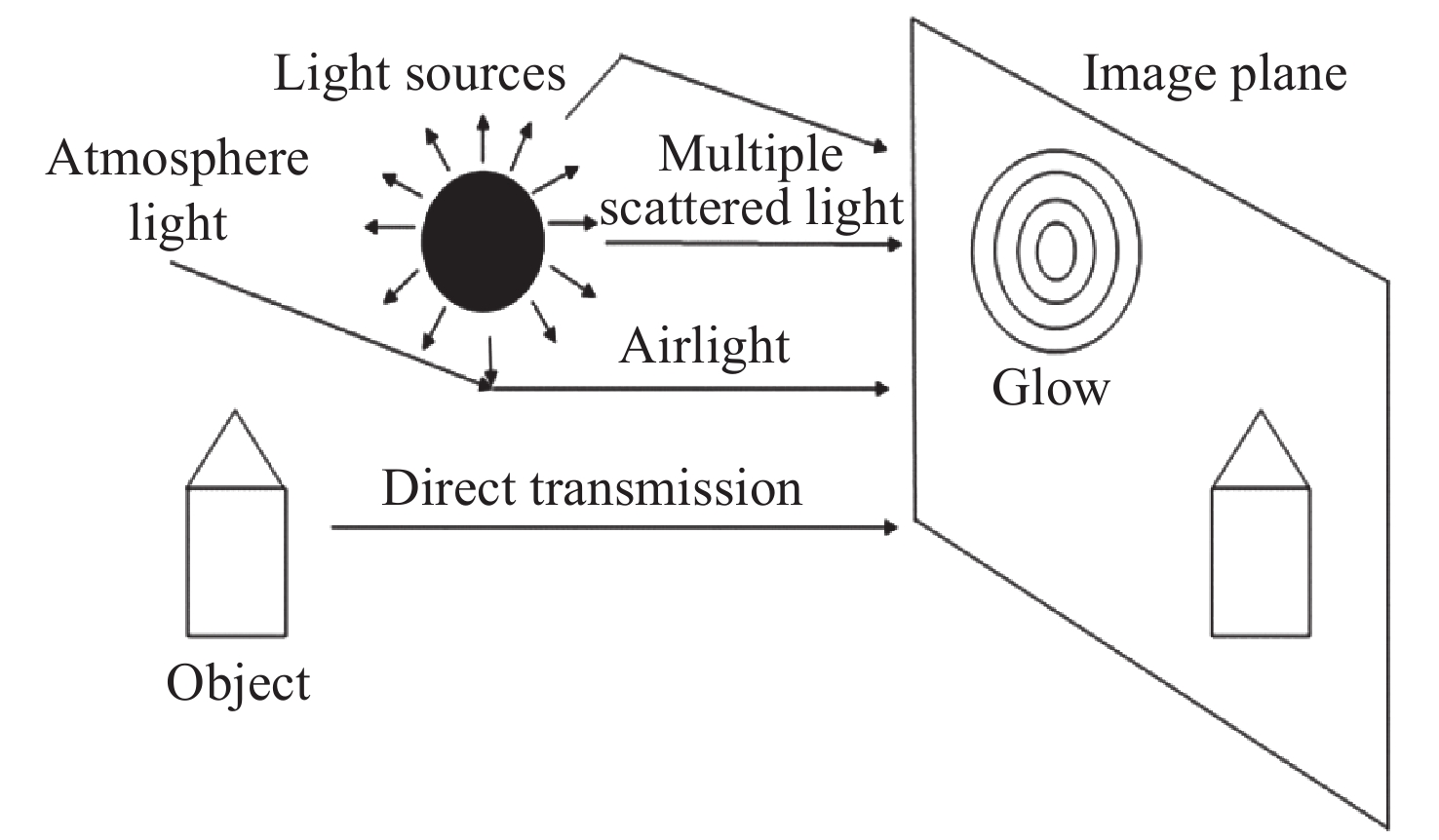
Nighttime image dehazing with a new light segmentation method and a linear image depth estimation model
-
摘要: 夜间有雾图像通常具有对比度低、光照不均匀、颜色偏移以及噪声较多等现象,这些退化现象使得夜间图像去雾具有极大的挑战性。针对夜间图像存在的退化问题,本文提出了一种能够在夜间图像中有效去雾并提高图像质量的方法。首先,将图像分解成光晕层和有雾层,并对有雾层进行颜色校正。其次,通过一种新提出的带有伽马变换的图像光源分割方法来分割光源,并设置分割阈值作为像素点属于光源区域的概率值。然后,将得到的概率值与最大反射先验相结合来估计光源和非光源区域的大气光值。最后,根据图像深度与亮度、饱和度以及梯度之间的关系建立线性模型,进一步估计透射率的值。实验得到的分割阈值为0.07,线性深度估计参数分别为1.0267、−0.5966、0.6735、0.004135。实验结果表明本文方法在夜间图像去雾、消除光晕、减少噪声,以及提高可视度方面取得良好的效果。Abstract: Image with the scene of haze at night has low contrast, non-uniform illumination, color cast and significant noise. These cause nighttime haze removal from single image to be problematic and challenging. In this paper, we put forward a method that can remove nighttime haze from images and improve image quality. The input image is first decomposed into a glow layer and a haze layer with a modified color channel transformation for glow artifacts and color correction. A new light segmentation function is proposed next by using gamma correction of the channel difference and setting the threshold levels as the probability of a pixel belonging to a light source region. Then we estimate the ambient illuminance map by combining the maximum reflectance prior value with the aforementioned probability and computing the atmospheric light in the light and non-light regions. Finally, we establish a novel linear model to build the connection between the image depth map and three image features including luminance, saturation and gradient map for the light source regions while using the dark channel prior for the non-light source regions. The result of the light segmentation is 0.07, and the parameters of the linear depth estimation are 1.0267, −0.5966, 0.6735 and 0.004135. Experimental results show the proposed method is reliable for removing nighttime haze and glow of active light sources, reducing significant noise and improving visibility.
-
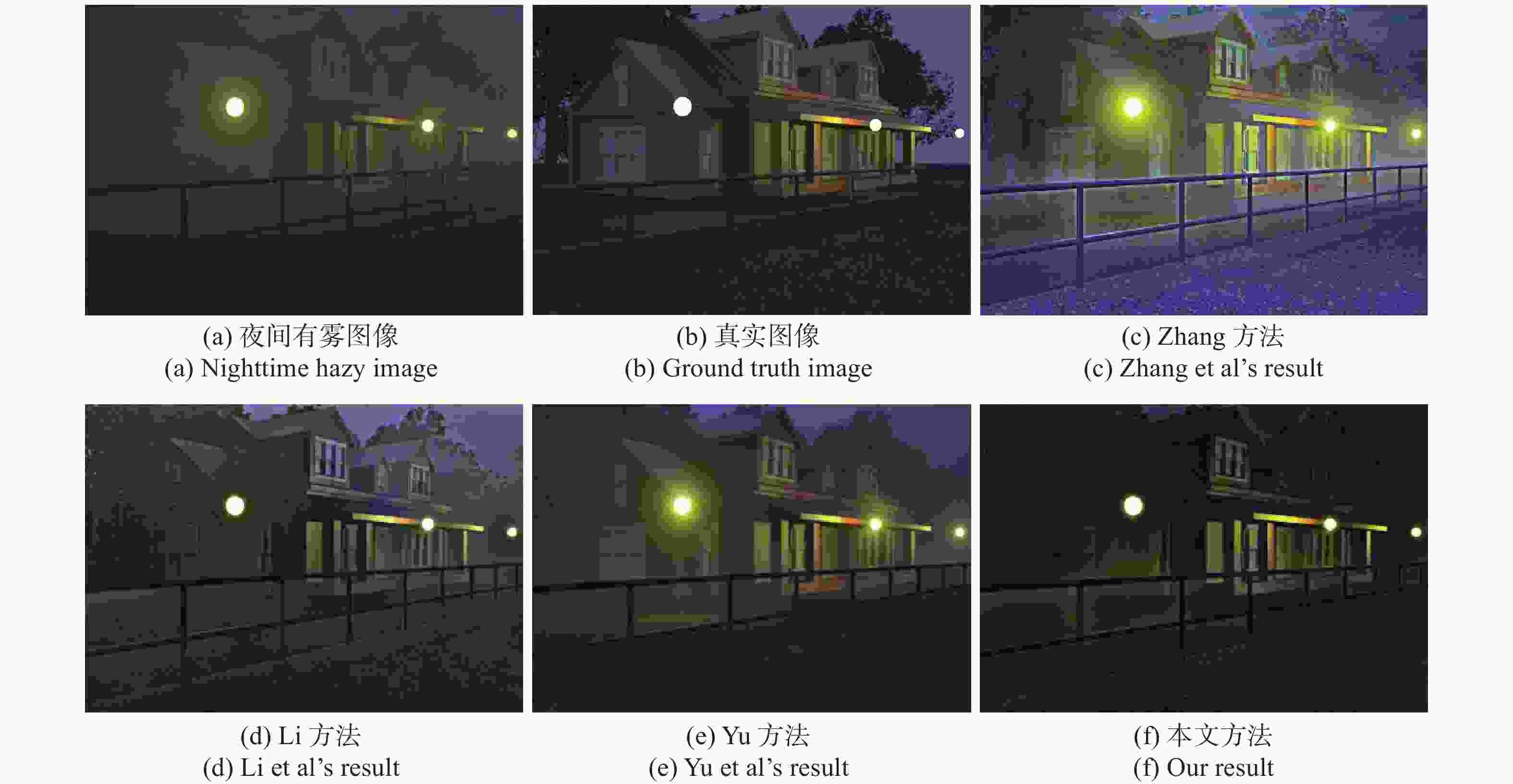
表 1 图像质量评价数据表
Table 1. The values of image quality assessment
Quality assessment Zhang et al Li et al Yu et al Ours e 26.7448 32.1134 23.2590 33.6594 IVM 8.0512 8.8646 7.2399 10.0275 SSIM 0.5557 0.7234 0.7520 0.7761 CG 0.3854 0.3991 0.3159 0.6566 VCM 43.6667 25.6667 56.0000 59.8333 PSNR 17.5994 20.2104 21.5560 21.8774 -
[1] 刘坤, 毕笃彦, 王世平, 等. 基于稀疏特征提取的单幅图像去雾[J]. 光学学报,2018,38(3):0310001. doi: 10.3788/AOS201838.0310001LIU K, BI D Y, WANG SH P, et al. Single image dehazing based on sparse feature extraction[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2018, 38(3): 0310001. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/AOS201838.0310001 [2] 韩昊男, 钱锋, 吕建威, 等. 改进暗通道先验的航空图像去雾[J]. 光学 精密工程,2020,28(6):1387-1394. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20202806.1387HAN H N, QIAN F, LV J W, et al. Aerial image dehazing using improved dark channel prior[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2020, 28(6): 1387-1394. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/OPE.20202806.1387 [3] 邓莉. 针对明亮区域的自适应全局暗原色先验去雾[J]. 光学 精密工程,2016,24(4):892-901. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20162404.0892DENG L. Adaptive image dehazing for bright areas based on global dark channel prior[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2016, 24(4): 892-901. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/OPE.20162404.0892 [4] ANCUTI C O, ANCUTI C, DE VLEESCHOUWER C, et al. Color channel transfer for image dehazing[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2019, 26(9): 1413-1417. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2019.2932189 [5] LI M D, LIU J Y, YANG W H, et al. Structure-revealing low-light image enhancement via robust retinex model[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2018, 27(6): 2828-2841. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2018.2810539 [6] NARASIMHAN S G, NAYAR S K. Shedding light on the weather[C]. Proceedings of 2013 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE, 2003. [7] HE K M, SUN J, TANG X O. Single image haze removal using dark channel prior[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2011, 33(12): 2341-2353. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2010.168 [8] TAN R T. Visibility in bad weather from a single image[C]. Proceedings of 2008 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE, 2008. [9] ANCUTI C O, ANCUTI C. Single image dehazing by multi-scale fusion[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2013, 22(8): 3271-3282. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2013.2262284 [10] MENG G F, WANG Y, DUAN J Y. Efficient image dehazing with boundary constraint and contextual regularization[C]. Proceedings of 2013 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, IEEE, 2013. [11] GUO X J, LI Y, LING H B. LIME: low-light image enhancement via illumination map estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2017, 26(2): 982-993. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2016.2639450 [12] PEI S C, LEE T Y. Nighttime haze removal using color transfer pre-processing and dark channel prior[C]. Proceedings of 2012 19th IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, IEEE, 2012. [13] ZHANG J, CAO Y, WANG Z F. Nighttime haze removal based on a new imaging model[C]. Proceedings of 2014 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, IEEE, 2014. [14] LI Y, TAN R T, BROWN M S. Nighttime haze removal with glow and multiple light colors[C]. Proceedings of 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, IEEE, 2015. [15] LI Y, BROWN M S. Single image layer separation using relative smoothness[C]. Proceedings of 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE, 2014. [16] 杨爱萍, 白煌煌. 基于Retinex理论和暗通道先验的夜间图像去雾算法[J]. 激光与光电子学进展,2017,54(4):041002.YANG A P, BAI H H. Nighttime image defogging based on the theory of Retinex and dark channel prior[J]. Laser &Optoelectronics Progress, 2017, 54(4): 041002. (in Chinese) [17] ZHANG J, CAO Y, FANG SH, et al.. Fast haze removal for nighttime image using maximum reflectance prior[C]. Proceedings of 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE, 2017. [18] YU T, SONG K, MIAO P, et al. Nighttime single image dehazing via pixel-wise alpha blending[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 114619-114630. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2936049 [19] YANG M M, LIU J CH, LI ZH G. Superpixel-based single nighttime image haze removal[J]. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2018, 20(11): 3008-3018. doi: 10.1109/TMM.2018.2820327 [20] XU L, ZHENG SH CH, JIA J Y. Unnatural L0 sparse representation for natural image deblurring[C]. Proceedings of 2013 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE, 2013. [21] BUCHSBAUM G. A spatial processor model for object colour perception[J]. Journal of the Franklin Institute, 1980, 310(1): 1-26. doi: 10.1016/0016-0032(80)90058-7 [22] GAO C, WANG Z, XU Y, et al. The von kries chromatic adaptation transform and its generalization[J]. Chinese Optics Letters, 2020, 18131: 6. [23] LAND E H. The retinex theory of color vision[J]. Scientific American, 1978, 237(6): 108-128. [24] HE K M, SUN J, TANG X O. Guided image filtering[C]. Proceedings of the 11th European Conference on Computer Vision, Springer, 2010. [25] WANG SH H, ZHENG J, HU H M, et al. Naturalness preserved enhancement algorithm for non-uniform illumination images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2013, 22(9): 3538-3548. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2013.2261309 [26] ZHU Q S, MAI J M, SHAO L. A fast single image haze removal algorithm using color attenuation prior[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2015, 24(11): 3522-3533. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2015.2446191 [27] LOU W H, LI Y J, YANG G W, et al. Integrating haze density features for fast nighttime image dehazing[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 113318-113330. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3003444 [28] ANCUTI C, ANCUTI C O, DE VLEESCHOUWER C. D-HAZY: a dataset to evaluate quantitatively dehazing algorithms[C]. Proceedings of 2016 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, IEEE, 2016. [29] MARQUARDT D W. An algorithm for least-squares estimation of nonlinear parameters[J]. Journal of the Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics, 1963, 11(2): 431-441. doi: 10.1137/0111030 [30] TRIPATHI A K, MUKHOPADHYAY S. Removal of fog from images: a review[J]. IETE Technical Review, 2012, 29(2): 148-156. doi: 10.4103/0256-4602.95386 -





 下载:
下载: