(2): 289-297. (in Chinese) [13] 韩东海, 常冬, 宋曙辉, 等. 小型西瓜品质近红外无损检测的光谱信息采集[J]. 农业机械学报,2013,44(7):174-178. doi: 10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2013.07.030HAN D H, CHANG D, SONG SH H, et al. Information collection of mini watermelon quality using near-infrared non-destructive detection[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2013, 44(7): 174-178. (in Chinese) doi: 10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2013.07.030 [14] 孙海霞, 薛建新, 张淑娟, 等. 基于光谱和水分补偿方法的鲜枣内部品质检测[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析,2017,37(8):2513-2518.SUN H X, XUE J X, ZHANG SH J, et al. Detection of internal quality in fresh jujube based on moisture compensation and visible/near infrared spectra[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2017, 37(8): 2513-2518. (in Chinese) [15] 刘燕德, 朱丹宁, 孙旭东, 等. 苹果可溶性固形物便携式检测实验研究[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析,2017,37(10):3260-3265.LIU Y D, ZHU D N, SUN X D, et al. Study on detecting soluble solids in fruits based on portable near infrared spectrometer[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2017, 37(10): 3260-3265. (in Chinese) [16] 许锋, 付丹丹, 王巧华, 等. 基于MCCV-CARS-RF建立红提糖度和酸度的可见-近红外光谱无损检测方法[J]. 食品科学,2018,39(8):149-154. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201808024XU F, FU D D, WANG Q H, et al. Nondestructive detection of sugar content and acidity in red globe table grapes using visible near infrared spectroscopy based on monte-carlo cross validation-competitive adaptive reweighted sampling-random forest (MCCV-CARS-RF)[J]. Food Science, 2018, 39(8): 149-154. (in Chinese) doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201808024 [17] 樊书祥, 黄文倩, 郭志明, 等. 苹果产地差异对可溶性固形物近红外光谱检测模型影响的研究[J]. 分析化学,2015,43(2):239-244.FAN SH X, HUANG W Q, GUO ZH M, et al. Assessment of influence of origin variability on robustness of near infrared models for soluble solid content of apples[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2015, 43(2): 239-244. (in Chinese) [18] 中华全国供销合作总社. GH/T 1022-2000 鲜葡萄[S]. http://down.foodmate.net/standard/sort/9/4163.html, 2000.All China Federation of Supply and Marketing Cooperatives. GH/T 1022-2000 Table grapes[S]. http://down.foodmate.net/standard/sort/9/4163.html, 2000. (in Chinese). [19] 中华人民共和国农业部. NY/T 2637-2014 水果和蔬菜可溶性固形物含量的测定——折射仪法[S]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2015.The Ministry of Agriculture of the People’s Republic of China. NY/T 2637-2014 Refractometric method for determination of total soluble solids in fruits and vegetables[S]. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2015. (in Chinese). [20] 中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会. GB 5009.3-2016 食品安全国家标准 食品中水分的测定[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2017.State Health and Family Planning Commission of the People’s Republic of China. GB 5009.3-2016 Determination of moisture in food[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2017. (in Chinese) [21] 王拓, 戴连奎, 马万武. 拉曼光谱结合后向间隔偏最小二乘法用于调和汽油辛烷值定量分析[J]. 分析化学,2018,46(4):623-629. doi: 10.11895/j.issn.0253-3820.170278WANG T, DAI L K, MA W W. Quantitative analysis of blended gasoline octane number using raman spectroscopy with backward interval partial least squares method[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2018, 46(4): 623-629. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11895/j.issn.0253-3820.170278 [22] 孙海霞, 张淑娟, 薛建新, 等. 变量优选补正算法的鲜枣可溶性固形物检测模型传递方法研究[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析,2019,39(4):1041-1046.SUN H X, ZHANG SH J, XUE J X, et al. Model transfer method of fresh jujube soluble solids detection using variables optimization and correction algorithms[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2019, 39(4): 1041-1046. (in Chinese) [23] DOGN J L, GUO W CH, WANG ZH W, et al. Nondestructive determination of soluble solids content of ‘Fuji’ apples produced in different areas and bagged with different materials during ripening[J]. Food Analytical Methods, 2016, 9(5): 1087-1095. doi: 10.1007/s12161-015-0278-4 [24] DONG J L, GUO W CH. Nondestructive determination of apple internal qualities using near-infrared hyperspectral reflectance imaging[J]. Food Analytical Methods, 2015, 8(10): 2635-2646. doi: 10.1007/s12161-015-0169-8 [25] 王浩云, 宋进, 潘磊庆, 等. 优化BP神经网络提高高光谱检测调理鸡肉菌落总数精度[J]. 农业工程学报,2020,36(5):302-309. doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2020.05.035WANG H Y, SONG J, PAN L Q, et al. Improving hyperspectral detection accuracy of total bacteria in prepared chicken using optimized BP neural network[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2020, 36(5): 302-309. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2020.05.035 [26] 王凡, 彭彦昆, 汤修映, 等. 樱桃番茄可溶性固形物含量的可见/近红外透射光谱无损检测[J]. 中国食品学报,2018,18(10):235-240.WANG F, PENG Y K, TANG X Y, et al. Near infrared nondestructive testing of soluble solids content of cherry tomato[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology, 2018, 18(10): 235-240. (in Chinese) [27] 史云颖, 李敬岩, 褚小立. 多元校正模型传递方法的进展与应用[J]. 分析化学,2019,47(4):479-487. doi: 10.1016/S1872-2040(19)61152-7SHI Y Y, LI J Y, CHU X L. Progress and applications of multivariate calibration model transfer methods[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2019, 47(4): 479-487. (in Chinese) doi: 10.1016/S1872-2040(19)61152-7 [28] 王键, 汪六三, 王儒敬, 等. 基于优选波长的复合肥总氮含量可见/近红外光谱分析[J]. 发光学报,2018,39(12):1785-1791. doi: 10.3788/fgxb20183912.1785WANG J, WANG L S, WANG R J, et al. Analysis of total nitrogen in compound fertilizers by VIS-NIR spectroscopy[J]. Chinese Journal of Luminescence, 2018, 39(12): 1785-1791. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/fgxb20183912.1785 -





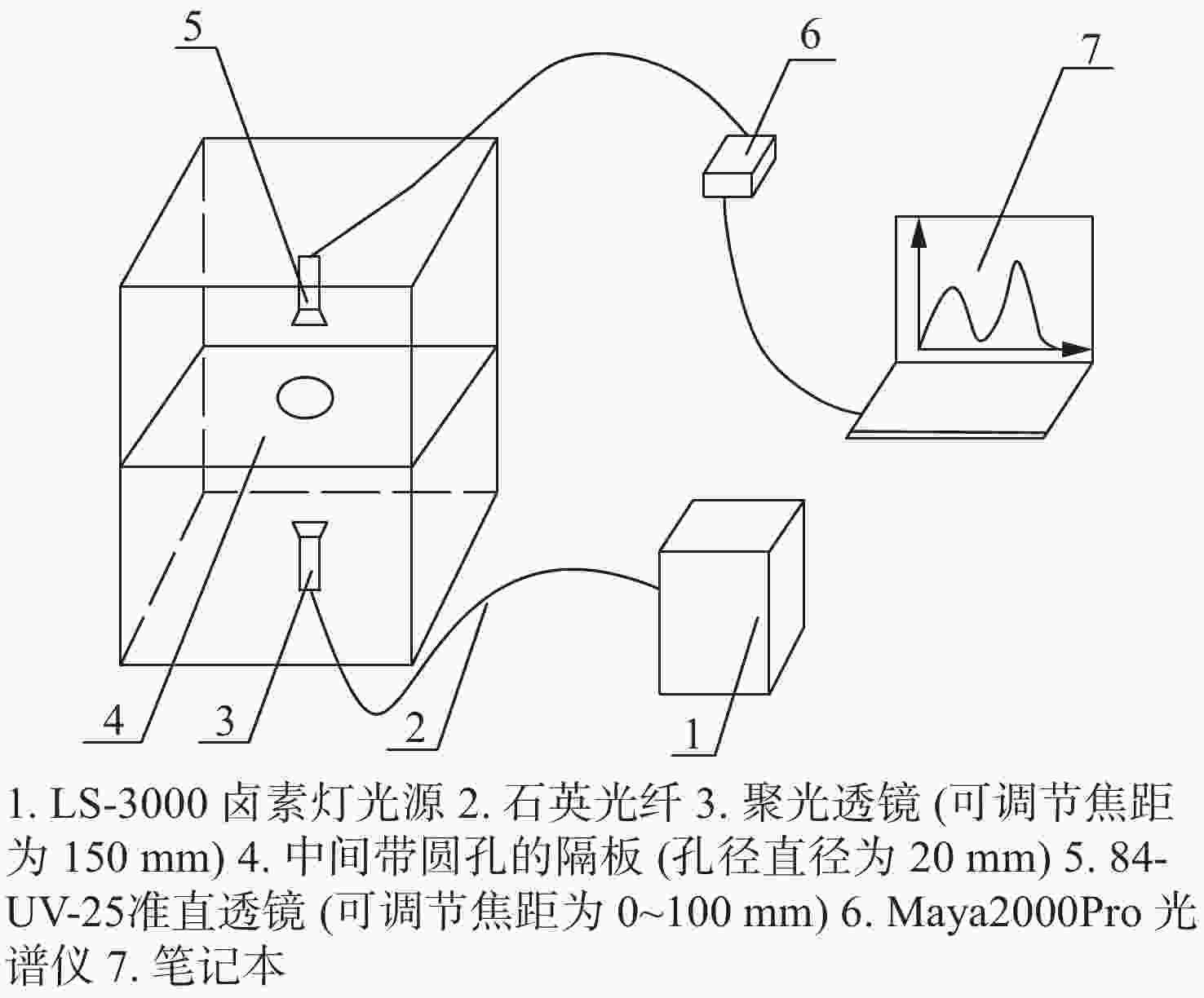
 下载:
下载: