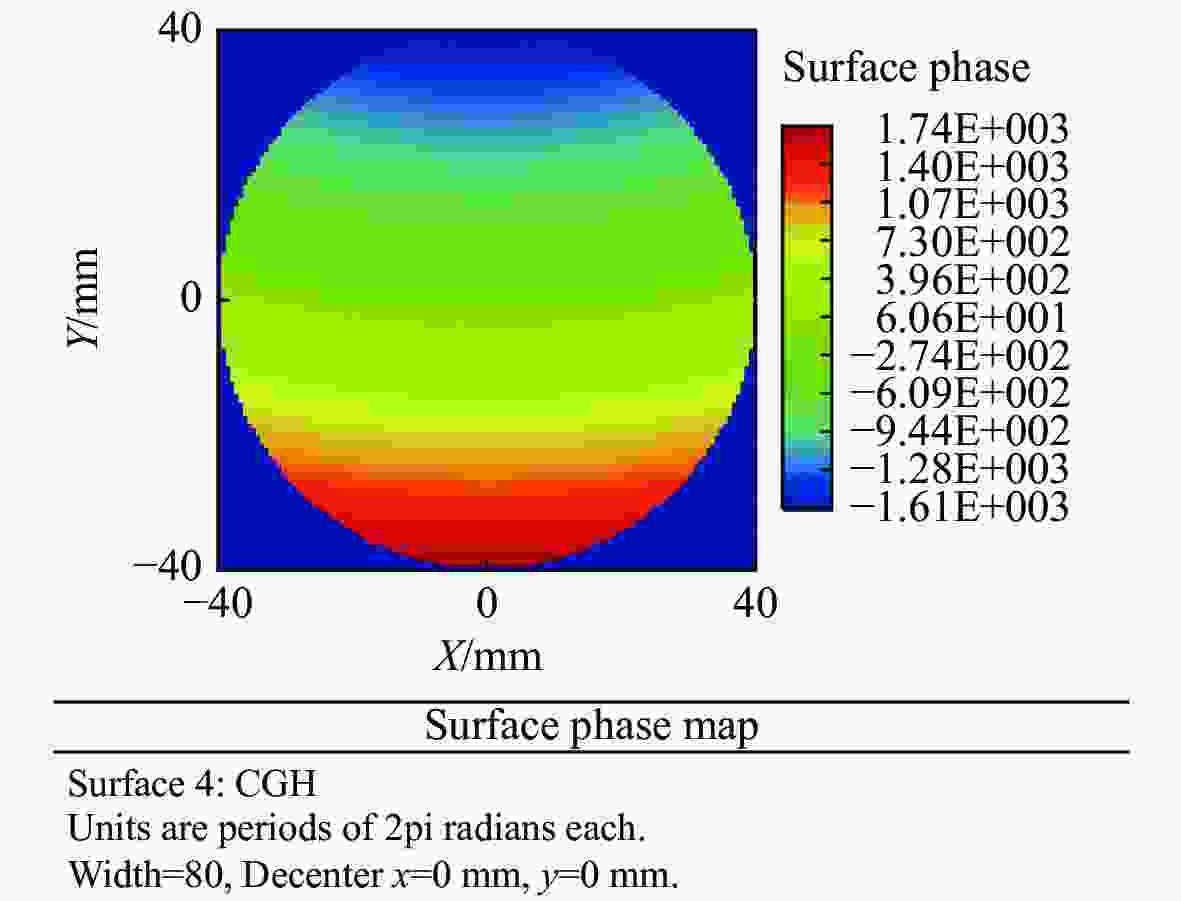
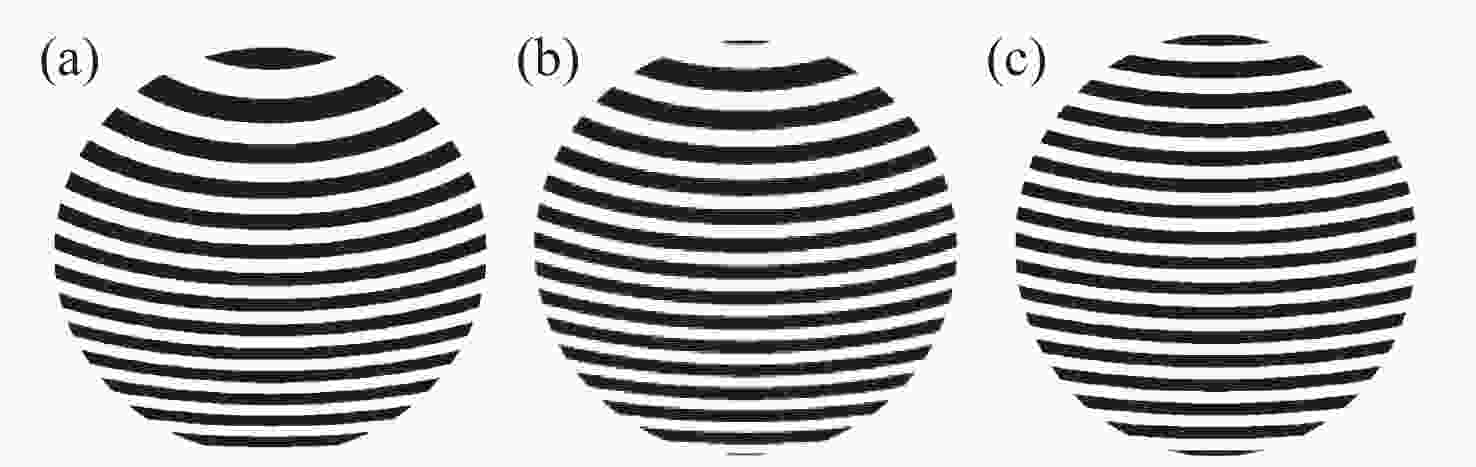
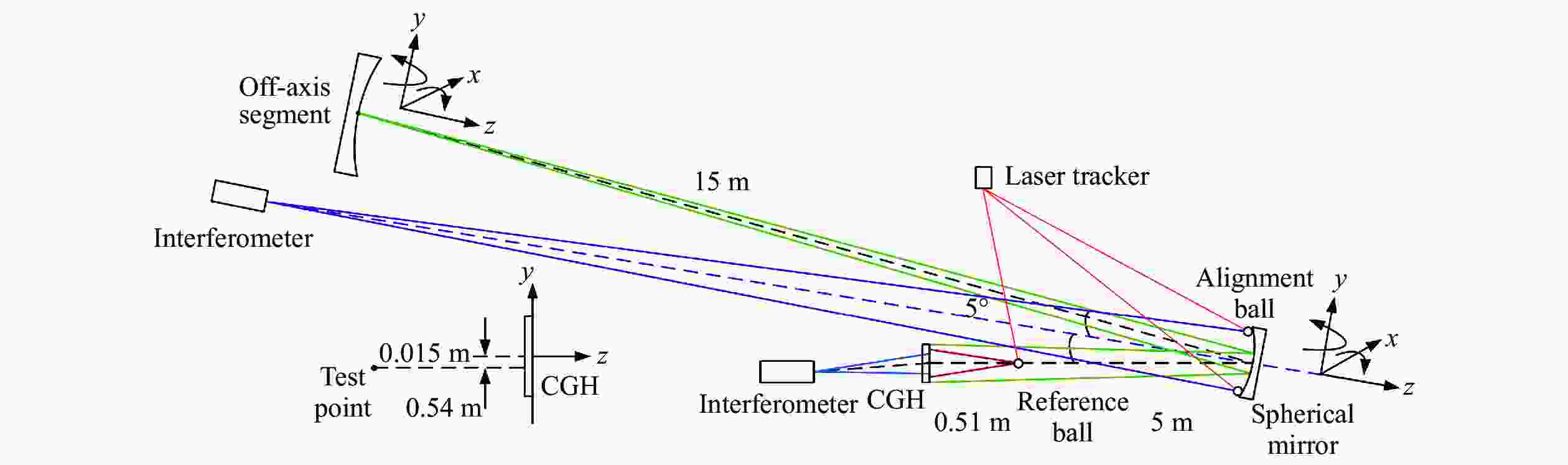
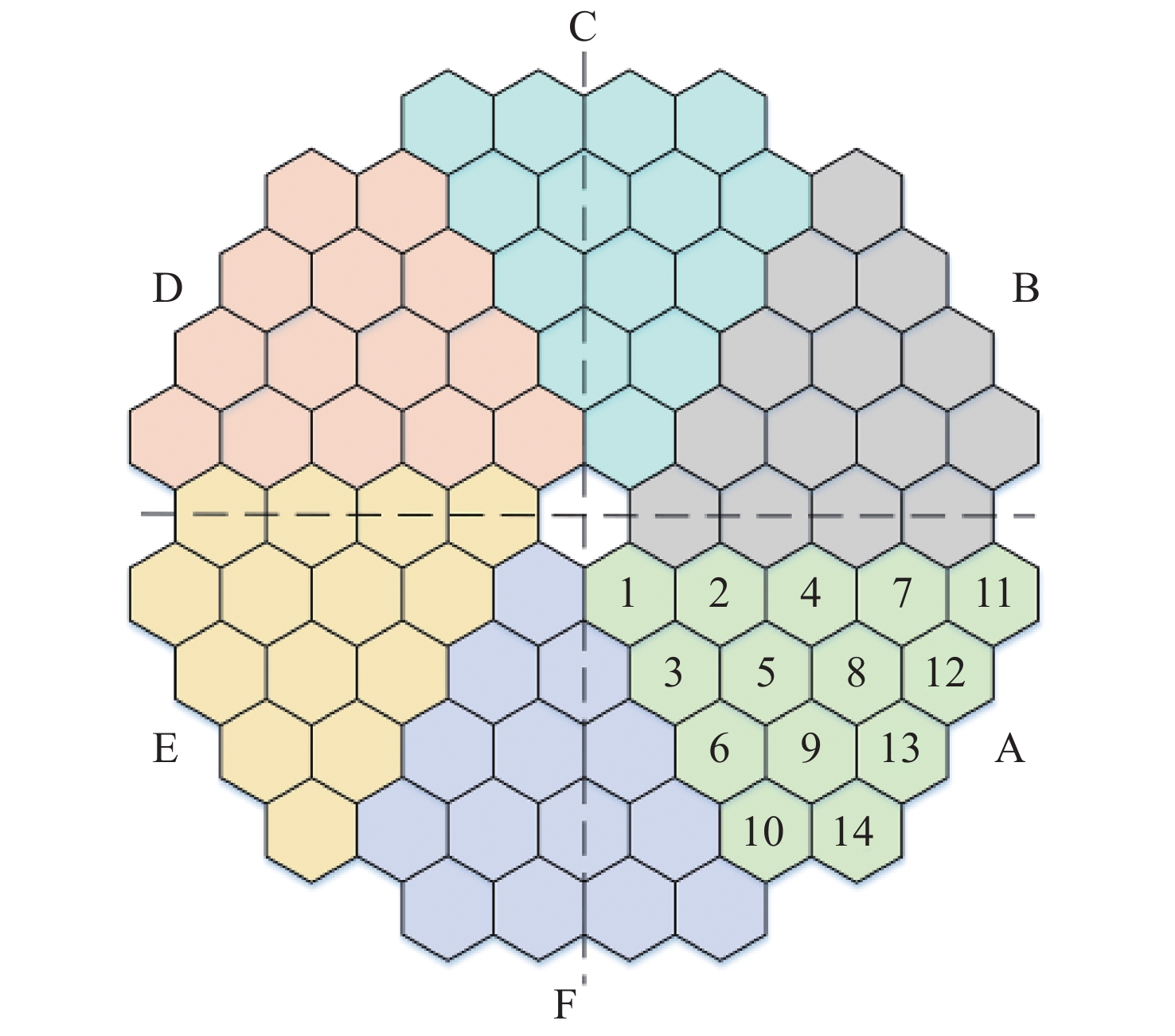
Optical testing path design for LOT aspheric segmented mirrors with reflective-diffractive compensation
-
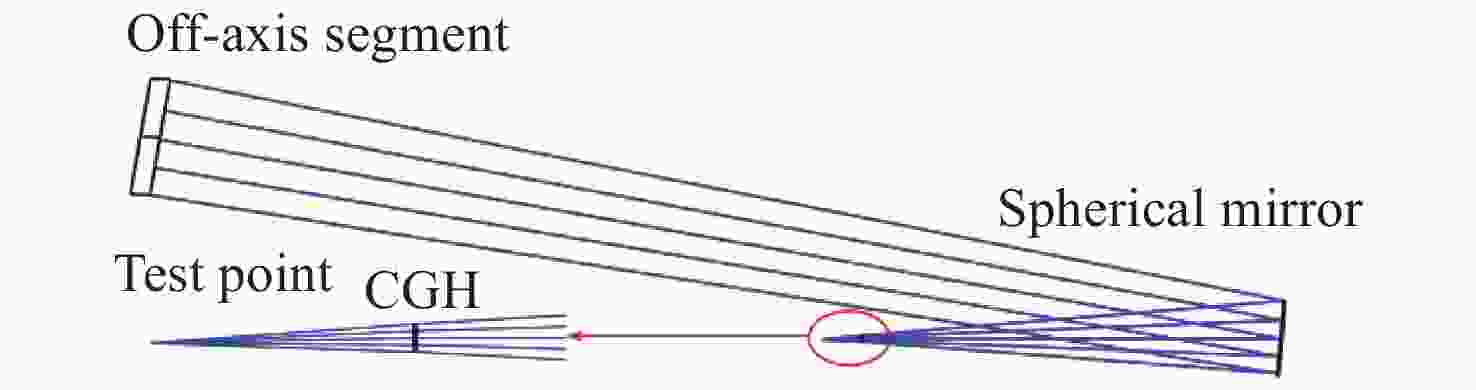
摘要: 为了实现大口径、长焦距、批量化离轴镜面的高精度面形检验,本文提出了一种零位反衍补偿检测方案,采用计算全息和球面反射镜共同对离轴镜面法向像差进行补偿,检测光路波像差残差接近于零。检测方案为非轴对称离轴结构,设计了相应的全息对准光路,以保证检测光路装调切实可行。不同离轴量子镜检测光路参数完全一致,仅需更换相应位置计算全息片、调整待测镜空间姿态,即可实现不同类型镜面的快速批量化检验。误差分析结果表明,由补偿元件制造误差、光路失调、干涉仪面形测量重复性以及干涉仪标准球面波偏差引起的待测镜面形误差小于λ/40 (RMS值,λ=632.8 nm)。Abstract: In order to achieve high precision surface testing for the large diameter and long focal length off-axis segmented mirrors, we designed a reflective diffractive compensation null testing system. Using a computer-generated hologram and a spherical mirror to compensate for normal aberration of the off-axis mirror. The design results show that the residual wavefront error of the optical path is close to zero. For a testing system, CGH alignment optical paths corresponding to the non-axisymmetric off-axis structure are designed to ensure the feasibility of the assembly. Parameters of the optical path testing for different off-axis distance mirrors are the same. Rapid high-precision null testing of different types of segmented mirrors can be achieved simply by replacing the CGH at corresponding position and adjusting the spatial positions of the mirror to be measured. Error analysis shows that the RMS error of the mirror surface to be measured is better than λ/40 (λ=632.8 nm), which is caused by the manufacturing error of the compensating elements, misalignment of the optical path, repeatability of the interferometer surface measurement and standard spherical wavefront deviation of the interferometer.
-
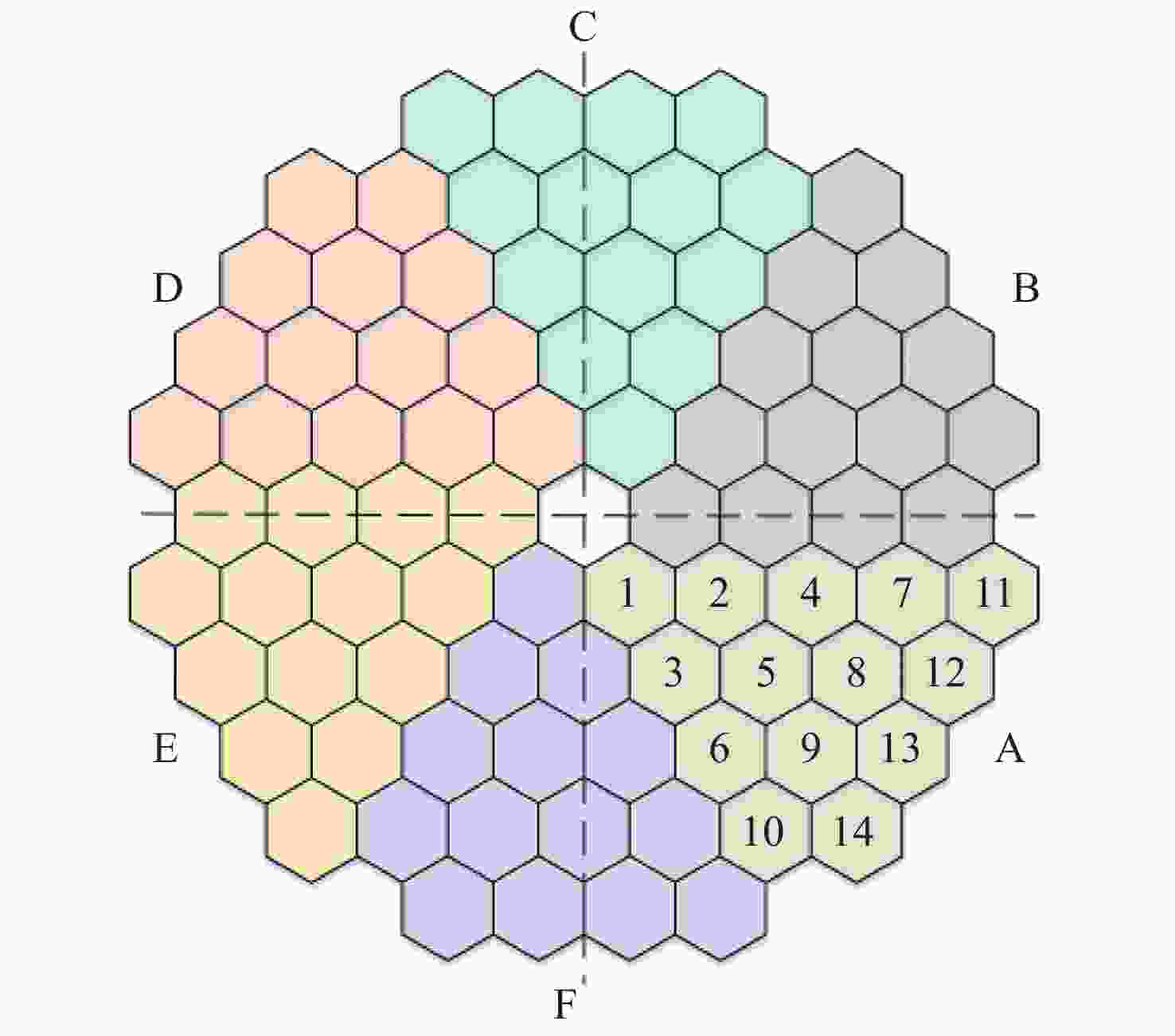
表 1 主镜光学参数
Table 1. Optical parameters of the primary mirror
Parameters ROC/m Diameter/m Conic Segment numbers Segment categories Values −38.4 12.799 −0.9837843 84 14 表 2 六边形子镜技术参数
Table 2. Technical parameters of hexagonal sub-mirror
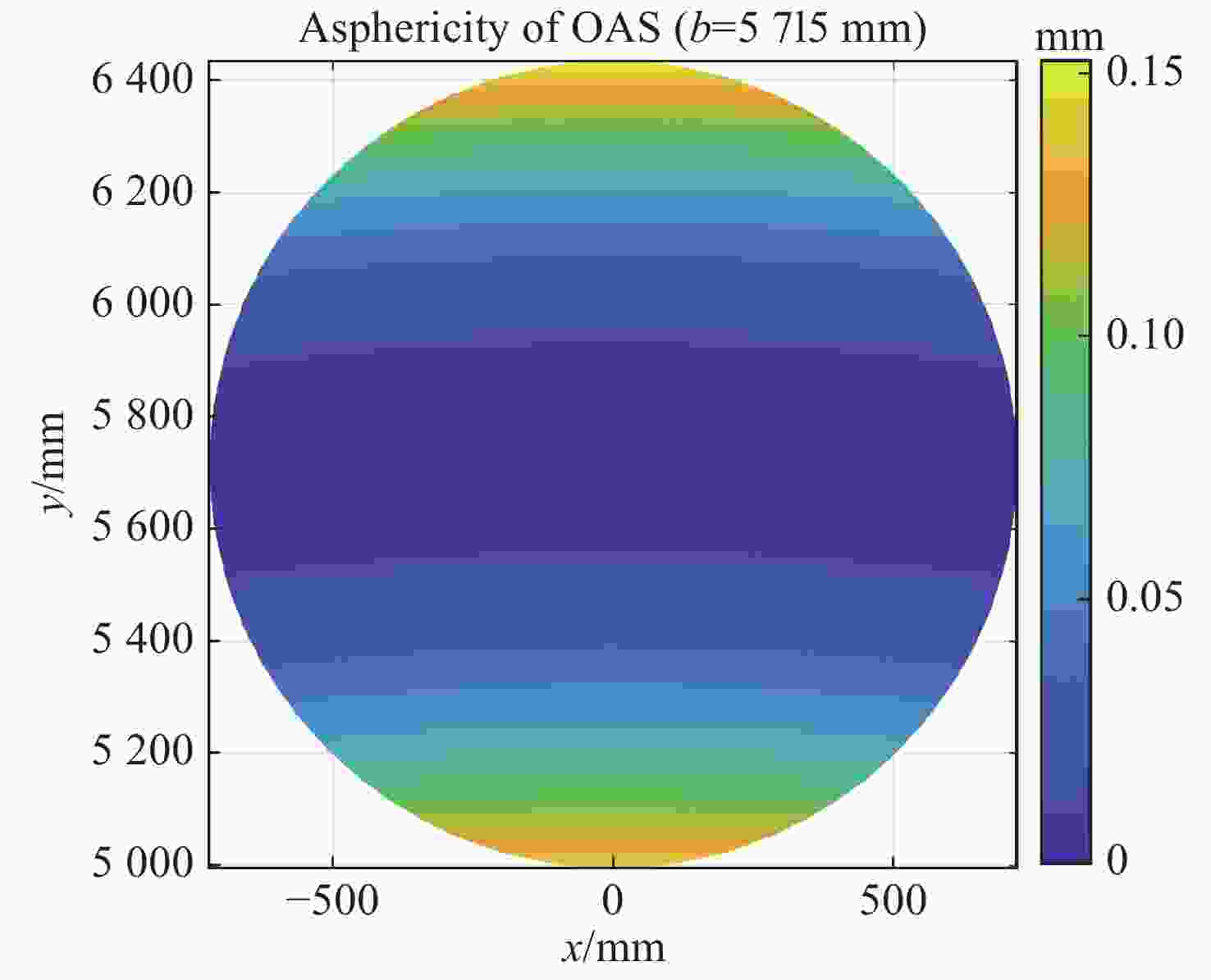
Number Off-axis distance/mm Off-axis angle φ/(°) Vertex sag/mm Best fit sphere ROC/mm Maximum deviation/μm 1 1247 1.8600 20.25 38425 8.27 6 3741 5.5647 182.23 38584 65.9 14 5715 8.4666 425.31 38821 152.4 表 3 不同离轴子镜检测光路CGH空间频率、空间周期
Table 3. CGH spatial frequency and spatial period of different off-axis segment testing systems
Number Elliptical etched area/mm Spatial frequency/mm−1 Spatial period/μm x radius y radius Max Min Max Min 1 34.2 32.1 61.5 14.6 68.3 16.3 6 35.1 34.4 47.2 13.2 75.9 21.2 14 36.0 38.0 47.1 31.5 31.8 21.2 表 4 补偿元件加工误差及其波像差变化
Table 4. Fabrication errors of compensation elements and corresponding wavefront aberration variations
Error type Error name International processing status First order RMS wavefront /nm CGH substrate error Transmitted wavefront 0.02λ 5.784 Thickness 1 μm 0.130 Refraction index 5×10−6 0.008 CGH pattern fabrication error Encoding 0.05 μm 1.492 Pattern distortion 0.1 μm 2.985 Etching depth 1 % 1.107 Duty cycle 0.5 % 0 Amplitude 0.1 % 0.026 Spherical mirror fabrication error Surface figure 0.01λ 6.328 ROC 0.01 % 4.632 RSS N/A N/A 10.360 表 5 检测光路元件装调公差及波像差变化
Table 5. Element adjustment tolerance of the testing system and the wavefront aberration variation
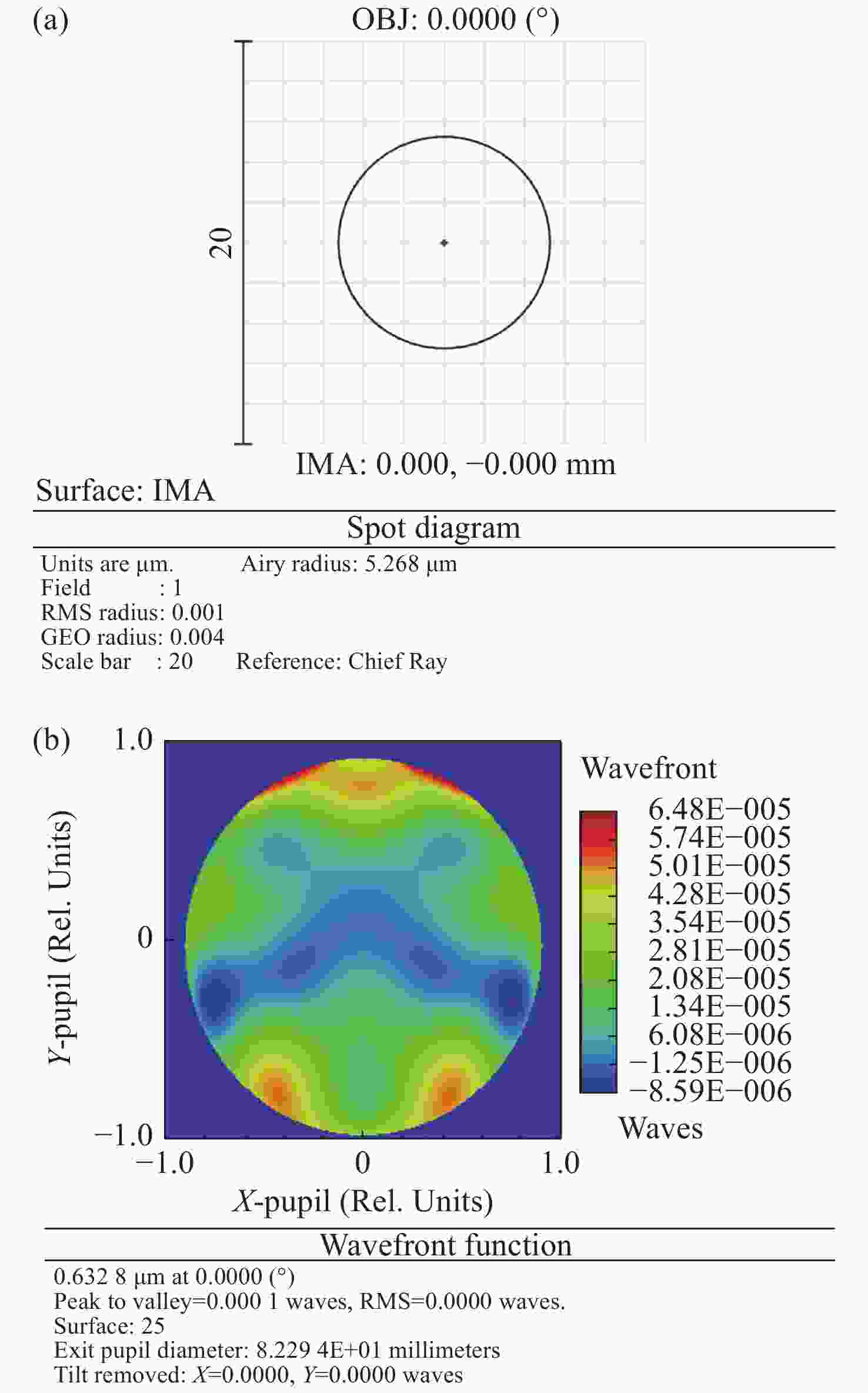
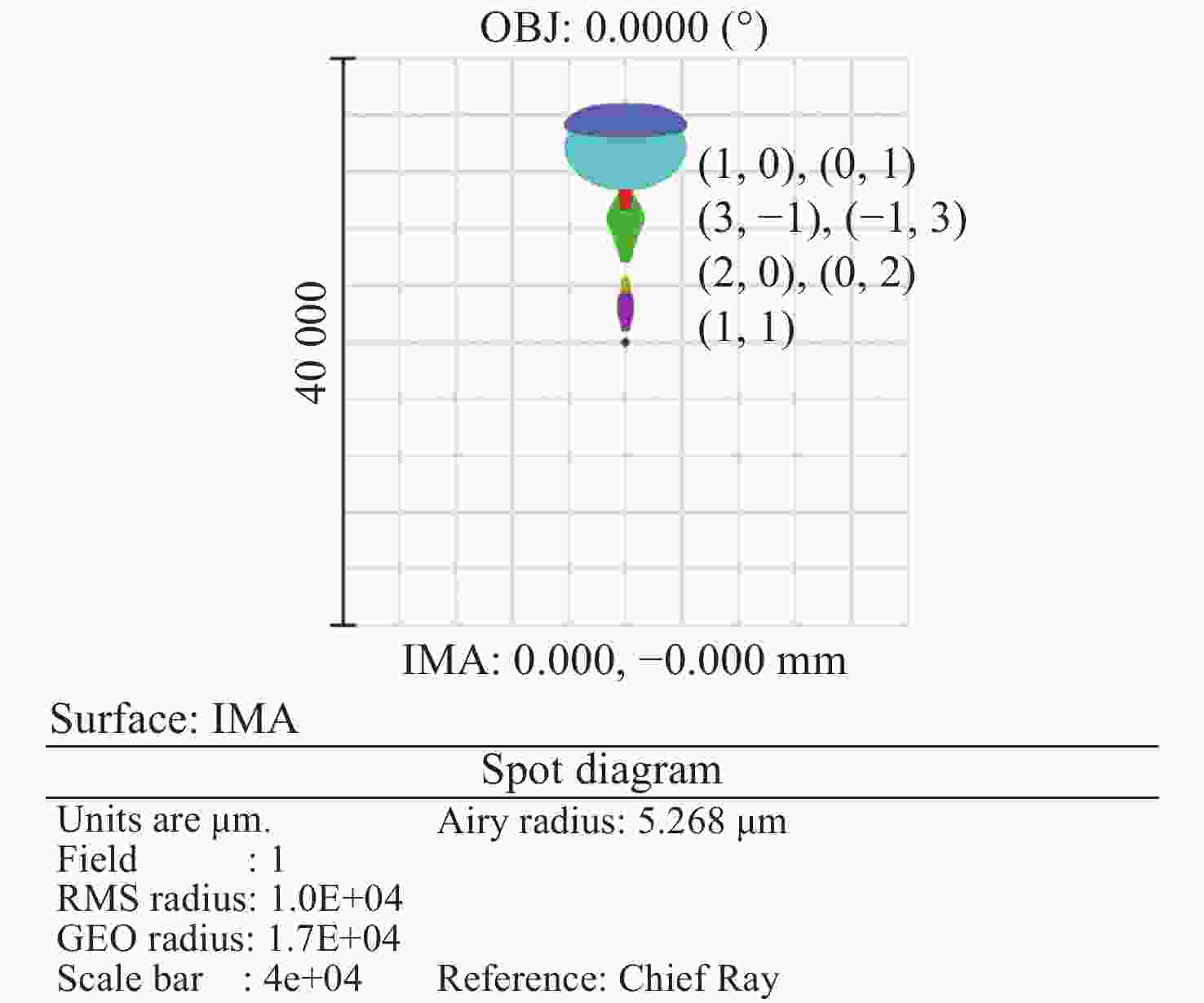
Element Tolerance (μm, arcsec) Wavefront error/nm Total wavefront RMS/nm Zernike fringe coefficients Z4 Z5 Z6 Z7 Z8 CGH dx 10 −0.001 0.001 0.001 −0.002 0.001 0.008 dy 10 0.005 0.000 0.001 −0.001 −0.043 0.017 dz 50 0.269 −1.605 0.001 −0.019 −8.819 3.233 tilt x 5 0.020 −0.141 −0.002 0.002 −0.772 0.283 tilt y 5 0.001 0.003 0.001 −0.004 0.001 0.027 tilt z 5 −0.003 −0.002 0.001 −0.002 0.002 0.009 spherical mirror dx 100 −0.001 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.001 0.009 dy 100 −0.017 0.125 0.003 −0.007 0.658 0.239 dz 1000 0.207 −1.255 0.001 −0.001 −6.966 2.526 tilt x 30 0.457 −2.784 0.000 −0.004 −15.383 5.577 tilt y 30 −0.002 −0.021 −0.008 0.022 −0.089 0.126 tilt z 30 0.000 0.003 0.000 0.000 0.001 0.008 LOT segment dx 100 −0.003 −0.002 0.000 0.000 0.002 0.008 dy 100 0.030 −0.179 0.002 −0.001 −1.009 0.365 Coefficients RSS/nm 0.571 3.460 0.009 0.031 19.105 N/A Wavefront RMS/nm 0.329 1.412 0.004 0.011 6.754 6.944 -
[1] 刘强, 王欣, 黄庚华, 等. 大视场大相对孔径斜轴离轴三反望远镜的光学设计[J]. 光子学报,2019,48(3):0322002. doi: 10.3788/gzxb20194803.0322002LIU Q, WANG X, HUANG G H, et al. Optical design of wide field view and large relative aperture off-axis three-mirror reflective system with tilted optical axis[J]. Acta Photonica Sinica, 2019, 48(3): 0322002. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/gzxb20194803.0322002 [2] NELSON J, SANDERS G H. The status of the Thirty Meter Telescope project[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2008, 7012: 70121A. doi: 10.1117/12.788238 [3] TAMAI R, SPYROMILIO J. European extremely large telescope: progress report[C]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2014, 9145: 91451E. [4] SU D Q, LIANG M, YUAN X Y, et al. The optical system of the proposed Chinese 12-m optical/infrared telescope[J]. Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 2017, 469(4): 3792-3801. doi: 10.1093/mnras/stx956 [5] 黄亚, 马骏, 朱日宏, 等. 基于计算全息的光学自由曲面测量不确定度分析[J]. 光学学报,2015,35(11):1112007. doi: 10.3788/AOS201535.1112007HUANG Y, MA J, ZHU R H, et al. Investigation of measurement uncertainty of optical freeform surface based on computer-generated hologram[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2015, 35(11): 1112007. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/AOS201535.1112007 [6] 李明, 罗霄, 薛栋林, 等. 考虑投影畸变设计大口径离轴非球面检测用计算全息图[J]. 光学 精密工程,2015,23(5):1246-1253. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20152305.1246LI M, LUO X, XUE D L, et al. Design of CGH for testing large off-axis asphere by considering mapping distortion[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2015, 23(5): 1246-1253. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/OPE.20152305.1246 [7] 曾雪锋, 闫锋, 薛栋林, 等. 计算全息图补偿检测离轴非球面中的投影畸变校正技术[J]. 中国激光,2013,40(11):1109003. doi: 10.3788/CJL201340.1109003ZENG X F, YAN F, XUE D L, et al. Distortion correction in testing of off-axis asphere with computer-generated hologram[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2013, 40(11): 1109003. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/CJL201340.1109003 [8] 高松涛, 武东城, 苗二龙. 大偏离度非球面检测畸变校正方法[J]. 中国光学,2017,10(3):383-390. doi: 10.3788/co.20171003.0383GAO S T, WU D CH, MIAO E L. Distortion correcting method when testing large-departure asphere[J]. Chinese Optics, 2017, 10(3): 383-390. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/co.20171003.0383 [9] 徐秋云, 徐晨, 李博, 等. 大口径批量化离轴非球面镜的检测光路设计[J]. 光学学报,2015,35(10):1012005. doi: 10.3788/AOS201535.1012005XU Q Y, XU CH, LI B, et al. Optical testing design for plenty of large off-axis aspherical mirrors[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2015, 35(10): 1012005. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/AOS201535.1012005 [10] BURGE J H, ZHAO CH Y, DUBIN M. Measurement of aspheric mirror segments using Fizeau interferometry with CGH correction[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2010, 7739: 773902. doi: 10.1117/12.857816 [11] ZHAO CH Y, ZEHNDER R, BURGE J H, et al. Testing an off-axis parabola with a CGH and a spherical mirror as null lens[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2005, 5869: 586911. doi: 10.1117/12.615465 [12] ZEHNDER R, BURGE J H, ZHAO CH Y. Use of computer generated holograms for alignment of complex null correctors[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2006, 6273: 62732S. doi: 10.1117/12.672139 [13] LI SH J, ZHANG J, LIU W G, et al. Measurement investigation of an off-axis aspheric surface via a hybrid compensation method[J]. Applied Optics, 2018, 57(28): 8220-8227. doi: 10.1364/AO.57.008220 [14] LINDLEIN N. Analysis of the disturbing diffraction orders of computer-generated holograms used for testing optical aspherics[J]. Applied Optics, 2001, 40(16): 2698-2708. doi: 10.1364/AO.40.002698 [15] PENG J T, REN J Y, ZHANG X X, et al. Analytical investigation of the parasitic diffraction orders of tilt carrier frequency computer-generated holograms[J]. Applied Optics, 2015, 54(13): 4033-4041. doi: 10.1364/AO.54.004033 [16] PENG J T, CHEN ZH, ZHANG X X, et al. Optimal design of tilt carrier frequency computer-generated holograms to measure aspherics[J]. Applied Optics, 2015, 54(24): 7433-7441. doi: 10.1364/AO.54.007433 [17] 何宇航, 李强, 高波, 等. 基于计算全息元件的大口径非球面透镜透射波前检测方法[J]. 激光与光电子学进展,2019,56(2):021202.HE Y H, LI Q, GAO B, et al. Measurement of the transmission wavefront of a large-aperture aspheric lens based on computer-generated hologram[J]. Laser &Optoelectronics Progress, 2019, 56(2): 021202. (in Chinese) [18] 高松涛, 武东城, 于长淞. 用于高精度非球面面形检测的计算全息图的设计[J]. 激光与光电子学进展,2016,53(9):090901.GAO S T, WU D CH, YU CH S. Computer-generated hologram design for high-precision aspherical surface testing[J]. Laser &Optoelectronics Progress, 2016, 53(9): 090901. (in Chinese) [19] BURGE J H, KOT L B, MARTIN H M, et al. Design and analysis for interferometric measurements of the GMT primary mirror segments[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2006, 6273: 62730M. doi: 10.1117/12.672484 [20] ZHOU P, BURGE J H. Fabrication error analysis and experimental demonstration for computer-generated holograms[J]. Applied Optics, 2007, 46(5): 657-663. doi: 10.1364/AO.46.000657 [21] ZHOU P. Error analysis and data reduction for interferometric surface measurements[D]. University of Arizona, 2009: 135-179. [22] ZHAO CH Y, BURGE J H. Optical testing with computer generated holograms: comprehensive error analysis[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2013, 8838: 88380H. [23] 费业泰. 误差理论与数据处理[M]. 第7版. 北京: 机械工业出版社, 2015: 59-99.FEI Y T. Error Theory and Data Processing[M]. 7th ed. Beijing: China Machine Press, 2015: 59-99. (in Chinese) [24] 徐德衍, 王青, 高志山, 等. 现行光学元件检测与国际标准[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2009: 25-59.XU D Y, WANG Q, GAO ZH SH, et al.. Current Optical Component Inspection and International Standards[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2009: 25-59. (in Chinese) -





 下载:
下载: