-
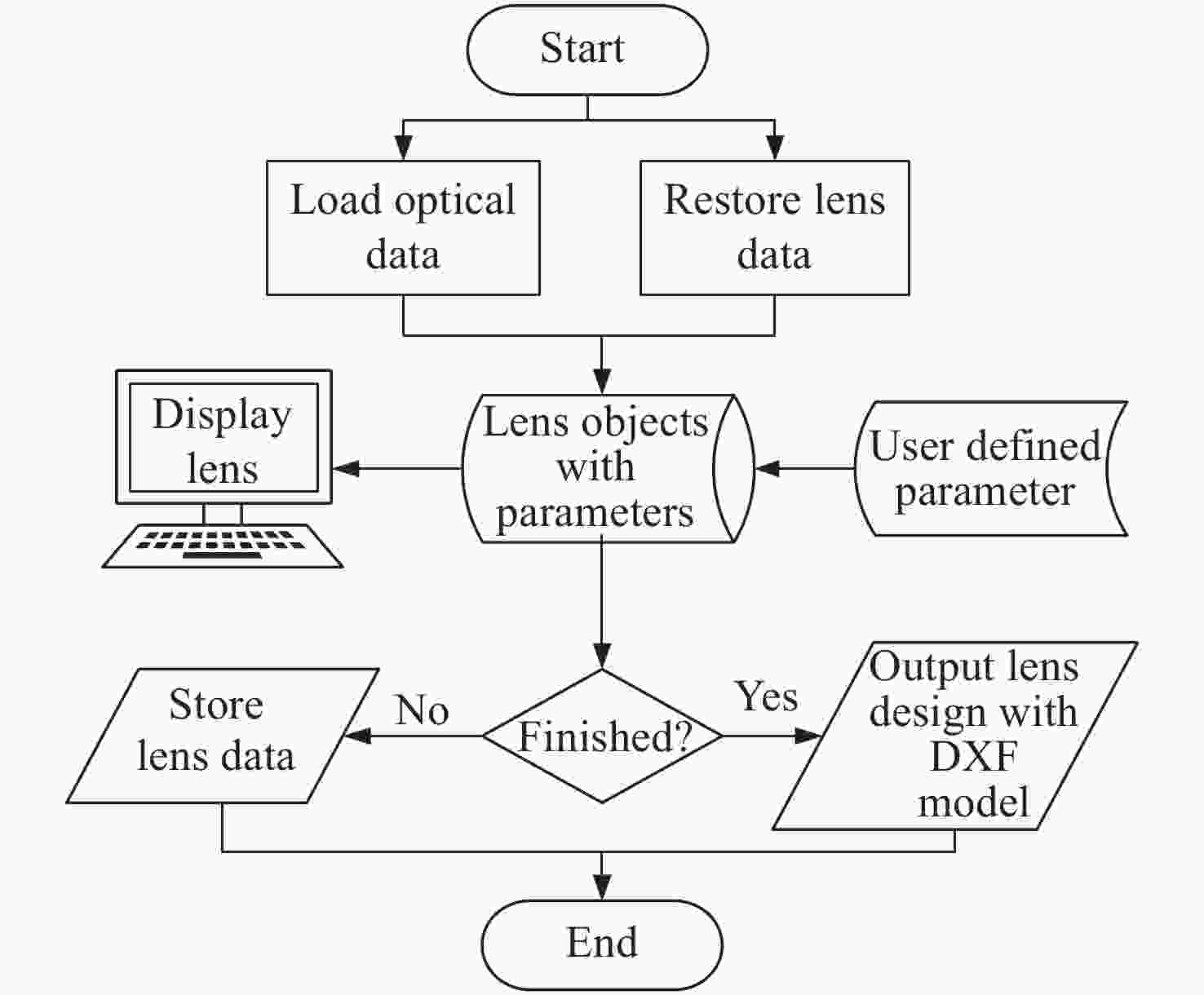
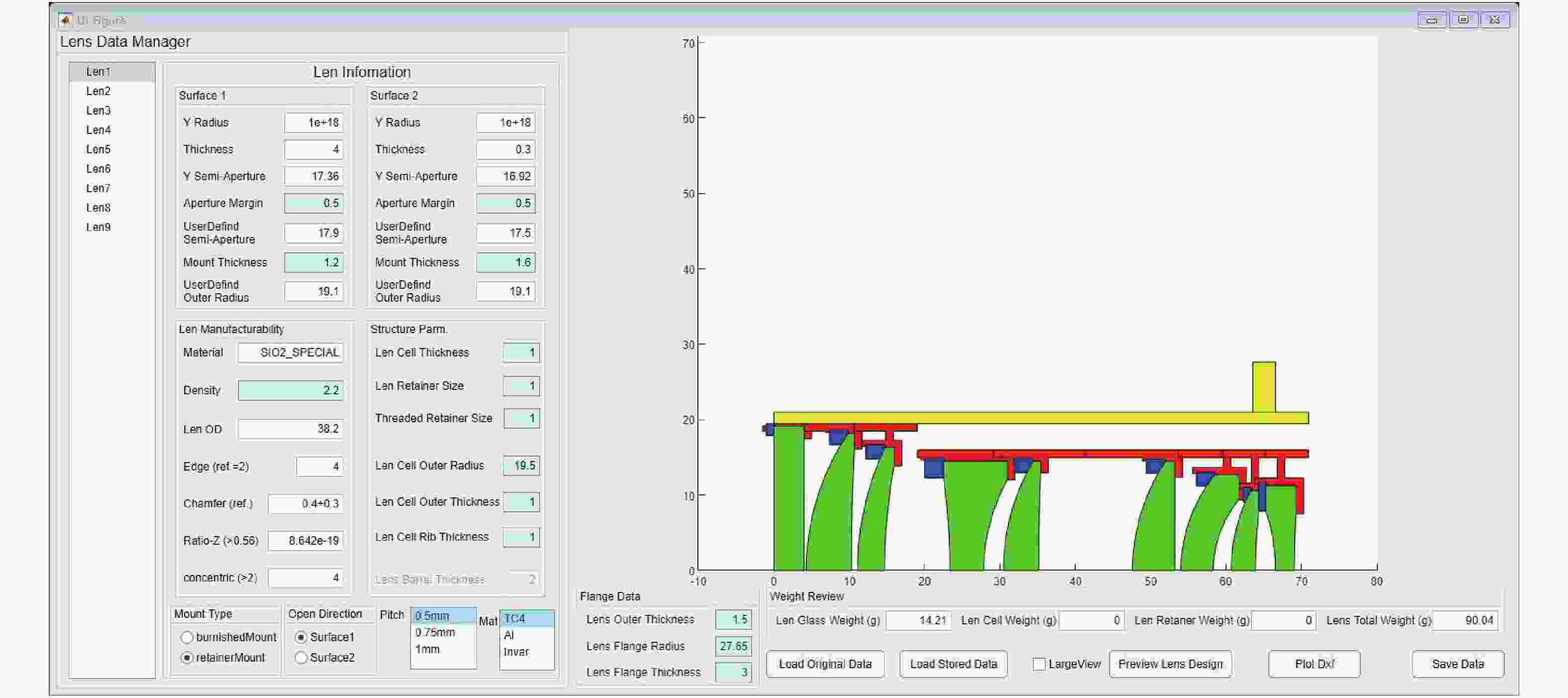
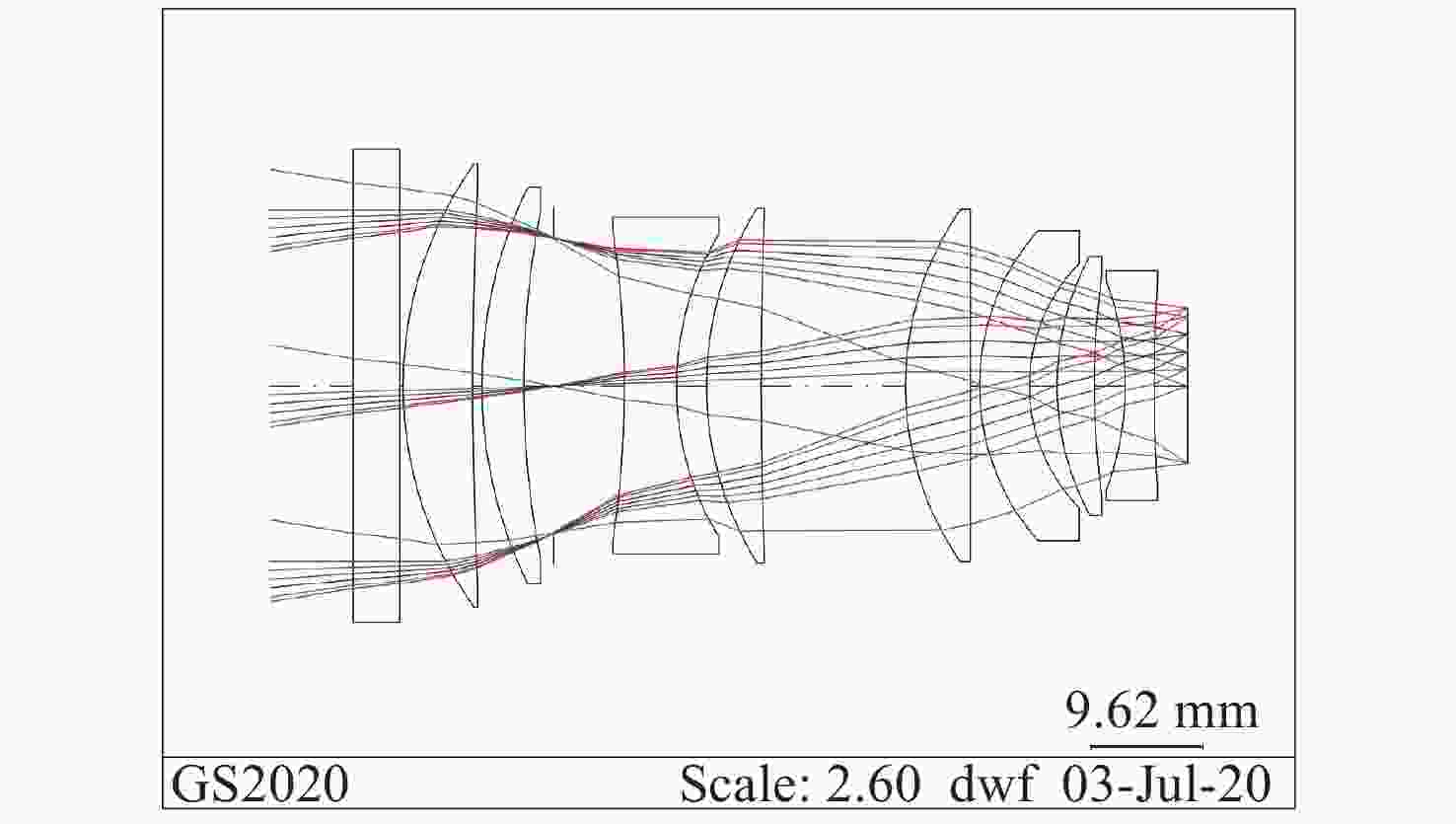
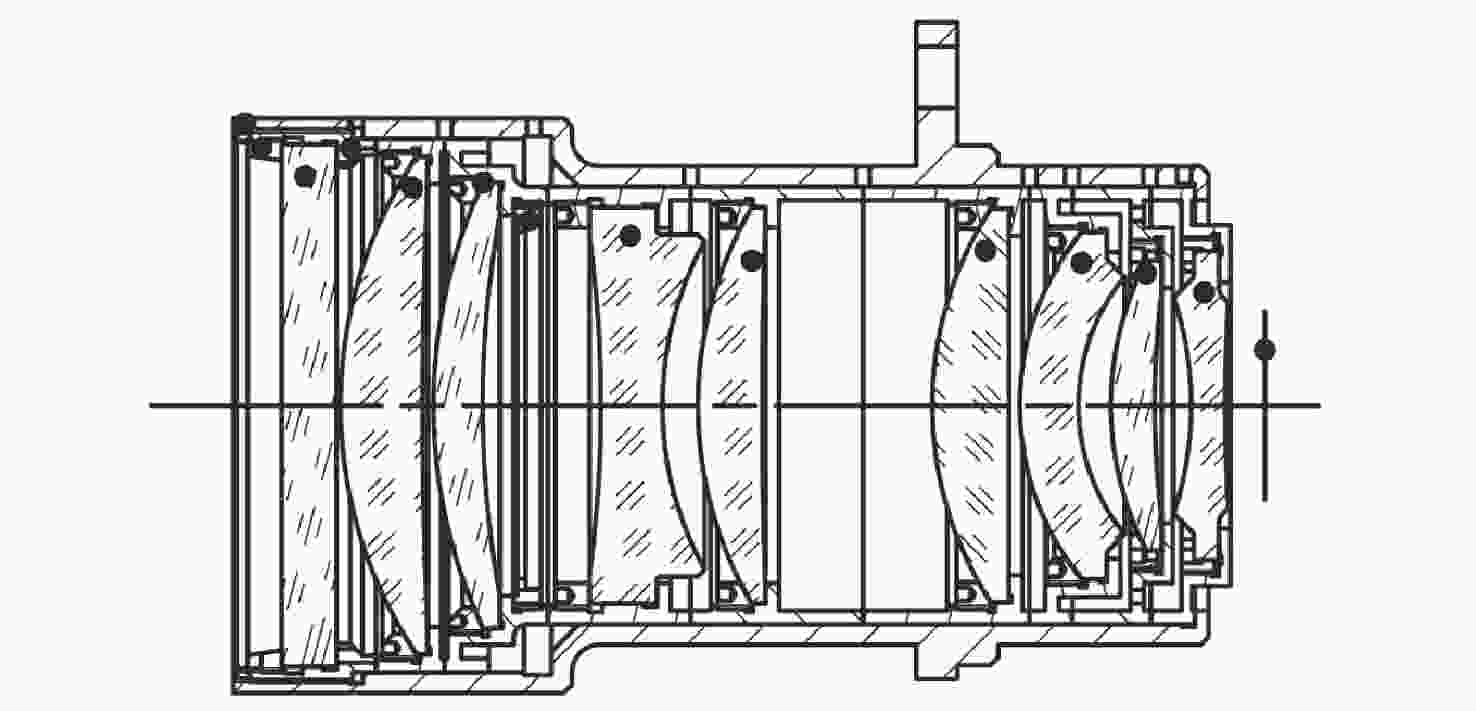
摘要: 为满足星敏镜头的标准化设计需求,建立了基于参数化建模的星敏镜头辅助设计系统,以缩短产品设计周期及提高镜头设计的工艺质量和可靠性。首先,梳理了光学定心取边工艺的星敏镜头结构设计参数及其相互关系,然后基于光学设计输入对镜片设计进行参数化建模,通过实时计算镜片的设计工艺性指标,辅助设计者合理调整透镜设计,将工艺保障落实到设计的全过程;对镜片结构部分进行基于尺寸链的回转体多段线参数化建模,对镜片组件的镜片安装方式、方位、结构尺寸等进行自动设计和图形呈现,替代了人工重复性的设计操作,通过装配图全局设计与镜片组件设计相结合,并实时反馈镜头重量等信息,辅助设计者合理设计空间布局、评估设计结果,从而快速迭代镜头设计。使用结果表明:9片透镜的星敏镜头的装配图设计用时从原来的约15小时降低到约3小时,极大地提高了设计效率,设计的工艺性和可靠性得到保障。本文设计方案满足星敏镜头的标准化设计需求,并为其他精密仪器的参数化建模提供思路。Abstract: In order to meet the requirements of standardized design of star sensor lens, a Computer Aided Design (CAD) system based on parametric modeling was established for star sensor lens to shorten the product design cycle and improve the technological quality and reliability of lens design. At first, the structural design parameters and their interactions of a star sensor lens designed by alignment turning process were confirmed. Then, the parametric modeling of the optical system was carried out on the lens’ design. By calculating the technology indicators of the lens in real time, the designer could adjust the lens design reasonably. The multi-segment parametric modeling for rotation body based on dimension chain was carried out for the lens structure. The installation, location, structure and size of lens components were automatically designed and graphically presented, rather than manually and repetitively designed. By combining the global design of assembly drawing with the design of lens components and giving real-time feedback of lens weight and other information, the designer could design the spatial layout reasonably and evaluate the design result, so as to quickly iterate over the lens design. The application results show that the time for designing the assembly drawing of a 9-in-1 star sensor lens is reduced from original ~15h to ~3h, thereby greatly improving the design efficiency. This system can ensure the design technology and reliability, meet the standardized design requirements of star sensor lens, and provide ideas for the parametric modeling of other precision instruments.
-
Key words:
- parametric modeling /
- computer-aided technology /
- star sensor /
- optimization design
-
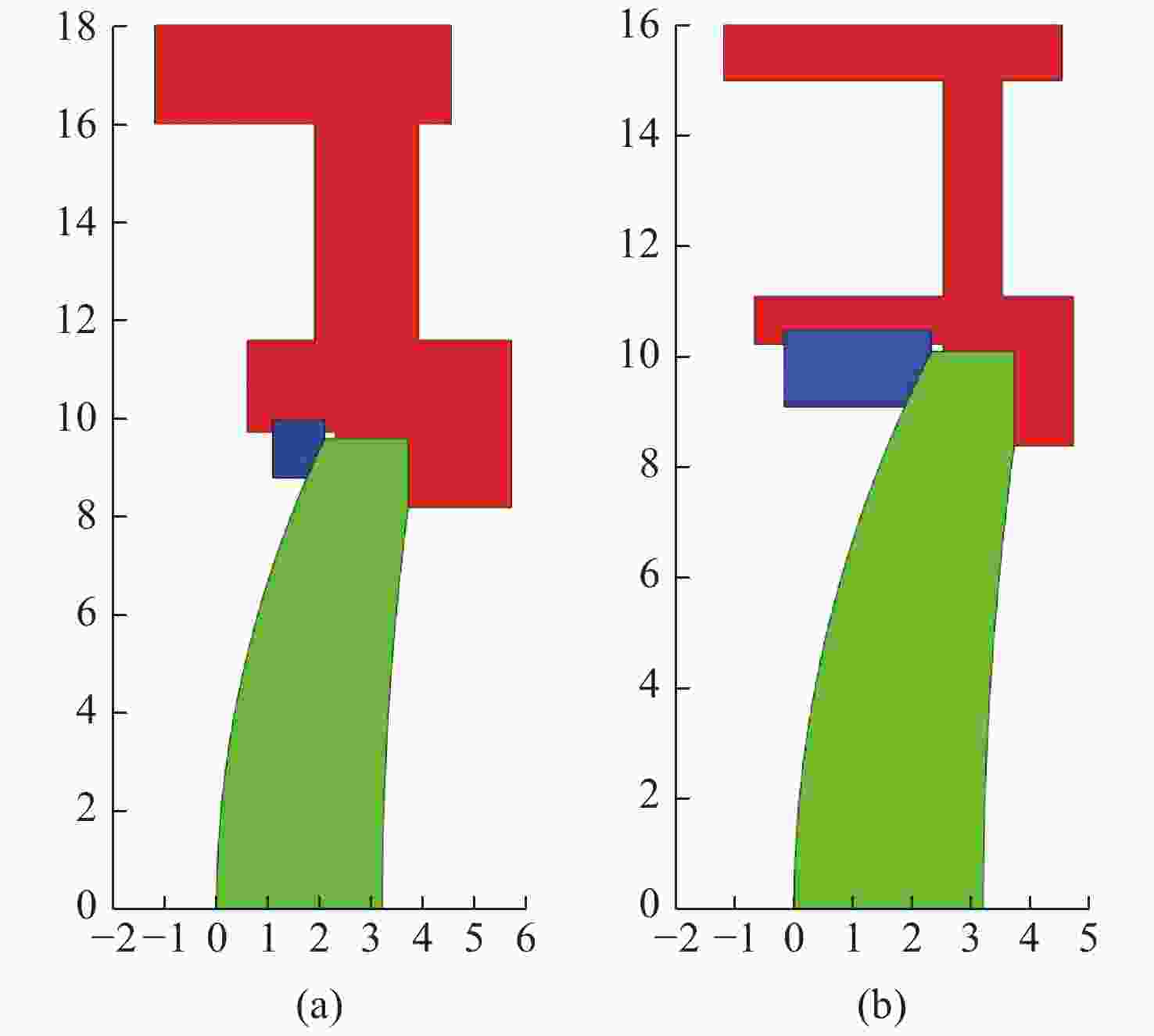
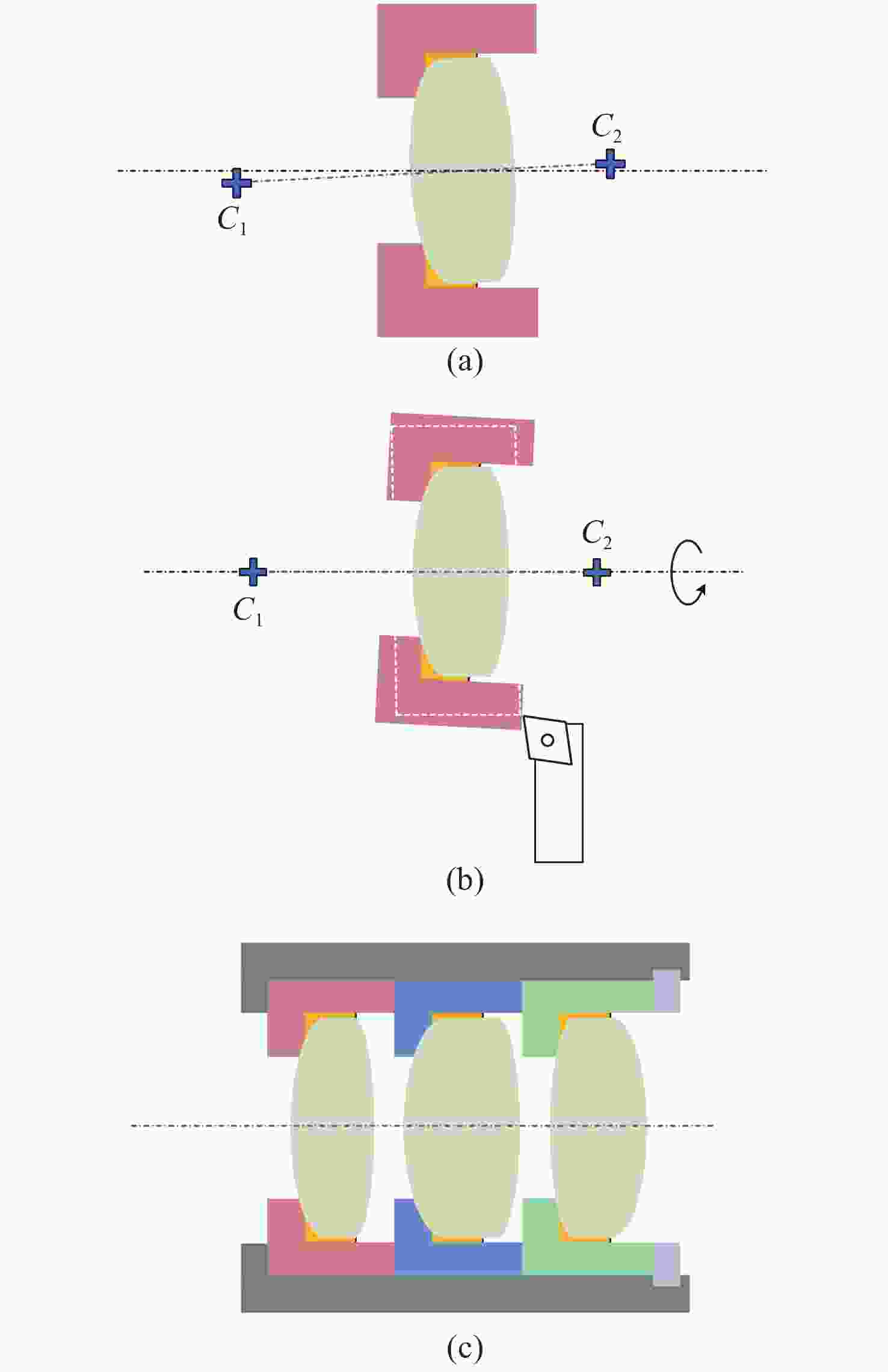
图 1 光学定心取边装调工艺示意图。(a)镜片安装在镜室内成组;(b)调整镜片组件光轴与车床主轴同轴;(c)镜片组件安装在镜筒内。
Figure 1. Framework of alignment turning process. (a) The mounted lens; (b) the mounted lens is positioned so that the optical axis corresponds to the rotation axis of the turning station; (c) the mounted lens is assembled in lens barrel.
表 1 光学零件的设计余量
Table 1. Design margin of optical parts
(mm) 通光口径 外径 最小厚度 辊边安装 压圈安装 正透镜边缘 负透镜中心 3~6 D+0.6 − 0.4 0.6 >6~10 D+0.8 D+1.0 0.6 0.8 >10~18 D+1.0 D+1.5 0.8~1.2 1.0~1.5 >18~30 D+1.5 D+2.0 1.2~1.8 1.5~2.2 >30~50 D+2.0 D+2.5 1.8~2.4 2.2~3.5 >50~80 D+2.5 D+3.0 2.4~3.0 3.5~5.0 >80~120 − D+3.5 3.0~4.0 5.0~8.0 >120~150 − D+4.5 4.0~6.0 8.0~12.0 表 2 工艺性评价方法
Table 2. Process performance evaluation method
名称 工艺评价指标 备注 Z值 >0.56 便于芯取 球心距 >2 mm 同心镜难加工 球面半径与外径比 >0.7 矢高>0.1 mm 表 3 压圈法尺寸参数
Table 3. Design parameters for threaded retainer mounted lens assembly
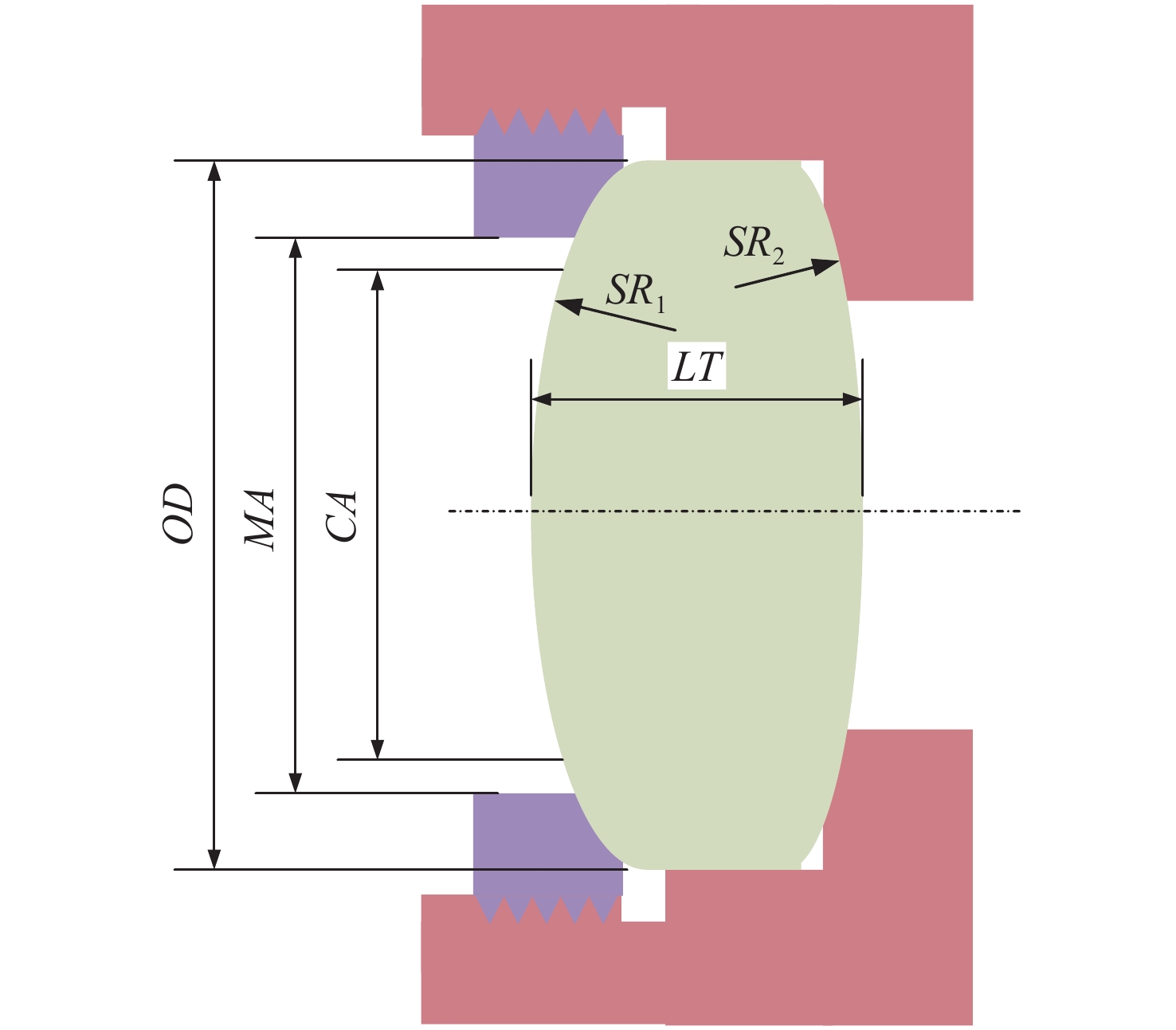
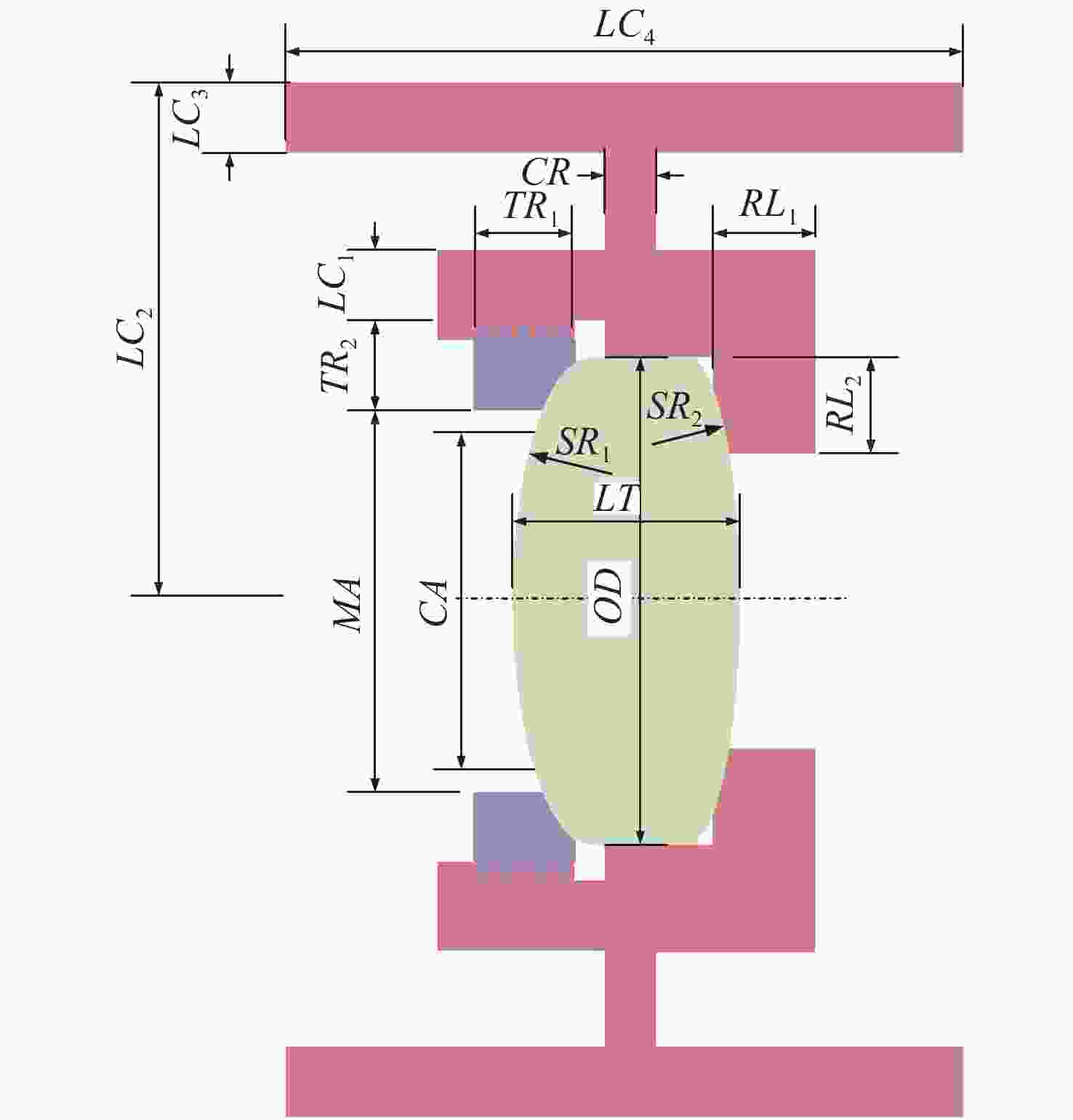
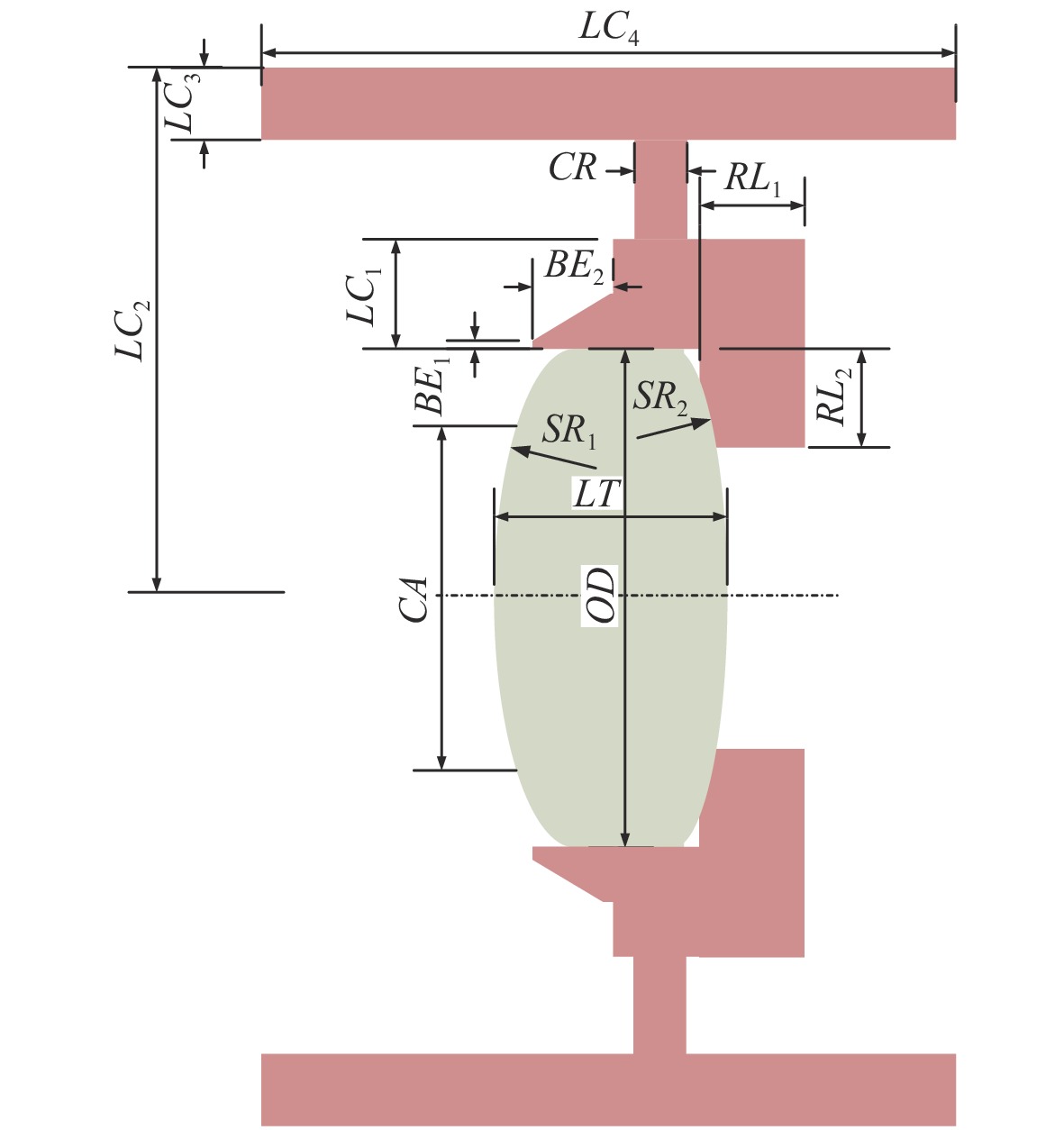
名称 尺寸描述 备注 压圈螺距 压圈螺纹的螺距 TR1 压圈宽度 ≥4~5倍螺距 TR2 压圈壁厚 由螺距和安装面尺寸决定 压圈方向 压圈旋入镜室的方向 RL1 透镜座长度 RL2 透镜座厚度 由安装面尺寸决定 LC1 镜室内环的壁厚 CR 镜室内加强筋宽度 LC2 镜室外圆半径 LC3 镜室外圆厚度 LC4 镜室外圆宽度 由系统布局决定 表 4 辊边法尺寸参数
Table 4. Design parameters for burnished edge mounted lens assembly
名称 尺寸描述 备注 BE1 包边口边缘的厚度 BE2 包边口锥体总高 包边方向 透镜的包边方向 RL1 透镜座长度 RL2 透镜座厚度 由安装面尺寸决定 LC1 镜室内环的壁厚 CR 镜室内加强筋宽度 LC2 镜室外圆半径 LC3 镜室外圆厚度 LC4 镜室外圆宽度 由系统布局决定 表 5 包边口尺寸参考值
Table 5. Dimensions for burnished edge
(mm) 透镜直径 BE1 BE2 ≤6 0.1 1.5 >6~10 0.13 1.5 >10~30 0.18 2 >30~50 0.20 2 -
[1] 马子轩, 李旭阳, 任志广, 等. 大视场超紧凑探测光学系统设计[J]. 光学 精密工程,2020,28(12):2581-2587. doi: 10.37188/OPE.20202812.2581MA Z X, LI X Y, REN ZH G, et al. Design of ultra-compact optical detection system with large field of view[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2020, 28(12): 2581-2587. (in Chinese) doi: 10.37188/OPE.20202812.2581 [2] 张刘, 张若曦, 雷景文, 等. 复合光学导航敏感器[J]. 光学 精密工程,2019,27(12):2534-2541. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20192712.2534ZHANG L, ZHANG R X, LEI J W, et al. Composite optical navigation sensor[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2019, 27(12): 2534-2541. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/OPE.20192712.2534 [3] 宿德志, 王玉良, 吴世永, 等. 基于相似三角形的星图识别[J]. 光学 精密工程,2019,27(11):2467-2473. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20192711.2467SU D ZH, WANG Y L, WU SH Y, et al. Star identification algorithm based on similar triangle principle[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2019, 27(11): 2467-2473. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/OPE.20192711.2467 [4] 王军, 何昕, 魏仲慧, 等. 基于多特征匹配的快速星图识别[J]. 光学 精密工程,2019,27(8):1870-1879. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20192708.1870WANG J, HE X, WEI ZH H, et al. Fast star identification algorithm based on multi-feature matching[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2019, 27(8): 1870-1879. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/OPE.20192708.1870 [5] 王军, 何昕, 魏仲慧, 等. 基于区域滤波的模糊星图复原方法[J]. 中国光学,2019,12(2):321-331. doi: 10.3788/co.20191202.0321WANG J, HE X, WEI ZH H, et al. Restoration method for blurred star images based on region filters[J]. Chinese Optics, 2019, 12(2): 321-331. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/co.20191202.0321 [6] 张洪伟, 丁亚林, 马迎军, 等. 红外双波段双视场成像告警系统设计[J]. 光学 精密工程,2020,28(6):1283-1294. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20202806.1283ZHANG H W, DING Y L, MA Y J, et al. Design of infrared dual-band /dual-FOV imaging early warning system[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2020, 28(6): 1283-1294. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/OPE.20202806.1283 [7] 姜洋, 全向前, 杜杰, 等. 全海深大视场超高清光学系统设计[J]. 光学 精密工程,2019,27(11):2289-2295. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20192711.2289JIANG Y, QUAN X Q, DU J, et al. Design of deep-sea optical imaging system with wide field of view and ultra-high resolution[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2019, 27(11): 2289-2295. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/OPE.20192711.2289 [8] COHAN L E, MILLER D W. Integrated modeling for design of lightweight, active mirrors[J]. Optical Engineering, 2011, 50(6): 063003. doi: 10.1117/1.3592520 [9] STAHL H P. Advanced ultraviolet, optical, and infrared mirror technology development for very large space telescopes[J]. Journal of Astronomical Telescopes,Instruments,and Systems, 2020, 6(2): 025001. [10] 杨劲松. 光学镜头机械结构参数化设计系统的开发[J]. 光学 精密工程,1999,7(6):6-9.YANG J S. A parameter design system for mechanical structure of optical lens[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 1999, 7(6): 6-9. (in Chinese) [11] 姜俊海, 石玉祥. 光学系统计算机辅助设计中镜头结构的特征描述[J]. 精密制造与自动化,2005(4):7-9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-962X.2005.04.002JIANG J H, SHI Y X. Characteristic description of lens structure in computer aided design of optical system[J]. Precise Manufacturing &Automation, 2005(4): 7-9. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-962X.2005.04.002 [12] 任志文, 方俊永, 刘训生. 光学镜头基本结构计算机辅助设计[J]. 光学技术,1999(2):74-76. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-1582.1999.02.009REN ZH W, FANG J Y, LIU X SH. Computer aided deign of lenses structure[J]. Optical Technology, 1999(2): 74-76. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-1582.1999.02.009 -





 下载:
下载: