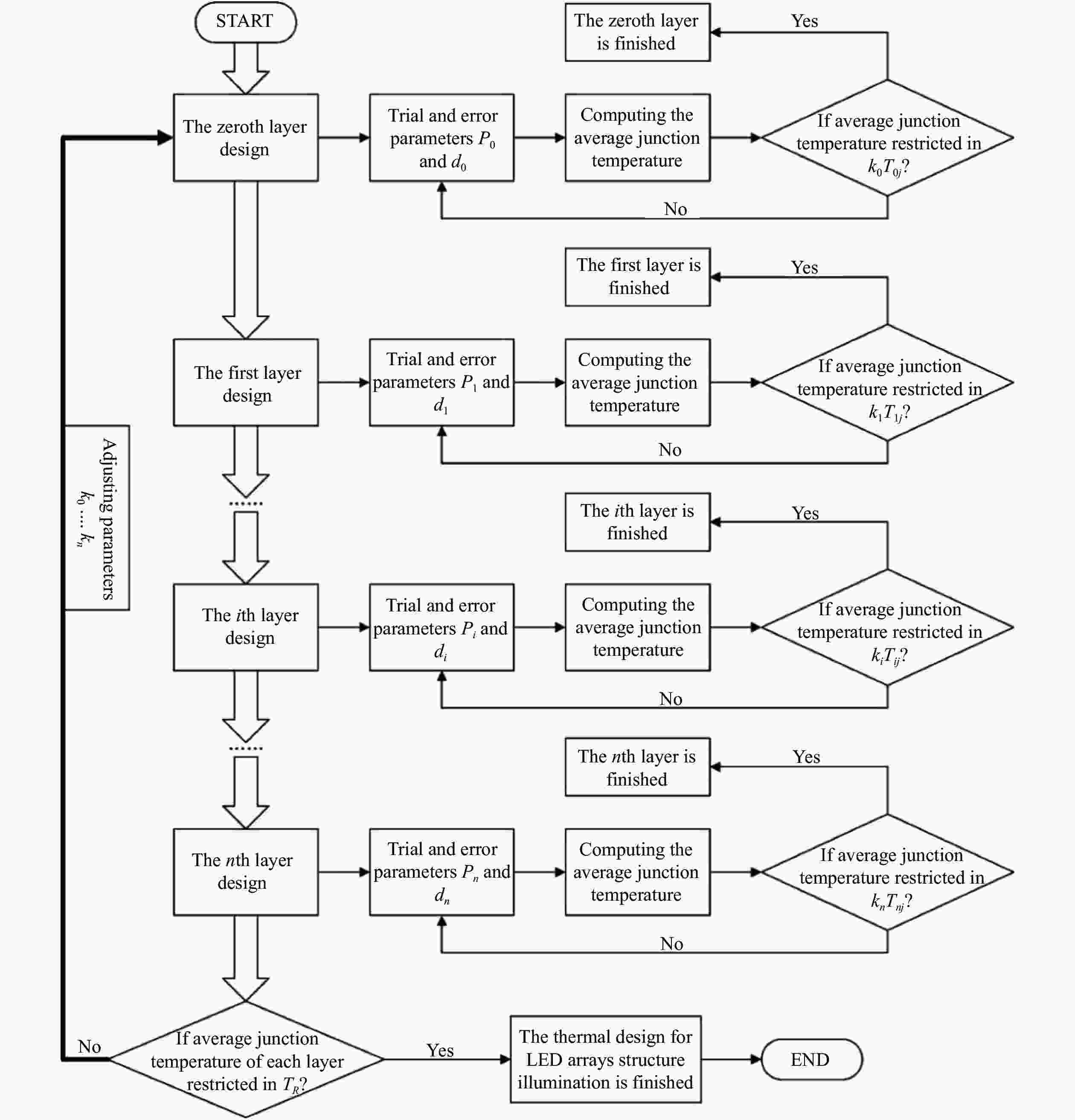
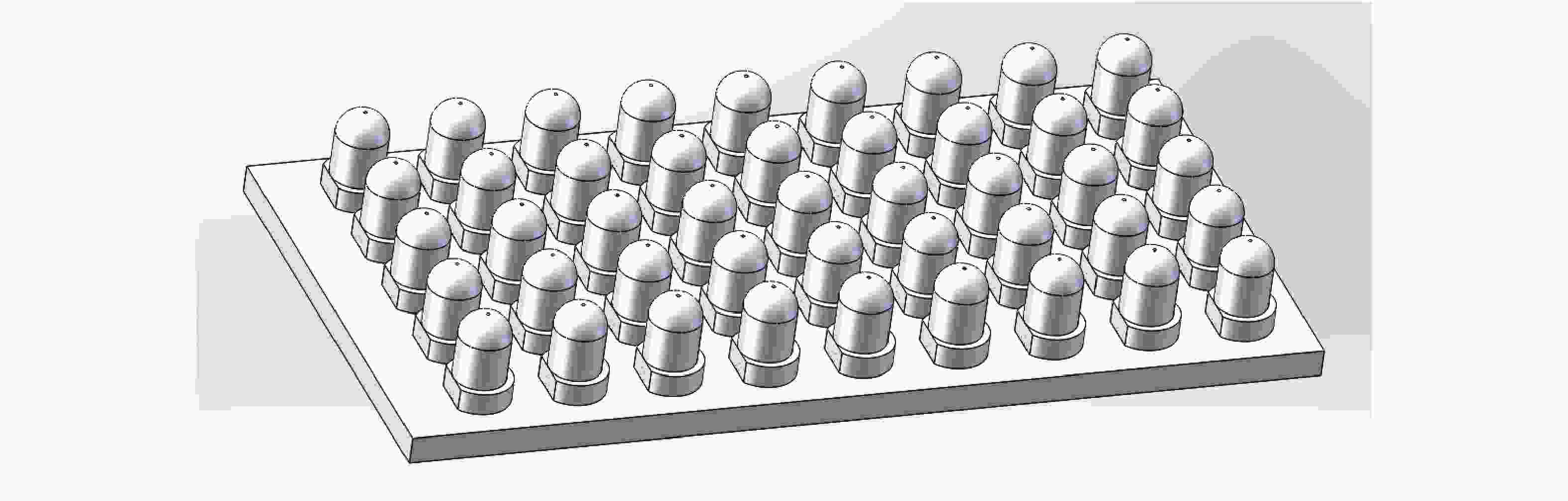
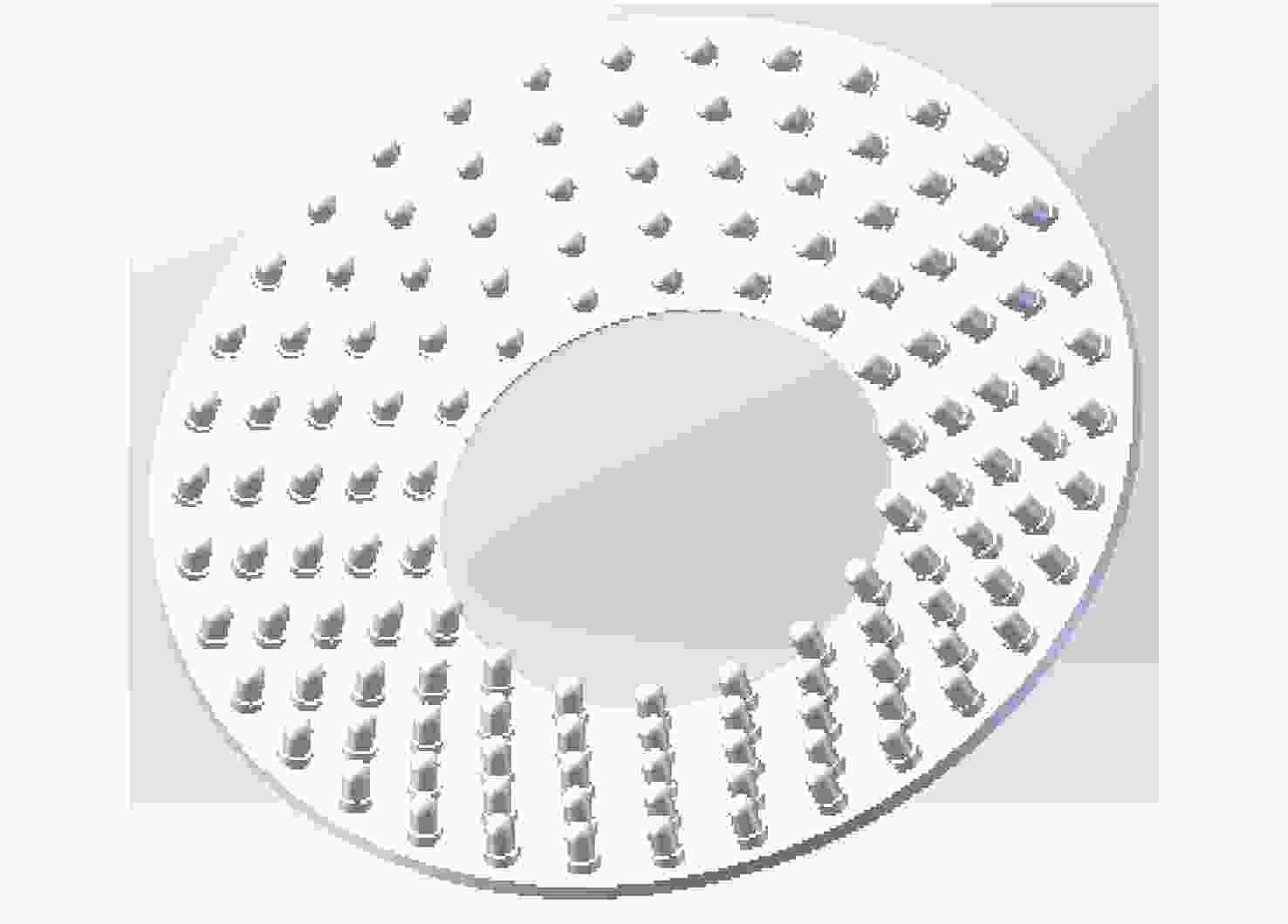
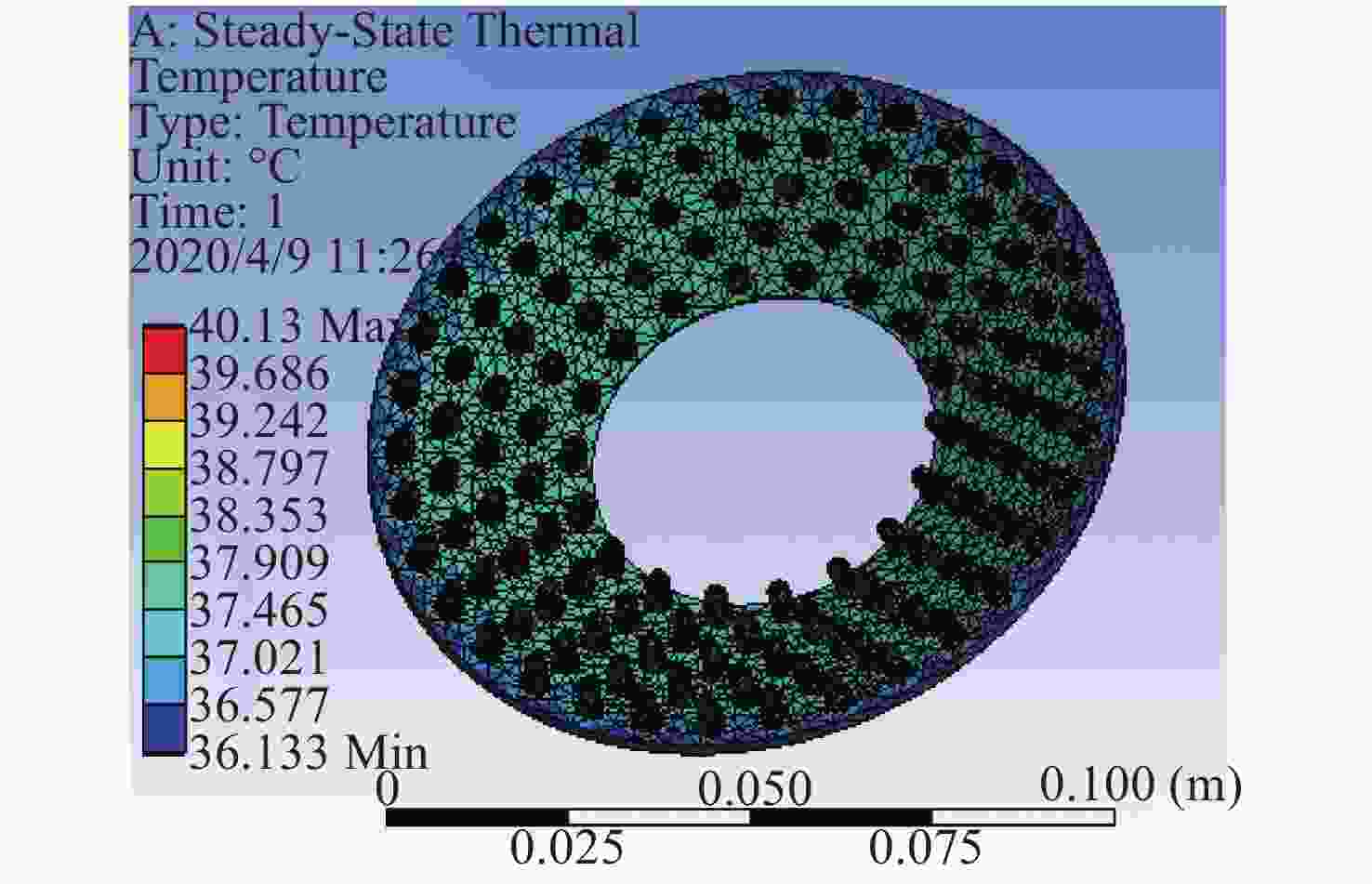
A thermal dissipation design method for LED array structure illumination
doi: 10.37188/CO.2020-0211
-
摘要: 在主动式自动光学检测系统中,获取高质量的图像具有重要意义。除相机外,光源热稳定性对获取的图像质量也会产生重要影响。为了确保光学检测系统光源的热稳定性以获取高质量的图像,论文提出了一种散热型LED阵列结构光源设计方法。首先,基于单个LED热阻特性建立单个LED的热阻模型。其次,以两个相邻的LED为例,分析同色光LED在单一阵列中的结温特性,并建立LED阵列结构光源的结温模型。最后,基于建立的结温模型,提出散热型LED阵列结构光源设计方法。特别地,论文提出了将散热型结构光源设计问题分解为两个相对简单子问题的方法,进而简化结构光源设计过程。实验结果表明,该设计方法的仿真结温偏差在−0.33%~0.33%之间,实验结温偏差为2.28%,验证了该方法的有效性。Abstract: Obtaining high-quality images plays an important role in active automatic optical inspection systems. Besides cameras, image quality is significantly affected by the illumination thermal stability. To ensure the illumination thermal stability and capture high-quality images in optical inspection systems, a thermal dissipation design method for LED array structure illumination is proposed in this paper. Firstly, the thermal resistance model of a single LED is built by analyzing its thermal resistance characteristics. Secondly, a setup with two adjacent LEDs is taken as an example to analyze junction temperature characteristics of the same color light in a LED array, and then the junction temperature model of the LED array structure illumination is developed. Finally, the thermal dissipation design method for LED array structure illumination is illustrated based on the proposed junction temperature model. Especially, the thermal design method is decomposed into two sub-problems to simplify the design process. Experimental results show that the junction temperature deviation is within −0.33%~0.33% by simulation and is 2.28% by experiment, which validates the effectiveness of the proposed method.
-
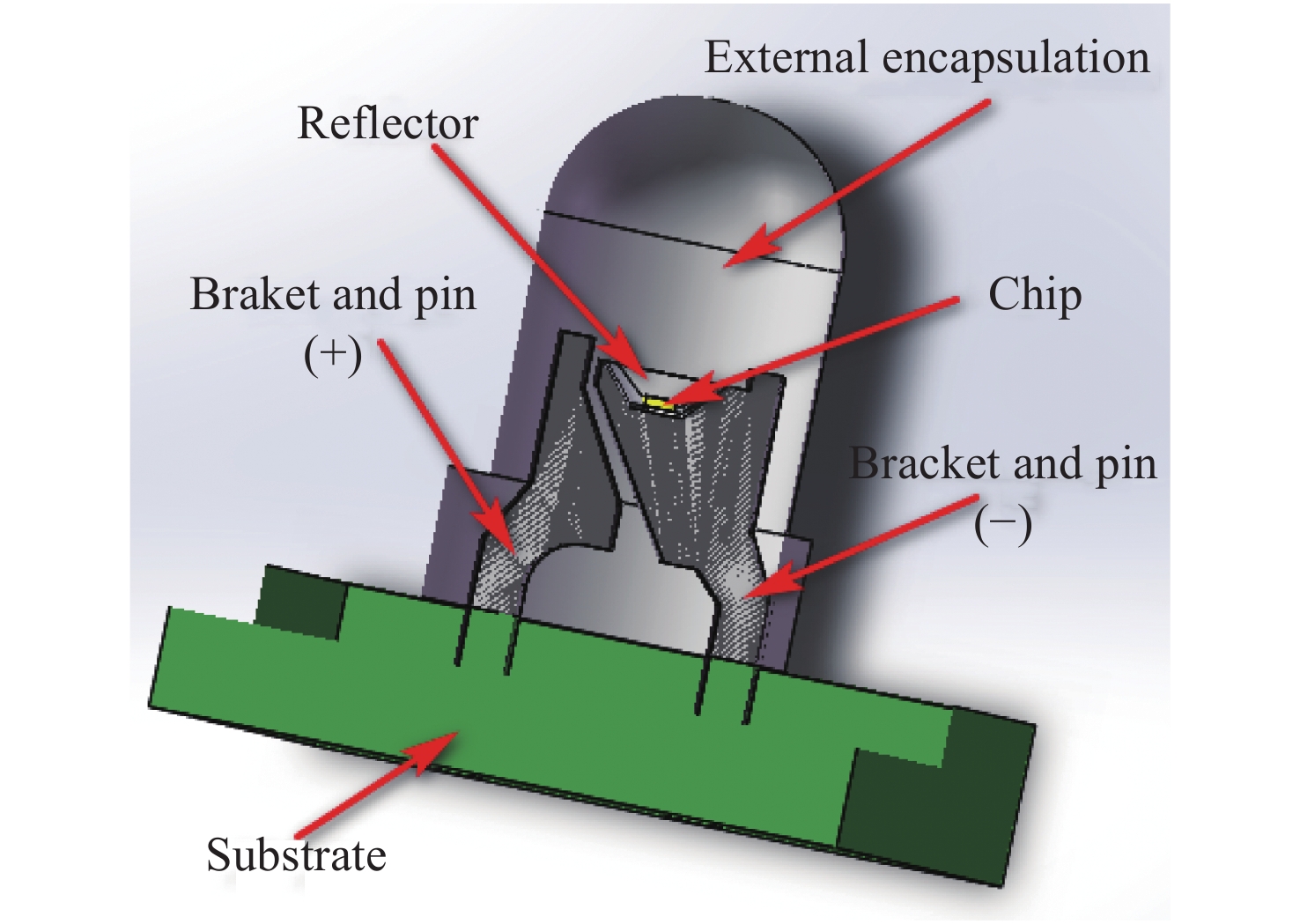
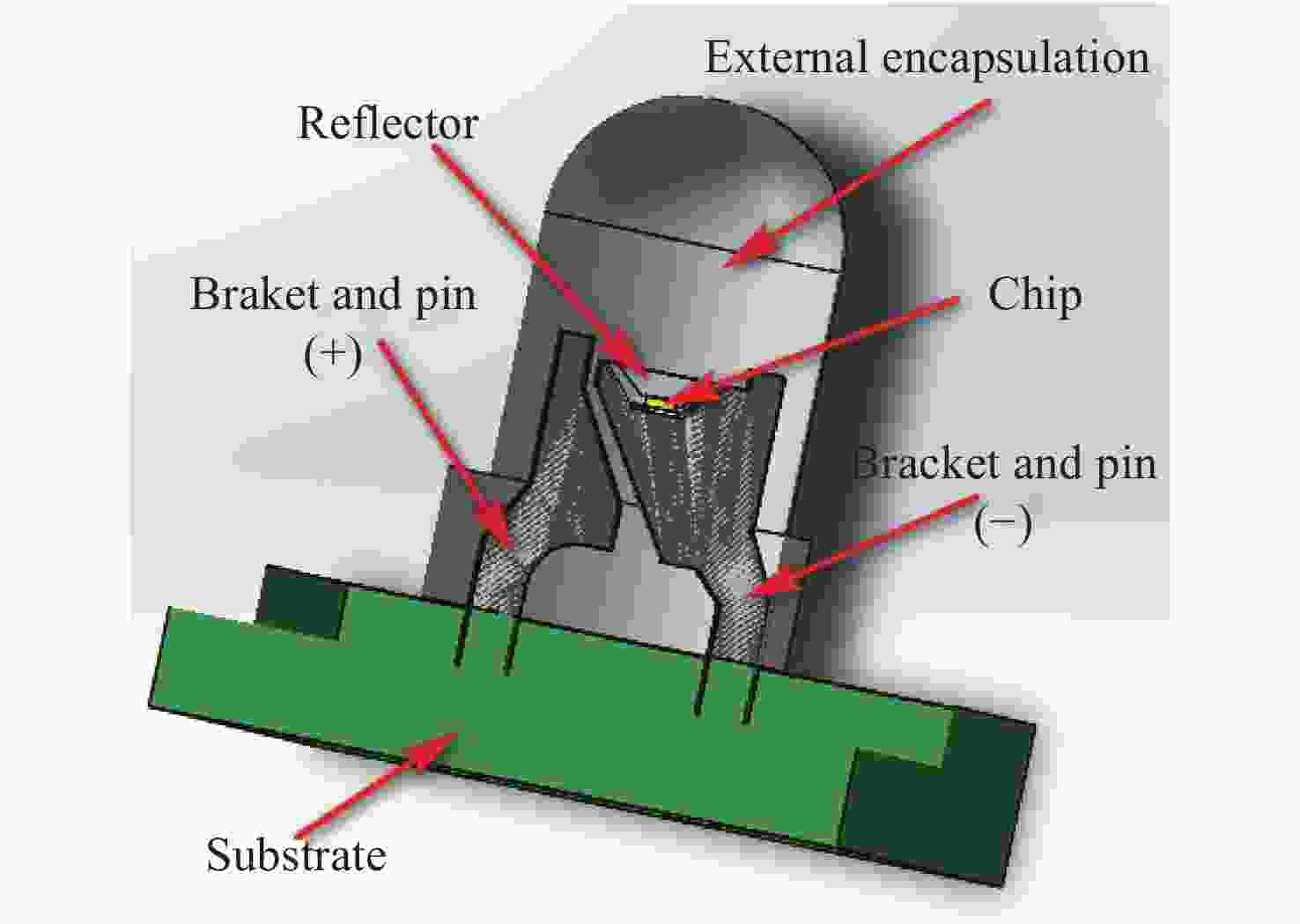
Table 1. Thermal conductivity of LED packaging material
Structural assembly Thermal conductivity (W·m−1·K−1) Chip 130 Reflector 155 Bracket and pin 73 External encapsulation 0.2 Substrate 0.8 Table 2. LED’s working parameters
Parameters Values $ {h}_{a} $ $10\;{\rm{W} }/({ {\rm{m} } }^{2}\cdot {\rm{K} })$ ${T}_{{\rm{sur}}}$ 27 ℃ $ P $ $0.022\;8\;{\rm{W}}$ ${P}_{{\rm{th}}}$ $0.018\;24\;{\rm{W}}$ $ V $ $9.439\times {10}^{-12}\;{{\rm{m}}}^{3}$ $ H $ $1\;932\;418\;560\;{\rm{W}}/{{\rm{m}}}^{3}$ Table 3. Surface temperatures of a single LED model in experiments
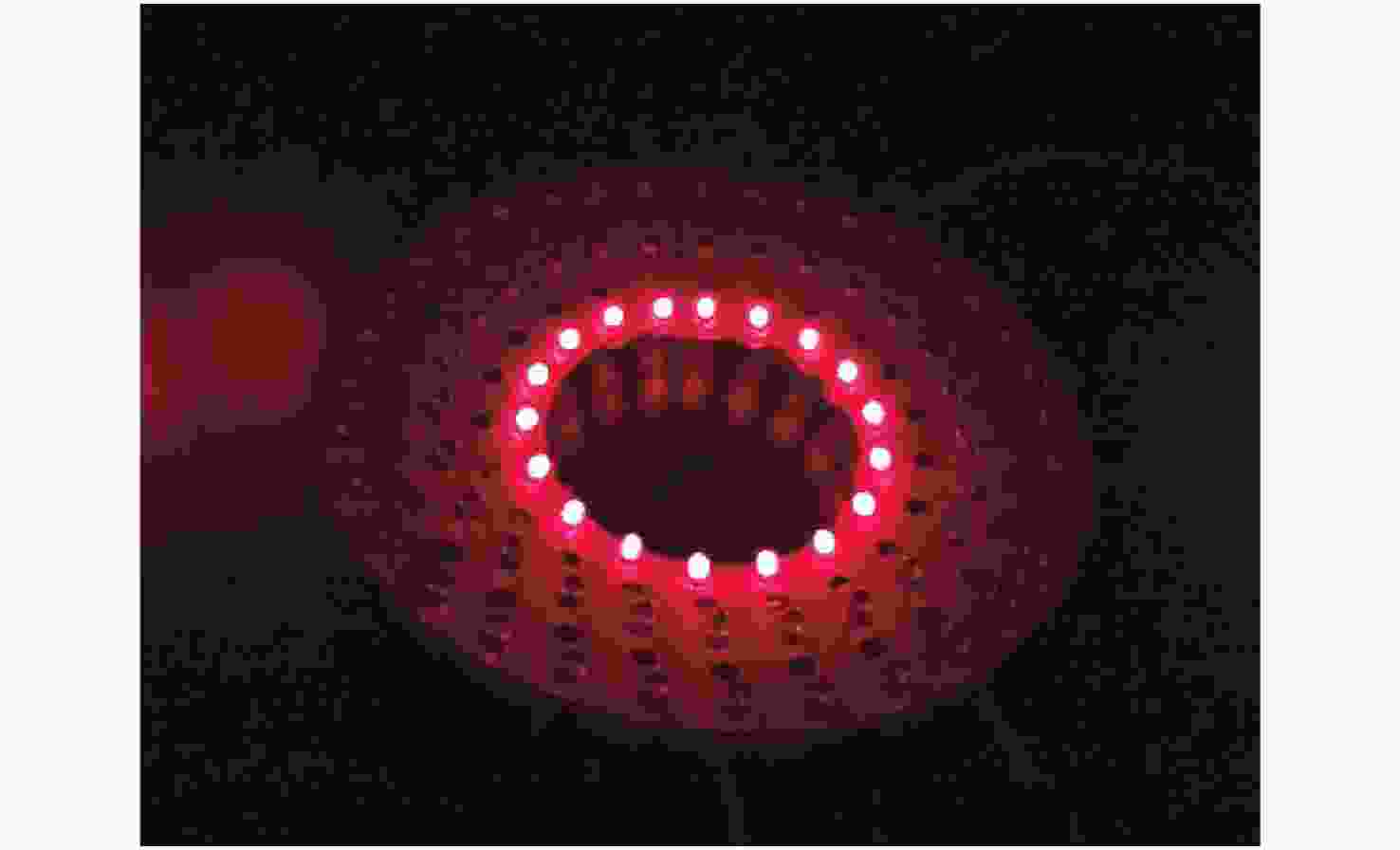
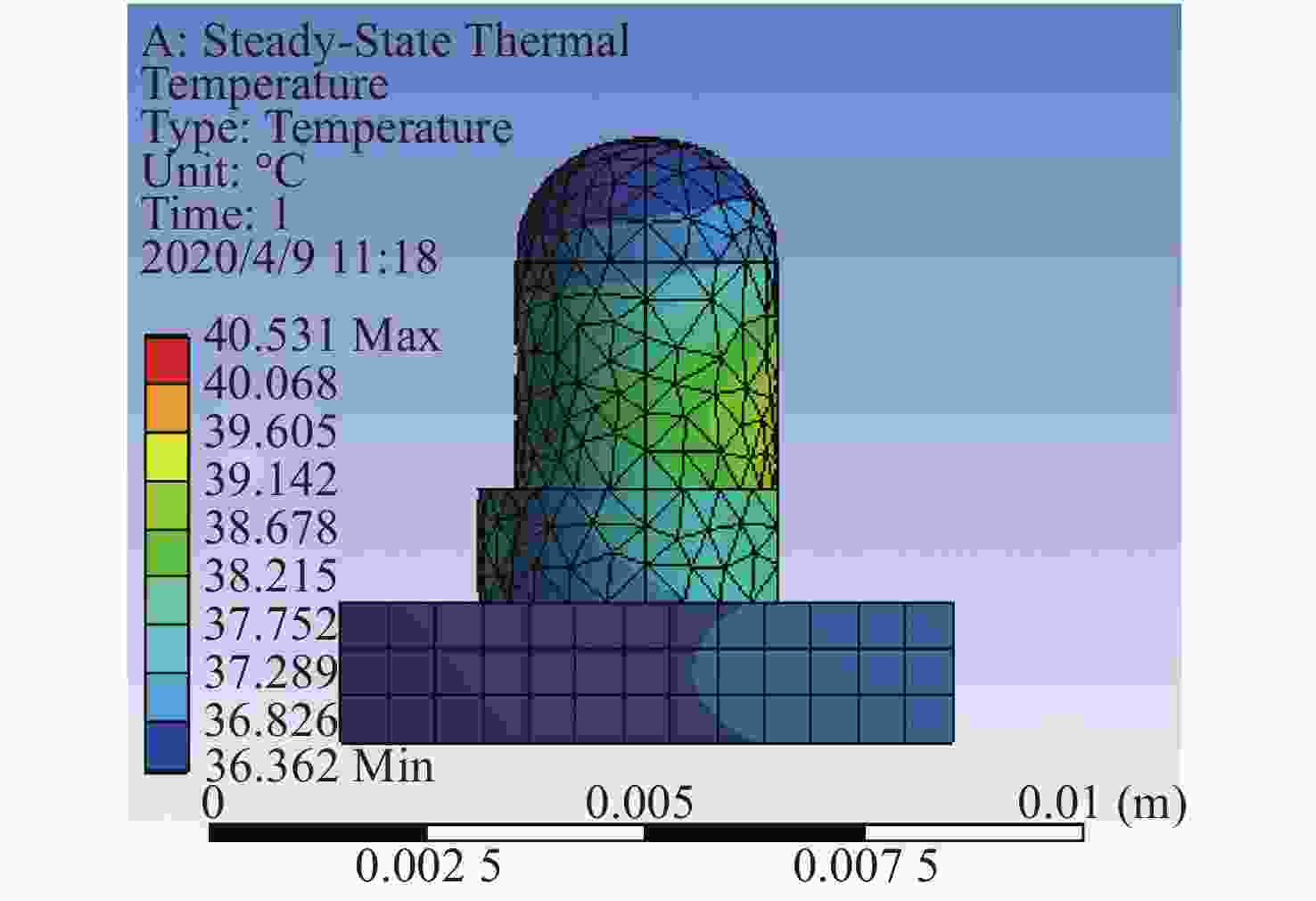
Group Maximum temperature (°C) Minimum temperature (°C) Group 1 40.90 39.70 Group 2 39.80 38.50 Group 3 38.50 37.60 The average 39.73 38.60 Table 4. Average temperature of the LED surface with different center distances in simulations
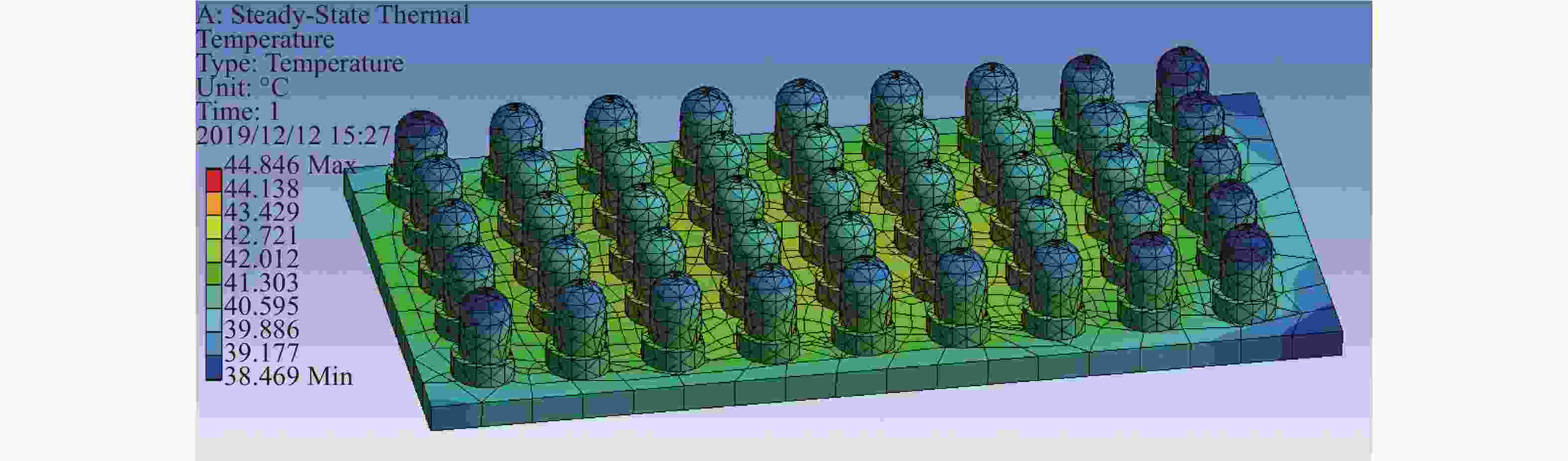
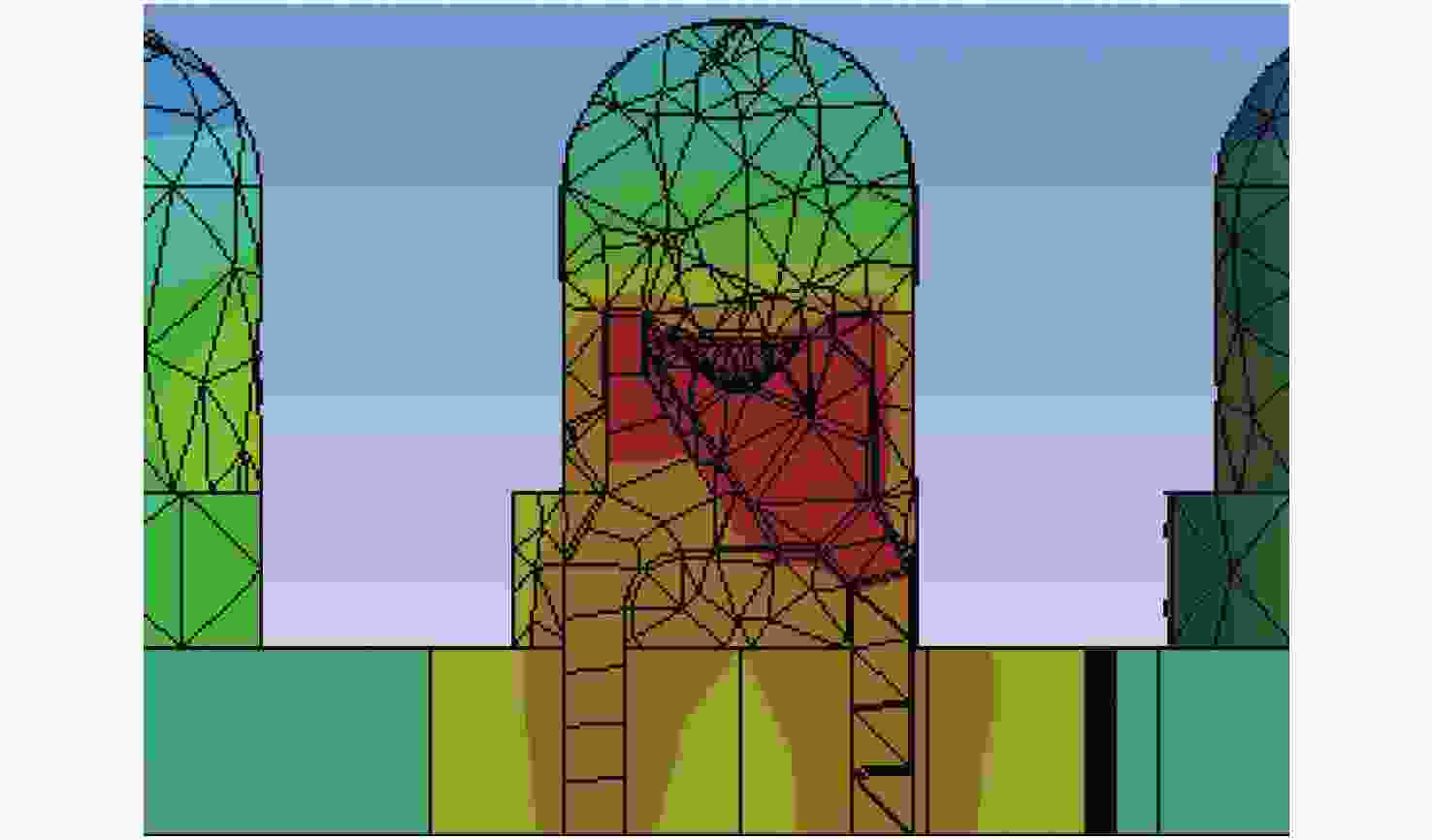
Center distance/mm 4.0 4.2 4.4 4.6 4.8 5.0 5.2 5.4 5.6 5.8 6.0 Average temperature/℃ 40.42 40.08 39.65 39.28 38.75 38.40 38.03 37.63 37.35 37.26 36.79 Table 5. The measurement and analysis of LEDs surface temperatures
Groups LEDs Minimum temperature
from experiments/°CMaximum temperature
from experiments/°CAverage surface temperature
from experiments/°CTemperature obtained
by fitting equation/°CFitting error Group 1 LED1 37.20 38.50 38.05 38.46 1.08% LED2 37.10 39.40 Group 2 LED3 36.50 38.00 37.45 38.46 2.70% LED4 37.00 38.30 Group 3 LED5 36.60 38.10 37.80 38.46 1.75% LED6 37.20 39.30 Table 6. Junction temperature properties of three and four adjacent LEDs
Center distance/mm Three LEDs Four LEDs Temperature obtained
by fitting equation/°CTemperature from
simulation/°CFitting error Temperature obtained
by fitting equation/°CTemperature from
simulation/°CFitting error 4.2 42.88 44.25 3.10% 42.88 44.54 3.73% 4.6 42.17 43.22 2.43% 42.17 43.45 2.95% 5.0 41.47 42.26 1.87% 41.47 42.51 2.45% 5.4 40.76 41.49 1.76% 40.76 41.70 2.25% 5.8 40.06 40.71 1.60% 40.06 40.92 2.10% Table 7. The number of LEDs in each layer array for ring structure illumination
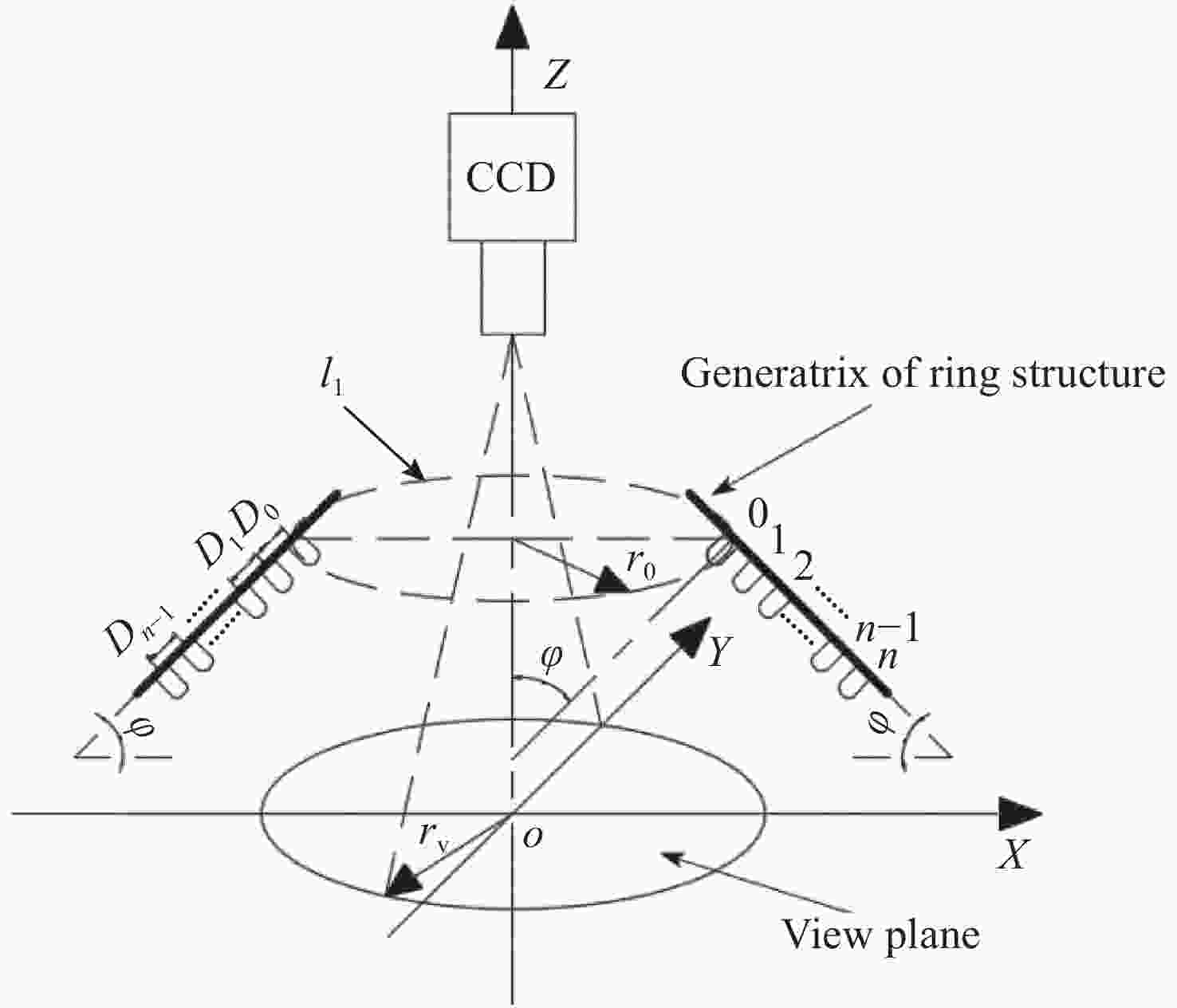
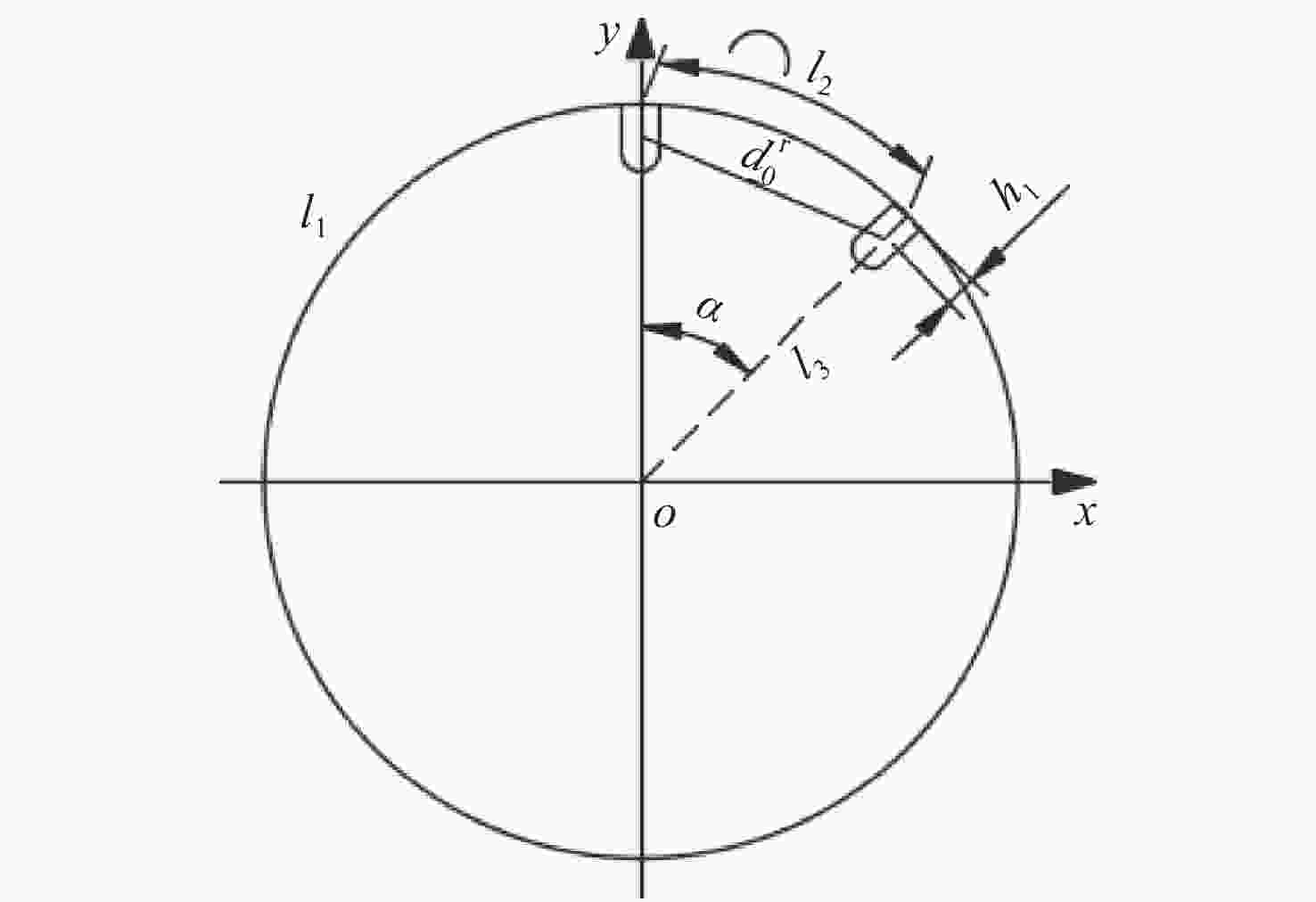
The $ i $th layer array Number of LEDs 0 18 1 22 2 26 3 30 4 34 -
[1] SUN X H, GU J A, TANG SH X, et al. Research progress of visual inspection technology of steel products-a review[J]. Applied Sciences, 2018, 8(11): 2195. doi: 10.3390/app8112195 [2] WU F P, LI SH P, ZHANG X M, et al. A design method for LEDs arrays structure illumination[J]. Journal of Display Technology, 2016, 12(10): 1177-1184. doi: 10.1109/JDT.2016.2593770 [3] WU X J, GAO G M. LED light design method for high contrast and uniform illumination imaging in machine vision[J]. Applied Optics, 2018, 57(7): 1694-1704. doi: 10.1364/AO.57.001694 [4] QU X H, LIU Q, WANG H, et al. System-level lifetime prediction for LED lighting applications considering thermal coupling between LED sources and drivers[J]. IEEE Journal of Emerging and Selected Topics in Power Electronics, 2018, 6(4): 1860-1870. doi: 10.1109/JESTPE.2018.2850845 [5] WANG X X, JING L, WANG Y, et al. The influence of junction temperature variation of LED on the lifetime estimation during accelerated aging test[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 4773-4781. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2885578 [6] HUANG D S, CHEN T C, TSAI L T, et al. Design of fins with a grooved heat pipe for dissipation of heat from high-powered automotive LED headlights[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2019, 180: 550-558. doi: 10.1016/j.enconman.2018.11.021 [7] KIM M Y, KOH K I. Shadow-free moire interferometer with dual projection for in-line inspection of light emitting diodes[J]. International Journal of Optomechatronics, 2007, 1(4): 404-424. doi: 10.1080/15599610701771645 [8] WU F P, ZHANG X M. An inspection and classification method for chip solder joints using color grads and Boolean rules[J]. Robotics and Computer-Integrated Manufacturing, 2014, 30(5): 517-526. doi: 10.1016/j.rcim.2014.03.003 [9] WU H. Solder joint defect classification based on ensemble learning[J]. Soldering &Surface Mount Technology, 2017, 29(3): 164-170. [10] SONG J D, KIM Y G, PARK T H. SMT defect classification by feature extraction region optimization and machine learning[J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2019, 101(5-8): 1303-1313. doi: 10.1007/s00170-018-3022-6 [11] HUANG C H, WANG G J. A design problem to estimate the optimal fin shape of LED lighting heat sinks[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2017, 106: 1205-1217. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2016.10.101 [12] XIANG J H, ZHANG CH L, ZHOU CH, et al. Heat transfer performance testing of a new type of phase change heat sink for high power light emitting diode[J]. Journal of Central South University, 2018, 25(7): 1708-1716. doi: 10.1007/s11771-018-3862-0 [13] JANG H, LEE J H, BYON C, et al. Innovative analytic and experimental methods for thermal management of SMD-type LED chips[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2018, 124: 36-45. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2018.03.055 [14] MOU Y, WANG H, PENG Y, et al. Enhanced heat dissipation of high-power light-emitting diodes by Cu nanoparticle paste[J]. IEEE Electron Device Letters, 2019, 40(6): 949-952. doi: 10.1109/LED.2019.2912458 [15] WANG Y W, CEN J W, CAO W J, et al. Thermal performance of direct illumination high-power LED backlight units with different assembling structures[J]. Heat and Mass Transfer, 2017, 53(5): 1619-1630. doi: 10.1007/s00231-016-1925-z [16] TIAN CH, GUO SH X, LIANG J Q, et al. Thermal analysis and an improved heat-dissipation structure design for an AlGaInP-LED micro-array device[J]. Optoelectronics Letters, 2017, 13(4): 282-286. doi: 10.1007/s11801-017-7048-z [17] BAN ZH, LIANG ZH ZH, LIANG J Q, et al. Thermal analysis and design of AlGaInP-based light emitting diode arrays[J]. Current Optics and Photonics, 2017, 1(2): 143-149. doi: 10.3807/COPP.2017.1.2.143 [18] BEN ABDELMLEK K, ARAOUD Z, CHARRADA K, et al. Optimization of the thermal distribution of multi-chip LED package[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2017, 126: 653-660. doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2017.07.136 [19] Dassault Systèmes SolidWorks Corporation. SOLIDWORKS 2016[CP/DK]. Waltham, USA: Dassault Systèmes SolidWorks Corporation, 2015. [20] ANSYS, Incuk. ANSYS 16.0[CP/DK]. Canonsburg, USA: ANSYS, Incuk, 2015. [21] XIE L H, CAI S Q. ANSYS Workbench 17.0 Finite Element Analysis and Simulation[M]. 2nd ed. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2017. (in Chinese) [22] SHE J, YANG W, YU T B, et al. Thermal analysis of LED filaments with three types of chip distributions[J]. Journal of Nanchang University (Engineering &Technology) , 2017, 39(3): 289-293, 306. (in Chinese) [23] LI Y F, ZOU J. Application of LED Thermal Management and Heat Dissipation Technology[M]. Shanghai: Shanghai Scientific & Technical Publishers, 2018. (in Chinese) [24] CHAI G Y, LI B, WANG G, et al.. Thermal Management of LED’s Packaging and Light Engine[M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2018. (in Chinese) [25] CHEN Y C, WEN SH SH, WU Y X. Thermal analysis for LED chip on board package based on plastic radiator without substrate[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2013, 33(8): 0823005. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/AOS201333.0823005 -





 下载:
下载: