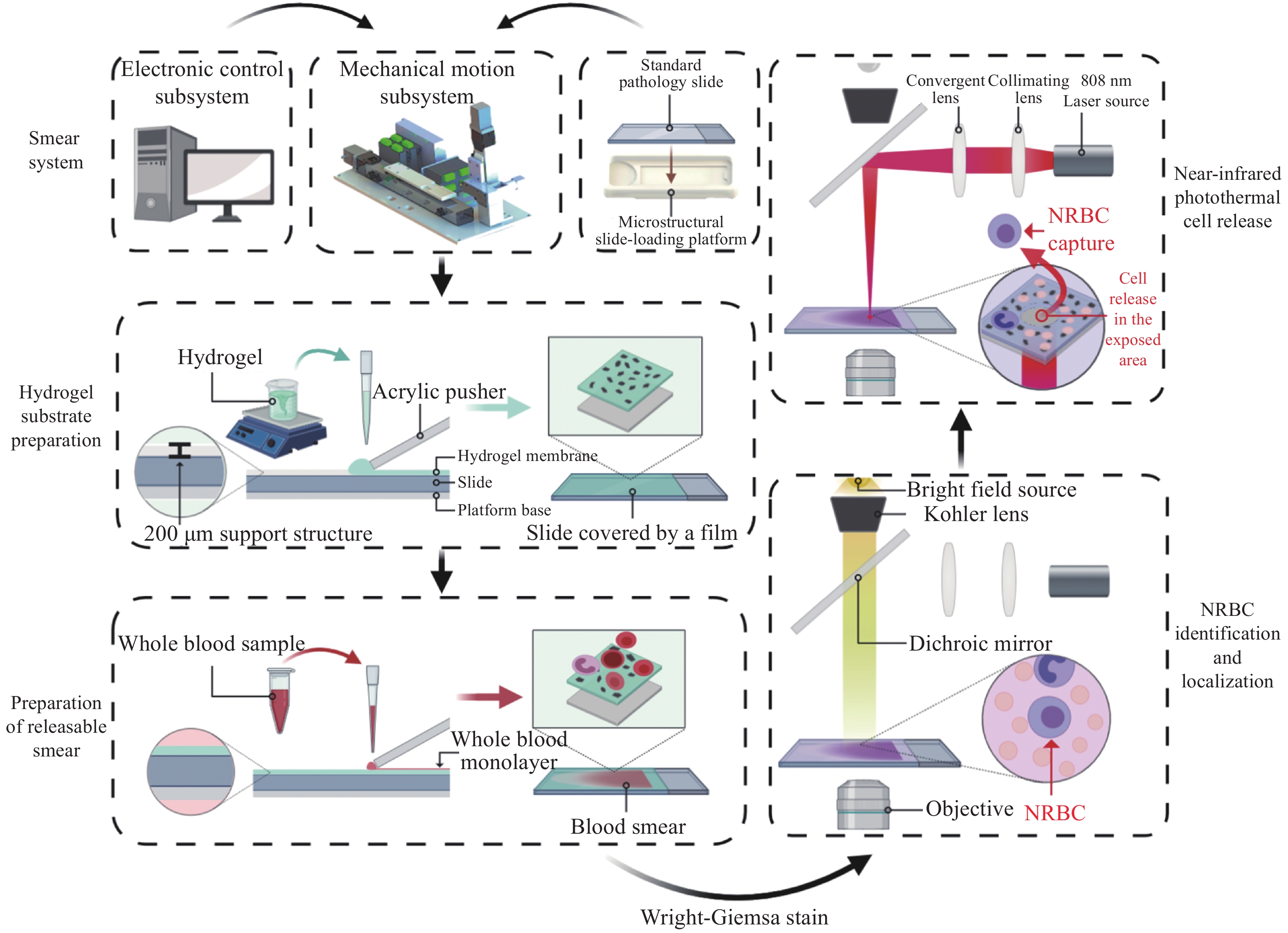
A new automatic cell smear and laser release system for near-infrared light responsive release of nucleated red blood cells
doi: 10.37188/CO.2021-0015
-
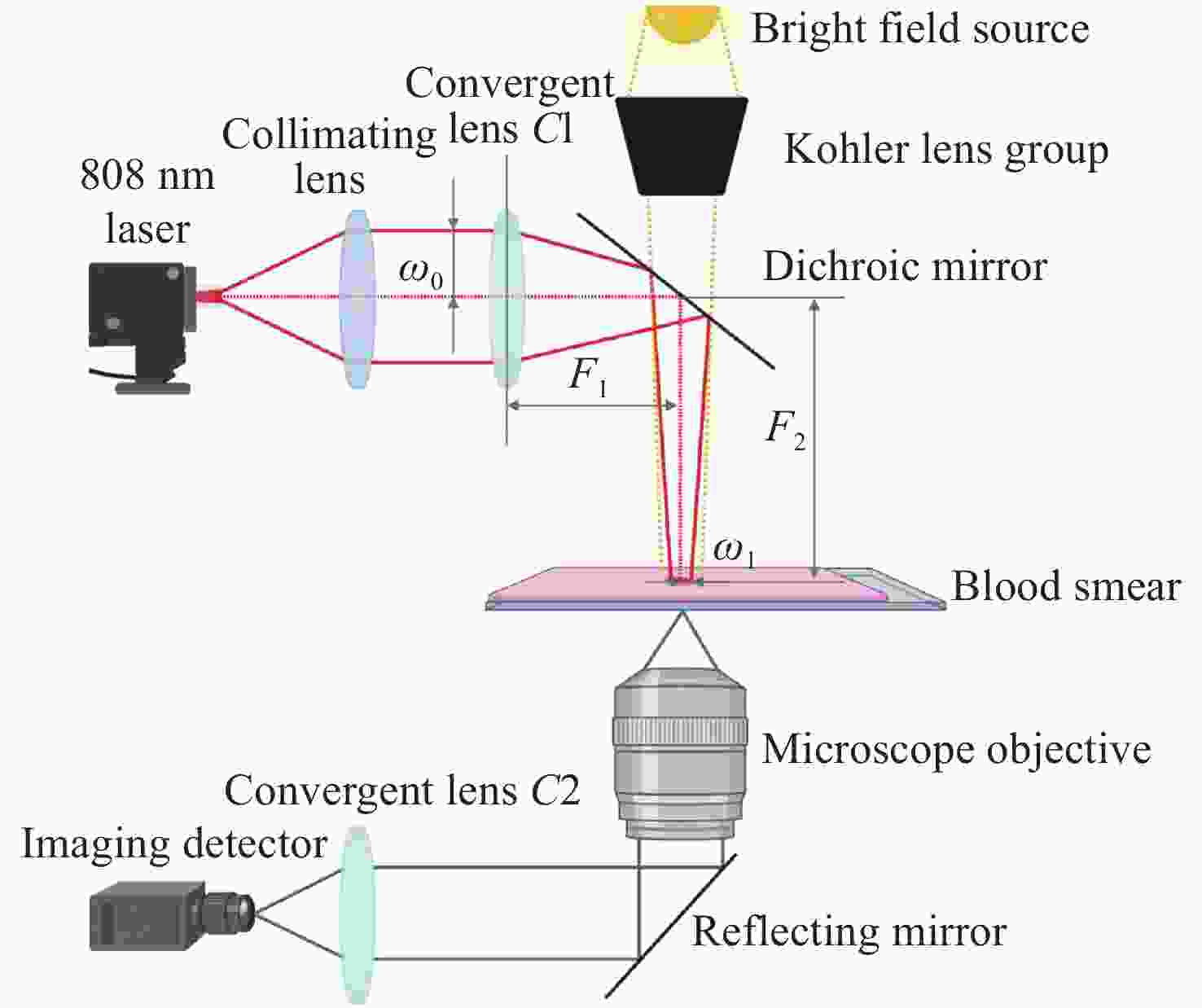
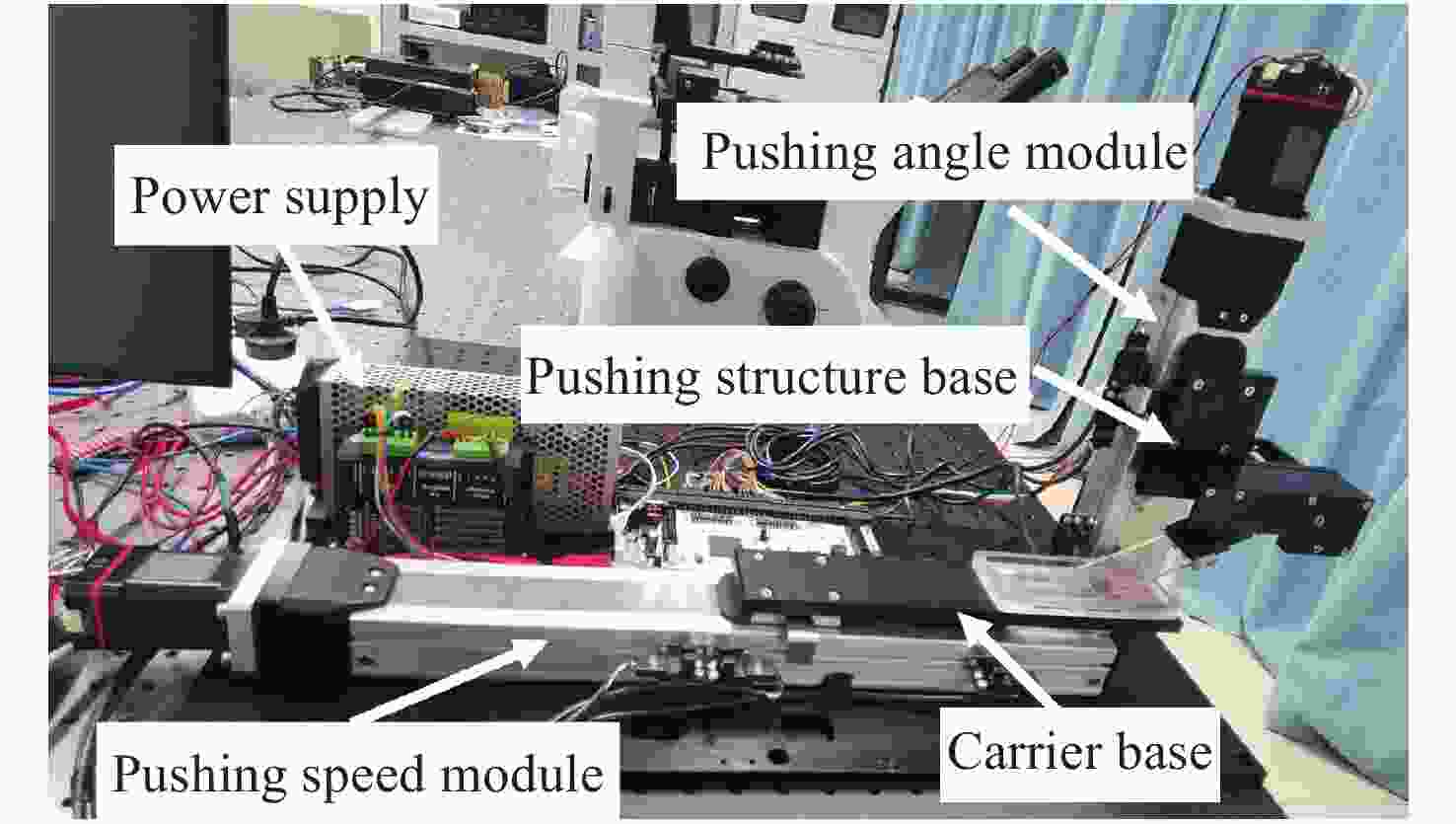
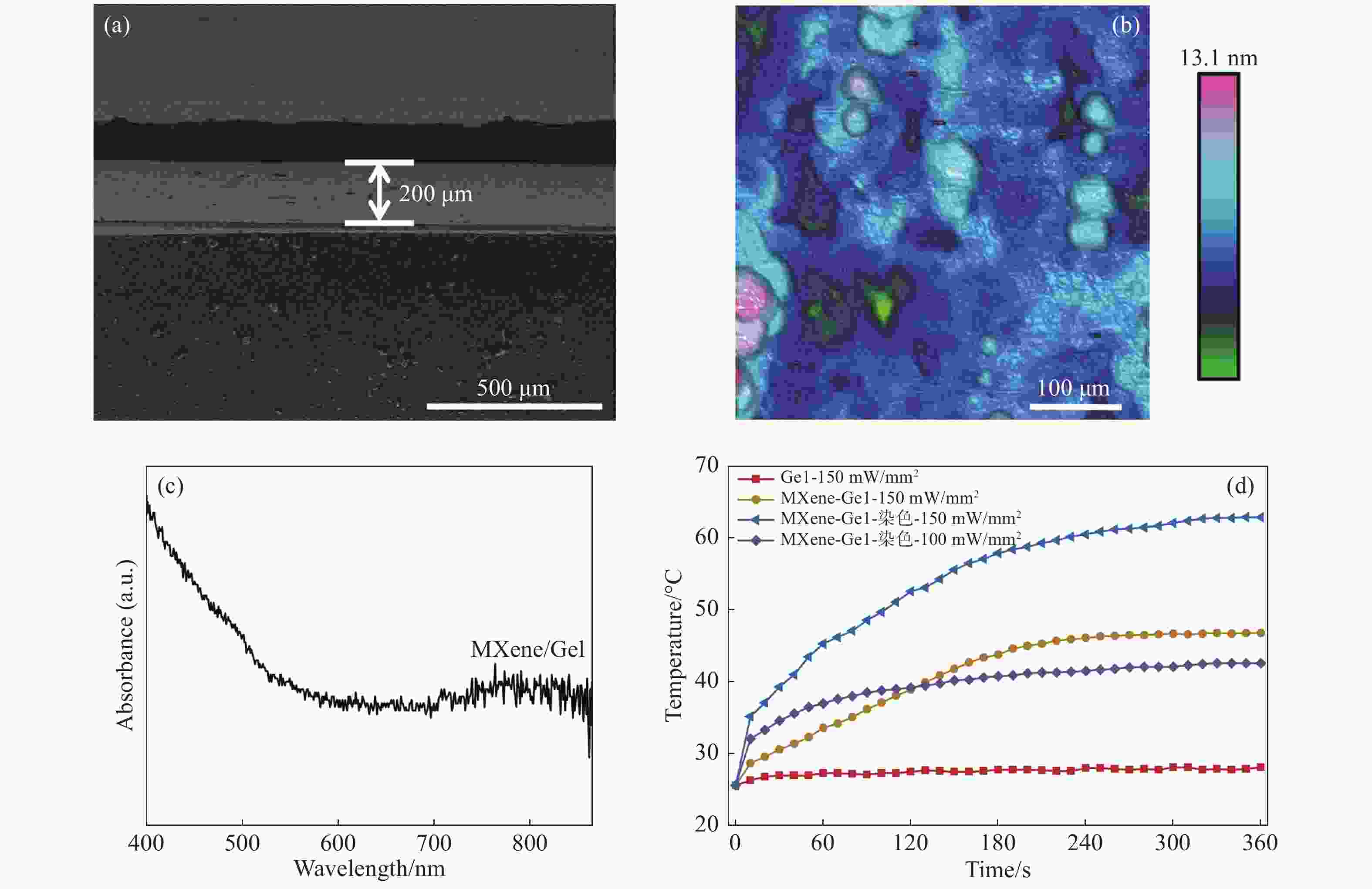
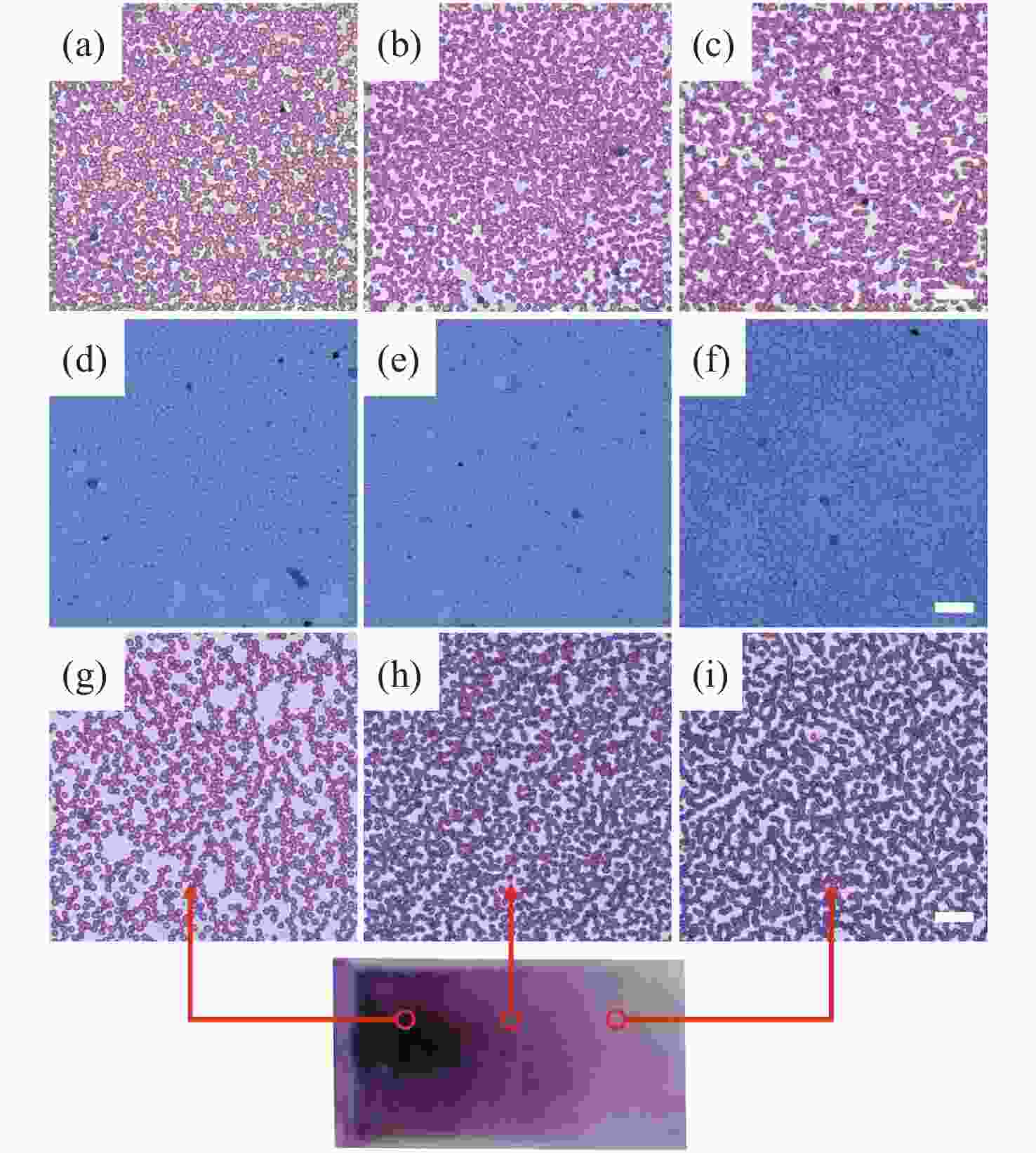
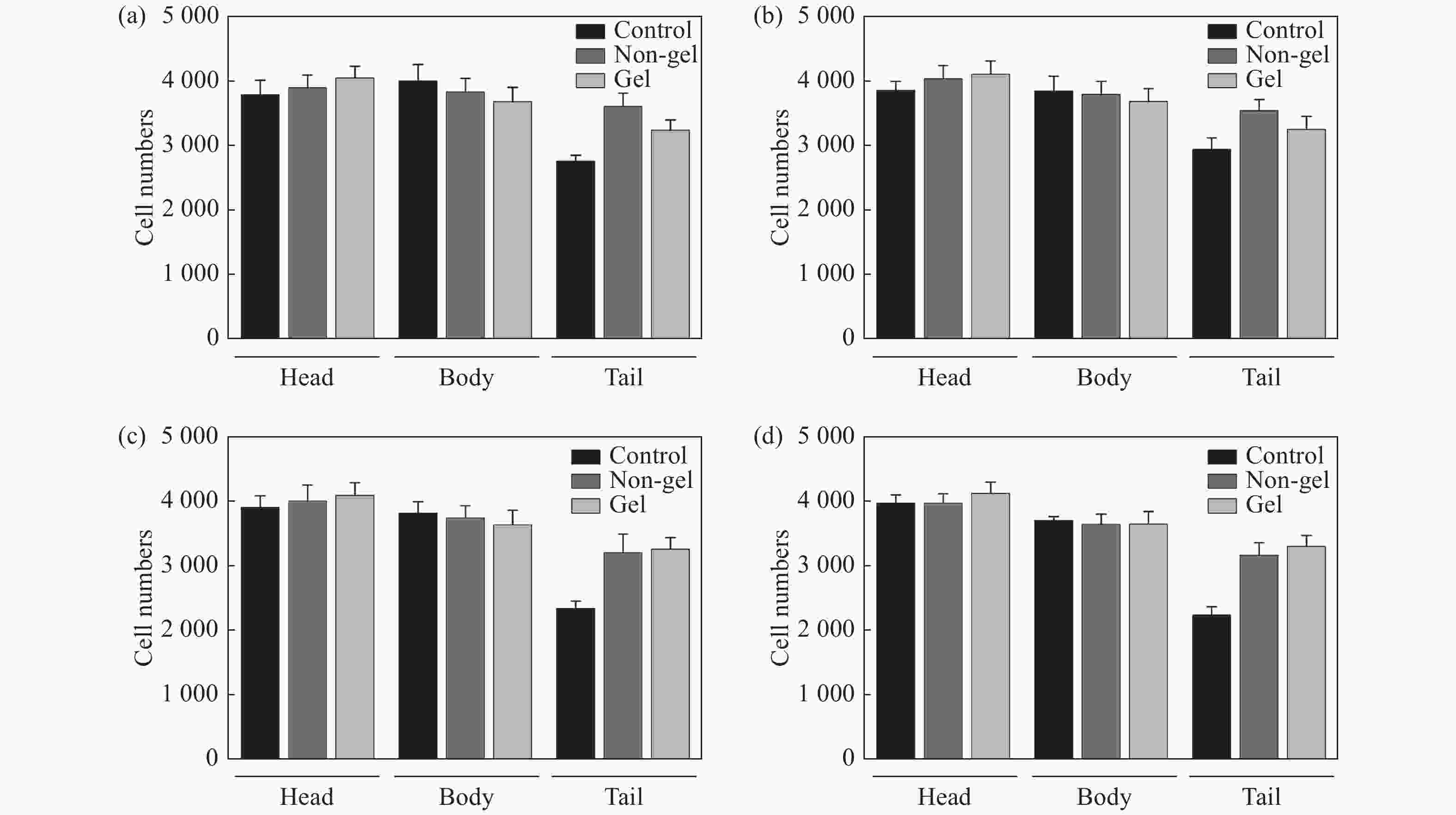
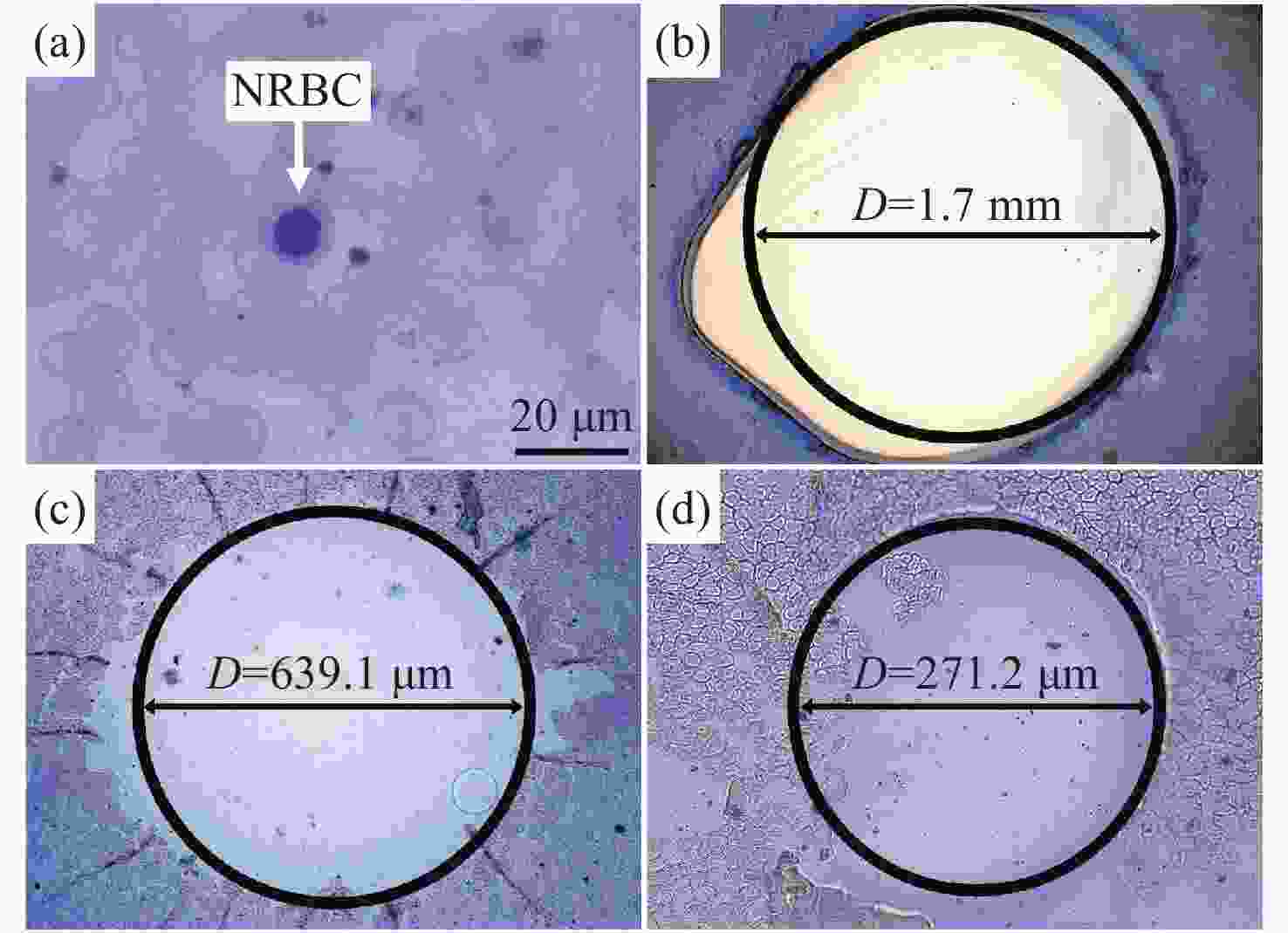
摘要: 为了实现外周血有核红细胞的分离与释放,开发安全有效的非侵入式技术分离有核红细胞以用于产前胎儿疾病诊断,本文以水凝胶材料为基底建立自动化细胞涂片制备系统,并构建用于识别释放有核红细胞的激光会聚和显微成像系统。首先,设计了细胞涂片制备机的机械结构,基于单片机制作上位机控制软件,优化推片角度和速度参数制备水凝胶膜基底涂片,在温敏水凝胶明胶中引入二维材料MXene,结合MXene的近红外光热转换特性,在水凝胶膜表面实现近红外光响应。然后,在水凝胶基底膜表面进行全血推片实验,优化血液推片参数,制备得到单层细胞涂片。最后,建立激光会聚和显微成像光路,对有核红细胞进行识别定位。808 nm激光器的光源经过准直镜和会聚镜聚焦到细胞涂片表面,产生光热效应进行细胞释放。此项工作实现了单层细胞涂片的加工制备,在808 nm近红外光下产生光热效应,经过激光会聚系统的调控,最终得到了光斑直径为300 μm的细胞定点释放区域。本文将自动推片技术应用于以水凝胶膜为基底的单层细胞涂片的制备,建立激光会聚与显微成像光路,通过水凝胶膜的近红外响应以及热响应特性,实现了有核红细胞的识别与定点释放,提高了有核红细胞分离富集效率,在产前筛选诊断领域中具备广阔的应用前景。Abstract: In order to realize the separation and release of nucleated red blood cells from peripheral blood and develop a safe and effective non-invasive technique to separate nucleated red blood cells for prenatal diagnosis of fetal diseases, an automatic cell smear preparation system based on hydrogel material was established, and a laser focusing and microscopic imaging system for recognizing and releasing nucleated red blood cells was constructed. Firstly, the mechanical structure of cell smear preparation machine was designed, the upper computer control software was designed based on single chip microcomputer, and a hydrogel membrane substrate smear was prepared by optimizing the slide-pushing angle and speed. MXene, a two-dimensional material, was introduced into temperature-sensitive hydrogel gelatin, and the near-infrared light response was realized on the surface of hydrogel membrane by using the near-infrared photothermal conversion characteristics of MXene. Then, the whole cell smear experiment was carried out on the surface of the hydrogel substrate membrane. A monolayer cell smear was prepared by optimizing the parameters of blood slide. Finally, the optical path of laser focusing and microscopic imaging was established. After the nucleated red blood cells were recognized and located, the light from an 808 nm laser source passed through a collimator lens and a convergent lens and was focused on the surface of the cell smear, which released cells under photothermal effect. A monolayer cell smear was processed and prepared, and then a photothermal effect was produced under the near-infrared light of 808 nm. After the control of the laser focusing system, a fixed cell-releasing area with a spot diameter of 300 μm was finally obtained. In this paper, the automatic slide-pushing technology was applied to the preparation of a monolayer cell smear based on hydrogel membrane, and the optical path of laser focusing and microscopic imaging was established. By using the near-infrared response and a thermal response of hydrogel membrane, the recognition and fixed-point release of nucleated red blood cells were realized, and the efficiency of separation and enrichment of nucleated red blood cells was improved. This technology has a broad application prospect in the field of prenatal screening and diagnosis.
-
Key words:
- cell smear /
- hydrogel /
- prenatal diagnostics /
- near-infrared light response /
- cell release
-
表 1 Performance comparisons between the proposed prototype and Mindray SC-120 automatic pushing-staining machine
Table 1. Performance comparisons between the proposed prototype and Mindray SC-120 automatic pushing-staining machine
Key parameters Mindray SC-120 Proposed prototype Purpose of pushing Standard blood smear Hydrogel-based smear,
releasable blood smearDegree of automation Fully automatic sample loading,
pushing and stainingAutomatic pushing, and manual
sample loading and stainingMode of pushing Backward blood scraping, wetting and
pushing (imitation manual production process)Blood wetting, and direct pushing Parameters of pushing Blood amount, extension time,
scraping angle, pushing speed/angleHydrogel amount, blood amount,
pushing speed/angleSample amount Blood amount: 40−200 μL Hydrogel amount: 200−300 μL
Blood amount: 4−15 μLSpeed range 70−150 mm/s 0−150 mm/s Angle range Detailed parameter reporting not available 20°−50° Mode of parameter adjustment Automatically calculate and adjust the
most matched pushing parameters according
to blood sample HCT and big data algorithmDo experiments in advance according to
the hydrogel viscosity and blood HCT
setting, obtain the optimum parameters
and adjust them by manual programmingPusher substrate Standard medical slide with glass substrate Standard medical slide with glass substrate
or hydrogel substrateModularized platform No Microstructural hydrogel-pushing platform
and blood-pushing platformAutomatic staining Yes No -
[1] WU Q M, ZHOU J. Advances in prenatal screening and prenatal diagnosis for birth defect[J]. Chinese Journal of Birth Health &Heredity, 2011, 19(1): 129-131. (in Chinese) [2] BIAN X M. Practical Prenatal Diagnosis[M]. Beijing: People’s Military Medical Press, 2008. (in Chinese) [3] TABOR A, VESTERGAARD C H F, LIDEGAARD Ø. Fetal loss rate after chorionic villus sampling and amniocentesis: an 11-year national registry study[J]. Ultrasound in Obstetrics &Gynecology, 2009, 34(1): 19-24. [4] HUI L S. Noninvasive approaches to prenatal diagnosis: historical perspective and future directions[J]. Methods in Molecular Biology, 2019, 1885: 45-58. [5] CHEN P J, TENG P C, ZHU Y ZH, et al. Noninvasive prenatal diagnostics: recent developments using circulating fetal nucleated cells[J]. Current Obstetrics and Gynecology Reports, 2019, 8: 1-8. doi: 10.1007/s13669-019-0254-x [6] SMITS G, HOLZGREVE W, HAHN S. An examination of different Percoll density gradients and magnetic activated cell sorting (MACS) for the enrichment of fetal erythroblasts from maternal blood[J]. Archives of Gynecology and Obstetrics, 2000, 263(4): 160-163. doi: 10.1007/s004040050273 [7] LIANG H, CHEN G J, YU Y, et al. Progress in isolation and enrichment of fetal nucleated read blood cells from maternal peripheral blood[J]. Chinese Journal of Cell and Stem Cell (Electronic Edition) , 2018, 8(1): 53-58. (in Chinese) [8] JANSEN M W J C, VON LINDERN M, BEUG H, et al. The use of in vitro expanded erythroid cells in a model system for the isolation of fetal cells from maternal blood[J]. Prenatal Diagnosis, 1999, 19(4): 323-329. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0223(199904)19:4<323::AID-PD534>3.0.CO;2-A [9] ZHANG H M, YANG Y Y, LI X R, et al. Frequency-enhanced transferrin receptor antibody-labelled microfluidic chip (FETAL-Chip) enables efficient enrichment of circulating nucleated red blood cells for non-invasive prenatal diagnosis[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2018, 18(18): 2749-2756. doi: 10.1039/C8LC00650D [10] WU X M, QUAN ZH B. Fundamentals of Clinical Laboratory[M]. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology Press, 2013. (in Chinese) [11] LI L, SCHEIGER J M, LEVKIN P A. Design and applications of photoresponsive hydrogels[J]. Advanced Materials, 2019, 31(26): 1807333. doi: 10.1002/adma.201807333 [12] LV S W, LIU Y, XIE M, et al. Near-infrared light-responsive hydrogel for specific recognition and photothermal site-release of circulating tumor cells[J]. ACS Nano, 2016, 10(6): 6201-6210. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.6b02208 [13] XIA W, YUE B H. Clinical Hematological Examination[M]. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology Press, 2014. (in Chinese) [14] XIAO Z X. Engineering Optical Design[M]. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2003. (in Chinese) [15] MA L, CHEN H J, LEI T, et al. Research on reference ranges of anemia related detection indicators in pregnant period[J]. Laboratory Medicine and Clinic, 2016, 13(1): 6-7, 10. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9455.2016.01.003 [16] HUANG ZH W, FONG CH Y, GAUTHAMAN K, et al. Novel approaches to manipulating foetal cells in the maternal circulation for non-invasive prenatal diagnosis of the unborn child[J]. Journal of Cellular Biochemistry, 2011, 112(6): 1475-1485. doi: 10.1002/jcb.23084 -





 下载:
下载: