Non-uniformity correction of airborne infrared detection system based on inter-frame registration
-
摘要: 机载红外点目标探测系统在搭载飞机飞行中探测系统的环境参数会发生变化,导致通过传统地面标定方法获取的非均匀性校正参数的准确性有所降低,故有必要进行机上基于场景的非均匀性校正。本文提出了一种基于帧间配准的机上非均匀性校正算法,首先对图像进行预处理,滤除探测器坏点影响,然后用两帧邻近图像计算互功率谱,求出互相关函数,确定配准位移。两帧连续图像完成配准后,通过误差函数最小化来实现校正参数的更新,最后对整个图像序列进行上述迭代计算,获取最终校正参数。本文模拟了一组非均匀性场景图像序列作为实验图像序列,通过实验分析,提出了帧间图像变化(平移、旋转、缩放)对本算法校正效果的影响,然后采用两个具有代表性的算法与本文提出的算法分别对该图像序列进行处理,并从图像质量和收敛速度两方面比较算法性能。结果表明:与其他两种算法相比,本文提出的算法非均匀性校正效果较好,峰值信噪比提高了20 dB以上,结构相似性则突破了0.99。本文提出的算法虽然比较复杂,但校正参数收敛速度较快,易于在硬件平台上实现,具有一定的工程应用前景。Abstract: During flight, changes in environmental parameters affect the accuracy of non-uniformity correction of airborne infrared point-target detection systems to some extent. Therefore, it is necessary to perform on-board scene-based non-uniformity correction. In this paper, we propose an algorithm based on inter-frame registration to achieve on-board non-uniformity correction. It first preprocesses the images to filter out dead pixels, then calculates a cross-power spectrum with two adjacent frames and determines their registration displacement according to a correlation function that is calculated from the cross-power spectrum. After registering an image, corrective parameters are updated by minimizing the error through a function. The corrective parameters are finally obtained after the above calculations are performed. In an experimental comparison, we simulate a set of non-uniform scene image sequences as the experimental image sequence. This experiment first identified the influence of changes between frames (including displacement, rotation and scaling) on the accuracy of non-uniformity correction. It then used two representative algorithms and the proposed algorithm to process the image series, and compared the performance of the algorithms from the perspective of image quality and convergence speed. The results show that the proposed algorithm has better non-uniformity corrective performance compared with the two other methods. The PSNR increased by over 20 dB, and the SSIM exceeded 0.99. The proposed algorithm has higher complexity, but its convergence speed is much faster, and it is easy to be implemented on hardware platforms, which gives the algorithm possible applications in engineering.
-
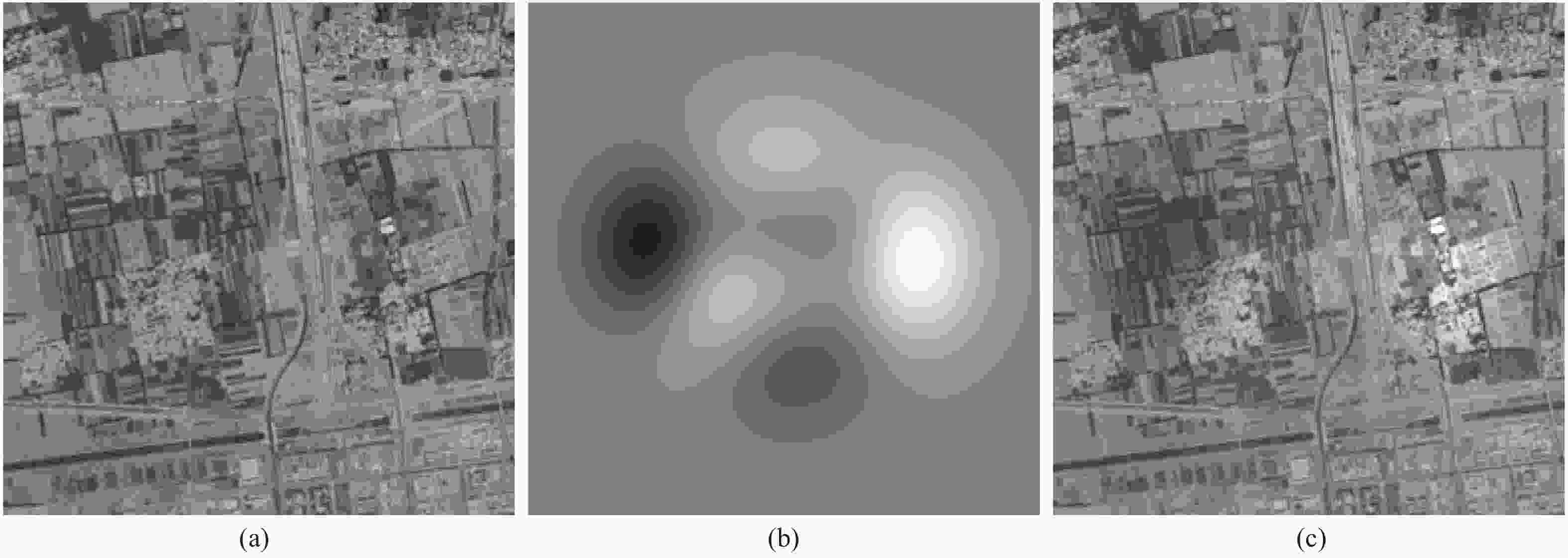
图 6 图像变换对配准的影响。(a)原图;(b)(c)(d)分别相对于(a)平移(120,120)、旋转2°、放大1.03倍,(e)(f)(g)分别是(b)(c)(d)与(a)计算的互功率谱
Figure 6. Registering accuracy affected by geometry transformation. (a) Original image; (b)(c)(d) are respectively translated by (120,120), rotated by 2 degrees, enlarged by 1.03 X relative to (a); (e)(f)(g) are the cross-power spectrum of (b)(c)(d) and (a), respectively.
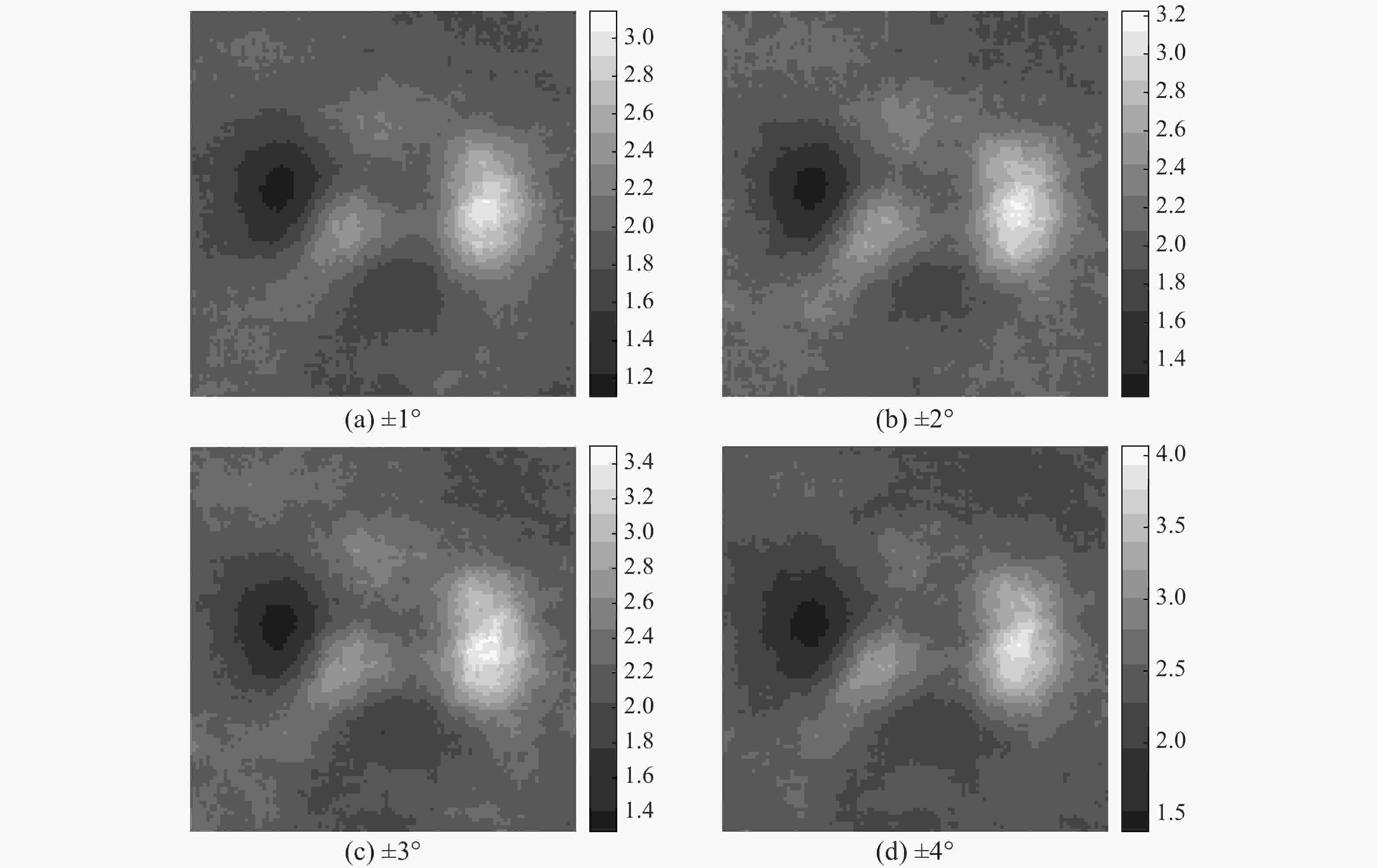
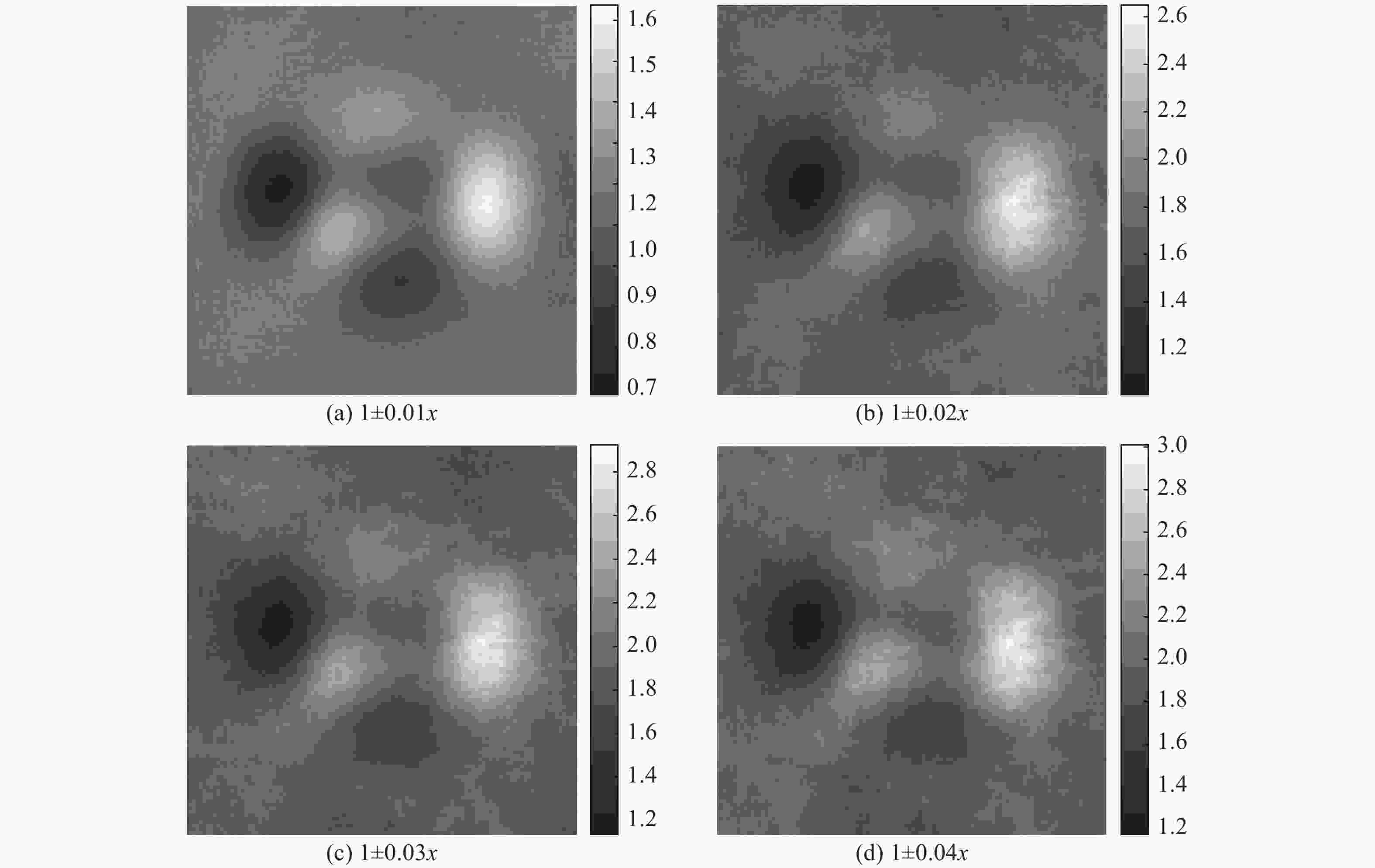
表 1 不同旋转或缩放范围对增益估计准确性的影响
Table 1. Influence of various ranges of random rotation or scaling on estimation correctness of gain coefficient
随机旋转范围 ±1° ±2° ±3° ±4° MSE 0.9424 1.2422 1.5848 2.1789 随机缩放范围 1±0.01 1±0.02 1±0.03 1±0.04 MSE 0.0357 0.5916 0.8911 1.0302 表 2 各种算法处理后图像的平均对比度(全局标准差)
Table 2. Average contrasts (global standard deviation) of the image processed by various algorithms
算法 Original THPF CS IRLMS 真值 GSTD 0.1524 0.1496 0.1606 0.1674 0.1684 表 3 各种算法处理后图像的平均峰值信噪比
Table 3. Average PSNRs of the images processed by various algorithms
(dB) 算法 Original THPF CS IRLMS PSNR 20.1949 15.2826 15.1871 38.1842 表 4 各种算法处理后图像的平均结构相似性
Table 4. Average SSIMs of the images processed by various algorithms
算法 Original THPF CS IRLMS SSIM 0.9431 0.3042 0.3002 0.9974 -
CHEN C L P, LI H, WEI Y T, et al. A local contrast method for small infrared target detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(1): 574-581. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2242477 杨会玲, 吴玉宏, 孙慧婷, 等. 基于杂波抑制的海平线红外弱小目标检测[J]. 液晶与显示,2017,32(4):316-324. doi: 10.3788/YJYXS20173204.0316YANG H L, WU Y H, SUN H T, et al. Small dim infrared target detection of horizon region based on clutter rejection[J]. Chinese Journal of Liquid Crystals and Displays, 2017, 32(4): 316-324. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/YJYXS20173204.0316 QIN Y, LI B. Effective infrared small target detection utilizing a novel local contrast method[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2016, 13(12): 1890-1894. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2016.2616416 HU J, XU ZH ZH, WAN Q Q. Non-uniformity correction of infrared focal plane array in point target surveillance systems[J]. Infrared Physics &Technology, 2014, 66: 56-69. doi: 10.1016/j.infrared.2014.05.012 韩亚君, 杨德东, 李勇, 等. 基于多特征融合相关滤波的红外目标跟踪[J]. 液晶与显示,2019,34(2):177-187. doi: 10.3788/YJYXS20193402.0177HAN Y J, YANG D D, LI Y, et al. Infrared target tracking based on correlation filter with multi-features fusion[J]. Chinese Journal of Liquid Crystals and Displays, 2019, 34(2): 177-187. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/YJYXS20193402.0177 李一芒, 何昕, 魏仲慧. 红外预警实时图像处理系统设计与实现[J]. 液晶与显示,2013,28(1):110-114. doi: 10.3788/YJYXS20132801.0110LI Y M, HE X, WEI ZH H, et al. Design and implement of real-time image processing system for IR warning system based on multi-passage[J]. Chinese Journal of Liquid Crystals and Displays, 2013, 28(1): 110-114. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/YJYXS20132801.0110 宁永慧, 郭永飞, 曲利新, 等. 多通道时间延迟积分CCD辐射标定和像元实时处理[J]. 光学 精密工程,2015,23(10):2952-2961. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20152310.2952NING Y H, GUO Y F, QU L X, et al. Radiometric calibration and pixel data real-time processing of multi-tip TDICCD[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2015, 23(10): 2952-2961. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/OPE.20152310.2952 ZHANG T X, SHI CH CH, LI J J, et al. Overview of research on the adaptive algorithms for nonuniformity correction of infrared focal plane array[J]. Journal of Infrared and Millimeter Waves, 2007, 26(6): 409-413. 王文华, 何斌, 韩双丽, 等. 星上CCD成像非均匀性的实时校正[J]. 光学 精密工程,2010,18(6):1420-1428.WANG W H, HE B, HAN SH L, et al. Real-time correction of nonuniformity in CCD imaging for remote sensing[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2010, 18(6): 1420-1428. (in Chinese) ZHOU B, MA Y, LI H, et al. A study of two-point multi-section non-uniformity correction auto division algorithm for infrared images[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2010, 7658: 76583X. doi: 10.1117/12.866403 李赓飞, 李桂菊, 韩广良, 等. 红外成像系统的非均匀性实时校正[J]. 光学 精密工程,2016,24(11):2841-2847. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20162411.2841LI G F, LI G J, HAN G L, et al. Real-time non-uniformity correction of infrared imaging system[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2016, 24(11): 2841-2847. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/OPE.20162411.2841 QIAN W X, CHEN Q, GU G H. Space low-pass and temporal high-pass nonuniformity correction algorithm[J]. Optical Review, 2010, 17(1): 24-29. doi: 10.1007/s10043-010-0005-8 HARRIS J G, CHIANG Y M. Nonuniformity correction using the constant-statistics constraint: analog and digital implementations[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 1997, 3061: 895-905. doi: 10.1117/12.280308 ZUO CH, CHEN Q, GU G H, et al. Scene-based nonuniformity correction algorithm based on interframe registration[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America A, 2011, 28(6): 1164-1176. doi: 10.1364/josaa.28.001164 OKORIE A, MAKROGIANNIS S. Region-based image registration for remote sensing imagery[J]. Computer Vision and Image Understanding, 2019, 189: 102825. doi: 10.1016/j.cviu.2019.102825 ZUO CH, CHEN Q, GU G H, et al. Improved interframe registration based nonuniformity correction for focal plane arrays[J]. Infrared Physics &Technology, 2012, 55(4): 263-269. doi: 10.1016/j.infrared.2012.04.002 PELI E. Contrast in complex images[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America A, 1990, 7(10): 2032-2040. doi: 10.1364/josaa.7.002032 DAOUD A O, TSEHAYAE A A, FAYEK A R. A guided evaluation of the impact of research and development partnerships on university, industry, and government[J]. Canadian Journal of Civil Engineering, 2017, 44(4): 253-263. doi: 10.1139/cjce-2016-0381 -






 下载:
下载: