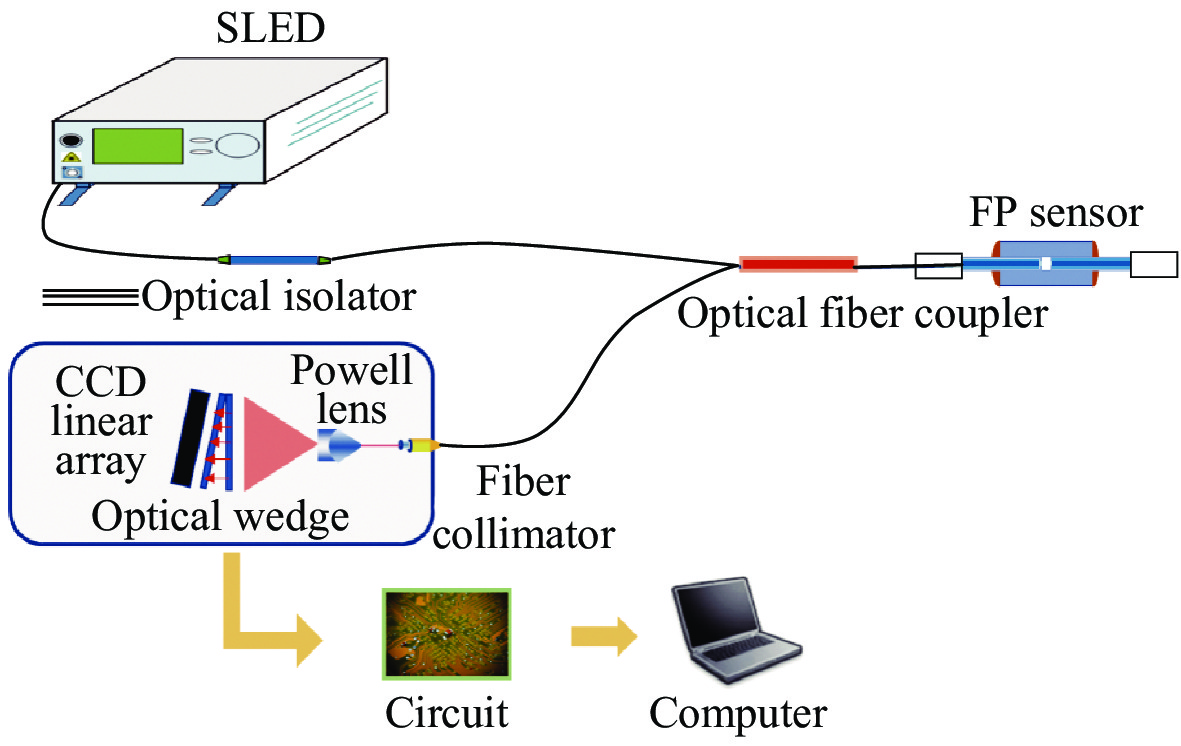
Design of optical wedge demodulation system for fiber Fabry-Perot sensor
doi: 10.37188/CO.2020-0204
-
摘要: 为了实现光纤法布里-珀罗(简称法珀)传感器腔长的解调,提出一种新型光楔式非扫描相关解调系统,对该系统所采用的器件特性及结构进行分析研究。首先,通过模拟不同光谱分布的光源及不同表面反射率的光楔,分析其相关干涉信号并给出系统器件的最优化结构参数。接着通过对比鲍威尔棱镜与柱透镜在线阵CCD上的光强分布特性,实现更均匀的光谱分布。最后,给出解调系统的具体实施方案及数据处理方法。实验结果表明:光源光谱具有高斯分布且谱宽较大及光楔表面反射率
$ R = 0.5$ 时,相关干涉信号特征明显,便于解调。最终解调系统实现在60~100 μm腔长范围内误差小于0.025%的解调。这种光楔式非扫描相关解调方案可以实现光纤法珀腔的传感解调,并可以提高不同类型光纤法珀传感器功率适应性。Abstract: In order to realize the demodulation of the cavity length of the fiber-optic FP sensor, a new optical wedge-type non-scanning correlation demodulation system is proposed, and the characteristics and structure of the devices used in the system are analyzed and studied. First, by simulating the light sources with different spectral distributions and the optical wedges with different surface reflectivities, the correlation interference signals are analyzed and the optimal structure parameters of the system components are given. Then by comparing the light intensity distribution characteristics of the Powell prism and cylindrical lens on the linear array CCD, more uniform spectral distribution is achieved. Finally, the specific implementation scheme and data processing method of the demodulation system are given. The experimental results show that when the light source spectrum has a Gaussian distribution and large spectral width and the reflectivity of the wedge surface is$R = 0.5$ , the characteristics of the correlation interference signal are obvious and convenient for demodulation. Finally, the demodulation system achieves the demodulation effect with an error of less than 0.025% within the cavity length range of 60 μm-100 μm. This optical wedge-type non-scanning correlation demodulation method can realize the sensing demodulation of the fiber-optic FP cavity and improve the power adaptability of different types of fiber-optic FP sensors. -
表 1 Test data
Table 1. Test data
Light source
power/mWDemodulation range of
Powell prism/μmDemodulation range of
cylindrical lens/μm5 59.988~100.163 6 58.950~97.83 68.612~84.542 7 59.728~100.531 65.757~86.286 8 59.728~100.531 65.776~94.506 9 59.733~101.993 65.637~94.512 10 60.217~100.739 64.856~93.776 11 60.306~98.514 65.103~95.525 12 59.601~98.966 63.339~94.497 13 59.844~98.817 63.699~95.04 -
[1] FENG W L, PENG J, YU J H, et al. Double Fabry-Pérot fiber optic temperature sensor based on end-face corrosion[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2019, 27(4): 766-770. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/OPE.20192704.0766 [2] XU N, DAI M. Design of distributed optical fiber sensor for temperature and pressure measurement[J]. Chinese Optics, 2015, 8(4): 629-635. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/co.20150804.0629 [3] POEGGEL S, TOSI D, FUSCO F, et al. Fiber-optic EFPI pressure sensors for in vivo urodynamic analysis[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2014, 14(7): 2335-2340. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2014.2310392 [4] CHEN Q CH, ZHAO H, ZHANG W CH. External oil cavity coupled with EFPI partial discharge ultrasonic detection sensor[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2020, 28(7): 1471-1479. (in Chinese) doi: 10.37188/OPE.20202807.1471 [5] ZHU T, KE T, RAO Y J, et al. Miniature all-fiber Fabry-Perot interferometric high temperature sensor based on a thin film[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2010, 18(5): 1054-1059. (in Chinese) [6] XIE J H, WANG F Y, PAN Y, et al. High resolution signal-processing method for extrinsic Fabry-Perot interferometric sensors[J]. Optical Fiber Technology, 2015, 22: 1-6. doi: 10.1016/j.yofte.2014.11.010 [7] ZHANG Y N, HUANG J, LAN X W, et al. Simultaneous measurement of temperature and pressure with cascaded extrinsic Fabry-Perot interferometer and intrinsic Fabry-Perot interferometer sensors[J]. Optical Engineering, 2014, 53(6): 067101. doi: 10.1117/1.OE.53.6.067101 [8] JIANG X F, LIN CH, XIE H H, et al. Optic fiber MEMS pressure sensor based on white light interferometry[J]. Acta Photonica Sinica, 2014, 43(10): 1006003. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/gzxb20144310.1006003 [9] MA G H, ZHANG J B, ZHANG H, et al. Resonant mode of Fabry-Perot microcavity regulated by metal surface plasmons[J]. Chinese Optics, 2019, 12(3): 649-662. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/co.20191203.0649 [10] CHEN Q Q, TANG Y, WANG K N, et al. Characteristic analysis of correlation interference signals in optical wedge type fiber Fabry-Perot sensors[J]. Laser &Optoelectronics Progress, 2018, 55(11): 110603. (in Chinese) [11] HAN M, ZHANG Y, SHEN F B, et al. Signal-processing algorithm for white-light optical fiber extrinsic Fabry-Perot interferometric sensors[J]. Optics Letters, 2004, 29(15): 1736-1738. doi: 10.1364/OL.29.001736 [12] YOSHINO T, KUROSAWA K, ITOH K, et al. Fiber-optic Fabry-Perot interferometer and its sensor applications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 1982, 30(10): 1612-1621. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.1982.1131298 [13] LI J SH, ZHU Y, WANG N, et al. An algorithm for improving the signal stability of the fast fiber optic Fabry-Perot nonscanning correlation demodulation system[J]. Acta Photonica Sinica, 2015, 44(1): 0106005. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/gzxb20154401.0106005 [14] WANG W, TANG Y, ZHANG X X, et al. Elliptical-fitting cavity length demodulation algorithm for compound fiber-optic Fabry-Perot pressure sensor with short cavity[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2019, 39(6): 0606001. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/AOS201939.0606001 [15] ZHAO Y, WANG D H. Mathematical model of optical wedges for cross-correlation demodulation of cavity length of optical fiber Fabry-Pérot sensors[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2011, 31(1): 0106007. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/AOS201131.0106007 [16] WU Y, XIA L, CAI N, et al. A highly precise demodulation method for fiber Fabry-Perot cavity through spectrum reconstruction[J]. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 2018, 30(5): 435-438. doi: 10.1109/LPT.2017.2787098 [17] VOLKOV P V, GORYUNOV A V, LUK’YANOV A Y, et al. Fiber-optic temperature sensor based on low-coherence interferometry without scanning[J]. Optik, 2013, 124(15): 1982-1985. doi: 10.1016/j.ijleo.2012.06.043 [18] MA ZH B, GUO T X, ZHANG T Y, et al. Compact Powell-lens-based low-coherence correlation interrogation system for fiber-optic Fabry-Perot sensors[J]. IEEE Photonics Journal, 2019, 11(4): 7102111. [19] CAI F H, TANG R N, WANG SH W, et al. A compact line-detection spectrometer with a Powell lens[J]. Optik, 2018, 155: 267-272. doi: 10.1016/j.ijleo.2017.11.022 -








 下载:
下载: