-
摘要: 超快激光技术的发展为基础研究和工业生产不断注入新的动力,促发了很多新学科、新技术的诞生。超快激光焊接作为近年来发展起来的一种新型材料连接技术,在航空航天、精密机械、集成光电、生物医疗等领域具有巨大的应用潜力,受到了人们的广泛关注。基于超快激光非线性选区能量沉积的基本特点,超快激光焊接具有广泛的材料适用性和空间选择性,可以在无嵌入层的前提下实现涉及透明材料的高质量选区焊接。本文从超快激光选区焊接的物理机制、主要影响因素、适用领域入手进行了归纳与分析,并对未来该技术发展和将面临的关键挑战进行了论述。Abstract: The development of ultrafast laser technology has continuously injected new impetus into fundamental research and production, promoted the emergence of new disciplines and technologies. As a new materials welding and joining technique developed in recent years, ultrafast laser welding has attracted extensive attention due to the potential application in the fields of aerospace, precision machinery, optoelectronics, biomedical, etc.. Based on the intrinsic characteristic of non-linear space-selective energy deposition, ultrafast laser welding possesses extremely high material applicability and spatial selectivity, and can realize high-quality space-selective welding involving transparent materials with no need inserting an absorption layer. In this paper, we firstly give an overview on the progress of this field. Then, the physical mechanism, key influencing factors, and application scope of ultrafast laser welding are elaborated. At last, the future development and key challenges of ultrafast laser welding are discussed.
-
Key words:
- ultrafast laser /
- welding /
- transparent materials /
- non-linear absorption
-
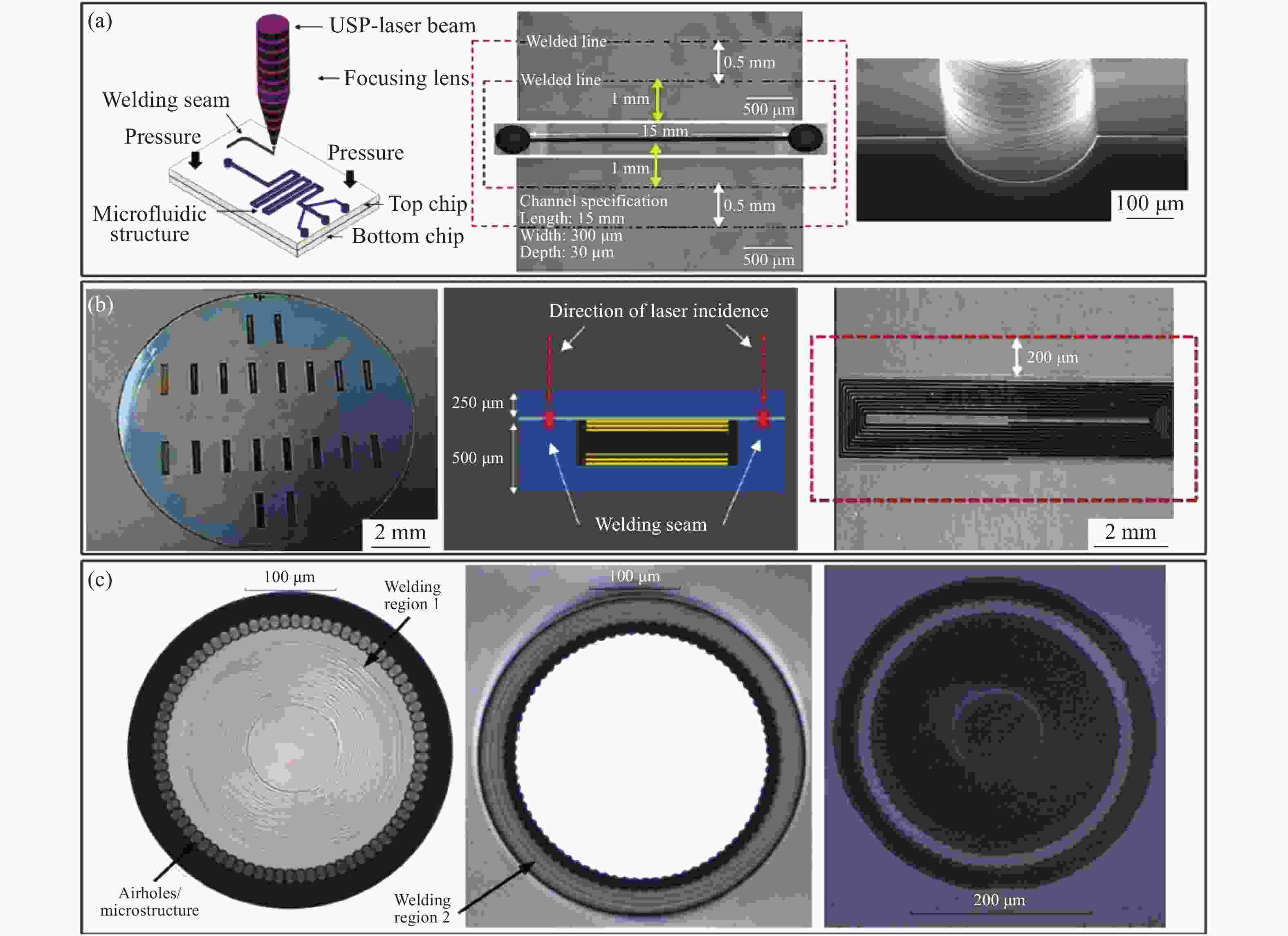
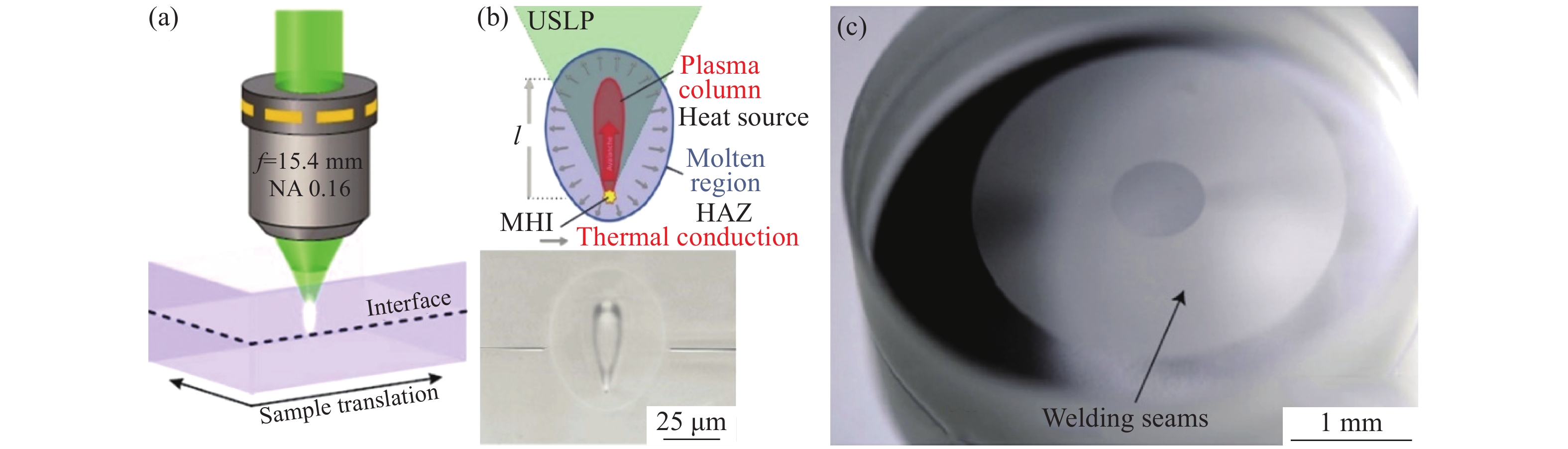
图 1 (a)超快激光选区焊接玻璃样品示意图[13];(b)高重频激光诱导材料内部改性示意图以及超快激光焊线横截面[14];(c)环形激光焊线封装的窗口玻璃[13]
Figure 1. (a) Diagram of ultrafast laser welding of glass[13]; (b) schematic diagram of internal modification induced by ultrafast laser with high pulse repetition rate and cross section of seal[14]; (c) image of two laser welded circular blanks of fused silica[13]
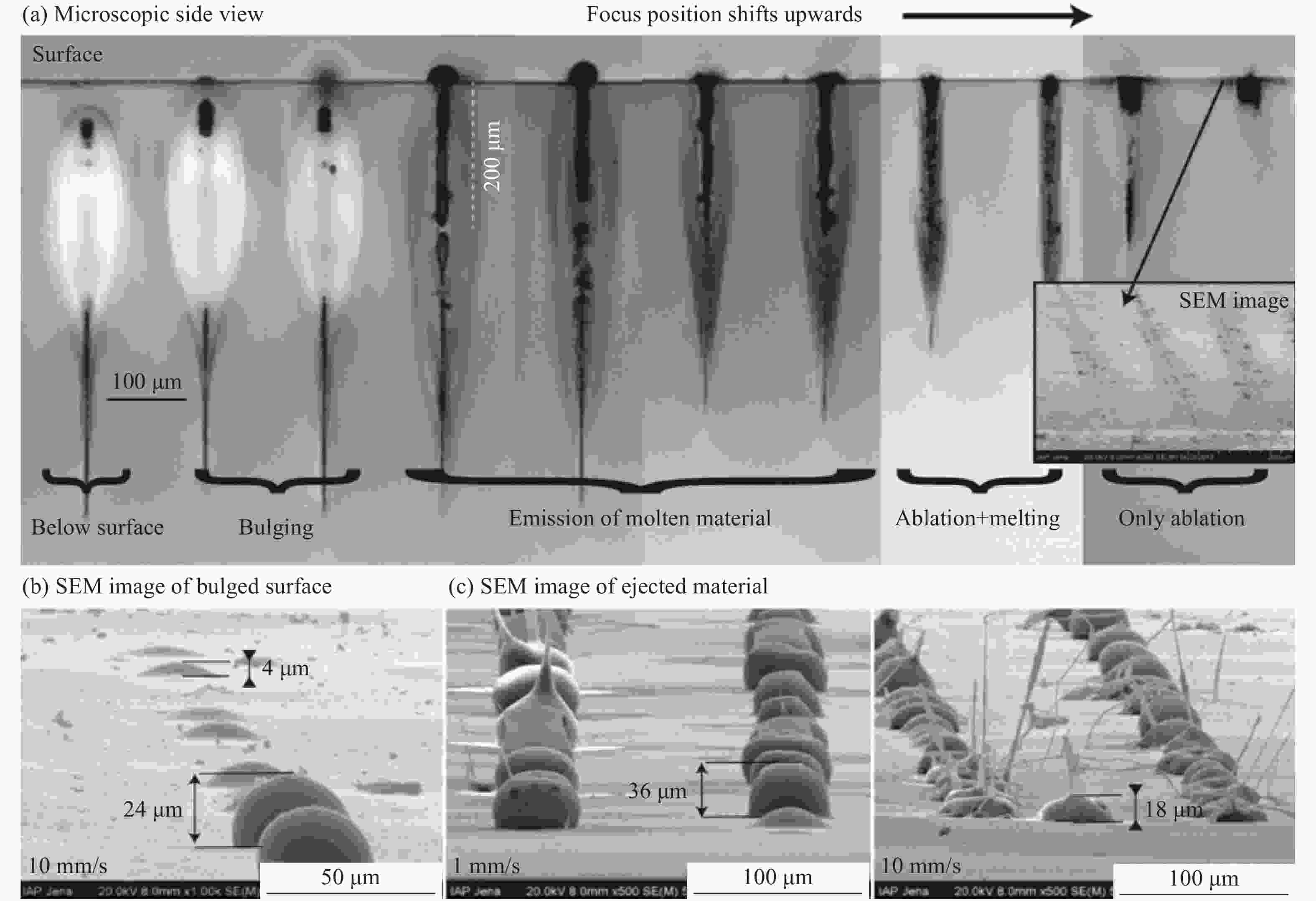
图 7 (a)激光能量为1.63 μJ、扫描速度为20 mm/s时激光诱导D263玻璃热熔区域的横截面;(b)扫描速度为20 mm/s时超快激光作用D263玻璃的无裂纹条件[45]
Figure 7. (a) Cross-sections of D263 glass melting area at scanning speed v = 20 mm/s and laser energy Φ0 = 1.63 μJ; (b) crack-free and cracking conditions at v = 20 mm/s when ultra-fast laser is applied in D263[45]
-
[1] WANG S F, ZHANG J, LUO D W, et al. Transparent ceramics: processing, materials and applications[J]. Progress in Solid State Chemistry, 2013, 41(1-2): 20-54. doi: 10.1016/j.progsolidstchem.2012.12.002 [2] 范志刚, 刘建军, 肖昊苏, 等. 蓝宝石单晶的生长技术及应用研究进展[J]. 硅酸盐学报,2011,39(5):880-891.FAN ZH G, LIU J J, XIAO H S, et al. Research progress on growth technique and application of sapphire single crystal[J]. Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2011, 39(5): 880-891. (in Chinese) [3] AXINTE E. Glasses as engineering materials: a review[J]. Materials &Design, 2011, 32(4): 1717-1732. [4] TAMAKI T, WATANABE W, NISHII J, et al. Welding of transparent materials using femtosecond laser pulses[J]. Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 2005, 44(22-23): L687-L689. [5] WATANABE W, ONDA S, TAMAKI T, et al. Space-selective laser joining of dissimilar transparent materials using femtosecond laser pulses[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2006, 89(2): 021106. doi: 10.1063/1.2221393 [6] HÉLIE D, LACROIX F, VALLÉE R. Bonding of optical materials by femtosecond laser welding for aerospace and high power laser applications[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2012, 8412: 841210. doi: 10.1117/12.2010265 [7] LUO CH, LIN L W. The application of nanosecond-pulsed laser welding technology in MEMS packaging with a shadow mask[J]. Sensors and Actuators A:Physical, 2002, 97-98: 398-404. doi: 10.1016/S0924-4247(01)00849-4 [8] GATTASS R R, MAZUR E. Femtosecond laser micromachining in transparent materials[J]. Nature Photonics, 2008, 2(4): 219-225. doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2008.47 [9] SUGIOKA K, CHENG Y. Ultrafast lasers—reliable tools for advanced materials processing[J]. Light:Science &Applications, 2014, 3(4): e149. [10] TAMAKI T, WATANABE W, ITOH K. Laser micro-welding of transparent materials by a localized heat accumulation effect using a femtosecond fiber laser at 1558 nm[J]. Optics Express, 2006, 14(22): 10460-10468. doi: 10.1364/OE.14.010460 [11] OZEKI Y, INOUE T, TAMAKI T, et al. Direct welding between copper and glass substrates with femtosecond laser pulses[J]. Applied Physics Express, 2008, 1(8): 082601. [12] PENILLA E H, DEVIA-CRUZ L F, WIEG A T, et al. Ultrafast laser welding of ceramics[J]. Science, 2019, 365(6455): 803-808. doi: 10.1126/science.aaw6699 [13] RICHTER S, ZIMMERMANN F, TÜNNERMANN A, et al. [INVITED] Laser welding of glasses at high repetition rates - Fundamentals and prospects[J]. Optics &Laser Technology, 2016, 83: 59-66. [14] MIYAMOTO I, CVECEK K, OKAMOTO Y, et al. Internal modification of glass by ultrashort laser pulse and its application to microwelding[J]. Applied Physics A, 2014, 114(1): 187-208. doi: 10.1007/s00339-013-8115-3 [15] ZHANG G D, CHENG G H. Direct welding of glass and metal by 1 kHz femtosecond laser pulses[J]. Applied Optics, 2015, 54(30): 8957-8961. doi: 10.1364/AO.54.008957 [16] MIYAMOTO I, OKAMOTO Y, HANSEN A, et al. High speed, high strength microwelding of Si/glass using ps-laser pulses[J]. Optics Express, 2015, 23(3): 3427-3439. doi: 10.1364/OE.23.003427 [17] CHEN J Y, CARTER R M, THOMSON R R, et al. Avoiding the requirement for pre-existing optical contact during picosecond laser glass-to-glass welding: erratum[J]. Optics Express, 2015, 23(21): 28104-28105. doi: 10.1364/OE.23.028104 [18] CVECEK K, ODATO R, DEHMEL S, et al. Gap bridging in joining of glass using ultra short laser pulses[J]. Optics Express, 2015, 23(5): 5681-5693. doi: 10.1364/OE.23.005681 [19] LACROIX F, HÉLIE D, VALLÉE R. Optical bonding reinforced by femtosecond laser welding[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2011, 8126: 812612. doi: 10.1117/12.892465 [20] ZOLOTOVSKAYA S A, TANG G, WANG Z B, et al. Surface plasmon resonance assisted rapid laser joining of glass[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2014, 105(8): 083109. doi: 10.1063/1.4894118 [21] MIYAMOTO I, HORN A, GOTTMANN J, et al. Fusion welding of glass using femtosecond laser pulses with high-repetition rates[J]. Journal of Laser Micro/Nanoengineering, 2007, 2(1): 57-63. doi: 10.2961/jlmn.2007.01.0011 [22] MIYAMOTO I, CVECEK K, SCHMIDT M. Evaluation of nonlinear absorptivity in internal modification of bulk glass by ultrashort laser pulses[J]. Optics Express, 2011, 19(11): 10714-10727. doi: 10.1364/OE.19.010714 [23] RICHTER S, DÖRING S, TÜNNERMANN A, et al. Bonding of glass with femtosecond laser pulses at high repetition rates[J]. Applied Physics A, 2011, 103(2): 257-261. doi: 10.1007/s00339-011-6369-1 [24] ZIMMERMANN F, RICHTER S, DÖRING S, et al. Ultrastable bonding of glass with femtosecond laser bursts[J]. Applied Optics, 2013, 52(6): 1149-1154. doi: 10.1364/AO.52.001149 [25] SUGIOKA K, IIDA M, TAKAI H, et al. Efficient microwelding of glass substrates by ultrafast laser irradiation using a double-pulse train[J]. Optics Letters, 2011, 36(14): 2734-2736. doi: 10.1364/OL.36.002734 [26] WU S ZH, WU D, XU J, et al. Characterization and mechanism of glass microwelding by double-pulse ultrafast laser irradiation[J]. Optics Express, 2012, 20(27): 28893-28905. doi: 10.1364/OE.20.028893 [27] WU S ZH, WU D, XU J, et al. Absorption mechanism of the second pulse in double-pulse femtosecond laser glass microwelding[J]. Optics Express, 2013, 21(20): 24049-24059. doi: 10.1364/OE.21.024049 [28] CARTER R M, CHEN J Y, SHEPHARD J D, et al. Picosecond laser welding of similar and dissimilar materials[J]. Applied Optics, 2014, 53(19): 4233-4238. doi: 10.1364/AO.53.004233 [29] ZHANG G D, BAI J, ZHAO W, et al. Interface modification based ultrashort laser microwelding between SiC and fused silica[J]. Optics Express, 2017, 25(3): 1702-1709. doi: 10.1364/OE.25.001702 [30] VOLPE A, DINISO F, GAUDIUSO C, et al. Welding of PMMA by a femtosecond fiber laser[J]. Optics Express, 2015, 23(4): 4114-4124. doi: 10.1364/OE.23.004114 [31] MIZUGUCHI Y, TAMAKI T, FUKUDA T, et al. Dendrite-joining of air-gap-separated PMMA substrates using ultrashort laser pulses[J]. Optical Materials Express, 2017, 7(7): 2141-2149. doi: 10.1364/OME.7.002141 [32] ROTH G L, RUNG S, HELLMANN R. Ultrashort pulse laser micro-welding of cyclo-olefin copolymers[J]. Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 2017, 93: 178-181. doi: 10.1016/j.optlaseng.2017.02.006 [33] WATANABE W. Volume gratings and welding of glass/plastic by femtosecond laser direct writing[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2018, 10456: 104562L. [34] RICHTER S, ZIMMERMANN F, EBERHARDT R, et al. Toward laser welding of glasses without optical contacting[J]. Applied Physics A, 2015, 121(1): 1-9. [35] HAM S S, KIM C H, CHOI S H, et al. Jig-free laser welding of Eagle XG glasses by using a picosecond pulsed laser[J]. Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology, 2019, 33(6): 2825-2832. doi: 10.1007/s12206-019-0529-1 [36] CHEN H, DENG L M, DUAN J, et al. Picosecond laser welding of glasses with a large gap by a rapid oscillating scan[J]. Optics Letters, 2019, 44(10): 2570-2573. doi: 10.1364/OL.44.002570 [37] HÉLIE D, BÉGIN M, LACROIX F, et al. Reinforced direct bonding of optical materials by femtosecond laser welding[J]. Applied Optics, 2012, 51(12): 2098-2106. doi: 10.1364/AO.51.002098 [38] HÉLIE D, LACROIX F, VALLÉE R. Reinforcing a direct bond between optical materials by filamentation based femtosecond laser welding[J]. Journal of Laser Micro/Nanoengineering, 2012, 7(3): 284-292. doi: 10.2961/jlmn.2012.03.0010 [39] ZHANG G D, STOIAN R, ZHAO W, et al. Femtosecond laser Bessel beam welding of transparent to non-transparent materials with large focal-position tolerant zone[J]. Optics Express, 2018, 26(2): 917-926. doi: 10.1364/OE.26.000917 [40] SUNDARAM S K, MAZUR E. Inducing and probing non-thermal transitions in semiconductors using femtosecond laser pulses[J]. Nature Materials, 2002, 1(4): 217-224. doi: 10.1038/nmat767 [41] RETHFELD B, SOKOLOWSKI-TINTEN K, VON DER LINDE D, et al. Timescales in the response of materials to femtosecond laser excitation[J]. Applied Physics A, 2004, 79(4-6): 767-769. doi: 10.1007/s00339-004-2805-9 [42] STOIAN R, BHUYAN M K, RUDENKO A, et al. High-resolution material structuring using ultrafast laser non-diffractive beams[J]. Advances in Physics:X, 2019, 4(1): 1659180. doi: 10.1080/23746149.2019.1659180 [43] BHUYAN M K, SOMAYAJI M, MERMILLOD-BLONDIN A, et al. Ultrafast laser nanostructuring in bulk silica, a "slow" microexplosion[J]. Optica, 2017, 4(8): 951-958. doi: 10.1364/OPTICA.4.000951 [44] MIYAMOTO I, CVECEK K, SCHMIDT M. Crack-free conditions in welding of glass by ultrashort laser pulse[J]. Optics Express, 2013, 21(12): 14291-14302. doi: 10.1364/OE.21.014291 [45] MIYAMOTO I, CVECEK K, OKAMOTO Y, et al. Novel fusion welding technology of glass using ultrashort pulse lasers[J]. Physics Procedia, 2010, 5: 483-493. [46] SAVASTRU D, SAVASTRU R, MICLOS S, et al. Simulation of laser induced absorption phenomena in transparent materials[J]. Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 2018, 110: 288-295. doi: 10.1016/j.optlaseng.2018.04.025 [47] WANG R, ZHANG Q B, LI D, et al. Identification of tunneling and multiphoton ionization in intermediate Keldysh parameter regime[J]. Optics Express, 2019, 27(5): 6471-6482. doi: 10.1364/OE.27.006471 [48] OUYANG ZH Y, OKAMOTO Y, OGINO Y, et al. Influence of numerical aperture on molten area formation in fusion micro-welding of glass by picosecond pulsed laser[J]. Applied Sciences, 2019, 9(7): 1412. doi: 10.3390/app9071412 [49] KISSI E O, BELLOUARD Y. Self-organized nanostructures forming under high-repetition rate femtosecond laser bulk-heating of fused silica[J]. Optics Express, 2018, 26(11): 14024-14037. doi: 10.1364/OE.26.014024 [50] CVECEK K, MIYAMOTO I, SCHMIDT M. Gas bubble formation in fused silica generated by ultra-short laser pulses[J]. Optics Express, 2014, 22(13): 15877-15893. doi: 10.1364/OE.22.015877 [51] ZHANG G D, CHENG G H, BHUYAN M K, et al. Ultrashort Bessel beam photoinscription of Bragg grating waveguides and their application as temperature sensors[J]. Photonics Research, 2019, 7(7): 806-814. doi: 10.1364/PRJ.7.000806 [52] ZHANG G, CHENG G, BHUYAN M, et al. Efficient point-by-point Bragg gratings fabricated in embedded laser-written silica waveguides using ultrafast Bessel beams[J]. Optics Letters, 2018, 43(9): 2161-2164. doi: 10.1364/OL.43.002161 [53] STOIAN R, BHUYAN M K, ZHANG G D, et al. Ultrafast Bessel beams: advanced tools for laser materials processing[J]. Advanced Optical Technologies, 2018, 7(3): 165-174. doi: 10.1515/aot-2018-0009 [54] CVECEK K, DEHMEL S, MIYAMOTO I, et al. A review on glass welding by ultra-short laser pulses[J]. International Journal of Extreme Manufacturing, 2019, 1(4): 042001. doi: 10.1088/2631-7990/ab55f6 [55] VILLERIUS V, KOOIKER H, POST J, et al. Ultrashort pulsed laser ablation of stainless steels[J]. International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture, 2019, 138: 27-35. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2018.11.003 [56] LOU R, ZHANG G D, LI G Y, et al. Design and fabrication of dual-scale broadband antireflective structures on metal surfaces by using nanosecond and femtosecond lasers[J]. Micromachines, 2020, 11(1): 20. [57] RICHTER S, ZIMMERMANN F, DÖRING S, et al. Ultrashort high repetition rate exposure of dielectric materials: laser bonding of glasses analyzed by micro-Raman spectroscopy[J]. Applied Physics A, 2013, 110(1): 9-15. doi: 10.1007/s00339-012-7478-1 [58] ROTH G L, RUNG S, HELLMANN R. Welding of transparent polymers using femtosecond laser[J]. Applied Physics A, 2016, 122(2): 86. doi: 10.1007/s00339-016-9605-x [59] BUTKUS S, GAIŽAUSKAS E, PAIPULAS D, et al. Rapid microfabrication of transparent materials using filamented femtosecond laser pulses[J]. Applied Physics A, 2014, 114(1): 81-90. doi: 10.1007/s00339-013-8108-2 [60] HORN A, MINGAREEV I, WERTH A, et al. Investigations on ultrafast welding of glass–glass and glass–silicon[J]. Applied Physics A, 2008, 93(1): 171. [61] ZHANG J J, XU S ZH, DONG Y K, et al. Microwelding of glass to silicon by green ultrafast laser pulses[J]. Optics &Laser Technology, 2019, 120: 105720. [62] QUINTINO L, LIU L, MIRANDA R M, et al. Bonding NiTi to glass with femtosecond laser pulses[J]. Materials Letters, 2013, 98: 142-145. doi: 10.1016/j.matlet.2013.02.051 [63] UTSUMI A, OOIE T, YANO T, et al. Direct bonding of glass and metal using short pulsed laser[J]. Journal of Laser Micro/Nanoengineering, 2007, 2(2): 133-136. doi: 10.2961/jlmn.2007.02.0005 [64] ROTH G L, ESEN C, HELLMANN R. A new approach to seal polymer microfluidic devices using ultrashort laser pulses[J]. Journal of Laser Micro/Nanoengineering, 2019, 14(1): 49-53. [65] KIM S, KIM J, JOUNG Y H, et al. Bonding strength of a glass microfluidic device fabricated by femtosecond laser micromachining and direct welding[J]. Micromachines, 2018, 9(12): 639. doi: 10.3390/mi9120639 [66] KIM S, PARK J, SO S, et al. Characteristics of an implantable blood pressure sensor packaged by ultrafast laser microwelding[J]. Sensors, 2019, 19(8): 1801. doi: 10.3390/s19081801 [67] HÉLIE D, GOUIN S, VALLÉE R. Assembling an endcap to optical fibers by femtosecond laser welding and milling[J]. Optical Materials Express, 2013, 3(10): 1742-1754. doi: 10.1364/OME.3.001742 -






 下载:
下载: