Development and application of urine biochemical detection system for a disc microfluidic chip
-
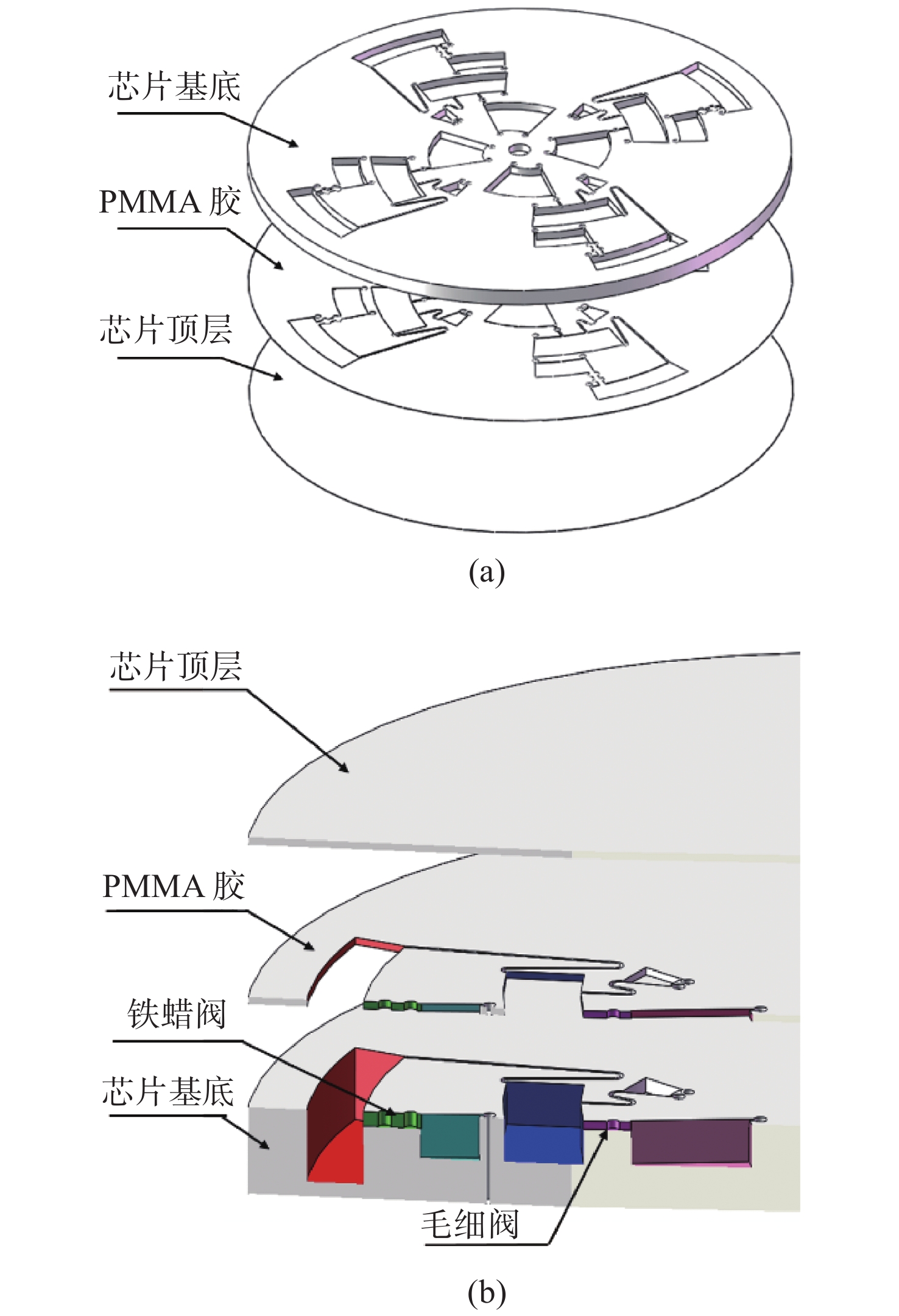
摘要: 针对尿液自动化、快速检测的需求,结合微流控技术与生化分析技术,设计并制备了一种基于离心力驱动的碟式微流控尿液生化检测芯片。该芯片采用微流道与毛细阀、虹吸阀和铁蜡阀结合可实现微量样品和试剂有序输送、混合及检测等集成功能,通过COMSOL多物理场仿真软件对芯片上毛细阀和虹吸阀结构进行仿真分析,优化转速。围绕微流控芯片,研制了一套小型化、全自动尿液生化检测系统。通过双光路设计和双波长检测方法降低光源波动和背景干扰对检测结果的影响,并在该系统上进行尿视黄醇结合蛋白重复性和校准分析。结果显示,该系统的精密度变异系数为1.3%~2.46%,说明系统具有较好的重复性。校准曲线表明浓度和吸光度值有良好的线性相关性(R2=0.995)。芯片上4个相同单元结构可完成多样本或多指标的并行检测,有望应用于尿液蛋白的快速检测。Abstract: In response to the need for the automated and rapid urine detection, microfluidic technology and biochemical analysis technology are adopted to design and fabricate a disc microfluidic chip used for urine biochemical detection. The chip consisted of microfluidic channels, capillary valve, siphon valve and ferrowax valve which can realize the sequential transportation of the sample and reagent, mixing and detection. COMSOL multiphysics software is used to model the structure of capillary valve and siphon valve and optimize the rotary frequency. Next a fully automatic urine biochemical detection system is generated based on a disc microfluidic chip. The effects of light source fluctuations and background interference on test results are reduced by dual optical path and dual wavelength detection. The detection system is characterized by urinary Retinol Binding Protein (RBP). The results demonstrate the Coefficient of Variation (CV) of the system is 1.3%−2.46%, indicating that the system has good repeatability. The calibration curve shows the linear correlation between urinary RBP concentration and the absorbance (R2=0.995). The four identical unit on the chip could perform a multi-sample or multi-parameter detection in parallel, in which it has a potential to be applied for the rapid detection of urinary protein.
-
表 1 芯片检测1 mg/L URBP质控品的吸光度差值
Table 1. Absorbance difference of 1 mg/L URBP quality control product measured by the microfluidic chip
检测次数 ΔA 检测次数 ΔA 1 0.00985 6 0.01014 2 0.01040 7 0.00979 3 0.01036 8 0.00973 4 0.01017 9 0.00985 5 0.00976 10 0.00987 表 2 芯片检测4.3 mg/L URBP质控品的吸光度差值
Table 2. Absorbance difference of 4.3 mg/L URBP quality control product measured by the microfluidic chip
检测次数 ΔA 检测次数 ΔA 1 0.03935 6 0.03814 2 0.03838 7 0.03839 3 0.03912 8 0.03860 4 0.03919 9 0.03784 5 0.03839 10 0.03793 -
[1] 林秉承,秦建华. 微流控芯片实验室[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2006.LIN B CH, QIN J H. Laboratory on a Microfluidic Chip[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2006. (in Chinese) [2] 范建华, 邓永波, 宣明, 等. PC微流控芯片黏结筋与溶剂的协同辅助键合[J]. 光学 精密工程,2015,23(3):708-713. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20152303.0708FAN J H, DENG Y B, XUAN M, et al. Synergistic bonding process of solvent and tendon for PC-based microfluidic chips[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2015, 23(3): 708-713. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/OPE.20152303.0708 [3] KIM C J, PARK J, SUNKARA V, et al. Fully automated, on-site isolation of cfDNA from whole blood for cancer therapy monitoring[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2018, 18(9): 1320-1329. doi: 10.1039/C8LC00165K [4] 王洪, 郑杰, 闫延鹏, 等. 数字微流控芯片上液滴驱动[J]. 光学 精密工程,2020,28(11):2488-2496. doi: 10.37188/OPE.20202811.2488WANG H, ZHENG J, YAN Y P, et al. Drop driving on digital microfluidic chip[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2020, 28(11): 2488-2496. (in Chinese) doi: 10.37188/OPE.20202811.2488 [5] CHEN J G, XU Y CH, YAN H, et al. Sensitive and rapid detection of pathogenic bacteria from urine samples using multiplex recombinase polymerase amplification[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2018, 18(16): 2441-2452. doi: 10.1039/C8LC00399H [6] KIM H O, NA W, YEOM M, et al. Host cell mimic polymersomes for rapid detection of highly pathogenic influenza virus via a viral fusion and cell entry mechanism[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2018, 28(34): 1800960. doi: 10.1002/adfm.201800960 [7] TANG M H, WANG G H, KONG S K, et al. A review of biomedical centrifugal microfluidic platforms[J]. Micromachines, 2016, 7(2): 26. doi: 10.3390/mi7020026 [8] TIAN F, LIU CH, DENG J Q, et al. A fully automated centrifugal microfluidic system for sample-to-answer viral nucleic acid testing[J]. Science China Chemistry, 2020, 63(10): 1498-1506. doi: 10.1007/s11426-020-9800-6 [9] 周武平, 唐玉国, 黎海文, 等. 高通量离心式液滴生成芯片设计[J]. 光学 精密工程,2020,28(12):2636-2645. doi: 10.37188/OPE.20202812.2636ZHOU W P, TANG Y G, LI H W, et al. Design of high throughput droplet generation chip[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2020, 28(12): 2636-2645. (in Chinese) doi: 10.37188/OPE.20202812.2636 [10] WANG Y Y, LIU SH Y, ZHANG T K, et al. A centrifugal microfluidic pressure regulator scheme for continuous concentration control in droplet-based microreactors[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2019, 19(22): 3870-3879. doi: 10.1039/C9LC00631A [11] 周文超, 吴一辉, 郝鹏, 等. 全血微流控芯片的高灵敏度多参数光探测[J]. 光学 精密工程,2013,21(11):2821-2828. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20132111.2821ZHOU W CH, WU Y H, HAO F, et al. Highly sensitive and multi-parameter optical detection for whole blood on centrifugal microfluidic chip[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2013, 21(11): 2821-2828. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/OPE.20132111.2821 [12] 徐刚. 尿蛋白与尿肌酐的比值、β2微球蛋白及视黄醇结合蛋白联合检测对糖尿病肾病的早期诊断价值[J]. 实用临床医药杂志,2020,24(21):86-89.XU G. Value of combined detection of urinary albumin-to-creatinine ratio, β2 microglobulin and retinol binding protein in early diagnosis of diabetic nephropathy[J]. Journal of Clinical Medicine in Practice, 2020, 24(21): 86-89. (in Chinese) [13] 杜亚琴, 张文松, 牟俊杰, 等. 胱抑素C、β2微球蛋白和视黄醇结合蛋白的测定在评估慢性肾脏疾病损害程度中的应用[J]. 西部医学,2021,33(2):231-234.DU Y Q, ZHANG W S, MOU J J, et al. Feasibility of the determination of cystatin C, β2 microglobulin and retinol binding protein in the assessment of renal damage in chronic kidney disease[J]. Medical Journal of West China, 2021, 33(2): 231-234. (in Chinese) [14] 俞俊文, 刘献文. 尿RBP胶乳增强免疫比浊检测方法的建立及性能评价[J]. 国际检验医学杂志,2016,37(17):2481-2483.YU J W, LIU X W. Establishment and performance evaluation of urine RBP latex enhanced immunoturbidity detection method[J]. International Journal of Laboratory Medicine, 2016, 37(17): 2481-2483. (in Chinese) [15] 方亮, 王芬, 刘献文, 等. 血清和尿液中黄醇结合蛋白胶乳增强免疫比浊试剂盒的制备及性能评价[J]. 国际检验医学杂志,2018,39(1):103-106.FANG L, WANG F, LIU X W, et al. Preparation and performance evaluation of xanthol-binding protein latex immunoturbidimetry enhancement kit in serum and urine[J]. International Journal of Laboratory Medicine, 2018, 39(1): 103-106. (in Chinese) [16] PARK J M, CHO Y K, LEE B S, et al. Multifunctional microvalves control by optical illumination on nanoheaters and its application in centrifugal microfluidic devices[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2007, 7(5): 557-564. doi: 10.1039/b616112j [17] NAGHDLOO A, GHAZIMIRSAEED E, SHAMLOO A. Numerical simulation of mixing and heat transfer in an integrated centrifugal microfluidic system for nested-PCR amplification and gene detection[J]. Sensors and Actuators B:Chemical, 2019, 283: 831-841. doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2018.12.084 [18] 李昌厚. 紫外可见分光光度计[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2005.LI CH H. Ultraviolet/Visible Spectrometer[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2005. (in Chinese) -






 下载:
下载: