Design and development of the optical system for the high resolution visual puncture needle
-
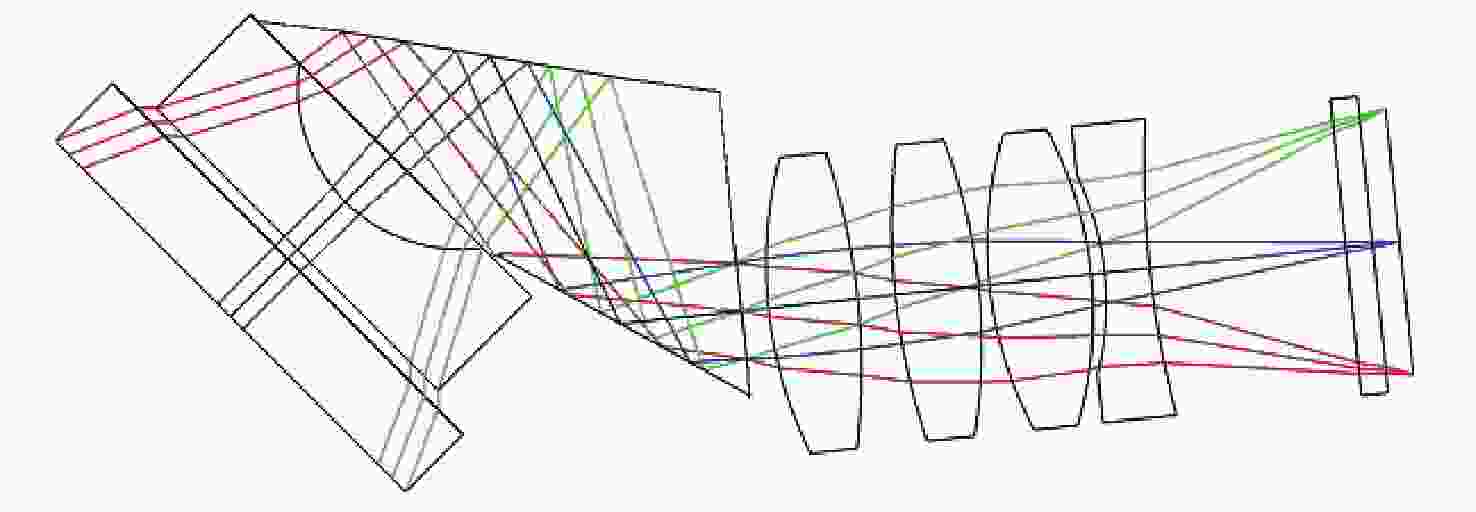
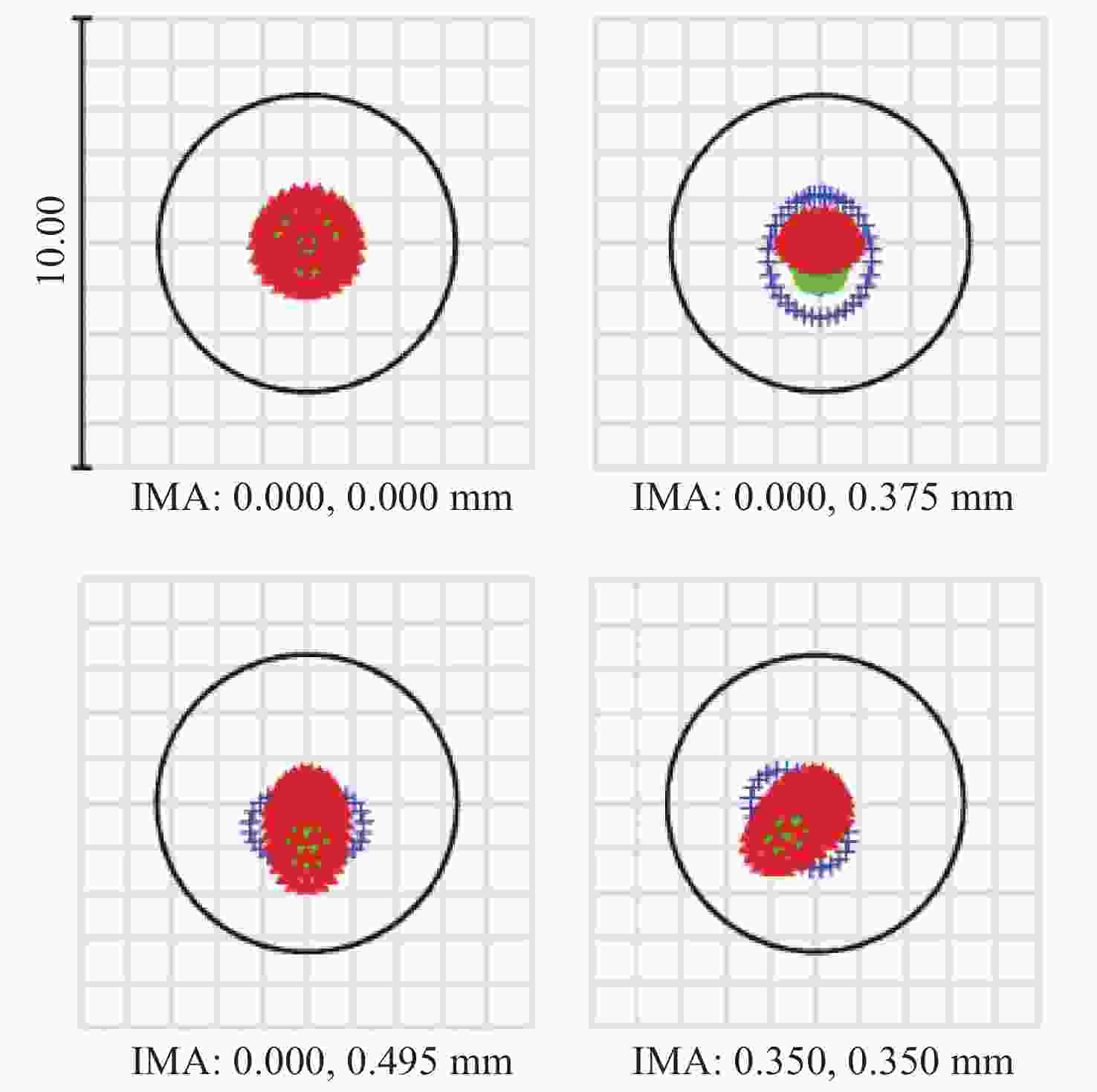
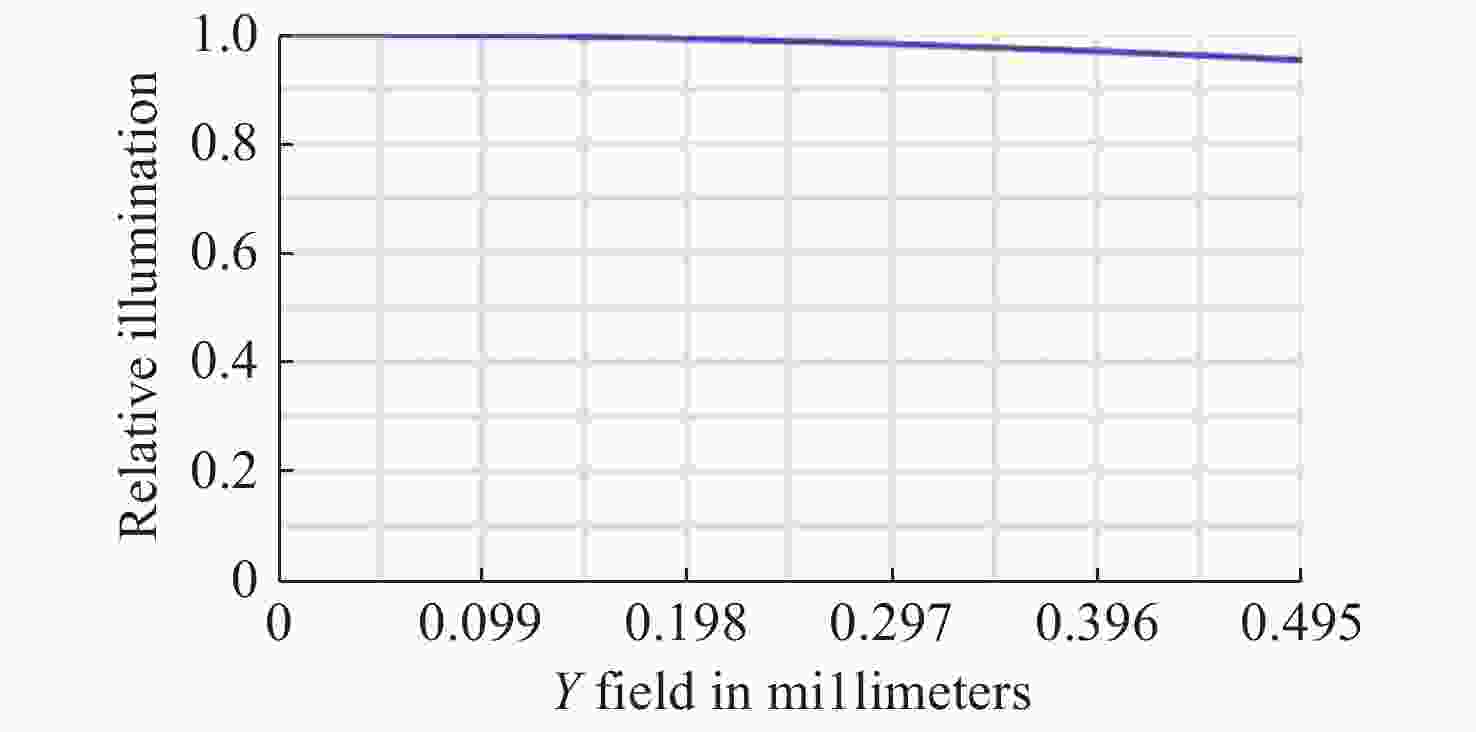
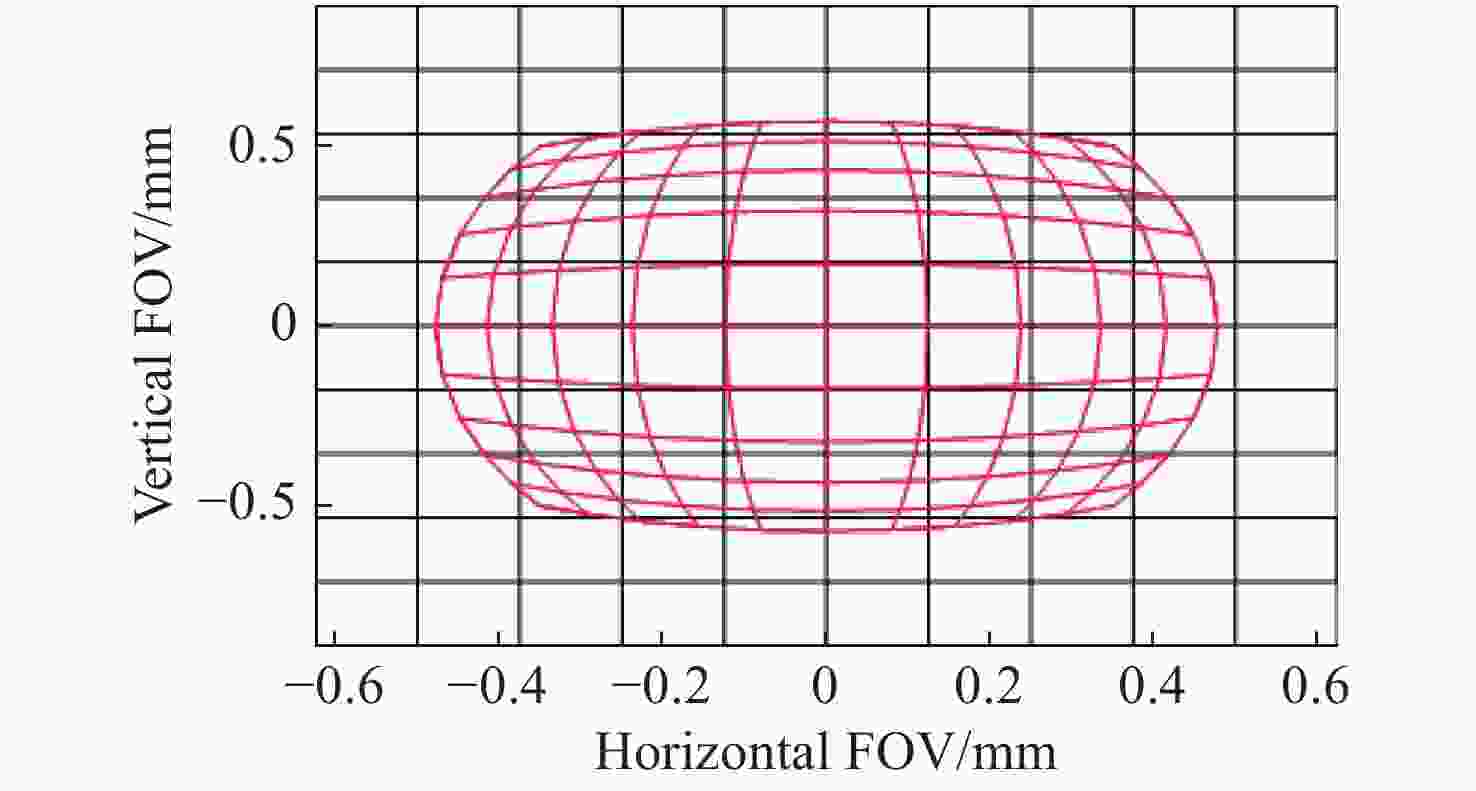
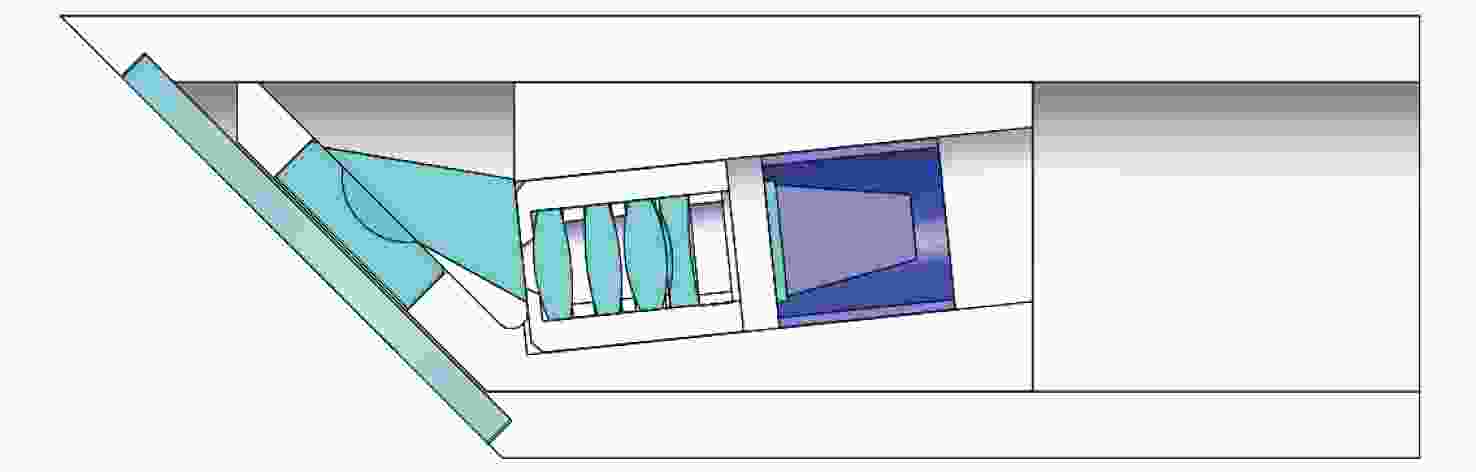
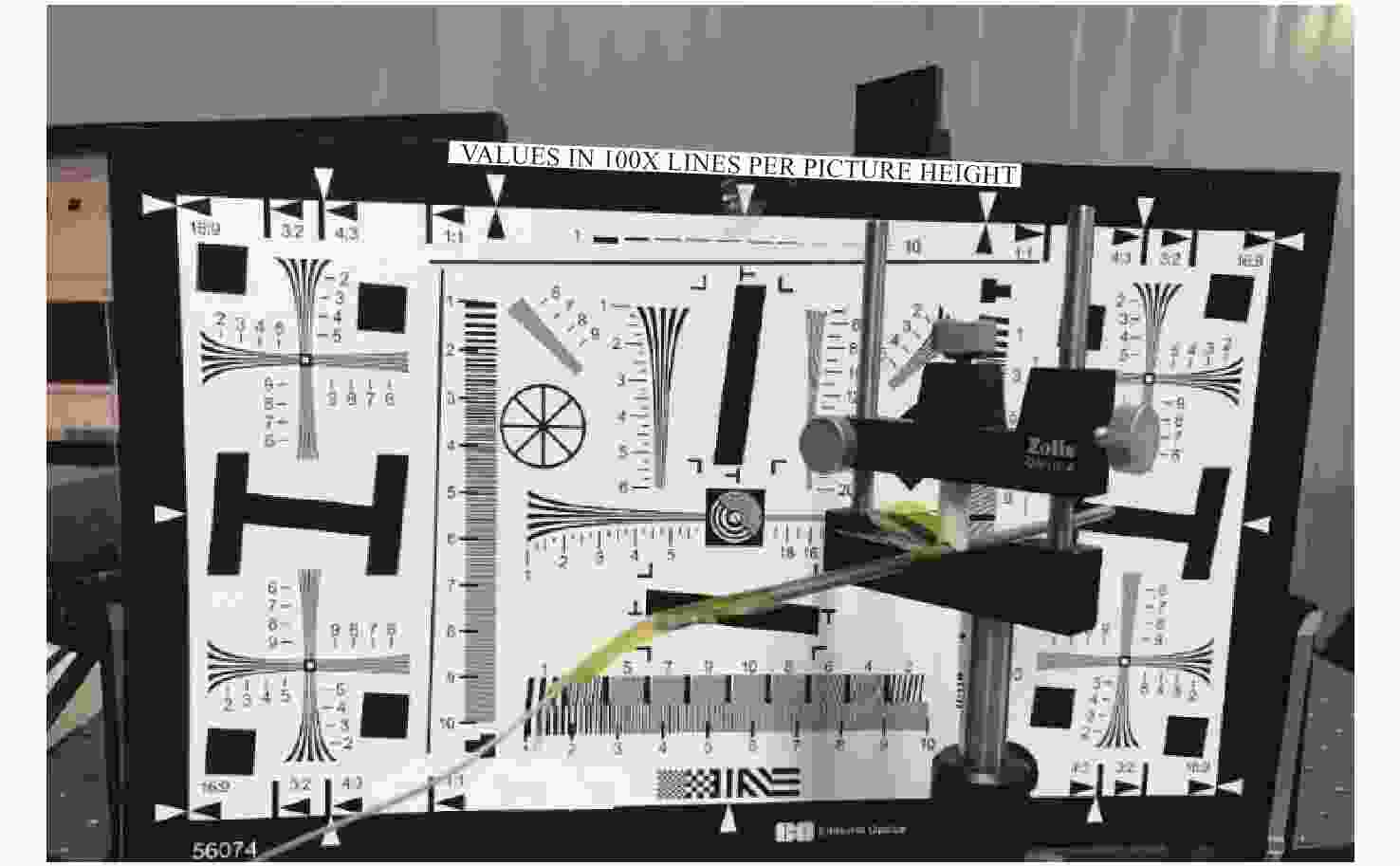
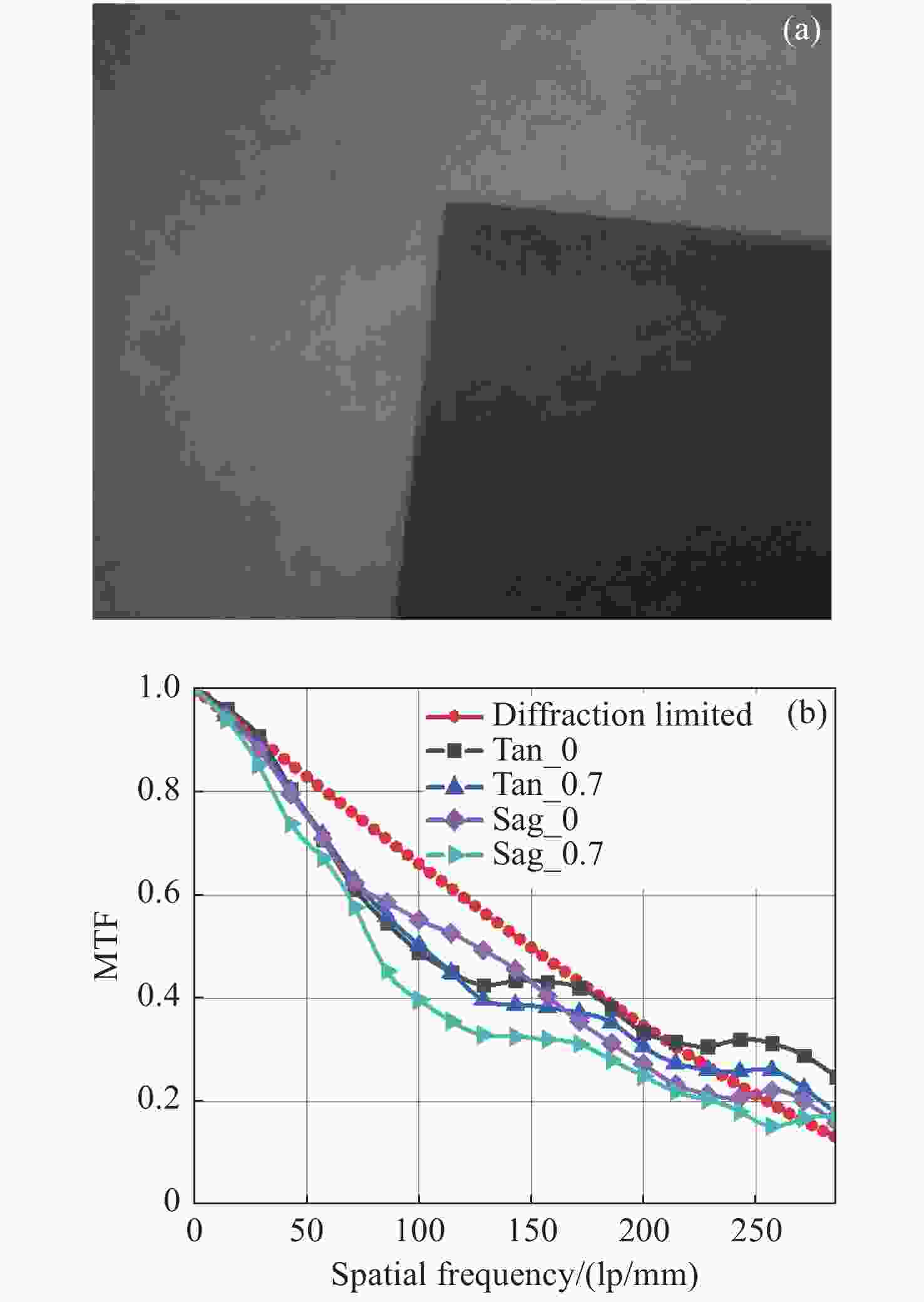
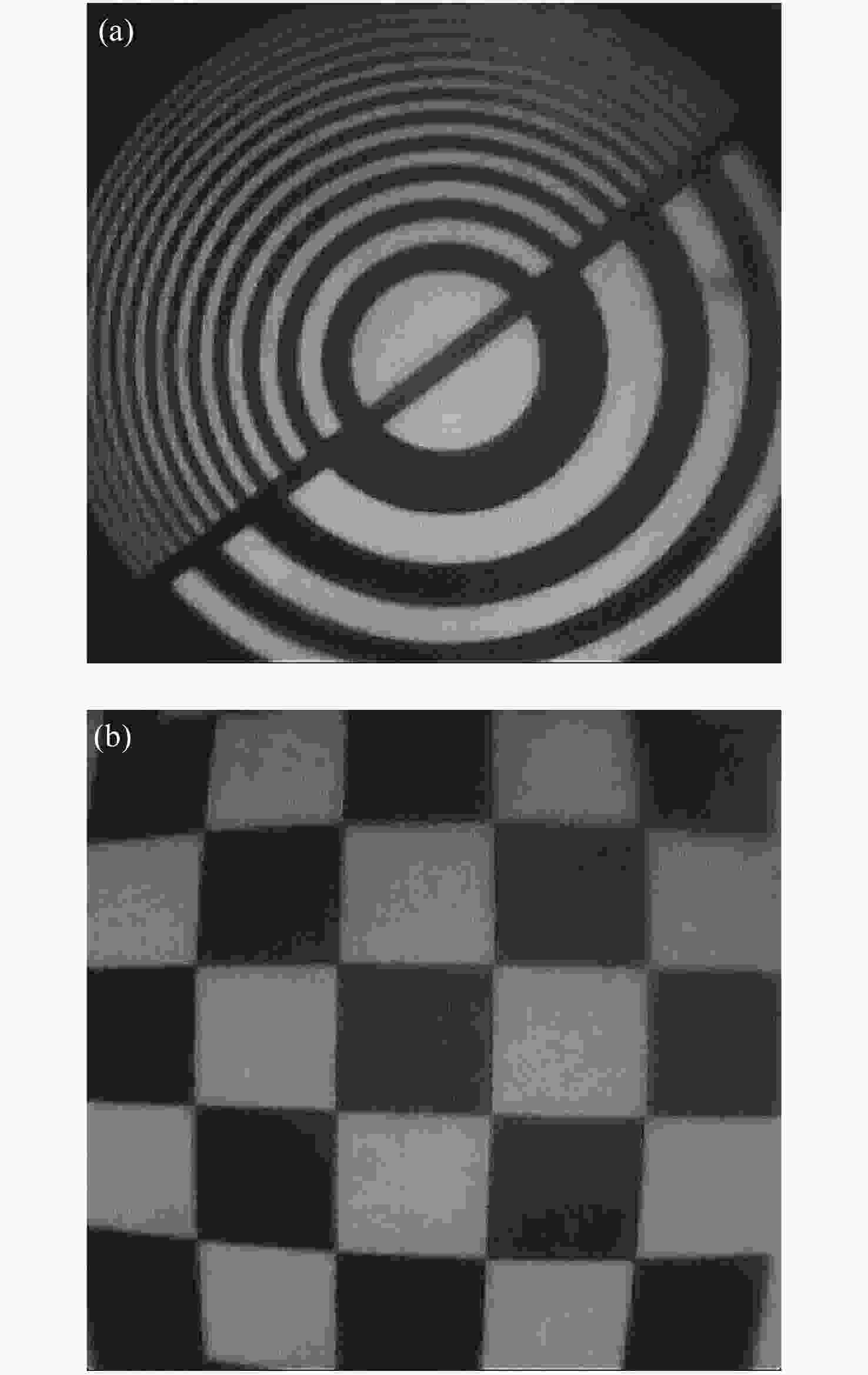
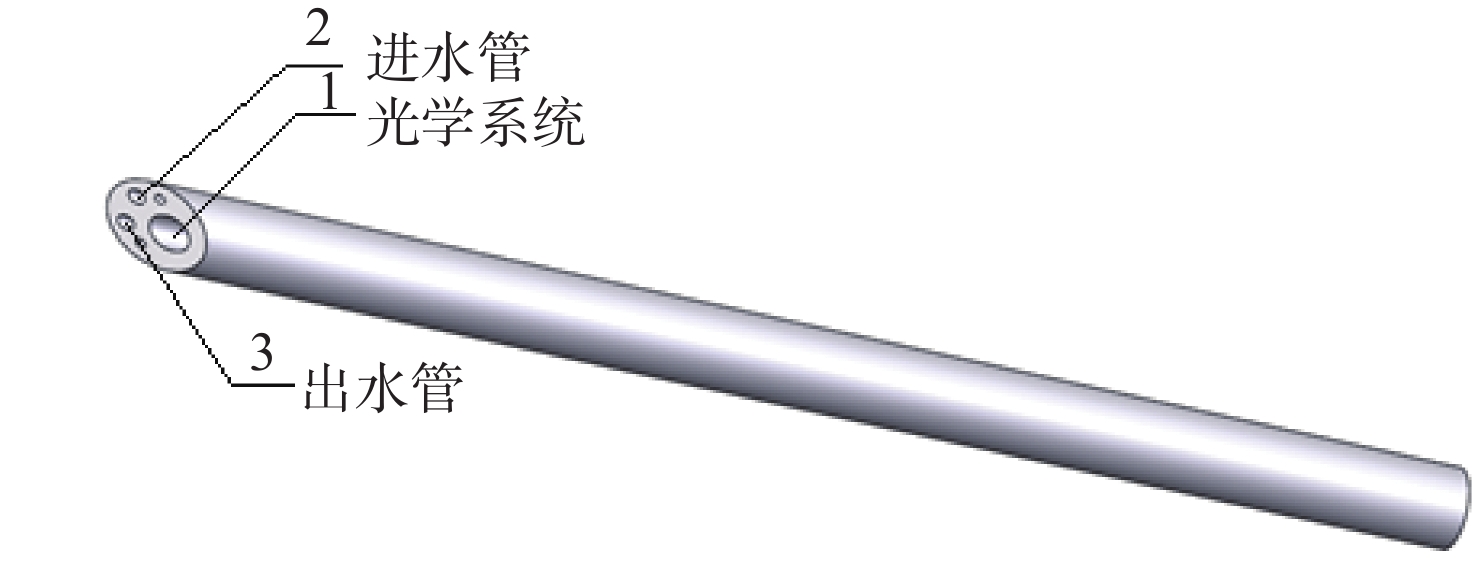
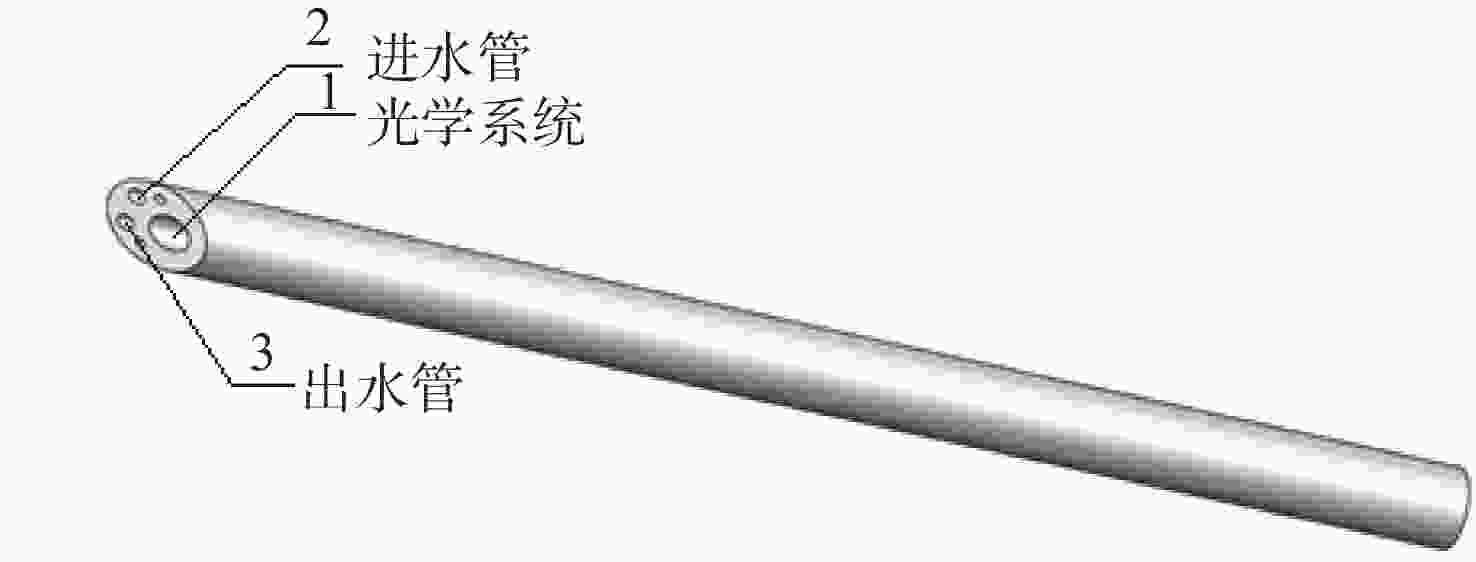
摘要: 为了实现穿刺过程中的精准定位,设计研制了一款视场角为90°,焦距为0.67 mm的高分辨率可视穿刺针光学系统。为使光学系统的光轴垂直于穿刺针的倾斜刃面,利用反射棱镜对光束进行转折,实现45°视向角。光学系统采用反远结构,并对初始结构参数的计算公式进行推导。经过优化设计后,系统成像质量接近衍射极限,最大光学元件尺寸小于1.5 mm。利用研制的光学系统和微型CMOS图像传感器,装配完成了一款直径为4 mm的可视穿刺针。对该可视穿刺针分别进行调制传递函数(MTF)测试和成像试验,测试结果表明,研制的光学系统具有较好的成像质量,物方分辨率优于18.03 lp/mm,能够实现清晰成像。Abstract: In order to realize accurate positioning during the puncture surgery, a high-resolution optical system with a 90° field of view and 0.67 mm focal length is designed and developed for the visual puncture needle. A 45° viewing angle is chosen to make the optical axis perpendicular to the inclined edge surface by using a reflection prism. The retrofocus structure is used and the formulas for the initial structure parameters calculation are derived. The imaging performance of the optimized system is nearly diffraction-limited and the maximum size of the optical component is less than 1.5 mm. The optical system is developed, and it is assembled in a 4 mm diameter puncture needle with a miniature CMOS image sensor. The assembled visual puncture needle is evaluated with the Modulation Transfer Function (MTF) measurement and the imaging experiment. The measurement results show that the imaging quality of the optical system is good and its object-space resolution reaches 18.03 lp/mm, thus it can realize the requirement for high-resolution imaging.
-
Key words:
- visual puncture needle /
- retrofocus system /
- viewing angle /
- modulation transfer function
-
表 1 主要参数的设计结果
Table 1. Optical parameters of designed optical system
Parameters Value Wavelength/μm 0.45~0.75 Focal length/mm 0.67 Field of view/(°) 90 F/# 4.6 Back focal length/mm 0.92 Working distance/mm 10 Magnification 0.0764 Image size/mm 0.7×0.7 MTF ≥0.2@246 lp/mm Maximum component size/mm ≤1.5 -
[1] LÖFGREN M, ANDERSSON I, BONDESON L, et al. X-ray guided fine-needle aspiration for the cytologic diagnosis of nonpalpable breast lesions[J]. Cancer, 1988, 61(5): 1032-1037. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19880301)61:5<1032::AID-CNCR2820610529>3.0.CO;2-R [2] VIDAL F P, JOHN N W, HEALEY A E, et al. Simulation of ultrasound guided needle puncture using patient specific data with 3D textures and volume haptics[J]. Computer Animation &Virtual Worlds, 2008, 19(2): 111-127. [3] XU H ZH, LV Y ZH, GUO D L, et al. Morphological structure of the infraorbital canal using three-dimensional reconstruction[J]. Journal of Craniofacial Surgery, 2012, 23(4): 1166-1168. doi: 10.1097/SCS.0b013e31824dfcfd [4] BADER M J, GRATZKE C, SEITZ M, et al. The "all-seeing needle": initial results of an optical puncture system confirming access in percutaneous nephrolithotomy[J]. European Urology, 2011, 59(6): 1054-1059. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2011.03.026 [5] 管喆恒. 可视化椎弓根穿刺针的初步设计与研究[D]. 苏州: 苏州大学, 2017: 14-18.GUAN ZH H. Preliminary design and study of visual pedicle probe[D]. Suzhou: Soochow University, 2017: 14-18. (in Chinese) [6] 禹璐, 程德文, 周伟, 等. 大景深高清硬性内窥镜光学系统的优化设计[J]. 光学学报,2013,33(11):1122003. doi: 10.3788/AOS201333.1122003YU L, CHENG D W, ZHOU W, et al. Optimization design of rigid endoscope with high definition and large depth of field[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2013, 33(11): 1122003. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/AOS201333.1122003 [7] 张树青, 王庆晨, 智喜洋, 等. 30°视向角硬质内窥镜光学设计[J]. 光学学报,2018,38(2):0222002. doi: 10.3788/AOS201838.0222002ZHANG SH Q, WANG Q CH, ZHI X Y, et al. Optical design of rigid endoscope with 30° viewing angle[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2018, 38(2): 0222002. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/AOS201838.0222002 [8] 沈为民. 大相对口径大视场红外光学系统[D]. 西安: 中国科学院西安光学精密机械研究所, 2004: 23-24.SHEN W M. High-speed infrared optical systems with wide field of view[D]. Xi'an: Xi'an Institute of Optics and Precision Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Science, 2004: 23-24. (in Chinese) [9] 电影镜头设计组. 电影摄影物镜光学设计[M]. 北京: 中国工业出版社, 1971: 24-27.The Optical Design Group of the Motion Picture Lenses. The Optical Design of the Motion Picture Lenses[M]. Beijing: China Industry Press, 1971: 24-27. (in Chinese) [10] XIANG CH CH, CHEN X H, CHEN Y G, et al. MTF measurement and imaging quality evaluation of digital camera with slanted-edge method[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2010, 7849: 78490A. [11] 徐宝腾, 杨西斌, 刘家林, 等. 高速扫描激光共聚焦显微内窥镜图像校正[J]. 光学 精密工程,2020,28(1):60-68. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20202801.0060XU B T, YANG X B, LIU J L, et al. Image correction for high speed scanning confocal laser endomicroscopy[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2020, 28(1): 60-68. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/OPE.20202801.0060 [12] 陈聪, 杨帆, 范立成, 等. 眼科手术导航的OCT图像畸变矫正[J]. 光学 精密工程,2020,28(1):182-188. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20202801.0182CHEN C, YANG F, FAN L CH, et al. Study on distortion correction method of OCT image in ophthalmic surgery navigation[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2020, 28(1): 182-188. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/OPE.20202801.0182 [13] 丛婧, 俎明明, 李洪涛, 等. 基于智能手机的眼底成像系统[J]. 中国光学,2019,12(1):97-103. doi: 10.3788/co.20191201.0097CONG J, ZU M M, LI H T, et al. Smart phone-based fundus imaging system[J]. Chinese Optics, 2019, 12(1): 97-103. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/co.20191201.0097 -





 下载:
下载: