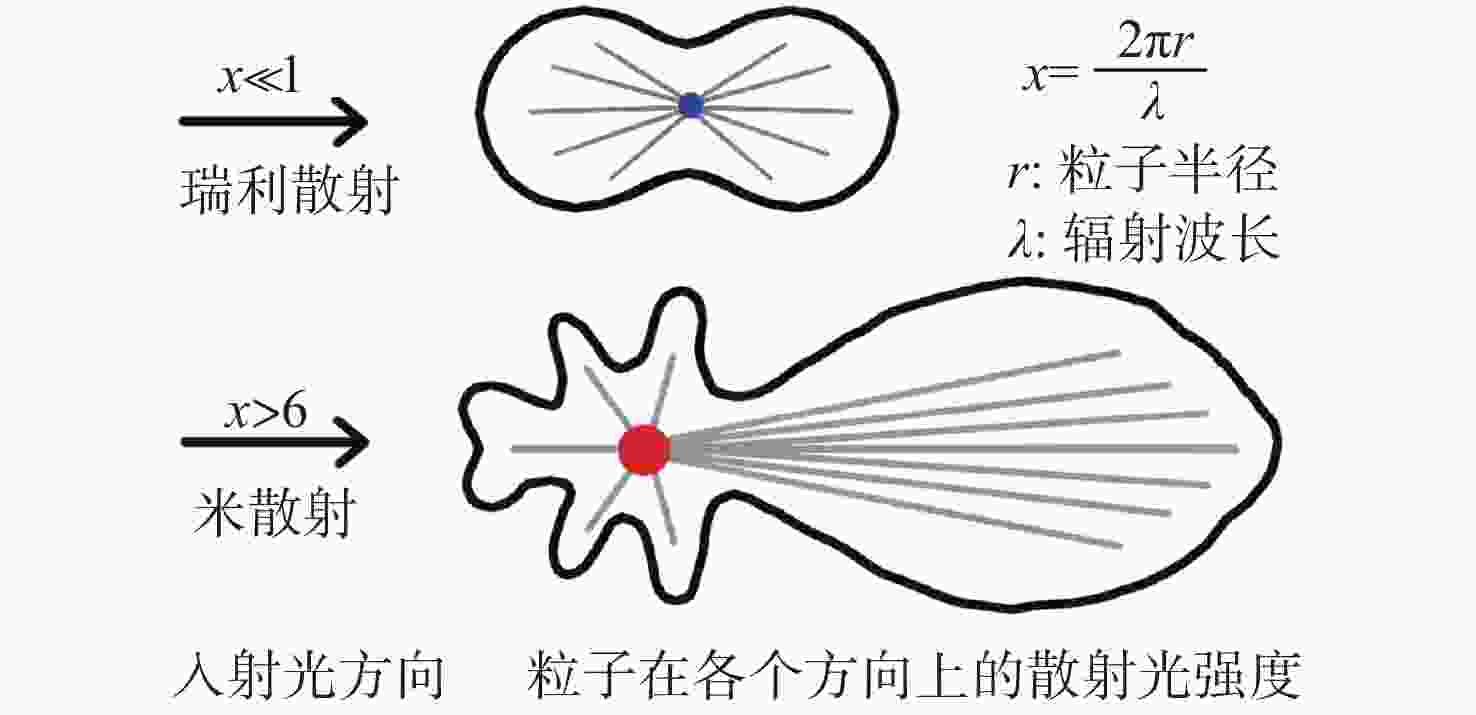
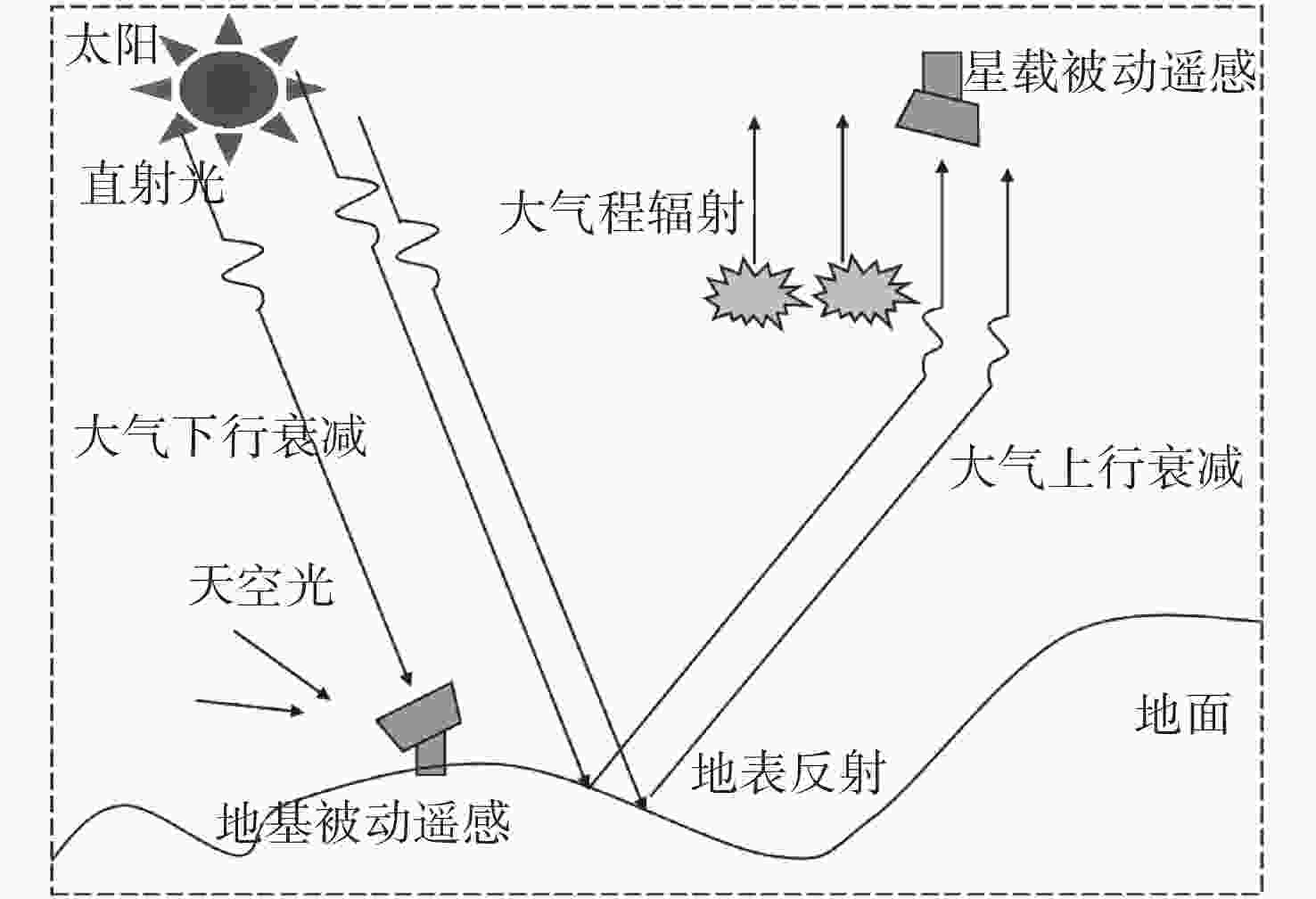
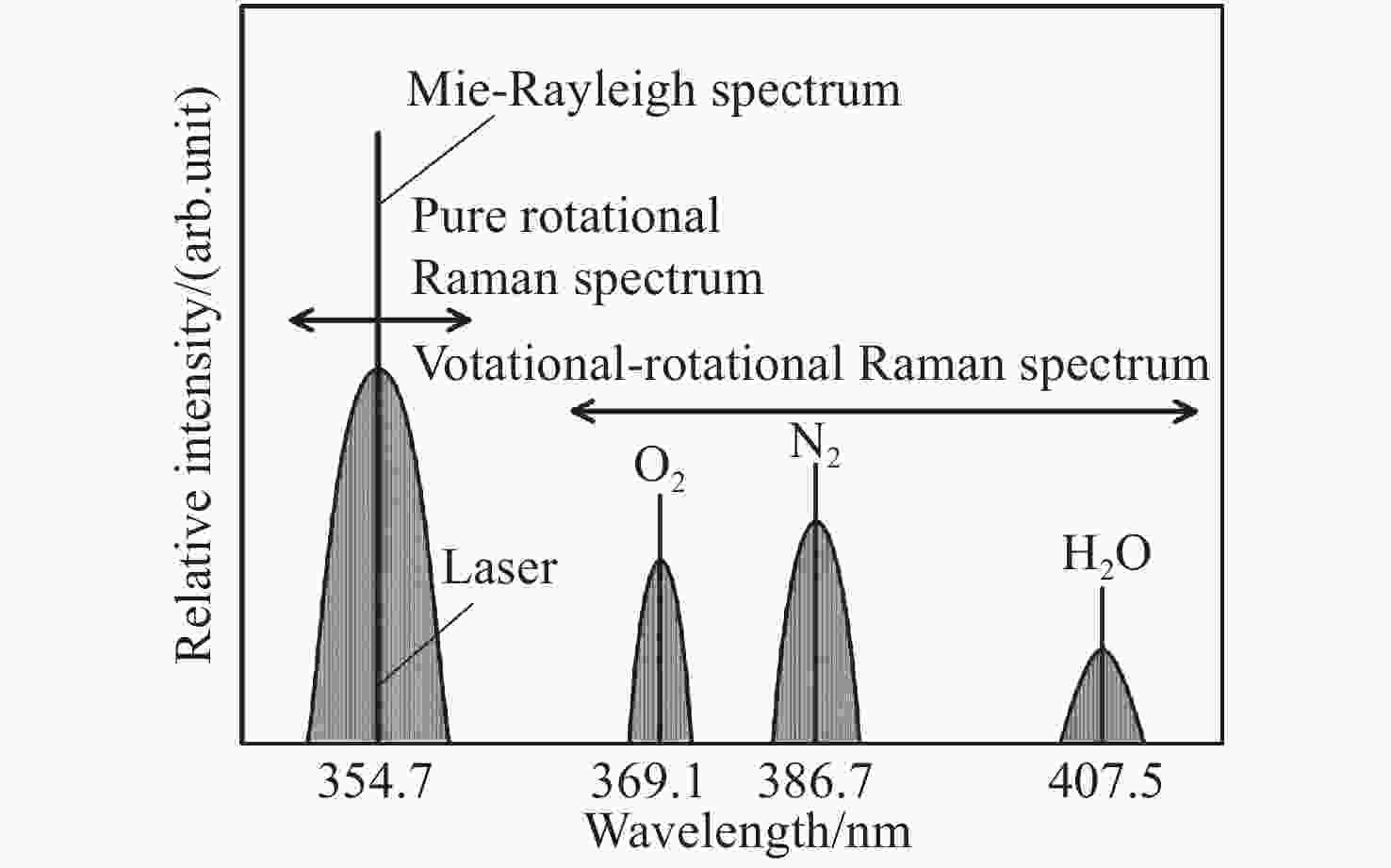
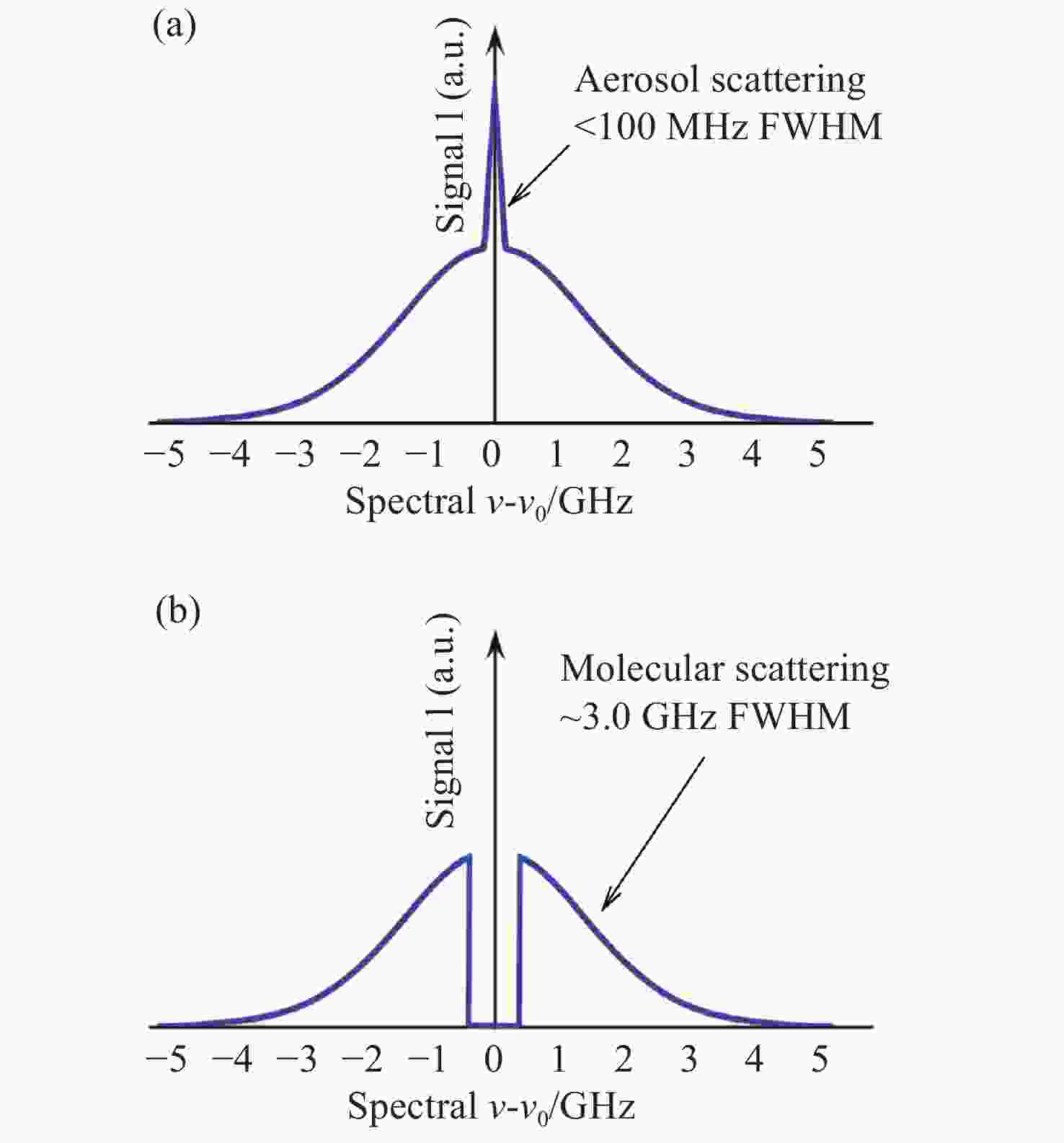
| [1] |
陈良富, 李莘莘, 陶金花, 等. 气溶胶遥感定量反演研究与应用[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2011.CHEN L F, LI SH SH, TAO J H, et al.. Research and Application of Aerosol Remote Sensing Quantitative Inversion[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2001. (in Chinese)
|
| [2] |
EVANS B T N. Sensitivity of the backscatter/extinction ratio to changes in aerosol properties: implications for lidar[J]. Applied Optics, 1988, 27(15): 3299-3305. doi: 10.1364/AO.27.003299
|
| [3] |
FERNALD F G. Analysis of atmospheric lidar observations: some comments[J]. Applied Optics, 1984, 23(5): 652-653. doi: 10.1364/AO.23.000652
|
| [4] |
KIM M H, OMAR A H, TACKETT J L, et al. The CALIPSO version 4 automated aerosol classification and lidar ratio selection algorithm[J]. Atmospheric Measurement Techniques, 2018, 11(11): 6107-6135. doi: 10.5194/amt-11-6107-2018
|
| [5] |
SALGUEIRO V, COSTA M J, GUERRERO-RASCADO J L, et al. Characterization of forest fire and Saharan desert dust aerosols over south-western Europe using a multi-wavelength Raman lidar and Sun-photometer[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2021, 252: 118346. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2021.118346
|
| [6] |
ZHAO G, ZHAO CH SH, KUANG Y, et al. Impact of aerosol hygroscopic growth on retrieving aerosol extinction coefficient profiles from elastic-backscatter lidar signals[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 2017, 17(19): 12133-12143. doi: 10.5194/acp-17-12133-2017
|
| [7] |
DIONISI D, BARNABA F, DIÉMOZ H, et al. A multiwavelength numerical model in support of quantitative retrievals of aerosol properties from automated lidar ceilometers and test applications for AOT and PM10 estimation[J]. Atmospheric Measurement Techniques, 2018, 11(11): 6013-6042. doi: 10.5194/amt-11-6013-2018
|
| [8] |
GASTEIGER J, WIEGNER M. MOPSMAP v1.0: a versatile tool for the modeling of aerosol optical properties[J]. Geoscientific Model Development, 2018, 11(7): 2739-2762. doi: 10.5194/gmd-11-2739-2018
|
| [9] |
DOHERTY S J, ANDERSON T L, CHARLSON R J. Measurement of the lidar ratio for atmospheric aerosols with a 180° backscatter nephelometer[J]. Applied Optics, 1999, 38(9): 1823-1832. doi: 10.1364/AO.38.001823
|
| [10] |
童奕澄, 童学东, 张凯, 等. 偏振激光雷达增益比定标方法对比研究[J]. 中国光学,2021,14(3):685-703. doi: 10.37188/CO.2020-0136TONG Y CH, TONG X D, ZHANG K, et al. Polarization lidar gain ratio calibration method: a comparison[J]. Chinese Optics, 2021, 14(3): 685-703. (in Chinese) doi: 10.37188/CO.2020-0136
|
| [11] |
曲艺. 大气光学遥感监测技术现状与发展趋势[J]. 中国光学,2013,6(6):834-840.QU Y. Technical status and development tendency of atmosphere optical remote and monitoring[J]. Chinese Optics, 2013, 6(6): 834-840. (in Chinese)
|
| [12] |
DUBOVIK O, SINYUK A, LAPYONOK T, et al. Application of spheroid models to account for aerosol particle nonsphericity in remote sensing of desert dust[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Atmospheres, 2006, 111(D11): D11208. doi: 10.1029/2005JD006619
|
| [13] |
YANG P, KATTAWAR G W, LIOU K N, et al. Comparison of Cartesian grid configurations for application of the finite-difference time-domain method to electromagnetic scattering by dielectric particles[J]. Applied Optics, 2004, 43(23): 4611-4624. doi: 10.1364/AO.43.004611
|
| [14] |
张朝阳, 苏林, 陈良富. 中国典型地区气溶胶激光雷达比反演与分析[J]. 中国激光,2013,40(5):0513002. doi: 10.3788/CJL201340.0513002ZHANG ZH Y, SU L, CHEN L F. Retrieval and analysis of aerosol lidar ratio at several typical regions in China[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2013, 40(5): 0513002. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/CJL201340.0513002
|
| [15] |
WU M X, LIU X H, YU H B, et al. Understanding processes that control dust spatial distributions with global climate models and satellite observations[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 2020, 20(22): 13835-13855. doi: 10.5194/acp-20-13835-2020
|
| [16] |
陶金花, 李小英, 王子峰, 等. 大气遥感定量反演算法与系统[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2014.TAO J H, LI X Y, WANG Z F, et al.. Atmospheric Remote Sensing Quantitative Inversion Algorithm and System[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2014. (in Chinese)
|
| [17] |
李正强, 谢一凇, 洪津, 等. 星载对地观测偏振传感器及其大气遥感应用[J]. 大气与环境光学学报,2019,14(1):2-17.LI ZH Q, XIE Y S, HONG J, et al. Polarimetric satellite sensors for earth observation and applications in atmospheric remote sensing[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Environmental Optics, 2019, 14(1): 2-17. (in Chinese)
|
| [18] |
马小雨, 陈正华, 宿鑫, 等. GF-4增强型地表反射率库支持法的气溶胶光学厚度反演[J]. 遥感学报,2020,24(5):578-595.MA X Y, CHEN ZH H, SU X, et al. GF-4 aerosol retrieval study of enhanced surface reflectance library support algorithm[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 2020, 24(5): 578-595. (in Chinese)
|
| [19] |
CHEN X F, DE LEEUW G, AROLA A. et al. Joint retrieval of the aerosol fine mode fraction and optical depth using MODIS spectral reflectance over northern and eastern China: artificial neural network method[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2020, 249: 112006. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2020.112006
|
| [20] |
BRÉON F M. Aerosol extinction-to-backscatter ratio derived from passive satellite measurements[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 2013, 13(17): 8947-8954. doi: 10.5194/acp-13-8947-2013
|
| [21] |
COMERÓN A, MUÑOZ-PORCAR C, ROCADENBOSCH F, et al. Current research in lidar technology used for the remote sensing of atmospheric aerosols[J]. Sensors, 2017, 17(6): 1450. doi: 10.3390/s17061450
|
| [22] |
田晓敏, 刘东, 徐继伟, 等. 大气探测激光雷达技术综述[J]. 大气与环境光学学报,2018,13(5):321-341.TIAN X M, LIU D, XU J W, et al. Review of lidar technology for atmosphere monitoring[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Environmental Optics, 2018, 13(5): 321-341. (in Chinese)
|
| [23] |
刘东, 刘群, 白剑, 等. 星载激光雷达CALIOP数据处理算法概述[J]. 红外与激光工程,2017,46(12):1202001. doi: 10.3788/IRLA201746.1202001LIU D, LIU Q, BAI J, et al. Data processing algorithms of the space-borne lidar CALIOP: a review[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2017, 46(12): 1202001. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/IRLA201746.1202001
|
| [24] |
JOSSET D, ROGERS R, PELON J, et al. CALIPSO lidar ratio retrieval over the ocean[J]. Optics Express, 2011, 19(19): 18696-18706. doi: 10.1364/OE.19.018696
|
| [25] |
SU J, MCCORMICK M P. Using multi-wavelength Mie-Raman lidar to measure low-level cloud properties[J]. Journal of Quantitative Spectroscopy and Radiative Transfer, 2019, 237: 106610. doi: 10.1016/j.jqsrt.2019.106610
|
| [26] |
BOVCHALIUK V, GOLOUB P, PODVIN T, et al. Comparison of aerosol properties retrieved using GARRLiC, LIRIC, and Raman algorithms applied to multi-wavelength lidar and sun/sky-photometer data[J]. Atmospheric Measurement Techniques, 2016, 9(7): 3391-3405. doi: 10.5194/amt-9-3391-2016
|
| [27] |
CÓRDOBA-JABONERO C, LOPES F J S, LANDULFO E, et al. Diversity on subtropical and polar cirrus clouds properties as derived from both ground-based lidars and CALIPSO/CALIOP measurements[J]. Atmospheric Research, 2017, 183: 151-165. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosres.2016.08.015
|
| [28] |
华雯丽, 韩颖, 乔瀚洋, 等. 敦煌沙尘气溶胶质量浓度垂直特征个例分析[J]. 高原气象,2018,37(5):1428-1439.HUA W L, HAN Y, QIAO H Y, et al. Profiling of dust aerosol mass concentration over Dunhuang: case studies[J]. Plateau Meteorology, 2018, 37(5): 1428-1439. (in Chinese)
|
| [29] |
TAO Z M, LIU ZH Y, WU D, et al. Determination of aerosol extinction-to-backscatter ratios from simultaneous ground-based and spaceborne lidar measurements[J]. Optics Letters, 2008, 33(24): 2986-2988. doi: 10.1364/OL.33.002986
|
| [30] |
SASANO Y, BROWELL E V. Light scattering characteristics of various aerosol types derived from multiple wavelength lidar observations[J]. Applied Optics, 1989, 28(9): 1670-1679. doi: 10.1364/AO.28.001670
|
| [31] |
KIM D, CHA H. Rotational Raman lidar for obtaining aerosol scattering coefficients[J]. Optics Letters, 2005, 30(13): 1728-1730. doi: 10.1364/OL.30.001728
|
| [32] |
ANSMANN A, WANDINGER U, RIEBESELL M, et al. Independent measurement of extinction and backscatter profiles in cirrus clouds by using a combined Raman elastic-backscatter lidar[J]. Applied Optics, 1992, 31(33): 7113-7131. doi: 10.1364/AO.31.007113
|
| [33] |
POVEY A C, GRAINGER R G, PETERS D M, et al. Retrieval of aerosol backscatter, extinction, and lidar ratio from Raman lidar with optimal estimation[J]. Atmospheric Measurement Techniques, 2014, 7(3): 757-776. doi: 10.5194/amt-7-757-2014
|
| [34] |
LI S W, DI H G, WANG Q Y, et al. Retrieval of the aerosol extinction coefficient of 1064 nm based on high-spectral-resolution lidar[J]. Journal of Quantitative Spectroscopy and Radiative Transfer, 2020, 256: 107298. doi: 10.1016/j.jqsrt.2020.107298
|
| [35] |
刘东, 周雨迪, 朱小磊, 等. 大气海洋高光谱分辨率激光雷达鉴频特性研究[J]. 大气与环境光学学报,2020,15(1):48-54.LIU D, ZHOU Y D, ZHU X L, et al. Investigation on discrimination characteristics of atmospheric and oceanic high-spectral-resolution lidar[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Environmental Optics, 2020, 15(1): 48-54. (in Chinese)
|
| [36] |
戎宇航, 沈雪, 王南朝, 等. 双波长高光谱分辨率激光雷达光谱鉴频器设计[J]. 光学学报,2021,41(4):0401001. doi: 10.3788/AOS202141.0401001RONG Y H, SHEN X, WANG N CH, et al. Design of dual-wavelength spectral discriminator for high-spectral-resolution lidar[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2021, 41(4): 0401001. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3788/AOS202141.0401001
|






 下载:
下载: