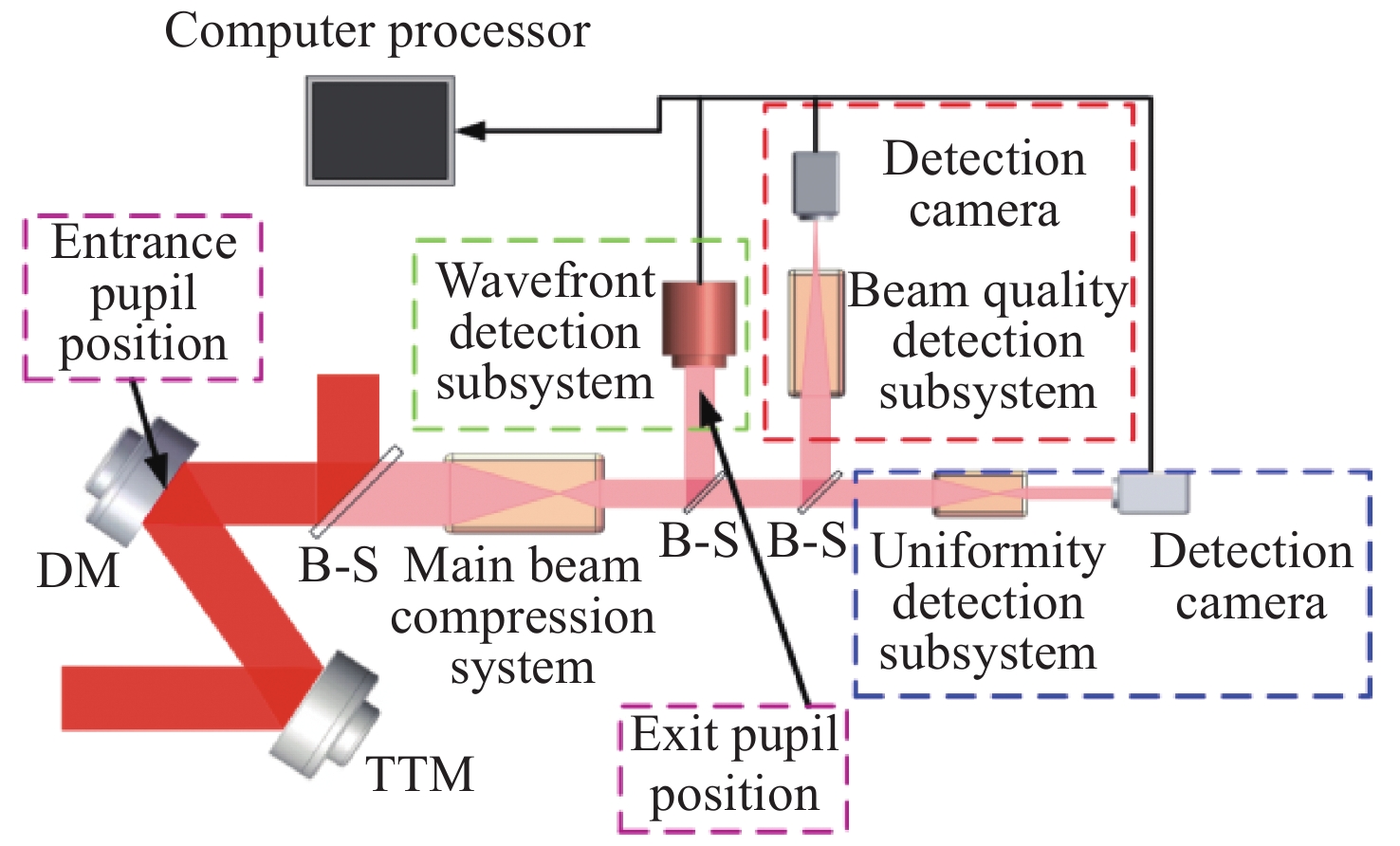
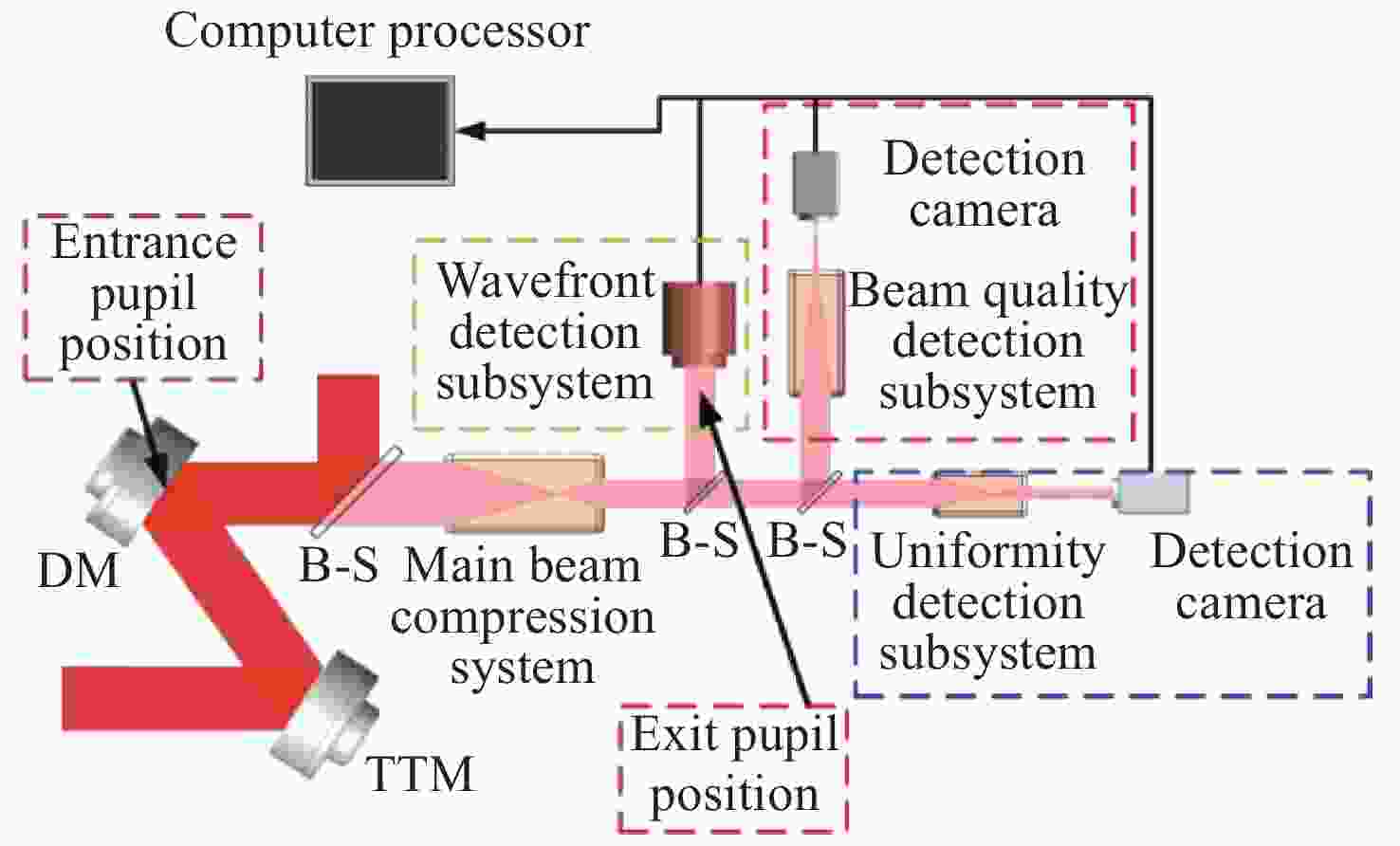
Design of optical system for quality evaluation of a large rectangular aperture laser beam
-
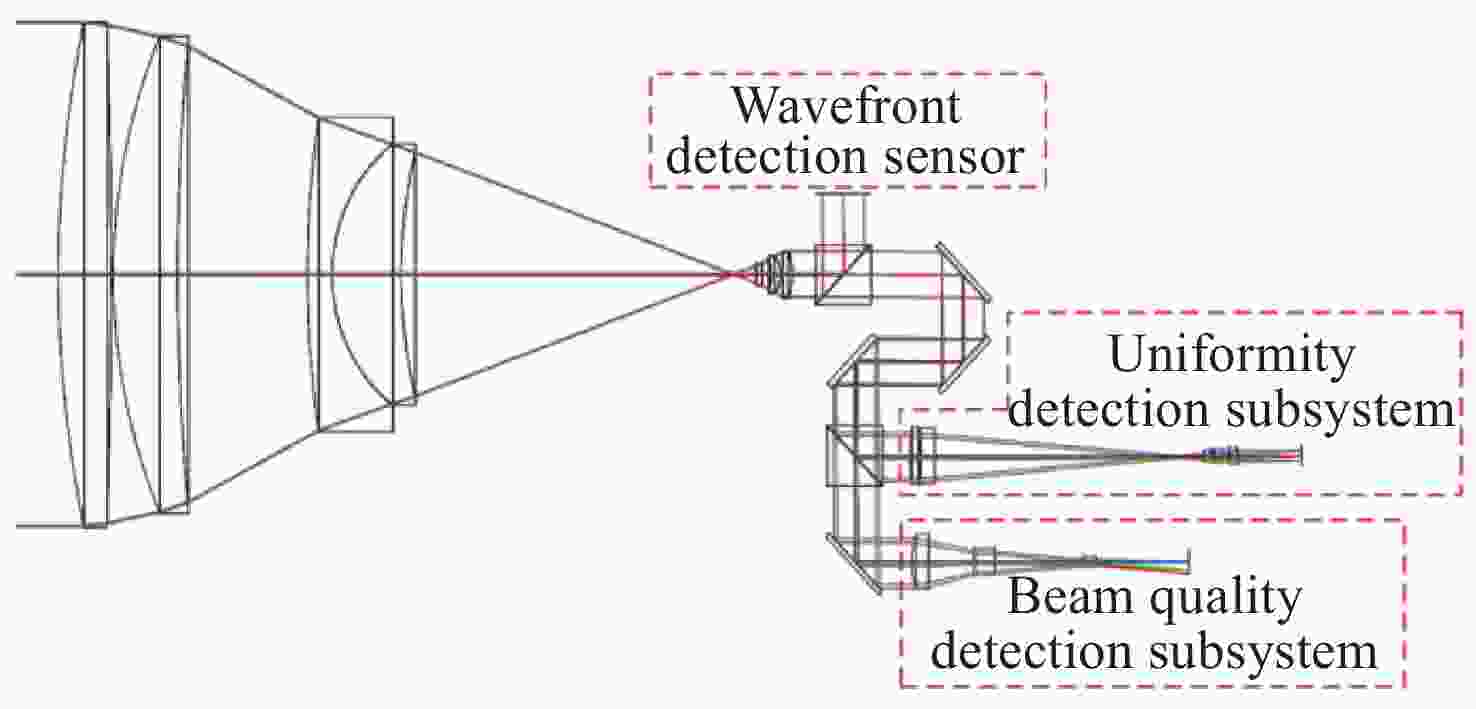
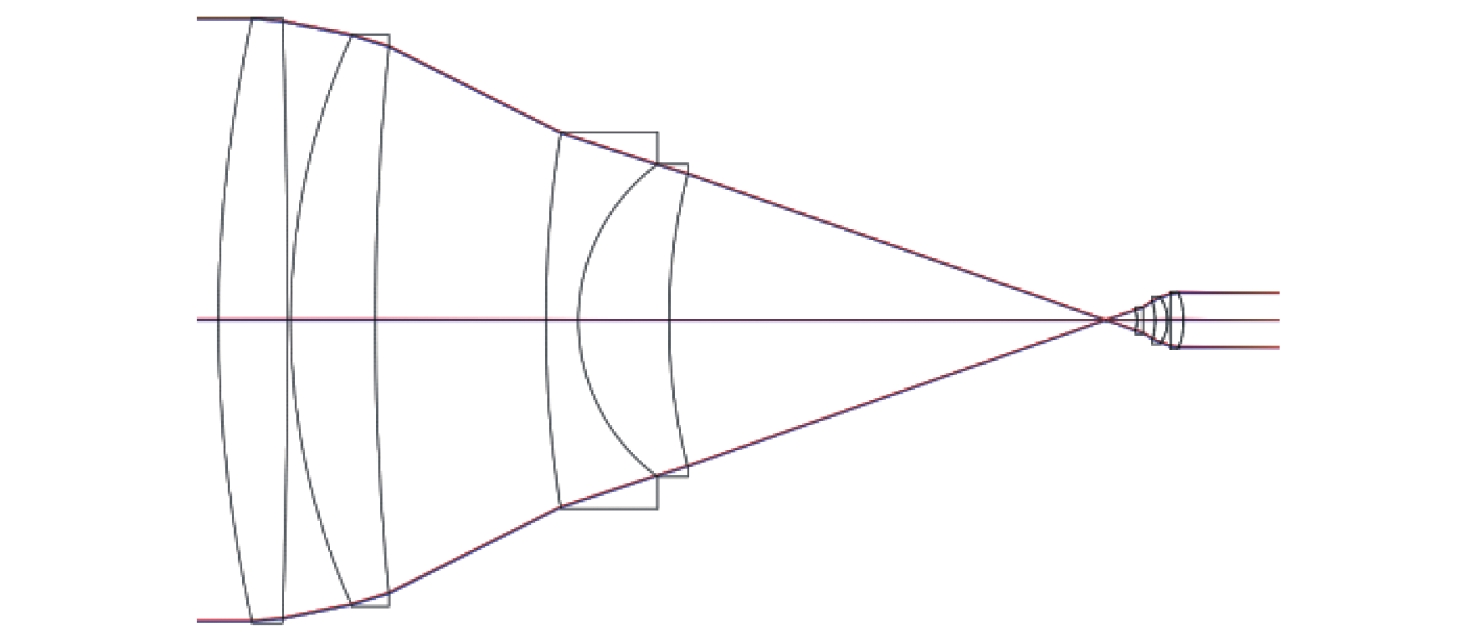
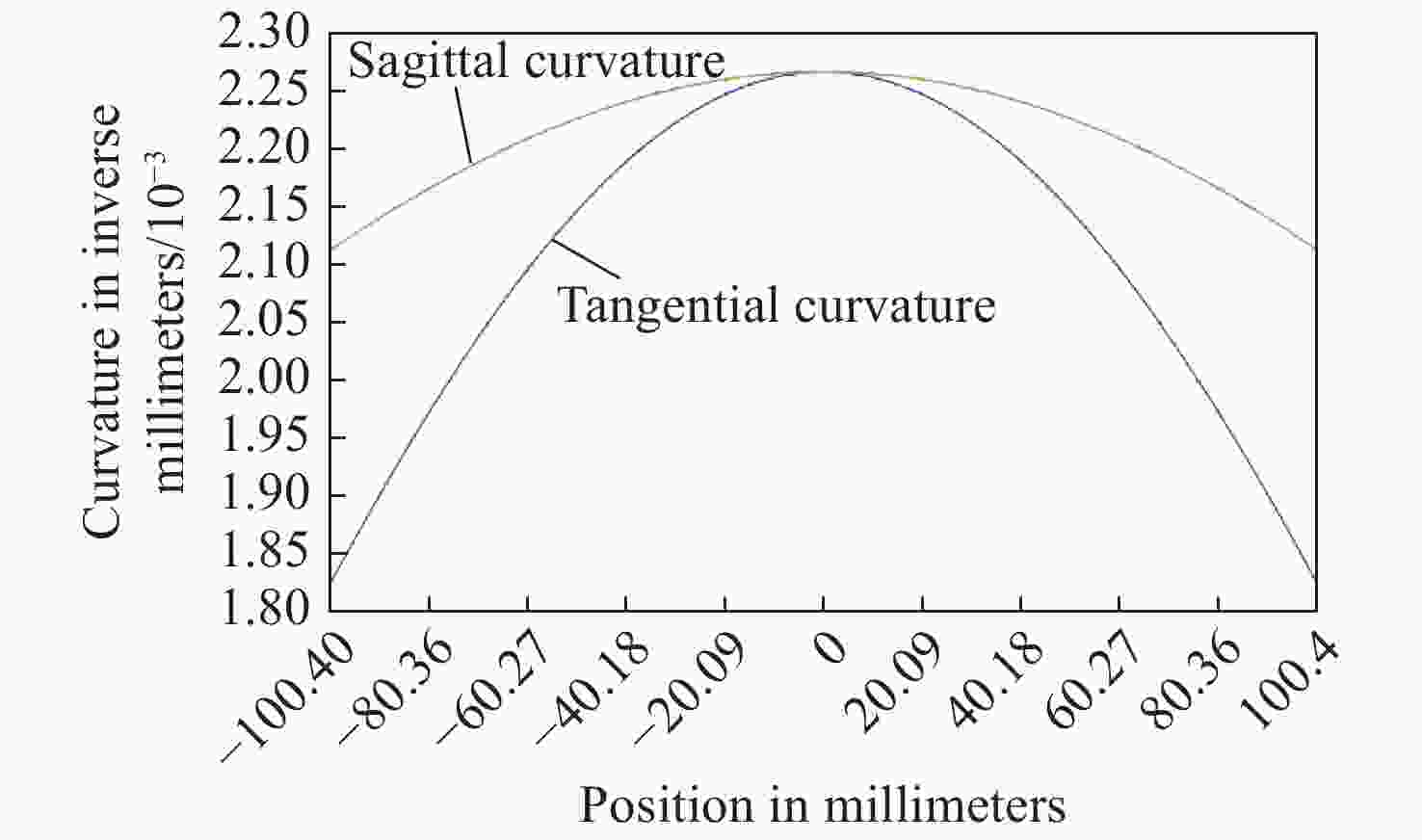
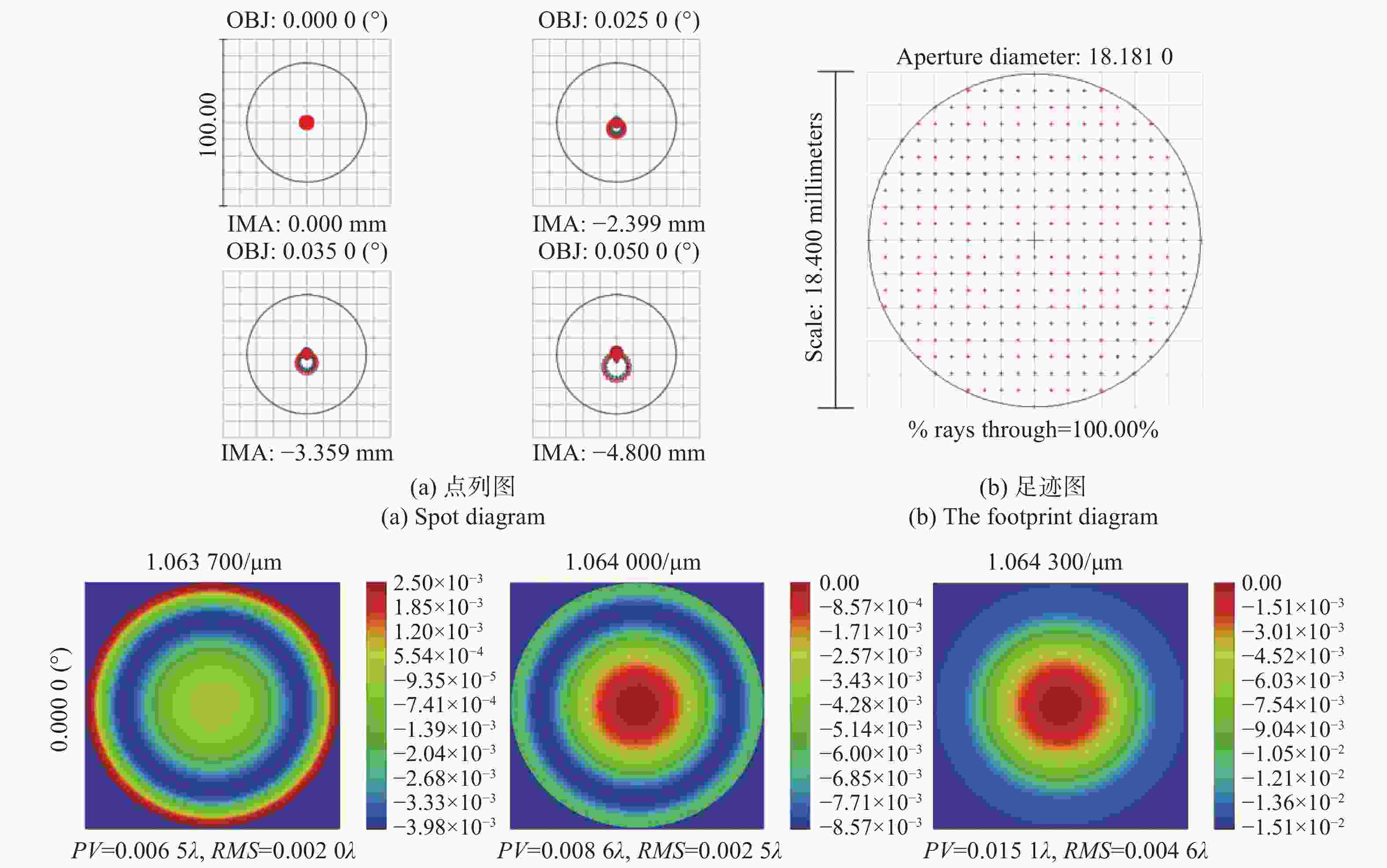
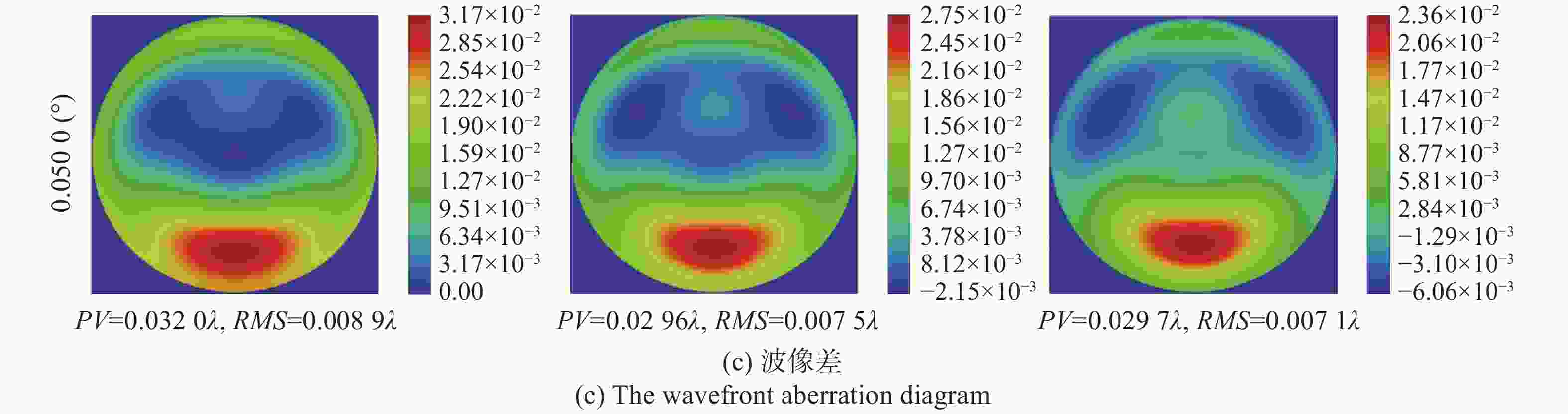
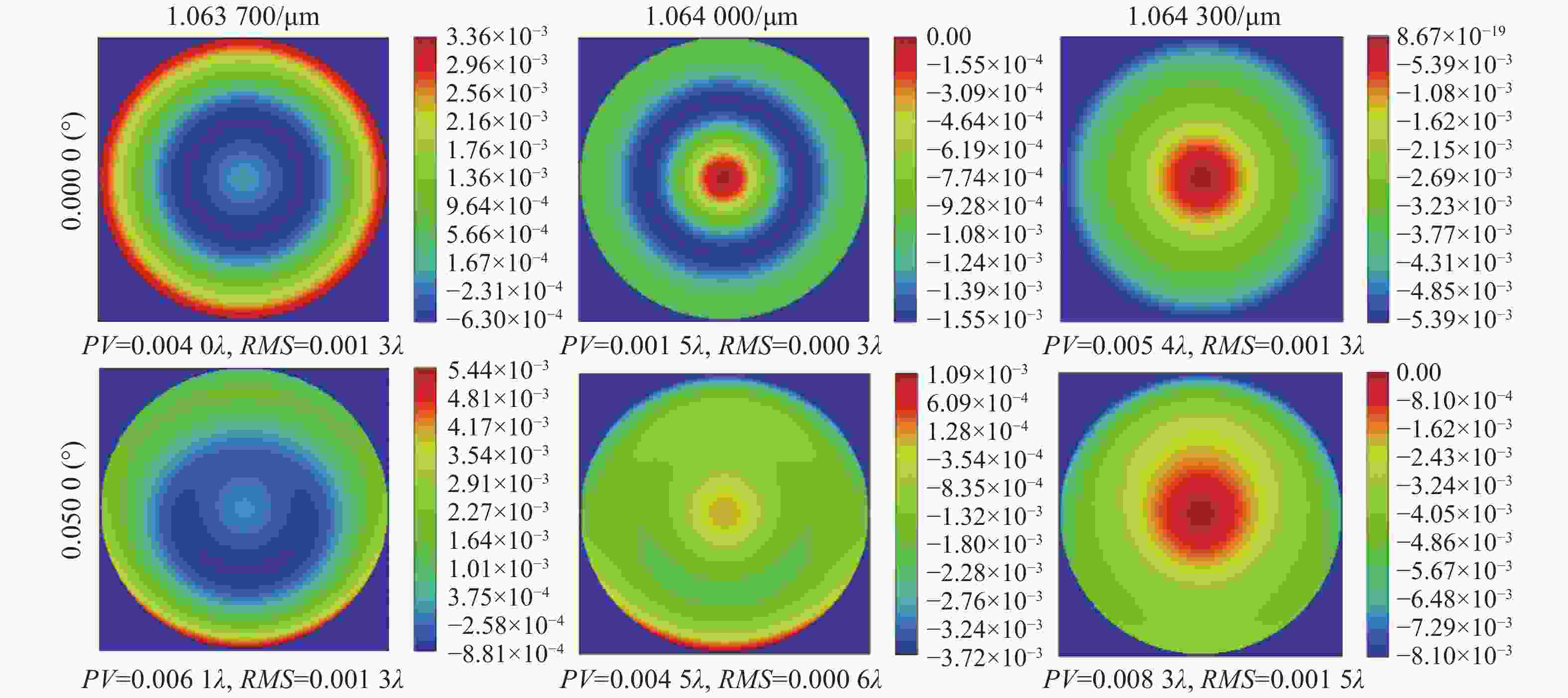
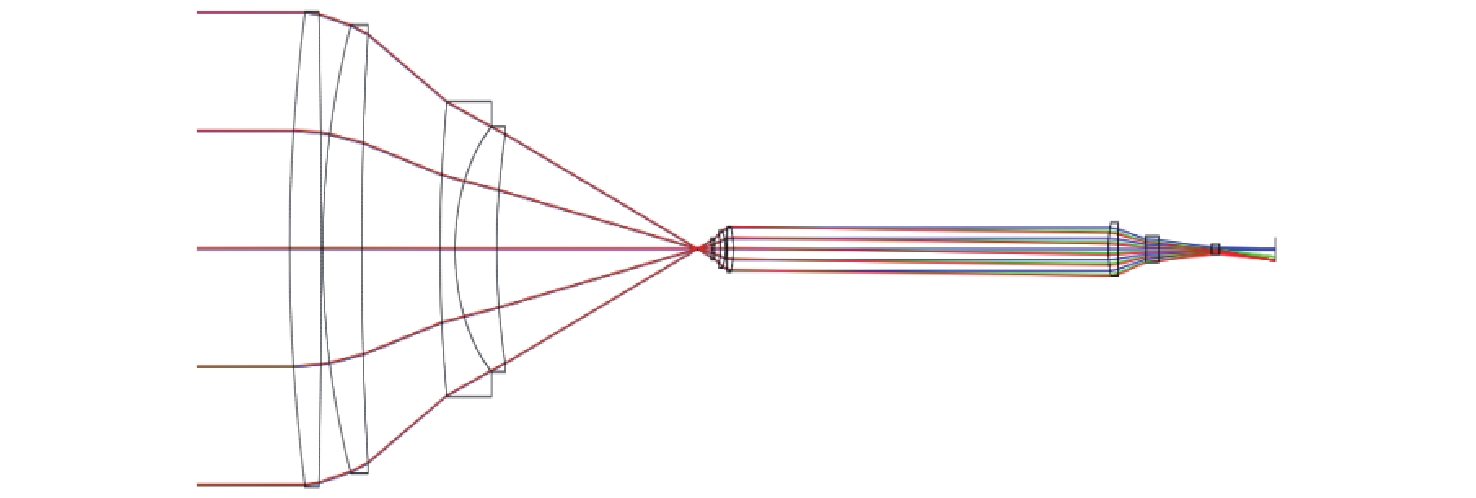
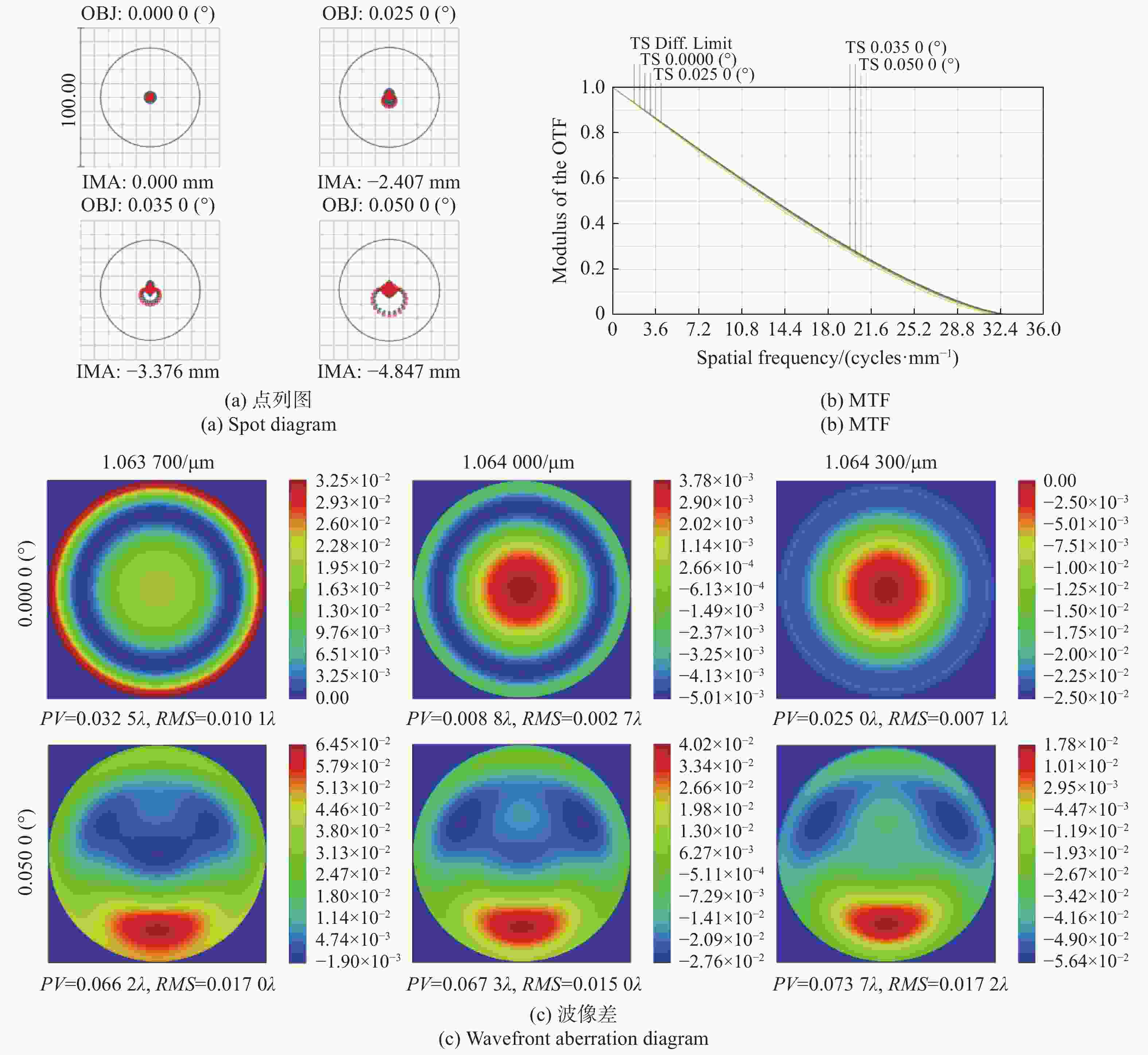
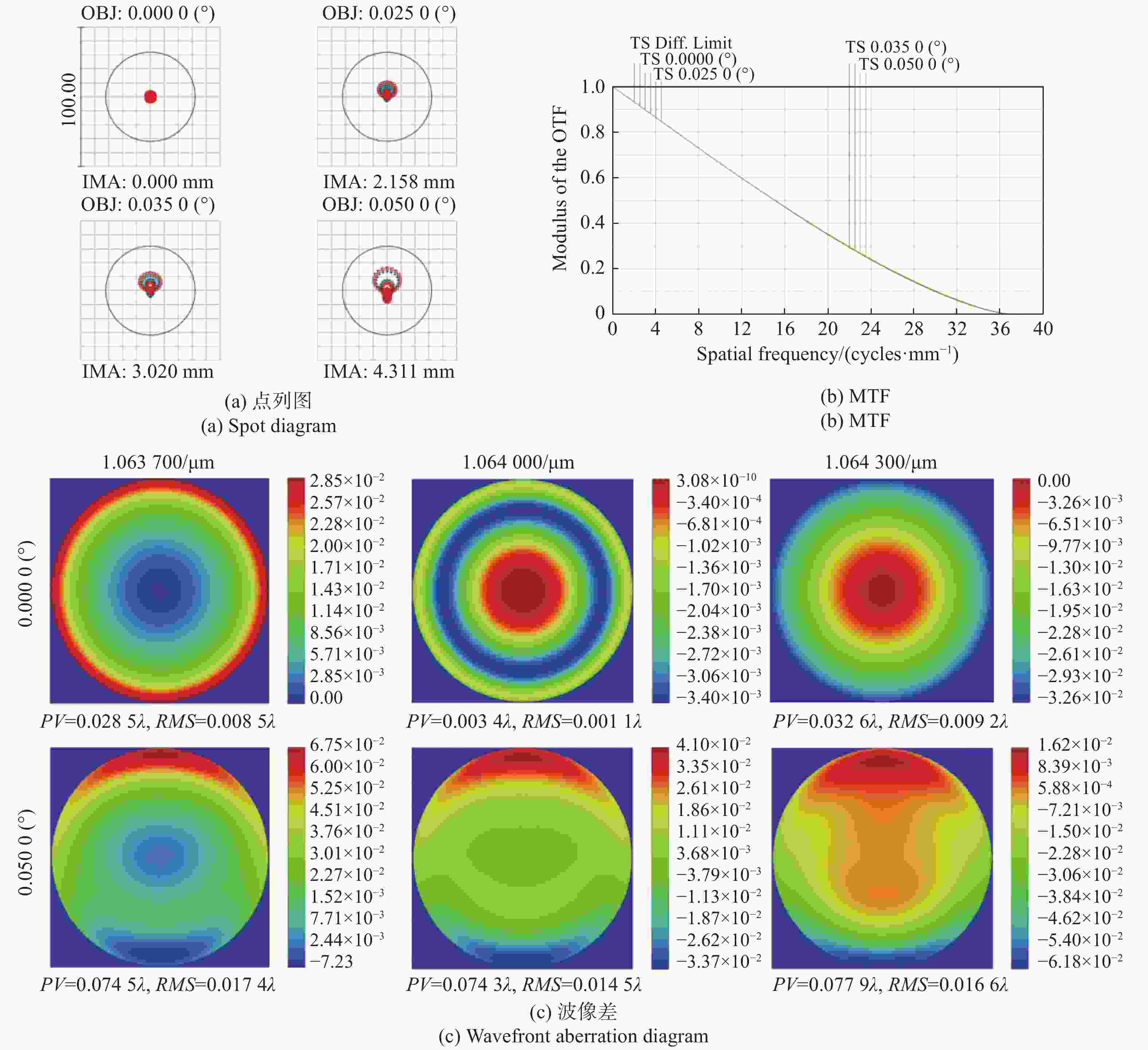
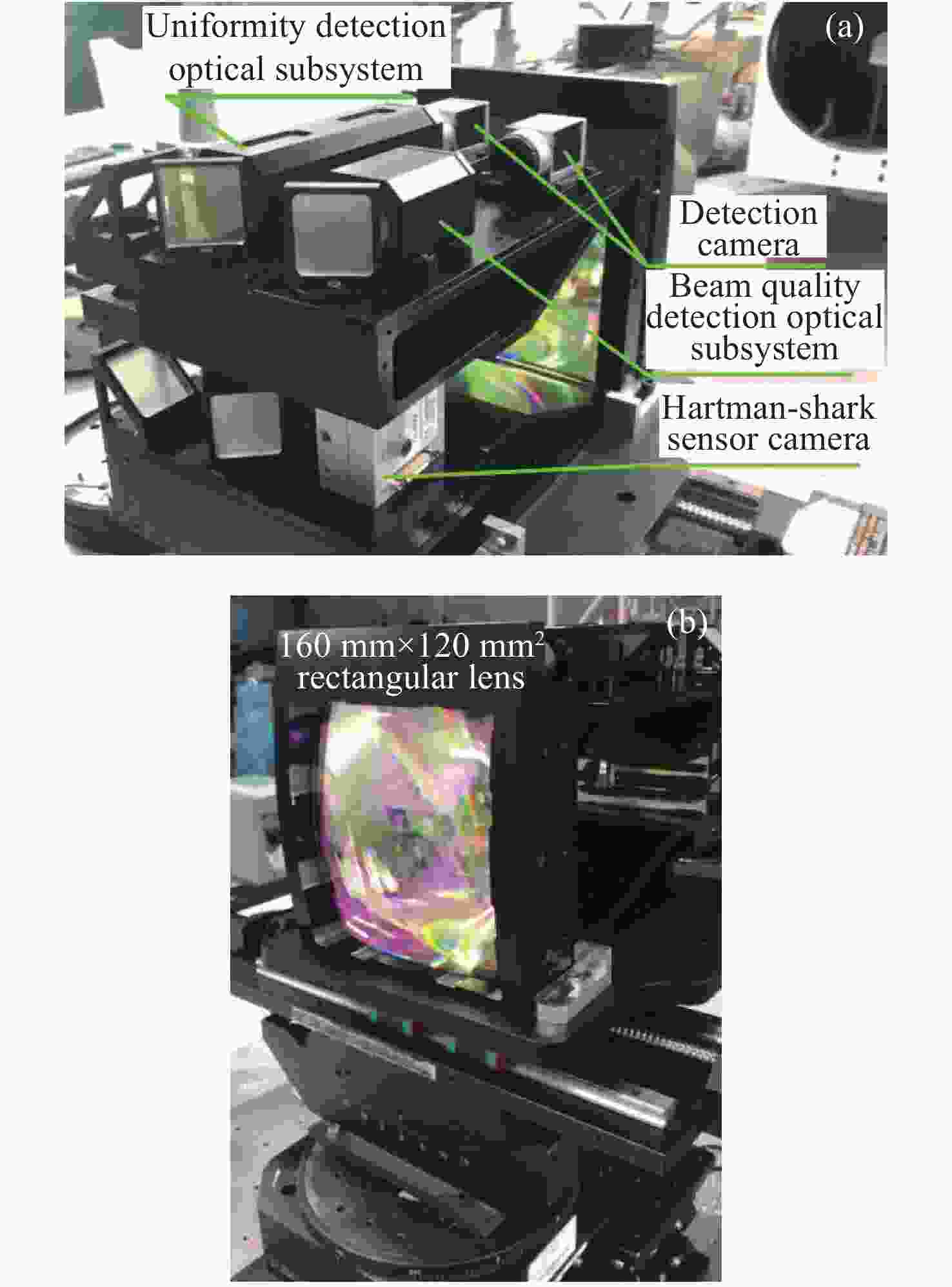
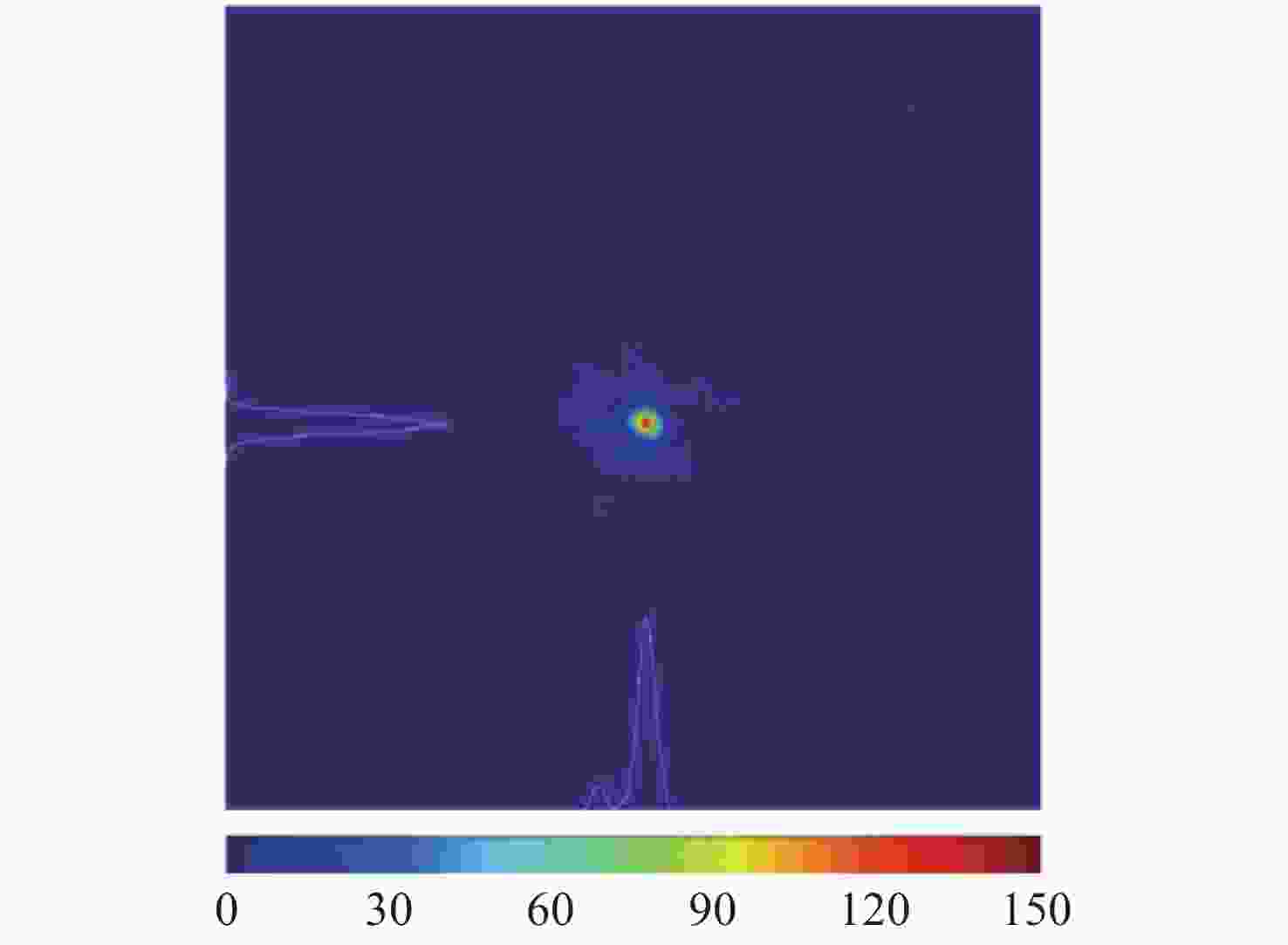
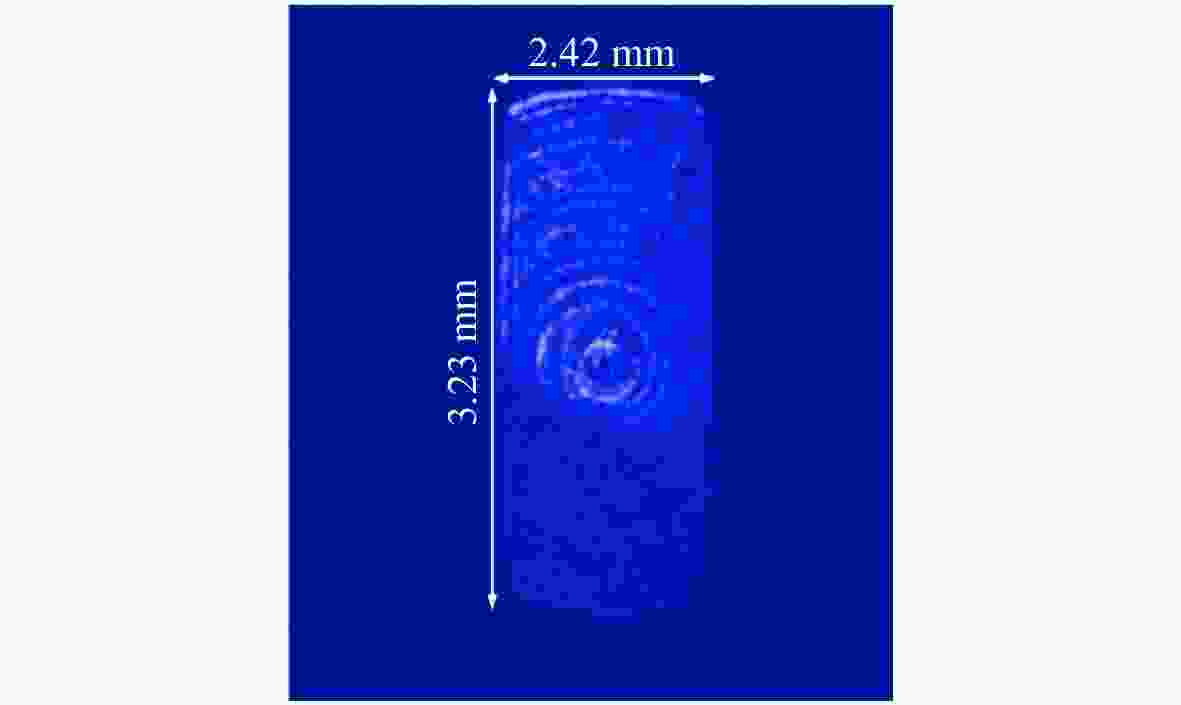
摘要: 自适应光学校正技术可有效提升固体板条激光器的光束质量,但随着激光器输出功率的提升,输出光束口径逐渐增加,系统体积逐渐增大,自适应光学校正系统的设计难度也增加了。因此,在满足自适应光学校正系统中共轭探测等需求的前提下,统筹优化系统的尺寸参数,同时实现波前相位、光束质量评估等多参数的检测具有一定的研究意义。本文在系统整体尺寸为350 mm×180 mm×220 mm(长×宽×高)的条件下,研究实现了板条激光器输出160 mm×120 mm矩形光束多参数的检测。针对探测口径大、筒长限制、长出瞳距等技术要求,首先,利用双高斯初始结构的消像差特点,结合非球面技术,采用大倍率光束压缩后分光探测的设计方案,实现多参数的同时探测。其次,基于摄远成像和共轭成像等原理,确定系统初始参数。接着,建立仿真模型分析系统的成像质量和公差,为实验的搭建提供依据。最后,搭建实验平台验证设计结果。结果表明:所设计系统可在满足物像共轭、尺寸约束等条件下,实现对大口径矩形光束的共轭波前探测、光强均匀度检测和光束质量评估。实验测得被测光束β因子为1.24倍衍射极限,均匀度为73.8%,满足技术指标要求。Abstract: The adaptive optical correction technology can effectively improve the beam quality of solid slab lasers, but with the increase of laser output power, the output beam aperture and the system volume increase gradually, which make the design of adaptive optical correction system more difficult. Therefore, under the premise of meeting the requirements of conjugate detection in the adaptive optical correction system, it is of certain research significance to optimize the size parameters of the detection system as a whole, and realize the detection of multiple parameters such as wavefront phase and beam quality evaluation. In this paper, we realized the multi-parameter detection of 160 mm×120 mm rectangular beam emitted by slab laser under the condition that the overall size of the system is 350 mm×180 mm×220 mm (length × width × height). According to the technical requirements of large detection apertures, limitation of tube length and long exit pupil distance, firstly, the dual-Gaussian initial structure was used to eliminate the aberration. Combined with the aspheric surface technology, the design scheme of splitting detection after high-ratio beam compression was adopted to realize the simultaneous detection and evaluation of multiple parameters. Secondly, the initial parameters of the system were determined based on the principles of telephoto imaging and conjugate imaging. Thirdly, the simulation model of the detection system was established to analyze the imaging quality and the tolerance of the system, which were implemented to provide the basis for the construction of the experiment. Finally, the experiments were carried out to verify the design results. Results indicate that the conjugate wavefront detection, light intensity uniformity detection and beam quality evaluation of 160 mm × 120 mm rectangular beam can be realized under the conditions of the object-image conjugation and size constraint conditions. In the experiment, the β factor of the measured beam is 1.24 times the diffraction limit, and the uniformity is 73.8 %, which meet the technical requirements.
-
表 1 激光光束质量评价系统的技术指标
Table 1. The technical specifications of the laser beam quality evaluation system
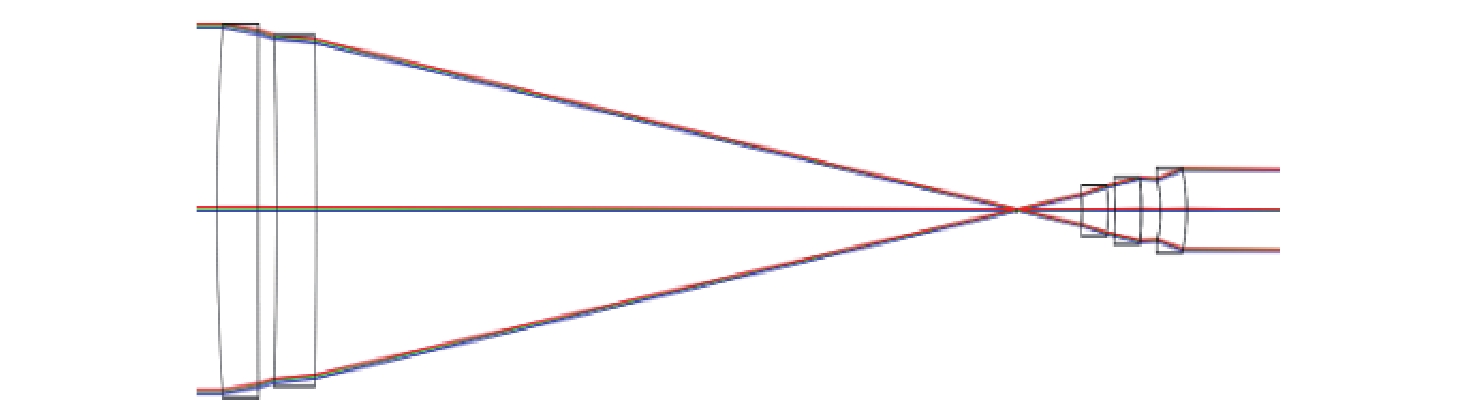
参数 数值 主缩束装置倍率 11× 主缩束系统通光口径 160 mm×120 mm 视场 ±3′ 波长 (1064±0.3) nm 主缩束入瞳位置 500 mm 主缩束出瞳位置 ≥40 mm 主缩束系统筒长 ≤320 mm 主缩束系统配合光束质量
探测光学系统EFFL5500 mm 光束均匀性探测光学系统
缩束倍率4.5× 光束质量β因子 ≤1.3×DL 系统整体尺寸 350 mm×180 mm×220 mm
(长×宽×高)表 2 主缩束系统透镜数据
Table 2. Lens data of the main beam compression system
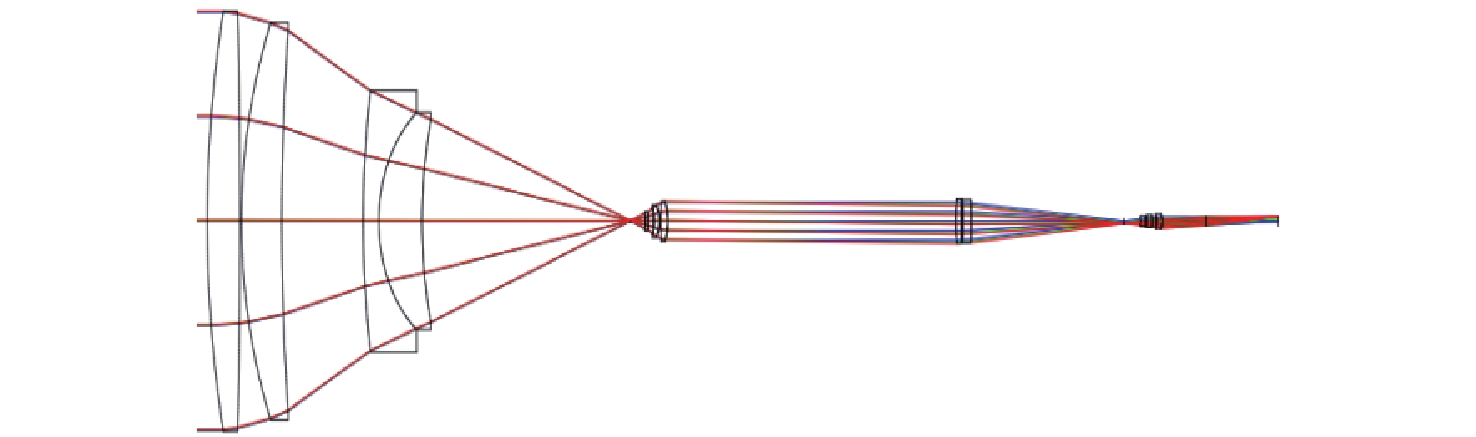
Type Radius Thickness Glass Even Asphere 440.000 22.893 H-ZLAF52A Standard −2924.268 1.000 − Standard 231.431 28.018 H-ZLAF55D Standard 925.079 56.403 − Standard 394.602 10.800 H-ZF73 Standard 64.282 30.000 H-ZLAF68C Standard 191.455 154.885 − Standard −13.435 2.009 H-ZLAF55D Standard −1053.154 4.077 − Standard −20.488 4.037 H-ZLAF53B Standard −13.485 0.811 − Standard 311.182 4.496 H-ZLAF53B Standard −25.212 41.405 − 表 3 光束质量探测子系统透镜数据
Table 3. Lens data of beam quality detection subsystem
Radius Thickness Glass 36.523 7.047 H-ZLA 415.691 20.267 — −38.384 8.628 H-ZF88 155.064 38.737 — −124.904 5.558 H-ZLA 12.285 45.272 — 表 4 光束质量探测系统的公差数据
Table 4. Tolerance data of beam quality detection system
No. Radius Thickness/mm Decenter
(X/Y)/mmTilt
(X/Y)/(′)Index Abbe. Len1 ±0.02 ±0.025 ±0.01 ±0.7 ±0.0005 ±0.08% Len2 ±0.02 ±0.025 ±0.01 ±0.6 ±0.0005 ±0.08% Len3 ±0.02 ±0.025 ±0.01 ±0.7 ±0.0005 ±0.08% Len4 ±0.03 ±0.025 ±0.03 ±0.1 ±0.002 ±0.2% Len5 ±0.03 ±0.0375 ±0.01 ±1.5 ±0.002 ±0.2% Len6 ±0.03 ±0.0375 ±0.02 ±1.5 ±0.002 ±0.2% Len7 ±0.03 ±0.0375 ±0.02 ±2 ±0.002 ±0.3% Len8 ±0.03 ±0.0375 ±0.02 ±2 ±0.002 ±0.3% Len9 ±0.03 ±0.0375 ±0.02 ±2 ±0.002 ±0.3% 表 5 光束质量探测系统的1000次蒙特卡罗分析结果
Table 5. 1000 Monte Carlo statistical analysis results of the beam quality detection system
Percentage of Monte Carlo/% RMS Wavefront 98 0.2715 90 0.1871 80 0.1586 50 0.1109 表 6 光束均匀性探测子系统透镜数据
Table 6. Lens data of the beam uniformity detection subsystem
Radius Thickness Glass 66.752 3.964 H-ZF7LA Infinity 0.800 − −154.456 6.000 H-ZF7LAGT −340.621 117.358 − −5.693 3.326 H-K9L −7.277 1.000 − −23.127 3.893 H-ZLAF68N −10.385 3.000 − −6.247 3.950 H-K9L −6.247 26.932 − 表 7 光束均匀性探测系统公差数据
Table 7. Tolerance data of the beam uniformity detection system
No. Radius Thickness Decenter (X/Y)/mm Tilt (X/Y)/(′) Index Abbe. Len1 ±0.02 ±0.025 mm ±0.01 ±0.8 ±0.0005 ±0.08% Len2 ±0.02 ±0.025 mm ±0.01 ±0.6 ±0.0005 ±0.08% Len3 ±0.02 ±0.025 mm ±0.01 ±0.8 ±0.0005 ±0.08% Len4 ±0.03 ±0.035 mm ±0.03 ±1.5 ±0.0005 ±0.2% Len5 ±0.03 ±0.035 mm ±0.01 ±1.5 ±0.003 ±0.2% Len6 ±0.03 ±0.035 mm ±0.03 ±1.5 ±0.003 ±0.2% Len7 ±0.03 ±0.035 mm ±0.03 ±3.0 ±0.001 ±0.2% Len8 ±0.03 ±0.035 mm ±0.03 ±3.0 ±0.003 ±0.2% Len9 ±0.03 ±0.035 mm ±0.03 ±3.0 ±0.003 ±0.2% Len10 ±0.03 ±0.035 mm ±0.03 ±3.0 ±0.003 ±0.2% Len11 ±0.03 ±0.035 mm ±0.03 ±3.0 ±0.003 ±0.2% 表 8 光束均匀性探测系统1000次蒙特卡罗分析结果
Table 8. 1000 Monte Carlo statistical analysis results of the beam uniformity detection system
Percentage of Monte Carlo RMS Wavefront 98% 0.2403 90% 0.1874 80% 0.1625 50% 0.1189 -
[1] KOSSOWSKY R, JELINEK M, WALTER R F. High Power Lasers——Science and Engineering[M]. Dordrecht: Springer, 1996. [2] LIU B L, WANG ZH CH, YANG F, et al. High brightness 556 nm laser by frequency doubling of a 1112 nm Nd∶YAG laser[J]. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 2014, 26(10): 969-972. doi: 10.1109/LPT.2014.2309795 [3] 唐睿, 高子叶, 吴正茂, 等. 基于SESAM被动调Q的激光二极管泵浦Yb∶CaYAlO4脉冲激光器[J]. 中国光学,2019,12(1):167-178. doi: 10.3788/co.20191201.0167TANG R, GAO Z Y, WU ZH M, et al. Output characteristics of diode-pumped passively Q-switched Yb∶CaYAlO4 pulsed laser based on a SESAM[J]. Chinese Optics, 2019, 12(1): 167-178. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/co.20191201.0167 [4] 刘学胜, 董剑, 徐爱东, 等. 双程放大740 mJ TEC冷却LD泵浦Nd∶YAG激光器[J]. 发光学报,2018,39(7):991-996. doi: 10.3788/fgxb20183907.0991LIU X SH, DONG J, XU A D, et al. Two-pass amplifier 740 mJ diode-pumped Nd∶YAG laser with thermoelectric cooler[J]. Chinese Journal of Luminescence, 2018, 39(7): 991-996. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/fgxb20183907.0991 [5] 岱钦, 张善春, 杨帆, 等. 高光束质量高斯非稳腔固体激光器研究[J]. 中国光学,2019,12(3):559-566. doi: 10.3788/co.20191203.0559DAI Q, ZHANG SH CH, YANG F, et al. Research on the high beam quality of Gaussian unstable resonators in solid state lasers[J]. Chinese Optics, 2019, 12(3): 559-566. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/co.20191203.0559 [6] YU X, DONG L ZH, LAI B H, et al. Automatic low-order aberration correction based on geometrical optics for slab lasers[J]. Applied Optics, 2017, 56(6): 1730-1739. doi: 10.1364/AO.56.001730 [7] FAN ZH W, QIU J S, KANG ZH J, et al. High beam quality 5 J, 200 Hz Nd: YAG laser system[J]. Light:Science &Applications, 2017, 6(3): e17004. [8] 于信. 板条激光低阶像差自动校正技术研究[D]. 成都: 电子科技大学, 2018: 1-14.YU X. Research on automatic low-order aberration correction of slab laser[D]. Chengdu: University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2018: 1-14. (in Chinese) [9] 相里微. 大功率激光波前测量系统设计[D]. 西安: 西安电子科技大学, 2012: 21-24.XIANG L W. Design of high-power laser wavefront measurement system[D]. Xi’an: Xidian University, 2012: 21-24. (in Chinese) [10] 张成栋. 激光光束质量诊断与测量研究[D]. 长沙: 国防科学技术大学, 2017: 30-38.ZHANG CH D. Diagnosis and measurement of laser beam quality[D]. Changsha: National University of Defense Technology, 2017: 30-38. (in Chinese) [11] 张禹, 杨忠明, 刘兆军, 等. 大口径多光谱通道波前测量系统设计[J]. 红外与激光工程,2020,49(8):20190559. doi: 10.3788/IRLA20190559ZHANG Y, YANG ZH M, LIU ZH J, et al. Design of large aperture multi-spectra channel wavefront measurement system[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2020, 49(8): 20190559. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/IRLA20190559 [12] 张禹. 共轴式大口径多光谱通道波前测量系统的研究[D]. 济南: 山东大学, 2020: 10-21, 41-43.ZHANG Y. Research on coaxial large aperture multi-spectra channel wavefront measurement system[D]. Ji’nan: Shandong University, 2020: 10-21, 41-43. (in Chinese) [13] FOURMAUX S, PAYEUR S, ALEXANDROV A, et al. Laser beam wavefront correction for ultra high intensities with the 200 TW laser system at the advanced laser light source[J]. Optics Express, 2008, 16(16): 11987-11994. doi: 10.1364/OE.16.011987 [14] LU H H, LIN CH Y, LU T C, et al. 150 m/280 Gbps WDM/SDM FSO link based on OEO-based BLS and afocal telescopes[J]. Optics Letters, 2016, 41(12): 2835-2838. doi: 10.1364/OL.41.002835 [15] 郁道银, 谈恒英. 工程光学[M]. 3版. 北京: 机械工业出版社, 2011.YU D Y, TAN H Y. Engineering Optics[M]. 3rd ed. Beijing: China Machine Press, 2011. (in Chinese) [16] 傅瑞斯. 摄远物镜初步设计的一种方法[J]. 云光技术,2002,34(2):21-24.FU R S. A method for primary design of telephoto objective[J]. Yunguang Technology, 2002, 34(2): 21-24. (in Chinese) [17] CHEN ZH ZH, XU Y T, GUO Y D, et al. 8.2 kW high beam quality quasi-continuous-wave face-pumped Nd: YAG slab amplifier[J]. Applied Optics, 2015, 54(16): 5011-5015. doi: 10.1364/AO.54.005011 [18] REDMOND S, MCNAUGHT S, ZAMEL J, et al. . 15 kW near-diffraction-limited single-frequency Nd: YAG laser[C]. 2007 Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics (CLEO), IEEE, 2005: 1-2. [19] 林星辰, 朱洪波, 王彪, 等. 均匀光强分布的5 kW半导体激光硬化光源研制[J]. 光学 精密工程,2017,25(5):1178-1184. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20172505.1178LIN X CH, ZHU H B, WANG B, et al. Development of 5 kW diode laser hardening source with homogenized intensity distribution[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2017, 25(5): 1178-1184. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/OPE.20172505.1178 -





 下载:
下载: