Dynamical optical beam produced in rotational metasurface based on coherent spin hall effect
doi: 10.37188/CO.2021-0097
-
摘要: 基于光子的自旋霍尔效应,超表面可用于光束的产生和控制。本文基于旋转变换利用一维纳米孔链设计了二维纳米孔旋转对称超表面。利用此样品,可以由左旋圆偏振(LCP)和右旋圆偏振(RCP)光的自旋霍尔效应同时产生贝塞尔光束。利用线偏振光激发,通过控制两个圆偏振光激发光束之间的相干干涉可动态调控贝塞尔光束的强度和偏振。同时,此方法还具有宽带调制的优点。Abstract: Based on the spin Hall effect of photons, a metasurface can be used to generate and control light beams. In this paper, by means of one-dimensional chains of nanohole, a metasurface with rotational symmetry is designed. The Bessel beam can be produced by the spin Hall effect of Left-handed Circularly Polarized (LCP) and Right-handed Circularly Polarized (RCP) light simultaneously. Through the excitation of linearly polarized light, we can dynamically control the intensity and polarization of Bessel beam by controlling the coherent interference between two circularly polarized light excitation beams. At the same time, this method has the advantage of broadband modulation range.
-
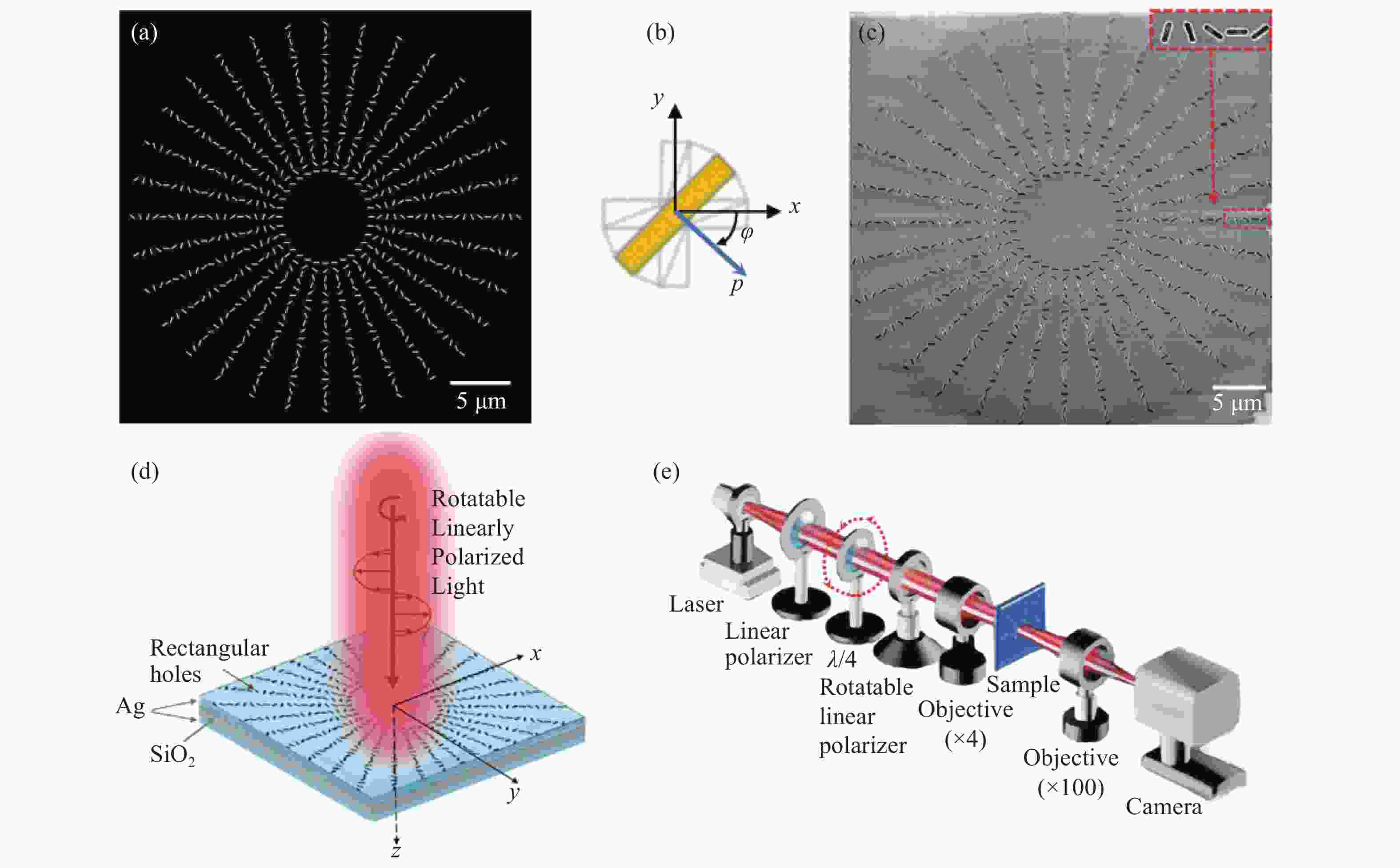
Figure 1. (a) Schematic of designed metasurface from the rotated chains of the nanohole arrays; (b) designed nanohole with configuration angle φ; (c) sample picture of the rotated metasurface fabricated by a focused ion beam; (d) illuminating rotated metasurface with a circularly polarized laser beam; (e) Optical experiment setup
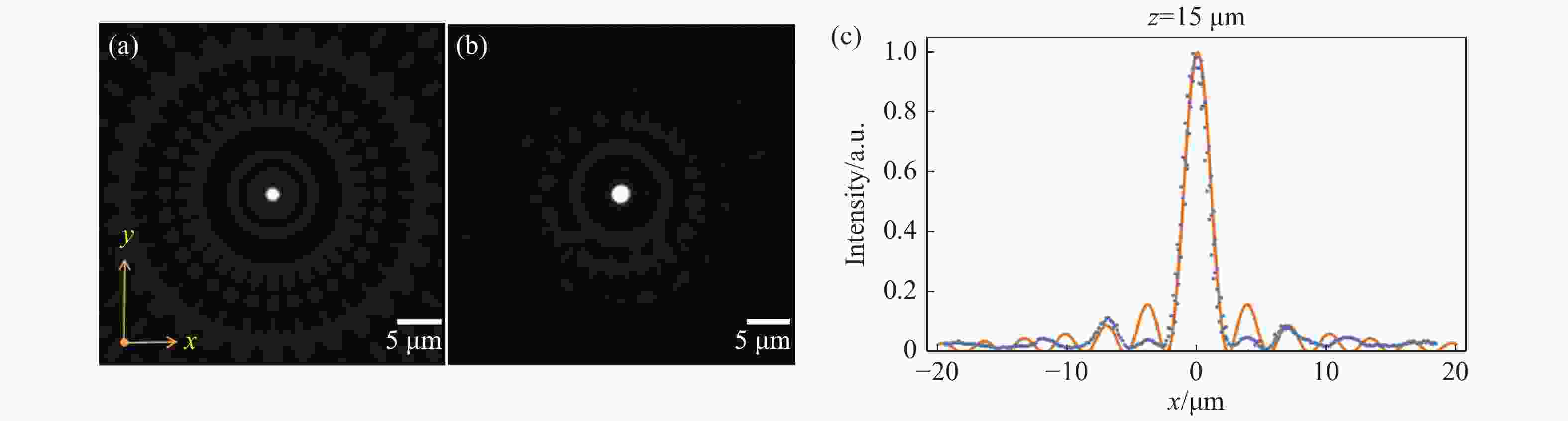
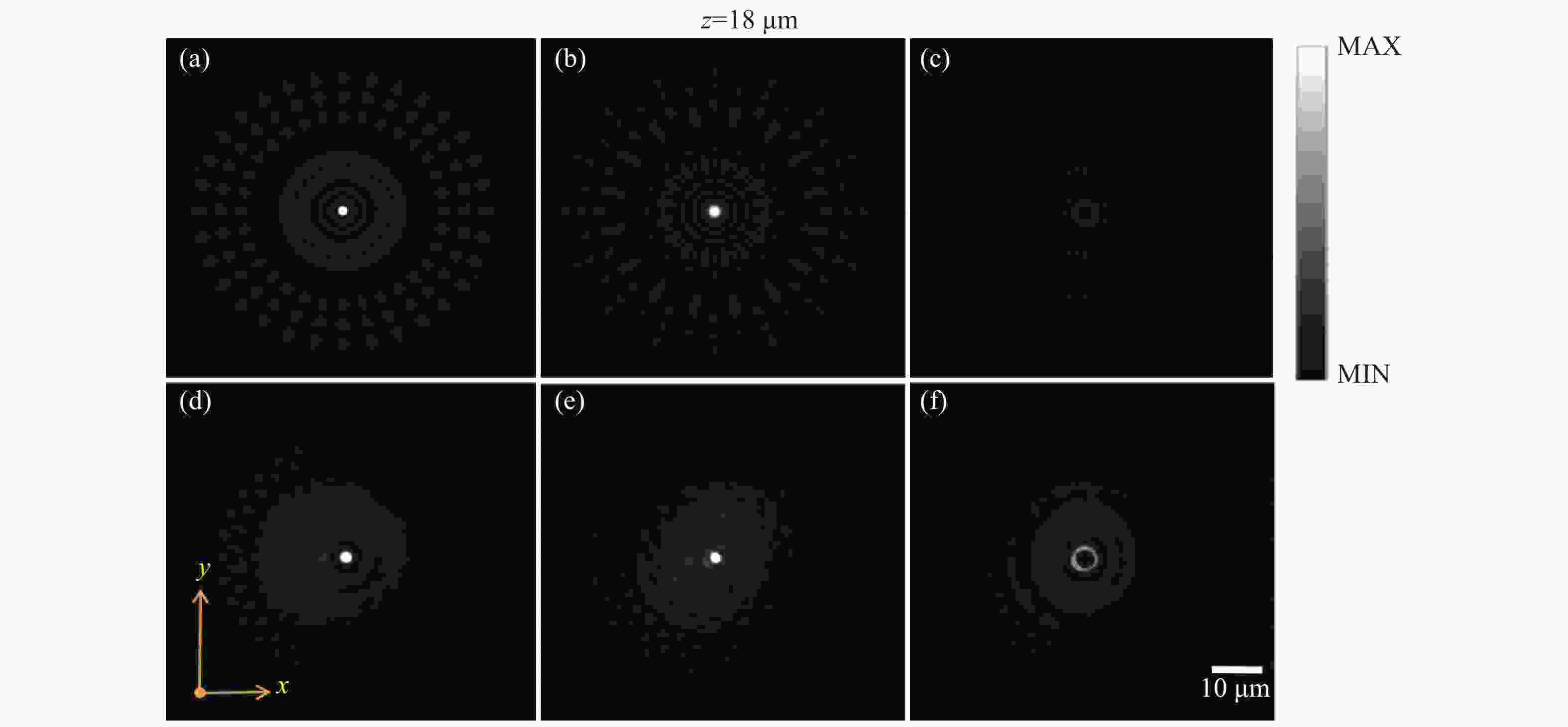
Figure 2. Beam spot profile at z=15 μm produced by the rotated metasurface illuminated by circularly polarized incident light. (a) From theoretical calculation; (b) from experimental measurement; (c) intensity distribution curves of beam spot along a central line (blue dots: from measurement; orange curve: from calculation)
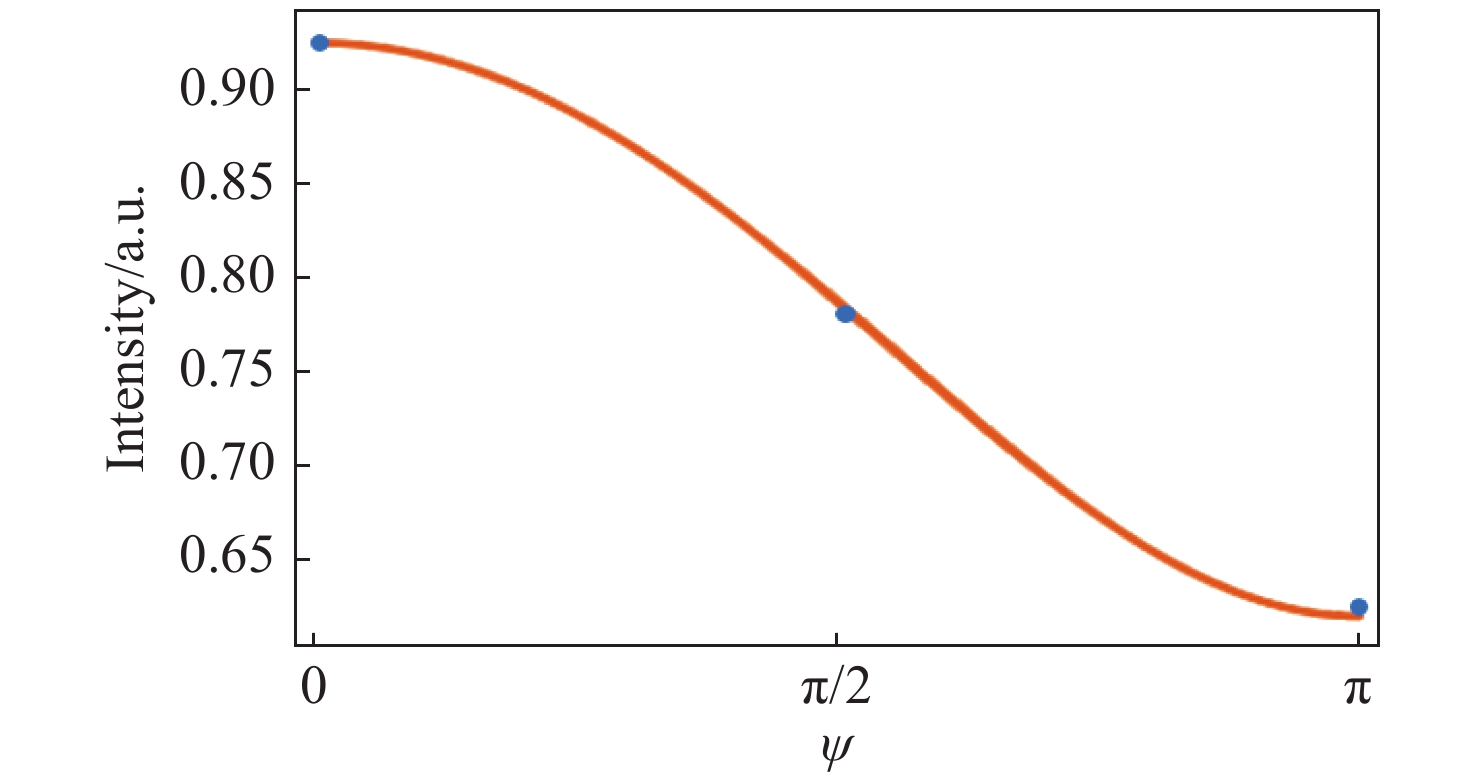
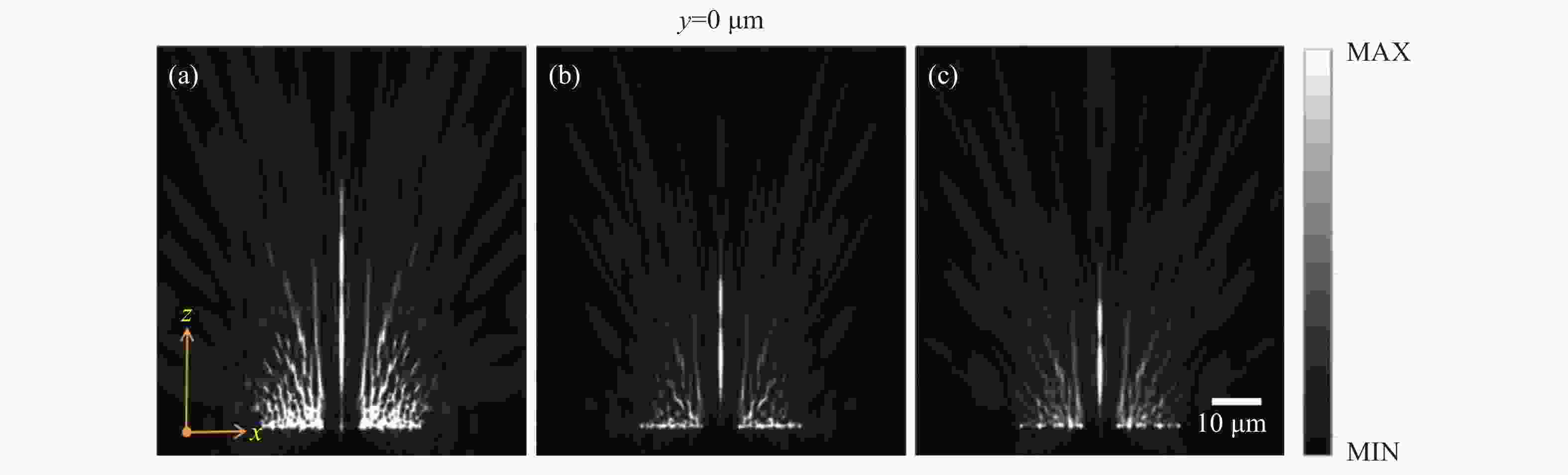
Figure 5. Detecting the polarization state of the output beam spot from rotated metasurface with linearly polarized light. A polarizer is put in front of the sample and an analyzer is put behind the sample. (a, c) the analyzer is parallel to polarizer; (b, d) the analyzer is perpendicular to the polarizer
-
[1] ANANDAN J. The geometric phase[J]. Nature, 1992, 360(6402): 307-313. doi: 10.1038/360307a0 [2] PANCHARATNAM S. Generalized theory of interference, and its applications[J]. Proceedings of the Indian Academy of Sciences - Section A, 1956, 44(5): 247-262. doi: 10.1007/BF03046050 [3] GARCÉS-CHÁVEZ V, MCGLOIN D, MELVILLE H, et al. Simultaneous micromanipulation in multiple planes using a self-reconstructing light beam[J]. Nature, 2002, 419(6903): 145-147. doi: 10.1038/nature01007 [4] YU N F, CAPASSO F. Flat optics with designer metasurfaces[J]. Nature Materials, 2014, 13(2): 139-150. doi: 10.1038/nmat3839 [5] LUO X G. Principles of electromagnetic waves in metasurfaces[J]. Science China Physics,Mechanics &Astronomy, 2015, 58(9): 594201. [6] PU M B, LI X, MA X L, et al. Catenary optics for achromatic generation of perfect optical angular momentum[J]. Science Advances, 2015, 1(9): e1500396. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.1500396 [7] GUO Y H, WANG Y Q, PU M B, et al. Dispersion management of anisotropic metamirror for super-octave bandwidth polarization conversion[J]. Scientific Reports, 2015, 5: 8434. doi: 10.1038/srep08434 [8] GAO H, PU M B, LI X, et al. Super-resolution imaging with a Bessel lens realized by a geometric metasurface[J]. Optics Express, 2017, 25(12): 13933-13943. doi: 10.1364/OE.25.013933 [9] SIVILOGLOU G A, CHRISTODOULIDES D N. Accelerating finite energy Airy beams[J]. Optics Letters, 2007, 32(8): 979-981. doi: 10.1364/OL.32.000979 [10] SIVILOGLOU G A, BROKY J, DOGARIU A, et al. Observation of accelerating airy beams[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2007, 99(21): 213901. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.99.213901 [11] ZHANG P, HU Y, LI T C, et al. Nonparaxial mathieu and weber accelerating beams[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2012, 109(19): 193901. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.109.193901 [12] ALEAHMAD P, MIRI M A, MILLS M S, et al. Fully vectorial accelerating diffraction-free helmholtz Beams[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2012, 109(20): 203902. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.109.203902 [13] KAMINER I, BEKENSTEIN R, NEMIROVSKY J, et al. Nondiffracting accelerating wave packets of Maxwell's equations[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2012, 108(16): 163901. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.108.163901 [14] CHONG A, RENNINGER W H, CHRISTODOULIDES D N, et al. Airy-Bessel wave packets as versatile linear light bullets[J]. Nature Photonics, 2010, 4(2): 103-106. doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2009.264 [15] BOUCHAL Z, OLIVIK M. Non-diffractive vector bessel beams[J]. Journal of Modern Optics, 1995, 42(8): 1555-1566. doi: 10.1080/09500349514551361 [16] PFEIFFER C, GRBIC A. Controlling vector Bessel Beams with metasurfaces[J]. Physical Review Applied, 2014, 2(4): 044012. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevApplied.2.044012 [17] MORENO I, DAVIS J A, SÁNCHEZ-LÓPEZ M M, et al. Nondiffracting Bessel beams with polarization state that varies with propagation distance[J]. Optics Letters, 2015, 40(23): 5451-5454. doi: 10.1364/OL.40.005451 [18] DAVIS J A, MORENO I, BADHAM K, et al. Nondiffracting vector beams where the charge and the polarization state vary with propagation distance[J]. Optics Letters, 2016, 41(10): 2270-2273. doi: 10.1364/OL.41.002270 [19] WU G F, WANG F, CAI Y J. Generation and self-healing of a radially polarized Bessel-Gauss beam[J]. Physical Review A, 2014, 89(4): 043807. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.89.043807 [20] GENEVET P, WINTZ D, AMBROSIO A, et al. Controlled steering of Cherenkov surface plasmon wakes with a one-dimensional metamaterial[J]. Nature Nanotechnology, 2015, 10(9): 804-809. doi: 10.1038/nnano.2015.137 [21] ZHONG F, LI J, LIU H, et al. Controlling surface plasmons through covariant transformation of the spin-dependent geometric phase between curved metamaterials[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2018, 120(24): 243901. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.120.243901 [22] XIAO SH Y, ZHONG F, LIU H, et al. Flexible coherent control of plasmonic spin-Hall effect[J]. Nature Communications, 2015, 6: 8360. doi: 10.1038/ncomms9360 [23] CAI B G, LI Y B, JIANG W X, et al. Generation of spatial Bessel beams using holographic metasurface[J]. Optics Express, 2015, 23(6): 7593-7601. doi: 10.1364/OE.23.007593 [24] COURTIAL J. Wave plates and the Pancharatnam phase[J]. Optics Communications, 1999, 171(4-6): 179-183. doi: 10.1016/S0030-4018(99)00473-3 [25] HUANG L L, CHEN X ZH, MÜHLENBERND H, et al. Dispersionless phase discontinuities for controlling light propagation[J]. Nano Letters, 2012, 12(11): 5750-5755. doi: 10.1021/nl303031j -





 下载:
下载: